
GFIS: Genetic Fuzzy Inference System for Speech Recognition
Washington Luis Santos Silva and Ginalber Luiz de Oliveira Serra
Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology
Department of Electroelectronics, Laboratory of Computational Intelligence Applied to Technology
Av. Getulio Vargas, 04, Monte Castelo, CEP: 65030-005, S˜ao Luis, Maranh˜ao, Brazil
Keywords:
Recognition Speech, Fuzzy Systems, Optimization, Genetic Algorithm, Discrete Cosine Transform.
Abstract:
The concept of fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic is widely used to propose of several methods applied to systems
modeling, classification and pattern recognition problem. This paper proposes a genetic-fuzzy recognition
system for speech recognition. In addition to pre-processing, with mel-cepstral coefficients, the Discrete Co-
sine Transform (DCT) is used to generate a two-dimensional time matrix for each pattern to be recognized.
A genetic algorithms is used to optimize a Mamdani fuzzy inference system in order to obtain the best model
for final recognition. The speech recognition system used in this paper was named Genetic Fuzzy Inference
System for Speech Recognition (GFIS). Experimental results for speech recognition applied to brazilian lan-
guage show the efficiency of the proposed methodology compared to methodologies widely used and cited in
the literature.
1 INTRODUCTION
Parameterization of an analog speech signal is the first
step in speech recognition process. Several popu-
lar signal analysis techniques have emerged as stan-
dards in the literature. These algorithms are intended
to produce a perceptually meaningful parametric re-
presentation of the speech signal, parameters that can
emulate some behavior observed in human auditory
and perceptual systems. Actually, these algorithms
are also designed to maximize recognition perfor-
mance (Picone, 1991),(Rabiner and Hwang, 1993).
The problem of pattern recognition might be formu-
lated as follows: Let S
k
classes, where k = 1,2,3...K,
and S
k
⊂ ℜ
n
. If any pattern space is take with dimen-
sion ℜ
x
, where x ≤ n, it should transform this space
into a new pattern space with dimension ℜ
a
, where
a < x ≤ n. Then assuming a statistical measure or
second order model for each S
k
, through a covariance
function represented by
h
Φ
(k)
x
i
, the covariance matrix
of the general pattern recognition problem becomes:
[Φ
x
] =
K
∑
k=1
P(S
k
)
h
Φ
(k)
x
i
(1)
where P(S
k
) is a distribution function of the class S
k
,
a priori, with 0 ≤ P(S
k
) ≤ 1. A linear transformation
operator through the matrix A maps the pattern space
in a transformed space where the columns are ortho-
gonal basis vectors of this matrix A. The patterns of
the new space are linear combinations of the original
axes as structure of the matrix A. The statistics of
second order in the transformed space are given by:
Φ
A
= A
T
[Φ
x
]A (2)
where Φ
A
is the covariance matrix which corresponds
to the space generated by the matrix A and the opera-
tor [·]
T
correspondsto the transpose of a matrix. Thus,
it can extract features that provide greater discrimina-
tory power for classification from the dimension of
the space generated (Andrews, 1971).
One of the most widespread techniques for pattern
speech recognition is the ”Hidden Markov Model”
(HMM) (Shenouda et al., 2006). A well known de-
ficiency of the classical HMMs is the poor modeling
of the acoustic events related to each state. Since the
probability of recursion to the same state is constant,
the probability of the acoustic event related to the
state is exponentially decreasing. A second weakness
of the HMMs is that the observation vectors within
each state are assumed uncorrelated, and these ve-
ctors are correlated (Wachter et al., 2007). To over-
come these drawbacks, robust recognizer has been
proposed, since it has been experimentally shown that
spectral variations are discriminant features for simi-
lar sounds (Fissore et al., 1997).
536
Luis Santos Silva W. and Serra G..
GFIS: Genetic Fuzzy Inference System for Speech Recognition.
