
Towards a Dynamic Adaptation of Documents within Pervasive
Information Systems
Karim Djemal
1
, Chantal Soule-Dupuy
2
and Nathalie Valles-Parlangeau
2
1
BSC France, Tour Montparnasse, 33 Avenue du Maine, 75755 Paris, France
2
IRIT/ University of Toulouse, 118 Route de Narbonne, F-31062 Toulouse Cedex 9, France
Keywords: Pervasive Computing, Document Adaptation, Dynamic Adaptation, Multistructurality, Contextual View,
Adaptation Process.
Abstract: Nowadays, Pervasive Information Systems has increasingly become a focus of communication technologies
development. In this paper, we focus on document adaptation within Pervasive Systems. Such adaptation is
reached using document multistructurality. In fact, each document structure may represent a different
document view which is adapted to a particular context. Thus, we introduce the MVDM model which
ensures on the one hand, the multistructured document management, and on the other hand, the generation
of new contextual views that are suited to different uses. In order to illustrate the feasibility of our approach,
we provide a process of document adaptation based on the MVDM model.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the advent of new information and
communication technologies, new needs have
emerged mainly requirements dealing with
exploitation of document that represents the biggest
information source. In fact, the rapid development of
mobile computing (mobile phone, laptop, PDA and
so on...) induces new applications and new
challenges. This development has promoted the
notion of Pervasive Computing. To be in such
context requires the design and the development of
the reliable and powerful methods and tools that
exploit the document information. These methods
and tools must make the information accessible at
anytime and anywhere, regardless of the devices
used.
The main goal of our work is to propose a
solution to dynamically manage and create adapted
document representations from the integration of all
available document information in function of
contextual situation. Thus, we present a solution for
the document adaptation in response to a user
request in a given context. The capacity offered by a
model of multistructured documents include the
consideration of different views attached to a
document, but also offer the option to add other
views linked to that document. These views can
generate different contextual representations of a
document adapted to context.
After presenting the general context of our work,
we present some related works which deal with
adaptation. In this paper we focus on the document
adaptation and therefore we detail the various issues
involved. We propose a solution based on the
document multistructurality. Thus, we formalize a
methodology for modeling these documents. This
methodology is based on a fragmentation technique:
the document is divided into structural nodes
connected by relations. This fragmentation allows to
link each piece to one or more views. From these
views, we propose to generate contextual
representations of the document. To illustrate our
proposal, we treat the example of a medical file that
must be adapted to the context of its use. Through
this example, we present some instantiations of our
model. Finally, we propose a process of dynamic
adaptation of documents. This process describes the
various possible cases of adaptation.
2 PROBLEM AND AIMS
Ubiquitous systems are designed to make
information available at anytime and anywhere.
These systems must be used in different contexts
according to user's profile, location, application and
devices (see Figure 1).
176
Djemal K., Soule-Dupuy C. and Valles-Parlangeau N..
Towards a Dynamic Adaptation of Documents within Pervasive Information Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0004002001760182
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2012), pages 176-182
ISBN: 978-989-8565-11-2
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure
1
environ
m
A c
o
p
aramet
e
several
these d
e
the conc
acc
o
incl
u
cha
r
is a
p
to
app
l
(Ch
a
outs
infl
u
its
d
b
e
d
app
l
Cont
mechani
informa
t
of conn
e
exchang
e
system
a
In th
to a pa
r
p
ropose
In this
c
design,
applicat
i
In t
h
types of
The
adj
u
tran
s
The
tran
s
acc
o
wit
h
data
for
t
1
: Componen
m
ent.
o
ntext reflec
t
e
rs related t
o
definitions
h
e
finitions, the
ern of this w
o
o
rding to (D
e
u
des all inf
o
r
acterize the s
p
erson, place
,
the interact
i
l
ication, inclu
d
a
ari et al., 20
0
ide paramete
r
u
ence its beh
a
d
ata and func
t
d
ynamic and
l
ication”.
extual adapt
a
sms in the
t
ion systems.
e
ction means
e
d involves
t
a
daptation an
d
e first catego
r
r
ticular conte
x
the develop
m
c
ase, the adj
u
implement
a
i
ons.
h
e approache
s
information
a
adaptation o
f
u
stment appli
e
s
formations a
r
adaptation
s
forming the
o
rding to data
h
specific con
t
(text, image,
t
heir adaptati
o
ts of a ub
i
t
s a combi
n
o
a particula
r
h
ave been p
most signifi
c
o
rk are the fol
l
e
y et al., 20
0
o
rmation that
ituation of a
n
,
or object th
a
i
on between
d
ing user and
0
7) define the
r
s of the appl
i
a
vior by defin
i
t
ionality. The
s
can change
d
a
tion is on
e
implementat
i
The heterog
e
, of users a
n
t
wo adaptati
o
d
the informat
i
r
y, there is a
x
t. (Aksit &
m
ent of adapt
u
stment affec
t
a
tion and
s
of the seco
a
daptation ha
v
f
presentatio
n
e
s to user int
e
r
e performed
of conte
n
information
types or for
m
t
ext. The natu
etc.) require
s
o
n.
i
quitous perv
a
ation of va
r
r
situation.
