
Adaptive Visualization of Segmented Digital Ink Texts in Chinese
based on Context
Xi-Wen Zhang
1
, Hao Bai
2
and Yong-Gang Fu
1
1
Department of Digital Media, College of Information Sciences, Beijing Language and Culture University, Beijing, China
2
College of Advanced Chinese Training, Beijing Language and Culture University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Digital Ink Text, Segmentation, Visualization, Adaptive, Context.
Abstract: Digital ink texts in Chinese can neither be converted into users’ desired layouts nor be recognized until they
are segmented correctly. There are many errors in automatically segmented results because the texts are free
forms and mixed with other languages, as well as their Chinese characters have small gaps and complex
structures. Paragraphs, text lines, and characters (recognizable language symbols) may be wrongly
extracted. It is a prerequisite to visualize segmented results for further correcting wrong extracted objects
using human-computer interaction. Thus, an adaptive approach based on context is proposed to visualize
segmented digital ink texts in Chinese. Each extracted object is adaptively visualized by shape and colour
labels according to relations between it and its neighbours. Confidences of extracted objects are also
visualized with bounding shapes with different line widths. Each object’s contexts are constructed from it
and other objects invoked by it, where an optimum visualization is identified. We have conducted
experiments using real-life segmented digital ink texts in Chinese and compared the proposed approach with
others. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach is feasible, flexible, and effective.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital pens, such as Anoto pen and Tablet PC (Eric,
2006), enable common users to enter continuously
Chinese texts into computers in a natural and easy
way. The digital pens record coordinates,
timestamps, and pressures of sampling points for
each stroke, and store entire multi-page documents
in a digital ink format (w3, 2012). It is necessary to
segment those digital ink texts in order to exploit
them in structure and symbol levels. This is because
that correctly segmented digital ink texts in Chinese
can be converted into users’ desired layouts and be
recognized as symbols encoded for some document
editors, such as Microsoft Word.
Digital ink texts in Chinese are free forms and
mixed with other languages, as well as their Chinese
characters have a large set and complex structures
(Wang, 2001). The digital ink characters include
Chinese characters, punctuations, digits, numbers,
English letters and words, as well as other
recognizable language symbols. Thus, in practical
segmented digital ink texts in Chinese resulted from
automatic approaches (Ao, 2006); (Zhang, 2007);
(Microsoft, 2005), there are many wrong extracted
paragraphs, text lines, and characters. It is
unavoidable to correct those wrong extracted objects
using human-computer interaction.
It is necessary to visualize all extracted objects in
segmented digital ink texts in Chinese in order to
facilitate users to identify wrong extracted objects.
Previous approaches visualize extracted objects
based on shapes (Ao, 2006); (Zhang, 2007);
(Microsoft, 2005); (Shilman, 2003) and colours
(Bhaskarabhatla, 2004), but they pay less attention
to neighbouring objects’ overlapping, objects’
confidence, and users’ identification burdens. This
paper proposes an adaptive visualization approach
based on context to address this task. Each extracted
object in segmented digital ink texts in Chinese is
adaptively visualized by shape and colour labels
according to relations between it and its neighbours.
Various line widths of bounding shapes in each
extracted object correspond to its inverse
confidences. Thicker objects have lower confidence,
prompting users to check them. Those adaptive
visualized information in segmented digital ink text
in Chinese facilitate users to identify efficiently
wrong extracted objects.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
227
Zhang X., Bai H. and Fu Y..
Adaptive Visualization of Segmented Digital Ink Texts in Chinese based on Context.
DOI: 10.5220/0004020102270232
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications and Wireless Information Networks and Systems
(SIGMAP-2012), pages 227-232
ISBN: 978-989-8565-25-9
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Section 2 reviews previous work related to
visualization of segmented digital ink texts in
Chinese. Section 3 presents our adaptive
visualization approach. In Section 4, detailed
experimental results and performance analyses are
reported, and some comparisons with other
approaches are also given. Finally, our conclusions
are drawn in Section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
There is some work available for automatically
segmenting digital ink texts in Chinese, such as
approaches (Ao, 2006); (Zhang, 2007) and tools
(Microsoft, 2005). But there is a little effort for
visualizing extracted objects. Extracted objects can
be labelled using colour and shape.
