
Study on a Fast OSPF Route Reconstruction Method
under Network Failures
Hiroki Doi
System Engineering Research Laboratory, Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry,
Iwado kita 2-11-1, Komae-shi, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords:
OSPF, Router Dead Interval, Delay Time, Route, Designated Router.
Abstract:
The Great East Japan Earthquake occurred on March 11, 2011. Many Japanese people and Japanese companies
were damaged by the disaster. Also, network failures occurred over a wide area because many facilities of
commercial ISPs (Internet Service Providers) were damaged. Thus, there is a need to reexamine the disaster
estimation and reconstruct a robust network system against disasters in Japan. The network must have higher
reliability and fast recovery. Although OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is used widely on networks, it has a
router dead interval problem. If a (backup) designated router has stopped operation due to failure, the other
OSPF routers miss the designated router and try to find it by multiple hello packets. The OSPF routers await
a hello packet acknowledgment from the designated router for the router dead interval. After the router dead
interval, those routers can recognize that the designated router has ceased the operation. The router dead
interval is 40 seconds. This interval time is not only long for many real-time applications but also involves
huge buffering of data and a burst of traffic after the router reconstruction. To avoid the router dead interval,
we propose a fast method of designated router detection by enhanced OSPF. In this report, we show how our
method reduces the route reconstruction time from 45 seconds to 10 or less on OSPF networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Japan, many Japanese people and Japanese com-
panies were damaged by the Great East Japan Earth-
quake. Following this disaster, Japanese commer-
cial ISPs and the government reexamined the plan
for disaster estimation and protection against disas-
ters. According to this protection plan, commercial
ISPs must reconstruct robust networks against disas-
ters. Networks require high reliability and fast re-
covery. One of the important problems for these re-
quirements is that of routing, since considerable time
is required to reroute paths on IP networks, when
multiple routers have ceased operation due to fail-
ures. To study this problem, we focus on OSPF (Open
Shortest Past First)(Moy, 1998b)(Moy, 1998a) behav-
ior, which is one of the major routing protocols used
worldwide, and presume a large company network,
namely a broadcast multi-access network with 400
OSPF routers.
OSPF works with 2 kinds of router, namely, the
Designated Router (DR) and its neighboring routers
(neighbors) on broadcast multi-access networks. An
adjacency should be formed with the DR and its neig-
hbor. The DR also has a list of all other routers at-
tached to the network. In this case, when the DR
has ceased the routing operation, neighbors attempt
to cast hello packets to the DR. If the DR does not
respond to 4 hello packets from a neighbor, a neigh-
bor detects DR failure and all neighbors start to elect
new DR among their own neighbors. The hello packet
interval is 10 seconds (Hello Interval, default value),
hence it takes 40 seconds (Router Dead Interval) for
neighbors to detect the DR failure. After the DR fail-
ure, it takes more than 40 seconds to reroute all paths
by original OSPF. General speaking, this time length
of communication failure is very long for many appli-
cations on networks. Thus, when the DR has ceased
the routing operation on OSPF networks by the net-
work failure, it takes long time to recover the network
operation.
There is a simple method to reduce Router Dead
Interval. We can set the value of the hello packet in-
terval under 10 seconds on an OSPF router. How-
ever, paper (Goyal, 2003) reports that any Hello In-
terval value less than 10 seconds leads to unaccept-
able number of false alarms, meaning neighbors mis-
takenly DR failure due to the successive discards of
13
Doi H..
Study on a Fast OSPF Route Reconstruction Method under Network Failures.
DOI: 10.5220/0004065800130022
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Communication Networking, e-Business and Optical Communication Systems (DCNET-2012),
pages 13-22
ISBN: 978-989-8565-23-5
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

hello packets.
There are another methods to detect OSPF fail-
ures. When the links fail, OSPF multicasts LSA
(Link State Advertisement) packets. The Paper
(Yuichiro Hei and Hasegawa, 2007) proposed a
method of OSPF failure identification based on LSA
flooding analysis taking these aspects into account.
However, if the OSPF on a router ceases the oper-
ation or the Layer-2 (L2) link fails (in this case, net-
work topology contains L2-network ), the other OSPF
routers cannot detect this failure and send LSA pack-
ets. Thus, this proposed method cannot detect OSPF
failure in these cases by monitoring LSA packets and
avoid Router Dead Interval.
To avoid this Router Dead Interval, we propose
an enhanced OSPF with a new DR failure detec-
tion mechanism added without the hello packet. Our
method uses user IP packets to detect the DR failure
and monitors user IP packets from the DR. When the
DR has ceased the operation, it no longer sends user
IP packets. Our method can detect DR failure faster
than the original OSPF by monitoring the behavior of
those IP packets.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section
2, we first indicate our objective for original OSPF.