T
roposed. A
m
c
ant accordi
n
l
owing ones:
0
1), “the co
n
can be use
d
n
entity. An e
n
a
t may be rele
the user
application”;
contex
t
as “
a
i
cation that
m
i
ng new vie
w
s
e parameters
d
uring use o
f
e
of the ce
n
i
on of perv
a
e
neity of dev
i
n
d of inform
a
o
n categories:
i
on adaptatio
n
system whic
h
Choukair, 2
0
able applicat
i
s the archite
c
deployment
n
d category,
v
e been propo
s
n
: in this case
,
e
rfaces. Thus
,
a
t the display
;
n
t: consists
to be prov
m
ats in accord
a
r
e diversity o
f
special treat
m
a
sive
r
ious
T
hus,
m
ong
n
g to
n
text
d
to
n
tity
e
vant
and
a
ll of
m
ight
w
s on
s
can
f
the
n
tral
a
sive
i
ces,
a
tion
the
n
.
h
fits
0
03)
i
ons.
c
ture
of
two
sed:
, the
,
the
;
in
v
ided
a
nce
f
the
m
ent
int
r
im
p
arc
h
These diffe
r
r
oduced th
r
p
lementation
w
h
itecture (Lei
Client-side
mechanisms
receiver (ter
m
adopted: t
h
transformati
o
representati
o
2001) that
adaptation,
adapting a p
(Fisher et a
l
adaptation.
T
solution f
o
heterogeneit
y
terminal c
h
adaptation t
o
generally h
a
capacity. T
h
execute the
a
Proxy-side
A
node betwe
ensures the
i
contextual
c
(Berhe et al.
al., 2003). (
C
to achieve t
h
al., 2004)
i
responsible
b
etween w
e
(Singh et al.
localize a v
e
adapted to t
h
transcode t
h
mechanisms
(Wee et al.,
approach is
p
roxy (any
p
one the han
d
ensure opti
m
ensure the
failure. But,
concerns th
e
access to an
y
Server-side
A
traditional
s
mechanisms
.
techniques
f
on the Inter
n
HTML/XM
L
b
ased on X
M
various ann
o
r
ent types
r
ee differe
n
w
ithin pervas
i
et al., 2001):
Adaptatio
n
are runnin
g
m
inal). Two t
y
h
e adaptati
o
o
n or by
o
n received.
W
offer solut
i
(Marriott et
a
rticular grap
h
., 1997) that
T
his approac
h
o
r manage
m
y
. The bes
t
h
aracteristics
o
the context.
a
s a low st
o
h
us, it is not
a
daptation me
c
A
daptation: P
r
en the clie
n
i
nformation a
c
onstraints (
C
, 2004) (Sing
h
C
haari et al.,
2
h
e adaptation
m
i
nclude spec
i
for establ
i
b services a
n
,
2004) sugg
e
e
rsion of ada
p
h
e context is f
o
e data to cre
of image “J
P
2003). The
m
that it does
n
p
roxy can b
e
d
to choose
t
m
um adaptat
i
continuity o
f
the main dra
w
e
security. I
n
y
information.
A
daptation: t
h
s
erver is ex
t
.
(Margaritid
i
f
or adapting
m
n
et. (Hori et
a
L
to guide the
i
M
L to ensur
e
o
tations and e
l
of adaptati
o
n
t approa
c
i
ve informati
o
n
: the
a
g
at the lev
e
y
pes of adapt
a
o
n of co
n
selecting
t
W
e discern (
L
t
ions for t
h
al., 2002)
p
hic fo
r
mat “
S
address the
w
h
provides a
d
m
ent of th
t
knowledg
e
allows an
However, th
e
o
rage and p
able in som
e
e
chanisms.
r
oxy is an int
e
nt
and the
s
a
daptation ac
c
Chaari et a
l
h et al., 2004
2
007) use we
b
m
echanisms.
ific Proxies
i
shing the
a
nd the local
e
st using the
P
p
ted data. If
n
fo
und, the pro
x
e
ate one. Tra
n
P
EG” were
d
m
ain advanta
g
n
ot depend o
n
e
chosen). T
h
t
he proper
m
ion, and se
c
f
process in
w
back of this
n
fact, any
p
.
h
e functional
i
t
ended by
a
d
is et al., 20
m
ultimedia d
a
l., 2000) an
n
e
ir adaptation.
e
the link be
t
lements of th
e
o
n have
c
hes of
o
n system
a
daptation
e
l of the
a
tions are
n
tent by
t
he best
L
ei et al.,
h
e media
a
imed at
S
VG” and
w
eb page
d
istributed
e client
e
of the
effective
e
terminal
rocessing
e
cases to
e
rmediary
s
erver. It
c
ording to
l
., 2007)
)
(Wee et
b
services
(Berhe et
that are
interface
Proxies.
P
roxies to
n
o version
x
y sees to
n
scription
d
efined in
g
e of this
n
specific
h
is allows
achine to
c
ondly to
case of
approach
p
roxy can
i
ty of the
a
daptation
0
1) offer
o
cuments
n
otate the
They are
t
ween the
e
original
TowardsaDynamicAdaptationofDocumentswithinPervasiveInformationSystems
177

document. (Mogul, 2001) focuses on the
transcript image for the web. The advantage of
these works is the centralization of adaptation
mechanisms. Thus, the entity adaptation for a
particular context is applied only once on the
server. Conversely, poor knowledge of the
client’s characteristics may be source of
erroneous information and therefore a source of
a bad adaptation. Moreover, despite their ability
of processing, the servers may be congested due
to many requests and may not be able to satisfy
some clients. To resolve this problem, (Luo et
al., 2004) have proposed an adaptation by
rewriting queries. This solution allows to secure
data exchanged through the creation of virtual
views.
