
A Tool to Evaluate Error Correction Resources and Processes Suited for
Documents Improvement
Arnaud Renard
1,2
, Sylvie Calabretto
1,2
and Béatrice Rumpler
1,2
1
Université de Lyon, CNRS, Lyon, France
2
INSA-Lyon, LIRIS, UMR5205, F-69621 Villeurbanne Cedex, France
Keywords:
Evaluation Model, Framework, Error Correction, Textual Documents, Distance and Similarity Measure,
Metrics, Information Retrieval.
Abstract:
In this article we present a solution to overcome the difficulties in the comparative evaluation of error correc-
tions systems and mechanisms. An overview of existing error correction approaches allowed us to notice that
most of them introduce their own evaluation process with the drawbacks it represents: i.e. it is not clear if one
approach is better suited than another to correct a specific type of error. Obviously each evaluation process in
itself is not completely original and consequently some similarities can be observed. In this context, we rely
on this fact to propose a generalist "evaluation design pattern" we fitted to the case of error correction in textual
documents. The idea lying beyond that is to provide a standard way to integrate required resources according
to the family (previously defined in the evaluation model) they belong to. Moreover, we developed a platform
which relies on OSGi specifications to provide a framework supporting the proposed evaluation model.
1 INTRODUCTION
In order to propose an accurate way to evaluate error
correction systems, it is interesting to pay a special
attention to their benefits and particularly to the dif-
ferent shape of errors they have to deal with. Indeed,
an error correction system will be susceptible to per-
form worse or better according to the type of errors
the system will have to face to. So, this will have to
lead to different evaluation mechanisms. In this paper,
we are particularly concerned by error correction of a
specific subset of data which consists in textual data.
Indeed, large amounts of data produced every day by
the growing number of the Web 2.0 services users are
error-prone. It makes it important to correct those er-
rors while they may disturb data management appli-
cations. While spell checkers are amongst the most
common Natural Language Processing (NLP) appli-
cations, many computer applications rely on clean
text processing techniques. It is only because of the
increase of noisy text (Subramaniam et al., 2009) that
these techniques have been adapted to take noise like
errors into account.
Most documents were formerly produced by pro-
fessionals who have to keep a minimum level of
quality while writing. Indeed their writings have to
conform to quality controls like newspaper editorial
chain, article review... At Web scale, the way infor-
mation is produced is different while most (but not
all) documents are created by ordinary users (Ros-
nay and Revelli, 2006). In this last case, informa-
tion is not provisioned as a result of a professional
work. Ordinary users are more likely to make mis-
takes while using an inappropriate terminology (or a
vocabulary they are not familiar with). It is there-
fore legitimate to have some reservations about the
quality of their writings (both about the form and the
substance). Moreover, web published content is not
constrained by quality control. For example, weblogs
have popularized the mass self-publishing with free
and immediate release.
According to the problem of information quality,
it might be interesting to consider errors in Informa-
tion Retrieval systems (IR) as well while it is one of
the principal ways to access data on the Web. Most
of the time attempts to correct errors with an IR im-
provement perspective consider only query correction
like the popular "Did you mean". There are few re-
searches aiming to correct documents themselves like
Ruch works (Ruch, 2002), and works related to for-
mer TREC-5 Confusion Track (Kantor and Voorhees,
2000) with OCR related errors and later TREC-6 with
Spoken document retrieval (Voorhees et al., 2000)
track. However, at web scale, it is an important area of
27
Renard A., Calabretto S. and Rumpler B..
A Tool to Evaluate Error Correction Resources and Processes Suited for Documents Improvement.
DOI: 10.5220/0003998800270035
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2012), pages 27-35
ISBN: 978-989-8565-11-2
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

improvement for IR systems (Varnhagen et al., 2009).
Our state of the art led us to identify difficulties in the
benchmarking of error correction systems. For ex-
ample there is no common (and realistic) evaluation
collection and some (Pedler, 2007; Atkinson, 2012)
publish their testing sets while many others do not.
It is important to have common testing environments
which rely on common collections and standardized
metrics in order to be able to compare solutions.
Our proposal consists in an evaluation model
which applies to error correction systems as well as
low-level resources they rely on. For our sake, evalu-
ations results obtained later thanks to the framework
implementing this model through our platform will
then allow the choice of the "best" error correction
system to use in the indexation phase of an IR system.
That is why the specialization of our model exposed
later will be particularly focused on this aspect.
