
Simulation of Real-time Data Grid Systems via DGridSim Simulator
Safai Tandoğan
1
, Mustafa Müjdat Atanak
2
and Atakan Doğan
3
1
C. Tech, TUBITAK MAM TEKSEB, Kocaeli, Turkey
2,3
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Anadolu University, 26470 Eskisehir, Turkey
Keywords: Data Grid, Real-time, Job Scheduling, Data Dissemination, Data Replication.
Abstract: In this study, DGridSim simulator will be introduced and some example simulation results will be
presented. DGridSim can simulate four different Data Grid system organizations. Furthermore, for every
system organization, the simulation of job scheduling, data dissemination, and data replication algorithms
are supported, while all related system resources including computing, data storage, and network are
reserved in advance in order to meet deadlines associated with jobs. DGridSim simulator is designed to be
modular and easily extensible.
1 INTRODUCTION
Data Grid systems are highly distributed systems
that are increasingly used in the analysis of large
amounts of data (Chervenak et al., 2000). There
exist a large number of parameters that affect the
performance of these sophisticated systems. Some of
these parameters change dynamically. Hence,
developing analytical models to study the impact of
any system parameter is a nontrivial task and, often,
simulators are used. Hence, a number of simulators
exist in the literature (Bell et al., 2003, Buyya et al.
2002, Lamehamedi et al. 2003, Casanova et al.
2003).
Any real-time Data Grid system should have a
set of services to support job scheduling, data
replication, data dissemination, and advance
reservation. Based on this rationale, this study
proposes a unique framework, DGridSim, for
simulating four different real-time Data Grid
systems based on well-defined services.
2 DGRIDSIM MODELS
DGridSim supports four different Data Grid system
models, some of which are based on the studies in
the literature, and the others are proposed herein.
Furthermore, DGridSim provides a unified platform
for simulating job scheduling, data dissemination,
and data replication algorithms for all four models.
The Data Grid system models supported by
DGridSim are listed in Table 1, whose details are
provided in (DGridSim Project).
Table 1: Data Grid system models of DGridSim.
Job Scheduling
Data Dissemination
Model I
Hierarchical
Hierarchical
Model II
Centralized
Centralized
Model III
Centralized
Centralized
Model IV
Distributed
Hierarchical
Model I: In order to simulate Data Grid systems
of Model I, Model I should be chosen under Grid
Model segment in General tab of the GUI. Figure 1
shows a sample screenshot of the GUI when Model I
is chosen.
In Model I, job scheduling is carried out in
hierarchical fashion. In DGridSim, seven different
Grid scheduling algorithms are realized: Random,
EDF (Earliest Deadline First), MCTF (Minimum
Completion Time First), MCTFwDP (Minimum
Completion Time First with Data Present), MMwDP
(MinMin with Data Present), RT MCTFwDS (Real-
Time Minimum Completion Time First with Data
Staging) and RT MMwDP (Real-Time MinMin with
Data Present). DGridSim is equipped with a sample
site scheduling algorithm, namely RT Max Max
(Real-Time MaxMax).
Data dissemination is carried out in hierarchical
fashion as well. DGridSim currently supports only
Minimum Delay Feasible Path First algorithm as a
part of its Data Management Service.
Model I implementation of DGridSim offers four
182
Tando
˘
gan S., Atanak M. and Do
˘
gan A..
Simulation of Real-time Data Grid Systems via DGridSim Simulator.