(1) Approaches based on colour. Bhaskarabhatla et
al. (Bhaskarabhatla, 2004) use a colour scheme to
label English text lines and Telugu and Amharic
letters in digital ink texts with mixed western
languages.
(2) Approaches based on rectangle. Other work
renders digital ink texts in black, and use shapes to
visualize extracted objects. Ao et al. (Ao, 2006) use
red enclosed rectangles to label characters and blue
ones to label text lines for digital ink texts in
Chinese. Zhang et al. (Zhang, 2007) use green
enclosed rectangles to label characters, blue ones to
label text lines, red ones to label paragraphs for
digital ink texts in Chinese. Shilman et al. (Shilman,
2003) label text lines using rectangles for digital ink
texts in English.
(3) Approaches based on underline. Shilman et al.
(Shilman 2006) use a under bar to label an word for
digital ink texts in English.
Digital ink texts can be easily converted into digital
image texts. There is a little work to visualize
extracted objects in segmented handwritten and
printed digital image text.
(1) Approaches based on path. Laurence et al.
(Laurence, 2007) use paths, strings, and baselines to
represent various text lines in segmented
handwritten digital images.
(2) Approaches based on rectangle. Chang et al.
(Chang, 2005) use rectangles to label characters and
text lines in segmented digital image with printed
texts in Chinese.
(3) Approaches based on shadings. Basu et al. (Basu,
2007) use shadings to highlight text lines in
segmented digital images handwritten in Bengali
and English.
During correcting segmented digital ink texts in
Chinese, many wrong extracted objects are invoked,
paragraphs, text lines, and characters (recognizable
language symbols) may be wrongly extracted; and
many segmentation errors are also invoked,
including under-segmentation, over-segmentation,
and their combination. In order to identify wrong
objects, each object should be vividly visualized, so
that users can easily identify its components.
So, an adaptive visualization approach for
segmented digital ink texts in Chinese based on
context is proposed. Many factors are considered,
including users’ identification burden, labels’
computation cost, memory requirement, and render
cost. Bounding shapes of extracted characters, text
lines, and paragraphs are drawn with red, green, and
blue, respectively. The colour sensibility of human
eyes corresponds to the number of objects. Each
object belonging to the same level (character, text
line, and paragraph) is first visualized by its
rectangle. According to the overlapping membership
of it and its neighbours, the rectangle evolves as tilt
rectangles (Kenneth, 1996), or convex hulls (Berg,
2008). If the convex hulls of characters are still
overlapping, their strokes are drawn in cyan. If the
convex hulls of text lines are still overlapping, their
bounding shapes are drawn in magenta. Each
extracted object is drawn with different line widths
with an inverse proportion to its confidence.
3 ADAPTIVE VISUALIZATION
Digital ink texts in Chinese are segmented using a
toolkit from MS (Microsoft, 2005). A segmented
digital ink text in Chinese contains characters, text
lines, and paragraphs. Figure 1.a is an original
digital ink text in Chinese, strokes are drawn in
black. Its extracted objects are labelled by bounding
rectangles as shown in Figure 1.b. In Figure 1.b,
characters, text lines, and paragraphs are labelled in
red, green, and blue rectangles, respectively.
Many extracted objects in segmented digital ink
texts in Chinese are overlapped because they are
produced in free-formal ways. It is difficult for users
to check whether an object belongs to its host object
when it and its neighbours overlap too much.
The extracted objects at the same level are
spatially sorted in order to identify neighbours of an
object.
It is implemented from objects of top level to
ones of bottom level. Paragraphs in the same page
SIGMAP 2012 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
228

(a) A digital ink text in Chinese is a song poem.
