
Adaptive Rate Control Scheme for Improving Quality of Multimedia
in Broadband Wireless Networks
Dooyeol Yoon, Dongchil Kim and Kwangsue Chung
Department of Communications Engineering, Kwangwoon University, Seoul, Korea
Keywords: Quality Adaptation Scheme, Video Streaming, Rate Control.
Abstract: In order to improve quality of streaming services in broadband wireless networks, many researches are in
progress. However, existing schemes do not guarantee a user perceived quality, because most of these
schemes do not consider both wireless channel states and video characteristics. To cope with these problems,
this paper proposes a NB-RC (Network and Buffer-aware Rate Control) scheme. The proposed scheme
adjusts the video transmission rate according to the wireless channel states. It also controls the video quality
based on buffer occupancy of clients. Through the simulation results, we prove that our scheme improves
the media quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to the explosive growth of the broadband
wireless network technologies, there has been a
significantly increasing demand for multimedia
streaming applications such as mobile IPTV (Park
and Jeong, 2009). Recent advances in high-speed
networks have made it feasible to provide high
quality of video streaming. Among the advanced
wireless standards, LTE (Long Term Evolution) is
an emerging wireless communication system that
provides high-data rate as well as long-range
converage. However, multimedia streaming service
in a wireless communication network environment is
largely affected by various network characteristics,
such as limited channel bandwidth and variant
transmission rate. The channel bandwidth variation
causes the network congestion when the video
transmission rate exceeds the channel bandwidth.
To solve these problems, several methods for
wireless video streaming have been proposed. An
end-to-end QoS-based adaptation scheme called
AWMECN (Application-level Wireless Multilevel
ECN) is suggested in heterogeneous wireless
networks by overcoming the congestion/loss mistake
problems (Karimi et al., 2010). A probing-based
channel adaptive video streaming method is
proposed to adjust the transmission rate to the
varying throughput of wireless 3G network (Kim et
al., 2006). Also, a WMSTFP (Wireless Multimedia
Streaming TCP-Friendly transmission control
Protocol) is proposed to effectively differentiate
erroneous packet losses from congestive losses and
to filter out the abnormal round-trip time values
caused by the highly varying wireless channel states
(Yang et al., 2004). A new single-rate multicast
congestion control scheme called ASMP (Adaptive
Smooth Multicast Protocol) for multimedia
transmission over best-effort networks is proposed
(Bouras et al., 2010). However, all of theses
schemes doesn’t consider the buffer states of a client
and require the bandiwdth estimation of wireless
network.
To cope with these problems, a new adaptive
streaming scheme has been proposed (Koo and
Chung, 2010). This scheme called MARC (Mobile-
aware Adaptive Rate Control), which adjusts the
quality of bit-stream and transmission rate of video
streaming based on the wireless channel states and
network states. However, the MARC scheme is
sensitive to packet loss rate. It could cause the
oscillation of transmission rate.
In this paper, we propose a NB-RC (Network
and Buffer-aware Rate Control) scheme for
improving the video quality in multimedia streaming
services. The NB-RC scheme considers not only the
wireless channel states but also the buffer occupancy
of clients. This paper shows that the proposed NB-
RC scheme can significantly improve the media
quality. The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
In the next section, we present the NB-RC scheme
for improving quality of multimedia. Simulation
7
Yoon D., Kim D. and Chung K..
Adaptive Rate Control Scheme for Improving Quality of Multimedia in Broadband Wireless Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0004020400070011
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications and Wireless Information Networks and Systems
(SIGMAP-2012), pages 7-11
ISBN: 978-989-8565-25-9
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

results
a
Section
4
2 N
B
Fig. 1 s
h
RC sch
transmis
feedbac
k
client fe
e
occupan
c
compon
e
module
w
the vid
e
states a
n
states i
n
N
oise
R
smoothl
y
server.