DOI: 10.5220/0004045705360541
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2012), pages 536-541
ISBN: 978-989-8565-21-1
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

1.1 Proposed Methodology
In this proposal, a speech signal is encoded and pa-
rameterized in a two-dimensional time matrix with
four parameters of the speech signal. After co-
ding, the mean and variance of each pattern are used
to generate the rule base of Mamdani fuzzy infe-
rence system. The mean and variance are optimized
using genetic algorithm in order to have the best
performance of the recognition system. This pa-
per consider as patterns the brazilian locutions (di-
gits): '0 ','1 ','2 ','3 ','4 ','5 ','6 ','7 ','8 ','9 ' . The
Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) (Ahmed et al.,
1974),(Zhou and Chen, 2009) is used to encoding the
speech patterns. The use of DCT in data compres-
sion and pattern classification has been increase in re-
cent years, mainly due to the fact its performance is
much closer to the results obtained by the Karhunen-
Lo`eve transform which is considered optimal for a
variety of criteria such as mean square error of trun-
cation and entropy (Fu, 1968). This paper demons-
trates the potential of DCT and fuzzy inference sys-
tem in speech recognition (Milner et al., 1994),(Silva
and Serra, 2011).
2 SPEECH RECOGNITION
SYSTEM
The proposed recognition system GFIS block dia-
gram is depicted in Fig.1.
Speech Signal
Segmentation
and
Windowing
Coding
Mel-Cepstral
Coefficients
Generation temporal
two-dimensional DCT
Matrix
Fuzzy Inference
System for Speech
Recognition
Rule Base
optimized by
genetic algorithm
Patterns
Figure 1: Block diagram of the proposed recongnition sys-
tem GFIS.
2.1 Two-Dimensional Time Matrix
DCT Coding
Initially, the speech signal is digitizing, so it is divided
in frames which are windowed and encoded in a set of
parameters defined by the order of mel-cepstral coef-
ficients (MFCC). The DCT coefficients are computed
and the two-dimensional time DCT matrix is genera-
ted, based on each speech signal to be recognized
(Ariki et al., 1989),(Milner et al., 1994). Let mfcc the
mel-cepstral coefficients. The two-dimensional time
matrix is the result of DCT in a sequence of T mel-
cepstral coefficients observation vectors on the time
axis, given by:
C
k
(n, T) =
1
N
T
∑
t=1
mf cc
k
(t)cos
(2t − 1)nπ
2T
(3)
where mfcc
k
are the mel-cepstral coefficients, and
k, 1 ≤ k ≤ K, is the k-th (line) component of t-th frame
of the matrix and n, 1 ≤ n ≤ N (column) is the or-
der of DCT. Thus, the two-dimensional time matrix
(Azar and Razzazi, 2008), where the interesting low-
order coefficients k and n that encode the long-term
variations of the spectral envelope of the speech sig-
nal is obtained (Fissore et al., 1997). Thus, there is
a two-dimensional time matrix C
k
(n, T) for each in-
put speech signal. The elements of the matrix are ob-
tained as follows:
1. For a given spoken word P(digit), ten examples
of utterances of Pare gotten. Each examples is
properly encoded in T frames distributed along
the time axis;
2. Each frame of a given example of the word P
generates a total of K mel-cepstral coefficients
and the significant features are taken for each
frame along time. The N-th order DCT is
computed for each mel-cepstral coefficient of
same order within the frames distributed along
the time axis, i.e., c
1
of the frame t
1
, c
1
of the
frame t
2
, ...,, c
1
of the frame t
T
, c
2
of the frame
t
1
, c
2
of the frame t
2
, ...,, c
2
of the frame t
T
, and
so on, generating elements {c
11
, c
12
, c
13
, ..., c
1N
},
{c
21
, c
22
, c
23
, ..., c
2N
}, {c
K1
, c
K2
, c
K3
, ..., c
KN
},
and the matrix given in equation (3). Thus, a
two-dimensional time matrix DCT is generated
for each example of the word P, represented
by: C
kn
, where k = 1, 2, ...K and n = 1, 2, ..., N.
In this paper, a two-dimensional time matrix is
generated by C
j
kn
for each spoken word, where
j = 0, 1, 2...9 and K = N = 2.
3. Finally, a matrix of mean and variances, for all
matrices C
j
kn
from the ten examples of spoken
words used as patterns, is generated in order to
produce gaussians to be used as fundamental in-
formation for implementation of the fuzzy recog-
nition system. The means and variances to be op-
timized by genetic algorithm maximize the total
of hits from the fuzzy recognition system.
