
Cooperative Autonomous Driving for Vehicular Networks
Lamia Iftekhar and Reza Olfati-Saber
Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH 03755, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Cyber-physical Systems, Autonomous Driving, Flocking Algorithms, Intelligent Transportation Systems.
Abstract:
In this paper, we introduce cooperative autonomous driving algorithms for vehicular networks in urban en-
vironments that take human safety into account and are capable of performing vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and
vehicle-to-pedestrian (V2P) collision avoidance. We argue that “flocks” are multi-agent models of vehicu-
lar traffic on roads and propose novel autonomous driving architectures for cyber-physical vehicles capable of
performing autonomous driving tasks such as lane-driving, lane-changing, braking, passing, and making turns.
These autonomous driving algorithms are inspired by the flocking theory of Olfati-Saber (Olfati-Saber, 2006),
though, there are notable differences between autonomous driving on urban roads and flocking behavior—
flocks have a single desired destination whereas most drivers on road do not share the same destination. We
demonstrate that lane-driving for a vehicular network with n > 3 vehicles cannot necessarily be performed
using pairwise vehicular interactions and might require triangular interactions among triplets of vehicles. The
self-driving vehicles in our framework turn out to be nonlinear switching systems with discrete states that are
related to the driving modes of the vehicles. Complex driving maneuvers can be performed using a sequence
of mode switchings. We present several examples of driving tasks that can be effectively performed using our
proposed driving algorithms.
1 INTRODUCTION
The existing transportation systems are mostly con-
trolled by humans who are prone to making errors
causing collisions and fatalities. According to a report
by World Health Organization (WHO, 2004), more
than 1.3 million road accident fatalities occur world-
wide every year. Accident fatalities have been the 9th
leading cause of death by 2004 and will be among the
top 3 by 2020. Thirty-two percent of fatal crashes in
the US are due to DUI
1
(FARS, 2011).
Some of the main causes of traffic accidents are 1)
weather and road conditions; 2) drivers and pedestri-
ans engaging in risky behaviors such as erratic driv-
ing, driving while being drowsy or intoxicated, and
jay-walking while texting or being distracted by mu-
sic; and 3) the inability of human drivers to predict
and quickly react to imminent collision threats.
The main focus of past research on autonomous
driving has been on detection and tracking of lanes,
pedestrians, and obstacles for an individual vehi-
cle with embedded laser radars and video cameras
(Schneiderman and Nashman, 1994; Soelo et al.,
2004; Kolski et al., 2006). The most notable of
1
Driving Under the Influence of drugs or alcohol.
these autonomous vehicles is Boss, the winner of
the DARPA Grand Challenge for autonomous driv-
ing in urban roads. There has been limited research
on cooperative autonomous driving for vehicular net-
works. Some notable examples with a primary idea
of forming rigid platoons of vehicles are in (Hedrick
et al., 1994; Swaroop and Hedrick, 1996; Kato et al.,
2002; Baber et al., 2005). The existing fluidic mod-
els of traffic flow (Helbing, 1995)—going back to the
1955 LWR model (Lighthill and Whitham, 1955)—
are ideal for modeling and analysis of congestion in
transportation networks. Fluidic models are incapable
of capturing V2V and V2P collisions as they ignore
the discrete nature of multi-agent interactions.
We propose flocking
2
as a multi-agent model of ve-
hicular traffic on roads. Unlike rigid platoons, flocks
are capable of performing split/rejoin maneuvers and
passing disabled vehicles stuck on lanes by squeezing
into a narrower road from a wider road. The two fun-
damental differences between driving on roads and
flocking are as follows: i) all drivers do not share the
same destination and ii) the objective of the drivers
2
Forming collision-free and flexible time-varying con-
formations that move towards the same direction (See Sec-
tion 2).
345
Iftekhar L. and Olfati-Saber R..
Cooperative Autonomous Driving for Vehicular Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0004048003450352
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2012), pages 345-352
ISBN: 978-989-8565-22-8
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

(a)
(b)
Figure 1: An intelligent transportation system with a mix of
manual vehicles (C), autonomous vehicles (iC), and pedes-
trians (P): a) a highway and b) an intersection.
on roads is not to form connected 1D-chains on lanes
(i.e. platoons). The main similarity between driving
and flocking is that the majority of drivers would like
to avoid collisions with other vehicles and pedestri-
ans
3
and they temporarily move towards the same di-
rection as they share the road.