In this paper we focus on the dynamic adaptation
of document content on the server side. The question
that arises is how to deliver the adapted document
for a suitable context. Should we define in advance
the contextual situations and jointly document
descriptions arising? Or must we generate
dynamically an adapted document according to a
suitable context?
The definition and storage of different document
versions according to any contextual situation ensure
adequate adaptation because there are as many
document versions as possible contextual
combinations. However, this solution generates a
complexity, redundant storage and a lack of
flexibility due to the difficulty of taking account of a
not predefined contextual situation.
The ad hoc generation of contextual
representations of the document provides a dynamic
adaptation. This generation may be done by a direct
matching between the original structure of the
document and the structure defined by the context.
In this case, the problem is the reliability of results
given the heterogeneity that might exist between the
two structures to compare.
3 FROM
MULTISTRUCTURALITY TO
ADAPTATION
Documents, complex or not, can be defined and
described through different structures that are linked
to the nature of documents or related to the uses that
may be done. These structures may be more or less
independent. They might contain their own
fragments or use those of one or many structures
while adding additional information. Therefore, a
same document may be represented through several
structures having a same nature according to the
context for using this document. The use of these
structures seems to be an appropriate solution to
generate a contextual representation of the
document. In fact, each structure has a particular
document organization. It allows to identify
unambiguously the information fragments that
compose the document, and their emplacement.
Thus, to be able to adapt the description of
document to any content, it is necessary to fragment
this document in structural nodes that are connected
through various kinds of relations. A relation
connects two nodes according to a particular view.
Each view represents a sub-structure of the overall
structure of a document. It is then composed of a set
of nodes included in the set of nodes extracted from
this document. The view notion is used to define the
several types of structures (Djemal et al., 2008).
Taking into account the different views related of
a same document seems to be an appropriate
solution to find the adequate document
representation according to a particular context.
Each view represents a particular context. For
example, we can get an “expert” view and a
“framework” view, etc.
Thus, we defined two types of views:
Structural views: to identify the different types
of structures.
Contextual views: to take into account the
various contextual representations of a
document.
To describe these structural and contextual
views, we propose the model MVDM presented in
what following, as well as adaptation capabilities it
offers.
3.1 MVDM Model
The model MVDM “Multi View Document Model”
is designed to manage multistructured documents. It
includes both levels generic one and specific one
(Djemal et al., 2008).
Generic Level. The generic level provides a
meta representation of documents. In this level, the
views are described of a generic way regardless of
the document specifications.
The notion of generic structure (GS) allows to
group documents in classes. Each document class is
considered as an homogenous and coherent
document set of a structural point of view.
Specific Level. The specific level characterizes
the special document features. Therefore, it
identifies the different fragments of this document
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
178
and thei
r
Eac
h
The GS
the all
o
represen
refers to
us, on t
h
on do
c
exploita
t
the othe
r
docume
n
schema
docume
n
Co
m
two lev
e
special
l
UML d
o
opted fo
r
I
nter
b
etween
describe
d
classes
a
generic
c
enriche
d
these cl
a
mother
c
Cha
r
complia
n
have, in
aspect, t
h
A c
h
met
a
cha
r
The
ho
m
gen
e
that
to a
Cla
s
set
o
frag
m
spe
c
3.2
S
The ori
g
p
ossibili
adaptati
o
adaptati
o
The
s
the diff
e
as we h
a
overlap
p
storage
d
r
organizatio
n
h
specific stru
c
embodies a
o
f sub-struct
u
n
ted b
y
gener
i
a class of s
p
h
e one hand, t
o
c
ument coll
e
t
ion paramet
e
r
hand, to de
fi
n
t. In fact, ea
c
for a differ
e
n
t.
m
pliance Lin
k
e
ls (specific
l
ink that we
o
es not have
t
r
a new stere
o
r
est of the Co
m
the specific
d
as an inh
a
re on one
h
c
lasses, and
o
d
by specific
a
sses are subc
c
lass.
r
acteristics o
f
n
ce link suc
h
addition to t
h
h
e following
c
h
ild meta cla
s
a
class. T
h
r
acteristics of
homomorp
h
m
omorphism
e
ric level. In
d
every specifi
c
generic frag
m
s
sification: ea
c
o
f specific fr
a
m
ent classes
c
ific fragment
.
S
tatic and
D
g
inality of th
ty of adopt
i
o
n: static
o
n.
static adaptat
i
e
rent SV of t
h
a
ve designed
p
ing betwee
n
d
uplication.
