
A PRACTICE FIELD FOR TEACHING ELECTRONIC
MARKETING
Luis Vaz and Nuno David
ISCTE-IUL - Lisbon University Institute
Department of Information Science and Technology, Lisboa, Portugal
Keywords: e-Learning, e-Learning environment, Practice Field, Tutorial System, Situated Learning, Electronic
Marketting.
Abstract: Professionals in electronic marketing make intensive use of information and communication technologies.
An intensity that makes the teaching of electronic marketing somewhat challenging and specific when
compared with other disciplines. Teaching electronic marketing will only be effective if the learning
environment reaches similar levels of technological intensity as the discipline itself. This suggests that
electronic marketing might be particularly appropriate to the use of e-learning as a teaching instructional
model. However, this carries risks and further challenges, resulting from difficulties in obtaining positive
results whenever learning is supported by e-learning platforms. If one wants to achieve lower failure risks
and effective and motivated learning, the e-learning model should be provided with features that strengthen
it pedagogically. This paper proposes a practice field for teaching electronic marketing, embedded and
tested in an e-learning platform provided with learning activities that implement a practice field.
1 TEACHING ELECTRONIC
MARKETING
The application of the traditional teaching systems to
the field of electronic marketing (EM) presents
instructional failures that will keep students from
obtaining important knowledge and skills needed in
their professions (Miller et al., 2003). These
insufficiencies become more pronounced when the
traditional model is used in disciplines where
students need to apply their knowledge in positions
that require environments with high technological
intensity (De Wulf et al., 2000). In a society where
information and communication technologies (ICT)
are present in all professions, the use of inadequate
teaching models tends to be widespread (Bundy,
1998).
For EM professionals, the core activity of their
business consists of electronic mail, interaction
social sites, and the internet in general, where they
promote products and services. The use of these
tools requires skills, literacies and practical abilities
that the normal teaching model – in which the
transmission is focused on the professor – does not
provide.
Aware of this fact, several teachers in higher
education are including in their teaching models new
learning activities, generically and transversally to
many disciplines, such as case studies, teamwork,
and assignments using ICTs, thus promoting the use
of information technologies and reinforcing
communication and access to contents via internet
sites.
But even with these efforts it proves difficult to
reproduce in a suitable pedagogical way the nature
of the interactions with ICTs, necessary for the good
fulfilment of disciplines with high technological
intensity, particularly in the EM case.
Alerted to these difficulties, as well as to the
increasing exigency on teaching EM, teachers are
required to find a solution to this problem, whose
importance is becoming more and more urgent
(Oliveira and Guimarães, 2010; Conole et al., 2007).
Teachers are asked to find and test instructional
models with innovative characteristics. Innovation
which ought to be intensively supported on ICTs.
Notwithstanding, the application of technology may
increase the risk of failure, lowering teachers’ and
institutions reputation rates, whenever pedagogical
innovation based on ICT fails. Failures risks and the
potential for resulting frustrations are well illustrated
484
Vaz L. and David N..
A PRACTICE FIELD FOR TEACHING ELECTRONIC MARKETING.
DOI: 10.5220/0003981704840489
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (ESEeL-2012), pages 484-489
ISBN: 978-989-8565-07-5
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
in cases described in biography related to the
application of information technologies to education
with e-learning approaches (Law, 2004; Huk et al.,
2002; Romiszowski, 2004; Dowes, 2005).
The analysis of failures reveals a poor design of
many e-learning supporting systems which are not
backed up by any idea of the teaching model the
learning system is meant to be based (Penna and
Stara, 2007). Failures in the effectiveness of e-
learning are also the result of an excessive focus on
contents when designing the learning solutions
(Brennan 2003).
But what really influences the success or failure
of the e-learning is the careful consideration of the
pedagogy subjacent to the construction of the
learning model, i.e how does learning work online
(Dalziel, 2005). Pedagogy has a central role in the
success of e-learning (Govindasamy, 2001). Only
through the insertion of pedagogy in the design of e-
learning will we create learning models where
students really learn. The e-learning platform should
be provided with an instructional model based on
recognized paradigms of teaching theory,
consolidated by learning activities, intensively
supported on ICTs. One way to implement these
paradigms in an e-learning solution consists of
adopting a model where education is based on the
practical use of specific skills that students are
intended to learn (Lee, 2009).
2 PRACTICE FIELDS
In order to implement this paradigm, we propose a
practice field (PF) where situated learning is based
on real learning activities.