In Section 3, we describe the mechanism of original
OSPF and its Router Dead interval problem and show
our proposed method to solve this problem. In Sec-
tion 4, we show the behavior examples of our pro-
posed method for several network facility failures. In
section 5, we evaluate path reroute processing time
of our proposed method and original OSPF in typi-
cal network model. Finally, in Section 6, the effect of
our proposal method is summarized and future works
mentioned.
2 OSPF BEHAVIOR FOR THE DR
FAILURE
OSPF can adapt to many network configurations,
peer-to-peer networks, point-to-multipoint networks,
broadcast multi-access networks and so on. We fo-
cus on the broadcast multi-access network, because
it is a major network configuration of company pri-
vate networks. OSPF works with 2 kinds of OSPF
router, DR and neighbors on broadcast multi-access
networks. The router will attempt to form adjacen-
cies with some of its newly acquired neighbors. Link-
state databases are synchronized between pairs of ad-
jacent routers. On broadcast multi-access networks,
the DR determines which routers should become ad-
jacent. Adjacencies control the distribution of routing
information. Routing updates are only sent and re-
ceived on adjacencies, hence the DR plays an impor-
tant role in OSPF networks.
If the DR has ceased routing operation due to fail-
ure, neighbors cannot detect this failure immediately
and cannot receive new link-state information from
the DR. Under these circumstances, the OSPF cannot
reroute paths to avoid failing routers or links until the
successful detection of DR failure. Neighbors send
hello packets to the DR to confirm such failure. Hello
interval is 10 seconds as the default value on an OSPF
router. If the DR does not respond to 4 hello pack-
ets from a neighbor, the neighbor detects DR failure,
meaning it takes 40 seconds is required for neighbors
to detect DR failure. This time interval is called the
Router Dead Interval.
Of course, the Hello Interval is one of the OSPF
parameters and there is a simple way for Hello Inter-
val to be set to under 10 seconds to reduce Router
Dead Interval. However, this is not feasible for com-
mercial ISPs. This method was analyzed by pa-
per (Goyal, 2003) by measuring ISPs topologies and
it was reported that any Hello Interval value un-
der 10 seconds led to an unacceptable number of
false alarms. Thus, we think that the Hello Interval
should remain 10 seconds and need to adapt a differ-
ent method.
There is also a backup DR in the general OSPF
network. When the DR has ceased operation, the
backup DR becomes the DR and a new backup DR
is elected among other neighbors. In this paper, we
assume that a DR and a backup DR have ceased the
operation due to simultaneous multiple failure.
3 ENHANCEMENT OSPF FOR
THE ROUTER DEAD
INTERVAL
3.1 Outline for Enhancement OSPF
Our objective is to avoid using the hello packet to re-
alize the faster path reroute mechanism. To achieve
this objective, we enhance the DR failure detection
mechanism part of OSPF.
We have 2 simple key ideas as follows for this en-
hancement
1. When a link or router fails, the flow of IP packets
stops or changes immediately.
2. An IP packet which traverses the DR has a hello
function.
For key idea 1, if the DR fails, a neighbor does not
receive IP packets from the DR. Also, in the case of
DCNET2012-InternationalConferenceonDataCommunicationNetworking
14

Case 1 : OSPF failure on the DR
DRNeighbor
Case 2 : L2 link failure and OSPF failure on the DR
DRNeighbor
L2 switch
L2 link
DRNeighbor
L2 switch
L2 link
Figure 1: Typical OSPF network failures.
Fig. 1, if the DR or an L2-link fails, a neighbor does
not receive IP packets. In other words, a neighbor can
detect DR failure by monitoring IP packets from the
DR.
For key idea 2, we can substitute a user IP packet
for a hello packet to detect DR failure, because we can
use an IP header option within the private network and
the IP is at the same layer as the OSPF.
We show the outline of the new DR failure detec-
tion mechanism based on the ideas.
1. The user IP packet which traverses the DR is
marked on an option of the IP header.
2. The neighbor monitors the marked IP packets.
3. If the receiving rate of user IP packets on the DR is
less than the threshold value (R
DR
), the DR sends
a marked dummy IP packet to its neighbor.
4. If the local time exceeds the threshold value (R
i
)
on an neighbor i, this neighbor casts missing mes-
sage packets to all neighbors.
