
Evaluation of a Joint Hysteresis Model in a Robot Actuated by
Pneumatic Muscles
Michael Kastner
1
, Hubert Gattringer
1
and Ronald Naderer
2
1
Institute for Robotics, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Altenberger Strasse 69, 4040 Linz, Austria
2
FerRobotics Compliant Robot Technology GmbH, Altenberger Strasse 69, 4040 Linz, Austria
Keywords:
Compliant Robotics, Pneumatic Muscles, Hysteresis Model.
Abstract:
Passively compliant drives are interesting alternatives to classical stiff actuators in emerging fields like human–
robot cooperation, service and rehabilitation robotics. Pneumatic muscles have been found to be interesting
low–cost actuators for such purposes. To fully realize the (desired) higher sensitivity and at the same time
maintain a good control quality, detailed models of the robot’s own components are required. For pneumatic
muscles, their hysteresis characteristic is a challenging property. In this paper we present a hysteresis model
based on a Prandtl–Ishlinskii operator approach and evaluate theresulting performance when the inverse model
is used for compensation in the position controller. The evaluation is done on a real multi–axes robot arm.
1 INTRODUCTION
Typical industrial robots are built as stiff as possi-
ble to ensure a high repeatability and tracking accu-
racy during free motion. For interaction tasks, the
use of compliant robotic systems has long been re-
searched. While this compliance is often added to
standard robots by means of additional control algo-
rithms and sensors, another approach is to use pas-
sively compliant drive technologies, i.e. actuators
with a low natural stiffness. Compliant actuation sys-
tems have been and are actively researched for a large
number of applications, including safe human/robot
interaction for industrial or service robotics, contact
processes, temporary energy storage, rehabilitation
devices and walking robots.
One type of actuation that is particularly inspired
by biological systems is the pneumatic muscle, which
was originally used by McKibben for prosthesis ap-
plications. It consists of a rubber tube and an inelas-
tic braided shell. When the tube is filled with pres-
surized air, the braid angle changes, causing a radial
expansion and a longitudinal contraction. Two such
muscles can be used in an antagonistic setup to create
a prismatic or revolute joint. Because of the low cost
of the muscle itself and the high forces it is able to
exert, its use in robotics has also been investigated by
several research groups.
Compared to pneumatic cylinders, the absence of
a stick–slip effect helps with an accurate position con-
trol, but the actuator characteristic is still very com-
plex and difficult to handle. Particularly, hysteresis
causes disturbances every time the drive direction is
reversed, while a creep/settling characteristic causes
the actuation force to slowly drift after a maneuver.
In this paper we present a model for the hystere-
sis effect based on a Prandtl–Ishlinskii approach and
discuss its use as a compensation term in the position
controller of a pneumatically actuated industrial ma-
nipulator. Section 2 will detail the considered robot
and joint setup. In Section 3 we will discuss advanced
pneumatic muscle models that can be found in the lit-
erature and present our hysteresis model. The gen-
eral controlstructure used and the incorporation of the
hysteresis compensatorare shown in Section 4, before
measurement results from the real robot are presented
in Section 5. Section 6 closes with conclusions and
an outlook on planned activities.
2 SYSTEM SETUP
The robot system that we are dealing with in this
contribution is an industrial robot arm manufactured
by FerRobotics Compliant Robot Technology GmbH,
called Romo (see Figure 1). It comprises seven rota-
tional joints of which five are actuated pneumatically.
The other two – used for longitudinal rotations – are
driven by Schunk PowerCubes (electrically commu-
230
Kastner M., Gattringer H. and Naderer R..
Evaluation of a Joint Hysteresis Model in a Robot Actuated by Pneumatic Muscles.
DOI: 10.5220/0004024102300235
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2012), pages 230-235
ISBN: 978-989-8565-22-8
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

4
5
3
2
1
7
6
B
Y
T
Y
T
Z
T
X
B
X
B
Z
Figure 1: Considered robot Romo with joints 1 to 7 and tool
(T) and base (B) coordinate systems.
tated motor modules). The three main joints (1, 2 and
4) are actuated by a pair of Festo DMSP–40 muscles
each. Only these three joints will be considered in this
paper. The basic joint principle is shown in Figure 2,
the controller will be presented later (see Figure 6).
q denotes the joint angle, Q the joint torque, F the
muscle forces, p the muscle pressures and u the valve
control voltages.