PFs are especially appropriate to teach EM
insofar as they grant specific knowledge on the
practical use of ICTs for developing marketing
activities. A PF also grants a high-maturity
education model, promoting alignment among
perceivable results, teaching, learning activities and
evaluation (Biggs, 2003).
The development of learning environments
supported on PFs arose from the need for developing
learning based not only on concepts but on real
activities, applied by students in their professional
lives (Barab and Duffy 2000). Practice models were
indicated, for example, as the best way, to develop
learning within organizations (Kofman and Senge
1993). Other fields include the teaching of project
management (Winston and Spiro, 1993) and the
teaching of medicine supported on ICTs (Garde et
al., 2005). In the models proposed by Winston and
Spiro students develop authentic activities related to
management. Our approach is a “hands on”
approach, where students develop authentic
activities that are in fact identical to the ones they
will develop in their professional practices of EM.
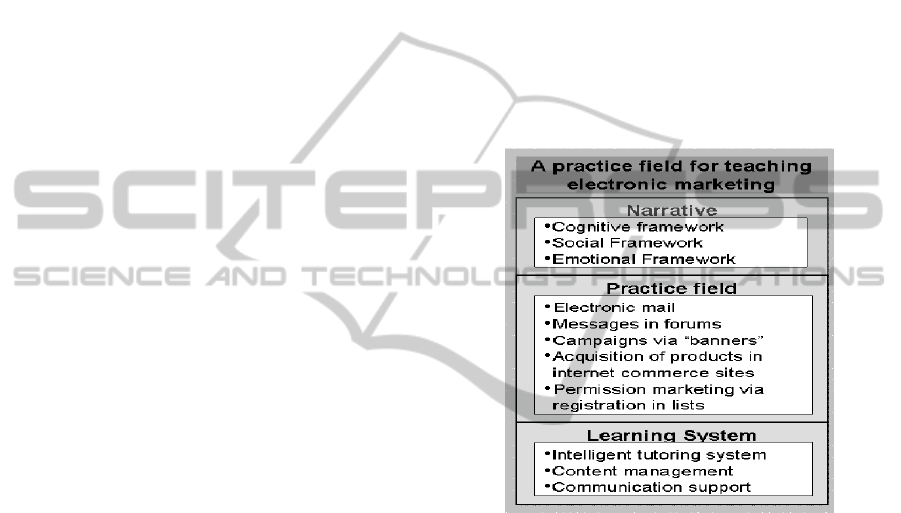
The PF we propose in this article has an
architecture that comprises three characteristics
important for teaching disciplines with high
technology intensity: (1) it must be integrated in an
e-learning environment extended with an intelligent
tutoring system; (2) practices should be authentic;
(3) dynamics created by the PF at the cognitive,
social and emotional dimensions should be
maintained by a narrative supported by hypermedia
means of the e-learning platform. Figure 1 shows the
proposed architecture for the case of EM.
Figure 1: The architecture for the case of EM.
3 THE INTELIGENT TUTORING
SYSTEM
An intelligent tutoring system (ITS) is a computer-
based system supported by a model specifying what
to teach and how it should be taught (Wenger,
1987).
The ITS developed for this PF may be classified
as one of having a special purpose, developed for an
instructional model based on authentic activities, in
which students are called to participate on an
organized and sequential way by the information
system itself (Murray, 1999).
In the tutoring system model the following are
embedded: i) the rules to make content available; ii)
the sequence of the authentic activities; iii) a model
of participation of each student, identified through
the role he plays in each of the activities.
APRACTICEFIELDFORTEACHINGELECTRONICMARKETING
485

Instructions to students specified by the ITS are
embedded in the learning support system, and duly
integrated hereinto, thus enlarging the learning
process. It also automatically promotes the specific
configuration of the hypermedia environment, thus
showing students the connections they have to
follow, offering easy access to the systems that
support authentic activities.
The tutoring system controls the timing of each
practice, shows the student what to study before
developing it and places him/her in the role s/he
plays in it.
4 AUTHENTIC ACTIVITIES
A PF must have several media available so that
students can practice. The PF developed for the EM
field uses the following:
Electronic mail
Messages in forums
Publicity on the internet via ‘banners’
Purchasing of products at an internet commerce
site
Permission marketing
4.1 A Students Market
The activities of EM developed at the PF are
intended to promote the selling of products in a
particular market.
The set of students defines this market; their role
is that of a typical consumer. Once they receive
structured messages from colleagues promoting
products, they will understand the effect that these
messages will have on consumers. They also learn
how to structure messages to be sent in an EM
campaign.