DOI: 10.5220/0004057801820185
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH-2012),
pages 182-185
ISBN: 978-989-8565-20-4
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
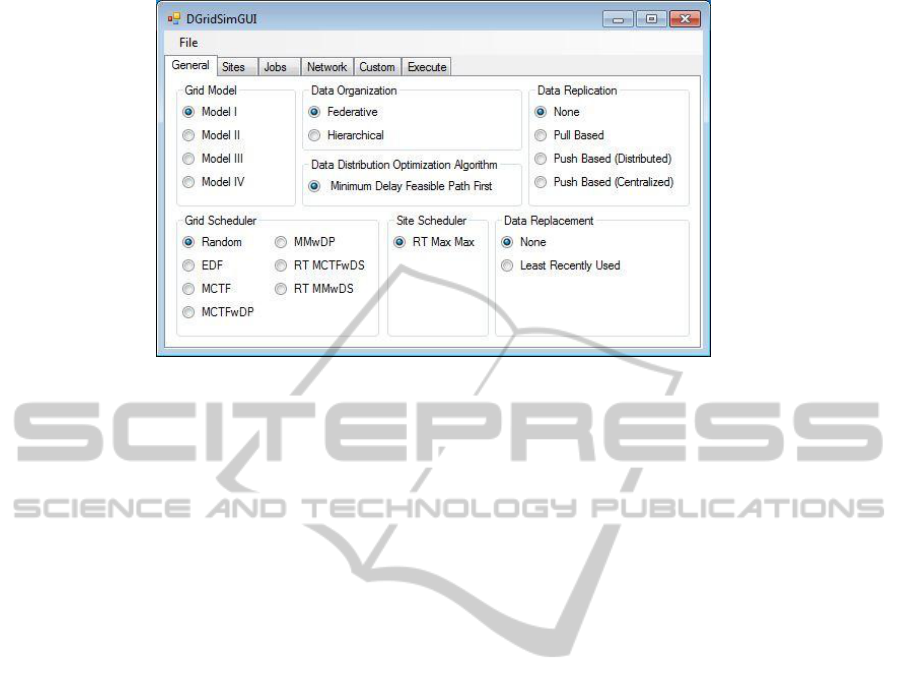
Figure 1: Sample snapshot of the GUI of DGridSim.
options for data replication: none, pull-based
distributed, push-based distributed, and push-based
centralized.
Models II and III: five different Grids
scheduling algorithms are implemented as part of
Model II and III: Random, EDF (Earliest Deadline
First), FACEF (Fastest Available Computing
Element First), FACEFwDP (Fastest Available
Computing Element First with Data Present), and
bFACEFwDP (Bulk - Fastest Available Computing
Element First with Data Present).
Random and EDF algorithms implemented for
Model I differ from the ones defined for Model II
and III. Furthermore, although the same names are
used for Model II and III, Grid job scheduling
algorithms are implemented differently for Model II
and III. Site scheduling algorithm simply forwards
the jobs to the corresponding computing elements
chosen by the Grid scheduling service.
Data scheduling in Model II and III Data Grid
systems conforms to centralized model in which
Minimum Delay Feasible Path First algorithm is
only supported.
Only two data replication options can be used for
Models II and III Data Grid systems: None and Push
based (centralized).
Model IV: Job scheduling in Model IV systems
is carried out in distributed fashion. In hierarchical
and centralized job scheduling models, jobs are
received by a global service, Grid Job Submission
Service. However, in distributed model, jobs are sent
to Site Job Submission Service that is a local service
available in every site. As a result, a Grid scheduling
algorithm, named Delegate, is simply used to
generate the job load to Site Job Submission Service.
Two different Site Scheduling Service
algorithms are currently running on DGridSim:
Distributed Real-Time Min-Max and Distributed
Real-Time Max-Min.
Hierarchical data dissemination in Model IV is
the same as in Model I.
Four different data replication models are
provided in Model IV. These models work similar to
the models in Model I.
Both federative and hierarchical data
organization models are supported in all four
models.
Two options are provided as data replacement
algorithm in all models: (1) None: Data items are not
copied to the data storage elements in sites. (2) Least
Recently Used (LRU): Data items are stored in local
storage elements. If a local storage element does not
have enough storage space to hold an incoming item,
data items in the storage element are erased within
Least Recently Used principle.
3 SIMULATION RESULTS
Using DGridSim, a set of simulation studies were
conducted to verify that it is operating as expected.