Each muscle pressure is measured by an according
sensor located at the inlet, while the robot’s original
joint position instrumentation has been changed from
cable extension sensors to optical encoders (17bit,
absolute) to improve the control performance. The
muscles are actuated by Festo MPYE–18HF 5/3-way
proportional directional slider valves. The control is
implemented on an industrial PC with a realtime op-
erating system (Bernecker and Rainer APC 620) with
a Pentium M CPU clocked at 1.4 GHz. The controller
cycle time is 0.5 ms. The Mathworks Realtime Work-
shop is used to generate C code for the PC from a
Simulink implementation of the controller, much like
on the well known dSpace rapid prototyping systems.
3 ADVANCED MUSCLE
MODELING
Beyond the static contraction/pressure/force charac-
teristic, several approaches for enhanced dynamical
models of pneumatic muscles can be found in various
publications. (Chou and Hannaford, 1994) observed
that the braided pneumatic muscles they used showed
a rate–independent hysteresis, which they attributed
to Coulomb friction in the shell or between the shell
and the bladder. They did not devise a mathematical
model but tried to improve the situation using lubri-
cants, which only led to small improvements. (Klute
Pressure
sensors
Position
sensor
Control
system
2 x
1 2
Tank
F
1
F
2
q, Q
Figure 2: Concept drawing of a pneumatic joint.
et al., 2002) from the same research group compared
the characteristic of the pneumatic artificial muscle
to the famous Hill model for skeletal muscle, (Hill,
1938). Again, they found the pneumatic muscle to be
very lightly damped and used an additional hydraulic
damper to create a mechanical system that resembles
the biological inspiration. The hysteresis effect is not
mentioned in this article. (Reynolds et al., 2003) de-
vise a model using spring and damper coefficients that
are affine functions in the muscle pressure. (Kerscher
et al., 2006) use a similar approach for modeling a
Festo fluidic muscle. They evaluate their model in
a quick–release setup inspired by Hill’s experiments
and conclude that the resulting force/velocity charac-
teristic shows nearly the same curve progression as
biological muscle. Around the same time (Tondu and
Zagal, 2006) performed basically the same tests with
custom braided muscles. They show that a version
with a braided iron shell can be modeled with a con-
stant viscous friction coefficient, while for a rayon
variant this constant has to be replaced by an ansatz
of the form a/(b+ v) (a and b are constant model pa-
rameters and v is the contraction speed). They demon-
strate that the latter resembles the behavior of biolog-
ical muscle, while the iron shell version leads to con-
siderably more oscillations. They also criticize (Klute
et al., 2002) for a misinterpretation of Hill’s model.
Again, none of the last three mentioned contribu-
tions consider hysteresis, although Tondu had used
Coulomb terms in older papers.
(Davis and Caldwell, 2006) took on ideas from
the already mentioned (Tondu and Lopez, 2000) and
(Chou and Hannaford, 1994) concerning Coulomb
friction to devise a very complex model of the braid’s
friction properties. Recently, (Minh et al., 2011)
presented a more phenomenological Maxwell–slip
model approach for single Festo MAS–20 muscles
EvaluationofaJointHysteresisModelinaRobotActuatedbyPneumaticMuscles
231

and the same was done for an antagonistic joint
in (Minh et al., 2010). They build on the rate–
independance assumption from the research group
around Hannaford and verify this assumption for the
Festo muscle. While this result is somewhat surpris-
ing when compared to the Hill’s model analogy previ-
ously found in (Kerscher et al., 2006) (who used ex-
actly the same muscle type), it seems that the main
reason for this discrepancy might be the different
considered speed ranges. For rotational joints the
arm transforms the muscle speed upwards to the tip.
