
A Model for Simulation of Application and Resource Behavior
in Heterogeneous Distributed Computing Environments
Per-Olov
¨
Ostberg
Dept. of Computing Science, Ume
˚
a University, SE-901 87, Ume
˚
a, Sweden
Keywords:
Discrete-event Simulation, Virtual Infrastructure, Distributed Computing.
Abstract:
Accurate modeling of the behavior of resources and scientific applications in distributed computing environ-
ments is complicated by factors such as resource heterogeneity, variability, and volatility. In this work we
present a simulation model for fine-grained simulation and analysis of resource environments composed by
multiple types of distributed computing resources. The simulation model is based on simulation of individual
computational resources and emulation of virtual infrastructures and resource environments. Application and
resource behavior are modeled in behavior profiles that capture the wide variability of distributed computing
applications and resources, and allow modeling of non-standard metrics such as heterogeneity, variability, and
volatility of resources and resource environments. Around the behavior profiles, virtual infrastructures are
emulated using discrete-event simulations where infrastructure components are independently modeled. The
design of the framework is aimed to facilitate both verification of middleware and application software as well
as experimentation with prototype infrastructure components.
1 INTRODUCTION
Distributed computing environments are becoming
increasingly heterogeneous and complex, and appli-
cation and resource behavior are becoming harder to
model and predict. A number of concurrent develop-
ments contribute to this phenomenon, for example:
• integration of multiple resource types, e.g., shared
and dedicated resources, in resource pools
• emergence of heterogeneous hardware platforms
that combine different types of computational re-
sources, e.g., on-chip CPU and GPU resources
• development of energy efficiency techniques that
allow CPUs to disable or vary the speed of cores
• provisioning of computational power as services
running virtual resources in compute clouds
Precise prediction and modeling of application
and resource behavior is of great interest in design
and construction of virtual infrastructure components
and tools for distributed computing. However, there is
currently a lack of simulation toolkits that are capable
of encompassing the heterogeneity and volatility of
resource (and application) behavior in heterogeneous
distributed computing environments.
In this work we propose an approach to discrete-
event simulation of heterogeneous distributed com-
puting environments based on profiling of computa-
tional applications and resources combined with em-
ulation of resource environments. In addition, we
also present preliminary findings from a prototype
implementation of a simulation framework based on
the model, and demonstrate the feasibility of the ap-
proach in a brief performance evaluation. The simula-
tion model is designed to be simple and computation-
ally efficient, yet flexible enough to accurately model
resource and application behavior (including failures
and varied availability) realistically.
The intended use case of the model is to create a
simulation framework that allows modeling of appli-
cation and resource behavior in mixed resource type
environments. As mixed resource environments have
unique compositions that may vary over time, the
framework emphasizes a simple and robust behavior
model coupled with an environment emulation toolkit
over generic resource environment models.
The proposed simulation model is intended to
model application and resource behavior at a very fine
level, while providing a generic interface to an emu-
lated distributed computing environment. The goal of
this approach is to provide a tool that allows existing
mechanisms to be integrated in an emulated environ-
ment and evaluated without modification.
144
Östberg P..
A Model for Simulation of Application and Resource Behavior in Heterogeneous Distributed Computing Environments.
DOI: 10.5220/0004061301440151
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH-2012),
pages 144-151
ISBN: 978-989-8565-20-4
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

A number of distributed computing simulation
toolkits exist, e.g., SimGrid (Casanova, 2001), Grid-
Sim (Buyya and Murshed, 2002), and MICRO-
GRID (Song et al., 2000) for grid computing. For
cloud computing there exists a set of resource envi-
ronment simulation tools including CloudSim (Cal-
heiros et al., 2009), iCanCloud (Nu
˜
nez et al., 2011),
GreenCloud (Kliazovich et al., 2010), and Cloud-
Stone (Sobel et al., 2008). For evaluation of produc-
tion tools some systems, e.g., OpenNebula (Miloji
ˇ
ci
´
c
et al., 2011), support execution in simulation mode,
which allows experimentation for integration and pro-
totype evaluation. However, as these systems are ori-
ented around specific infrastructure types, they make
strong assumptions about the behavior and construc-
tion (homogeneity, capacity consistency, etc.) of re-
sources and resource environments.
While the more generic models exposed by these
tools are sufficient for modeling of infrastructures
built on a single resource type, the assumptions they
are based on make it hard to capture fine-grained anal-
ysis of resource behavior in multiple resource type
environments. On the network side, tools such as Su-
perna (Superna Network Planning Engine, 2012) and
OPNet (Chang, 1999), allow modeling of throughput
and capacity of networks. Integration of these in mod-
eling of resource behavior is however difficult as these
tools generally only consider network as a resource.
