
A Study on Older Adult Students’ Behavioural Intention and
Learning Satisfaction of Blended e-Learning Course at the Active
Aging University
Horng-Jyh Chen
1
, Chien-Jen Liu
2
, Chien-Liang Lin
3
, Yi-Fang Chen
4
and Hung-Liang Chen
5
1
Department of Information Management,Kao-Yuan University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
2
Institute of Education, National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
3
Department of Management Information Systems, National Cheng Chi University, Taipei, Taiwan
4
Institute of Education, National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
5
Department of Safety and Health,Chia-Nan University, Tainan, Taiwan
Keywords: Active Aging University, Blended e-Learning, Behavioural Intention, Learning Satisfaction, Structural
Equation Model (SEM).
Abstract: Recently, the blended e-learning is implemented in many fields more and more popularly. In this paper, the
program of ceramics teaching at the Active Aging University is also applied blended e-learning without
exception in order to raise older adult students’ behavioural intention and learning satisfaction. Because of
the unfamiliar with IT technology application for these older adult students the different results from most
of younger students in this investigation are expected. In this study, the questionnaire is designed for 44
older adult students whose ages are all over 55 years old. The teaching experiment of blended e-learning for
ceramics teaching course is performed at the Active Aging University in the southern of Taiwan. And the
Structural Equation Model (SEM) quantitative analysis is carried out that the conclusions are got with the
perceived usefulness of learning contents has positive relationship with learning satisfaction. Also, the
perceived ease of use for interfaces has positive relationship with the perceived usefulness of learning
contents and learning satisfaction. Therefore, these conclusions could be applied to develop and design for
all the blended e-learning programs at the Active Aging University with the best teaching and learning
strategy in the future.
1 INTRODUCTION
Because of the improvement of medicine
technology, the subtle changes of proportion of
different age population have been happened. For
example, the aging society exists in Taiwan since
1993. Till 2010 the ratio of aging population rises to
10.7% of total population (OEPD, 2010). Hence, the
Ministry of Education in Taiwan proposes the White
Book of the education policy for most of the aging
populations. This objective becomes one of the most
important government social policies. Therefore, this
live to old to learn policy gives most of older adult
students the opportunity to learn so many suitable
courses at the Active Aging University in Taiwan. In
this paper, the course of ceramics teaching at the
Active Aging University is also applied blended e-
learning in order to raise older adult students’
behavioural intention and learning satisfaction.
Because of the unfamiliar with IT technology
application of these older adult students the different
results from most of younger students in this
investigation are expected.
On the other hand, the user cognitive behaviour and
attitude for information technology application have
been investigated for younger students at many
universities (Davis, 1989). And also, due to the
development of information technology, DeLone
and McLean (2003) suggested the model to explain
the successful experiment of information technology
application. According to the DeLone and McLean
(2004) researched results the user satisfaction has
relationship with user behavioural intention. In
addition, the Expectation Confirmation Theory
(ECT) and models suggested that the factor of
perceived usefulness has close relationship with user
satisfaction (Bhattacherjee, 2001a). Therefore, In
this research the authors try to combine these three
137
Chen H., Liu C., Lin C., Chen Y. and Chen H..
A Study on Older Adult Students’ Behavioural Intention and Learning Satisfaction of Blended e-Learning Course at the Active Aging University.
DOI: 10.5220/0004006801370140
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Communication Networking, e-Business and Optical Communication Systems (ICE-B-2012),
pages 137-140
ISBN: 978-989-8565-23-5
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
research frameworks and models to study
simultaneously many older adult students’
behavioural intention and learning satisfaction of
blended e-learning for ceramics teaching course at
the Active Aging University in the southern of
Taiwan. The quite different results for this special
group in the investigation are concluded.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
HYPOTHESE
The Extended Technology Acceptance Models are
also suggested by many researchers (Park et al.,
2011, Palvia, 2009, Hsu and Lin, 2008).