The context and positioning of this article is pre-
sented in section 2 which defines the key concepts
used along the article and establishes a classifica-
tion of common errors. In the section 3 we present
an overview of different error correction approaches
as well as practical issues related to the difficulties
of evaluating them. In order to address this prob-
lem, section 4 presents our evaluation model across
a generic meta-model which is derived in a model we
use to evaluate error correction systems. The evalua-
tion platform implementing this model is presented
in section 5. It allowed the analysis of some er-
ror correction mechanisms. Implemented resources
are described in section 6 as well as our first eval-
uation results. Finally, section 7 provides our con-
clusions on the evaluation of error correction systems
and presents our perspectives for their future integra-
tion into IR systems.
2 CONTEXT AND POSITIONING
According to Shannon works related to information
theory (Shannon, 1948), noise can be described as a
corruption of information resulting in a difference be-
tween the expected information (which is supposed to
be correct) and the information obtained (which might
contain errors). At first, it is important to define what
an error is, and at least to clarify the definition re-
tained in this article.
2.1 Key Concepts Definition
2.1.1 Alphabet
If we consider textual information and take A, a finite
set which we call alphabet (in the case of the English
language, A is matching all possible characters in En-
glish). Thus, every character c belongs to the alpha-
bet A, (c ∈ A).
2.1.2 Word
Let A
k
be the set of words w composed by a sequence
of k ordered characters.
w ∈ A
k
⇔ w = c
1
, c
2
, . . . , c
k−1
, c
k
(1)
2.1.3 Dictionary (or Lexicon)
We call dictionary d (or lexicon), all valid words of a
language coming from an alphabet A (i.e. currently or
formerly used by native speakers of the language).
2.1.4 Error
An error e can be defined as the presence of at least
one character which differs from the expected charac-
ter at a given position in the sequence corresponding
to a word w. Let w be in A
k
and c
i
(w) denote the
character at position i in w :
w
1
, w
2
∈ A
k
: w
1
6= w
2
⇔ ∃i : c
i
(w
1
) 6= c
i
(w
2
) (2)
This definition covers all errors like ones due to
the insertion, the deletion, or the substitution of a
character by another one as well as any other oper-
ation which modify the sequence of characters com-
posing a word.
2.1.5 Wrong Word (Resp. Target Word)
We define a word with at least one error (as w
2
) as a
wrong word different from the correct intended target
word (as w
1
).
2.1.6 Error Correction System
According to previous definitions, an error correc-
tion system is a mechanism which allows to retrieve
the correct intended target word corresponding to a
wrong word.
This preliminary definition of an error stays at
high level so that it is possible to refine it like we pro-
pose in the following section.
2.2 Taxonomy of Errors
Errors in digital documents may have multiple ori-
gins. Indeed, errors can occur (and accumulate) at
each step in the process which leads to an electronic
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
28
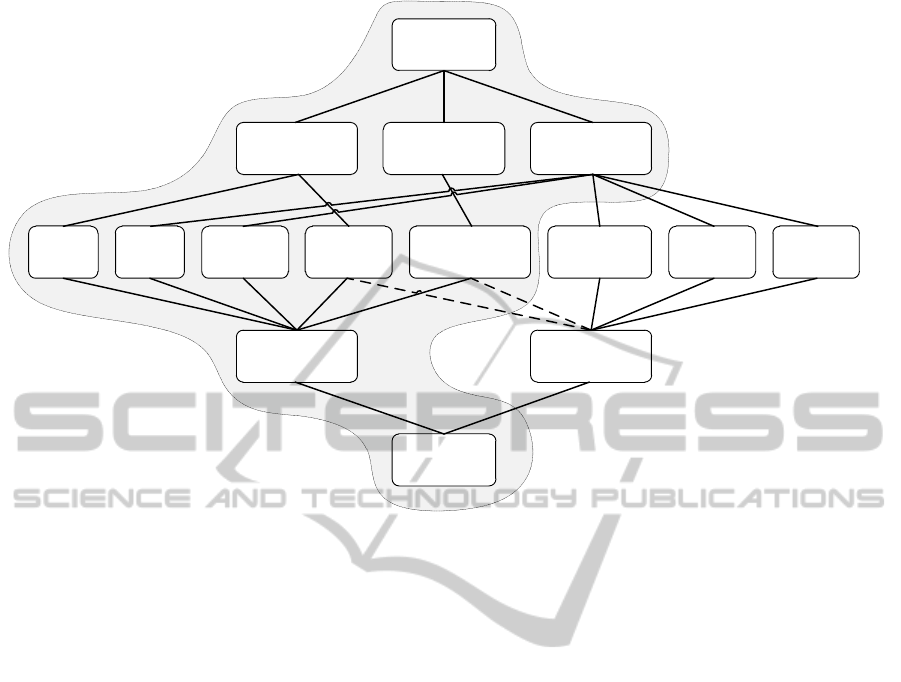
error
real-word
(word∈lexicon)
digitization materialization
non-word
(word∉lexicon)
«abstract »
information
invented
word
word
frontier
~word
phonetics
wrong
recognized
character
~wordgraphy
orthography
grammarmistyping/ typo
word∈
other
lexicon
error origin
Figure 1: Multi facet errors classification (error origin / type).