A large amount of general simulation and model-
ing toolkits, ranging from service-oriented modeling
frameworks (Tsai et al., 2006) to tools such as Load-
Runner (Booth et al., 2007) also exist. These tools
are very efficient for construction of simulation mod-
els and modeling of specific phenomena such as re-
source load, but again these are hard to use in integra-
tion of multiple models for evaluation of infrastruc-
tures. The model proposed in this work is focused on
a specific use case, modeling and analysis of resource
behavior in distributed computing environments. As
such, it aims to facilitate development of computa-
tional tools and components for virtual infrastructures
for distributed computing.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows.
Section 2 introduces the simulation model of the
framework, and details the modeling of individual
applications and resources as well as the computa-
tional model used in resource simulations. Section 3
presents a brief performance evaluation to demon-
strate the feasibility of the approach and illustrate the
computational performance of the model. Finally,
Section 4 discusses the contributions and the results,
and Section 5 concludes the paper.
2 SIMULATION MODEL
Traditional application performance metrics are pri-
marily concerned with the characteristics of computa-
tional resources and how well applications make use
of available resource capacity. However, when view-
ing application performance from a virtual infras-
tructure perspective (and considering metrics such as
application computational throughput), factors such
as resource availability, resource predictability, and
application fault tolerance become more important.
Factors such as these are not easily captured by
performance-oriented metrics, but require a model
that allows heterogeneity and volatility in resources
and variation of resource behavior over time.
The model of this simulation framework is con-
cerned with capturing the behavior (as seen from the
virtual infrastructure perspective) of computational
applications and resources, rather than the perfor-
mance and characteristics of the applications and re-
sources themselves. Hence, the primary focus of
modeling lies on the computational throughput, here
defined in terms of provided and utilized resource ca-
pacity over time. The model presented here is based
on definition of capacity profiles for individual di-
mensions of resource capacity (e.g., computational or
network transfer capacity) and combination of appli-
cation and resource profiles to compute the through-
put of applications on resources.
The computational model of the simulation frame-
work proposed here is for reasons of computational
efficiency simple. The expressive power of model-
ing resource and application behavior in profiles, and
use of these to simulate computational throughput, is
however strong enough to encapsulate the wide and
varied behavior of computational resources in dis-
tributed computing environments.
2.1 Application Behavior Profiles
To model application behavior over time in a fine-
grained yet computationally efficient way, we define
a model of application behavior that characterizes re-
quired task processing capacity in quantifiable dimen-
sions, e.g., network, computational (CPU), or storage
capacity. The capacity usage is measured at finite pe-
riodical time steps and quantified relatively against
maximal capacity. As illustrated in the left part of Fig-
ure 1, which details an example one-dimensional ap-
plication profile, the value space of capacity profiles
is [0, 1]. For scaling and comparison between profiles,
profiles are assigned a weight to scale the profile to
comparable resource capacities.
AModelforSimulationofApplicationandResourceBehaviorinHeterogeneousDistributedComputingEnvironments
145
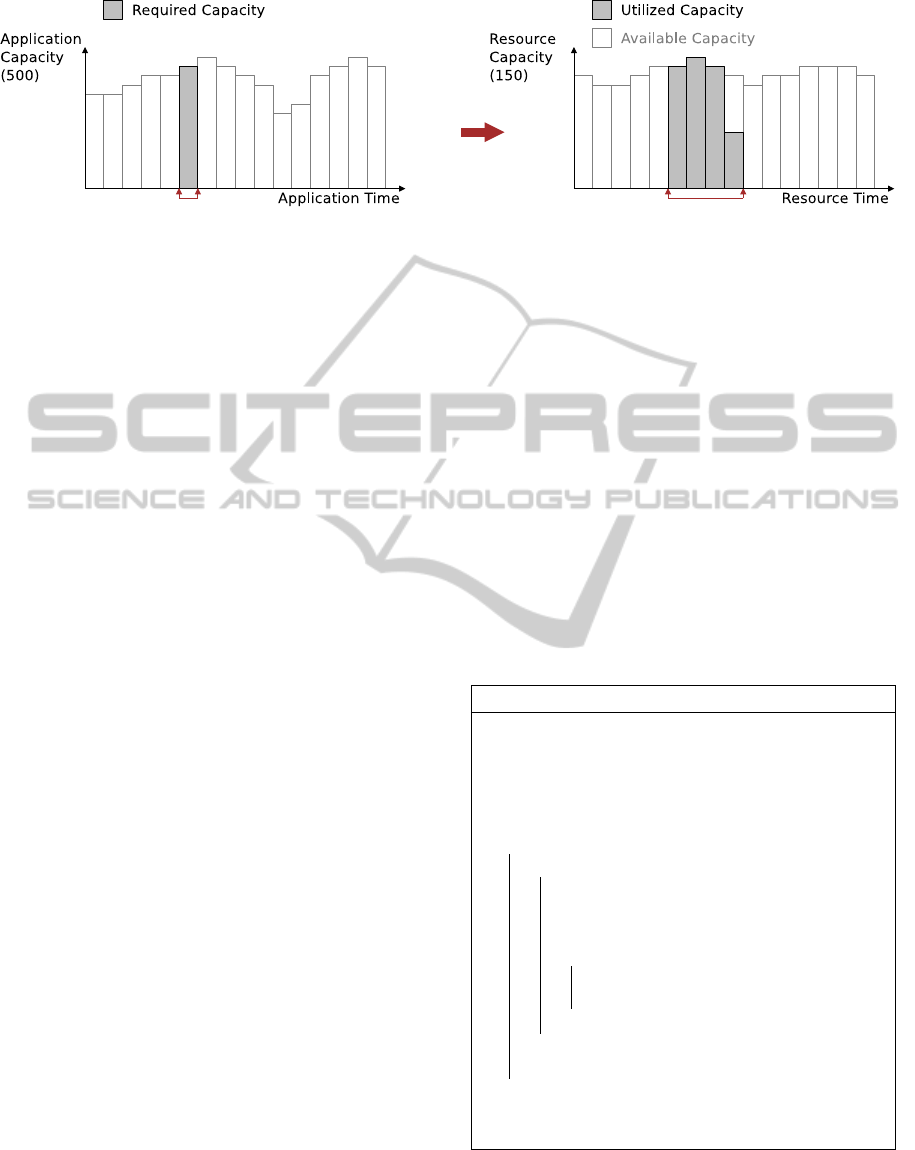
Figure 1: Capacity integration.
2.2 Resource Behavior Profiles
To predict and simulate infrastructure behavior, a sim-
ulation model requires not only a model of application
behavior, but also one of resource behavior. Like their
application counterparts, resource behavior profiles
can be formulated by characterizing the amount of re-