5. If another neighbor j receives a missing message
packet, it monitors the arrival interval time of
marked IP packets. If the marked IP packet in-
terval time is under the threshold value (R
j
), this
neighbor sends an alive message packet.
6. If the neighbor i does not receives an alive mes-
sage packet, this neighbor detects the DR failure.
A new DR is elected among all neighbors and re-
constructs the new routing table.
Here, we presume the DR writes 1 as a mark in an
option of the IP packet header, which is sent from the
DR to a neighbor. When a neighbor receives a marked
IP packet, it writes 0 as an unmark in an option and
sends the user IP packet.
Next, we define the threshold value R. To calcu-
late R, we borrow the idea of the TCP timeout mech-
anism (Stevens, 1994).
TCP monitors all RTT (Round Trip Time) of TCP
packets at the TCP interfaces and calculates the av-
erage RTT and its deviation. The time out value is
the average RTT + 2×deviation (Jacobson, 1988). (In
1990, the paper (Jacobson, 1990) revised this equa-
tion, average RTT + 4×deviation. We select the for-
mer equation for the performance of our method.)
TCP decides on the packet loss event based on this
time out value and retransmits the packet.
Our proposed method decides the DR failure event
by comparing the threshold value R with the arrival
interval time of the marked IP packets. R is calculated
by the following equation
Err = M − A
A → A+ gErr
D → D+ h(|Err| − D)
R = A+ 2D
where M is the arrival interval time of the marked
IP packet (measurement value), A is the average of M,
g is the coefficient 1/8, Err is the difference M and A,
h is the coefficient 1/4, D is the mean deviation. The
value of coefficients is equal to one of the original
TCP timeout mechanism.
3.2 Our Proposal Algorithm
We describe our proposed new DR failure detection
mechanism. We show the state transitions diagram of
DR and its neighbor in Fig. 2.
Neighbor Side.
1. Measurement.
The neighbor monitors the marked IP packets and
calculates M and R. If the local time exceeds R,
this state transits into state 2. If M is less than R,
there is no transition of state. If a missing message
packet is received, this state transits into state 3.
2. Missing.
The neighbor multicasts a missing message
packet to all OSPF routers. It corrects the R
i
of other neighbors i and calculates the maximum
value R
max
among R
i
If an alive message packet is
received by R
max
, the neighbor knows that the DR
is alive and there is path failure on an adjacency
path. This state transits into state 5 to reconstruct
adjacency with the DR. If an alive message packet
is not received by R
max
, the neighbor detects DR
failure and this state transits into state 6.
3. Confirm R.
The neighbor i having received the missing mes-
sage packet confirms R
i
and sends it to the sender
of the missing message packet, whereupon this
state transits into state 4.
4. Confirmation.
If a marked IP packet is received by R
i
, an alive
message packet is multicast. Also, if an alive mes-
sage packet is received from the other neighbor,
this state transits into state 1.
StudyonaFastOSPFRouteReconstructionMethodunderNetworkFailures
15

DR side
Neighbor side
1. Measurement
2. Dummy Packet Generation
3. Confirmation Acknowledge
Rec : “Missing message”
Send : “Alive message”
M>R
Send : “Dummy IP packet”
8. Full*
1. Measurement
2. Missing
3. Confirmation threshold R
6. OspfRestart
Rec : “Missing message”
M > R
Rec : “Alive message”
Rmax>timer
5. OspfInit
Rec/Send : “Alive message”
4. Confirmation
Send: “Threshold R”
8. Full*
1. Down*
6. Exchange*
* original OSPF state.
Figure 2: Proposed state transition diagram.
5. Ospf-Init.
In this state, the neighbor sends an LSA to the DR.
6. Ospf-Restart.
In this state, the neighbor detects DR failure and
multicasts an init message packet. The state of all
neighbors which receive an init message packet
transits into the down state of OSPF.
DR Side.
1. Measurement.
The DR marks a user IP packet and sends it to a
neighbor. Subsequently, the DR measures M and
calculate R
DR
. If the DR does not receive a user
IP packet by R
DR
, this state transits into 2. If the
DR receives a missing message packet, this state
transits into 3.
2. Dummy Packet Generation.
The DR generates a dummy marked IP packet and
sends it to a neighbor.
3. Confirmation Acknowledgement.
The DR multicasts alive message packets and this
state transits into state 1.
3.3 Path Reroute Processing Time
In this section, we mention the path reroute process-
ing flow of our proposed method for various network
facility failure. Various network facilities and OSPF
network configuration patterns exist. We assume a
DR, neighbor, L2 switch and link to comprise the
main network facilities for simplicity and show the
path reroute processing flow of our proposed method
for failure of those facilities in Fig. 3.
