
A UML & Spatial OCL based Approach for Handling Quality Issues
in SOLAP Systems
Kamal Boulil, Sandro Bimonte and Francois Pinet
Irstea, UR TSCF, 24 avenue des Landais, 63172 Aubière, France
Keywords: Spatial DataWarehouse, Spatial OLAP, Quality, UML, OCL, Integrity Constraints.
Abstract: Spatial Data warehouses and Spatial OLAP systems are Business Intelligence technologies allowing
efficient and interactive analysis of large geo-referenced datasets. In such a kind of systems the goodness of
analysis depends on: the warehoused data quality, how aggregations are performed, and how warehoused
data are explored. In this paper, we propose a framework based on a UML profile and OCL-defined
integrity constraints to grant quality in the whole SOLAP system. We also propose an automatic
implementation in a classical ROLAP architecture to validate our proposal.
1 INTRODUCTION AND
MOTIVATION
Spatial Data Warehouse (SDW) and Spatial OLAP
(SOLAP) systems are Business Intelligence (BI)
technologies allowing effective storage and on-line
spatio-multidimensional analysis of huge volumes of
geo-referenced data which can be collected from
multiple heterogeneous data sources (Malinowsky et
al., 2008). These systems are based on the spatio-
multidimensional model, which extends the
conventional OLAP model with spatial concepts
such as spatial measures and spatial dimensions
which provide support for the representation and
storage of spatial data, and spatial operators
allowing users to interactively explore and aggregate
warehoused data. A typical Spatial Relational OLAP
(Spatial ROLAP) architecture is composed of three
tiers: (i) the SDW tier historizes and manages
integrated (spatial) data using a spatial Relational
DBMS; (ii) the SOLAP server implements SOLAP
operators that compute and handle spatial data
cubes; (iii) the SOLAP client tier provides decision-
makers with interactive visual displays that trigger
SOLAP operators.
The heterogeneity of data sources in these
systems may lead to several data quality problems
(Boulil et al., 2011). In order to grant data quality in
SDW, some approaches have been proposed to
“repair” data by means of statistical techniques, data
mining techniques, etc. (Ribeiro et al., 2011). At the
same time, Integrity Constraints (IC) have been
recognized as effective methods to express rules that
control the consistency and completeness of
warehoused spatial data (Salehi, 2009). Moreover,
the goodness of spatio-multidimensional analysis
also depends on the correct aggregation of measures
in respect to summarizability conditions (or
aggregation constraints), which check for example
that the measure and aggregate function types are
compatible (Lenz et al., 1997). However, in SOLAP
systems the goodness of the analysis also requires
another control when exploring (aggregated) data in
order to avoid misinterpretation of meaningless
SOLAP query results (Levesque et al., 2007), e.g.,
the query "Sales per country after December 26,
1991" returns empty results for USSR that could be
interpreted by users as an absence of sales instead of
realizing that a result is impossible for this period.
On the other hand, conceptual design of complex
systems such as data warehouses has been widely
recognized as being necessary for successful BI
projects (Malinowski and Zimányi, 2008) since it
allows designers defining schemas that are easy to
understand by decision makers. In this context,
UML (Unified Modeling Language) is widely
accepted as the Object-Oriented standard for
modelling various aspects of software systems, and
also SDW systems (Pinet and Schneider, 2009).
Indeed, any approach using UML minimizes the
efforts of designers and decision-makers in
developing and implementing the data schema. It
can be also interpreted by CASE tools. In the same
99
Boulil K., Bimonte S. and Pinet F..
A UML & Spatial OCL based Approach for Handling Quality Issues in SOLAP Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0003967100990104
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2012), pages 99-104
ISBN: 978-989-8565-10-5
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
way, defining IC at a conceptual level allows
handling quality issues at the early stages of
development (Boulil et al., 2011), minimizing
implementation efforts. In this context, (Ghozzi et
al., 2003) propose ad-hoc conceptual
multidimensional models allowing the expression of
some data IC by means of logical predicates.