source capacity provided (in individual dimensions)
over time. While the behavior of individual com-
putational resources may be stable and conform to
predictable patterns, the behavior variations between
different types of resources will vary greatly in dis-
tributed computing environments, implying that dif-
ferent resource types should modeled independently.
For interpretation, application profiles can be seen
to express minimum requirements for capacity, while
resource profiles express upper bounds (maximums)
for provisioned capacity. Interpretation of resource
profiles requires a semantic for modeling failures.
2.3 Resource Behavior Simulation
The majority of the distributed computing applica-
tions in use today perform computations in the form
of batch jobs, i.e. batch executions of programs. From
a simulation point of view, this is attractive as batch
jobs imply distinct phases and lifetimes for compu-
tations. The model for batch computation used here
defines four (resource-oriented) phases for a job:
• stage in (transfer of data to resources),
• queue wait time,
• execution,
• stage out (transfer of data from resources).
In addition to these, jobs will naturally go through
other phases in, e.g., batch queue wait and schedul-
ing cycles. As these are not part of the local resource
queue processing phases, they are not considered in
the core resource simulation.
For calculation of the computational throughput
of an application on a resource, the proposed simula-
tion framework matches the capacity required by ap-
plications with the capacity provided by resources to
estimate the processing time of a job task. The to-
tal capacity required by an application is divided into
discretely sampled timesteps, and the capacity of each
time step is matched against the discretely sampled
capacity provided by a resource, as illustrated in Fig-
ure 1. A configurable constant is applied to scale the
required resource capacity to the metrics used in the
simulation, e.g., CPU seconds. As application pro-
files and resource profiles are scaled independently, a
single application profile time step may result in uti-
lization of multiple resource time steps.
In simulation of the resource processing of tasks,
the resource capacity profile is sampled at finite time-
steps and summed until the (by the application) re-
quired resource capacity is met in each dimension. In
the discrete case, this means that a formulation like
Algorithm 1 is used in implementation.
Algorithm 1: Capacity integration.
Input: Application profile appPro f ile
Input: Resource profile resPro f ile
Output: Estimated application run-length
timesteps = 0;
foreach time step t in appProfile do
foreach dimension d in appProfile do
capacity
a
= appProfile(t,d);
capacity
r
= 0;
nrT (d) = 0;
while capacity
r
< capacity
a
do
capacity
r
+= resProfile(nrT (d),d);
nrT (d) += 1;
end
end
timesteps += max(nrT );
end
return timesteps * sizeof(time step);
As modern computers contain hardware con-
structs that allow overlapping of network transfers
and computations with little performance degrada-
SIMULTECH2012-2ndInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
146

Figure 2: Execution pipeline of a local resource queue.
tion, the simulation framework employs a model
where jobs can perform staging of data in parallel
with execution of other tasks in the local resource
queue. For the simulation, this means that resource
capacity is integrated in at least two dimensions (net-
work transfer and computational capacity) for the four
distinct task processing phases, and that the total job
completion time will be made up by four components
as illustrated in Figure 2. Note that while the integra-
tion of application and resource capacity is performed
as a discrete-time simulation, the computational re-
sults from this process is fed to a discrete-event simu-
lation of the resource queue processing pipeline. Us-
ing this simple computational model, an estimation of
the processing time for each task execution phase is
established. The estimated processing times for jobs
are then used to offset time steps in discrete-event
simulations of virtual infrastructures.