The Path reconstruction process is the original
OSPF process, SPF calculation, SPF Delay and LSA
processing and so on, but this process is used by our
DR
failure occured
Path reconstruction
DR election
failure
non-failure
failure
OSPF router
(exclude DR)
non-failure
DR failure detection
Figure 3: Processing flow for network facilities failure.
proposed method. The DR election includes hello
processing.
The Fig. 3 shows that there are 3 cases of process-
ing flow, namely, (1) Path reconstruction, (2) Path re-
construction + DR failure detection and (3) Path re-
construction + DR failure detection + DR election.
But there are only 2 processing time cases (2) and (3)
for the failure of those facilities to evaluate our pro-
posed method. We will evaluate the case (2) in section
5.2 and the case (3) in section 5.1.
DCNET2012-InternationalConferenceonDataCommunicationNetworking
16

Marked IP packet
DRNeighbor
Router A
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Router A sends missing packets
R < local time at router A
Other routers send Ri
NeighborNeighbor
Missing
Missing
Missing
R
1
R
Calculating Rmax
Init
Init
Init
After Rmax, router A sends init packets
The state of each router transitions into Down state.
Marked IP packet lost
2
Figure 4: Example 1: the DR failure.
4 EXAMPLES OF
ENHANCEMENT OF OSPF
BEHAVIOR
In this section, we show some examples of working
mechanisms of our proposed method in the event of
failure of various network facilities.
4.1 Example 1: The DR Failure
We assume that the DR is connected to a neighbor,
whereupon the DR has ceased operation due to OSPF
function failure but not link failure. For the original
OSPF, Router Dead Interval occurs in this case. We
explain our method with Fig. 4 in this case.
1. In a stable state, router A receives marked IP
packets from the DR. Each router calculates R
DR
and R.
2. The OSPF function on the DR stops due to failure,
but the link state is ready.
3. Router A cannot receive a marked IP packet by R
and multicasts missing message packets.
4. The other routers multicast their R. Router A cal-
culates R
max
.
5. The other routers cannot receive a marked IP
packet from the DR by R and does not send an
alive message packet. Router A cannot receive an
alive message packet by R
max
and multicast init
message packets. Subsequently, the state of all
routers transits into the down state of OSPF.
4.2 Example 2: L2 Link Failure
In this case, we assume that there is a L2 link between
router A and the DR. When an L2 link fails, neither
router A nor the DR can detect it. Hence, Router Dead
Interval occurs in the case of the original OSPF. We
explain our method with Fig. 5 in this case.
1. In this stable state, router A receives marked IP
packets from the DR. Each router calculates R
DR
and R.
2. The L2 link fails, but OSPF routers and other links
are ready.
3. Router A cannot receive a marked IP packet by R
and multicasts missing message packets. The DR
sends marked IP packets to router A and cannot
detect the failure on an L2 link.
4. The other routers receive a missing message
packet from router A and multicast R.
5. The other routers receive marked IP packets from
the DR and multicast alive message packets.
6. Router A receives an alive message packets and
sends LSA to the DR.
4.3 Example 3: Few User IP Packets
In this example, there is no network failure. However,
few user IP packets traverse the DR. The detection
time of our proposed method depends on the aver-
age packet arrival interval time. If the amount of user
IP packets declines further, the packet arrival interval
time increases to an ever greater extent, and hence the
detection time of our proposed method follows suit.