document from an initial "abstract" information. In-
formation is qualified as abstract as it is not material-
ized in a physical medium digital or not. It is then pos-
sible to distinguish digital documents whether they
are produced from a direct materialization (e.g. key-
board input), or they passed through another state
(e.g. handwritten) before being digitized. We can
make a distinction between errors related to human
intervention during information creation (false initial
idea), expression (verbalization of idea, association of
idea with a word, spelling or pronunciation problem),
and writing of information (dysgraphia, poor typog-
raphy), and secondly, errors coming from computer
data processing which occurs during OCR phase.
In some cases, errors can be valid words as de-
fined above. This type of error is called real-word
error (e.g. "diary" and "dairy"). Although this type
of error preserves most of the time the "syntactic" va-
lidity of the sentence in which it occurs, it breaks its
semantic coherence making the sentence unintelligi-
ble by humans. Such errors cannot be detected (and
hence corrected) efficiently without the presence of a
context such as words adjacent to the error. The con-
text makes it possible to identify semantic inconsis-
tencies generated by the error, or at least the low sta-
tistical probability for this word to be surrounded by
the words which compose its context. In most cases,
errors result in invalid words that we call non-words
errors (e.g. "tree" and "teer"). This last type of error
is easier to detect because a simple comparison with
valid words of a dictionary is sufficient. Although the
presence of a context may help to identify more pre-
cisely a proper correction it is not mandatory while
these errors can be considered as isolated words out
of context.
Most real-words errors come from abstract infor-
mation, i.e. there is difficulty in the ability of author
to associate the correct word according to his thought
(see Figure 1). This problem occurs most frequently
with children, non-native writer, and dyslexic people.
However, typos and errors in character recognition
rarely belong to real-words.
The different types of errors being defined, we of-
fer an overview of approaches to correct them accord-
ing to their type.
3 CONSIDERATIONS ABOUT
EVALUATION OF ERROR
CORRECTION SYSTEMS
In this section, we will introduce the most impor-
tant approaches developed for the correction of errors.
While this is a very active topic, it is not an exhaus-
tive state of the art in terms of references. Neverthe-
less, we believe that great families of approaches are
represented.
ATooltoEvaluateErrorCorrectionResourcesandProcessesSuitedforDocumentsImprovement
29

3.1 Overview of Error Correction
Approaches
In this article, we do not choose to consider one type
of error (non-word or real-word) in particular even if
the latter one is more difficult to identify as an error.
Works on non-words error correction are refer-
enced by (Kukich, 1992; Mitton, 2008). However,
approaches having the best results rely on context, as
well as approaches to correct real-words errors.
Works on real-words error correction can be clas-
sified into two categories: methods based on semantic
information (or a human lexical resource) and meth-
ods based on machine learning (or information likeli-
hood).
Approach based on "information semantics" was
first proposed by (Hirst and St-Onge, 1998), and de-
veloped later by (Hirst and Budanitsky, 2005). It de-
tects semantic anomalies but is not limited to word
verification from predefined confusion sets (at least
pairs of commonly confused words) which model am-
biguity between words. This approach is based on
the observation the words the writer intends to write
are usually semantically related to surrounding words
while some errors resulting real-words are not. The
problem of detecting real-word errors is the same as
the problem of homonyms. This is an application of
disambiguation methods to correct errors.
(Mays et al., 1991) propose a statistical method
using probabilities of trigrams of words to detect and
correct real-words errors without requiring predefined
confusion sets. (Wilcox-O’Hearn et al., 2008) analyze
advantages and limitations of the method proposed
by (Mays et al., 1991). They present a new evalua-
tion of the algorithm in order to be able to compare
the results with other methods. They also built and
evaluated some variants of the algorithm using fixed-
size windows.
3.2 Problems with Evaluation of Error
Correction Systems
All these works refer to difficulties in the evaluation
of their approaches compared to the others. That is
why works such as those of (Wilcox-O’Hearn et al.,
2008) are very important. Used resources (reference
dictionary, collections of errors, evaluation metrics)
differ significantly from the evaluation of one ap-
proach to another. Thus, collections of errors (or col-
lections of documents which contain errors) are rarely
employed in the evaluation and most of the time based
on randomly generated errors in a collection of docu-
ments. A significant work from Pedler (Pedler, 2007)
has been to collect and make available documents
produced by dyslexic people.
We propose a flexible evaluation model adapted
for our needs to the evaluation of error correction
mechanisms. However, it could relatively easily be
adapted to evaluate other kind of systems.
4 PROPOSAL OF AN
EVALUATION MODEL
In order to allow a maximum level of re-usability, we
have defined a generic approach to evaluate systems.
