
Natural Language Processing based Shape Grammar
Arus Kunkhet, Bernadette Sharp and Len A. Noriega
Faculty of Computing, Engineering and Technology, Staffordshire University,
Beaconside, Stafford ST18 0AD, U.K.
Abstract. Currently shape grammars are designed for static models and applied
in limited domains. They demand extensive user skills and cannot guarantee
aesthetic results. Although the current approaches to shape grammar produce
infinite designs the final designs lack context and harmony. The aim of this pa-
per is to address the contextual and harmonisation issues in shape grammar by
proposing a shape grammar framework inspired by the field of natural language
processing. The new shape grammar framework make use of the four levels of
analysis namely lexical, syntactic, semantic, and pragmatic levels, to enhance
the overall design process. In satisfying these semantically and pragmatically
well-formed constraints, the generated shapes can be contextual and harmoni-
ous.
1 Introduction
Design is defined as the process of creating new structures characterised by new pa-
rameters, aimed at satisfying specific requirements [17]. It consists of several phases,
namely the conceptual design, the detailed design, the evaluation and iterative rede-
sign [17]. For the past three decades, shape grammars have been mostly used to study
architectural design, paintings and product design [21]. In recent years the design
generation of harmonious characters began to play an important role in computer
graphics, computer games and animation [9], [16]; however manual generation of
such characters is expensive as it requires highly skilled designers [10]. Computation-
al approaches have been employed for all these stages of design except the creative
conceptual design phase. This phase of design is often considered as a “black art”
based on fuzzy design procedures and rules [8].
The theory of shape grammar, developed by Stiny and Gips [19], has provided a
methodology to formalise the design process based on the use of primitive shapes and
the transformation rules of geometric elements; however it is unable to handle organi-
sational and contextual information. In spite of the existence of design principles and
transformational rules shape grammar cannot guarantee aesthetic and harmonious
results [9]. This paper aims at demonstrating how Natural Language Processing
(NLP) can address these contextual and harmonisation issues in shape grammar by
adding context to the original three levels. To have a harmony in character design, the
four levels must be embedded in the generation engine. The Vocabulary of a shape
grammar is a lexicon consisting of points, lines, and planes. The Rules define a set of
syntactic structures which constrain the possible spatial and functional transfor-
Kunkhet A., Sharp B. and Noriega L..
Natural Language Processing based Shape Grammar.
DOI: 10.5220/0004085100150023
In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Natural Language Processing and Cognitive Science (NLPCS-2012), pages 15-23
ISBN: 978-989-8565-16-7
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

mations specific to the design object. The Derivation interprets these transformations
by a semantic model to ensure legitimacy, consistency and compatibility. The Con-
text, legitimate shapes and elements of the objects must adhere to certain contextual
properties and principles of the design to achieve harmony. This approach is validated
by applying it to the design of a family of humanoid characters, which are particularly
relevant to the domains of computer graphics and computer games.
2 The Definition of Harmony in Character Designs
Design is the process of transforming an initial set of requirements into the explicit
and complete specification of an object that fulfils those requirements [3]. A composi-
tion is harmonious when the interrelationships between its parts fulfil aesthetic requi-
sites or are mutually beneficial [15]. In music, harmony is the technical term for the
coincidence of three or more different pitches [20]. In Fine Arts, it means a union or
blend of aesthetically compatible components. In colour studies, harmonious colours
mean two or more colours seen together to produce a pleasing affective response [4].
In 3D character design, designers must combine elements, shapes, and personality to
create a new character. In order to generate harmonious characters, the interrelation-
ships between the colour, elements, shapes, and forms of the characters being de-
signed must fulfil some aesthetic requisites. As a principle of design, harmony refers
to a way of combining elements of art to accentuate their similarities and bind the
picture parts into a whole.
3 Shape Grammar
A shape grammar begins with a vocabulary of shapes (e.g. points, lines, planes or
volumes) and spatial relations between shapes [19] (Fig. 1). A shape is generated by
beginning with an initial shape and recursively applying various transformational
rules (e.g. shifting, mirroring and rotating) and shape operations (e.g. addition, sub-
traction) [11]. The main foundation of shape grammar lies in the clear understanding
of the diagrammatic and parametric rules. Both rules are found quite similar in their
principles; however they produce distinct results in different situations.
Diagrammatical shape grammar rules are based on a generic 2D diagram. The
process starts by applying a rule to a vocabulary, one rule at a time. The applied
rule(s) can be repeated several times. The structure is simple, as the vocabulary will
be formulated until the satisfied shapes are achieved. Diagrammatical shape grammar
is used in applications of pattern design, abstract painting and sculpture, and architec-
ture [11], [19], [7].
A Parametric Shape Grammar is an advanced form of shape grammars which al-
lows variation of parameters, for example changes in lines and angles of shapes [1].
The new vocabulary created by the rules is defined by parameters extending the pa-
rameter concept to all design elements. Being parametric, a greater variety of forms
can be created. Derivations can be used as a new vocabulary, and the process is re-
peated again to generate a new shape or form.
16