Nevertheless, in this research the authors also adopt
the model being suggested by Venkatesh and Davis
(2000). That is how two factors of the perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use affect the user
behavioural intention Therefore, the following
conditions are assumed
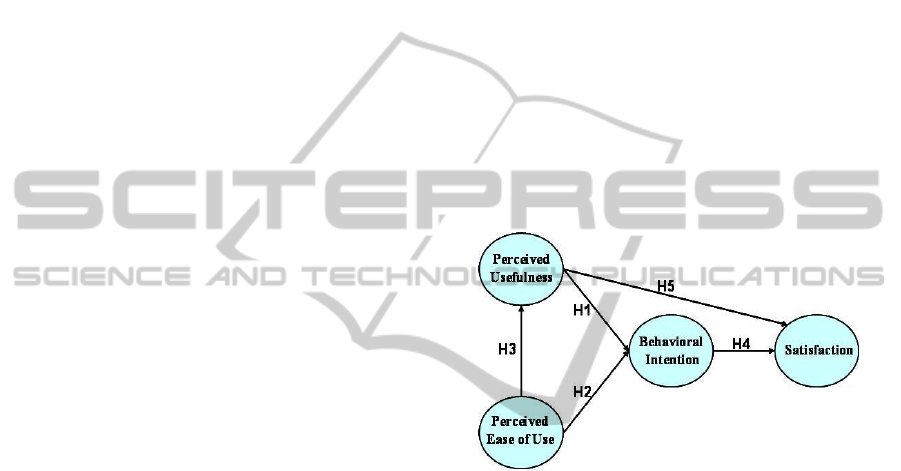
H1: Perceived usefulness with positively
influence behavioural intention of blended e-
learning.
H2: Perceived of ease of use positively influence
user behavioural intention of blended e-learning.
H3: Perceived of ease of use positively influence
perceived usefulness of blended e-learning.
Due to the development of information
technology, DeLone and McLean (2003) suggested
the model to explain the successful experiment of
information technology application. And, according
to the Seddon (1997), DeLone and McLean (2004)
researched results the user satisfaction has
relationship with user behavioural intention.
Therefore, the following additional assumption is:
H4: Behavioural intention positively influences
satisfaction of blended e-learning.
According to the conclusions of the Expectation
Confirmation Theory (ECT) and models, research
suggested that the factor of perceived usefulness has
relationship with user satisfaction (Roca and Gagné,
2008, Bhattacherjee, 2001b). Hence, in this study the
following additional assumption is also suggested.
H5: Perceived usefulness with positively
influence user satisfaction of blended e-learning.
3 RESEARCH DESIGN AND
METHOD
3.1 Measurement Design and Research
Framework
According to the above discussions, the research
model is shown in figure 1. Before the questionnaire
is performed, two experts have evaluated the
questionnaire scales. And also, two professors of
information management department have examined
the questionnaire scales for content validity. The
details of final scales for the factors of perceived
usefulness, perceived ease of use and user
behavioural intention are revised from the scales
which were developed by Davis (1989).And then,
the scales of user satisfaction are modified from the
original copies of Bhattachjee (2001b).Finally, the
measuring scales are all with Likert 5 scales.
Figure 1: Extended technology acceptance model.
3.2 Experimental Design and Objects
In this research the one group posttest only design is
adopted. The authors select one group of the older
adult students who has attended the blended e-
learning for ceramics teaching course to participate
in this experiment. Finally, the research objects are
this special group of the older adult students at the
Active Aging University in the southern of Taiwan.
The research objects of 44 older adult students
whose ages are all over 55 years old. The ratio of
male is 41.9% and female is 58.1% and the
experience in using of computer for all the older
adult students is less than one year.
3.3 Experimental Procedure
Because of the less experience in using of computer
for all the older adult students, the contents of
ceramics teaching course are explained previously
by experts in the real classroom and laboratory. And
ICE-B 2012 - International Conference on e-Business
138

then the experiment let all the students learn blended
e-learning digital contents at home at any time after
the real classroom learning. The blended e-learning
program of ceramics teaching course takes three
hours per week for one semester. After the
experiment finished, the authors implement the
questionnaire to all the older adult students and
collect all the effective data for the quantitative
analysis.