Figure 1
2.1
A
The rat
e
transmis
p
hysical
where
D
the mod
u
4 for 16
-
represen
example
Coding
p
hysical
18.432 (
accordi
n
summar
i
the initi
a
Eq. (2),
w
a
nd conclusio
n
4
, respectivel
y
B
-RC SC
H
h
ows the arc
h
h
eme. The s
t
sion rate and
k
informatio
n
e
dbac
k
s its n
e
c
y to the
s
e
nt of this
a
w
hich decide
s
e
o quality le
v
n
d buffer oc
c
n
clude CINR
R
atio). In ord
e
y
, the buffer
s
: Architecture
o
A
daptive R
a
e
adaptation
sion rate w
h
data rate, R
P
D
rate
is the dat
u
lation gain t
h
-
QAM, and
m
n
ts the codi
n
, if the cu
r
Scheme) le
v
data rate,
R
=3.6864x(5/6
)
n
g to the CIN
R
i
zed in Table
a
l transmissio
n
w
e can reflec
t
r
PHY
DR =
ini
t
R
n
s are given
y
.
H
EME
h
itecture of t
h
t
reaming ser
v
video qualit
y
n
received
f
e
twork acces
s
s
treaming s
e
a
rchitecture
i
s
both the tra
n
v
el
b
ased on
c
upancy. The
(Carrier to
e
r to control
s
tates are use
d
o
f a multimedi
a
a
te Contro
module co
m
h
en CINR h
a
P
HY
, is calcul
a
a subcarrier
r
h
at
m
gain
= 2
f
m
gain
= 6 for 6
n
g rate (bit
s
r
rent MCS
(
v
el is 5/6 6
4
R
PHY
,
for do
w
)
xlog
2
64)Mbp
R
and the cor
r
1 (Kim et al.,
n
rate,
R
init
, t
o
t
the network
rat
e
gain
r
ate
cm ⋅⋅
PHY
t
R=
in Section 3
h
e
p
roposed
N
v
er controls
y
according t
o
f
ro
m
client.
s
states and b
u
e
rve
r
. The
m
i
s the adapt
a
n
smission rate
wireless ch
a
wireless ch
a
Interference
the video qu
a
d
in the strea
m
a
streaming sys
t
l
m
putes an i
n
a
s changed.
a
ted with Eq.
r
ate,
m
gain
de
n
f
or QPSK,
m
g
4-QAM. The
s
/subcarrier).
(
Modulation
4
-QAM, then
n
link is equ
a
s
. The MCS
l
esponding
R
P
H
2008). By se
t
o
R
PHY
as sho
w
p
hysical state
and
NB-
the
o
the
The
u
ffer
m
ain
a
tion
e
and
a
nnel
a
nnel
and
ality
m
ing
t
em.
n
itial
The
(1),
n
otes
g
ain
=
c
rate
For
and
the
a
l to
l
evel
P
HY
is
t
ting
w
n in
e
s.
(1)
(2)
rat
e
rat
e
p
a
p
wi
r
dat
a
tar
g
ser
v
Th
e
an
d
ch
o
of
net
w
dif
f
tra
n
sin
c
var
i
rap
i
int
e
rat
e
are
Th
e
Th
e
CI
N
is c
Table 1: P
h
CINR (dB)
M
26
6
23
6
20
6
18
16
14
12
10
6
3
1
-1
After setting
e
adaptation
m
e
,
R
,
b
ased
o
p
er, we define
eless channel
a
rate,
R
DL
,
a
g
et bit rate
f
v
er decides th
e
video trans
m
d
(5), where
α
o
ice of
α
ha
s
network ch
a
w
or
k
states,
f
erent
α
ha
s
n
sient change
s
c
e large
α
i
ation, its inst
i
dly. Such
e
rruptions on
v
e
s for the larg
transmission
⎩
⎨
⎧
=R
e
r
ate adaptat
i
e
initial tra
n
N
R has chan
g
omputed
b
as
e
WHILE
I
F CIN
R
THEN
R
init
ELSE
R
=
END IF
END WHILE
Figure 2:
A
h
ysical data rat
e
M
odulation Co
d
6
4-QAM
6
4-QAM
6
4-QAM
1
6-QAM
1
6-QAM
1
6-QAM
1
6-QAM
QPSK
QPSK
QPSK
QPSK
QPSK
up the initia
l
m
odule calc
u
o
n wireless
c
a new matric
,
states, which
a
s shown in
E
fo
r video de
c
e
network sta
t
−
=
DL
t
DL
R
R
M
m
ission rate is
α
represents
a
directly im
p
a
nnel states.
the propos
e
s
a differen
t
s
of network
r
is very se
n
a
ntaneous tra
n
behaviour
m
v
ideo playba
c
est level,
R
LL
,
rate limits.
