
A Synthesis of a Knowledge Management Framework for Sports
Event Management
Azizul Rahman Abdul Ghaffar
1
, Ghassan Beydoun
1
, Jun Shen
1
, Will Tibben
1
and Dongming Xu
2
1
School of Information Systems and Technology, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia
2
School of Business, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Sports Event Management, Framework, Sports Technology.
Abstract: Due to rapid social development in Asia, sports events have grown larger and many new countries are also
hosting them for their first time. In addition to required increase in expenditures and more efficient
management, various instances of inadequate planning highlighted the needs for more effective and better
sustainable structures to support knowledge transfer between organizers, from one event to the next. The
research presented in this paper aims to facilitate the deployment of systematic knowledge management
practices to sports event management, to enable sustainable planning. The research in this paper synthesizes
is carried out on the Malaysian Games as an example of a sports event management. Furthermore, we
introduce knowledge management (KM) framework that was developed based on studies and observations
of processes and activities in this organization. The focus is on knowledge that is key to the success of the
Malaysian Games and that which can be used to the development of the organization and in future games.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sports events are more than ever important on a
global scale – economically, socially, politically and
technologically. According to Fuhrer (2002) the
Olympic Games, particularly over the last 20 years,
has experienced unparalleled growth and universal
popularity. Similar expectation are placed on other
international sporting events such as the
Commonwealth Games. Applying knowledge
management (KM) practices to sports event
management can offer much needed support the
multi-billion dollar industry growth (Halbwirth,
2001). Systematic handling of knowledge following
an explicit framework underpins successful
knowledge transfer and sharing (Heisig 2009, Sadrei
et al 2007). A KM framework assumes that
knowledge is a crucial factor to production and the
sets about to improve the performance of processes,
organization and systems (Van der Spek and
Sijkervet 2005). The framework can be the basis for
enhanced performance and utilization of resources
because it can be used as a tool to leverage
organizational knowledge resources (Aidemark and
Sterner 2003). It provides a structure for a
systematic process to harness the various benefits of
KMS. We identified seven possible frameworks
(Table 1) that were potentially applicable to sports
event management areas in terms of business
process and organizational structure.
2 THE BENEFITS OF A KM
FRAMEWORK IN SPORTS
EVENTS MANAGEMENT
Whilst various sports event management
organisations are similar in goals and in scope, they
differ in a number of ways: their structures and
practices are often dependent on different staff and
budgetary constraints, different technologies,
different sports systems, different political climate,
different culture and so forth. The Malaysian Games
(MG) follows the execution format of Olympic
events. It belongs to the National Sports Council of
Malaysia (NSCM) and MG has recently seen a
drastic growth in the participation of athletes,
operating expenses and expenses for technological
information. The event size is steadily increasing.
With this increasing size, it is important to introduce
practices to ensure transfer of knowledge into the
future as long been advocated and currently being
instituted into the Olympic Games (Fuhrer, 2002).
494
Rahman Abdul Ghaffar A., Beydoun G., Shen J., Tibben W. and Xu D..