StudyonaFastOSPFRouteReconstructionMethodunderNetworkFailures
17
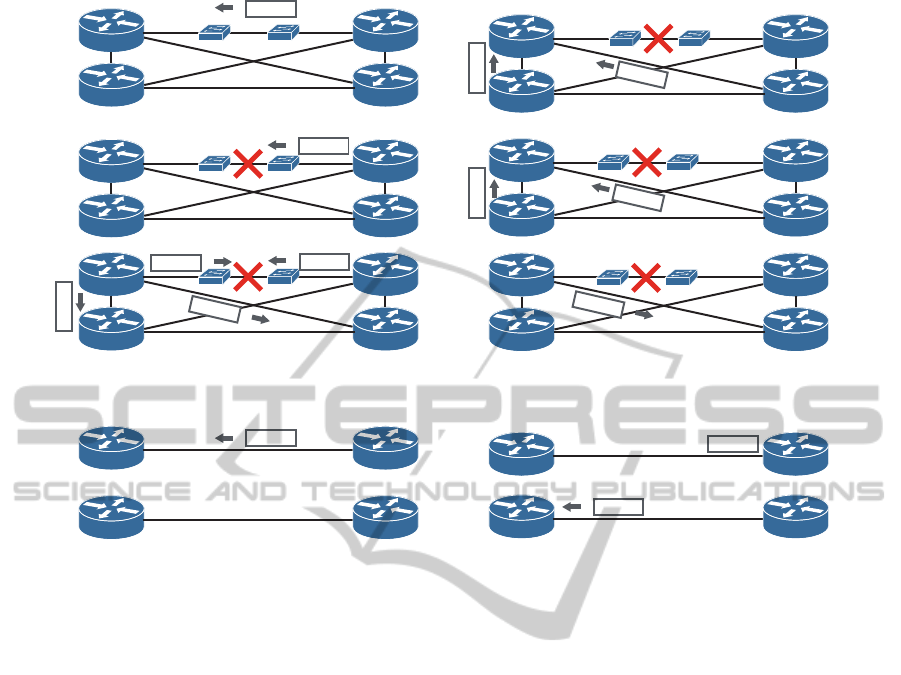
Marked IP packet
DRNeighbor
Router A
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Router A sends
missing packets
R < local time at router A
Neighbors send R packets
NeighborNeighbor
Missing
Missing
Missing
R
R
Alive
Alive
Router A calculates Rmax
Router A receives alive packets
L2 switch
Marked IP packet
Marked IP packet
Router A sends LSA to the DR
LSA
2
1
Figure 5: Example 2: L2 link failure.
Marked IP packet
DRNeighbor
Router A
1.
2.
3.
4.
After threshold R time,
Router A receives a marked (dummy) IP packet.
the DR generates a marked dummy IP packet.
Silent priod
(There is no user (marked) IP packet)
Figure 6: Example 3: few user IP packets.
We confirm the mechanism of our proposal in this sit-
uation with Fig. 6.
1. In this stable state, router A receives marked IP
packets from the DR. Each router calculates R
DR
and R.
2. The user applications temporarily stop communi-
cations.
3. When the DR does not receive a user IP packet
by R, it generates a marked dummy IP packet and
sends it to the router A.
4. Router A receives a marked dummy IP packet and
can confirm that the DR is alive.
4.4 Example 4: Loss of Message Packets
In this example, we assume that some of the marked
IP packets, missing message packets and alive mes-
sage packets are lost. We confirm the mechanism of
our proposal in this situation with Fig. 7.
1. In a stable state, router A receives marked IP
packets from the DR. Each router calculates R
DR
and R.
2. Marked IP packets are lost due to some failures.
3. Router A cannot receive a marked IP packet by R
and multicasts missing message packets. How-
ever, we assume that certain missing message
packets are lost due to some failures.
4. Some neighbors receive missing message packets
and send R to router A. Here, we also assume that
some of those missing message packets are lost.
However router A can receive R from some neigh-
bors, because there are many neighbors and we as-
sume that some of their packets can reach router
A. Router A calculates R
max
and awaits an alive
message packet.
5. Some neighbors can multicast alive message
packets, because the DR is alive, some of which
can be received by router A Subsequently, router
A sends LSA to the DR.
5 EVALUATION OF THE PATH
REROUTING TIME
In the previoussection 3.3, we explainedthat there are
2 cases of the path reroute processing time of our pro-
posed method for network facility failure. We evalu-
ate the path reroute processing time for our proposed
method in those 2 cases.
We show the network configuration in Fig. 8
as the typical network model. There are 2 types of
network, a backbone network and many local net-
DCNET2012-InternationalConferenceonDataCommunicationNetworking
18

Marked IP packet
DRNeighbor
Router A
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Router A sends missing packets
R < local time at router A
NeighborNeighbor
Missing
Missing
Missing
R
R
Alive
Alive
Router A receives alive packets
and reconstruct adjacencies.
Neighbors send R packets
Router A calculates Rmax
Marked IP packet lost
Missing packet lost
1
2
Figure 7: Example 4: message packets lost.
Area 0
DR
Router A
Router B
Backbone network
local
network
local
network
local
network
Backup DR
Backup DR
DR
DR
DR
Backup DR
Backup DR
Figure 8: Evaluation network model.
works. All local networks are connected to a back-
bone network. OSPF manages the network area. The
backbone is area 0 and local networks are area i
(i = 1, 2, . . . , N) on typical OSFP networks. But we
set only area 0 on all networks for simplicity. Be-
cause we focus on the effect of our proposal method
on the path reroute processing time. If the OSPF net-
works have many areas, the path reroute processing
time needs to include path information propagation
time from a area to the other area.