4 DATA ANALYSIS AND
RESULTS
4.1 Measurement Model
A confirmatory factor analysis is performed to
examine the measurement model. The partial least
squares (PLS) method using SmartPLS 2.0 (Ringle
et al., 2005) is chosen because it presumes no
distributional form for measured variables, nor does
it posit a strong requirement for large sample sizes
(Chin et al., 2003, Chin, 1998). PLS supports both
exploratory and confirmatory research (Gefen et al.,
2000) and gives optimal prediction accuracy because
it is prediction-oriented (Fornell and Cha, 1994).
Internal consistency can be assured by examining
the composite reliability of the constructs (Fornell
and Larcker, 1981), and all composite reliability
values in this study ranged from 0.9705 to 0.9872,
surpassing the suggested threshold value of 0.7
(Bagozzi and Yi, 1988, Gefen et al., 2000). And
then, Convergent validity refers to the degree to
which multiple items measure one construct.
Convergent validity in this study is evaluated by
checking whether (1) the average variance extracted
(AVE) values are larger than 0.5 (Gefen et al.,
2000), and (2) the factors loadings of the all items
are significant and higher than 0.7 (Nunnally, 1978).
All these conditions are met, indicating acceptable
convergent validity of the measurement.
Besides, to assess discriminant validity, the
square root of AVE of each construct is computed
and compared with the correlation between
constructs (Chin et al., 2003, Chin, 1998). Based on
the results, all square roots of AVE are larger than
the correlation coefficients between constructs,
indicating that each construct is more closely related
to its corresponding measurement items than to
those of other constructs. This again supports the
discriminant validity of the measures. In sum, the
positive evidence supporting good reliability,
convergent validity, and discriminant validity of the
measurement model shows the appropriateness of
this model to be used in subsequent hypotheses
testing.
4.2 Structural Model
The test of the hypotheses involves estimating path
coefficients of the Structural Model, which indicate
the strength of the relationship between the
dependent and independent variables, and the R-
square value, which indicates the amount of variance
explained by the independent variables. Moreover,
the bootstrap re-sampling procedure is used to
examine the stability of the PLS estimates (Chin,
1998). This study chose re-samples of 100.
The model explained 92.1 percent of the
variances in satisfaction to adopt blended e-learning.
In addition, the model explained 53.8 percent of the
variances in behavioural intention, and 78.6 percent
in perceived usefulness. The path coefficients
perceived ease of use (H1, β=-0.046, t=0.926) no
significantly affected behavioural intention, and
perceived ease of use (H5, β=0.055, t=2.898) was
positively affected learning satisfaction. And then,
perceived ease of use (H2, β=0.774, t=15.065) has
significantly effect on behavioural intention, and
perceived ease of use (H3, β=0.887, t=26.477) also
significant effect on perceived usefulness. Finally,
the effect of behavioural intention on satisfaction
(H4, β=0.924, t=46.450) is significant at the p<0.05
level.
5 DISCUSSION AND RESULT
According to the results, perceived usefulness of
contents and ease of use for interfaces has
significant effect on user behavioural intention. This
result has the same conclusion with the Technology
Acceptance Model having been investigated by
many researchers before (Liu et al., 2009, Venkatesh
and Davis, 2000).This result shows some meanings
for the future research on all of the blended e-
learning courses for older adult students. First of all,
the most important factor is to strengthen the ease of
use for interfaces. And then, the usefulness of
contents should be improved effectively. The results
provide another direction of thinking that is the
design of e-learning contents should consider the
requirements of the older adult students and let the
interfaces operation easier. Simple to learn can
enhance the learning outcome of the older adult
students. As for the ease of use is defined as the
operation of e-learning platform and interface easily.
A Study on Older Adult Students' Behavioural Intention and Learning Satisfaction of Blended e-Learning Course at the
Active Aging University
139

Therefore, because the operation of interface is
relatively simple that will raise the behavioural
intention of and also improve the overall quality of
learning.
Moreover, user behavioural intention and ease of
use for interfaces are the important factors for user
learning satisfaction. The higher of user behavioural
intention and the easier operation of interfaces are
the higher of user learning satisfaction will be.