(Malinowskiand Zimányi, 2008) propose an
extension of the ER model for the design of spatio-
temporal data warehouses. They define a set of ad-
hoc pictograms to express spatial data IC (i.e.,
spatial topological relationships between spatial
members). (Glorioand Trujillo, 2008) propose a
UML profile for SDW, but they consider a very
small number of data IC. A survey on aggregation
issues is presented in (Mazón et al., 2009). They
express simple structural constraints (e.g., facts
should be linked to dimensions with one-to-many
associations) with UML multiplicities. In (Pinetand
Schneider, 2009), complex structural aggregation
constraints are expressed with Object Constraint
Language (OCL). OCL represents an effective
solution to define data IC at the conceptual level in a
clear, non-ambiguous and platform-independent
way. Indeed, (Boulil et al.2011) present the
definition, on the top of a UML-based SDW
conceptual model, of a large number of data IC on
warehoused spatial data by means of Spatial OCL,
which is an extension of OCL for spatial data (Pinet
et al., 2007). They also propose an automatic
implementation in the Spatial DBMS Oracle Spatial
11g. (Lavesque et al., 2007) propose a framework
for identifying quality risks in ETL, and SOLAP
systems. They define 3 types of quality problems
(data sources, OLAP data cubes and GIS
functionalities) and define them by means of paper
forms. They also propose an implementation in the
JMAP SOLAP system.
Finally, to best of our knowledge, no work
proposes a unique framework to express at the
conceptual abstraction level IC on spatial
warehoused data, aggregation, and spatio-
multidimensional queries, and their automatic
implementation in a classical ROLAP architecture.
Thus, in this paper we present three main
contributions.
For first, we extend/reformulate the definition of
(S)DW IC for handling quality issues in SOLAP
systems; we use IC to perform three quality control
types:
(a) Data quality control ensures that warehoused
spatial data are valid (e.g., geometries of cities must
be topologically included in the geometries of their
states);
(b) Aggregation quality control ensures that
aggregations of measures are correct and meaningful
(e.g., the sum of the unit prices does not make sense)
(Lenz et al., 1997);
(c) SOLAP exploration control avoids problems of
interpretation induced by meaningless SOLAP query
results (e.g., sales in USSR after 26 December 1991)
(misuse data cube risks as defined by (Levesque et
al., 2007)).
Secondly, motivated by a lack of a unique
conceptual framework to define SOLAP IC, we
propose a UML-OCL based conceptual framework.
Finally, we propose an automatic implementation of
such framework in a classical Relational SOLAP
architecture.
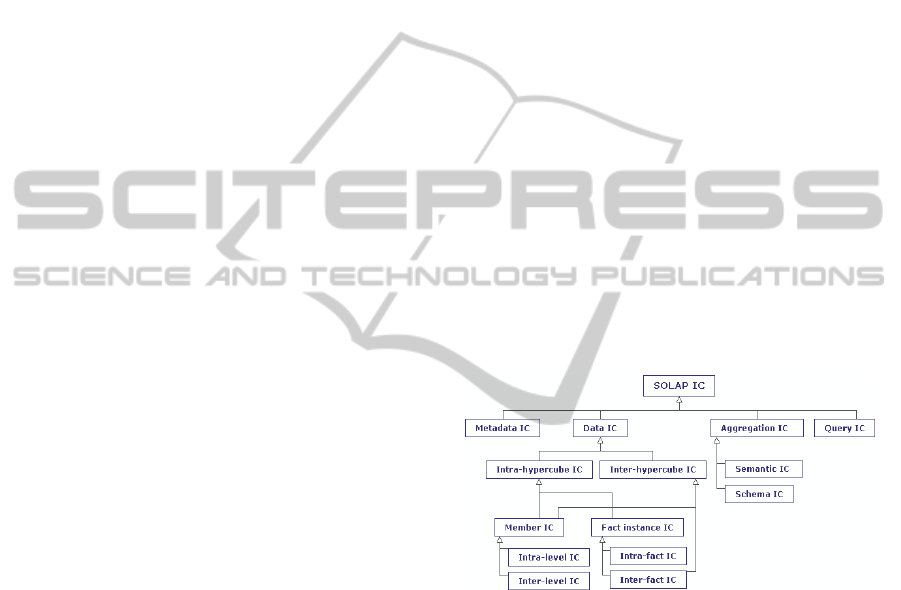
2 SOLAP IC CLASSIFICATION
In this section, we present an extension of our
previous SDW IC classification (Boulil et al., 2011)
by introducing a new class, Query IC class. This
classification (Figure 1) serves as a reference guide
for the process of handling the three types of quality
issues in a SOLAP system.