(b) It is segmented and visualized by rectangles.
(c) The segmented result is visualized adaptively.
(d) The correct version.
Figure 1: A song poem is segmented and visualized.
are first sorted according to their top-most points’ y
values. Then text lines in the same paragraph are
sorted according to their top-most points’ y values.
Finally, characters in the same text line are sorted
according to their left-most points’ x values.
The adaptive visualization is implemented from
objects of bottom level to ones of top level. It is easy
for users to identify complex objects in their host
object labelled by a closed shape. Thus, rectangles
are used to label non-overlapped characters.
Overlapped characters are adaptively distinguished
with proper shapes. If one character overlaps its
previous neighbour, its rectangles evolve as from tilt
rectangles to convex hull, the neighbour’s bounding
shape evolves to find non-overlapped one. If their
convex hulls are still overlapping, the current
character’ strokes are drawn in cyan.
It is easy for users to identify linear objects in
their host object labelled by a rectangle because it
just needs users to find four lines. Thus non-
overlapped text lines and paragraphs are visualized
with rectangles. Overlapped text lines and
paragraphs are visualized using tilt rectangles and
convex hulls. If the convex hulls of text lines are
overlapping, the current text line’s characters’
bounding shapes are drawn in magenta. If the
convex hulls of paragraphs are overlapping, the
current paragraph’s text lines’ bounding shapes are
drawn in yellow.
3.1 Adaptive Visualization of
Characters
(1) For each character in the same text line
{
(2) If its rectangle does not overlap its previous (left)
neighbour, then it is labelled by its rectangle in red, and
go to step (1).
(3) If its tilt rectangles do not overlap its previous one,
then it is labelled by its tilt rectangle in red, and go to
step (1).
(4) If its convex hulls do not overlap its previous one,
then it is labelled by its convex hull in red, and go to step
(1).
(5) Its previous neighbour’ bounding shape evolves to
convex hull.
(6) If their convex hulls overlap, its strokes are
visualized using cyan.
}
Figure 2: An adaptive algorithm is to visualize characters.
Each character in the same text line is first
visualized. Rectangle, tilt rectangle, convex hull are
selected as bounding shapes. Characters are more
Adaptive Visualization of Segmented Digital Ink Texts in Chinese based on Context
229

than text lines and paragraphs in segmented digital
ink text in Chinese. Thus red is used to label them
because of its higher sensibility than green for
human eyes. Red and cyan are used as label colours
because they are complementary.
The adaptive visualization algorithm for
characters is shown in Figure 2. In Figure 1.c,
characters are adaptively labelled using bounding
shapes with red and cyan. Rectangles, tilt rectangles,
and convex hulls are used adaptively.
3.2 Adaptive Visualization of Text
Lines
Each text line in the same paragraph is then
visualized. Rectangle, tilt rectangle, convex hull are
selected as bounding shapes. Text lines are less than
characters in segmented digital ink text in Chinese.
Thus green is used to label text lines because of its
lower sensibility than red for human eyes. Green and
magenta are used as label colours because they are
complementary. The adaptive visualization
algorithm for text lines is shown in Figure 3. In
Figure 1.c, text lines are adaptively labelled using
bounding shapes with green. Rectangles, tilt
rectangles, and convex hulls are used adaptively.
(1) For each text line in the same paragraph
{
(2) If its rectangle does not overlap its previous (top)
neighbour, then it is labelled by its rectangle in green,
and go to step (1).
(3) If its tilt rectangle does not overlap its previous one,
then it is labelled by its tilt rectangle in green, and go to
step (1).
(4) If its convex hull does not overlap its previous one,
then it is labelled by its convex hull in green, and go to
step (1).
(5) Its previous neighbour’ bounding shape evolves to
convex hull.
(6) If their convex hulls overlap, its characters’ bounding
shapes are visualized using magenta.
}
Figure 3: An adaptive algorithm is to visualize text lines.