A Synthesis of a Knowledge Management Framework for Sports Event Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0004065004940499
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends (ICSOFT-2012), pages 494-499
ISBN: 978-989-8565-19-8
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
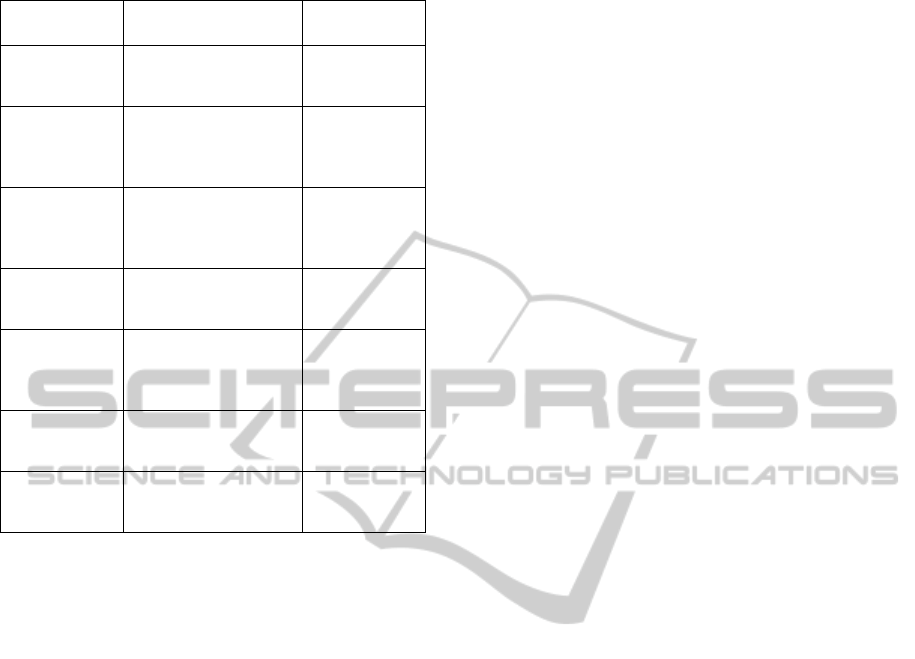
Table 1: KM Framework Comparison.
Framework
User Organization, Usage
Goal
Knowledge
Agents
KM/BSC
Model (Aidermark
and Sterner, 2003)
Matsushita ltd, source of
competitive intelligence for
business
Systemic, resource
oriented/technical,
organizational
European KM
Framework (Weber
et.al, 2002)
European KM Organization,
Standardization of European
KM services
Intellectual,
scientific,
technological and
economic
HA/DR KM
framework
(Dongsong, Zhou and
Nunamaker, 2002)
Humanitarian Assistance/
Disaster Relief, Knowledge
as a power to make decision
Architecture, internet
as channel,
knowledge base
KM Network (V. d.
Spek and Spijkervet,
2002)
CIBIT Consultants, KM as a
continuous learning process
Internal influences
and external
influences
KM Systems (Lacher
and Koch, 2000)
Organizations with KMIT
systems, KM support
functionalities in a distributed
environment
Shared info and team
knowledge domain
KM Support
Framework (Hahn
and Subramani 2001)
Organizations with KMS
Systems to balance info
overload and maintenance
Motivation of users
to use KM systems
KM SECI Model
(Nonaka and
Takeuchi, 1995)
Common in KM practice KM
Process (SECI) to support
knowledge creation
KM methodology
and technique
This fast growth is creating a number of challenges.
Schumakrer et al (2009) demonstrate that there is a
vast amount of knowledge associated with sports
events. This includes:
knowledge relating to the actual sporting
happenings (for example, relating to players
and coaching); and
knowledge about the actual organising of the
events (for example, relating to the venues and
cost (Schumaker et al., 2009).
Making sense of both types of knowledge is
important for different decision making stakeholders
such as the managers, organisers and coaches. Our
focus in this research is on the second area identified
by Shumaker et; al which is knowledge relating to
enabling more effective event organising. From a
governance perspective, this is quite significant
given the large-scale public investment made in
organising events. For example, many new facilities
and venues may be required. These may turn out to
be a financial burden on the host cities, and thus
constitute a financial risk. Previous work in this
research was directed at better defining knowledge
process failures and bottlenecks in the MG (Ghaffer
et al., 2011). We methodically applied the context
analysis templates of knowledge analysis
methodology, CommonKADS (Schreiber et al,
2000), to analyse the context of the Malaysian
Games. That analysis uncovered these key existing
problems in the MG current practices:
Duties and responsibilities are not sustained
between events;
The IT Unit’s overreliance on outsourcing;
and
subsequent problems related to ownership of
games management systems.
Most sports events management problems
encountered are often unexpected and can invariably
be traced to inadequate coordination or specialized
knowledge/resources. We aim to improve the
coordination of information, the usage of resources
or identify lacking areas within the sports
organization. We pursue a KM framework which
can offer incremental improvements. KM
frameworks have been presented in many other
areas. Heisig (2009) identified 160 KM frameworks
that have been built from 1995 to 2003. None of
which however is geared towards sports events
organising. Our own research could not find any
specific sports events KM framework in (2003-
2011) other than that produced by Schumaker et.al
(2009) which has resulted in a Sports Knowledge
Framework, but its focus is on the use of data
mining and data management (via statistics analysis
and machine learning).