M
RR
⋅
α
+
=
),,max(
),,
m
in(
BL
LL
RR
RR
i
on algorithm
smission rat
e
ed. After tha
t
e
d on the
M
DL
.
R
has change
= R
PHY
R + αxM
DL
A
lgorithm for t
h
e
with CINR le
v
d
ing Rate R
PH
Y
5/6
1
3/4
1
2/3
1
5/6
1
3/4
1
2/3
9
1/2
7
2/3
4
1/2
3
1/3
2
1/6
1/12
0
l
transmissio
n
u
lates the tra
n
c
hannel state
s
,
M
DL
, to dete
h
consider the
E
q. (3), whe
r
c
oding. The
s
t
es by
M
DL
.
1
−
s
calcualted
w
a
rate control
r
p
act on respo
n
In highly
e
d rate con
t
t
response
p
r
esources. Fo
r
n
sitive to
b
n
smission rat
e
m
ay cause
c
k. The video
,
and a base l
a
DL
M
<
>
0
0
DL
DL
M
M
is described
e
is calcula
t
t
, the transmi
s
.
e
d
h
e rate adaptati
o
v
el.
Y
(Mbps)
8.43
6.59
4.74
2.29
1.05
9
.83
7
.37
4
.91
3
.69
2
.46
1
.23
0
.61
n
rate, the
n
smission
s
. In this
r
mine the
downlink
r
e
R
t
is a
s
treaming
(3)
ith Eq. (4)
r
atio. The
n
siveness
dynamic
t
rol with
p
attern to
r
example,
b
andwidth
e
changes
frequent
decoding
a
yer,
R
BL
,
(4)
(5)
in Fig. 2.
t
ed when
s
sion rate
o
n.
SIGMAP2012-InternationalConferenceonSignalProcessingandMultimediaApplications
8

2.2
Q
The qu
a
quality
a
and buf
f
the algo
r
WHIL
E
I
E
E
E
END
W
Fi
g
In Fi
quality
l
occupan
c
the ma
x
respecti
v
b
andwi
d
b
uffer
o
threshol
d
the othe
b
andwi
d
higher
t
quality
l
the qual
i
b
uffer o
v
3 SI
M
In this s
e
RC sc
h
Simulat
o
Laborat
o
Fig.4.
I
transmit
s
receiver
s
are two
One is
t
UDP p
a
transmit
t
rates fo
r
idle tim
e
BS (Ba
s
The lin
k
at 2Mb
p
_
30.yuv
layers
u
Q
ualit
y
Ad
a
a
lity adaptati
o
a
ccording to t
h
f
er states fee
d
r
ithm of the q
u
E
I
F (R ≤ B
CQ
)
THEN
CQ = CQ
E
ND IF
E
LSE IF (R
>
THEN
CQ = CQ
E
ND IF
W
HILE
g
ure 3: Algorit
h
g. 3
B
CQ
den
o
l
evel,
CQ
.
B
O
c
y.
TH
min
an
d
x
imum thre
s
v
ely. If the t
r
d
th of current
o
ccupancy i
s
d
, the current
er
hand, if tr
a
d
th of
CQ+1
a
t
han the ma
x
l
evel is incr
e
i
ty adaptatio
n
v
erflow or un
d
M
ULATI
O
e
ction, the
p
e
r
h
eme is eva
l
o
r) of LBML
o
ry). The si
m
I
n this sim
u
s
video str
e
s
are connect
background
t
t
he Pareto tr
a
a
ckets. Ano
t
t
ed by using
T
r
both traffic
e
are both set
s
e Station) a
n
k
between tra
ff
p
s. For the e
x
video clip
w
u
sing the ref
e
a
ptation
o
n module c
o
h
e transmissi
o
d
back fro
m
cl
i
u
ality adaptat
i
& (BO < T
H
m
- 1
>
B
CQ+1
) & (
B
+ 1
h
m fo
r
the quali
t
o
tes bandwidt
h
O
represents
t
d
TH
max
are
t
s
hol
d
of b
u
r
ansmission r
video quality
s
lower tha
n
quality level
a
nsmission r
a
a
nd current b
u
x
imum thres
h
e
ased. Throu
g
n
algorithm c
a
d
erflow.