Figure 1: SOLAP IC classification.
Before detailing the classification, we present the
case study which will be used all along the paper to
describe our proposal. It concerns an environmental
SDW, with a temporal dimension that groups days
into months and months into years, and a spatial
dimension representing cities with their regions and
countries. The measure is the temperature value.
Using this SDW, decision-makers can answer to
SOLAP queries like these:”What is the minimal
temperature per year and country?” or “What is
average temperature per month and country?”. In
order to answer these queries, decision-makers use
the min and average aggregate functions to
aggregate the temperature values.
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
100

Let us now provide explanations and some
examples of these IC classes using the previously
described case study.
As shown in (Boulil et al., 2011), Metadata IC
verify the consistency of metadata of different
integrated data sources (e.g., spatial members and
measures must be defined with the same geographic
scale).
Data IC ensure the logical consistency and
completeness of warehoused spatial data, for
example:
Example 1: “the geometry of each city must be
topologically included in the geometry of its region”
or
Example 2: "no facts (e.g., temperature values)
should exist for USSR after 26 December 1991".
These constraints can be defined on all elements of
the SDW such as facts, members, etc.
Aggregation IC guarantee correct and
meaningful aggregations of measures. In particular,
semantic constraints address the problem of the
applicability of aggregate functions to measures
according to the semantic nature and the type of
measures, aggregate functions and dimensions. For
example:
Example 3: “Sum of temperature values does not
make sense”
Schema constraints are conditions that must be
satisfied by dimension hierarchies and dimension-
fact relationships to avoid double counting and
incomplete aggregates. For example, dimensions and
facts should be linked by one-to-many relationships
(Mazón et al., 2009).
Query IC refer to conditions that guarantee that
SOLAP queries are valid in the sense that their
results are not always empty in order to avoid
problems of misinterpretation. For example, the
SOLAP query “What are the average temperatures
in USSR in 2010?” returns an empty result since no
temperature value is stored for USSR after 26
December 1991 (the previous data IC of Example 2).
Even if this IC is implemented as data IC, classical
SOLAP tools allow decision-makers to formulate
this query by combining these two members (USSR
and 2010) returning an empty value. This leads to a
problem of interpretation: this empty value may be
perceived as if there were no temperature values
registered for USSR during 2010, instead of
realizing that this combination of members (USSR
and 2010) is invalid. Consequently, to avoid this
misinterpretation we define the following query
constraint:
Example 4: "It is incorrect to combine USSR with
days after 26 December 1991 in a SOLAP query".
Although, this query example could be resolved by
using particular spatio-multidimensional data
structures such as DW versioning structures, Query
IC allow designers to model any invalid query which
can be independent of time-versioning aspects (for
example, some products cannot be sold in certain
stores).
3 THE FRAMEWORK
Before describing our conceptual framework for
defining SOLAP IC, we present main concepts of a
UML profile and Spatial OCL.
The UML profiles are a way to customize UML
for particular domains or platforms by extending its
metaclasses (class, property, etc.). A profile is
defined using three extension mechanisms:
stereotypes, tagged values and constraints. A
stereotype is an extension of a UML metaclass.