3.3 Adaptive Visualization of
Paragraphs
Each paragraph in the same page is finally
visualized. Rectangle, tilt rectangle, convex hull are
selected as bounding shapes. Blue and yellow are
used as label colours because they are
complementary. Paragraphs are less than text lines
and characters in segmented digital ink text in
Chinese. Thus blue is used to label paragraphs
because of its lower sensibility than red and green
for human eyes. The adaptive visualization
algorithm for paragraphs is shown in Figure 4. In
Figure 1.c, paragraphs are adaptively labelled using
bounding shapes with blue and yellow. Rectangles,
tilt rectangles, and convex hulls are used adaptively.
(1) For each paragraph in the same page
{
(2) If its rectangle does not overlap its previous (top)
neighbour, then it is labelled by its rectangle in blue, and
go to step (1).
(3) If its tilt rectangle does not overlap its previous one,
then it is labelled by its tilt rectangle in blue, and go to
step (1).
(4) If its convex hull does not overlap its previous one,
then it is labelled by its convex hull in blue, and go to
step (1).
(5) Its previous neighbour’ bounding shape evolves to
convex hull.
(6) If their convex hulls overlap, its text lines’ bounding
shapes are visualized using yellow.
}
Figure 4: An adaptive algorithm is to visualize paragraphs.
3.4 Visualization with Confidences
The confidence of each extracted object is identified
according to its constraints and context. Bounding
shape of each extracted object is drawn with
different line widths with an inverse proportion to its
confidence. Two levels for confidence are used.
(1) The confidence of one character is identified
according to its aspect ratio compared with others in
the same text line. The 15% Characters, whose
aspect ratios are within the minimum, or the
maximum, are drawn in the line width of two pixels.
Others are drawn in the line width of one pixel.
(2) The confidence of one text line is identified
according to the linear membership of its characters’
centers. If the maximum of their standard errors are
more than 3 pixels, then the shape is drawn in the
line width of two pixels; else in one pixel.
(3) The confidence of one paragraph is identified
according to the height homogeneity of its text lines.
If the maximum of their standard errors are more
than 5 pixels, then the bounding shape is drawn in
the line width of two pixels; else in one pixel.
In Figure 1.c, bounding shapes of extracted
paragraphs, text lines, and characters are labelled in
various line widths. From it, users can easily identify
each object because overlapping objects are
distinguished with different shape, colour, and line
SIGMAP 2012 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
230
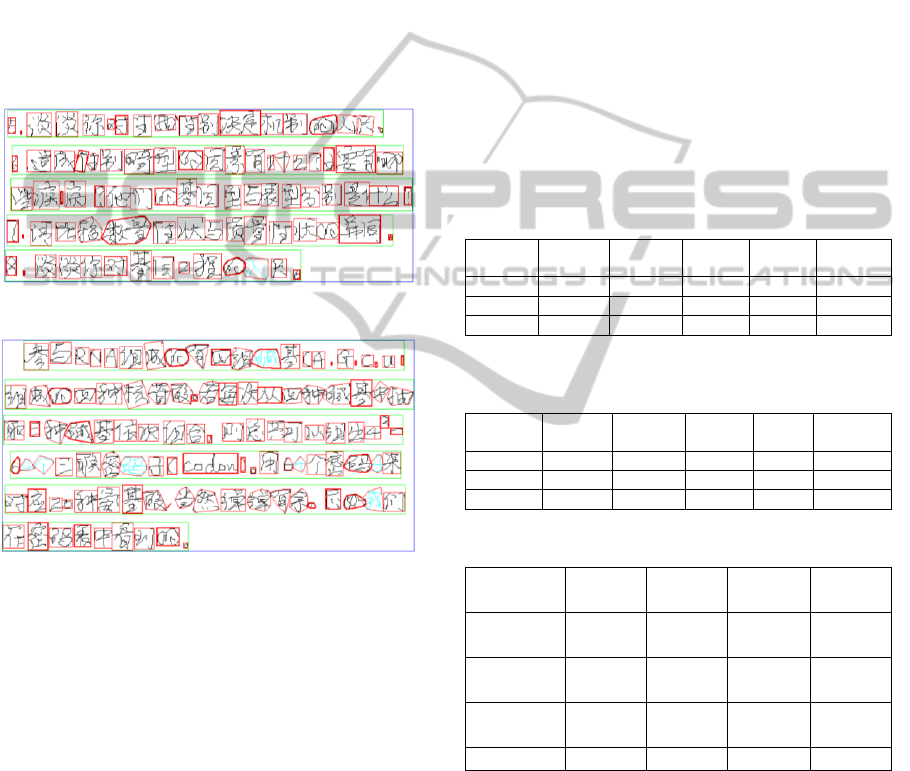
width labels. Figure 1.d is the correct version.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND PERFORMANCE
ANALYSES
Based on the proposed approach, a software
prototype has been developed in Visual C++ R7.0.