O
N RES
U
r
formance of
t
l
uated using
(Lawrence
B
m
ulation topo
l
u
lation, the
e
ams via ro
u
ed using wir
e
t
raffic flows
i
a
ffic flow tra
n
t
he
r
is a
F
T
CP packets.
flows are 1.
5
to 0.5ms. Th
e
n
d the router
i
ff
ic sources a
n
x
periments, S
O
w
as encoded
e
rence softw
a
o
ntrols the
v
o
n rate calcu
l
i
ent. Fig. 3 s
h
i
on scheme.
H
m
in
)
O
> TH
max
)
t
y adaptation.
h
of current v
t
he current b
u
t
he minimum
u
ffer occup
a
a
te is lower
level and cu
r
n
the mini
m
is decreased
.
a
te is higher
u
ffer occupan
c
h
old, the cu
r
g
h this opera
t
a
n prevent a c
l
U
LTS
t
he proposed
NS2 (Net
w
B
erkeley Nati
l
ogy is show
n
streaming s
e
u
te
r
. The v
e
less links. T
i
n the simula
t
n
smitted by
u
F
TP traffic
f
The transmi
s
5
Mbps; burst
e
link betwee
n
i
s set at 10
M
n
d the router i
O
CCER_352
x
into SVC pr
o
a
re, JSVM (
J
v
ideo
l
ated
h
ows
v
ideo
u
ffer
and
a
ncy,
than
r
rent
m
um
. On
than
c
y is
r
rent
t
ion,
lient
NB-
w
ork
i
onal
w
n in
e
rver
v
ideo
T
here
t
ion.
u
sing
f
low
s
sion
and
n
the
M
bps.
s set
x
288
o
file
J
oint
Sc
a
Fig
u
p
er
f
Qu
a
sch
loa
d
los
s
RC
b
e
c
Fig
u
and
tra
n
sch
Th
e
is
l
kb
p
tra
n
22
2
ini
t
co
n
sch
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Packet Loss Rate (%)
a
lable Video
M
u
re 4: Net
w
f
ormance of th
e
Table 2: C
h
a
lity Level Re
s
0 3
5
1 3
5
2 3
5
3 3
5
4 3
5
Fig. 5 shows
eme and TF
R
d
s. Two sch
e
s
rate in vario
u
scheme cont
r
c
ause it is rob
u
u
re 5: Average
TFRC under
d
Fig. 6 sho
w
n
smission ra
t
eme and T
F
e
average tra
n
l
arger than t
h
p
s. Then th
e
n
smission rat
e
2
.8. Because
ial transmiss
n
trols a trans
m
eme by 2 sec
o
TCP 1, UDP 1
M
ode), as sho
w
w
ork configur
a
e
proposed rate
aracteristics of
s
olution Fram
e
5
2x288
5
2x288
5
2x288
5
2x288
5
2x288
p
acket loss r
a
R
C under thr
e
e
mes compar
e
u
s environme
r
ols the trans
m
u
s
t
to packet l
o
packet loss ra
t
i
fferent loads.
w
s the comp
t
e between
t
RC (TCP-Fr
i
smission rate
h
at of the T
F
e
standard
d
e
is smaller th
a
the
p
ropose
d
i
on rate by
m
ission rate
fa
o
nd.