T
n
s.
c
ture (SS) is
global struct
u
u
res. These
s
i
c views (GV
)
p
ecific views
(
o
establish an
e
ctions by
e
rs on multip
fi
ne several re
p
c
h view serve
s
e
nt structural
k
. The relatio
n
and generic)
define as “
c
t
his type of l
i
o
type: “ ”
m
pliance Lin
k
and the gen
eritance bec
a
h
and, fully c
o
o
n the other
h
information.
lasses; and n
o
f
the Comp
l
h
as we hav
h
e generaliza
t
c
haracteristic
s
s
s is an insta
n
h
is instanc
e
the derived
m
h
ism: This l
i
between t
h
d
eed, this rel
c
fragment ne
m
ent,
c
h generic fr
a
a
gments. Thi
s
that facilitat
e
.
Dy
namic A
d
e MVDM m
o
i
ng both ty
p
adaptation
i
on is perfor
m
h
e document.
T
allow to sha
r
n
the view
s
T
hus, the doc
u
attached to a
u
re which c
o
s
ub-structures
)
. Thus, each
(
SV). This al
l
a
lysis and qu
e
combining
le views, an
d
p
resentations
s
as a gramm
a
description
o
n
ship betwee
n
is ensured
b
c
ompliance l
i
i
nk; therefore
k
. The relatio
n
e
ric level ca
n
a
use the spe
c
o
nsistent wit
h
h
and, they ca
n
But, in this
c
o
t instances o
f
l
iance Lin
k
.
e
defined sh
o
t
ion/specializ
a
s
:
n
ce of the m
o
e
has all
m
eta class,
i
nk provides
h
e specific
ationship en
s
e
ds to be atta
c
a
gment inclu
d
s
allows to c
r
e
the access
d
aptation
o
del rests o
n
p
es of docu
m
and dyn
a
m
ed by stora
g
T
hese views
s
r
e of nodes.
T
s
eliminates
u
ment content
s
GS.
o
vers
s
are
GV
l
ows
e
ries
the
d
on
of a
a
r or
o
f a
n
the
b
y a
i
n
k
”.
, we
n
ship
n
be
cific
h
the
n
be
c
ase,
f
the
The
ould
a
tion
o
ther
the
the
and
s
ures
c
hed
d
es a
r
eate
to a
n
the
m
ent
a
mic
g
e of
s
uch
This
the
s
are
sto
r
are
co
n
the
b
et
w
ge
n
an
d
of
a
str
u
is
a
on
e
att
a
onl
y
the
SS
fur
t
int
e
the
ful
l
an
d
3.
3
To
of
Fig
do
c
str
u
cla
r
lin
k
use
a s
e
of
a
ser
v
aid
thr
e
M
V
sa
m
r
ed once in
s
based on t
h
n
textual repre
s
The generic
l
dynamic a
d
w
een a GV a
n
n
erate a new
d
whose a str
u
a
GV used.
The complia
n
u
ctures. Acco
r
a
class of str
u
e
or more G
V
a
ched to a G
y
one SV “S
V
original doc
u
and each of
t
t
her SV. I
n
e
rsection of “
S
SV “SV
13
”.
l
coverage of
d
the original
G
Figure 2: Ge
n
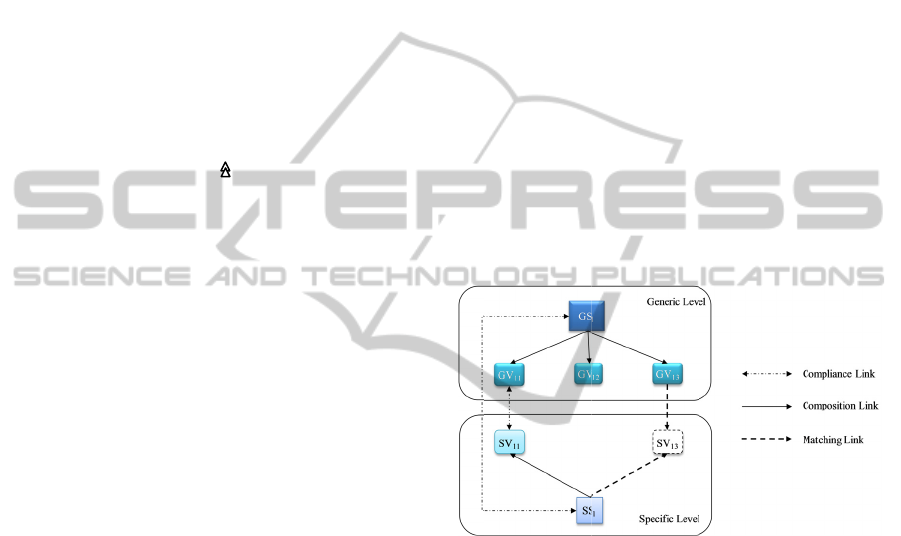
3
Examp
l
illustrate our
a medical f
i
u
re 4 (AP
P
c
ument. Thi
s
u
cture to all c
o
r
ity, we hav
e
k
s that might
e
Each medica
rs according
t
e
cretary to ed
i
a
patient, it
m
v
ice that aske
d
to a patient,
o
e
e contextual
V
DM model
t
m
e GS “Medi
c
s
pecific node
s
h
ese nodes
t
s
entations of
a
l
evel of the
M
d
aptation. I
n
n
d the SS of t
h
SV sharing
t
u
ctural descr
i
n
ce link allo
w
r
ding to the
M
u
ctures. A G
S
V
s. Suppose
S
“GS
1
” (se
e
V
11
” that rep
r
u
ment. The in
t
t
he GV alrea
d
n
the exam
p
S
S
1
” with “G
V
Thus, the co
the organiza
t
G
V.
n
eration princip
l
e
proposals, w
e
le of a pati
e
ENDIX) sh
o
s
structure
o
ntextual vie
w
e
not present
e
e
xist in a GS.
l
file can be
t
o several con
t
i
t the persona
l
m
ay be reque
d
urgency inf
o
o
r it is consu
l
situations a
r
t
hrough thre
e
c
alFile” (see
F
s
. The differ
e
t
o form the
a
document.