In this paper, we introduce a multi-agent frame-
work for safety-aware cooperative autonomous driv-
ing for vehicular networks that involves making major
modifications to the existing theory and algorithms of
flocking in (Olfati-Saber, 2006). We propose novel al-
gorithms that enable cyber-physical vehicles
4
(shown
in Fig. 1) to autonomously perform driving tasks
such as lane-driving, lane-changing, braking, pass-
ing, turning left and right, and avoiding tailgating and
collision with other vehicles and pedestrians. Our
main contribution is to introduce multi-objective
flocking (or autonomous driving) algorithms as a sig-
nificant modification of (Olfati-Saber, 2006) that en-
able cyber-physical vehicles to perform all the afore-
mentioned tasks in a single distributed control frame-
work. Our driving algorithm creates networks of au-
tonomous vehicles with nonlinear switching dynam-
ics that is extremely challenging to analyze. Stability
3
The drivers who commit DUI or criminals who inten-
tionally collide with other drivers and pedestrians are ex-
cluded.
4
Vehicles with embedded sensing, control, computing,
and communication devices.
analysis of the novel autonomous driving algorithms
is a major open problem that simply cannot be ad-
dressed using the existing analytical tools in nonlinear
control and switching systems.
Readers who expect the authors to provide stabil-
ity analysis of the nonlinear switching systems arising
in autonomous driving are greatly underestimating the
complexities involved in such an analysis. One of our
objectives is to present autonomous driving as a ma-
jor open problem in nonlinear stability to the control
community. Our algorithms result in natural forms of
autonomous driving in urban environments for fleets
of vehicles with linear and nonlinear dynamics based
on multi-objective flocking that simply do not exist in
the literature and that is our main contribution.
Extension of our autonomous driving algorithms
to networked vehicles with nonlinear and nonholo-
nomic dynamics is presented in a separate paper
and relies on the use of near-identity transformations
(Olfati-Saber and Iftekhar, 2012).
Here is an outline of the paper: Some background
and notations on flocking are provided in Section 2.
Our proposed autonomous driving algorithms for sep-
arate tasks are presented in Section 3. Our main re-
sult is a unified autonomous driving algorithm that
is given near the end of that section. Simulation re-
sults are provided in Section 4. Finally, concluding
remarks are made in Section 5.
2 FLOCKING ALGORITHMS
AND THEORY: BACKGROUND
AND NOTATIONS
In this section, we provide some background and no-
tations on Olfati-Saber’s flocking algorithms and the-
ory (Olfati-Saber, 2006). Consider a group of n α-
agents moving in an m-dimensional space with the
dynamics
˙q
i
= p
i
˙p
i
= u
i
(1)
where q
i
, p
i
,u
i
∈ R
m
denote the position, velocity,
and control of agent i, respectively. Let us denote the
conformation of all α agents by q = col(q
1
,...,q
n
) ∈
R
mn
. The proximity network of the agents is a dy-
namic graph G(q) = (V,E(q)) with the set of nodes
V = {1,2,...,n} and set of edges
E(q) = {(i, j) ∈V ×V : kq
j
−q
i
k ≤ r}.
where r is the interaction range between two agents.
The adjacency matrix of G(q) is a non-negative
matrix A(q) = [a
i j
(q)] with smooth elements 0 ≤
a
i j
(q) ≤ 1 defined in (Olfati-Saber, 2006). The set of
ICINCO2012-9thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
346

neighbors of agent i are denoted by N
i
(q){j : (i, j) ∈
E(q)}. A conformation q is called a quasi al pha-
lattice iff every agent is approximately equally dis-
tanced from all of its neighbors, i.e.
∃ε,d > 0 : −ε ≤ kq
j
−q
i
k−d ≤ ε, ∀j ∈ N
i
(q)
where d is the desired distance between two neigh-
bors. An α-lattice is a quasi α-lattice with ε = 0.
Based on (Olfati-Saber, 2006) (but slightly modified
for autonomous driving), a group of α-agents perform
flocking behavior if they asymptotically achieve the
following three objectives:
1. quasi self-alignment, ∃ε > 0 : kp
j
−p
i
k< ε,∀j 6=
i;
2. form a quasi α-lattice; and
3. form a connected proximity network G(q).