It may be closed systems considered as black boxes as
well as composites systems created from an original
combination of resources to evaluate.
This evaluation approach is described at a macro-
scopic level by a meta-model we call the Generic
Evaluation Model (GEM). Our main concern in the
context of this paper is the evaluation of different er-
ror correction mechanisms. So, we rely on a Specific
Evaluation Model (SEM) derived from the GEM and
adapted to this case. The SEM is tuned to evaluate the
wanted type of system and only needs to be instanti-
ated to perform an experiment.
4.1 Definition of a Generic Evaluation
Model (Meta-Model)
The GEM is a generic abstract representation of an
evaluation model which consists of five elements, so
that the GEM can be defined by the 5-tuple:
GEM = hR
D
, R
P
, s, R
E
, ai (3)
Where R
D
, R
P
and R
E
are input resources families
to the model. These resources respectively belongs to
the following families:
• Data D: noted R
D
(e.g. data to process),
• Processing P: noted R
P
(e.g. algorithms to apply
to data),
• Evaluations E: noted R
E
(e.g. evaluation metrics,
reference values).
Each resource family includes a set of types of re-
sources of its own and is dependent on the derivation
of the GEM in SEM.
s is a data processing module based on the re-
sources R provided to produce results (e.g. scores).
e is a module to evaluate data processing s results
and produces performance indicators (e.g. accuracy).
This meta-model is too generic to be usable for
evaluation task. It must be instantiated in a specific
model SEM defined relatively to an experiment eval-
uation needs.
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
30

4.2 Derivation of a Specific Evaluation
Model for Evaluation of Error
Correction Systems (Model)
The SEM is a derivation of the GEM for the needs of a
particular evaluation. In this paper, it has been derived
to evaluate error correction mechanisms. These can
be full autonomous error correction systems which
have their own resources (this is a special case which
will be specified later), or composite systems as men-
tioned above. To define the SEM, we will initially de-
fine each family of resources based on resource types
it accepts.
Thus R
D
consists of resources r
t
of type Coll and
Dict. Where, Coll represents the type Collection of
documents which is represented by a list of pairs of
the form: wrongword, targetword. And Dict repre-
sents the Dictionary type which is a list of the form:
word, word f requency.
Similarly, R
P
consists of resources r
t
of type SDM
or AS. The use of one of these two types excludes
the use of the other type of resource. Where, SDM
represents the type Similarity and Distance Measure
whose values are normalized in [0, 1] interval. While
employed measures are standardized, the similarity is
1−distance and vice versa. And AS, is a Autonomous
error correction System.
Finally, we can define R
E
as resources r
t
of type
EM. Where EM represents the type Evaluation Met-
rics whose values are normalized in [0, 1] interval.
Each family of resources is subject to constraints
on its cardinality which can be different if the eval-
uated error correction system is autonomous or com-
posite.
Thus, evaluation of a composite system (the gen-
eral case) requires the instantiation of a resource of
each type:
∀t ∈ {Coll, Dict, SDM, EM}, |r
t
| ≥ 1 (4)
The SEM is then represented by the following 5-
tuple:
SEM
composite
= h{Coll, Dict}, SDM, s, EM, ai (5)
However, when evaluating an autonomous system,
it is considered as a processing resource AS instead
of SDM. In addition, the system is autonomous, and
does not require any dictionary.
The SEM is then represented by the following 5-
tuple:
SEM
autonomous
= h{Coll}, AS, s, EM, ai (6)
The proposed model formalizes concepts and fol-
lows intuitive evaluation logic. However, this formal-
ization is necessary for large scale evaluation. The
genericity of the model enables it to apply to the eval-
uation of various types of systems via the instantia-
tion of suitable resources. In this case, the model was
adapted to evaluate error correction mechanisms. The
model was then implemented in a platform which can
serve as a framework for evaluation.
5 IMPLEMENTATION OF THE
EVALUATION MODEL
The implemented evaluation platform is based on the
above model which defines its different modules.
s a
List <error,
ordered_suggestion_list>
score
R
D
Coll
Dict
I
I
R
P
SDM
AS
I
I
R
E
EM
I
Figure 2: Evaluation model and overall architecture of the
evaluation platform.
The platform was developed in Java and uses the
OSGi standard (OSGi-Alliance, 2012) for modules
implementation. This allowed us to use the modular-
ity of the proposed model by defining common stan-
dard interfaces for each type of resources. This makes
it possible for a given type of module to replace it eas-
ily without impacting the rest of the platform. Each
module respect a contract has its own life cycle and
can be dynamically deployed on the platform. Pro-
cessing module s and assessment module a ensure the
availability of the minimum needed set of resources
for testing.