2.2 Fuzzy Inference System for Speech
Recognition Decision
Given the fuzzy set A input, the fuzzy set B output,
should be obtained by the relational max-t composi-
tion(Monserratet al., 2007). This relationship is given
GFIS:GeneticFuzzyInferenceSystemforSpeechRecognition
537

by.
B = A◦ Ru (4)
where Ru is a fuzzy relational rules base.
The fuzzy rule base of practical systems usually
consists of more than one rule. In this paper the
compositional inference is used (Wang, 1994),(Gang,
2010).
Ru
l
:IF x
1
is A
l
1
and...and x
n
is A
l
n
THEN y is B
l
(5)
where A
l
i
and B
l
are fuzzy set in U
i
⊂ ℜ and V ⊂ ℜ,
and x = (x
1
, x
2
, ..., x
n
)
T
∈ U and y ∈ V are input and
output variables of fuzzy system, respectively. Let M
be the number of rules in the fuzzy rule base; that is,
l = 1, 2, ...M.
From the coefficients of the matrices C
j
kn
with j =
0, 1, 2, ..., 9, k = 1, 2 and n = 1, 2 generated during the
training process, representing the mean and variance
of each pattern j a rule base with M = 40 individual
rules is obtained and given by:
Ru
j
: IF C
j
kn
THEN y
j
(6)
In this paper,the training process is based on the fuzzy
relation Ru
j
using the Mamdani implication. The rule
base Ru
j
should be considered a relation R(X ×Y) →
[0, 1], computed by:
µ
Ru
(x, y) = I(µ
A
(x), µ
B
(y)) (7)
where the operator I should be any t-norm (Babuska,
1998), (Seki et al., 2010), (Gosztolya et al., 2009).
Given the fuzzy set A
′
input, the fuzzy set B
′
output
might be obtained by max-min composition, (Wang,
1994). For a minimum t-norm and max-min compo-
sition it yields:
µ
(B
′
)
= max
x
min
x,y
(µ
A
′
(x), µ
(Ru)
(x, y)) (8)
The elements of the matrix C
j
kn
were used to gene-
rate gaussians membership functions in the process
of fuzzification. For each trained model j the gaus-
sians memberships functions µ
c
j
kn
are generated, cor-
respondingto the elements c
j
kn
of the two-dimensional
time matrix C
j
kn
with j = 0.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, where
j is the model used in training. The training system
for generation of fuzzy patterns is based on the en-
coding of the speech signal s(t), generating the pa-
rameters of the matrix C
j
kn
. Then, these parameters
are fuzzified, and they are related to properlyfuzzified
output y
j
by the relational implications, generating a
relational surface µ
(Ru)
, given by:
µ
Ru
= µ
c
j
kn
◦ µ
y
j
(9)
This relational surface is the fuzzy system rule base
for recognition optimized by genetic algorithm to
Fuzzification
Coding of
speech signal
Fuzzy
Inferece
(Relational
Surface)
Fuzzy
Relational
Models for
Recognition
(PATTERNS)
s(t)
j
c
11
j
c
12
j
c
21
j
c
22
j
c
11
m
j
c
12
m
j
c
21
m
j
c
22
m
Optimization of
memberships functions of
the rule base models with
Genetic Algorithm
0=
J
m
1=
J
m
2=
J
m
3=
J
m
4=
J
m
5=
J
m
6=
J
m
7=
J
m
8=
J
m
9=
J
m
Figure 2: Generation Systems Fuzzifieds Models.
maximize the speech recognition. The training sys-
tem is shown in Fig.2.