Algorithm 2, u
i
= f
α
i
+ f
γ
i
, in (Olfati-Saber, 2006)
leads to emergence of flocking behavior and can be
described as follows:
u
i
=
∑
j∈N
i
φ
α
(kq
j
−q
i
k
σ
)n
i j
| {z }
gradient-based term
+
∑
j∈N
i
a
i j
(q)(p
j
−p
i
)
| {z }
consensus term
+ f
γ
i
(2)
where n
i j
= (q
j
−q
i
)/
p
1 + εkq
j
−q
i
k
2
is a bounded
vector along the line connecting q
i
to q
j
and ε ∈
(0,1). Moreover ksk
σ
=
1
ε
(
p
1 + εksk
2
−1) denotes
the σ-norm of vector s. The potential function of the
group is defined as V (q) =
∑
j6=i
ψ
α
(kq
j
−q
i
k
σ
) where
ψ
α
(s) =
R
s
kdk
σ
φ
α
(h)dh. The scalar function φ
α
(s) is
defined in eq. (15) of (Olfati-Saber, 2006). f
γ
i
is a
linear tracking controller
f
γ
i
= −c
γ
1
(q
i
−q
r
) −c
γ
2
(p
i
−p
r
); c
γ
1
,c
γ
2
> 0 (3)
where (q
r
, p
r
) is the state of the γ-agent, i.e. a vir-
tual moving rendezvous point (with double integrator
dynamics). The objective of all α-agents is to asymp-
totically track a single γ-agent (or common goal) as
depicted in Fig. 2.
Figure 2: The schematic diagram of the flocking algorithm
in (2).
The assumption of “tracking one γ-agent” needs
to change entirely in the design of autonomous driv-
ing algorithms as different drivers do not necessarily
share the same destination.
3 COOPERATIVE AUTONOMOUS
DRIVING
In this section, we introduce a theoretical framework
for design and analysis of novel autonomous driv-
ing algorithms for vehicular networks in urban envi-
ronments that enables cyber-physical vehicles to au-
tonomously perform a variety of driving tasks such
as lane-driving, lane-changing, braking, passing other
vehicles, making turns, and avoiding collision with
pedestrians and nearby vehicles. The autonomous
driving framework relies on the basic elements of the
flocking theory described in Section 2, but requires
making significant number of changes and new agent
types that are necessary for urban driving.
3.1 Lane-driving
Lane-driving means moving along the mid-lane curve
µ(t) of a lane without collision with other neighbor-
ing vehicles. This is one of the most basic driving
tasks on roads, yet performing this task in a coopera-
tive manner with other vehicles is rather challenging
contrary to common belief.
We propose a lane-driving algorithm illustrated in
Fig. 3 (a) where each α
i
-agent has its own dedicated
γ
i
-agent with position ˆq
i
that is the projection of q
i
on its desired mid-lane curve µ(t) with a unit tangent
ξ
i
and normal π
i
. We refer to this model as multi-
objective flocking on curves. The velocity ˆp
i
of γ
i
is
defined based on the desired velocity v
d
i
of vehicle i
and the curvature κ
i
of the midlane curve at ˆq
i
:
ˆp
i
=
1
1 + κ
i
v
d
i
ξ
i
(4)
For a straight midlane curve passing through a point
ζ along ξ, the projection ˆq
i
of point q
i
can be readily
calculated as
ˆq
i
= Pq
i
+ (I −P)ζ
where P = I − π
i
π
T
i
is the projection matrix. The
tracking term of lane-driving algorithm takes the form
f
γ
i
= −c
γ
1
(q
i
− ˆq
i
) −c
γ
2
(p
i
− ˆp
i
) (5)
Unfortunately, a group of at least n ≥ 4 applying a
flocking-based lane-driving algorithm u
i
= f
α
i
+ f
γ
i
cannot always asymptotically achieve lane-driving
even on a straight lane (see Fig. 3 (b)) due to the
existence of structurally stable entangled formations
such as the one shown in Fig. 3 (c) that are undesir-
able local minima of a potential function for a 1D α-
lattice. Structural stability of flocks and formations
is defined and analyzed in (Olfati-Saber and Murray,
2002a; Olfati-Saber and Murray, 2002b; Olfati-Saber,
2006).
CooperativeAutonomousDrivingforVehicularNetworks
347

(a)
(b) (c)
Figure 3: Multi-objective flocking-based model of lane-
driving: (a) curved lanes, (b) straight lanes, and (c) en-
tangled conformations with n > 3 vehicles that require ap-
pyling area-potential based forces f
ap
i
.