TCP 2, UD
P
NB-RC TF
R
w
n in Table
2
a
tion to ev
a
control.
f
the video stre
a
e
Rate (fps) Bit
r
30
30
30
30
30
a
te of both t
h
e
e cases with
e
d have simil
e
nts. Howeve
r
m
ission rate
s
oss.
a
te of the NB-
R
p
arisons of t
h
t
he propose
d
r
iendly Rate
of the NB-R
C
F
RC scheme
d
eviation o
f
a
n that of the
d
scheme se
t
physical dat
a
f
aster than th
e
P
2 TCP 3,
U
R
C
.
a
luate the
a
ms.
r
ate (kbps)
503.4
735.4
1037.9
1794.3
2265.5
e NB-RC
different
ar packet
r
, the NB-
s
moothly,
R
C scheme
h
e video
d
NB-RC
Control).
C
scheme
by 572.6
f
NB-RC
TFRC by
t
s up the
a
rate, it
e
existing
U
DP 3
AdaptiveRateControlSchemeforImprovingQualityofMultimediainBroadbandWirelessNetworks
9
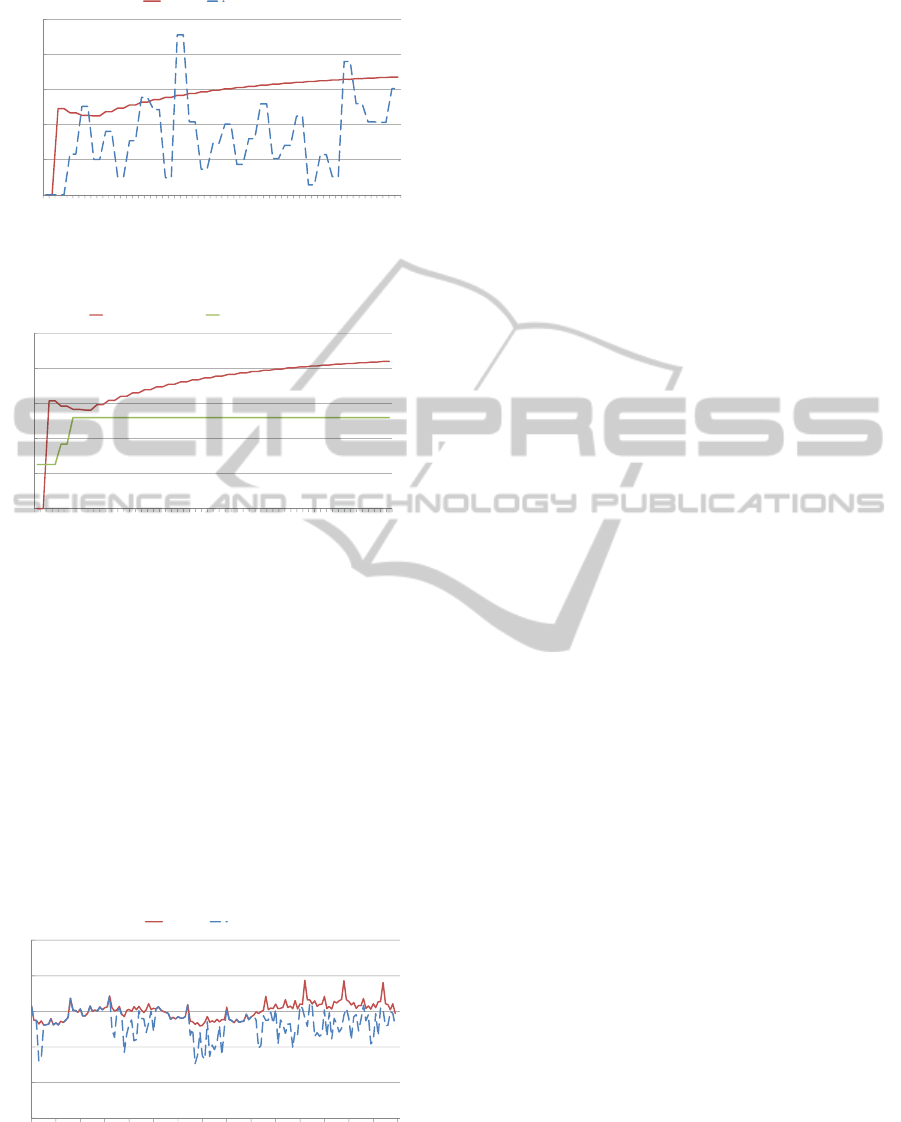
Figure 6: Comparison of the transmission rate between the
NB-RC scheme and TFRC.