The decision phase is performed by a fuzzy infe-
rence system based on the set of rules obtained from
the mean and variance matrices of two dimensions
time of each spoken digit. In this paper, a matrix with
minimum number of parameters (2 × 2) in order to
allow a satisfactory performance compared to pattern
recognizers available in the literature. The elements
of the matrices C
j
kn
are used by the fuzzy inference
system to generate four gaussian membership func-
tions corresponding to each element c
j
kn
k=1,2;n=1,2
of
the matrix. The set of rules of the fuzzy relation is
given by:
Rule Bases
IF c
j
kn
k=1,2;n=1,2
THEN y
j
(10)
Modus Ponens
IF c
′
j
kn
k=1,2;n=1,2
THEN y
′
j
(11)
From the set of rules of the fuzzy relation between an-
tecedent and consequent, a data matrix for the given
implication is obtained. After the training process,
the relational surfaces is generated based on the rule
base and implication method. The speech signal is en-
coded to be recognized and their parameters are eva-
luated in relation to the functions of each patterns on
the relational surfaces and the degree of membership
is obtained. The final decision for the pattern is taken
according to the max− min composition between the
input parameters and the data contained in the rela-
tional surfaces.
µ
y
′
j
= µ
c
′
j
kn
◦ µ
(Ru)
(12)
2.3 Optimization of Relational Surface
with Genetic Algorithm
The continuous genetic algorithm (Haupt and Haupt,
2004),(Tang et al., 1997) is configured with a popu-
lation size of 100, generations of 300, with mutations
ICINCO2012-9thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
538
probability of 15% and two chromosomes, with 40
genes each, to optimize a cost function with 80 varia-
bles, which are the means and variances of the pat-
terns to be recognized by the proposed fuzzy recog-
nition system. The genetic algorithm was used to op-
timize the variations of mean and variances of each
pattern in order to maximize the successful recogni-
tion process.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
3.1 System Training
The patterns to be used in the recognition process
were obtained from ten speakers who are speaking the
digits 0 until 9. After pre-processing of the speech
signal and fuzzification of the matrix C
j
kn
, its fuzzi-
fieds components µ
c
j
kn
had been optimized by the GA
that maximize the total of successful recognition. The
optimization process was performed with 16 realiza-
tions of the genetic algorithm. The best result of the
recognition processing by GFIS is shown in Fig.3.
The total number of hits using GA was 92 digits cor-
rectly identified in the training process. The relational
surface generated for this result was used for valida-
tion process. The best individual in the first genera-
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
−0.95
−0.9
−0.85
−0.8
−0.75
−0.7
−0.65
−0.6
generation
cost
Population Average
Best
Figure 3: Plot of the best results obtained in the training
process.
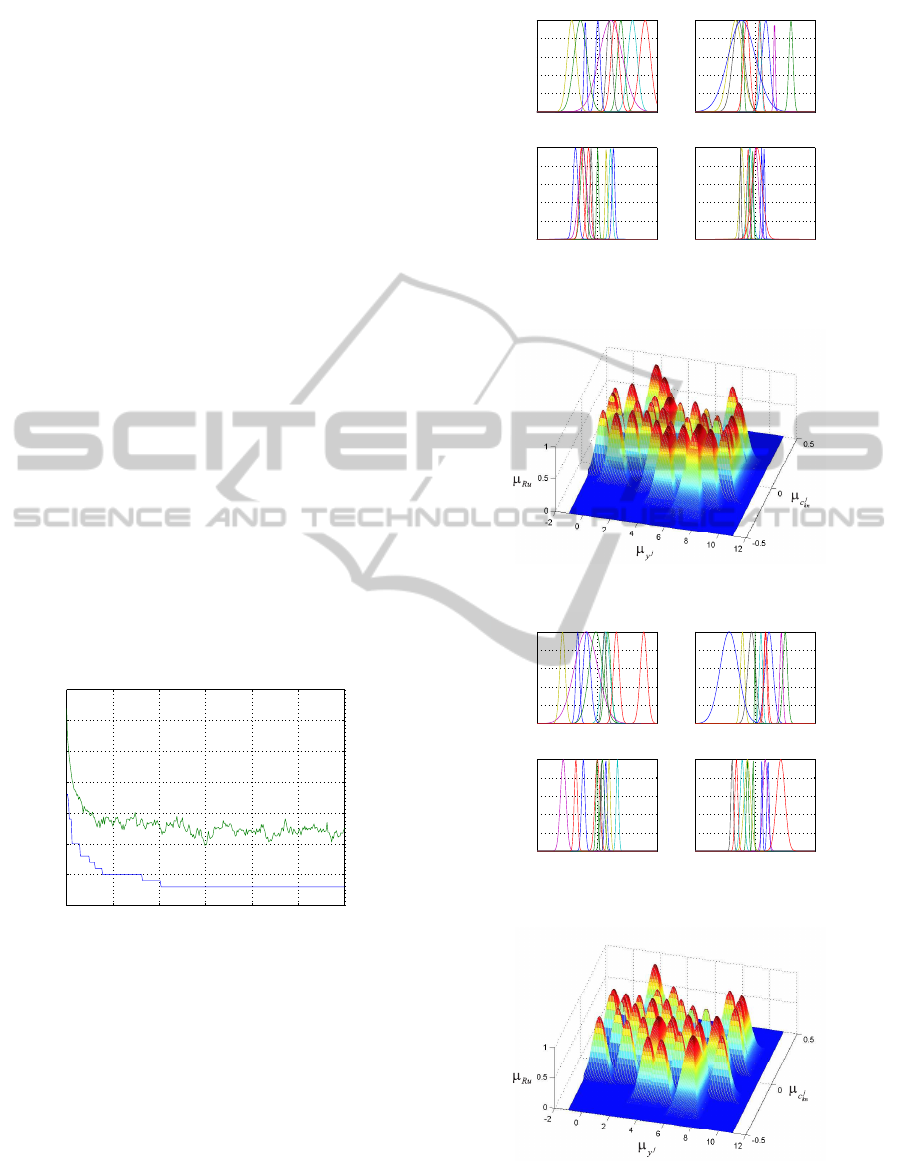
tion is shown in Fig.4. In this case the total number of