Parametric shape grammars offer more flexibility in modifying shapes compared
with diagrammatical shape grammar; they are used widely in applications such as
product design, industrial, architecture, urban design and engineering applications
[11]. However, parametric shape grammars can be difficult to implement because of
the increase in complexity of local design decisions and the increase in the number of
elements to which attention must be paid in task completion [22].
Although shape grammars are useful for generating a large variety of designs they
still operate in limited experimental domains and fall short in support for real designs
[5]. They are designed for static models [10] and demand high user skills [12]. They
use only rectilinear basic elements and are mostly limited to 2D spaces or primitive
3D shapes; they also lack support for high quality design such as complex 3D geome-
try and cannot guarantee aesthetic results [9]. Current research approaches are primar-
ily focused on the need to reduce the time-consuming design process and to allow
designers to concentrate on their design activities, such as evaluation of designs and
making design decisions [12]. However there is a greater need for a framework to
support the aesthetic aspects of design, ensuring that the final design products are
harmonious and contextually relevant to the technical requirements. These issues have
led us to investigate the field of natural language processing as a potential solution.
Fig. 1. Shape Grammar Basic Stages.
4 Natural Language Processing based Shape Grammar
Natural language processing (NLP) aims at developing a computerised approach to
text analysis by applying both, a set of theories and of a set of technologies [13]. The
traditional approach is to translate the utterances into a formal specification that can
be processed further by the computer. In linguistic terms, NLP consists of six levels
(Fig 2). The first two levels deal with phonology and morphology of words. The lexi-
cal level focuses on the meaning of words and their part(s)-of-speech (e.g. determiner,
noun, and verb). The syntactic level is concerned with analysing the words in a sen-
tence and uncovering its grammatical structure. The output of this level of processing
is a representation of the sentence revealing the structural dependency relationships
between the words. The semantic processing level determines the possible meanings
of a sentence by focusing on the interactions among word-level meanings in the sen-
tence [2]. For example, amongst other meanings, ‘file’ as a noun can mean either a
folder for storing papers, or a tool to shape one’s fingernails, or a line of individuals
17

Fig. 2. Natural Language Processing Levels.
in a queue. To disambiguate the meaning of polysemous words this requires consider-
ation of the local context, which is the task of the pragmatic level making use of
knowledge of the domain. We believe that this approach can be extended to the theory
of shape grammars, focusing on the last four levels in particular. Primitive shape
vocabulary can be assembled together using the shape grammar rules to form a new
design in the same way as lexical items can be combined using natural language
grammar rules to form a well-formed sentence. The semantic level can provide a solid
framework to assign meaning to the new design while the pragmatic level can focus
on the context and harmony of the final design outcome (Fig 3).
Fig. 3. Natural Language Processing Based Shape Grammar Framework.
The proposed new framework extends the traditional shape grammar by adding
context to the original three levels, namely Vocabulary, Rules, and Derivation (Fig.
3). To have a harmony in character design, the four levels must be embedded in the
generation engine. The Vocabulary of a shape grammar is a lexicon consisting of
points, lines, and planes. The Rules define a set of syntactic structures which constrain
the possible spatial and functional transformations specific to the design object; these
transformations will be interpreted by a semantic model embedded in Derivation to
ensure legitimacy, consistency and compatibility. In Context, legitimate shapes and
elements of the objects must adhere to certain contextual properties and principles of
the design to achieve harmony.
The proposed framework is validated by applying it to generate a set of harmo-
nised humanoid characters. According to Oxford dictionary, a humanoid is defined as
“a being resembling a human in its shape”. In our research we define a humanoid as a
being having human form or human characteristics. In the design of humanoid char-
acters one has to take into consideration the concept of the uncanny valley studied by
Mori who argues that near-humanlike robots/characters can appear strange [14]. The
appearance of these characters can be very close to a human but not fully so that they
18