Figure 7: Transmission rate and video quality adaptation
of NB-RC scheme.
These results mean that the proposed NB-RC
scheme controls transmission rate smoothly and
quickly by utilizing the available bandwidth. Since
the transmission rate of the NB-RC changes
smoothly as shown in Fig. 7, it does not control the
video quality level frequently.
Fig. 8 shows a comparison of the PSNR (Peak
Signal to Noise Ratio) between the NB-RC scheme
and TFRC. The PSNR of NB-RC scheme is higher
than that of TFRC as our scheme is robust to packet
loss. The NB-RC scheme controls the data
transmission rate smoothly, because it utilizes M
DL
.
Figure 8: Comparison of the PSNR between the NB-RC
scheme and TFRC.
4 CONCLUSIONS
To improve the video quality in multimedia
streaming services, we propose a NB-RC scheme
that considers not only network conditions but also
buffer states. The NB-RC scheme consists of the rate
adaptation method and the quality adaptation
method. The rate adaptation algorithm decides the
initial transmission rate by physical data rate. After
that, it calculates transmission rate based on M
DL
which is a matric using downlink data rate to
determine if the network is congested. The quality
adaptation algorithm controls the level of video
quality according to the transmission rate and the
occupancy of client’s buffer. Our simulation results
show that the proposed scheme can provide quickly
utilizing the available bandwidth and smooth
playback. It can also significantly improve the media
quality in terms of PSNR.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was financially supported by
Knowledge Economy Technology Innovation
Programs - International Collaborative R&D
Programs.
REFERENCES
Bouras, C., Gkamas, A., Kioumourtzis, G., (2010).
Adaptive smooth multicast protocol for multimedia
transmission: Implementation details and performance
evaluation. In International Journal of
Communication Systems. Vol. 23, No. 3, pp. 299-333.
Karimi, O. B., Fathy, M., Yousefi, S., (2010). Adaptive
end-to-end QoS for multimedia over heterogeneous
wireless networks. In Computers & Electrical
Engineering. Vol. 36, No. 1, pp. 45-55.
Kim, H. S., Nam, H. M., Jeong, J. Y., Kim, S. H., (2008).
Measurement based channel-adaptive video streaming
for mobile devices over mobile WiMAX. In IEEE
Transactions on Consumer Electronics. Vol. 54, No. 1,
pp. 171-178.
Kim, J. W., Nam, H. M., Lee, S. J., Lee, J. Y., Ko, S. J.,
(2006). Probing-based channel adaptive video
streaming for wireless 3G network. In IEICE
Transactions on Communications. Vol. E89-B, No. 2,
pp. 357-363.
Koo, J. H., Chung, K. S., (2010). MARC: Adaptive Rate
Control Scheme for Improving the QoE of Streaming
Services in Mobile Broadband Networks. In
International Symposium on Communications and
Information Technologies. pp. 105-110.
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
0 5 10 15 20 25
Rate (kbps)
Time (s)
NB-RC TFRC
0
400
800
1200
1600
2000
0 5 10 15 20 25
Rate (kbps)
Time (s)
Transmission Rate Video Bit Rate
20
25
30
35
40
45
0 30 60 90 120 15
0
PSNR (dB)
Frame Numbe
r
NB-RC TFRC
SIGMAP2012-InternationalConferenceonSignalProcessingandMultimediaApplications
10

Park, S., Jeong, S. H., (2009). Mobile IPTV: approaches,
challenges, standards, and QoS support. In IEEE
Internet Computing. Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 23-31.
Yang, F., Zhang, Q., Zhu, W., Zhang, Y. Q., (2004). End-
to-end TCP-friendly streaming protocol and bit
allocation for scalable video over mobile wireless
internet. In IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in
Communication. Vol. 22, No. 4, pp. 777-790.
AdaptiveRateControlSchemeforImprovingQualityofMultimediainBroadbandWirelessNetworks
11