This section presents more experimental results on
real-life segmented digital ink texts in Chinese, and
gives a quantitative evaluation of the proposed
approach’s performance.
Figure 5: A text with lists is visualized adaptively.
Figure 6: A text with English letters is visualized.
4.1 Experimental Results
To evaluate the performance of the proposed
method, we applied our software prototype to 20
digital ink texts in Chinese containing 50 pages.
They cover the situations mentioned in Section 2.
They were collected from many different sources
without any restriction on the style or content of the
data, which may include Chinese texts and English
texts. The Maxell digital pen (Maxell, 2012), from
Hitachi Maxell Corporation Ltd., Japan, is used to
handwrite Chinese texts on Anoto papers. Some
experimental results are shown in Figure 5, and
Figure 6, respectively, in order to illustrate the
effectiveness of our approach.
4.2 Comparison with Related Work
To evaluate the performance of our approach,
identification speeds of wrong extracted objects are
first evaluated with different visualization ways.
Table 1 and Table 2 show extracted objects’
overlapping number and identification speeds
(characters per second) when they are visualized
with rectangles, tilt rectangle, convex hull, and
adaptive labels.
We compare our approach and others in four
aspects: users' identification burden, labels’
computation cost, memory requirement, and render
cost. The comparison results are listed in Table 3.
The proposed approach has the lower identification
burden for users, not the higher computation cost,
render cost, and memory requirement.
Table 1: Comparison of character visualization approaches
for overlapping number.
Number
Character
Rectangle
Tilt
rectangle
Convex
hull
Adaptive
shape
Figure 1
166
153
88
11
0
Figure 5
88
83
30
1
0
Figure 6
110
104
52
7
0
Table 2: Comparison of visualization approaches for
identification speed.
Speed
Character
Rectangle
Tilt
rectangle
Convex
hull
Adaptive
shape
Figure 1
166
1.3
2
6
8
Figure 5
88
1.6
3
6
10
Figure 6
110
1.4
3
5
10
Table 3: Comparison of visualization approaches.
Rectangle
Tilt
rectangle
Convex
hull
Adaptive
way
Identification
burden
Higher
High
Low
Lower
Computation
cost
Lower
Low
Higher
High
Memory
requirement
Lower
Low
Higher
High
Render cost
Lower
Low
Higher
High
4.3 Discussions
From the above experimental results and our
performance analyses, it can be concluded that the
proposed approach adaptively visualizes three levels
of objects, so that users can easily and quickly
identify wrong extracted objects. Consequently, the
proposed approach is able to achieve satisfactory
results for visualizing automatically segmented
digital ink texts in Chinese.
Adaptive Visualization of Segmented Digital Ink Texts in Chinese based on Context
231

5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposes an adaptive approach to
visualize segmented digital ink texts in Chinese.
