
Some Remarks on Keystroke Dynamics
∗
Global Surveillance, Retrieving Information and Simple Countermeasures
Marek Klonowski, Piotr Syga and Wojciech Wodo
Faculty of Fundamental Problems of Technology, Wrocław University of Technology, Wrocław, Poland
Keywords:
User Identification, Keystroke Dynamics, Digraphs, Distribution, Impersonation.
Abstract:
In this paper we discuss some security issues related to keystroke dynamics. Up to now these methods have
been used mainly for supporting authentication protocols. We point out that they can be also used against
privacy and potentially lead to some other malicious behavior like for example impersonation. We also present
some simple fairly realistic and usable countermeasures. We discuss fundamental issues about efficient and
accurate representation of user’s profile in keystroke dynamic methods. More precisely, we discuss statistics
of so–called timings used for building user’s profile. We give some observations about distributions of timings
that substantially differ from assumptions used in numerous papers. Some of our theories are supported by
experimental results.
1 INTRODUCTION
Keystroke dynamics is one of the methods used
mainly for behavioral biometric authentication. Being
behavioral, thus more variable and less dependable,
biometric keystroke dynamics it is commonly used as
a secondary security mechanism typically with pass-
word authentication. This method requires no addi-
tional infrastructure and authentication is possible re-
motely. In our paper we discuss this behaviometrics
methods from a different perspective – we point out
some possible threats as well as some related issues
including representation of individuals’ profiles.
Our Contribution and Organization of the Paper.
In the rest of this section we recall some related re-
sults. Section 2 is devoted to description of possible
risks brought by keystroke methods. In Section 3 we
describe a number of issues related to representation
of user’s profiles - in particular we analyze statisti-
cal properties of so–called timings of n-graphs used
commonly as characteristic of individuals. We sup-
port some our conjectures with experimental results.
In Section 4 we outline several simple protocols for
protecting privacy and preventing impersonation-type
attacks. We conclude in Section 5.
∗
This research was partially supported by NCN/M-
NiSW scientific project 2010-2013 - grant number N N206
369839.
Related Work. There is a long list of papers as
well as implementations based on keystroke dynam-
ics. To the best of our knowledge in (Gaines et al.,
1980) authors presented their study about typing pat-
terns for the first time. However, these observations
were not used in the context of behaviometrics un-
til the seminal paper (Joyce and Gupta, 1990), when
authors presented their algorithm to measure laten-
cies of pressing keys during typing and comparing
it with previously stored information. In (Cho and
Hwang, 2006) authors suggest using artificial rhythm
of typing and long pauses between some characters
to enhance security and in (Revett et al., 2007) au-
thors use neural networks to improve classification
accuracy. In (Bergadano et al., 2002), followed by
(Zhang et al., 2006) a method of continuous iden-
tification is proposed, where user’s activity is con-
stantly monitored and thus their typing latencies have
to be predicted. In (Stefan et al., 2012) authors make
first attempt to implement software protecting from a
bot attacker. Many further references can be found
in (Chudá and Durfina, 2009; Revett, 2009). Prac-
tical use of keystroke data has been implemented in
BioPassword (BioPassword Inc., 2007) an authentica-
tion system that employs most of current knowledge.
296
Klonowski M., Syga P. and Wodo W..
Some Remarks on Keystroke Dynamics - Global Surveillance, Retrieving Information and Simple Countermeasures.
DOI: 10.5220/0004072602960301
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT-2012), pages 296-301
ISBN: 978-989-8565-24-2
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 GLOBAL RISK
In this section we point out some risks related to
methods of keystroke dynamics. Two main risks we
have in mind are
• Privacy threat - the individual can be recognized
against their will.
• Impersonation - someone can collect the biomet-
ric data and pretend to be a particular individual.
To the best of our knowledge those problems were
not addressed in literature except the paper (Stefan
et al., 2012), wherein authors study the threat of im-
personating user by a bot. Note that the privacy threat
is not limited to biometric authentication systems. In-
deed, collected data in one system can be used to rec-
ognize the user in other systems. Generally, such
attacks seem to be applicable to all biometric sys-
tems, however there are some peculiarities that in-
crease the risk that one can be recognized by char-
acteristic keystroke dynamics. Among most notable
risks are the following:
• data about keystroking of individuals can be col-
lected over long period of time leaving user un-
aware of such process;
• keyboards are still a very important and most
common computer interface device; most popu-
lation in many countries use systems with a key-
board to perform many operations including com-
munication, entertainment or various e-service;
• the users may unwittingly be susceptible to data
collection by various kinds of keyloggers while
performing their regular tasks;
• simple and compact data representation, results
in ease of collecting and storing the information
about keystroke patterns (i.e. profiles of users) for
huge number of individuals for a long time;
• collecting as well as storing information does not
require any significant resources.