We assume that each local and backbone net-
work has a DR, a backup DR and 18 OSPF neighbor
routers. In this network configuration, we evaluate
the processing time for path rerouting from router A
to router B. We assume that backup DR and DR fail
at the same time in this evaluation.
Next, we set the evaluation parameters. The pa-
per (Goyal, 2003) lists different standards and vendor
introduced delays that affect the OSPF operation in
networks of popular commercial routers. We show
those delays which are used in our evaluation in table
1.
Also, the DR failure detection time of our pro-
posal methods depends on the arrival interval time of
user IP packets. In this evaluation, we set the follow-
ing constant arrival interval time of user IP packets on
each link for simplicity.
• Arrival interval: 1, 0.5, 0.1 seconds.
5.1 Case 1: DR Failure
Initially, we evaluate the path reroute processing time
for both our proposed method and the original OSPF
in the case of DR failure on the backbone network as
a typical case.
In the case of the original OSPF, new DR and
StudyonaFastOSPFRouteReconstructionMethodunderNetworkFailures
19

Table 1: Various delays affecting the operation of OSPF
protocol(Goyal, 2003)(CISCO Systems, 2007).
Name Processing time and description
Hello Interval The time delay between succes-
sive Hello packets. Usually 10
seconds.
Router Dead
Interval
The time delay since the last
Hello before a neighbor is de-
clared to be down. Usually 4
times the Hello Interval.
SPF Delay The delay between the short-
est path calculation and the first
topology change that triggered
the calculation. Used to avoid fre-
quent shortest path calculations.
Usually 5 seconds.
SPF calcula-
tion delay
0.00000247× x
2
+ 0.000978 sec
(Cisco 3600 series)
Route install
delay
The delay between shortest path
calculation and update of for-
warding table. Observed to be 0.2
seconds.
LSA process-
ing delay
<0.001 sec
Hello pro-
cessing delay
<0.001 sec
∗
*In (CISCO Systems, 2007), CISCO Systems, Inc. showed
the OSPF processing log with time stamp. The time
resolution of this log is 0.001 seconds and we can see that
hello processing delay is less than 0.001 seconds. Thus, we
set that hello processing delay is less than 0.001 seconds.
backup DR are elected among neighbors after Router
Dead Interval, whereupon OSPF routers reconstruct
the path table.
In the case of our proposed method, new DR and
backup DR are elected without Router Dead Interval
by a new failure detection mechanism using marked
IP packets.
We sum up the overall processing delay time of
the path rerouting according to the original OSPF al-
gorithm and our proposed method. The Fig 9 shows
the path reroute processing time for the original OSPF
and proposed method. When the number of OSPF
routers increases, so does the SPF calculation de-
lay. However, this increase is minor in terms of to-
tal processing delay. The Fig 10 shows the details
of processing time in the case of 400 routers. The
major contribution to path reroute processing time is
SPF delay and Router Dead Interval. Thus, we can
say that our proposed method reduces this processing
time very effectively, because it avoids Router Dead
Interval.
Also, if the arrival interval time of the marked IP
0 100 200 300 400
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Number of OSPF routers
Path reroute processing time (sec)
Original OSPF
Proposal method (arrival interval time of IP Packet : 1 sec)
Proposal method (arrival interval time of IP Packet : 0.5 sec)
Proposal method (arrival interval time of IP Packet : 0.1 sec)
Figure 9: Path reroute processing time for case 1.
0
10
20
30
40
50
original OSPF Proposal method
Router Dead
Interval
LSA processing time (0.001sec)
Hello processing time (0.02sec)
SPF Calculation,
SPF Delay
LSA processing time (0.001sec)
Hello processing time (0.4sec)
DR failure
detection time
(0.603sec)
Path reroute processing time (sec)
SPF Calculation,
SPF Delay
Figure 10: The details of path reroute processing time for
case 1. (Number of OSPF routers is 400).
packets exceeds 0.1 seconds, our proposed method
can send dummy marked IP packets every 0.1 sec-
onds. In this case, the bandwidth consumed is
5.12kbps (The size of a dummy packet is 64 bytes).
This bandwidth consumption can be considered neg-
ligible.
5.2 Case 2: Marked Packet Loss
In this case, we assume that certain marked IP pack-
ets, missing message packets and alive message pack-
ets are lost in the network. This case is similar to ex-
ample 4 in section 4.4.
Both the DR and backup DR are operating nor-
mally. However, the original OSPF and proposed
method determine that the DR and backup DR have
stopped the OSPF operation, because hello packets
and marked IP packets are lost.