3 THE PROPOSED SPORTS
EVENT MANAGEMENT KM
FRAMEWORK
Rubenstein-Montano et al. (2001) distinguish three
types of KM frameworks: Prescriptive frameworks
prescribing different ways to engage in knowledge
management activities; Descriptive frameworks
identifying attributes of knowledge management
important for their influence on the success or
failure of knowledge management initiatives; or
hybrid frameworks combining both. We develop a
hybrid KM framework that can be applied to various
sports event organisational environments. It
describes a method to connect entities involved
through their perspectives of needing use of
information and improved knowledge standard. This
new KM framework, The Sports Event Management
KM framework (SEMKM Framework), aims to
overcome knowledge sharing problems related
sports event management. It focuses on core
resources of knowledge, communication enablers,
KM activities, business processes and sports
knowledge databases. The preparation of the
A Synthesis of a Knowledge Management Framework for Sports Event Management
495

SEMKM Framework will identify problems and
prescribe opportunities to resolve them through
improved KM practices. Based on the context
analysis that we carried out previously in (Ghaffer
et. Al, 2011), we intend to apply our framework to
the Malyasian Games context. The use of this new
KM framework will highlight the need of some
organisational reform actions. It will highlight the
need to add new elements to existing processes to
solve existing problems based on strengthening the
KM processes in the organization. New or modified
business processes are expected to enable positive
impact for the current operations of the sports event
management. Towards developing our SEMKM
Framework, we have identified four views of
knowledge as used with the context of sports events
organising and management:
Knowledge in People: The management must
identify those people with the necessary knowledge
(guided by the KM framework). Through a planned
strategy, staff will be directly involved in KM
initiatives conducted. Knowledge, qualifications and
experiences will be fully utilized in achieving the
goals of the organization. Staff are also encouraged
to share ideas and always use quality knowledge
with efforts to improve work performance.
Knowledge in Organization: The organization
should carry out variety of programs that can foster
the development of KM. This will involve business
process reengineering and requires thorough
analysis. Once the information is collected and
analysed, the organization must commit to undertake
KM strategic planning. Specifically for sports event
management, all elements of internal, external,
business process and operations of the whole must
be studied and understood before the introduction of
a new business process.
KM Infrastructure: KM is new in sports event
organization. Therefore, planning should be done to
enable the provision of infrastructure performed
well. In the sports event in Malaysia as an example,
it involved only a small group of sub-department
and the focus will only be given to them. In
preparing the infrastructure, the most attention are
the guidelines, financial aspects, knowledge basic
needs and appropriate technology to use. This
infrastructure will function well if all the KM
prerequisites have been met and any existing
inadequacies should be highlighted by the
framework.
KM Activities: To ensure that the principles of KM
functions properly, the sports event organization
should be cognisant of KM practices and goals as
relating to their activities and the measures that need
to be in place. This is an implementation awareness,
with emphasis on continuous knowledge creation
process, storage, efficient distribution in conformity
with the sports event requirements. In the rest of this
section, we describe this synthesis layered process,
justifying the need for each layer.
Layer 1: Knowledge Resources
Figure 1: Layer 1 (L1).
Individual Knowledge: Each individual in the
organization has the resources needed to generate
knowledge management. Individual knowledge
refers to knowledge of those who have long worked
in this field.
Organizational Knowledge: Knowledge from
several subunits or groups can be combined and
used to create new knowledge. Tacit and explicit
knowledge capabilities become a key of
organizational knowledge. Using the Games
Management Systems as a point of reference, during
and after the MG leads to lessons learned over the
events conducted.
Corporate Memory: A corporate memory for
this area focuses on the combination of a repository,
data and information that allow sports communities
to interact with the systems (Beydoun 2009;
Beydoun 2011). For example, in MG, The National
Sports Council Athletes and Coaches databases
currently facilitates the related tasks. However, there
is still much room for improvement as much
knowledge and information especially from 2000
and previous years have not managed properly.