• to some extent, historical data can be used for a
long time. More precisely, to launch an attack the
adversary may use data much older than the secu-
rity mechanism that they try to by-pass.
Another fact that has to be underlined is that iden-
tification using keystroke dynamics can be at least in
some cases carried out in a remote manner. When
using SSH1 protocol an eavesdropper can easily de-
rive inter-key times as every key-press generates data
package (see e.g. (Song et al., 2001)). Such attack
cannot be carried out easily using much more com-
mon nowadays SSH2. Nevertheless one cannot ex-
clude that similar attacks exist and can be exploited
while using other protocols.
Aforementioned facts make building user profile
quite realistic. Moreover users are potentially ex-
posed to profiling attacks on different systems. Then
his profile can be transfered and even if these destina-
tion systems employ some privacy protection means
his identity could be recovered. Let us stress that
we do not claim that such attacks can be realistic in
all cases. We do claim however that there are some
potential risks that should be investigated more care-
fully.
3 REPRESENTATION OF USER'S
PROFILE
In this section we discuss issues related to representa-
tion of a user’s profile in widely-understood keystroke
dynamic methods. User’s typing behavior is reflected
in several values. The most general values are so-
called timings, or delays that occur when pressing var-
ious keys. In the literature of the subject one can en-
counter dwell time – the time between events of key
down and key up, flight time – the time between press-
ing two consecutive keys. Two consecutive keys are
called digraph. By trigraphs we mean three consec-
utive keys and consequently we use term n-graphs to
describe n keys in a row.
One can easily see that timings for each digraph
for the same individual can differ - it is a random vari-
able. Collection of such random variables is a natural
representation of an individual. Below we give some
observations and experimental results about their dis-
tribution.
3.1 On Normality of Digraphs
In several papers there has been explicitly stated that
the flight time for each single digraph could be as-
sumed Gaussian (i.e., (Monrose and Rubin, 1997;
Sheng et al., 2005; Zhang and Wang, 2009)). Such
approach seems to be essentially unjustified. In fact,
to the best of our knowledge, there is no reason why
flight times could have normal distribution. In partic-
ular it is hard to use Central Limit Theorem in this
case. It should be stressed that in the paper (Sim and
Janakiraman, 2007) one can find a suggestion that the
distribution of flight times for digraphs is (in general)
not Gaussian. In this section we present some results
of statistical tests that say that digraph timings’ distri-
bution is not normally distributed.
Experimental Results. Let us start with method-
ological remarks. We have collected over 60 000 in-
dividual samples of digraphs with flight time in range