To resolve the triangular entanglement shown in
Fig. 3 (c), we propose to add signed-area poten-
tial function terms to the structural potential V (q)
of the agents. Signed-area potentials were first ap-
plied to formation control in (Olfati-Saber and Mur-
ray, 2002c). Let q
i
,q
j
,q
k
be the position of three
agents that form a triangle. Then, the signed-area er-
ror term of the triangle, or face (i, j, k) is in the form
η
i jk
= (q
j
−q
i
) ⊗(q
k
−q
i
) − ¯a
i jk
(6)
where ¯a
i jk
is the desired signed-area (zero for lane-
driving on a straight lane) and ⊗ is a tensor prod-
uct defined by u ⊗v = u
T
·v
⊥
= v
T
·u
⊥
and v
⊥
=
(v
2
,−v
1
)
T
is right orthogonal to the vector v =
(v
1
,v
2
)
T
. The signed-area potential is ψ(η
i jk
) with
a scalar potential function ψ(s) =
√
1 + s
2
−1.
Let F denote the set of all faces in the Delaunay
triangulation of q
1
,...,q
n
. The triplets (i, j,k) are or-
dered such that i < j < k. Then, the set of neighboring
faces F
i
of node i is the set of faces that include node
i.
Define the subunit vector n
i
= ( ˆq
i
−
q
i
)/
p
1 + εkˆq
i
−q
i
k
2
that is orthogonal to ξ
i
and let ρ
i
= n
i
+ n
⊥
i
be a perturbation vector associ-
ated with the α
i
-agent. We define the area potential
force as a perturbation force given by
f
ap
i
=
∑
(i, j,k)∈F
i
ψ((q
j
−q
i
) ⊗(q
k
−q
i
))ρ
i
(7)
Suppose that an agent i is very close to its associ-
ated γ
i
-agent, or kˆq
i
−q
i
k ≤ ε. If agent i belongs to
a face with an area of order O(1), kρ
i
k < 2ε and thus
Figure 4: The schematic diagram of the lane-changing ma-
neuver.
agent i feels a relatively small perturbation of order
O(ε) (e.g. the front and end agents in the diamond
formation of Fig. 3 (c) that lie on the midlane curve).
However, if agent i is relatively far from its associ-
ated γ
i
agent, or kˆq
i
−q
i
k = O(1), and it belongs to
a face with an area of order O(1), then agent i feels
a significant perturbation of order O(1) along π
i
as
shown in Fig. 3 (c) for the two agents far from the
midlane curve. Here is our cooperative lane-driving
algorithm:
u
i
= f
α
i
+ f
γ
i
+ f
ap
i
. (8)
The area potential term f
ap
i
has a major role in
avoiding vehicle-to-vehicle collisions while two lanes
merge (e.g. the highway up-ramp and the highway),
or when multi-lane roads get narrower.
3.2 Lane-changing and the ϕ-Agent
Lane-changing maneuver is schematically depicted in
Fig. 4. A vehicle can initiate a lane-changing ma-
neuver if its danger zone (i.e. an obtuse isosceles
triangle) does not contain other vehicles—it is safe
to change lanes. The obtuse angle of the zone is
θ = 2 arctan(εkp
i
k/l
w
) where l
w
is the lane-width and
ε > 0 is an appropriate small constant.
If it is safe to change lanes at time t = t
0
, an
autonomous vehicle switches its desired lane vari-
able l(t
0
) = 1 to l(t
+
0
) = 2 and as a result its γ-agent
switches from midlane curve 1 to midlane curve 2.
Note that l, the desired lane, is a discrete state of the
γ-agent that takes a finite set of values in multi-lane
roads.
If the α-agent tries to directly track its γ-agent,
the lane-changing maneuver will be rather abrupt and
“jerky.” Most human drivers engage in a gradual lane-
changing maneuver to avoid accidents and possible
getting out of the passing lane. To create a grad-
ual lane-changing maneuver, we introduce a “filtering
agent” called the ϕ-agent with the state ( ¯q
i
, ¯p
i
) that
acts as a low-pass filter on the motion of the γ-agent.