Layer 2: Communication Enabler
Communication Channels: The sports KM systems
will offer multiple communication platforms to
connect specific knowledge, functions and sub-units
with users, as well as sharing ideas, knowledge and
understanding.
a) Internet/Intranet: The most common
problems encountered concern on the internet
infrastructure is for the preparation of the venues
which is quite distant from major cities as well as
needed technology. In Addition, there are hosting
states that do not host have a strong internet
ICSOFT 2012 - 7th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
496

infrastructure and requires additional work to be
done in advance .
b) Websites: A games website is the most
important source of information. It should be able to
effectively disseminate sports knowledge.
c) Sports Portals: A sports portal has been
developed by the NSCM and is being used in
everyday tasks. Nevertheless, it does not have any
direct relationship to all the systems used in MG has
been provided by external providers. Therefore,
knowledge sharing does not occur effectively.
d) Networking, Wireless, Cabling Based on
the current situation, every time MG will be held,
almost all matters relating to infrastructure will be
repeated and should be developed from scratch.
Figure 2: Layer 2 (L2).
Interconnections: The work undertaken here requires
expertise in ICT, mass communications and
engineering. There is much specialized knowledge
to be shared, especially in terms of procedures and
protocols used to ensure the event takes place
effectively and efficiently.
Layer 3: KM Activities
The task to be done in the sports event management
will be implemented in stages. Certainly it involves
processes deployed and arranged to meet the
recommendations made. KM activities carried out
are as follows:
K-Identification: Internal Analysis/Identification of
Existing Knowledge/Identification of current
steps/ Methods and tools.
K-Acquisition: Acquire knowledge –
suppliers/customers/specialists/sports
products/sports partnership.
K-Application: Ensure appropriate knowledge used
in organizations/knowledge needs/knowledge to be
created, stored and shared/Identify knowledge
gaps/representation of new knowledge.
K-Sharing: Transfer of knowledge/sharing in various
way – manual or computerized/Methods and
tools/ acceptance of knowledge provided by
colleagues, partners and suppliers.
K-Development: Compliments K-Acquisition/Build
Distinctiveness Competencies/Focus on
conceptual, behavioural and technical
abilities/overall improvement.
K-Creation: Creation of new knowledge – social
interaction/services improvement
activities/Research and development/Communities
of Practice/encourage staff to bring in their explicit
and tacit knowledge.
K-Preservation: Through Culture – Promote
knowledge sharing and Communities of
Practice/Through
Technology – store selective current/ retrieve
specialized knowledge for constant usage /Capture,
Use and Reuse and Update concept.
K-Measurement: To measure the effectiveness of
KM/Individual reactions and feelings/Individual
knowledge assessment exercise/Evaluate overall k-
base/Performance focus.
Figure 3: Layer 3 (L3).
Layer 4: KM Input/KM Output/ Business
Process/Business Focus
KM Input: This process refers to the internal and
external MG particular items, product, devices or
mechanisms that can be used for the purpose of
triggering the progression of a KM process in sports
event management. Examples are: data and
information of individual results, athletes, Officials
and contingents.
KM Output: A final product in the MG after
passing through the diversity of the KM knowledge
process in the organization and is ready for use by
sports users. An example is the daily results report.
Business Process: A collection of MG
management activities designed to produce a
specific sports managment output. It implies a strong
emphasis on how sports event management is done.
Currently, the MG Standard Procedure by the
NSCM has been used as the basis for organizing the
MG. There seems to be room to improve the
business process. KM can be included as an
additional element. Example: decision making in
A Synthesis of a Knowledge Management Framework for Sports Event Management
497

accessing athletes and contingent performance.
Business Focus: Helps in defining the MG
organization, give direction and avoid problems. It
can help motivate members by communicating what
the organization is striving for as well as providing a
basis for recognizing accomplishments and
successes. Example: Decision about the focus of the
MG and the allocation for the next organizing.
Figure 5: Layer 4 (L4).