SomeRemarksonKeystrokeDynamics-GlobalSurveillance,RetrievingInformationandSimpleCountermeasures
297
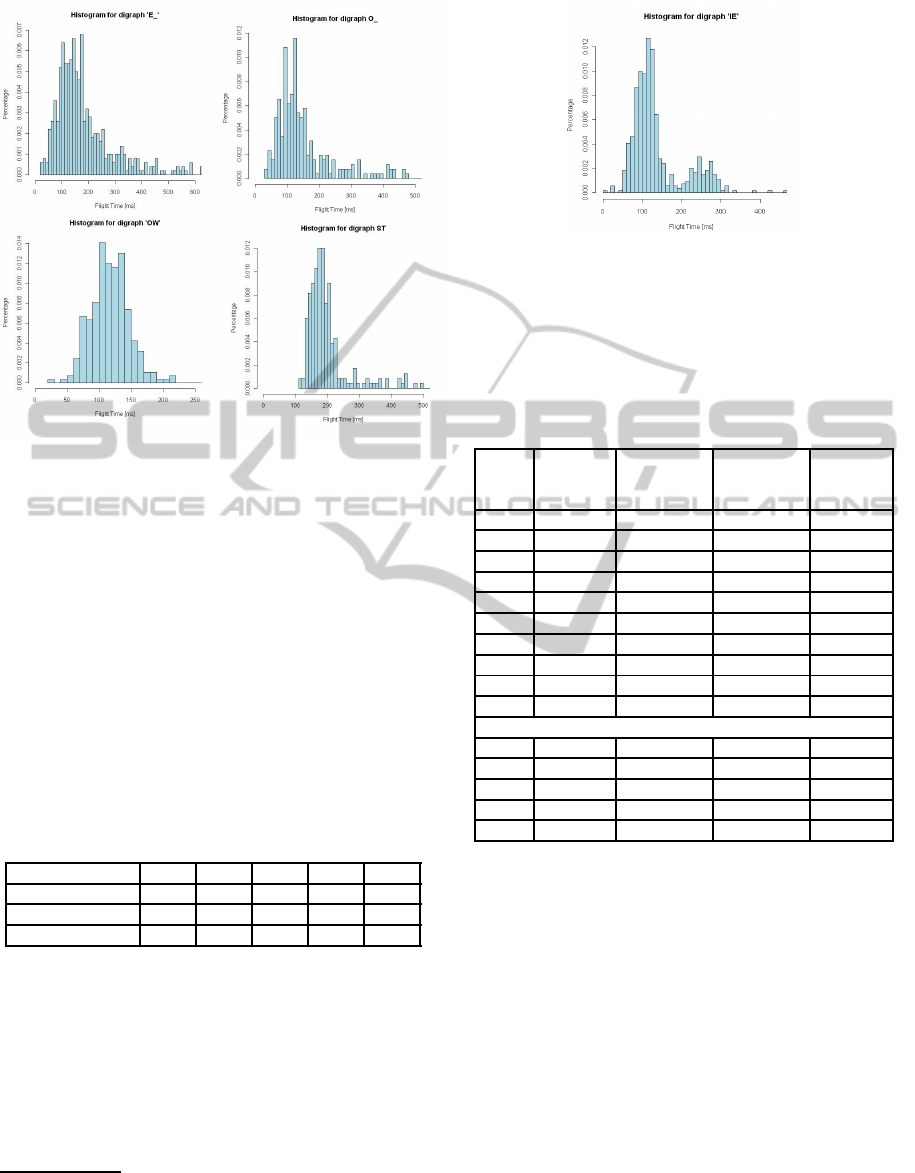
Figure 1: Distribution of flight time timing for digraphs
"OW", "E_", "ST", "O_".
from 21 up to 800 ms. We rejected samples which
include flight time greater than 800 ms treating them
as breaks in typing. Entire dataset was collected in a
controlled environment from trained typists, typing in
Polish as a native language
2
. The results are obtained
from form so-called free text – i.e., the data was col-
lected using special key-logger during regular work
of the typist. We believe that such approach reflects
real settings of keystroke dynamics.
Our first goal was to examine whether the distri-
bution of the digraphs is normal. For tests we chose
digraphs with largest amounts of collected data to ob-
tain reliable results.
Table 1: Occurrence of ten the most common digraphs.
Digraph IE E_ A_ NI _P
Occurrence[%] 2.12 1.96 1.71 1.67 1.30
Digraph OW ” ZE _O PO
Occurrence[%] 1.11 1.07 1.06 1.01 1.00
Below we present histograms for some of investi-
gated digraphs.
Even perfunctory analysis of histograms suggests
that the distribution of timings of digraphs is not nor-
mal. Indeed, in the case of some histograms one can
see that they are bi-modal (e.g., Figure 2). To pro-
vide more reliable evidence we performed normality
tests for ten most numerous digraphs. We used two
2
We believe that language does not affect the type of dis-
tribution and only parameters can be changed, provided that
this is a native-language of the typist (compare (Bergadano
et al., 2002)).
Figure 2: Distribution of flight time timing for digraph "IE".
tests: Lilliefors test (Lilliefors, 1967) and Shapiro -
Wilk (Shapiro and Wilk, 1965) The level of signifi-
cance is set to α = 0.05 (statistically significant). The
null hypothesis H
0
- flight time timings are normally
distributed is tested.
Table 2: Normality tests for some digraphs.
Graph Amount Test (p-val) Test (p-val) Rejection
of probes Shapiro- Lilliefors H
0
Wilk
ie 542 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
e_ 501 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
a_ 438 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
ni 426 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
_p 332 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
ow 284 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
” 273 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
ze 271 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
o_ 259 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
po 256 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
wa 170 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
do 152 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
ad 100 5.612e-15 < 2.2e-16 YES
io 64 8.741e-11 1.262e-14 YES
el 50 1.097e-08 3.228e-11 YES
Results presented in Table 2 allow us to safely reject
the hypothesis about normality of digraphs timings.