Therefore, lower muscle speeds than in linear appli-
cations are typically used in such setups. While Minh
et al. use speeds of 1 mm/s and 16mm/s to support
their rate–independence assumption, the force/speed
characteristic by Kerscher et al. presumably
1
ranges
from 0 to 900mm/s.
(Minh et al., 2009) is the only contribution we
are aware of, where a hysteresis compensator is used
in a pneumatic muscle position controller and the
improvements are evaluated. (Boblan, 2009) pro-
vides some hysteresis modeling ideas for single Festo
muscles and also mentions that they are very lightly
damped. The lack of measurement data for the hys-
teresis behavior of the complete joint is given as a
reason for neglecting it in the control scheme. Sim-
ilarly, (Van Damme, 2009) develops a Preisach hys-
teresis model for pleated pneumatic artificial muscles
but states that without knowledge of the initial hys-
teresis state the utilization in a controller is too cum-
bersome. Other recent publications on position con-
trol, for example (Aschemann and Schindele, 2008)
or (Krichel et al., 2010) show a good controller per-
formance without explicitly considering effects like
hystersis, damping or friction in their models.
Here, we want to evaluate the usefulness of a local
compensator for the hysteresis in the joint angle for
quasi–static pressure differences. In our approach we
completely separate the nonlinear static characteristic
and the hysteresis model.
Our joint hysteresis model is based on a Prandtl–
Ishlinskii operator approach as described in (Kuhnen,
2003) for a magnetostrictive actuator. The nominal
pressure difference for a certain joint angle under the
zero load assumption, i.e. Q = 0, can be calculated
from the static joint model as
∆p
nom
=
1
B(q)
(−A(q) p
m
−C(q)) , (1)
where p
m
is the mean pressure and A, B and C are
polynomials that approximate pointwise, global (i.e.
1
In the referred to Figure 11 no explanation of the used
scaling value v
max
is given, so this assumption is based on
maximum speed values found in other plots.
(b)
(∆p− ∆p
nom
) + q
(a)
q in rad
∆p in bar
−1 0 1−2 0 2
−1
0
1
−1
0
1
Figure 3: Hysteresis in the joint angle for slow variations
of ∆p (a). The nominal pressure difference was subtracted
and as a purely mathematical procedure the joint angle was
added to get a hysteresis loop around the 45
◦
line (b).
over the whole pressure/torque/angle range), calibra-
tion measurements. Additionally, we applied a local
calibration (i.e. for p
m
= 3bar and Q= 0) with a poly-
nomial fit to really just extract the hysteresis cycle.
For the hysteresis parameter identification pro-
cess we arranged the loop around the 45
◦
line by
adding the joint angle (in rad) to the difference be-
tween actualand nominal pressure differences (in bar)
as shown in Figure 3.
For the hysteresis model we adopted the nomen-
clature used in (Kuhnen, 2003). The output signal, y,
(which is q in our case) is directly the result of the
Prandtl–Ishlinskii operator,
y = H [x] = w
T
H
H
r
H
[x,z
H0
] , (2)
which is a linear superposition, weighted by factors
w
H
=
w
H,1
w
H,2
... w
H,N
T
, (3)
of N elementary so–called play–operators,
H
r
H
[x,z
H0
] =
H
r
H,1
[x,z
H0,1
] ...
T
, (4)
depending on the input signal, x, (∆p− ∆p
nom
+ q for
us) and the vector of initial internal states,
z
H0
=
z
H0,1
z
H0,2
... z
H,N
T
. (5)
Like the vector of weights, the vector of thresholds,
r
H
=
0 r
H,2
... r
H,N
T
, (6)
is a parameter of the model.
The play operator (see Figure 4),
z = H
r
H
[x,z
H0
] , (7)
is usually defined recursively as
z = H (x,z,r
H
) (8)
with the initial condition
z
t=0
= z
H0
(9)
ICINCO2012-9thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
232

and the threshold parameter r
H
∈ R
+
0
. Here,
H (x, z,r
H
) = max{x− r
H
,min{x+ r
H
,z}} (10)
is the sliding, symmetrical dead–zone function. For a
discrete time system, Equation 8 can be written as
z
k
= H (x
k
,z
k−1
,r
H
) (11)
with the index k denoting the k–th sample of a signal.
z
x
−r
H
0 r
H
0
Figure 4: Example input/output trajectory of the play oper-
ator, starting at an initial position z = 0. Note, that the slope
of the elementary operator is always 1.