In other words, for lane-driving or lane-changing, we
propose that an α-agent i should track its ϕ-agent and
ICINCO2012-9thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
348

the ϕ-agent should track the γ-agent associate with α-
agent i. The new multi-lane lane-driving and lane-
changing algorithm for a vehicular network has the
following form
α :
˙q
i
= p
i
˙p
i
= f
α
i
+ f
ap
i
+ f
ϕ
i
f
ϕ
i
= −c
ϕ
1
(q
i
− ¯q
i
) −c
ϕ
2
(p
i
− ¯p
i
)
ϕ :
(
˙
¯q
i
= ¯p
i
˙
¯p
i
= −c
γ
1
( ¯q
i
− ˆq
i
) −c
γ
2
( ¯p
i
− ˆp
i
)
(9)
3.3 Braking and Stopping
Braking is a mode (or action) that occurs during lane-
driving when a vehicle i gets too close to the vehicle
j in front of it. Let δ
b
∈ {0,1} denote the braking
state and d
1
,d
2
satisfying d
1
< d < d
2
be the mini-
mum and maximum distances between vehicles i and
j that trigger and end braking, respectively (Recall,
d is the desired distance between two neighbouring
α-agents, i.e, two consecutive vehicles here). Then,
δ
b
switches from 1 to 0 and 0 to 1 according to the
following conditions
δ
b
=
1 if kq
j
−q
i
k ≤ d
1
0 if kq
j
−q
i
k ≥ d
2
once it brakes
The braking force is defined as f
b
i
= −c
b
(p
i
− p
j
)
with c
b
> 0. In cases of low-speed braking with the
possibility of the vehicle coming very close to a stop,
the desired velocity is set to 0. The cooperative lane-
driving algorithm with braking ability is given by
u
i
= f
α
i
+ f
ap
i
+ (1 −δ
b
) f
ϕ
i
+ δ
b
f
b
i
(10)
If there is no vehicle in front of vehicle i, then the
following braking force is applied for stopping with a
braking state δ
b
= 1
f
b
i
= −¯c
b
(ρ)p
i
(11)
where ρ ≥ 0 is the target stopping range (the distance
to the target stopping point), as shown in Fig. 5 (b),
and ¯c
b
(ρ) is defined by
¯c
b
(ρ) =
1
2
(c
1
+c
2
)+ (c
1
−c
2
)σ(ρ−ρ
0
); c
2
> c
1
> 0
(12)
with σ(s) = s/
√
1 + s
2
. The constants c
1
and c
2
cor-
respond to the minimum and maximum strength of
braking, respectively, and ρ
0
> 0 is a critical range of
switching from soft braking to hard braking. In addi-
tion, the desired velocity of the vehicle is set to 0.
Let us define δ
s
∈ {0,1} as a stopping flag. Every
time the stopping flag is triggered (δ
s
= 1), the vehicle
(a)
(b)
Figure 5: (a) Turning left or right amounts to a lane-
changing maneuver and (b) stopping is a form of braking
that avoids collision with pedestrians at a crosswalk, or jay-
walkers.
enters the braking mode and δ
b
= 1. The following
equation determines the braking force:
f
b
i
=
c
b
(p
j
−p
i
), δ
s
= 0
−¯c
b
(ρ)p
i
, δ
s
= 1
(13)
3.4 Turning and Collision Avoidance
with Pedestrians
Making left or right turns amounts to performing
lane-changing maneuvers with lanes that are orthogo-
nal to each other as illustrated in Fig. 5 (a). Stopping
is one possible way to avoid V2P collisions without
changing lanes. and by entering the braking mode
with flags δ
b
= δ
s
= 1 as shown in Fig. 5 (b). Sim-
ilarly, the intention state for stopping is the stopping
flag δ
s
∈ {0,1} that appears in (13).
3.5 Intention State for Lane-changing
Before an autonomous vehicle physically engages in
lane-changing or stopping, it needs to “anticipate”
performing such actions in advance by triggering its
intention states associated with those actions since its
“danger zone” might not be empty for a safe lane-
changing maneuver.
Let δ
l
∈ {−1, 0, 1} denote the lane-changing in-
tention state where δ
l
= 0 means no lane-changing,
and δ
l
= 1 and δ
l
= −1 mean changing lanes to the
left and right lanes, respectively, whenever such lanes
(or shoulders) exist.
CooperativeAutonomousDrivingforVehicularNetworks
349

3.6 Tailgating behavior and
Asymmetric Weights
Consider the braking mode. If the speed of vehicle i is
significantly greater than vehicle j, or kp
i
k kp
j
k,
after some finite time their distance becomes smaller
than d
1
and braking is triggered which temporarily in-
creases the distance between the two vehicles. The
mode resulting from frequent switches in the braking
flag δ
b
of agent i is commonly known as tailgating
behavior that is illegal and often could result in acci-
dental collisions.