The tests presented herein evaluate the impact of
increasing number of real-time jobs to Data Grid
system of four different models.
The base tests are conducted with a Grid system
of sites having U~[24, 36] computing elements and a
single storage element, where U~[A, B] implies a
uniform distribution between A and B. The
computing elements have a MIPS rating of U~[800,
1200]. Sites are connected with a network of U~[8,
12] routers and U~[16, 24] links. The links have a
bandwidth of U~[120, 180] Mbytes/sec and a delay
Siation of ati Data id St ia DidSi Siato
value of U~[0.0025, 0.0075] sec.
There exists 10000 data items in the system, each
of which is U~[800, 1200] Mbytes. The system with
federative data organization models consists of 20
sites, each of which has a storage capacity of
U~[80000, 120000] Mbytes. Hierarchical systems
consist of a single Tier-0 site, 4 Tier-1 sites and 20
Tier-2 sites. Tier-1 sites have storage capacity of
U~[200000, 300000] Mbytes and Tier-2 sites have
storage capacity of U~[40000, 60000] Mbytes. Tier-
0 has enough storage space to store all data items.
Job sizes are U~[4800000, 7200000] millions of
instructions and job deadlines are U~[400, 600] sec.
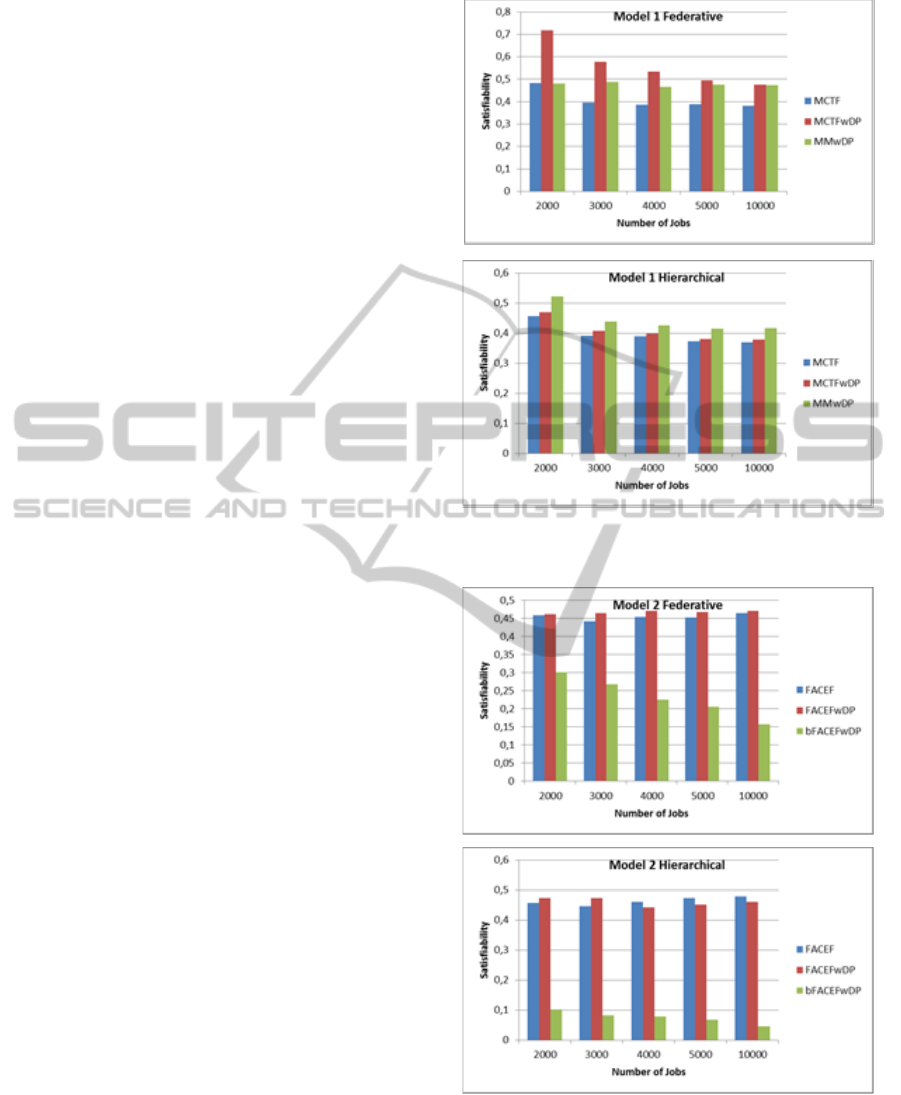
Three Grid scheduling algorithms are chosen for
Model I sample simulation studies: MCTF,
MCTFwDP and MMwDP. Figure 2 shows the
results for Model I. According to the figure, the
performance of these algorithms decreases slowly as
the number of jobs increase. The best performance is
obtained by MCTFwDP, which is followed by
MMwDP and MCTF in federative model. In
hierarchical model, however, the best results are
obtained by MMwDP, which is followed by
MCTFwDP and MCTF. MCTFwDP and MMwDP
algorithms take into account the location of data and
they both perform better than MCTF.