do not evoke a very negative human reaction [18]. In our research the user can define
the humanoid morphology to suit the specified application; this morphology is cap-
tured in terms of ontology and embedded into the NLP shape grammar.
Duffy [6] argues that the anthropomorphic features, such as a head with eyes and a
mouth may facilitate social interaction and therefore are important. Consequently, our
experimental approach focused on designing humanoid characters that can provide a
positive relationship between how human characters must look like and how comfort-
able users are with their appearance. The humanoid characters must perform functions
similar to those of human workers and appear human like consisting of a head, two
arms, two legs, and a torso.
With this in mind the new shape grammar framework includes an ontological rep-
resentation of what constitutes a humanoid character in its lexical, syntactic, semantic
and pragmatic levels of analysis (Fig.4). The goal is to achieve context and harmony
by capturing the morphology, function and organisation of the humanoid world as
well as the hierarchical and contextual relationships among the characters. Conse-
quently, the lexical level consists of the primitive geometrical shapes (e.g. polygon
sphere and cube) whereas the syntactic level applies spatial and emergent transfor-
mation rules to manipulate these shapes in agreement with the ontological definition
of a humanoid body. For example, the syntactic rules manipulate the polygon sphere
to design the head and the cube to create the torso, arms and legs, The assembling of
these design components are then refined by the semantic level, acting as the deriva-
tion phase, and dictating their spatial relations, size, weight and height, function and
habitat. The generated humanoid character has to be harmonious with other members
of the humanoid family, in terms of its morphology, attributes, and personality. The
pragmatic level ensures that the final humanoid character design meets aesthetic crite-
ria, context, and harmony in agreement with the design principles. For example con-
text focuses on cohesion and coherence of humanoid features, the combination of
various elements to emphasise similarities with other humanoid characters and bind
the picture parts into a whole.
Fig. 4. Humanoid Shape Grammar.
19

4.1 Implementation and Discussion
The NLP based shape grammar is implemented using Maya Embedded Language
(MEL) which is a scripting language commonly used in three-dimensional computer
design software. As depicted in Fig. 5, the lexicon level starts with the two primitive
vocabulary shapes, namely a 3D representation of a polygon sphere and a polygon
cube. The syntax level is implemented using rules which manipulate the primitive
shapes to create the basic morphological body components of a humanoid (e.g. head,
limbs, torso). This level ensures that these components are cohesive and coherent and
adhere to the defined morphology captured by an ontological representation (Fig.6).
The head, body and limbs are generated using the spatial and emergent transfor-
mations grammar rules. For example, a head must be attached to a body not to limbs
whilst limbs can be attached to a body but not to a head, and the size of the head must
be proportional to the body. The semantic level applies the rules relevant to the habi-
tat and associated functions; for example a terrestrial humanoid requires legs to walk
whilst an aquatic character needs fins to swim. A further set of rules specify how to
arrange these limbs (e.g. vertically for biped for terrestrial characters and horizontally
for aquatic characters). The pragmatic level focuses on context and harmony and
assigns morphological characteristics associated with a specific type of behaviour and
personality (e.g. aggressive vs. friendly). For example, an aggressive humanoid char-
acter may be oversized and exhibit scars and deep wounds on his torso whilst a
friendly humanoid is always smiling and gentle. Context and harmony are also
achieved through appropriate selection of attributes such as colour scheme, texture,
and material as dictated by the design principles (Fig 5). At the end of this level a
contextual and harmonious set of humanoid parents are designed.
Applying the traditional shape grammars the derivation rules can produce 332,640
different shapes, however these shapes are randomly generated and consequently lack
context, harmony and meaning. The proposed novel shape grammar provides a ro-
bust framework to generate shapes according to specific desired requirements and in
agreement with an ontological representation. This shape grammar produces the first
generation of humanoid characters with specific characteristics which will be manipu-
lated by a genetic programming algorithm to generate the second and future genera-
tion of humanoid characters.
5 Conclusions
This paper has described a novel approach to shape grammar design by applying the
natural language processing levels of analysis to address the lack of context and har-
mony in design. To validate the approach the new shape grammar is applied to the
design of a set of harmonious humanoid characters which can be deployed in comput-
er games, computer graphics and animations. This paper has described the first stage
of this research project which is aimed at developing the extending the basic shape
grammar. The current work has developed the ontological structure capturing the
morphology of the humanoid characters and has implemented the three levels of natu-
ral language processing, namely lexical, syntactical and semantic levels in the design
of humanoid characters. The next stage will require the implementation of the prag-
20
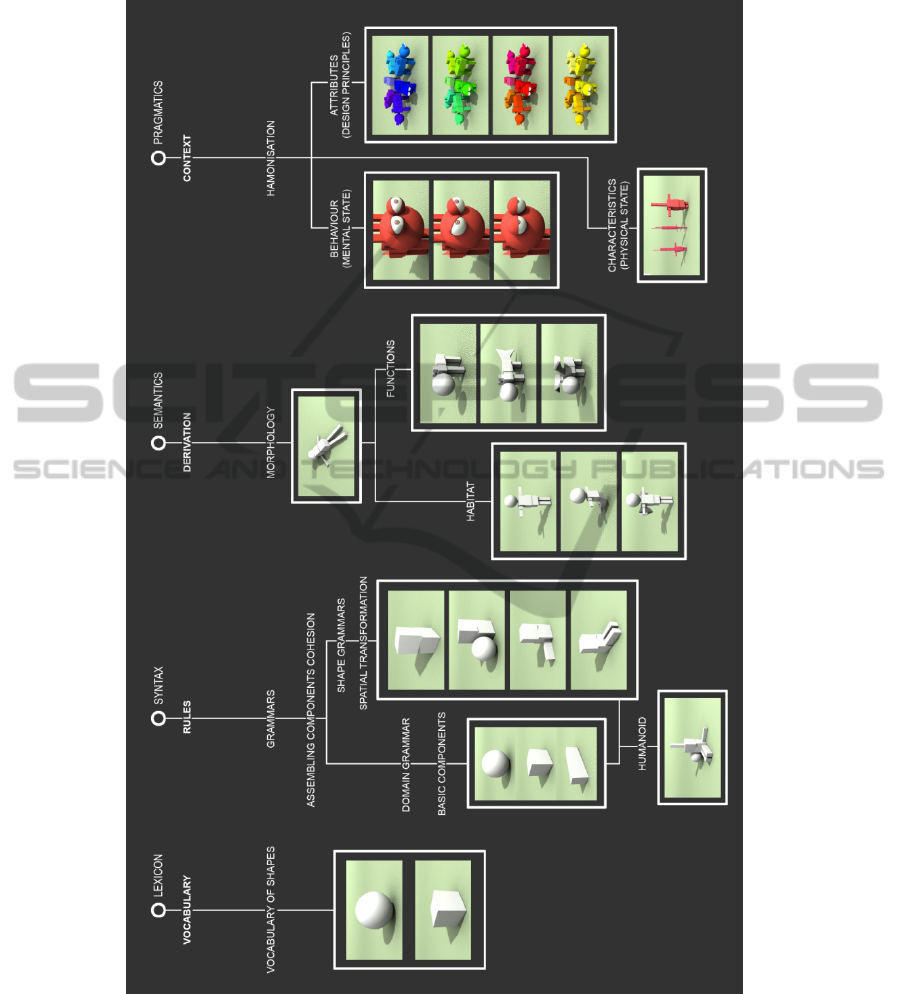
Fig. 5. Humanoid Shape Grammar using Maya MEL scripts.
matic level which involves the creation of a family of harmonious humanoid charac-
ters and the generation of offspring; this stage will focus not only on the interrela-
21