The developed platform was used for our evalua-
tion of some composite systems built from dictionar-
ies, similarity (or distance between strings) measures
commonly used in error correction systems.
6 EVALUATION
6.1 Instantiation of Evaluation Model
Resources
Evaluations conducted in this article consider only a
reduced set of composite systems. Resources used
in the composition of these systems are exposed in
following paragraphs.
ATooltoEvaluateErrorCorrectionResourcesandProcessesSuitedforDocumentsImprovement
31
6.1.1 Errors Collection
Our evaluations only concern errors corrected regard-
less of any context (at first time). This collection of
errors has been compiled from common mistakes on
Wikipedia, Wikipedia List of Common Misspellings
WCM (Wikipedia Community, 2012). Errors come as
a list of 4408 couples of the form:
<wrong word,target word>
This collection contains non-words as well as real-
words errors. While real-words errors are already la-
belled as errors, it is possible to suggest a correction
without the need for a context (which is not available).
6.1.2 Dictionary
In our first experiments, we implemented three dif-
ferent dictionaries. A dictionary based on Word-
net (Miller, 1995; Fellbaum, 1998), a unigram dictio-
nary provided by the AtD system (Mudge, 2012), and
an online collaborative dictionary Wiktionary (Wik-
tionary Community, 2012).
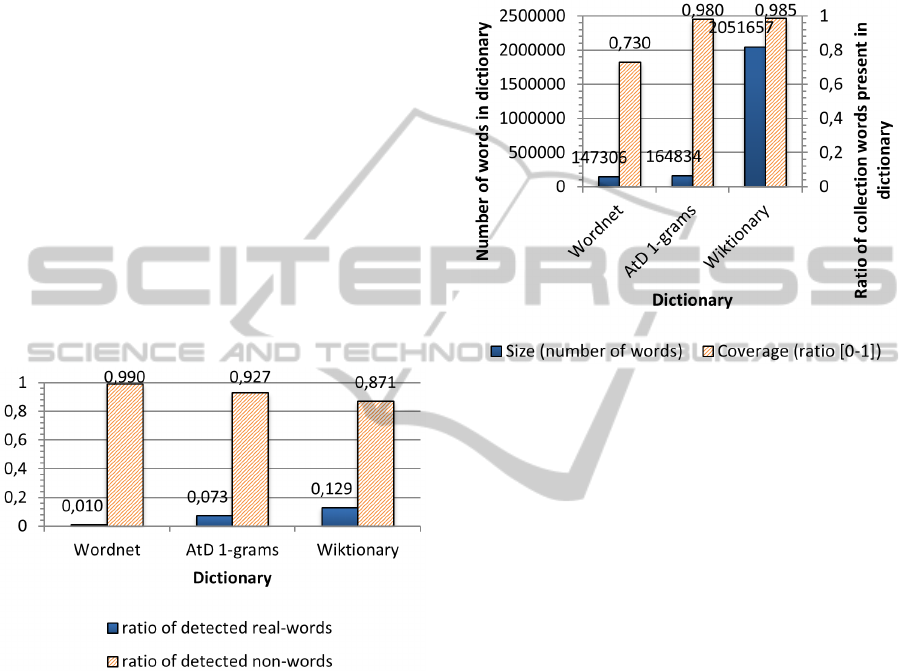
Figure 3: Proportion of words in the collection identified as
real-words (resp. non-words) according to the used dictio-
nary.
Although a correction can be proposed both for
non-words and real-words errors, identification of the
belonging of these errors to one or other of the cat-
egories is interesting to segment the collection and
provide independent indicators. This is a difficult task
because the identification of the category is dependent
of the chosen dictionary (Figure 3). Thus, new words
not yet integrated in a dictionary can be wrongly con-
sidered as non-words while unusual words may per-
sist. The temporal aspect is difficult to manage.
It may be noted on the histogram above that a
larger dictionary tends to identify more errors as real-
words errors than a dictionary with fewer words. In
that sense, Figure 4 highlights the difficulty to choose
a dictionary.
Indeed, the Wordnet based dictionary contains
147,000 words, and covers only 73% of target words
corresponding to errors, while AtD dictionary has
coverage of 98% with nearly 165,000 words only.
Wiktionnary dictionary has coverage of about 98.5%
with over 2 million words.
Figure 4: Dictionaries size and collection of errors target
words coverage.
AtD dictionary leverage the coverage of target
words in the collection of errors according to the num-
ber of words in the dictionary. Indeed it is the result
of a learning phase which allowed to keep only most
frequent words.
6.1.3 Similarity / Distance Measures
As part of a first series of experiments, only three
similarity / distance measures were evaluated: Lev-
enshtein distance, Jaro and Jaro-Winkler distance.
These three measures will then have to be compared
and maybe combined with other similarity measures
such as phonetic encoding based measures.