Each extracted object is adaptively visualized by
shape and colour labels according to relations
between it and its neighbours. Red, green, blue, and
their complementary colour are used. Rectangle, tilt
rectangles, and convex hulls are used. Confidences
of extracted objects are also visualized with various
line widths.
The proposed approach and its software
prototype have been tested with various
automatically segmented digital ink texts in Chinese.
The performance is reported, including the test
results and comparative evaluation relative to other
published methods. The analyses confirm that the
proposed approach is more effective than other
approaches currently available.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work described in this paper was substantially
supported by the National Natural Science
Foundation of P.R. China and the Microsoft Asia
Research (Grant No. 60970158), Beijing Language
and Culture University supported project for young
researchers program (supported by the Fundamental
Research Funds for the Central Universities) (Grant
No. 09JBT014) .
REFERENCES
Anquetil, Eric, Lorette, Guy, 2006. New advances and
new challenges in online handwriting recognition &
electronic ink management, B. B. Chaudhuri (ed.),
Digital Document Processing: Major Directions and
Recent Advances (Advances in Pattern Recognition).
Springer Verlag, German, pp: 143-164.
Ao, Xiang, Li, Junfeng, Wang, XuGang, Dai, Guozhong,
2006. Structuralizing digital ink for efficient selection,
Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on
Intelligent User Interfaces. January 29- February 1,
Sydney, Australia, pp: 148-154.
Basu, S., Chaudhuri, C., Kundu, M., Nasipuri, Basu, M.,
D.K., 2007. Text line extraction from multi-skewed
handwritten documents, Pattern Recognition, 40 (6):
1825-1839.
Berg, Mark de, Cheong, Otfried, Kreveld, Marc van,
Mark, 2008. Computational Geometry Algorithms and
Applications, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Third Edition, pp: 243-258.
Bhaskarabhatla, A. S., Madhvanath S., Pavan Kumar, M.
N. S. S. K., Balasubramanian, A., Jawahar, C. V.,
2004. Representation and annotation of online
handwritten data, Ninth International Workshop on
Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (IWFHR),
September, pp: 136-141.
Castleman, Kenneth R., 1996. Digital Image Processing,
Prentice Hall, Inc., pp: 492.
Chang, Fu, Chu, Shih-Yu, Chen, Chi-Yen, 2005. Chinese
document layout analysis using an adaptive
regrouping strategy, Pattern Recognition, 38 (2): 261-
271.
Laurence, Likforman-Sulem, Abderrazak, Zahour, Bruno,
Taconet, 2007. Text line segmentation of historical
documents: a survey, International Journal on
Document Analysis and Recognition, 9 (2-4):123-138.
Maxell, 2012. The Maxell Digital Pen,
http://www.maxell.co.jp/e/products/industrial/digitalpe
n/index.html.
Microsoft, 2005. Microsoft Windows XP Tablet PC
Edition Software Development Kit 1.7,
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/.
Shilman, Michael, Tan, Desney S., Patrice, 2006. CueTIP:
a mixedinitiative interface for correcting handwriting
errors, The nineteenth annual ACM Symposium on
User Interface Software and Technology. October 15-
18, 2006, Montreux, Switzerland, pp: 323-332.
Shilman, Michael, Wei, Zile, Raghupathy, Sashi, Simard,
Patrice, Jones, David, 2003. Discerning structure from
freeform handwritten notes, Proceedings of Seventh
International Conference on Document Analysis and
Recognition. 3-6 Aug., vol.1, pp: 60-65.
W3, 2012. Ink Markup Language, http://www.w3.org/
TR/InkML/.
Wang, An-Bang, Fan, Kuo-Chin, 2001. Optical
recognition of handwritten Chinese characters by
hierarchical radical matching method, Pattern
Recognition, 34 (1): 15-35.
Zhang, Xi-Wen, Lyu, Michael R., and Dai, Guo-Zhong,
2007. Extraction and segmentation of tables from
Chinese ink documents based on a matrix model,
Pattern Recognition, 40 (7): 1855-1867.
SIGMAP 2012 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
232