M
VDM mod
e
n
fact, the
t
he documen
t
t
he documen
t
i
ption is an
“
w
s to manage
c
M
VDM model
,
S
can
b
e co
m
we have a
S
e
Figure 2)
“
r
esents the st
r
t
ersection bet
w
d
y defined ca
n
m
ple (Figure
V
13
” allows t
o
o
mpliance lin
k
t
ion of the S
V
p
le of specific
v
e
consider th
e
e
nt within a
o
ws the GS
represents
a
w
s already de
f
t
ed a non hi
e
consulted by
texts. It can b
l
data (“Perso
n
e
sted by an a
m
fo
rmation to d
o
l
ted by a doc
t
r
e represente
e
GVs attach
e
F
igure 3).
e
nt views
different
e
l ensures
matching
allows to
t
contents
“
instance”
c
lasses of
,
each GS
m
posed of
S
S “SS
1
”
“
SS
1
” has
r
ucture of
w
een this
n
provide
2), the
o
generate
k
ensures
V
created
v
iews.
e
example
hospital.
of this
a
global
f
ined. For
e
rarchical
different
e used by
n
alData”)
m
bulance
o
the first
t
or. These
d by the
e
d to the
TowardsaDynamicAdaptationofDocumentswithinPervasiveInformationSystems
179

Fig
u
4 P
R
A
D
In our
accordi
n
reposito
r
appropri
we prop
p
rocess
i
4.1
A
Phase 1
p
hase is
define t
h
these c
h
p
aramet
e
(PDA a
n
characte
r
2005), o
u
p
rofile.
characte
r
specific
detect t
h
matchin
g
Pha
s
requires
p
aramet
e
using, f
o
ensure t
h
from th
e
system
m
docume
n
Pha
s
one of
t
corresp
o
Algorith
develop
e
and sec
u
structur
e
system
m
of the c
o
has bee
n
u
re 3: Generic
r
R
OCESS
O
D
APTATI
approach, th
n
g to the MV
D
r
y located i
n
ate documen
t
ose a proces
s
i
s composed
o
A
daptation
1
. Detection
o
activated to i
d
h
e context p
a
h
aracteristics
m
e
rs. For exa
m
n
d Smart Pho
n
r
istics. In e
a
u
r tea
m
mod
e
Relationship
s
r
istics are b
a
naming spa
c
h
e features t
o
g
of views.
s
e 2. Struc
t
the comb
i
e
rs. These
p
o
r example, t
h
h
e intersecti
o
e
context. Fr
o
m
ust determi
n
n
t to provide.
s
e 3. GV Sel
e
t
he GVs sto
r
o
nding to tha
t
h
ms of com
p
e
d to achieve
u
re adaptati
o
e
s to compar
e
m
ust find the
i
o
ntext. Thus,
n
selected th
e
r
epresentation
o
O
F DOC
U
ON
e documents
D
M model
w
n
serve
r
-side.
t
for each co
n
s
of documen
t
o
f eight phase
Phases
o
f Context
P
d
entify new
c
a
rameters. O
n
m
ay be iden
t
m
ple, two d
i
n
e) may hav
e
a
rlier works
(
e
led these fea
t
s
and matchi
n
a
sed on a s
c
e (rdfs,...).
o
be used an
d
t
ure Extrac
t
i
nation of
d
p
arameters c
a
h
e first orde
r
o
n of differe
n
o
m the conte
x
n
e the conte
x
e
ction. The s
y
r
ed in the d
a
t
representati
v
p
arisons str
u
this phase. T
o
o
n, the dista
n
e
must be e
q
i
dentical vie
w
two cases th
a
e
n the syste
m
o
f medical file.
U
MENT
are represe
w
ithin a docu
m
To provide
n
textual situa
t
t
adaptation.
T
s
.
P
arameters.
T
c
haracteristics
n
the same
a
t
ical for diff
e
i
fferent term
i
the same dis
(
Chevalier et
t
ures as a reso
n
g between t
h
t
andard or
o
This is don
e
d
in our cas
e
t
ion. This p
h
d
etected co
n
a
n be comb
r
logic which
n
t criteria ext
r
tual situation
,
x
tual view o
f
y
stem must s
e
a
tabase, the
v
v
e of the con
t
u
ctures must
o
ensure a co
r
n
ce between
q
ual to zero.
w
as represent
a
a
t arise: if no
m
generates a
e
nted
m
ent
the
t
ion,
This
This
that
a
xis,
e
rent
i
nals
s
play
t
al.,
o
urce
hese
o
n a
e
to
e
for
hase
n
text
b
ined
can
r
acts
, the
f
the
e
lect
v
iew
n
text.
t
be
r
rect
the
The
a
tive
GV
new
G
V
SV
ca
n
vie
w
cre
a
wh
i
req
u
the
sel
e
vie
w
SV
the
ab
o
res
u
or
re
pr
inf
o
the
ref
l
all
o
or
d
co
n
co
n
ge
n
p
ro
ap
p
4.