correct answers was 46 digits. The ralational surface
of the best individual in the first generation is shows
in Fig.5.
The optimum individual, GFIS, presents the fea-
tures in Fig.6 and Fig.7.
3.2 System Test - Validation
In this step, 100 locutions uttered in a room with con-
trolled noise level and 500 locutions uttered in an
−0.5 0 0.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Membership functions for:C11
Pertinence Degree
−0.5 0 0.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Membership functions for:C12
Pertinence Degree
−0.5 0 0.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Membership functions for:C21
Pertinence Degree
−0.5 0 0.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Membership functions for:C22
Pertinence Degree
Figure 4: Membership functions for c
j
kn
in the 1st genera-
tion.
Figure 5: Relational surface (µ
Ru
) in the 1st generation.
−0.5 0 0.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Membership functions for:C11
Pertinence Degree
−0.5 0 0.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Membership functions for:C12
Pertinence Degree
−0.5 0 0.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Membership functions for:C21
Pertinence Degree
−0.5 0 0.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Membership functions for:C22
Pertinence Degree
Figure 6: Membership functions for c
j
kn
optmized by GA.
Figure 7: Relational surface (µ
Ru
) optmized by GA.
environment without any kind of noise control were
used. For every ten examples of each spoken digit,
GFIS:GeneticFuzzyInferenceSystemforSpeechRecognition
539

was generated two-dimensional time matrix cepstral
coefficients C
j
kn
and they were used in the test proce-
dure. Where performed six types of tests:
Training: Recognition Optimized by GFIS (5 Fe-
male and 5 Male Speakers)
TEST 1: Validation - Strictly speaker dependent
recognition, where the words used for training and
testing were spoken by a same group of 10 spea-
kers(5 Female and 5 Male Speakers).
TEST 2: Validation test- Recognition based on the
partial dependence of the speaker with two exam-
ples for each ten examples of each digit(Female
Speaker).
TEST 3: Validation test- Recognition based on the
partial dependence of the speaker with two exam-
ples for each ten examples of each digit(Male
Speaker).
TEST 4: Validation test- Recognition independent
of the Speaker, where the speaker does not have
influence in the training process(Female Speaker).
TEST 5: Validation test- Recognition independent
of the Speaker, where the speaker does not have
influence in the training process(Male Speaker).
The tables from 1 to 6 presents the comparative
analysis of the HMM with three state, three gaussian
mixture by state and order analysis, i.e., the number of
mel-cepstral parameter equal 8 and 12. The number
of hits, using the HMM and GFIS for speech recog-
nition. In the table for HMM, sn = state number,
and pn = parameters number( Mel-cepstrais coeffi-
cients).
Table 1: Results for the digits used in the training.