In the role of consumers, students answer
messages, causing in the students that sent those
messages a learning effect on how a campaign really
works.
4.2 Campaigns of Electronic Mail
The development of a campaign of electronic mail
must follow specific rules and good practices so that
clients do not see electronic mail as ‘spam’ but are
persuaded to read received messages.
For those who are learning, if the sending of
electronic mail is appropriately developed, the PF
should help students understand the characteristics
that the messages should have. This is possible
provided the sender has previously had the chance to
read contents explaining how the message should be
constructed so as to obtain certain objectives. While
developing and sending electronic emails according
to certain rules, students come to understand the
basis of performing a campaign.
4.3 Campaigns with Forums
The creation of lists in which students playing the
role of a marketer leave messages for promoting the
traffic of an electronic commerce site, introduces a
collective learning process leveraged by the access
of other students. Access is encouraged insofar as
one of the exercises to be carried out by students is
answering such messages in the list.
A learning sequence is developed that will
transform the PF in a learning community, insofar as
it creates a two-way communication dynamic,
between students in the role of consumer and
students in the role of marketers.
In the platform, a system is available to place
messages in forums, and students create messages
according to rules previously learned. The intelligent
tutoring system asks students to place messages and
notifies other students to respond.
4.4 Purchasing of Products at an
Electronic Shop
The emergence of electronic commerce introduced
into the commercial world a completely new way of
selling products, which is often not understood or
even known by managers and students. Even when
managers play the role of consumers themselves,
this kind of market is not part of their previous
commercial activities, making it more difficult to
use past experiences.
Therefore, it is reasonable that future managers
have informational literacy on electronic commerce,
especially those working in the EM field. The PF
provides the possibility of buying at electronic
shops.
4.5 Development of Online Publicity
Internet media, whichever they are, are crucial
vehicles to promote the image of enterprises. In EM
a main activity is promoting and managing the brand
of an enterprise via electronic channels; thus,
knowing what a “banner” is and how it is developed
becomes important.
One should know the best way to create a
“banner”, not only regarding costs but also
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
486

considering the communication efficiency for
achieving better sales. There are several and diverse
ways of creating a “banner”. Specific tools available
at sites on the internet make it possible to construct
several kinds of “banners”.
A PF that puts in contact students who may be
working with EM, or with deep connections to
advertising on the internet, should allow the
construction of a “banner” and its placement at an
electronic shop.
Students are called to build a “banner” in groups,
in line with a story describing the PF.
4.6 Permission Marketing
Permission marketing can be understood as the
explicit desire by a consumer for receiving relevant
messages. The consumer subscribes to sites and fills
out information that enables the sender to target
messages. Understanding how permission marketing
works is nowadays an important issue for the EM
professional.
In the PF, students will play the role of consumer
and will be called to subscribe in sites where they
can register and give information to receive target
messages.
The dynamics that emerge in such sites will help
students acquire the skills necessary for an EM
manager and, in particular, skills associated with
permission marketing.
5 THE NARRATIVE
EM is based on the exploration of a hypermedia
environment used to promote enterprises and
products in the eyes of consumers.
A PF in this area should aggregate several
components for exploring the hypermedia
environment, making them available to students so
that they can practice EM activities. In such
practices students create a consumer market and play
different roles introduced by a narrative.
5.1 The Development of the Narrative
The narrative enables us to contextualize, introduce
simplifications, adjust and explain certain dynamics
of the PF, which necessarily represent a simplified
view of some world (Barab and Landa, 1997).
One way to structure and develop a narrative is
based on the dynamics of development of a case
study.
The
narrative used in this PF was developed
from the structure of a problem, by suggesting how
the firm sees the problem and what alternative
solutions are available (Linder, 1990). The narrative
shows the student the context of the problem and
indicates the importance of the practices students
will carry on (Barab et al., 1998).
The narrative also introduces students to the
various roles they will have in the PF.
Apart the aspects of contextualization, a good
narrative reinforces motivational aspects and
develops a framework that helps with the solution of
practical problems (Dickey, 2006).
5.2 Narrative Description
The narrative is based on a situation where an
enterprise has just bought an electronic commerce
business and has to maximize its publicity
campaigns.
5.2.1 The Events
“It was late in the afternoon of a very busy day.
Expectations were high as meetings with top
management and marketing professionals were not
frequent. We all knew that our president was a keen
adept of the use of the internet to commercialize
products, mainly books. The room was silent.
Without any kind of introduction or perspective
comment Luis [the president] said ´We did it, we just
bought a firm that sells books via internet!´”.