Therefore, in order to improve the user learning
satisfaction of older adult students effectively how to
strengthen the design of contents and improve the
user intention of blended e-learning program for all
the older adult students is more important. However,
the result of the perceived usefulness of the contents
does not meet with the basic assumption of the
Technology Acceptance Model. This result is still
worthy of discussing. Perhaps, older adult students
believe that the use of blended e-learning platform
for ceramics teaching course being necessary but
usefulness to the extent not yet bigger enough to
affect the user behavioural intention of learning.
REFERENCES
Bagozzi, R. P. & Yi, Y. 1988. On the Evaluation of
Structural Equation Models. Journal of the Academy
of Marketing Science, 16, 74-94.
Bhattacherjee, A. 2001a. An empirical analysis of the
antecedents of electronic commerce service
continuance. Decision Support Systems, 32, 201-214.
Bhattacherjee, A. 2001b. Understanding information
systems continuance: an expectation-confirmation
model. MIS Quarterly, 25, 351-370.
Chin, W. W. 1998. Issues and opinion on structural
equation modeling. MIS Quarterly, 22, VII-XVI.
Chin, W. W., Marcolin, B. L. & Newsted, P. R. 2003. A
Partial Least Squares Latent Variable Modeling
Approach for Measuring Interaction Effects: Results
from a Monte Carlo Simulation Study and an
Electronic-Mail Emotion/Adoption Study. Information
Systems Research, 14, 189-217.
Davis, F. D. 1989. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease
Of Use, And User Acceptance of Information
Technology. MIS Quarterly, 13, 319-339.
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P. & Warshaw, P. R. 1989. User
Acceptance of Computer Technology: A Comparison
of Two Theoretical Models. Management Science, 35,
982-1003.
DeLone, W. H. & McLean, E. R. 2003. The DeLone and
McLean model of information systems success: A ten-
year update. Journal of Management Information
Systems, 19, 9-30.
DeLone, W. H. & McLean, E. R. 2004. Measuring e-
Commerce Success: Applying the DeLone & McLean
Information Systems Success Model. International
Journal of Electronic Commerce, 9, 31-47.
Fornell, C. & Cha, J. (eds.) 1994. Partial least squares:
Advanced Methods of Marketing Research, Blackwell
Publishers, Oxford, 52-78.
Fornell, C. & Larcker, D. F. 1981. Evaluating Structural
Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and
Measurement Error. Journal of Marketing Research
(JMR), 18, 39-50.
Gefen, D., Straub, D. W. & Boudreau, M. C. 2000.
Structural equation modeling and regression:
Guidelines for research practives. Communication of
the Association for Information Systems, 7, 1-79.
Hsu, C.-L. & Lin, J. C.-C. 2008. Acceptance of blog
usage: The roles of technology acceptance, social
influence and knowledge sharing motivation.
Information & Management, 45, 65.
Liu, S.-H., Liao, H.-L. & Pratt, J. A. 2009. Impact of
media richness and flow on e-learning technology
acceptance. Computers & Education, 52, 599-607.
Nunnally, J. (ed.) 1978. Psychometric Theory, New York:
Mcgraw-Hill.
OEPD. 2010. Estimation Report of Populations in Taiwan,
http://www.cepd.gov.tw/m1.aspx?sNo=0000455 (acce-
ssed 15 February 2012)
Palvia, P. 2009. The role of trust in e-commerce relational
exchange: A unified model. Information &
Management, 46, 213-220.
Park, N., Jin, B. & Annie Jin, S.-A. 2011. Effects of self-
disclosure on relational intimacy in Facebook.
Computers in Human Behavior, 27, 1974-1983.
Ringle, C. M., Wende, S., and Will, S. 2005. SmartPLS
2.0, available at: http://www.smartpls.de (accessed 15
June 2011), Hamburg, Germany.
Roca, J. C. & Gagn , M. 2008. Understanding e-learning
continuance intention in the workplace: A self-
determination theory perspective. Computers in
Human Behavior, 24, 1585-1604.
Seddon, P. B. 1997. A respecification and extension of the
DeLone and McLean model of IS success. Information
Systems Research, 8, 240-253.
Venkatesh, V. & Davis, F. D. 2000. A Theoretical
Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model: Four
Longitudinal Field Studies. Management Science, 46,
186.
ICE-B 2012 - International Conference on e-Business
140