3.2 n-Graphs Approach
In the paper (Sim and Janakiraman, 2007) one can
find a very important observation – the distribution
of digraph flight times depends on their contexts (key
pressed before and after the digraph) and the longer
context is the more the shape of the histogram resem-
bles Gaussian distribution. In other words, this means
that n-graphs for n ≥ 3 should have distribution closer
to Gaussian.
In Fig. 3 a histogram for ie digraph is disunited in
histograms of contributing trigraphs.
Let us investigate Fig. 3. We can observe two
peaks: first over 100ms and the second around 250ms.
SECRYPT2012-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
298

Figure 3: Distribution of flight time timing for trigraphs in-
cluded in the digraph "IE".
One can conjecture that in general the distribution of
timings of a digraph xy would be a combination
3
of
some other, basic unimodal distributions defined as
follows:
X
xy
=
∑
pre,post
Y
pre||xy||post
1[Prefix = pre,Postfix= post]
Where Y
a
are from the same family of distribution,
however with different parameters depending on indi-
vidual user and particular string a. Note that 1[W] de-
notes an indicator function, i.e., it is equal 1 if asser-
tion W is true, otherwise it is 0. Such approach would
be coherent with observation from (Sim and Janakira-
man, 2007) and seems to be, at least to some extent,
justified. Indeed, typing a digraph for a fixed context
can be treated as an experiment that is repeated under
the same conditions. In such model close approxima-
tion of X can take into account only prefixes of length
1 - i.e., trigraphs.
It is not not clear, however, if Y
a
for different a’s
are Gaussian, at least for short context. One can ob-
serve that histograms of trigraphs have high skewness
that suggests that normal distribution is very unlikely.
Initial analysis suggests that this may be Lognormal,
Beta or Burr distribution, though due the small size of
dataset these experiments could not be very reliable.
We performed some tests and obtained following re-
sults given in Table 3.
Presented results are ambiguous – we cannot def-
initely reject any hypothesis about real distribution of
3
This is not a mixture of distribution.
Table 3: Normality tests for some trigraphs.
Graph Amount Test (p-val)Test (p-val)Rejection
of probes Shapiro- Lilliefors H
0
Wilk
nie 137 < 2.2e-16 < 2.2e-16 YES
wie 26 1.059e-06 0.0001074 YES
sie 44 2.354e-09 1.440e-09 YES
pre 51 0.06108 0.02186 NO
cji 42 0.9153 0.9535 NO
Table 4: Occurrence of all trigraphs forming the space of
"?IE".
Trigraph EIE BIE ZIE PIE KIE
Occurrence[%] 0.89 2.37 4.45 5.64 6.53
Trigraph MIE WIE CIE SIE NIE
Occurrence[%] 6.53 7.72 11.57 13.06 40.65
trigraphs since collected dataset is too small. Investi-
gating this problem as well as testing the conjecture
about the distribution remains future work.
Beyond n-Graphs. We believe that there is many
other data that can be used for recognizing particular
typist. One example is frequency of some character-
istic mistakes. Another rich source of information is
the usage of SHIFT key with digraphs containing a
key of double meaning (e.g. : / ; or " / ’).
Due to space limitation we do not present experimen-
tal results.
4 EFFECTIVE
COUNTERMEASURES
In this section we present methods that can, to some
extent, protect users from threats pointed out in Sec-
tion 2. The algorithms we present below relay on in-
terception of pressed keys and obfuscating real tim-
ings by injecting artificial delays. The defense meth-
ods should be planted on a level when modification
is possible before the attacker can intercept the data,
though basically they acts similar to keyloggers. We
can think about a hardware device installed on a key-
board’s plug or a special software controlling mes-
sages sent later thorough the network. One may argue
that in many distributed systems some delays occur
as side effects of realizing basic functionalities (e.g.,
SSH2). Nevertheless usually one cannot have any
control when we aim at providing mechanisms that
guarantee provable security.
The most challenging aim in designing security
mechanisms of that kind is to provide high level of
security without affecting significantly the usability
of the system. One can easily notice that idea behind
SomeRemarksonKeystrokeDynamics-GlobalSurveillance,RetrievingInformationandSimpleCountermeasures
299

our protocols leads to lags in communication, that can
significantly lower responsiveness of the system and
be unacceptable for users. This pertains in particular
to users working in an interactive mode.