Tagged values are properties of stereotypes. Finally,
a set of OCL constraints precise each stereotype's
application semantics. OCL provides a platform-
independent method to model constraints. It can be
interpreted by code generators to generate code
automatically. OCL constraints can be defined at the
meta-model level (e.g., UML profile) and also at the
model level (the profile instance). Spatial OCL is an
extension of OCL that supports spatial topological
relationships (inside, intersect, etc.) (Pinet et al.,
2007).
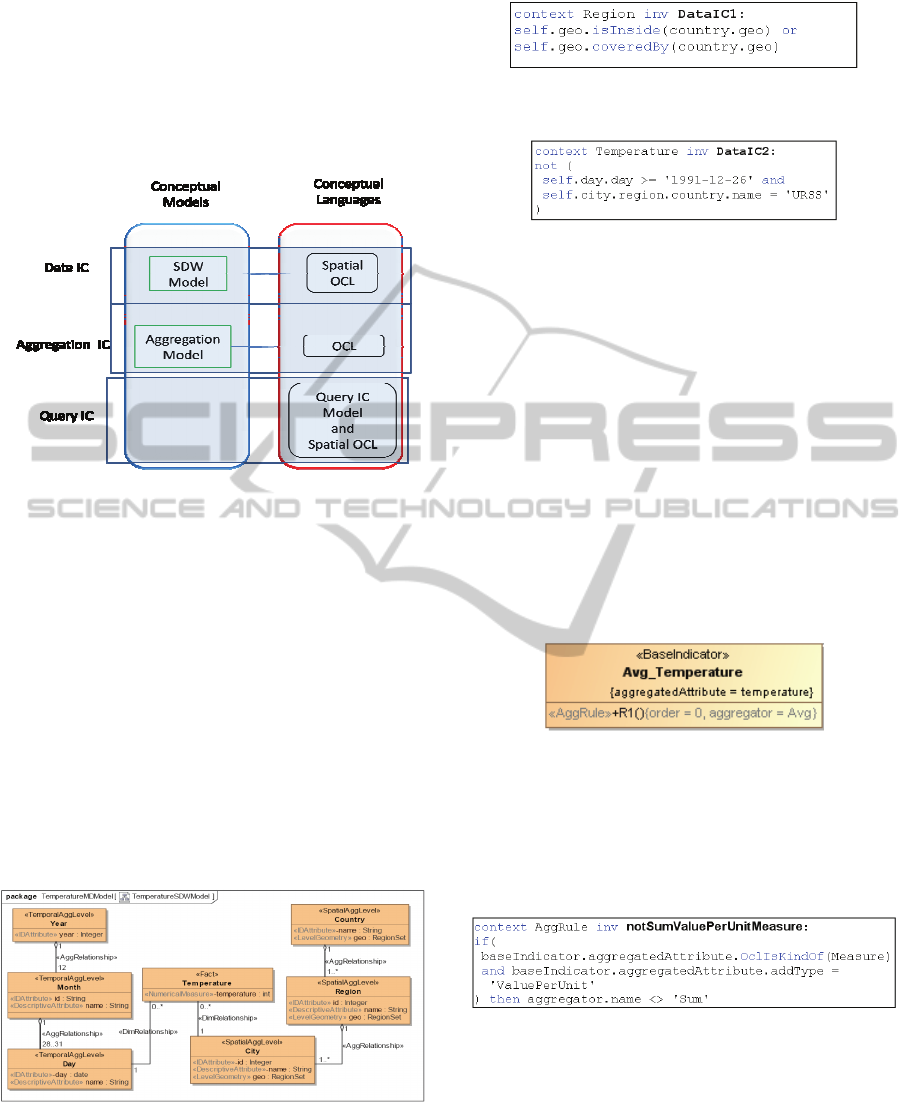
In order to define SOLAP data, aggregation and
query IC at a conceptual level, we propose a
framework based on a UML profile and Spatial OCL
(Figure 2).