As the simulation of individual resources is inde-
pendent of the simulation of other resources, simula-
tion is embarrassingly parallel and can be performed
concurrently. Resource simulations are grouped and
queued in computational task bins, which are orches-
trated by a coordinator in the simulation engine. Note
that construction (and evaluation) of application and
resource profiles are independent of resource simula-
tion, and can be performed in advance or on-demand
by the simulation process. The entire simulation pro-
cess is highly parallel, and consists of multiple com-
putationally cheap and independent tasks that can be
efficiently implemented using concurrent program-
ming constructs such as multi-threading on multi-core
machines, or (with modification of the simulation co-
ordinator) be distributed over multiple machines.
2.4 Modeling of Resource Types
While the model described in Section 2.3 is computa-
tionally very simple, the expressive power of model-
ing resource behavior using capacity profiles is great.
Variability in behavior profiles describes not only
fluctuations in resource capacity, but also indirectly
discontinuities such as variations in availability and
volatilities due to errors.
Using this model, the behavior of distributed com-
puting resources can be classified by, e.g., resource
type, availability schedule, and volatility. One of the
primary indicators of overall resource behavior is re-
source type. For example, well maintained dedicated
computational resources such as High-Performance
Computing (HPC) servers typically exhibit fairly con-
stant performance and high availability under stable
load. Resource Grid (Foster and Kesselman, 2004)
machine pools (typically constructed through collab-
orative interconnection of dedicated HPC resources)
will exhibit similar behavior, while being subject to
more restrictive availability schedules.
Shared computational resources such as volunteer
computing (Sarmenta and Hirano, 1999) or desktop
grid (Chien et al., 2003) resources are however harder
to model, as they exhibit high seasonality in availabil-
ity (e.g., with increased availability during nights and
weekends) and higher volatility in both load and per-
formance. Shared resources are subject to different
types of resource contention than dedicated resources,
which can lead to unpredictable behavior and volatil-
ity. Modeling of virtualization-based resources such
as cloud computing (Armbrust et al., 2010) resources
is easier from an availability perspective as virtual-
ized cloud resources are instantiated on demand, but
can (due to resource contention on the underlying
hardware level) instead exhibit higher variations in re-
source performance (Ostermann et al., 2010).
In addition to resource type and availability, re-
source volatility is also a factor with substantial im-
pact on overall resource performance. In this concept
we here include factors such as natural variations in
resource capacity (e.g., network bandwidth variations
due to medium contention), unscheduled variations
in resource availability (e.g., job preemption forc-
ing check-pointing in volunteer computing environ-
ments), and hardware and software errors. In general,
shared computational resources exhibit higher volatil-
ity than dedicated resources as they present more het-
erogeneous environments with greater variability in
(and less predictable) performance. Shared computa-
tional resource pools are also more likely to be con-
structed using commodity computer components run-
ning greatly varied software stacks, and are as such
more prone to hardware and software errors.
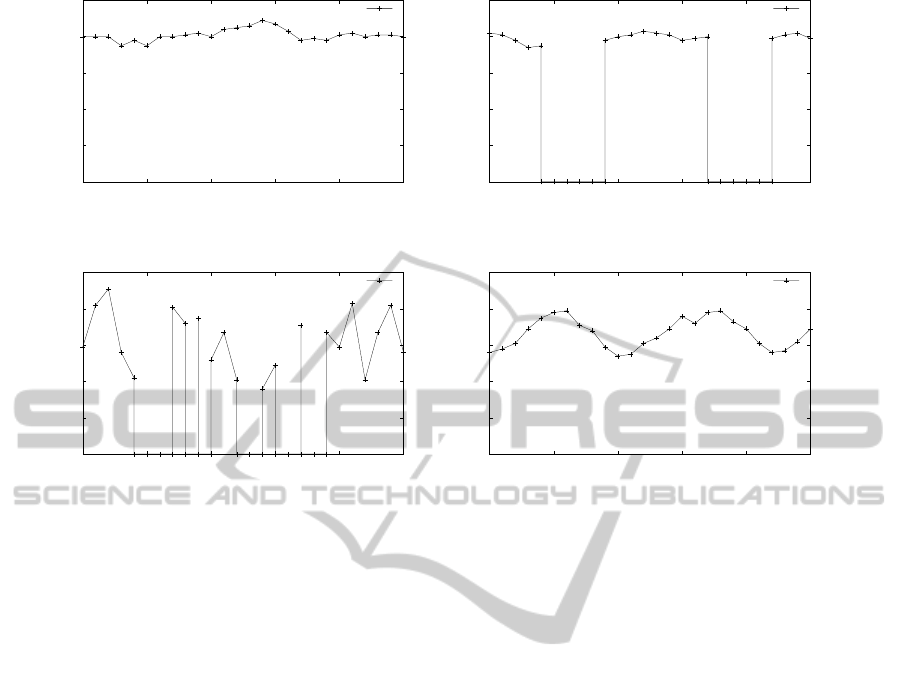
Figure 3 presents four resource behavior profiles
that are here used to illustrate differences in resource
behavior between resource types. Figure 3a illustrates
the behavior of a dedicated, well-maintained high-end
computational resource with stable load. This type
of behavior profile well encapsulates the behavior of
dedicated HPC resources with high uptime and infre-
quent hardware errors. Similarly, Figure 3b illustrates
the behavior of a dedicated resource with scheduled
availability, e.g., a resource grid machine. In contrast
AModelforSimulationofApplicationandResourceBehaviorinHeterogeneousDistributedComputingEnvironments