6.1.4 Evaluation Metrics
As a perspective we would like to integrate an error
correction system to an information retrieval system
in order to improve its performance Indexation Time
Error Correction (ITEC) process described in further
works of section 7). If the error correction process is
conventional, it is necessary to differentiate interac-
tive or online error correction, and non-interactive or
offline error correction.
Indeed, in the case of online error correction, the
system benefits from contextual information about
user input according to the device (smartphone, tablet,
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
32

Table 1: Synthesis of online and offline error correction sys-
tems constraints.
Online error cor-
rection (standard)
Offline error cor-
rection (ITEC)
Contextual
data
Yes: directly us-
able
No: metadata as-
sumptions
Users in-
teractions
Yes: choice
among many
proposals (˜ 5)
No: no choice
high accuracy re-
quired
netbook, laptop) and the physical layout of the key-
board keys. Moreover, it is possible to suggest mul-
tiple corrections to the user at the same time. This
allows the user to choose the suggestion which fits
best. Therefore, it is more important to suggest the
appropriate correction among propositions rather than
ranking it at the first position among them.
In the case of offline error correction, the problem
is more complex. Indeed, no contextual information
about input of data (and available metadata are rel-
atively poor). Nevertheless, it is possible to assume
that English texts should be linked to standard QW-
ERTY keyboard layout. It is particularly important
to promote accuracy in the case of offline error cor-
rection systems. Indeed, it is important to suggest
the proper correction in first place because the sys-
tem cannot rely on a user to choose the final correc-
tion. This phenomenon is necessarily present when
one wishes to reduce the responsibility of the user.
It is therefore necessary to have a correction system
with maximum accuracy.
These characteristics guided our evaluation met-
ric choice to the Mean Reciprocal Rank noted
MRR (Voorhees et al., 2000):
MRR =
1
|errorCouples|
|errorCouples|
∑
i=1
1
sugTW R
i
(7)
Where sugTW R stands for the rank of the suggestion
which is effectively the same as the target word.
This metric seems to be suited to the constraints of
offline error correction evaluation. Indeed, the MRR
applies a significant penalty if the correct result does
not occur in first ranks. High MRR value means that
the correct result belongs to top ranked results. On
the opposite, a low MRR value doesn’t mean that the
correct result is ranked very far, but only not in the
first ones.
Instances of employed resources being defined,
the next section presents the results of initial exper-
iments.
6.2 Results
Instances of previously defined resources allowed us
to build a composite error correction system to be
evaluated for each combination dictionary/similarity
measure, nine systems found in nine Evaluation
Model Instances rated EMI:
EMI
1
= h{WCM, Wikt}, J −W, s, MRR, ai
EMI
2
= h{WCM, Wikt}, Jaro, s, MRR, ai
EMI
3
= h{WCM, Wikt}, Leven, s, MRR, ai
EMI
4
= h{WCM, AtD}, J −W, s, MRR, ai
EMI
5
= h{WCM, AtD}, Jaro, s, MRR, ai
EMI
6
= h{WCM, AtD}, Leven, s, MRR, ai
EMI
7
= h{WCM, W N}, J −W, s, MRR, ai
EMI
8
= h{WCM, W N}, Jaro, s, MRR, ai
EMI
9
= h{WCM, W N}, Leven, s, MRR, ai
(8)
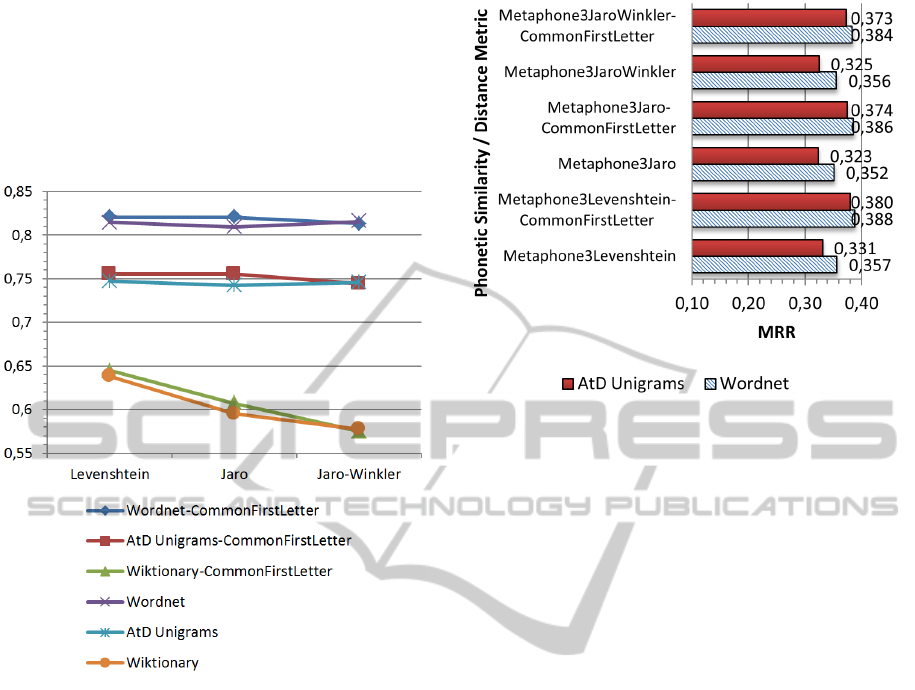
Figure 5 shows MRR scores obtained by each of
instantiations of the model. As it can be seen, big-
ger dictionary (see Figure 4) as Wiktionary allows a
maximum coverage of target words in the collection
of errors at the cost of a lower rank of the target word
among the suggestions.