Brazilian English HMM HMM GFIS
Digits Digits sn=3 pn=8 sn=3 pn=12 pn=4
ZERO (zero) 9 10 10
UM (one) 9 10 8
DOIS (two) 7 8 10
TRES (three) 8 9 9
QUATRO (four) 7 8 8
CINCO (five) 10 8 10
SEIS (six) 7 10 10
SETE (seven) 9 10 9
OITO (eight) 10 10 10
NOVE (nine) 9 8 8
Total(%) 85% 91% 92%
4 CONCLUSIONS
Evaluating the results, it is observed that the proposed
speech recognizer GFIS, even with a minimal param-
eters number in the generated patterns was able to
extract more reliably the temporal characteristics of
Table 2: Validation Test 1.
Brazilian English HMM HMM GFIS
Digits Digits sn=3 pn=8 sn=3 pn=12 pn=4
ZERO (zero) 9 10 9
UM (one) 9 10 8
DOIS (two) 7 7 9
TRES (three) 8 8 8
QUATRO (four) 7 8 9
CINCO (five) 10 10 10
SEIS (six) 7 8 9
SETE (seven) 9 9 9
OITO (eight) 9 9 10
NOVE (nine) 9 9 9
Total(%) 84% 88% 90%
Table 3: Validation Test 2.
Brazilian English HMM HMM GFIS
Digits Digits sn=3 pn=8 sn=3 pn=12 pn=4
ZERO (zero) 9 9 10
UM (one) 9 9 7
DOIS (two) 6 6 7
TRES (three) 10 9 8
QUATRO (four) 9 9 8
CINCO (five) 6 7 10
SEIS (six) 6 7 6
SETE (seven) 6 7 9
OITO (eight) 7 8 7
NOVE (nine) 9 9 9
Total(%) 77% 80% 81%
Table 4: Validation Test 3.
Brazilian English HMM HMM GFIS
Digits Digits sn=3 pn=8 sn=3 pn=12 pn=4
ZERO (zero) 7 9 8
UM (one) 8 9 8
DOIS (two) 7 8 10
TRES (three) 6 8 7
QUATRO (four) 7 8 9
CINCO (five) 8 8 8
SEIS (six) 8 7 9
SETE (seven) 7 8 9
OITO (eight) 9 9 8
NOVE (nine) 8 9 8
Total(%) 75% 83% 84%
Table 5: Validation Test 4.
Brazilian English HMM HMM GFIS
Digits Digits sn=3 pn=8 sn=3 pn=12 pn=4
ZERO (zero) 6 6 10
UM (one) 2 3 2
DOIS (two) 4 5 5
TRES (three) 5 5 8
QUATRO (four) 5 7 4
CINCO (five) 7 8 10
SEIS (six) 4 8 5
SETE (seven) 5 6 9
OITO (eight) 4 6 4
NOVE (nine) 5 5 9
Total(%) 49% 59% 66%
the speech signal and produce good recognition re-
sults compared with the traditional HMM. To obtain
equivalent results with HMM is necessary to increase
the state number and/or mixture number. An increase
in the order of the analysis above 12 does not improve
significantly the performance of HMM. Any particu-
ICINCO2012-9thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
540

Table 6: Validation Test 5.
Brazilian English HMM HMM GFIS
Digits Digits sn=3 pn=8 sn=3 pn=12 pn=4
ZERO (zero) 4 5 8
UM (one) 5 9 4
DOIS (two) 9 9 4
TRES (three) 3 4 3
QUATRO (four) 4 5 5
CINCO (five) 9 7 10
SEIS (six) 5 6 5
SETE (seven) 8 6 8
OITO (eight) 9 8 10
NOVE (nine) 6 6 10
Total(%) 62% 65% 67%
lar technique of noise reduction, such as those com-
monly used in HMM-based recognizers, was not used
during the development of this paper. It is believed
that with proper treatment of the signal to noise ratio
in the process of training and testing, the GFIS Rec-
ognizer may improve its performance:
1. Increase the speech bank with different accents;
2. Improve the performance of genetic algorithm to
100% recognition in the training process;
3. Use Nonlinear Predicitve Coding for feature ex-
traction in speech recognition;
4. Use Digital Filter in the speech signal to be rec-
ognized.