147
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 5 10 15 20 25
Relative Capacity (%)
HPC profile
(a) High availability, low volatility.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 5 10 15 20 25
Relative Capacity (%)
Grid profile
(b) Scheduled availability, low volatility.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 5 10 15 20 25
Relative Capacity (%)
HTC profile
(c) Varied and seasonal availability, high volatility.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 5 10 15 20 25
Relative Capacity (%)
Cloud profile
(d) High availability, low volatility.
Figure 3: Variations in resource behavior profiles.
to these, Figure 3c instead illustrates the behavior of
a shared computational resource with high seasonal-
ity in availability, and high volatility in capacity dur-
ing the shared time periods. Finally, Figure 3d illus-
trates the behavior of a virtualization-based resource
that exhibits high availability, but with more or less
periodically varied capacity.
The differences between these types of resource
behavior well describes the challenges of construction
of virtual infrastructure components, such as meta-
scheduling and brokering systems, in mixed resource
type environments. To enable efficient modeling
of resource behavior in such heterogeneous environ-
ments simulation tools need to capture variations in
resource behavior, including multi-dimensional het-
erogeneity, not just performance.
To fully model resource behavior, simulation
frameworks also needs to apply some level of in-
terpretation to behavior profiles in resource simula-
tion. For example, simulation of a resource with high
volatility of a nature that can cause job preemption
should incorporate information of whether the appli-
cation supports (and induces overhead from) check-
pointing in resource simulations. To encompass such
differences, we propose that simulation frameworks
expose resource simulation algorithms as customiza-
tion points, so that resource simulation implementa-
tions can be replaced using third party plug-ins.
3 EVALUATION
For the purpose of this evaluation, to demonstrate use
and characterize the computational performance of
the simulation model, we consider a two-dimensional
performance metric that contains application and re-
source profiles for computational and network trans-
fer capacity. To illustrate the computational perfor-
mance of the framework, we construct four sets of
tests that combined demonstrate the scalability of the
simulation model and the computational efficiency of
the framework. To demonstrate the scalability of the
model we simulate a simple HPC-based virtual in-
frastructure and vary the amount of jobs, the amount
of resources, and the time step in simulations. To
demonstrate parallelization of the model, we then run
a set of tests where we vary the amount of threads
used to simulate the resources in the simulation.
3.1 Test Environment
For ease of analysis, all evaluation tests are performed
on the same machine where the simulation engine is
the only load process in tests. The testbed consists of
a quad Intel Xeon X3330 2.66GHz with 7GB RAM
running 64 bit Ubuntu v11.04 interconnected with a 1
Gbps Ethernet network. The Java version used in tests
is Sun Java 1.6, and Java memory allocation pools
SIMULTECH2012-2ndInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
148

range from 512 MB to 1 GB in size.
3.2 Evaluation Tests
To demonstrate the resource simulation mechanics,
we define a simple environment model of an HPC
cluster consisting of a job queue (that in tests is fully
saturated at all times), a scheduler (that performs a
simple round robin scheduling algorithm), and a set
of computational resources with fully saturated re-
source queues. In experiments we run a set of jobs
with a predefined simulation time step and a fixed set
of resources to simulate. We then vary the differ-
ent parameters (simulation time step, number of re-
sources, number of jobs) to investigate how the simu-
lation framework scales versus the simulation param-
eters. To compensate for natural variations in simula-
tion accuracy due to machine load and performance
variations, all experiments are repeated at least ten
times and data presented is based on average exper-
iment values.