To avoid the tailgating behavior, we propose the
use of asymmetric interaction weights w
i j
as multi-
plicative factors of a
i j
(q) (recall eq. (2)) in vehicular
networks. Consider a pair (i, j) of α-agents in which
one has a significantly higher desired speed than the
other. Let us assume the slower vehicle i is driving on
a two-lane road and consider two cases: 1) the slow
vehicle is driving in the slower lane l
i
= 1 and 2) the
slow vehicle is driving in the faster lane l
i
= 2. Define
w
i j
=
1 −tanh(k
w
kp
j
k/kp
i
k) Case 1
1 Case 2
(14)
with 0 < k
w
< 1. In Case 1, w
i j
≈ 0 and vehicle i ig-
nores a relatively fast vehicle j behind it. In this case,
vehicle j has to engage in lane-changing to avoid tail-
gating vehicle i. In Case 2, vehicle i sets its weight to
w
i j
= 1 forcing it to go as fast as vehicle j and eventu-
ally change lanes to a slower lane whenever possible.
Note that there is nothing about the tailgating behav-
ior that limits it to two-lane roads, though we chose
this scenario for clarity of presentation.
3.7 Algorithm and Modes of Driving
Self-driving vehicles applying our cooperative au-
tonomous driving algorithms have three basic modes
of driving m
1
= lane-driving, m
2
= lane-changing,
and m
3
= braking as shown in Fig. 6. For exam-
ple, passing another vehicle amounts to a sequence
of lane-changing and lane-driving modes (and if nec-
essary) followed by another lane-changing. There-
fore, passing can be achieved using consecutive mode
switchings and is not an independent mode of driv-
ing. The changes in the discrete state vector Q =
(δ
b
,δ
s
,δ
l
,l)
T
can directly trigger mode switchings.
Here is our main autonomous driving algorithm:
Algorithm 1: Every vehicle applies the following co-
operative autonomous driving algorithm:
Figure 6: The modes of driving for self-driving vehicles and
the logical conditions for mode switchings.
vehicle i :
α
i
:
˙q
i
= p
i
˙p
i
= f
α
i
+ f
ap
i
+ (1 −δ
b
) f
ϕ
i
+ δ
b
f
b
i
f
ϕ
i
= −c
ϕ
1
(q
i
− ¯q
i
) −c
ϕ
2
(p
i
− ¯p
i
)
ϕ
i
:
(
˙
¯q
i
= ¯p
i
˙
¯p
i
= −c
γ
1
( ¯q
i
− ˆq
i
) −c
γ
2
( ¯p
i
− ˆp
i
)
γ
i
:
(
ˆq
i
= Pq
i
+ (I −P)ζ
l
ˆp
i
= v
d
i
ξ
i
(15)
where ζ
l
is a point on the midlane curve of lane l
and P = I −π
i
π
T
i
is the projection matrix (note: for
curved lanes, the last two equations need to be modi-
fied based on the definition of the γ
i
-agent). Note that
the choice of desired lane state l directly influences
the continuous-time dynamics of vehicle i via ζ
l
.
The autonomous vehicle in (15) is a hybrid sys-
tem with a nonlinear switching dynamics and the con-
tinuum state Σ
i
= col(q
i
, p
i
, ¯q
i
, ¯p
i
), the discrete state
Q
i
= (δ
b
,δs,δ
l
,l
i
), and the input ϒ
i
= (τ, ζ
l
,v
d
i
,ρ
i
)
where ρ
i
is the target stopping range whenever it ex-
ists. The γ
i
-agent with the state ( ˆq
i
, ˆp
i
) acts as an in-
put signal to the ϕ
i
-agent and thus the γ-agents in au-
tonomous driving are not dynamic systems unlike in
flocking; yet, we take the liberty to refer to the pair
( ˆq
i
, ˆp
i
) as the state of the γ
i
-agent.
3.8 Fundamental Challenges and
Differences with Stability Analysis
of Flocking
The dynamics of an α-agent for flocking behavior can
be stated as follows:
˙q
i
= p
i
, ˙p
i
= f
α
i
+ f
γ
i
(16)
where the state of the γ-agent is independent of all α-
agents that have fixed dynamics. In comparison, the
dynamics of vehicle i in (15) is far more complex and
ICINCO2012-9thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
350

the states of the γ-agents depend on both the inputs
and continuum and discrete states of the autonomous
vehicles. Moreover, unlike in flocking, the interac-
tion weights between vehicles is no longer symmet-
ric. The complexities of dynamics, asymmetric inter-
agent interactions, and interactions with the environ-
ment makes the structural stability analysis of self-
driving vehicular networks tremendously more chal-
lenging. Formal stability analysis of the autonomous
vehicular networks will be presented in upcoming pa-
pers and fundamentally relies on flocking theory.