2
To
we
Fig
vie
w
“D
o
co
n
inf
o
is
d
sys
t
de
fi
alg
o
de
fi
the
(ph
p
ro
(ph
ge
n
co
m
“M
V
(phase 4), o
t
(phase 5).
Phase 4. Ge
n
n
not find a G
V
w
of the d
a
tion one. It
i
le taking int
o
u
ested.
Phase 5. Sel
e
system try
t
e
cted GV an
w
does not e
x
(phase 6).
O
document (p
h
Phase 6. G
e
o
ut to create a
u
lt of the mat
c
the GV gen
e
r
esents the
o
rmation abo
u
SS determin
e
Phase 7.
D
l
ects the struc
o
ws to presen
t
ered nodes.
T
n
tents. Thus,
i
n
textual repre
s
Phase 8. Do
c
n
erated docu
m
cess. In this
p
ropriate term
i
2
Examp
l
illustrate so
m
take up the
u
re 4 in AP
P
w
s accordi
n
o
ctor”, “Amb
u
n
sider now a
o
rmation. In
t
d
efined (phas
e
t
em compare
s
fi
ned. After t
h
o
rithms (phas
fi
ned represen
t
system mus
t
ase 4).
When the
n
ceeds to the
ase 6). Fig
n
erating proc
e
m
bines the
s
edicalFile”
w
t
herwise it se
l
n
eration of
V
V
that is ide
n
o
cument to
will be atta
c
o
account the
n
e
ction of the
V
t
o select the
d
the docu
m
x
ist, the syste
m
O
therwise, th
e
h
ase7).
neration of
V
new specific
c
hing of the
G
e
rated in ph
a
document.
u
t the structu
r
e
s the specific
D
ocument
G
t
ural organiz
a
t
a document
T
he leave no
d
i
t is entirely
p
s
entation of d
o
c
ument Send
i
m
ent is the
phase, the d
o
i
nal.
l
e of Adap
t
m
e phases of
o
example of
G
ENDIX). Th
i
n
g to three
u
lanceServic
e
nurse want
s
h
is case, a n
e
e
2). Before
a
s
this new v
i
h
e running o
f
e 3), it appea
r
t
the new con
t
t
generate a
n
ew GV is
g
creation of
t
u
re 5 (AP
P
e
ss of a S
V
s
pecific nod
e
w
ith a view
l
ects the corr
e
V
G. Where t
h
n
tical to the
c
provide, it
c
hed to a G
S
n
ature of the
d
VS. During t
h
SV that m
a
m
ent requeste
d
m
must gener
a
e
system will
VS. In this
c
view. This v
i
G
V selected i
n
a
se 4, with
a
The GV
r
e of the ne
w
content of th
i
G
eneration.
a
tion of a do
c
as a set of n
d
es refer the
d
possible to
g
o
cument fro
m
i
n
g
. The send
latest phas
e
o
cument is s
e
t
ation
o
ur adaptatio
n
G
S “Medical
F
i
s GS consist
s
e
different
e
” and “Secre
t
s
to access
t
e
w contextua
l
a
dding a ne
w
i
ew with G
V
f
structure c
o
r
s that no G
V
t
extual situat
i
n
ew view G
V
g
enerated, th
t
he correspo
n
P
ENDIX) s
h
V
. Indeed, th
e
s related t
o
generic “N
u
e
sponding
h
e system
c
ontextual
proceeds
S
selected
d
ocument
h
is phase,
tches the
d
. If this
a
te a new
generate
c
ase, it is
i
ew is the
n
phase 3
a
SS that
provides
w
SV, and
i
s SV.
The SV
c
ument. It
e
sted and
d
ocument
g
enerate a
m
its SV.
i
ng of the
e
in our
e
nt to the
n
process,
F
ile” (see
s
of three
contexts:
t
ary”. We
t
o patient
situation
w
GV, the
V
s already
o
mparison
V
s already
on. Thus,
V
“nurse”
e
system
n
ding SV
h
ows the
e
system
o
the SS
u
rse” (see
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
180

Figure 5 in APPENDIX).
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposes a solution for the document
adaptation within pervasive information systems.
This solution is based on the management of
document representations through contextual views.
The representation and the coordination of these
views are established according to MVDM Model.
In fact, this model manages two kinds of views:
structural views and contextual views. Through
these views, it is possible to define several structures
for a same document. From these structures, context
adapted documents are generated.
To achieve these goals, we propose an adaptation
process based on the MVDM Model. This process
ensures:
the document adaptation to a contextual
predefined situation. This kind of adaptation is
guaranteed by the matching between the SS of
the original document and the GV representing
the contextual situation,
the document adaptation to a undefined
contextual situation. This done through the
generation of new GVs adapted to new contexts.
There are two approaches to manage the
multistructurality: one based on models (Bruno et
al., 2006) (Chatti et al., 2007) (Le Maitre, 2006) and
another based on syntax (Huitfeldt, 1993) (Sperberg-
McQueen et al., 2004). The MVDM model is part of
the first category of approaches. The breakdown of
multistructurality related works is presented in
(Djemal et al., 2008). The use of approaches has
shown the need of further treatment to exploit these
documents. In fact, the syntactic approaches require
a specific parser to the proposed solution, while the
approaches based on models require specific
language (for example some extensions of XQuery
languages).