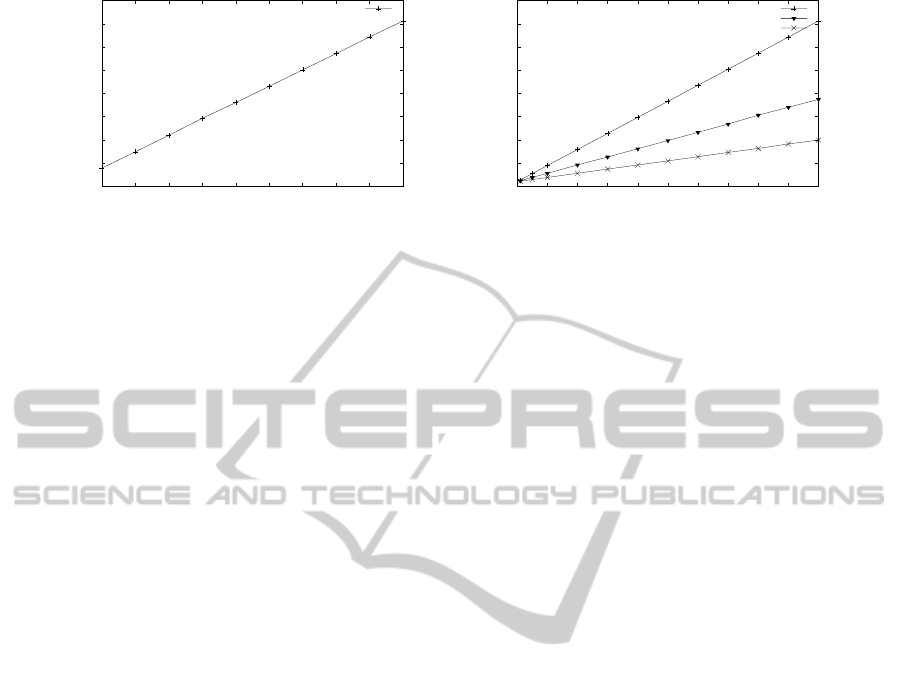
3.2.1 Varied Time Step
In the first experiment we vary the time step used in
simulation. Use of a smaller time step in applica-
tion and resource behavior profiles allows for more
fine-grained simulation of behavior, but increases the
computational load of the simulation. As can be seen
in the graph of Figure 4a, decreasing the application
time step (increasing the amount of time steps per job)
increases the amount of computations linearly in the
experiment.
3.2.2 Varied Amount of Jobs
In the second experiment we vary the amount of jobs
used in simulation. As in the case of increasing the
time step resolution, increasing the amount of jobs
will also increase the computational burden of sim-
ulations. In essence variation of these two parameters
yield the same result, more application timesteps to
translate to resource timesteps. As illustrated by the
first (single-thread) graph of Figure 4b, increasing the
amount of jobs to run linearly increases the amount
of timesteps to run, and also the computational cost
of the simulation.
3.2.3 Varied Amount of Resources
In the third experiment we vary the amount of re-
sources used to simulate a fixed set of jobs. In this
experiment we do not observe any major fluctuations
in the computational cost of simulations (compared to
the experiment illustrated in Figure 4a). This stems
from the computational burden of a simulation de-
pending on the number of application timesteps. As
resources are simulated independent of each other,
variation of the number of resources will not majorly
affect the computational burden of the simulation of
resources. Inclusion of higher level components of
virtual infrastructures such as schedulers will natu-
rally be affected by the inclusion of more resources.
3.2.4 Parallelization
As a final experiment in the analysis of the behav-
ior of the model, we repeat the previous experiment
but now bundle the resources in spatially segmented
groups of resources that are each simulated in sep-
arate threads. As illustrated in Figure 4b, resources
that are simulated independently of each other are
parallelizable and the total simulation time can there-
for be reduced through parallelization. As illustrated
in the figure, the system suffers some overhead from
management of thread pools that limit the scalability
of the model. Further analysis of ways to improve
the scalability of this model, including distribution of
the simulation communication to allow processing of
the resource simulation on multiple computational re-
sources is subject for future work.
3.3 Results
As demonstrated in tests, the computational cost of
the model scales with the amount of timesteps per-
formed in resource simulation. Reducing the time
step size in resource simulation increases simulation
resolution, but also the amount of computations re-
quired for simulations. Increasing the amount of jobs
simulated also increases the required amount of com-
putations, while increasing the amount of resources
(without increasing the amount of jobs) does not im-
pact the amount of computations much. As resources
are simulated independent of each other (and grouped
to match the amount of hardware threads available),
increasing the amount of threads used allows for near
linear scaling of the performance of the model.
Quality-oriented tests, that more extensively mea-
sure simulation model ability to capture the behavior
of real applications and real resources are planned and
subject for future work. For this contribution how-
ever, extensive studies of construction of application
and resource profiles are deemed out of scope. In
the evaluation, we perform only simulations of artifi-
cial resources and models, i.e. with synthetic profiles
for applications and resources. In tests we use sim-
ulated profiles composed of the application and re-
source model base functions described in Figure 3.