4 SIMULATIONS
Fig. 7 shows the consecutive snapshots of a vehicular
network applying the autonomous lane-driving algo-
rithm in (8). Four 1D α-lattices of autonomous vehi-
cles (or platoons) asymptotically emerge. These pla-
toons closely resemble 1D flocks of birds on power
lines as seen in Fig. 7 (b)). The role of the area po-
tential forces f
ap
i
is critical in untangling challenging
initial conditions of the vehicles with several triangu-
lar faces in Figs. 7 (c) through (f).
Fig. 8 shows the snapshots of the passing maneu-
ver for a fast vehicle behind a group of slower vehicles
with random desired speeds in a collision-free manner
for all the vehicles involved. The sequence of mode
switching of the fast vehicles are as follows: lane-
driving, braking, lane-changing, lane-driving (for a
relatively long period until all three slower vehicles
in front of it change lanes), lane-changing, and lane-
driving. The slower vehicles in the fast lane engage
in lane-driving, lane-changing, and lane-driving. All
other vehicles perform lane-driving throughout the
passing maneuver of the fast vehicle. Notice that the
slower vehicles in the fast lane can easily merge into
the slower lane without collisions.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We introduced a multi-objective flocking framework
for cooperative autonomous driving for vehicular net-
works and design of safety-aware intelligent trans-
portation systems. We demonstrated that flocking
is a valid particle-based model of vehicular traffic
on roads. Using significant modifications of Olfati-
Saber’s flocking algorithms, we proposed novel al-
gorithms for three basic modes of autonomous driv-
ing, namely, lane-driving, lane-changing, and brak-
ing. The combination of these three modes en-
ables autonomously performing the passing maneu-
ver, making turns, stopping, avoid tailgating, and V2P
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
−200
−150
−100
−50
0
50
100
150
200
t=15.00
(a) (b)
t=0.07
t=2.70
(c) (d)
t=3.52
t=5.02
(e) (f)
t=7.12
t=9.67
(g) (h)
t=12.09
t=15.00
(i) (j)
Figure 7: Autonomous driving for a vehicular network with
n = 20 vehicles with random initial conditions (uniform)
and desired velocities (Gaussian). Three 1D α-lattices (or
platoons) asymptotically emerge and the vehicles within
each platoon move with a consensus speed. (a) the track;
(b) a 1D flock of birds forming α-lattices; (c) though (j)
consecutive zoomed snapshots of the self-driving vehicular
networks on the track in (a). Snapshot (a) is the global view
of (j). The red circles show the γ-agents.
and V2V collision avoidance. Our main contribu-
tion is to introduce a unified autonomous driving al-
gorithm called “Algorithm 1” in (15) which encom-
passes all the individual driving algorithms for ev-
ery mode as special cases. The γ and ϕ agents are
novel types of agents that did not exist in the origi-
nal flocking theory in (Olfati-Saber, 2006). Our sim-
ulation results demonstrate that the proposed cooper-
ative autonomous driving algorithm is effective and
capable of successfully performing complex maneu-
vers such as lane-driving from random initial condi-
tions and passing without collisions.
CooperativeAutonomousDrivingforVehicularNetworks
351
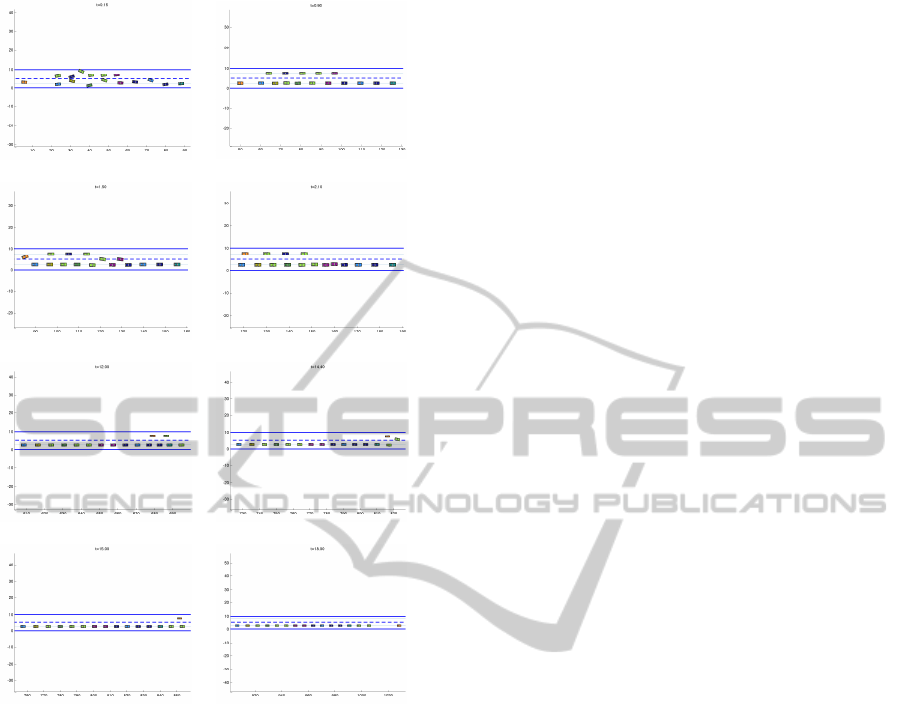
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
(e) (f)
(g) (h)
Figure 8: Consecutive snapshots of the passing maneu-
ver for a fast vehicle behind a number of slower vehicles
moving with a random set of uniformly distributed desired
speeds on a two-lane highway starting from a random set of
positions/velocities in (a). The slower vehicles in the fast
lane perform lane-changing as soon as they detect a faster
vehicle on the fast lane according to mode switching rules
in Fig. 6.