All methods described below use a kind of buffer
and require access to precise time. Pressed keys are
stored in the buffer and are released with some pre-
cisely assigned delay, thus every key in the buffer
needs to have a special auxiliary data (a timestamp)
when the key was put into the buffer. Of course size
of the buffer should be possibly small. Nevertheless
limiting the size of the buffer is much less important
than limiting the delay.
4.1 Threshold-constant Time Delays
Method
The most obvious defense strategy is to withhold
sending keys so that all flight times would be per-
ceived as constant that is equal the longest observable
flight time over all digraphs. Such an approach cannot
be implemented directly, since in some cases Flight
Times can be extremely long (e.g., pause in typing).
In Algorithm 1 we obfuscate all timings up to a given
threshold. That is, ∆ is the threshold value beyond
which obfuscating ends.
Main Features. The proposed solution is very sim-
ple in implementation and does not require knowl-
edge of distribution of flight times. Moreover
changing the parameter ∆ regulates obfuscation/delay
threshold. Heuristic approach providing high level of
security would be setting ∆ = 800 ms. According to
some data revealed in (Monrose and Rubin, 1997) one
may expect that bulk of all digraphs fall to “obfus-
cated interval”. On the other hand, flight time of most
common in our data digraph ’IE’ is slightly larger
than 100ms, and other common digraphs have flight
time around 200ms. Thus the time of inserting the
message can be over 4 times longer. Moreover basic
observations of queuing theory suggests that one can
expect the required size of the buffer up to size equal
to the length of the input text. On the other hand, this
method provides very strong level of security - indeed
- most timings are totally obfuscated and the picture
seen by the adversary is oblivious. In effect, the ad-
versary gets no knowledge about the typist.
Algorithm 1 works best for consistent typists and
in a scenario where the user types short texts and in-
teraction is needed. It can be also considered for sys-
tems with texts of moderate size where delay is ac-
cepted.
Algorithm 1: Threshold-constant strategy.
Read Key
1
; Release Key
1
Read Key
2
; Release Key
2
if FlightTime(Key
1
,Key
2
) < ∆ then
FlightTime ← ∆
else
FlightTime ← FlightTime(Key
1
,Key
2
)
end if
4.2 Pool Buffer Method
For protecting user privacy in typing longer text one
may apply another strategy. Algorithm described in
this section follows two simple rules: gather and
flush. We ensure a large buffer of size n and in first
stage of algorithm, when the user types, algorithm
withholds the pressed keys until
n
2
slots are filled.
Starting at that point second stage begins and buffer
outputs stored data in short and constant time inter-
vals (e.g. 5 ms), simultaneously receiving new input
and storing it in the second half of the buffer. Note
that this approach is similar to some kinds of MIX
protocol used for protecting anonymity in communi-
cation (Serjantov and Newman, 2003).
Problem with short texts can be solved by fixing
a time parameter T depicting time period after which
we consider typing as completed. One solution is as
follows – when time since last key press is longer that
T, buffer, starting from current position up to
n
2
, is
filled with neutral symbol (i.e., NULL) and the proce-
dure continues until all positions from 0 to
n
2
contain
only neutral symbols. Of course choice of protocol
parameters n and T depends on particular scenario.
Main Features. One can easily see that security of-
fered by the protocol depends on parameter n. Instead
of timings T
1
,T
2
,. .., T
n/2
the adversary obtains only
their sum i.e., S = T
1
+ .. . + T
n/2
that provides sig-
nificantly less information. Generally security guar-
antees offered by this algorithm are lower than those
offered by algorithm described in 4.1, especially for
small buffer size n. However, this protocol clearly has
some unquestionablemerits - size of the buffer as well
as delay are strictly controllable and limited. More-
over some extremely long flight times are to some ex-
tent hidden. This can be important since very long
timings can provide significant information about dis-
tinctive behavior of individuals.
SECRYPT2012-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
300

4.3 Masquerade Method
Another approach is to replace the real flight time for
particular digraph XY by a random δ
XY
chosen ran-
domly from some distribution defined for XY. Such
approach not only hides real timings of the user but
also can pretend other individual. Similarly, this ap-
proach can be extended to n-graphs. The method of-
fers moderate delay and requires relatively long size
of the buffer.The main disadvantage is the need of
keeping distribution of the digraphs, which is quite
difficult as shown in Section 3.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we discussed several issues related to
keystroking biometric techniques. We pointed out
some potential risks with particular focus on privacy
threat as well as some simple countermeasures. We
believethat issues related to this area are generally un-
derestimated. In effect many fundamental questions –
theoretical as well as practical are left unanswered. In
particular there is no convincing and possibly exact
statistical model of timings of n-graphs. It is also not
clear which other information (e.g., mistakes in typ-
ing ) can be used for recognizing individuals.