In the case of the original OSPF, both the DR
DCNET2012-InternationalConferenceonDataCommunicationNetworking
20
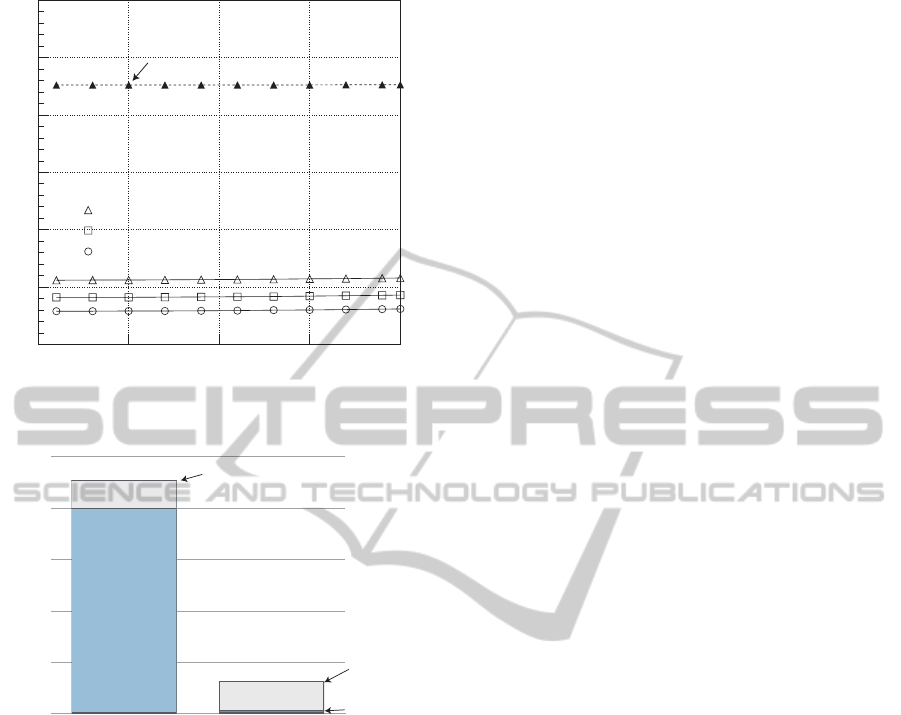
0 100 200 300 400
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Number of OSPF routers
Path reroute processing time (sec)
Original OSPF
Proposal method (arrival interval time of IP Packet : 1 sec)
Proposal method (arrival interval time of IP Packet : 0.5 sec)
Proposal method (arrival interval time of IP Packet : 0.1 sec)
Figure 11: Path reroute processing time for case 2.
0
10
20
30
40
50
original OSPF Proposal method
Router Dead
Interval
LSA processing time (0.001sec)
Hello processing time (0.02sec)
SPF Calculation,
SPF Delay
LSA processing time (0.001sec)
DR failure
detection time
(0.603sec)
SPF Calculation,
SPF Delay
Path reroute processing time (sec)
Figure 12: The details of path reroute processing time for
case 2. (Number of OSPF routers is 400).
and backup DR are elected among OSPF routers af-
ter Router Dead Interval and the path table is recon-
structed.
In the case of the proposed method, some neigh-
bors cannot detect either the DR or backup DR. How-
ever, there are many OSPF routers (neighbors) and all
routers monitoring the marked IP packets. We can-
not assume that all marked IP packets are lost. Thus,
neighbors can receive some marked IP packets and
multicast alive message packets. Also, we assume
that some alive message packets can reach neighbors,
if some alive message packets are lost. Neighbors
which receive alive message packets send the LSA
packets to the DR and reconstruct the routing table.
In the case of the proposed method, the DR election
process is omitted, because the neighbor can confirm
that the DR is alive.
The Fig 11 shows the results of the path reroute
processing time for the original OSPF and proposed
method in this case and Fig 12 shows the detail of
results. We confirm that our proposed method can
reduce the path reroute processing time, because it
avoids Router Dead Interval.
6 RELATED WORK
There have been several approches and proposals for
the network failure detection method on OSPF net-
works. OSPF has the complex processing algorithms
and many factors of processing delay to recover the
link failure. There are mainly 2 kinds of delay type.