REFERENCES
Baber, J., Kolodko, J., Noel, T., Parent, M., and Vlacic, L.
(2005). Cooperative autonomous driving: intelligent
vehicles sharing city roads. IEEE Robotics & Automa-
tion Magazine, 12(1):44–49.
FARS (2011). FARS: traffic fatality at NHTSA. http://
www-fars.nhtsa.dot.gov/Main/index.aspx.
Hedrick, J. K., Tomizuka, M., and Varaiya, P. (1994). Con-
trol issues in automated highway systems. IEEE Con-
trol Systems Magazine, 14(6):21–32.
Helbing, D. (1995). Improved fluid-dynamic model for ve-
hicular traffic. Physical Review E, 51(4):3164–3169.
Kato, S., Tsugawa, S., Tokuda, K., Matsui, T., and Fuji,
H. (2002). Vehicle control algorithms for cooperative
driving with automated vehicles and intervehicle com-
munications. IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transporta-
tion Systems, 3(3):155–161.
Kolski, S., Ferguson, D., Bellino, M., and Siegwart, R.
(2006). Autonomous driving in structured and un-
structured environments. IEEE Intelligent Vehicles
Symposium, pages 558–563.
Lighthill, M. J. and Whitham, G. B. (1955). On Kinematic
waves II. A theory of traffic flow on long crowded
roads. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Lon-
don. Series A., Mathematical and Physical Sciences,
229(1178):317–345.
Olfati-Saber, R. (2006). Flocking for Multi-Agent Dynamic
Systems: Algorithms and Theory. IEEE Trans. on Au-
tomatic Control, 51(3):401–420.
Olfati-Saber, R. and Iftekhar, L. (2012). Flocking for net-
works of nonholonomic robots with nonlinear dynam-
ics. Proc. of the 51st IEEE Conf. on Decision and
Control.
Olfati-Saber, R. and Murray, R. M. (2002a). Distributed co-
operative control of multiple vehicle formations using
structural potential functions. The 15th IFAC World
Congress, Barcelona, Spain.
Olfati-Saber, R. and Murray, R. M. (2002b). Distributed
structural stabilization and tracking for formation of
dynamic multi-agents. Proceedings of the IEEE Int.
Conference on Decision and Control.
Olfati-Saber, R. and Murray, R. M. (2002c). Graph rigid-
ity and distributed formation stabilization of multi-
vehicle systems. 41st IEEE Conference on Decision
and Control, 3:2965–2971.
Schneiderman, H. and Nashman, M. (1994). A discrim-
inating feature tracker for vision-based autonomous
driving. IEEE Trans. on Robotics and Automation,
10(6):769–775.
Soelo, M. A., Rodriguez, F. J., Magdalena, L., Bergasa,
L. M., and Boquete, L. (2004). A color vision-based
lane tracking system for autonomous driving on un-
marked roads. Autonomous Robots, 16(1):95–116.
Swaroop, D. and Hedrick, J. K. (1996). String stability of
interconnected systems. IEEE Trans. on Automatic
Control, 4(3):349–357.
WHO (2004). WHO Report: The global burden of disease:
2004 update. http://www.who.int/.
ICINCO2012-9thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
352