Three Grid scheduling algorithms are chosen for
simulations with Model II: FACEF, FACEFwDP,
and bFACEFwDP. As can be seen from Figure 3,
both FACEF and FACEFwDP retain the
performance values as the number of jobs increase.
However, the performance of bFACEFwDP
algorithm decreases to a large extent when the
number of jobs increases. Best performance results
for federative data organization are obtained with
FACEFwDP, followed by FACEF and
bFACEFwDP. In hierarchical data organization,
FACEF shows the best results when number of jobs
is small. FACEFwDP surpasses FACEF when the
number of jobs increases. bFACEFwDP performs
the worst in all cases.
Three Grid scheduling algorithms are chosen for
sample simulation studies of Model III: FACEF,
FACEFwDP, and bFACEFwDP. The simulations
are repeated for both federative and hierarchical data
organization models. Push based centralized data
replication and LRU data replacement schemes are
employed in sample simulation studies. Figure 4
shows the results for Model III. As can be seen from
the figure, the performance results decrease with the
increase in the number of jobs. In most cases,
FACEFwDP shows the best results.
Figure 5 shows the results obtained from
simulating Model IV with DGridSim. As can be
Figure 2: The effect of the increase in the number of jobs
to the performance of Model I algorithms.
Figure 3: The effect of the increase in the number of jobs
to the performance of Model II algorithms.
ST nd ntnationa onfn on Siation and odin todooi Tnooi and
Aiation
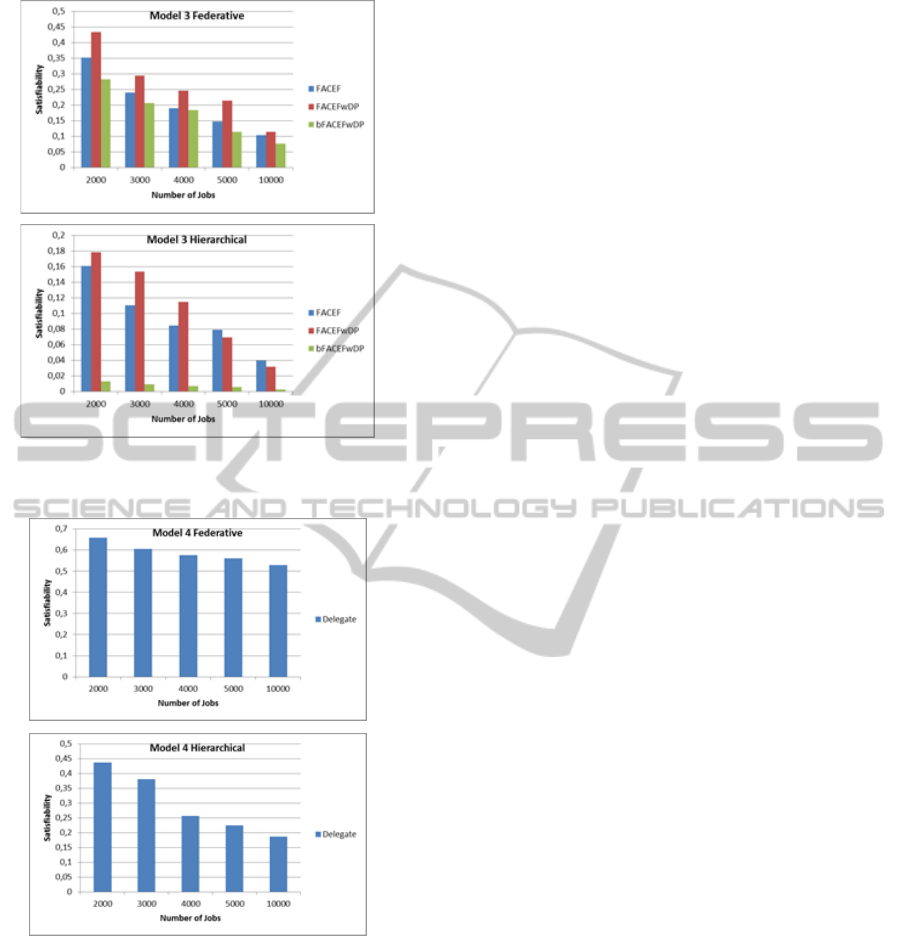
Figure 4: The effect of the increase in the number of jobs
to the performance of Model III algorithms.
Figure 5: The effect of the increase in the number of jobs
to the performance of Model IV algorithms.
seen from the figure, the real-time performance of
the system decreases with increasing number of jobs
in both federative and hierarchic data organization
models.
4 CONCLUSIONS
DGridSim simulator embodies many unique features
compared to similar simulator studies in the