5. Increase the parameters number used.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank FAPEMA for fi-
nancial support, research group of computational in-
telligence applied to technology at the IFMA by its
infrastructure for this research and experimental re-
sults, and the Master and PhD program in Eletrical
Engineering at the Federal University of Maranh˜ao
(UFMA).
REFERENCES
Ahmed, N., Natajaran, T., and Rao, K. R. (1974). Discrete
cosine transform. IEEE Transaction on Computers,
C-23:90–93.
Andrews, H. C. (1971). Multidimensional rotations in fea-
ture selection. IEEE Transaction on Computers, C-
20:1045–1051.
Ariki, Y., Mizuta, S., Nagata, M., and Sakai, T. (1989).
Spoken- word recognition using dynamic features
analysed by two-dimensional cepstrum. IEEE Pro-
ceedings, 136(v.2):133–140.
Azar, M. Y. and Razzazi, F. (2008). A dct based nonlin-
ear predictive coding for feature extraction in speech
recognition systems. IEE International Conference on
Computational Intelligente for Measurement Systems
and Applications, pages 19 – 22.
Babuska, R. (1998). Fuzzy Modeling for Control. Kluwer
Academic Publishers.
Fissore, L., Laface, P., and Rivera, E. (1997). Using
word temporal structure in hmm speech recongnition.
ICASSP 97, v.2:975–978.
Fu, K. S. (1968). Sequential Methods in Pattern Recog-
nition and Machine Learning. Acadmic Press, New
York.
Gang, C. (2010). Discussion of approximation properties of
minimum inference fuzzy system. Proceedings of the
29th Chinese Control Conference, pages 2540–2546.
Gosztolya, G., Dombi, J., and Kocsor, A. (2009). Applying
the generalized dombi operator family to the speech
recognition task. Journal of Computing and Informa-
tion Technology, pages 285–293.
Haupt, R. L. and Haupt, S. E. (2004). Pratical Genetic Al-
gorithms. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Milner, B. P., Conner, P. N., and Vaseghi, S. V. (1994).
Speech modeling using cepstral-time feature and hid-
den markov models. Communications, Speech and Vi-
sion, IEE Proceedings I, v.140(5):601–604.
Monserrat, M., Torrens, J., and Trillas, E. (2007). A survey
on fuzzy implication functions. IEEE Transactions on
Fuzzy Systems, v.15(6):1107–1121.
Picone, J. W. (1991). Signal modeling techiniques in speech
recognition. IEEE Transactions, v.79:1214–1247.
Rabiner, L. and Hwang, J. B. (1993). Fundamentals of
Speech Recognition. Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Seki, H., Ishii, H., and Mizumoto, M. (2010). On the mono-
tonicity of fuzzy inference methods related to ts infer-
ence method. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems,
v.18(3):629–634.
Shenouda, S. D., Zaki, F. W., and Goneid, A. M. R. (2006).
Hybrid fuzzy hmm system for arabic connectionist
speech recognition. The 23rd National U.Jio Science
Conference (NRSC 2006), v.0:1–8.
Silva, W. L. S. and Serra, G. L. O. (2011). Proposta de
metodologia tcd-fuzzy para reconhecimento de voz. X
SBAI:Simposio Brasileiro de Automacao Inteligente,
pages 1054–1059.
Tang, C., Lai, E., and Wang, Y. C. (1997). Distributed fuzzy
rules for preprocessing of speech segmentation with
genetic algorithm. Fuzzy Systems, Proceedings of the
Sixth IEEE International Conference on, v.1:427–431.
Wachter, M., Matton, M., Demuynck, K., Wambacq, P.,
Cools, R., and Compernolle, D. V. (2007). Template-
based continuous speech recognition. IEEE Trans-
actions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing,
v.15:1377–1390.
Wang, L. X. (1994). A course in Fuzzy Systems and Control.
Prentice Hall.
Zhou, J. and Chen, P. (2009). Generalized discrete cosine
transform. Circuits, Communications and Systems,
PACCS 2009, Pacific Asia Conference on, pages 449–
452.
GFIS:GeneticFuzzyInferenceSystemforSpeechRecognition
541