To determine the parameters of the model, r
H
, z
H0
and w
H
, we first select evenly spaced threshold val-
ues,
r
H,i
=
i− 1
N
kxk
∞
, (12)
and initial states
z
H0,i
= 0 (13)
with i = 1..N. Then, the weights are calculated by
minimizing
J =
Z
t
e
t
0
kek
2
dt, (14)
with the error
e = y− w
T
H
H
r
H
[x,z
H0
] , (15)
subject to the inequality constraint
w
H
≥
ε
0
.
.
.
0
, (16)
where ε is a positive, but arbitrarily small constant.
The time t
0
is the start and t
e
the end time of the mea-
sured hysteresis cycle (see Figure 3) towards which
the parameters are optimized.
For our application we chose N = 100 and ε =
0.001. We solved the quadratic optimization prob-
lem, Equations 14 and 16 for our time discrete mea-
surement data of x and y using the qpOASES package
from (Ferreau et al., 2008). Of the 100 weights only
14 turned out to be non–zero. Consequently, the ele-
mentary play operators associated with the remaining
weights were dropped for the final model.
The inequality constraint, Equation 16, guarantees
an invertible model by limiting the slope of the hys-
teresis model to strictly positive values. The parame-
ters of the inverse operator,
H
−1
[y] = w
′
T
H
H
r
′
H
y,z
′
H0
, (17)
can be calculated from
r
′
H,i
=
i
∑
j=1
w
H, j
(r
H,i
− w
H, j
)
, (18)
w
′
H,i
=
1
w
H,1
i = 1
−
w
H,i
∑
i
j=1
w
H, j
∑
i−1
j=1
w
H, j
i = 2...N
and
(19)
z
′
H0,i
=
i
∑
j=1
w
H, j
z
H0,i
+
N
∑
j=i+1
w
H, j
z
H0, j
. (20)
Figure 5 shows a comparison of the inverse model
– corrected by the previously added q–term – to the
measurement data.
model output
measurement
q in rad
∆p− ∆p
nom
in bar
−1 −0.5 0 0.5 1
−0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
Figure 5: Inverse hysteresis model output compared to mea-
surement data.
4 CONTROL
The implemented joint controllers (see Figure 6) use a
cascaded structure with inner, flatness based, pressure
control loops. The position controller uses a PID con-
trol law for feedback and and additional feedforward
action from the inverse dynamics. A linear, local joint
observer estimates the states. It uses a nominal mo-
ment of inertia of the joint as model informationin ad-
dition to an integral estimation of the remaining load
torque components. A gain–scheduling anti–windup
logic has been added. However, it becomes only ac-
tive in case of fast and large disturbances, since our
target trajectories are designed to obey the actuator
flow and pressure limits.
The calculated pressure difference of the compen-
sator is added to the output of the inv. joint character-
istic. Note, that for the flatness based pressure control
the time derivative of the desired pressure is required,
which is generated by numerical differentiation.
EvaluationofaJointHysteresisModelinaRobotActuatedbyPneumaticMuscles
233

P
I
D
R
q
d
State observer
−
˙q
q
˙q
d
Anti-windup
logic
Inverse
dynamics
P
q
sensor
Q
d
Q
d
, p
d,1
, p
d,1
, u
d,1
, u
d,2
Q, p
1
, p
2
, u
1
, u
2
−
p
m,d
Q
d
Pressure
controller
p
1
, q
Pressure
controller
p
2
, q
p
d,1
p
d,2
u
d,1
u
d,2
Q
ff
Inv. joint
torque
character-
istic
q
q
d
, ˙q
d
, ¨q
d
Hysteresis
compensator
q
d
Figure 6: Implemented joint controller structure. Subscript d denotes desired values.