We also see the need of providing much more ex-
perimental results about statistics that appear in our
paper. The volume of data we used allows us to test
only a few simple hypothesis e.g., about normality of
distribution of digraphs. With this respect, this pa-
per is a preliminary work revealing only a fraction of
problems in the area of profiling based on keystroke
dynamics.
REFERENCES
Bergadano, F., Gunetti, D., and Picardi, C. (2002). User au-
thentication through keystroke dynamics. ACM Trans.
Inf. Syst. Secur., 5(4):367–397.
BioPassword Inc. (2007). Authentication Solutions
Through Keystroke Dynamics. Technical report.
Cho, S. and Hwang, S. (2006). Artificial rhythms and
cues for keystroke dynamics based authentication. In
(Zhang and Jain, 2006), pages 626–632.
Chudá, D. and Durfina, M. (2009). Multifactor authentica-
tion based on keystroke dynamics. In Rachev, B. and
Smrikarov, A., editors, CompSysTech, page 89. ACM.
Gaines, R. S., Lisowski, W., Press, S. J., and Shapiro, N.
(1980). Authentication by keystroke timing: Some
preliminary results. Technical report, RAND Corpo-
ration.
Joyce, R. and Gupta, G. K. (1990). Identity authentica-
tion based on keystroke latencies. Commun. ACM,
33(2):168–176.
Lilliefors, H. W. (1967). On the kolmogorov-smirnov
test for normality with mean and variance un-
known. Journal of the American Statistical Associ-
ation, 62(318):399–402.
Monrose, F. and Rubin, A. D. (1997). Authentication via
keystroke dynamics. In Graveman, R., Janson, P. A.,
Neumann, C., and Gong, L., editors, ACM Conference
on Computer and Communications Security, pages
48–56. ACM.
Revett, K. (2009). A bioinformatics based approach to user
authentication via keystroke dynamics. International
Journal Of Control Automation And Systems, 7(1):7–
15.
Revett, K., Gorunescu, F., Gorunescu, M., Ene, M., de Mag-
alhães, S., and Santos, H. (2007). A machine learning
approach to keystroke dynamics based user authenti-
cation. J. Electronic Security and Digital Forensics,
1(1):55–70.
Serjantov, A. and Newman, R. E. (2003). On the anonymity
of timed pool mixes. In Gritzalis, D., di Vimercati, S.
D. C., Samarati, P., and Katsikas, S. K., editors, SEC,
volume 250 of IFIP Conference Proceedings, pages
427–434. Kluwer.
Shapiro, S. S. and Wilk, M. B. (1965). An analysis
of variance test for normality (complete samples).
Biometrika, 52(3/4):591–611.
Sheng, Y., Phoha, V. V., and Rovnyak, S. M. (2005). A par-
allel decision tree-based method for user authentica-
tion based on keystroke patterns. IEEE Transactions
on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B, 35(4):826–
833.
Sim, T. and Janakiraman, R. (2007). Are digraphs good
for free-text keystroke dynamics? In CVPR. IEEE
Computer Society.
Song, D. X., Wagner, D., and Tian, X. (2001). Timing anal-
ysis of keystrokes and timing attacks on ssh. In Pro-
ceedings of the 10th conference on USENIX Security
Symposium - Volume 10, pages 25–25, Berkeley, CA,
USA. USENIX Association.
Stefan, D., Shu, X., and Yao, D. D. (2012). Robustness
of keystroke-dynamics based biometrics against syn-
thetic forgeries. Computers & Security, 31(1):109–
121.
Zhang, D. and Jain, A. K., editors (2006). Advances in Bio-
metrics, International Conference, ICB 2006, Hong
Kong, China, January 5-7, 2006, Proceedings, vol-
ume 3832 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science.
Springer.
Zhang, K. and Wang, X. (2009). Peeping tom in the neigh-
borhood: Keystroke eavesdropping on multi-user sys-
tems. In USENIX Security Symposium, pages 17–32.
USENIX Association.
Zhang, S., Janakiraman, R., Sim, T., and Kumar, S. (2006).
Continuous verification using multimodal biometrics.
In (Zhang and Jain, 2006), pages 562–570.
SomeRemarksonKeystrokeDynamics-GlobalSurveillance,RetrievingInformationandSimpleCountermeasures
301