The main idea is to a have a unique UML profile
that defines 3 interconnected models to conceptually
represent:
a) SDW data structures (SDW model),
b) how measures are aggregated to meet the
analysis requirements (Aggregation model), and
c) Query IC model
and then define IC with Spatial OCL using these
models. In particular Data IC are defined by
designers using Spatial OCL on the top of the
instance of SDW model, Aggregation IC are defined
as Aggregation model’s stereotypes constraints
using OCL, and Query IC are defined using the
Query IC model and Spatial OCL. Due to space
reasons we do not detail the proposed profile, but we
provide some examples. Details on the SDW and
aggregation models can be found in (Boulil et al.,
AUML&SpatialOCLbasedApproachforHandlingQualityIssuesinSOLAPSystems
101
2011). It is important to note that we have chosen to
define a UML profile instead of a metamodel since
the UML metamodel’s elements are sufficient to
capture all the SOLAP applications' semantics
including all the multidimensional data structures
(Glorioand Trujillo, 2008) and all the identified IC
types.
Figure 2: UML-OCL based conceptual framework.
The SDW model allows the definition of SDW
data structures and the expression of Data IC on the
top of these structures using Spatial OCL (Boulil et
al., 2011).
The SDW case study represented using the SDW
model is shown on Figure 3. This SDW model
instance contains two dimensions: (i) a spatial
dimension composed of 3 spatial levels (stereotyped
as <<SpatialAggLevel>>), City, Region and
Country; and (ii) a temporal dimension composed of
three temporal levels Day, Month and Year. The
numerical measure temperature
(<<NumericalMeasure>> stereotype) is defined as
an attributed of the fact class Temperature
(<<Fact>> stereotype).
Figure 3: A SDW model instance.
Once the SDW model instance has been defined,
data integrity constraints can be expressed using
Spatial OCL. For example, the Data IC of Example
1 is expressed as follows:
The Data IC of Example 2 is expressed using
OCL in the following way:
The Aggregation model represents how measures
are aggregated along dimensions according to
decision-makers' analysis needs. The instance of
Aggregation model for our case study, which
represents that the temperature measure
(aggregatedAttribute tagged value) is aggregated
along all the dimensions using the average aggregate
function (aggregator=Avg tagged value), is depicted
in Figure 4.
In (Boulil et al., 2011) we have identified a set of
aggregation constraints that grant meaningful
aggregations of measures. These constraints are
valid for all SOLAP applications. Thus, we have
implemented them as OCL constraints in the
Aggregation Model package of the profile. They are
checked by the CASE tool at the design stage when
validating the conceptual model.
Figure 4: Aggregation model instance.
For example, in order to force the user to not
aggregate non-additive (or value per unit) measures
(for example the temperature; Example 3) using the
sum aggregate function, the following OCL
statement is defined in the profile:
Finally, designers can express IC on SOLAP
queries using the Query IC model. Typically, a
SOLAP query is a combination of measures and
members from different dimensions. Thus, the
Query IC model can be used for example to define
invalid combinations of member sets. These member
sets are specified as attributes with the
<<MemberSet>> stereotype. The value domain of a
<<MemberSet>> attribute is a subset of members of
a dimension level, whose definition is precised with
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
102
the condition tagged value, which is an OCL
statement defined on the context of the dimension
level to select a subset of its members.
An example of an instance of the Query IC
model is depicted on Figure 5, where the user states
that combining days (<<MemberSet>> day) after 26
December 1991 (condition= After1991-12-26,
whose OCL expression is shown in Figure 6) with
the USSR (<<MemberSet>> country) is meaningless
in any SOLAP query.
Figure 5: Query IC model instance.
Figure 6: OCL used by the Query IC of Figure 5.