t in st in s
q
1
− q
1,d
in mrad
Q
1,d
− Q
1,ff
in Nm
0 100 200 3000 100 200 300
0
100
200
300
0 100 200 300
0 10 20 30 400 10 20 30 40
−10
0
10
−20
0
20
−10
0
10
−20
0
20
−20
0
20
−20
0
20
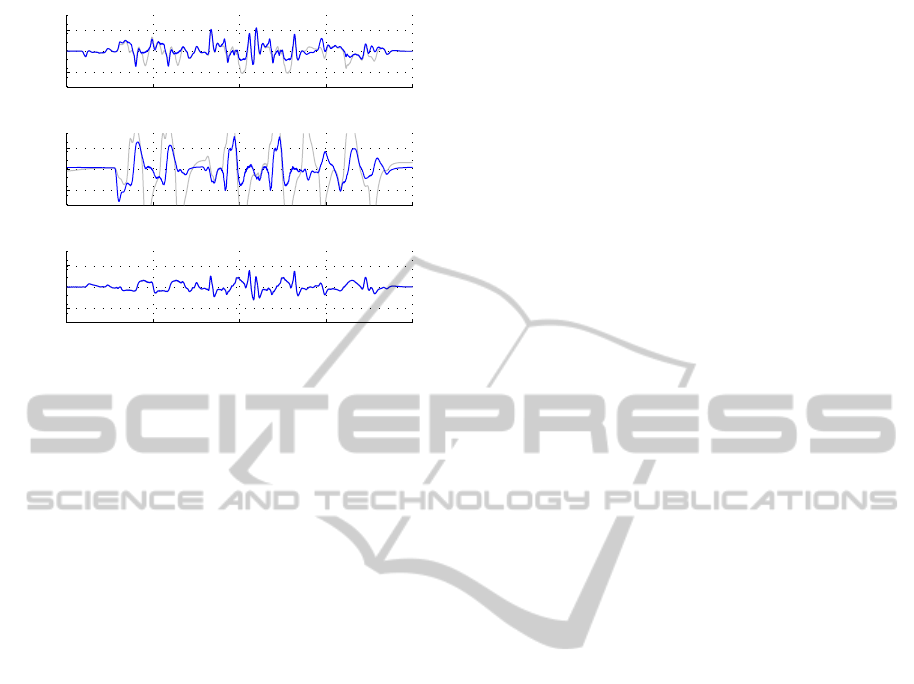
Figure 7: Evaluation results of the hysteresis compensator for the first joint of the Romo robot. Regular lines were taken with
enabled and light lines with disabled hysteresis compensator. The first row is from the fast experiment while for the second a
time scaling of 1/10 was used. In the third the integrator part of the position controller was disabled for the slow experiment.
5 EVALUATION
The evaluation of the control performance when us-
ing the hysteresis compensator in the first joint was
done tracking a trajectory designed to the recommen-
dations of the ISO 9283 norm (rounded rectangles,
cirles and lines in space) at different speeds. The re-
sults are shown in Figure 7. Especially in the slow
trial there is a significant improvement in the control
quality. An interesting observation is that there seems
to be some interplay between the hysteresis compen-
sation and the integrator part of the controller – see
the difference in the torque errors at t = 130s where
the first joint is at rest.
We have not yet created a hysteresis model for the
other two joints in the way described above. However,
in these joints the feedback part is working much bet-
ter than in the first joint (see Figure 8, q
1
mainly in-
fluences the y direction – see Figure 1).
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we discussed the advanced modeling
of robot joints actuated by pneumatic muscles using
hysteresis compensation. We evaluated the result-
ing compensator in the position controller of a robot,
which led to promising results. In the future we want
to look into the observed interplay between the inte-
ICINCO2012-9thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
234
t in s
z− z
d
in mm
y− y
d
in mm
x− x
d
in mm
0 10
20 30 40
0 10 20 30 40
0 10 20 30 40
−10
0
10
−10
0
10
−10
0
10
Figure 8: Tracking errors during the fast ISO 9283 test with
(regular line) and without (light line) hysteresis compensa-
tion in the first joint.
grator part and the hysteresis compensator as well as
devise models for the other joints. Furthermore, us-
ing the compensator in a disturbance force observer
would be an interesting scenario.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Austrian Center
of Competence in Mechatronics (ACCM) and the
ODEUO project, an experiment funded in the context
of the European Clearing House for Open Robotics
Development (ECHORD) project.