5.2.2 Characteristics of the Buying
Company
“The firm ‘All books’ has around 25 employees
distributed across four locations. A big space at a
pedestrian street in the busy centre of Lisbon and
three other spaces in different locations. Each one of
these shops with five employees.
‘All books’ has been a quite profitable business
but the selling of books via the internet raised some
concern about its future. This new reality led the
owner to buy a business in order to sell books via
the internet”.
5.2.3 Characteristics of the Acquired
Company
“The firm ‘e-Books’ was created two years ago. An
analyst programmer with skills in the internet area
decided to create a site to sell books via this new
channel.
However, lack of knowledge about this business
took the company to a difficult financial situation
APRACTICEFIELDFORTEACHINGELECTRONICMARKETING
487

and the owner started looking for an expert partner
in this kind of business.
He started by contacting ‘All Books’ but they
were not interested in this kind of partnership. After
long negotiations ‘e-Books’ decided to sell all its
stock to ‘All Books’”.
5.2.4 Business Model of the Newly Acquired
Company
“‘e-Books’ is a bookshop that sells exclusively via
the internet. With a market share of 5%, it does not
yet have profits, which is possible only with a 50%
share. Having this in mind the former management
bought a campaign of electronic marketing. The
campaign is supposed to occur consecutively,
divided into five campaigns.
5.2.5 The First Meeting
“Luis, the owner of ‘All Books’, arrived at the
meeting room and gave us a paper showing what he
thought would be necessary to reach profitability
and clearly explaining the role of each management
team for this purpose. The main role of the
marketing management team will be to maximize the
EM campaign already in place.”
5.2.6 The Campaign of Electronic
Marketing
“The campaign of EM will be based on four
different techniques.
Banners
Messages in forums
Campaigns of electronic mail
Sponsorships
‘e-Books’ had already decided to put banners: i)
in our site; ii) in other sites of the internet market by
exchanging banners with other enterprises; iii) in a
high traffic site.
The electronic mail campaign will be created for
clients who voluntarily registered at our site and for
lists of clients whose email addresses were bought.
Messages will also be placed at a forum where
internet users express their opinions on books.
We will also look for sites on the internet that
will sponsor this new enterprise on the internet”.
5.2.7 The Activities
“The EM team is supposed to develop practical
activities on EM according to the promotional
campaigns of the enterprise”.
5.3 Student Roles
In the PF, students participate by playing different
roles. A role is associated with a specific narrative in
order to provide the adequate mental and operational
framework. In this PF the students play the roles of
student, marketer, and consumer.
6 RESULTS
The architecture of the PF here described is part of
an instructional model based on an enlarged e-
learning system, where students develop learning
activities in a PF, as well as other features as
simulation and games.
This education model was applied to 293 post-
graduate students, involving one quarter, with good
results in terms of the above mentioned
characteristics.
We used a set of inquiries (Cashin and Downey,
1992) that led us to understand results along five
dimensions: i) evaluation of the teacher; ii)
evaluation of progress, iii) quality of given contents;
iv) interest levels during course and v) a global
evaluation of the course.
Space limitations prevent us from offering a full
report and analysis of results in this paper.
Concerning the instructional model, student
reactions were positive, but further work is
necessary (mean of 3.0 from a maximum score of
5.0). Students ranked as the most valued
characteristic the ability to progress in “Acquiring
skills in working with others as a member of a team”
(3.9 points) and as the least valuated the progress in
“the development of skills related in expressing
myself orally or in writing” (2.3 points).
Considering that the main purpose of the PF was
to gain literacies and learn real activities connected
with the development of EM campaigns, we
measured two specific characteristics: a) the
capacity of the teacher to promote practical activities
(3.5 points); b) the capability the instructional model
shows in developing specific abilities and skills
related with EM (3.1 points).
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
DEVELOPMENTS
The inclusion of a practice field in a management
learning environment supported in ICT is a
demanding exercise implying the use of an
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
488

intelligent tutoring system and, for the case of EM, a
set of five other systems: i) electronic mail; ii)
forums; iii) publicity in “banners”; iv) Web shops;
and v) hypermedia links allowing students to enter
sites where they can register themselves in an “opt-
in” model in order to receive information.
Results obtained by applying the practice field to
the teaching of EM are significant, which possibly
may be generalised to other fields of high
technological intensity. The motivational and
socializing aspects are still to be explored by
improving the intelligent tutoring system and the
interaction it promotes among elements of the
narrative.
This narrative may be further improved by
developing multimedia elements, like enhanced
video, integrated in the e-learning environment, or
by including virtual characters to embody narrative
in a simulated environment.