Layer 5: Sports KM Database (SKMD)
A sports KM database is a collection of sports
knowledge that is organized so that it can easily be
accessed, managed and updated. This aspect is the
responsibility of the ICT Unit of the NSC. Currently,
the system in use is operated separately and have the
two entities that manage them, consisting of the
NSC IT Unit and developers from outside of the
organization. Improvements process should be done
to create a foundation that can support the proposed
knowledge management implementation
accordingly.
Figure 6: Layer 5 (L5).
4 DISCUSSION, VALIDATION
PLAN AND CONCLUSION
Our SEMKM framework is flexible. Its use will be
based on needs and size of the future events.
Foreseen advantages of using it are as follows:
SEMKM Framework can be used as a tool for
decision making to provide a description of all
kinds of knowledge and information needed by the
organization. Knowledge requirements are
identified and the analysis is the basis for
systematic development.
It can improve the quality of the organisational
processes, targeting specific characteristics of
organizational management, data management and
knowledge flow networks.
With all aspects of processes will documented,
it aims to reduce repetition of work, provide
guidance and prepare for new changes. In addition,
it will provide updates, current guidelines and is
easily accessible by all involved in the MG.
SEMKM Framework will provide methods of
information sharing, knowledge capture and
knowledge generation. It can also be used to
coordinate the knowledge effectively.
SEMKM Framework can also be used to
introduce a knowledge-based decision support tool
for use in the management of the organization, and
possibly other methods aimed at cultivating a
technology based organization with methods to
strengthen the knowledge management in the
sports event management.
The framework will be initially validated and refined
through a detailed case study applying it to MG. We
have developed a detailed survey to capture the
contextual conditions, focussing is on contemporary
events, and the experience of the actors involved.
We conducted a pilot test on 35 respondents with the
aim to test the effectiveness of the validation
methods to be used for SEMKM Framework
developed. Respondents were given a set of
questionnaire containing 76 questions which are
linked directly to the problem being studied. A total
of eight categories were determined. Questions were
submitted in the categories of KM Adoption, Sports
Knowledge in MG, Knowledge in SE organizing,
Awareness KM, KM Systems, Knowledge and IT,
KM and IT Performance and others. From the
analysis, we found that all categories of questions,
showed the respondents chose agree and strongly
agree responses for each question. It indicated that
50-60% of the respondents agreed with our
assumption in strengthening knowledge
management in the sports event management. For
the next task, the number of questions is to be
increased to 84 questions, 405 respondents have
been identified, and the questionnaire has been
strengthened to ensure that the data obtained later
will be accurate.
The developed framework is a road map to
improve the sports event management. By creating
KM centric processes, it can be used in improving
the effectiveness of the organization's management.
We have been assuming that there are advantages
and disadvantages in running the sports event
management and it has been sketched in the
framework. Further validation is required. Survey
based methods have been identified as a suitable tool
for the validation process of frameworks (Tran et al,
2006; Beydoun et al 2006). They will identify
ICSOFT 2012 - 7th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
498

specific aspects of the review and see whether the
proposed framework can be used or not. The
proposed survey will be at the same time a tool to
apply KM in the organization after identifying the
needs of the organization and having examined all of
the assumptions made. Through the survey, data and
information required to be obtained accurately. The
questions answered by the respondents would give a
sign of an impact on the development and
implementation of this framework. After the
analysis is made, the proposed KM framework will
be reviewed and improved before it is proposed to
use the field of sports event management on a
second validation case study.
REFERENCES
Aidemark, J., and Sterner, H. 2003. “A Framework for
Strategic Balancing of Knowledge Management
Initiatives.” Proceedings of the 36th Hawaii
International Conference on System Workshop
Sciences. 6 -9 Jan 2003, Hawaii, USA.
Alavi, M., and Leidner, D. E. 2001. “Knowledge
Management Systems: Conceptual Foundations and
Research Issues.” Management Information Systems
Quarterly (25:1), pp 107-136.
Benbasat I, Goldstein D and Mead M (1987) „The Case
Research Strategy in Studies of Information Systems‟
MIS Quarterly Vol. 11, pp. 369-386.
Beydoun, G., Gonzalez-Perez, C., et al. (2006).