The originality of the MVDM model lies on the
definition of the generic level. This level has two
particular meta classes: “GenStr” and “GenView”.
The “GensStr” serves as a grammar or schema for a
multistructured document. “GenView” represents
one of the structural descriptions of this document.
Thus, each GV allows to define clearly the structural
organization of a SV which is used to generate the
adapted version of a document.
Our proposals have been validated through a tool
entitled MDOCREP (Multimedia Document
Repository), which integrates and analyzes the
multistructured documents and especially
multimedia documents. We have shown the ability
of this tool to manage the incorporation of multiple
views of a document. Therefore, it can generate the
adapted documents according to these views.
The evaluation of our system within dynamic
context is a major concern, which we will consider
in our future work. Concretely, we will try to define
interchange mechanisms and protocols in order to
transfer contextual parameters and adapted
documents. These must be done within an
architecture specific to our proposals.
REFERENCES
Aksit, M., Choukair, Z., 2003. Dynamic, adaptive and
reconfigurable systems overview and prospective
vision. In: Proceedings of 23rd International
Conference on Distributed Computing Systems
Workshops, pp. 84-89.
Berhe, G., Brunie, L., Pierson, J. M., 2004. Modeling
service-based multimedia content adaptation in
pervasive computing. In: Proceedings of the 1st
conference on Computing frontiers, pp. 60-69. ACM
New York, NY, USA.
Bruno, E., Murisasco, E., 2006. MSXD: A Model and a
Schema for Concurrent Structures Defined over the
Same Textual Data. In LECTURE NOTES IN
COMPUTER SCIENCE 4080, pp. 172-181. (2006)
Chaari, T., Ejigu, D., Laforest, F., Scuturici, V. M., 2007.
A comprehensive approach to model and use context
for adapting applications in pervasive environments.
In: The Journal of Systems & Software, pp. 1973-
1992.
Chatti, N., Calabretto, S., Pinon, J. M., Kaouk, S., 2007.
MultiX, an XML-based formalism to encode multi-
structured documents. In: Proceedings of Extreme
Markup Languages 2007.
Chevalier, M., Soulé-Dupuy, C., Tchienehom, P., 2005.
Profiles Semantics and Matchings Flexibility for
Ressources Access. In: IEEE international Conference
on Signal Image Technology and Internet based
Systems, pp. 224–231.
Dey, A. K., Abowd, G. D., Salber, D., 2001. A conceptual
framework and a toolkit for supporting the rapid
prototyping of context-aware applications. In Human-
Computer Interaction 16, 2-4, pp. 97-166.
Djemal, K., Soule-Dupuy, C., Valles-Parlangeau, N.,
2008. Formal modeling of multistructured documents.
In: Proceeding of Second International Conference on
Research Challenges in Information Science, RCIS
2008, pp. 227-236. IEEE.
Fisher, B., Agelidis, M., Dill, J., A, P. T., B, G. C., C, C.
J., 1997. CZWeb, Fish-Eye Views for Visualizing the
World-Wide Web. In: Proc. of the 7th Int. Conf. on
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI International '97),
pp. 719-722, Elsevier.
TowardsaDynamicAdaptationofDocumentswithinPervasiveInformationSystems
181
Hori, M.
,
2000.
Com
p
Huitfeldt
,
Syste
m
Le Mait
r
docu
m
of t
h
engin
Lei, Z.,
adapt
Com
p
Luo, B.,
L
grain
e
quer
y
A
C
M
know
l
York
,
Margariti
techn
APPE
,
Kondoh, G.,
Annotation-
b
p
uter Networks
,
C., 1993.
m. ACH-
A
LL
C
r
e, J., 2006.
D
m
ents by mea
n
h
e 2006 A
C
n
eering, pp. 15
5
Georganas, N.
ation in perva
s
p
uter Engineer
i
L
ee, D., Lee,
W
e
d run-time X
M
y
rewriting. I
n
M
international
l
edge manag
e
,
NY, USA.
dis, M., Pol
y
iques for ub
i
NDIX
INSEE
Ono, K., Hir
o
b
ased web c
o
33, 1-6, pp. 19
MECS-A M
u
C
, pp. 16-19.
D
escribing m
u
n
s of delay nod
C
M
s
ymposiu
m
5
-164. ACM N
e
D., 2001. C
o
s
ive computing
i
ng.