literature. The most distinguished features of
DGridSim can be listed as: (1) DGridSim supports
for four different system models as opposed to
single system model support of the simulators in the
literature. (2) DGridSim supports the advance
reservation of all computing, storage and network
resources. (3) GUI of DGridSim easily allows the
setting of the Data Grid system that will be
simulated. (4) DGridSim uses all the cores of the
computer on which the simulation runs. DGridSim is
designed in a modular and flexible fashion so that
the researchers can add their own job scheduling,
data dissemination and data replication algorithms to
any of the four models. (6) DGridSim includes the
source codes of many job scheduling, data
dissemination and data replication algorithms. This
helps the researchers to write their own codes.
REFERENCES
Chervenak, A., Foster, I., Kesselman, C., Salisbury, C.,
Tuecke, S., 2000. The Data Grid: Towards an
Architecture for the Distributed Management and
Analysis of Large Scientific Datasets. In Journal of
Network and Computer Applications, 23(3), 187-200.
Bell, W. H., Cameron, D. G., Capozza, L., Millar, A. P.,
Stockinger, K., Zini, F., 2003. OptorSim - A Grid
Simulator for Studying Dynamic Data Replication
Strategies. In International Journal of High
Performance Computing Applications, 17 (4).
Buyya, R., Murshed, M., 2002. GridSim: A Toolkit for the
Modeling and Simulation of Distributed Resource
Management and Scheduling for Grid Computing. In
Journal of Concurrency and Computation: Practice
and Experience, 1–32.
Lamehamedi, H., Shentu, Z., Szymanski, B., Deelman, E.,
2003. Simulation of Dynamic Data Replication
Strategies in Data Grids. In Proc. of 12th
Heterogeneous Computing Workshop.
Casanova, H., Legrand, A., Marchal, L., 2003. Scheduling
Distributed Applications: The Simgrid Simulation
Framework. In Proc. of the 3rd IEEE International
Symposium on Cluster Computing and the Grid, pp:
138–144.
DGridSim Project, http://home.anadolu.edu.tr/ ~atdogan/.
Siation of ati Data id St ia DidSi Siato