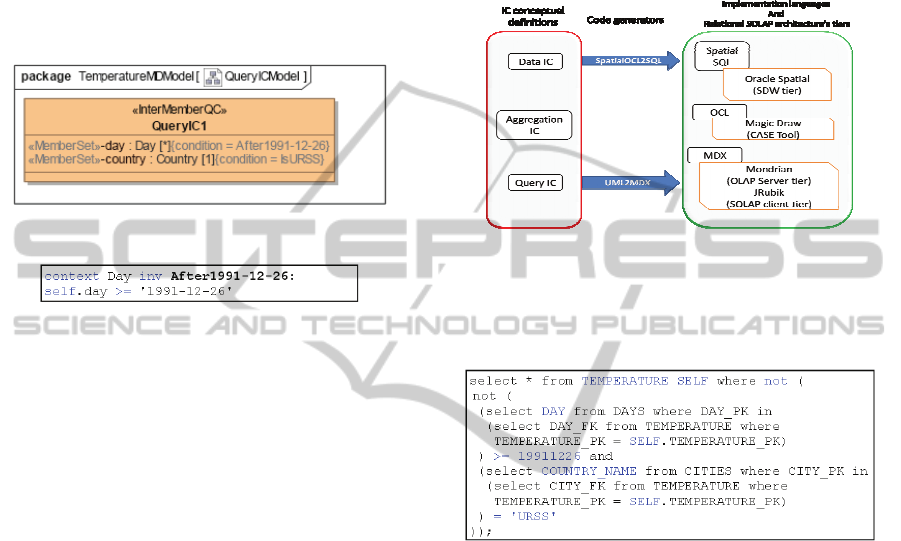
4 IMPLEMENTATION
In this section, we present our architecture to
automatically implement SOLAP IC (Figure 7). The
main idea is to automatically implement each kind
of IC in a different tier of the SOLAP architecture.
The conceptual definition of each IC is
automatically translated into the implementation
language used by each tier. In particular, Data IC are
translated using SpatialOCL2SQL and implemented
in the SDW tier; Query IC are translated by our
automatic code generator (called UML2MDX) and
implemented in the OLAP server and the SOLAP
client, and finally Aggregation IC are implemented
in our UML profile using OCL and controlled
during the design stage by the MagicDraw CASE
tool.
Our SOLAP architecture (Figure 7) is based on:
the Spatial DBMS Oracle Spatial 11g, the ROLAP
Server Mondrian and a SOLAP client JRubik.
Mondrian connects to a relational database and
enables the execution of OLAP queries expressed
using MDX (MultiDimensional eXpressions) that is
a standard language for querying multidimensional
databases. JRubik provides a graphical presentation
layer on top of Mondrian and allows cartographic
representations of OLAP queries using the SVG
format.
In order to automatically implement data IC in
the Oracle Spatial 11g, we have used the code
generator Spatial OCL2SQL. Spatial OCL2SQL is a
Java open source tool which integrates the spatial
extensions of OCL called OCL 9IM and OCL ADV
(Pinet et al., 2007). It automatically generates SQL
scripts for Oracle Spatial from Spatial OCL
conceptual constraints.
Figure 7: Automatic implementation of SOLAP IC.
In our case study, the previously defined OCL
data IC of Example 2 is transformed in the following
SQL query:
This query selects the facts (TEMPERATURE
table's tuples) that do not satisfy the constraint of
Example 2.
The Aggregation IC are implemented as OCL
profile inherent constraints in the MagicDraw CASE
tool. MagicDraw supports OCL at the meta-model
level (UML profile). In other terms, MagicDraw is
able to check OCL constraints defined on UML
stereotypes. This allows checking Aggregation IC at
design stage independently of the specific SOLAP
architecture used and without providing any
implementation efforts. For example, if the designer
defines an instance of the Aggregation model by
using the Sum for the temperature measure,
MagicDraw checks the OCL Aggregation IC of
Example 3 and informs him that the constraint is
violated.
In order to implement Query IC, we use MDX,
which is the defacto standard of OLAP Servers and
Clients. Thus, the choice of Mondrian as OLAP
server is not a limitation for our generic architecture.
The main idea is to translate the Query IC into MDX
AUML&SpatialOCLbasedApproachforHandlingQualityIssuesinSOLAPSystems
103

formula, which are stored in the OLAP Server and
then visualized in the SOLAP client. These
formulas, when executed, inform user about the
quality of query results. For each Query IC type we
have defined an MDX template. The templates are
fulfilled using a Java method (UML2MDX) that
parses the XMI files associated to the Query IC.