“Developing and Evaluating a Generic Metamodel for
MAS Work Products“. Software Engineering for
Multi-Agent Systems IV: Research Issues and
Practical Applications. A. Garcia, R. Choren, C.
Lucenaet al. Berlin, Springer-Verlag. LNCS 3914:
126-142.
Beydoun, G. (2009). "Formal concept analysis for an e-
learning semantic web". Expert Systems with
Applications 36(8).
Beydoun, G., Lopez-Lorca, A. et al. (2011). “How do we
measure and improve the quality of a hierarchical
ontology?” Journal of Systems and Software 84 (12):
2363-2373.
CEN (2004), European Guide to good Practice in
Knowledge Management. CWA 14924, Part 1 – 5,
European Committee for Standardization, Brussels.
Dongsong Z., Hou, L., and Nunamaker, Jr. J. F. 2002. “A
Knowledge Management Framework for The Support
of Decision Making in Humanitarian
Assistance/Disaster Relief.” Knowledge and
Information Systems Springer-Verlag (4:3) July, pp
370-385.
Eisenhardt K (1989). Building Theories from Case Study
Research‟ Academy of Management Review Vol.14,
No 4, pp. 532-550.
Fuhrer, F. 2002. Sustainable Olympic Games: a dream or
reality? Bollettino della Societa Geografica, Italiana,
Serie XII, Vol VII, 4.
Ghaffar A. R. A., Beydoun G., Shen J., Tibben W. 2011.
“Towards Knowledge Management in sports event
management: Context Analysis of Malaysian biannual
games with CommonKADS”, Proceedings of the 6
th
International Conference on Software and Database
Technologies (ICSOFT2011), Volume 2, pp. 377-383.
Halbwirth, S., and Toohey, K. 2001. The Olympic Games
and Knowledge Management: A Case Study of the
Sydney Organising Committee of the Olympic Games.
European Sport Management Quarterly (1:2), June,
pp. 91-111.
Heisig, P. (2009). Harmonisation of knowledge
management – comparing 160 KM frameworks around
the globe. Journal of Knowledge Management. vol. 13
no.4, pp 4-31.
Hevner, A. R, March, S. T, Park, J. and Ram, S. 2004.
‘Design science in information systems research’. MIS
Quarterly, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 75–106.
Lacher, M. S., and Koch, M. 2000. “An Agent-based
Knowledge Management Framework.” American
Association for Artificial Intelligence Workshop on
Bringing Knowledge to Business Processes, 20-22
March, 2000.
Nonaka, I., and Takeuchi, H. 1995. The Knowledge-
Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create
the Dynamics of Innovation. New York: Oxford
University Press.
Rubenstein-Montano, B., Liebowitz, J., Buchwalter, J.,
McCaw, D., Newman, B., Rebeck, K and The
Knowledge Management Methodology Team (2001),
‘‘A systems thinking framework for knowledge
management’’, Decision Support Systems, Vol. 31, pp.
5-16.
Sadrei, E., Aurum, A., et al. “A Field Study of the
Requirements Engineering Practice in Australian
Software Industry”, International Journal
Requirements Engineering Journal 12 (2007), pp.
145–162.
Schreiber, G., Akkermans, H., Anjewierden, R., Hoog, R.,
Shadbolt, N., Velde, W.V., and Wielinga, B. 2000.
Knowledge Engineering and Management: the
CommonKADS Methodology. Boston, MA: MIT
Press.
Schumaker, R., Solieman, O., & Chen, H., (2009). Sports
Knowledge Management and Data Mining. Annual
Review of Information Science and Technology, 44.
Tran, QNN, Low, GC et. al, “A Methodological
Framework for Ontology Centric Agent Oriented
Software Engineering”, International Journal of
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, 21, 117-
132, 2006.
Weber, F., Wunram, M., Kemp, J., Pudlatz, M., and
Bredehorst, B. 2002. “Standardisation in Knowledge
management – towards a common KM framework in
Europe.” Proceedings of UNICOM Seminar. 27
February, 2002. London.
A Synthesis of a Knowledge Management Framework for Sports Event Management
499