REFERENCES
Aschemann, H. and Schindele, D. (2008). Sliding-mode
control of a high-speed linear axis driven by pneu-
matic muscle actuators. Industrial Electronics, IEEE
Transactions on, 55(11):3855–3864.
Boblan, I. (2009). Modellbildung und Regelung eines flu-
idischen Muskelpaares. PhD thesis, Technical Univer-
sity Berlin.
Chou, C.-P. and Hannaford, B. (1994). Static and dynamic
characteristics of McKibben pneumatic artificial mus-
cles. In Robotics and Automation, 1994. Proceedings.,
1994 IEEE International Conference on, volume 1,
pages 281–286.
Davis, S. and Caldwell, D. G. (2006). Braid effects on con-
tractile range and friction modeling in pneumatic mus-
cle actuators. The International Journal of Robotics
Research, 25(4):359–369.
Ferreau, H., Bock, H., and Diehl, M. (2008). An online ac-
tive set strategy to overcome the limitations of explicit
MPC. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear
Control, 18(8):816–830.
Hill, A. V. (1938). The heat of shortening and the dy-
namic constants of muscle. Proceedings of the Royal
Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences,
126(843):136–195.
Kerscher, T., Albiez, J., Z¨ollner, J., and Dillmann, R.
(2006). Evaluation of the dynamic model of fluidic
muscles using quick-release. First IEEE / RAS-EMBS
International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and
Biomechatronics.
Klute, G. K., Czerniecki, J. M., and Hannaford, B. (2002).
Artificial muscles: Actuators for biorobotic sys-
tems. The International Journal of Robotics Research,
21(4):295–309.
Krichel, S., Sawodny, O., and Hildebrandt, A. (2010).
Tracking control of a pneumatic muscle actuator us-
ing one servovalve. In American Control Conference
(ACC), 2010, pages 4385–4390.
Kuhnen, K. (2003). Modeling, identification and compen-
sation of complex hysteretic nonlinearities: A modi-
fied Prandtl-Ishlinskii approach. European Journal of
Control, 9:407–418.
Minh, T., Tjahjowidodo, T., Ramon, H., and Van Brussel,
H. (2009). Control of a pneumatic artificial mus-
cle (PAM) with model-based hysteresis compensa-
tion. In Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, 2009.
AIM 2009. IEEE/ASME International Conference on,
pages 1082–1087.
Minh, T. V., Kamers, B., Tjahjowidodo, T., Ramon, H.,
and Van Brussel, H. (2010). Modeling torque-
angle hysteresis in a pneumatic muscle manipula-
tor. In Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM),
2010 IEEE/ASME International Conference on, pages
1122–1127.
Minh, T. V., Tjahjowidodo, T., Ramon, H., and Van Brussel,
H. (2011). A new approach to modeling hysteresis in
a pneumatic artificial muscle using the Maxwell-slip
model. Mechatronics, IEEE/ASME Transactions on,
16(1):177–186.
Reynolds, D. B., Repperger, D. W., Phillips, C. A., and
Bandry, G. (2003). Modeling the dynamic character-
istics of pneumatic muscle. Annals of Biomedical En-
gineering, 31:310–317.
Tondu, B. and Lopez, P. (2000). Modeling and control of
McKibben artificial muscle robot actuators. Control
Systems, IEEE, 20(2):15–38.
Tondu, B. and Zagal, S. (2006). McKibben artificial mus-
cle can be in accordance with the Hill skeletal muscle
model. In Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics,
2006. BioRob 2006. The First IEEE/RAS-EMBS Inter-
national Conference on, pages 714–720.
Van Damme, M. (2009). Towards Safe Control of a Com-
pliant Manipulator Powered by Pneumatic Muscles.
PhD thesis, Vrije Universiteit Brussel.
EvaluationofaJointHysteresisModelinaRobotActuatedbyPneumaticMuscles
235