Figure 5: MRR of different combinations between similar-
ity measures and dictionaries.
Indeed, the correct target word is lost in the quan-
tity of words syntactically close to the misspelled
word, which leads to a low MRR. A dictionary of
smaller size allows a better ranking of the target word
at the cost of an increased risk that suggestion list
misses the target word.
If we consider string similarity measures, we can
see they have different behaviors according to the dic-
tionary (although they seem to be close most of the
time). Thus, Levenshtein seems to be the least sen-
sitive of the three to the size of the dictionary, while
Jaro-Winkler which obtained good results associated
with Wordnet (small dictionary) seems to be less ef-
fective when combined with Wiktionary. The differ-
ence between these measures is not very important be-
cause they are not fundamentally different.
The study of the WCM collection allowed us to
determine that among the 4408 couples that the col-
lection contains 4274 wrong words share their first
ATooltoEvaluateErrorCorrectionResourcesandProcessesSuitedforDocumentsImprovement
33
character with their associated target word. It means
that 97% of errors couples share their first character.
We modified previously used similarity measures so
that they return a null similarity to dictionary words
which do not share the same first character as the mis-
spelled word to correct. The results of nine new EMI
are shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Comparison of MRR values obtained with and
without taking into account a common first character.
We can observe from the Figure 6 that the heuris-
tic which consists in the use of the first character
slightly improves the MRR of two of the three mea-
sures. Only the Jaro-Winkler measure sees its MRR
lowered. Moreover, this heuristic reduced signifi-
cantly the computing time of suggested corrections by
eliminating a large number of candidate words each
time an error is processed. This heuristic thus seems
interesting to integrate in composite systems.
In order to evaluate different kind of similarity
measures, we decided to apply previous string simi-
larity measures on phonetic encodings of both errors
and candidates words. This allows the creation of a
phonetic similarity measure. We can observe on Fig-
ure 7 that the combination of both measures is getting
worse results than simple string similarity measures
(about half the MRR of sring similarity measures).
This can be explained by the fact that the phonetic
encoding made many word candidates to be encoded
by the same phonetic key. The problem comes from
the pessimistic computation of the rank of the cor-
rect result. Indeed, in the case where many candidate
Figure 7: Comparison of MRR values obtained with a com-
bination of String similarity measures applied over a Meta-
phone 3 phonetic encoding.
words obtain the same score after the scorer pass, our
assessor consider that the rank of the correct result is
the rank of the worst one. So, if the ten best words
candidates including the correct result have the max-
imum score of 1, the assessor will consider that its
rank is 10, not 1, not 5. It should be better to be more
fair in this case by using word frequency as a second
criterion to sort the results (or in the worst case by
putting the rank of the correct word at the mean rank
of the same scored candidates).
7 CONCLUSIONS & FURTHER
WORKS
In this paper, we proposed a formal definition of key
concepts related to error correction. We also proposed
a classification of these errors according to their ori-
gins and their types and their related difficulties. Our
state of the art about error correction systems allowed
us to identify a problem in the evaluation of these sys-
tems. We have proposed a comprehensive evaluation
model including a meta-model derived in a model that
we instantiated. Afterwards, this evaluation model
was implemented in a modular and extensible evalua-
tion platform we used to evaluate 18 instances of the
model through composite systems. While this is not
sufficient to validate the model in itself, it is hard to
provide a meta-evaluation with regards to other eval-
uation approaches. It only proves that it works for
evaluated cases.
As the developed platform is extensible we will
integrate other similarity measures between strings,
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
34

as well as phonetic similarity measures. We will
also incorporate other heuristics such as those pro-
posed in (Wong et al., 2006). Other collections of
errors such as the one used by Aspell (Hirst and St-
Onge, 1998) will be included as well as collections
of documents tagged with errors such as the one used
by (Pedler, 2007). The platform can then be used to
determine optimal parameters in the combination of
different approaches and heuristics. We wish to eval-
uate complete error correction systems on the same
platform. The results are more difficult to interpret
because we do not control the resources (including
dictionaries) they rely on, but they will provide refer-
ence results to locate raw performance of the evalu-
ated approaches.