One is compute part, such as generation of routing
and forwarding tables, processing hello packets or
link state packets (LSP) and so on. The other is wait
or time out part, such as SPF hold delay, Router Dead
Interval and so on. The main cause of former type is
CPU load. But the newest OSPF routers are equipped
high performance CPU and this case should be ne-
glected(Goyal, 2003). The latter comes from OSPF
algorithms and parameters. Thus, OSPF algorithms
and parameters should be modified to achieve the fast
failure recovery. First, the simple way is that the value
of wait timer is reduced. In paper (Basu and Riecke,
2001), authors analyzed the effect of Hello Interval
parameter reduction and reported 275ms to be an op-
timal value for providing fast failure detection while
not resulting in too many route flaps due to frequent
timeouts. However, this paper did not consider the
network congestion and topology characteristics.
The paper (Goyal, 2003) examined the Hello In-
terval considered the network congestion and topol-
ogy characteristics. The authors claimed that the op-
timal value for Hello Interval is strongly influenced
by the expected congestion levels and the number of
links in the topology. The simulation results indicated
that Hello Interval under 10 seconds leads to increase
the frequency of false alarms which are generated if
the Hello message gets queued behind a huge burst of
LSAs and can not be processed in time. Although the
false alarms can be suppressed by the RED mecha-
nism which can suppress the network congestion, it is
difficult to set the suitable parameters of RED mecha-
nism for the network traffic characteristics in general.
The Paper (Yuichiro Hei and Hasegawa, 2007)
proposed a method of OSPF failure identification
based on LSA flooding analysis taking these aspects
into account. This aproach works suitable on OSPF
networks. Also, the paper (Nelakuditi et al., 2007)
proposed the failure insensitive routing (FIR). This
proposal method is proactive routing approach and
computes interface - specific forwarding and back-
warding tables for link failures. When this method de-
StudyonaFastOSPFRouteReconstructionMethodunderNetworkFailures
21

tects link failures, it can avoid link failures and reroute
effectively. However, if the OSPF on a router ceases
the operation or the L2 link failures (in this case, net-
work topology contains L2-network), these proposed
method cannot detect those failures and avoid Router
Dead Interval.
7 CONCLUSIONS
We proposed a fast DR failure detection mechanism
for OSPF to reroute paths when the DR has ceased
operation. The original OSPF uses hello packets to
detect DR failure, but it takes Router Dead Interval.
Our new DR failure detection mechanism substitutes
user IP packets for the hello packets to avoid Router
Dead Interval.
Our proposed method involves the 2 processing
procedures for network facility failures. We evaluated
it in each case on the typical OSPF network models
and results showed that our proposed method can re-
duce the path reroute processing time, due to avoiding
Router Dead Interval. Our proposed method is very
effective in rerouting paths when the DR and backup
DR fails.
In this paper, we showed the results by the calcu-
lating the sum of processing the time according to the
original algorithms and the proposed method. We will
install our proposed method on a test OSPF router and
evaluate the performance in the event of network fail-
ure.
REFERENCES
Basu, A. and Riecke, J. (2001). Stability issues in ospf rout-
ing. In Proceedings of the 2001 conference on Ap-
plications, technologies, architectures, and protocols
for computer communications, SIGCOMM ’01, pages
225–236, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
CISCO Systems, I. (2007). Troubleshooting the routing
protocols : Rst-3901. In Cisco Networkers.
Goyal, M. (2003). Achieving faster failure detection in ospf
networks. In in Proceedings of the International Con-
ference on Communications (ICC), pages 296–300.
Jacobson, V. (1988). Congestion avoidance and control.
Computer Communication Review, 18(4):314–329.
Jacobson, V. (1990). Berkeley tcp evolution from 4.3-tahoe
to 4.3-reno. In in Proceedings of the Eighteenth Inter-
net Engineering Task Force, page 365.
Moy, J. T. (1998a). OSPF: Anatomy of an Internet Routing
Protocol. Addison-Wesley Professional.
Moy, J. T. (1998b). Ospf version 2. Request For Com-
ments (Standard) RFC 2328, Internet Engineering
Task Force.
Nelakuditi, S., Lee, S., Yu, Y., li Zhang, Z., nee Chuah, C.,
and Member, S. (2007). Fast local rerouting for han-
dling transient link failures. IEEE/ACM Trans. Net-
working, 15:359–372.
Stevens, W. R. (1994). TCP/IP Illustrated, Volume 1 : Pro-
tocols. Addison Wesley Longman.
Yuichiro Hei, Tomohiko Ogishi, S. A. and Hasegawa, T.
(2007). Ospf failure identification based on lsa flood-
ing analysis. In 10th IFIP/IEEE International Sympo-
sium on Integrated Network Management (IM), 2007,
pages 717–720.
DCNET2012-InternationalConferenceonDataCommunicationNetworking
22