AModelforSimulationofApplicationandResourceBehaviorinHeterogeneousDistributedComputingEnvironments
149
0
50000
100000
150000
200000
250000
300000
350000
400000
1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
Simulation Time (ms)
Number of Application Timesteps per Job
10000 jobs
(a) Simulation time (ms) as a function of time step
size.
0
50000
100000
150000
200000
250000
300000
350000
400000
0 100000 200000 300000 400000 500000 600000 700000 800000 900000 1e+06
Simulation Time (ms)
Number of Jobs
1000 time steps per job, 1 thread
1000 time steps per job, 2 threads
1000 time steps per job, 4 threads
(b) Simulation time (ms) as a function of number of
jobs.
Figure 4: The scalability of the computational model.
4 DISCUSSION
With the application behavior profile formulation of
Section 2.1, example profiles that model basic (e.g.,
cyclic or bursty) application behavior are easily con-
structed for resource simulation purposes. For sim-
ulation of application behavior, sophisticated applica-
tion behavior profiles can be developed through meth-
ods such as application profiling (Feng et al., 2005),
analysis of workload traces from archives such as
the parallel workloads archive (Feitelson, 2007) and
the grid workload archive (Iosup et al., 2008), or by
use of external monitor tools that measure application
behavior through operating system constructs (Mor-
shed and Meagher, 2004). Naturally, measurements
of application behavior should be performed on sta-
ble, high-performance resources to minimize the in-
fluence of variations in resource behavior. While de-
velopment of accurate models for application behav-
ior is of great interest for the purposes of this work,
it is deemed out of scope for this contribution as the
focus here is the simulation model.
It should be noted that not all applications behave
as described in Section 2.3. With the increased popu-
larity of cloud computing, where virtual machines are
enacted as services (instead of programs executed as
batch jobs), the balance of application-resource be-
havior changes substantially. Modeling of the be-
havior of computational applications and resources
in virtualization-based environments is subject for fu-
ture work, but considered out of scope for the current
contribution as these phenomena are not captured by
the current environment and process model.
For development of descriptive resource profiles,
which is an area of great interest to, e.g., meta-
scheduling and distributed computing broker frame-
works, a number of tools can be used to quantify re-
source behavior. Common approaches here include,
e.g., running pilot jobs that benchmark resources, or
performing analysis of run-time logs for applications.
While the peak computational capacities of resources
can be measured with great accuracy, actual provided
capacity will vary with a number of factors such as
load, availability schedules, and (hardware and soft-
ware) failures.
The network capacity of resources will like com-
putational capacity have a quantifiable peak, but will
likely exhibit higher variability as it is subject to not
only local resource contention but also to contention
of shared (bandwidth) capacity with other resources.
To reduce complexity in modeling, we here model
network capacity for each resource independently.
For construction of accurate models of network be-
havior, a number of approaches ranging from mea-
surements using tools such as iPerf (Tirumala et al.,
2005) to historical analysis of logs exist.
Development of sophisticated models for applica-
tion and resource behavior is of interest and subject
for future work. For example, to model application
behavior in cloud environments, it is expected to be
of interest to be able to assign cost functions for trans-
ferring data in and out of (commercial) clouds.
As the simulation framework exposes customiza-
tion points for all modeled infrastructure components
and simulation algorithms, more advanced (multi-
dimensional) metrics can be incorporated in model-
ing. It should be noted that this model formula-
tion allows for efficient and parallelizable computa-
tion of simulation timesteps operating on data struc-
tures (profiles) that can be segmented both spatially
and temporally, i.e. simulation resources are mod-
eled independently and profiles can be defined inde-
pendent of simulations. It should also be noted that
even with well defined application and resource pro-
files, exact simulation of computational throughput is
difficult to achieve due to variations in computation
SIMULTECH2012-2ndInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
150

behavior, data dependencies, resource contention, etc.
The aim of the framework here is to provide a mecha-
nism for experimentation, where behavior models can
be iteratively refined for increased precision.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we discuss simulation of application and
resource behavior in distributed computing environ-
ments. We note a current lack of simulation toolkits
that encompass the dynamic behavior and resource
heterogeneity of such environments, and propose a
simulation model for combined discrete-time simula-
tion of resources and discrete-event simulation of vir-
tual infrastructures. In a brief performance evaluation
we demonstrate that the proposed approach is scal-
able and parallelizable, and discuss how the formu-
lation of (application and resource behavior) profiles
capture modeling of resource heterogeneity, variabil-
ity, and volatility.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors extend their gratitude to the anony-
mous reviewers for valuable feedback and interest-
ing discussions. This work is done in collaboration
with the High Performance Computing Center North
(HPC2N) and is funded by the Swedish Government’s
strategic research project eSSENCE.