Different visual policies are associated with different
combinations of members from these sets to be
displayed in the SOLAP client tier: green colour for
valid cells, yellow colour for aggregated cells that
include valid and invalid cells and red colour for
invalid cells. Figure 8 shows an example of OLAP
query where these visual policies are applied
according the MDX formula implementing the
Query IC of Figure 6: valid cells such as those
combining USSR with dates before 1991-12-26 (e.g.
1991-12-01) are displayed with green colour; invalid
cells that involve for example USSR and dates after
1991-12-26 (e.g. 1991-12-27, 2010-1, 2010) are
displayed with red colour, other cells are displayed
with yellow colour, such as 1991-12 with USSR
because it is the aggregation of valid (e.g. 1991-12-
01 with USSR) and invalid cells (e.g. 1991-12-27
with USSR).
Figure 8: Query IC visualization of Example 4.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we first show that the SOLAP analysis
goodness depends on 3 quality types: data,
aggregation and query qualities. Thus, we (i) extend
the concept of integrity constraints to consider all
these quality types; (ii) propose a framework based
on a UML profile and Spatial OCL to express these
SOLAP IC at the conceptual level; and (iii) show
their automated implementations in a typical
ROLAP architecture. Our current work is on
improving the UML2MDX tool by integrating
Spatial MDX expressions and defining cartographic-
related visualization policies in order to implement
spatial query IC.
As in our current automatic implementation only
considers the snowflake schema SDW
implementations, we are working on the
consideration of the star-schema implementations.
Finally, we will work on the formal validation of the
completeness of our classification, and the
expressiveness of our conceptual framework.
REFERENCES
Boulil, K., Bimonte, S., Pinet, F. (2011). Un modèle UML
et des contraintes OCL pour les entrepôts de données
spatiales : De la représentation conceptuelle à
l'implémentation. Ingénierie des Systèmes
d'Information, 16(6) 11-39
Ghozzi, F., Ravat, F., Teste, O., Zurfluh, G. (2003).
Constraints and Multidimensional Databases. In 5th
International Conference on Enterprise Information
Systems, 104-111
Glorio, O. and Trujillo, J. 2008. An MDA Approach for
the Development of Spatial Data Warehouses. In 10th
International Conference on Data Warehousing and
Knowledge Discovery, Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer,
23-32
Lenz, H.-J. and Shoshani, A. 1997. Summarizability in
OLAP and statistical data bases. In International
Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database
Management, IEEE, 132-143
Levesque, M.-A., Y. Bédard, M. Gervais, R. Devillers,
(2007). Towards managing the risks of data misuse for
spatial datacubes. In 5th International Symposium on
Spatial Data Quality, June 13-15, Enschede,
Netherlands
Malinowski, E. and Zimányi, E. (2008). Advanced Data
Warehouse Design: From Conventional to Spatial and
Temporal Applications. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Mazón, J.-N., J. Lechtenbörger, et al. (2009). A survey on
summarizability issues in multidimensional modeling.
Dataand Knowledge Engineering 68(12): 1452-1469.
Pinet, F., Duboisset, M. and Soulignac, V. (2007). Using
UML and OCL to maintain the consistency of spatial
data in environmental information systems.
Environmental modellingand software, 22(8) 1217-
1220
Pinet, F., Schneider, M. (2009) A Unified Object
Constraint Model for Designing and Implementing
Multidimensional Systems. Journal of Data Semantics
13, 37-71
Ribeiro, L., Goldschmidt, R., Cavalcanti, M. 2011.
Complementing Data in the ETL Process. In 13th
International Conference Data Warehousing and
Knowledge Discovery, Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer,
112-123
Salehi, M. (2009). Developing a Model and a Language to
Identify and Specify the Integrity Constraints in
Spatial Datacubes. Doctoral thesis. Faculté des études
supérieures de l’Université Laval, Canada.
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
104