W
. C., Liu, P.,
M
L access con
t
n
: Proceeding
s
conference o
n
e
ment, pp. 5
4
y
zos, G. C.
i
quitous inter
n
PersonalData
Name Birthday
A
o
se, S., Singha
l
o
ntent transco
d
7
-211.
u
lti-Element
C
u
ltistructured
X
e
s. In: Procee
d
m
on Docu
m
e
w York, NY,
U
o
ntext-
b
ased
m
. In: Electrica
l
2
004. QFilter:
t
rol via NFA-
b
s
of the thirt
e
n
Information
4
3-552.ACM
2001. Adapt
a
n
et multimedi
a
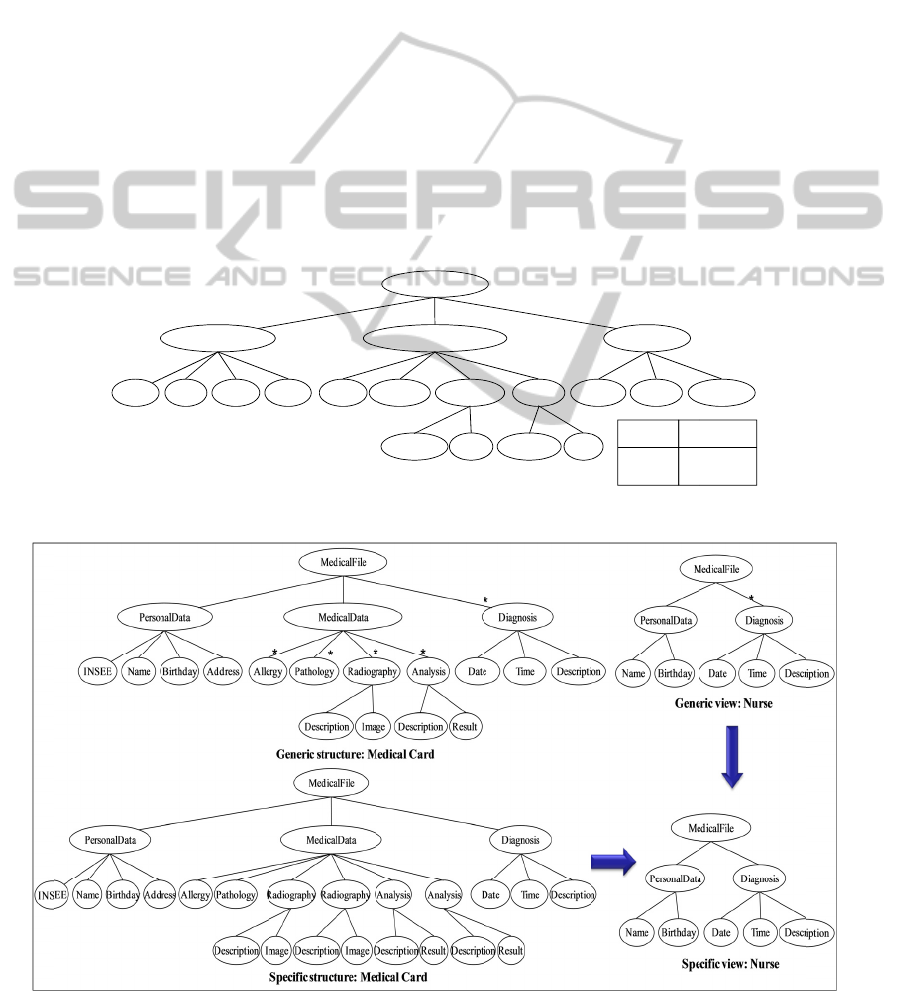
Figure 4: Ge
n
Figure 5:
G
A
ddress Allergy
P
*
l
, S.,
d
ing.
C
ode
X
ML
d
ings
ment
U
SA.
m
edia
l
and
fine-
b
ased
e
enth
and
New
ation
a
. In
Ma
r
Mo
g
Sin
g
Spe
We
e
n
eric structure
o
G
enerating of s
p
MedicalFile
MedicalData
P
athology Radiogra
p
Description Imag
e
*
*
Wireless com
m
pp. 141-163.
r
riott, K., M
e
efficient cli
e
Proceedings
of
World Wide
W
USA.
g
ul, J. C., 2001
Communicatio
g
h, A., Trive
d
2004. PTC:
P
heterogeneous
Wide Web Jou
r
rberg-McQuee
n
A Data Struc
L
ECTURE N
O
139-160.
e
, S., Apost
o
streaming and
IEEE, Interna
t
o
f Medical File.
p
ecific view.
p
hy Analysis
D
e
Description Resu
l
*
m
unications an
d
yer, B., Tar
d
nt-side adap
t
f
the 11th int
e
W
eb, pp. 496-50
. Server-direct
e
n
s 24, 2, pp.15
5
d
i, A., Rama
m
P
roxies that t
Web client
e
r
nal 7, 1, pp. 7
-
n
, C. M. Huitfe
t
ure for Over
l
O
TES IN CO
M
o
lopoulos, J.,
secure transco
d
t
ional Confe
r
e
n
Diagnosis
D
ate Tim e
D
l
t
*
Operator
«* »
«»
C
a
0
o
d
mobile comp
d
if, L., 2002.
t
ivity for
S
e
rnational con
f
0
7. ACM New
Y
e
d transcoding.
5
-162.
m
ritham, K., S
h
t
ranscode and
e
nvironments.
I
-
28.
e
ldt, C., 2004.
G
r
lapping Hiera
r
M
PUTER SCI
E
2003. Secur
e
d
ing with JPE
G
n
ce on Image
P
D
escription
a
rdinality
o
r several
1
u
ting 1, 2.
Fast and
S
VG. In:
f
erence on
Y
ork, NY,
Computer
h
enoy, P.,
cache in
I
n: World
G
ODDAG:
r
chies. In:
E
NCE, pp.
e
scalable
G
-2000. In:
P
rocessing
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
182