REFERENCES
Armbrust, M., Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A., Katz, R.,
Konwinski, A., Lee, G., Patterson, D., Rabkin, A.,
Stoica, I., et al. (2010). A view of cloud computing.
Communications of the ACM, 53(4):50–58.
Booth, G., Raymond, P., and Oh, N. (2007). Load-
runner. software and website. Yale Univer-
sity, New Haven, CT¡ http://environment. yale.
edu/raymond/loadrunner.
Buyya, R. and Murshed, M. (2002). Gridsim: A toolkit for
the modeling and simulation of distributed resource
management and scheduling for grid computing. Con-
currency and Computation: Practice and Experience,
14(13-15):1175–1220.
Calheiros, R., Ranjan, R., De Rose, C., and Buyya, R.
(2009). Cloudsim: A novel framework for modeling
and simulation of cloud computing infrastructures and
services. Arxiv preprint arXiv:0903.2525.
Casanova, H. (2001). Simgrid: A toolkit for the simulation
of application scheduling. In Cluster Computing and
the Grid, 2001. Proceedings. First IEEE/ACM Inter-
national Symposium on, pages 430–437. IEEE.
Chang, X. (1999). Network simulations with opnet. In Sim-
ulation Conference Proceedings, 1999 Winter, vol-
ume 1, pages 307–314. IEEE.
Chien, A., Calder, B., Elbert, S., and Bhatia, K. (2003).
Entropia: architecture and performance of an enter-
prise desktop grid system. Journal of Parallel and
Distributed Computing, 63(5):597–610.
Feitelson, D. (2007). Parallel workloads archive. URL
http://www. cs. huji. ac. il/labs/parallel/workload.
Feng, X., Ge, R., and Cameron, K. (2005). Power and en-
ergy profiling of scientific applications on distributed
systems. In Parallel and Distributed Processing Sym-
posium, 2005. Proceedings. 19th IEEE International,
pages 34–34. IEEE.
Foster, I. and Kesselman, C. (2004). The grid: blueprint for
a new computing infrastructure. Morgan Kaufmann.
Iosup, A., Li, H., Jan, M., Anoep, S., Dumitrescu, C.,
Wolters, L., and Epema, D. (2008). The grid work-
loads archive. Future Generation Computer Systems.
Kliazovich, D., Bouvry, P., Audzevich, Y., and Khan,
S. (2010). Greencloud: a packet-level simulator
of energy-aware cloud computing data centers. In
GLOBECOM 2010, 2010 IEEE Global Telecommu-
nications Conference, pages 1–5. IEEE.
Miloji
ˇ
ci
´
c, D., Llorente, I., and Montero, R. (2011). Open-
nebula: A cloud management tool. Internet Comput-
ing, IEEE, 15(2):11–14.
Morshed, F. and Meagher, R. (2004). Coordinated appli-
cation monitoring in a distributed computing environ-
ment. US Patent 6,760,903.
Nu
˜
nez, A., V
´
azquez-Poletti, J., Caminero, A., Carretero, J.,
and Llorente, I. (2011). Design of a new cloud com-
puting simulation platform. Computational Science
and Its Applications-ICCSA 2011, pages 582–593.
Ostermann, S., Iosup, A., Yigitbasi, N., Prodan, R.,
Fahringer, T., and Epema, D. (2010). A performance
analysis of ec2 cloud computing services for scientific
computing. Cloud Computing, pages 115–131.
Sarmenta, L. and Hirano, S. (1999). Bayanihan: Build-
ing and studying web-based volunteer computing sys-
tems using java. Future Generation Computer Sys-
tems, 15(5):675–686.
Sobel, W., Subramanyam, S., Sucharitakul, A., Nguyen, J.,
Wong, H., Patil, S., Fox, A., and Patterson, D. (2008).
Cloudstone: Multi-platform, multi-language bench-
mark and measurement tools for web 2.0. In Proc.
of CCA.
Song, H., Liu, X., Jakobsen, D., Bhagwan, R., Zhang, X.,
Taura, K., and Chien, A. (2000). The microgrid: a
scientific tool for modeling computational grids. In
Supercomputing, ACM/IEEE 2000 Conference, pages
53–53. IEEE.
Superna Network Planning Engine (2012).
http://www.superna.net/network-planning-
engine.php, march 2012.
Tirumala, A., Qin, F., Dugan, J., Ferguson, J., and Gibbs, K.
(2005). Iperf: The tcp/udp bandwidth measurement
tool.
Tsai, W., Fan, C., Chen, Y., and Paul, R. (2006). A service-
oriented modeling and simulation framework for rapid
development of distributed applications. Simulation
Modelling Practice and Theory, 14(6):725–739.
AModelforSimulationofApplicationandResourceBehaviorinHeterogeneousDistributedComputingEnvironments
151