The study of this impact may conduct us to
important conclusions on the way these
technological devices may increase the efficiency of
the e-learning environment.
REFERENCES
Barab, S., Landa A., 1997. Designing effective interdisci-
plinary anchors. Educational Leadership 54(6), 52-55.
Barab, S., Duffy, T., 2000. From practice fields to
communities of practice. Theoretical foundation of
learning environments. Lawrence Erlbaum.
Barab, S., Duffy, T., Kenneth H., 1998. Grounded
constructions and how technology can help. CRLT
Technical Report no. 12-00.
Biggs, J., 2003. Aligning Teaching and Assessing to
Course Objectives. Teaching and Learning Education:
New Trends and Innovations. University of Aveiro,
13-17 April, 2003.
Brennan, R., 2003. One size doesn’t fit all – Pedagogy in
the online environment. NCVER, Adelaide.
Bundy A., 1998. Information Literacy: The Key
Competency for the 21st Century. IATUL Conference,
Pretoria, South Africa, volume 18.
Cashin, W.E., Downey, R.G., 1992. Using global student
rating items for summative evaluation. Journal of
Educational Psychology, 1992, 84(4), pp.563-572.
Conole, G., Thorpe M., Weller M., Wilson P., Nixon S.,
Grace P., 2007. Capturing practice and scaffolding
learning design. The open University, UK.
Dalziel. J, 2005. From reusable e-learning content to
reusable learning designs: Lessons from LAMS.
http://www.lamsfoundation.org, 2006.
Dickey, M., 2006. Game design narrative for learning:
approaching adventure game design narrative devices
and techniques for the design of interactive learning
environments. ETR&D, 54(3), 245-263.
Dowes, S., 2005. E-learning 2.0. eLearn Magazine.
Garde, S., Bauch, M., Haag, M., Heid, J., Huwendiek S.,
Ruderich, F., Singer, R., Leven, F., 2005. CAMPUS -
Computer based training in medicine as part of a
problem-oriented educational strategy. Studies in
LEID, 2(1), 10-19.
Govindasamy, T., 2002. Successful implementation of e-
learning. Pedadagogical considerations. Internet and
Higher Education 4, 287-299.
Floto C., Huk T., Lipper T., Steinke M., 2002. The role of
navigation and motivation in e-learning – the crimp-
approach within a swedish-german research
cooperation. In Procs of the EDEN Annual
Conference, Granada, Spain, 364-369.
Kofman F., Senge P., 1993. Communities of commitment:
the heart of learning organizations. Organizational
Dynamics 22(3)..
Law, N., Chow, A., Yuen, H.K., 2004. Methodological
approaches to comparing pedagogical innovations
using technology. Education and Information
Technologies, 10(1-2):7-20.
Lee G., 2009. E-learning Practice: A Framework for the
implementation of Online Learning. ANZMAC
conference.
Linder, J., 1990. Writing cases: tips and pointers. Harvard
Business School Press, 9-391-026, 1-9, Harvard
College, Boston USA.
Miller, R., Stace, R., Howell G., 2003. A developmental
approach to teaching internet marketing. Proceedings
of ANZMAC’2003, Adelaide, Australia.
Murray, T., 1999. Authoring intelligent tutoring systems:
an analysis of state of the art. International Journal of
Artificial Intelligence in Education, 10, 98–129.
Oliveira ED, Guimarães IC, 2010. Employability through
competencies and curricular innovation: a Portuguese
account. Faculty of Economics and Management,
Catholic University of Portugal.
Penna, M., Stara, V., 2007. The failure of e-learning: why
should we use a learner centred design. Journal of e-
Learning and Knowledge Society 3(2), pp. 127-135.
Romiszowski, A., 2004. How’s the E-learning Baby?
Factors Leading to Success or Failure of an
Educational Technology Innovation. Educational
Technology, 44(1), pp. 5–27.
De Wulf K., Schillewaert N., Van Vooren E., 2000.
Simulating the Principle of Database Marketing
through DARTS. Journal of Database Marketing. 7(3).
Wenger, E., 1987. Artificial Intelligence and Tutoring
System: Computational and Cognitive Approaches to
the Communication of Knowledge. Morgan Kaufmann
Publishers, California.
Winston L., Spiro M., 1998. Improving project
performance with simulation and practice. In the 29th
annual project management institute, seminars &
symposium. Long Beach, CA, USA.
APRACTICEFIELDFORTEACHINGELECTRONICMARKETING
489