An Indexation Time Error Correction (ITEC) sys-
tem can be used in the analysis of documents to cor-
rect errors they contain and allowing creation of more
representative indexes. We wish to make indirect
evaluation of error correction approaches by compar-
ing the results obtained by information retrieval sys-
tems on evaluation campaigns such as TREC (Kantor
and Voorhees, 2000) or INEX without ITEC and with
it enabled.
REFERENCES
Atkinson, K. (2012). Aspell Spellchecker. http://aspell.net.
Last access 15 Jan. 2012.
Fellbaum, C. (1998). WordNet: An Electronic Lexical
Database. Cambridge, mit press edition.
Hirst, G. and Budanitsky, A. (2005). Correcting real-word
spelling errors by restoring lexical cohesion. Natural
Language Engineering, 11(1):87–111.
Hirst, G. and St-Onge, D. (1998). Lexical chains as repre-
sentations of context for the detection and correction
of malapropisms. In Fellbaum, C., editor, WordNet An
Electronic Lexical Database, volume 305, chapter 13,
pages 305–332. The MIT Press.
Kantor, P. B. and Voorhees, E. M. (2000). The TREC-5
Confusion Track: Comparing Retrieval Methods for
Scanned Text. Information Retrieval, 2(2):165–176.
Kukich, K. (1992). Techniques for Automatically Correct-
ing Words in Text. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR),
24(4):439.
Mays, E., Damerau, F. J., and Mercer, R. L. (1991). Context
based spelling correction. Information Processing &
Management, 27(5):517–522.
Miller, G. A. (1995). WordNet: A Lexical Database for
English. Communications of the ACM, 38(11):39–41.
Mitton, R. (2008). Ordering the suggestions of a
spellchecker without using context. Natural Language
Engineering, 15(02):173–192.
Mudge, R. (2012). After the Deadline. http://
static.afterthedeadline.com. Last access 15 Jan. 2012.
OSGi-Alliance (2012). Open Services Gateway initiative.
http://www.osgi.org. Last access 15 Jan. 2012.
Pedler, J. (2007). Computer Correction of Real-word
Spelling Errors in Dyslexic Text. PhD thesis, Birk-
beck, London University.
Rosnay, J. and Revelli, C. (2006). Pronetarian Revolution.
Ruch, P. (2002). Using contextual spelling correction to im-
prove retrieval effectiveness in degraded text collec-
tions. In Proceedings of the 19th international con-
ference on Computational linguistics-Volume 1, vol-
ume 1, page 7. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics.
Shannon, C. (1948). A mathematical theory of communi-
cation. Bell System Technical Journal, 27:379–423,
623–656.
Subramaniam, L. V., Roy, S., Faruquie, T. A., and Negi, S.
(2009). A Survey of Types of Text Noise and Tech-
niques to Handle Noisy Text. Language, pages 115–
122.
Varnhagen, C. K., McFall, G. P., Figueredo, L., Takach,
B. S., Daniels, J., and Cuthbertson, H. (2009).
Spelling and the Web. Journal of Applied Develop-
mental Psychology, 30(4):454–462.
Voorhees, E. M., Garofolo, J., and Sparck Jones, K. (2000).
The TREC-6 Spoken Document Retrieval Track. Bul-
letin of the American Society for Information Science
and Technology, 26(5):18–19.
Wikipedia Community (2012). Wikipedia List of Com-
mon Misspellings. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
Wikipedia:Lists_of_common_misspellings. Last ac-
cess 15 Jan. 2012.
Wiktionary Community (2012). Wiktionary Online Col-
laborative Dictionary. http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/
Wiktionary:Main_Page. Last access 15 Jan. 2012.
Wilcox-O’Hearn, A., Hirst, G., and Budanitsky, A. (2008).
Real-Word Spelling Correction with Trigrams: A Re-
consideration of the Mays, Damerau, and Mercer
Model. In A. Gelbukh, editor, In Proceedings of
CICLing-2008 (LNCS 4919, Springer-Verlag, pages
605–616.
Wong, W., Liu, W., and Bennamoun, M. (2006). Integrated
Scoring for Spelling Error Correction, Abbreviation
Expansion and Case Restoration in Dirty Text. In
5th Australasian conference on Data mining and ana-
lystics (AusDM’06), pages 83–89, Sydney, Australia.
Australian Computer Society.
ATooltoEvaluateErrorCorrectionResourcesandProcessesSuitedforDocumentsImprovement
35