Fig. 6. Ontological representation of humanoid character.
tionships between colours, texture, and material but also on their personality, behav-
iour and attributes. It is proposed to augment the framework with genetic algorithms
to produce the next generations to ensure that the aesthetic components are compati-
ble and can bring a realistic feeling of belonging to the same world or story, and can
combine design elements to accentuate similarity and bind parts into a whole.
Acknowledgements
The work has been supported by both, the Chiang Mai University and Staffordshire
University.
References
1. Agarwal, M. and Cagan, J. (1998) A Blend of Different Tastes: The language of coffee
makers, Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, vol. 25, no.2, pp. 205-226.
2. Allen, J. (1995) Natural Language Understanding, University of Rochester, The Benjamin
Cummings Publishing Company, Inc., Redwood City.
3. Brown, K. (1997) Grammatical Design, AI in design, University of Aberdeen, March-April,
pp. 27-33.
4. Burchett, K. E. (2002) Colour Harmony, Colour Research and Application, vol. 27, Issue 1,
pp. 28-31.
22

5. Chau, H. H., Chen, X., McKay, A. and Pennington, A. (2004) Evaluation of a 3D Shape
Grammar Implementation, JS Gero, Ed., Design Computing and Cognition’04, pp. 357-
376.
6. Duffy, B. R. (2003) Anthropomorphism and the Social Robot, Robotics and Autonomous
System, vol. 42, pp. 177-190.
7. Flemming, U. (1987) More than the sum of its parts: the grammar of Queen Anne houses,
Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, vol. 14, pp. 323-350.
8. Goldberg, D. E. and Rzevski, G. (1991) Genetic algorithms as a computational theory of
conceptual design, Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Engineering VI, pp. 3-16.
9. Huang, J., Pytel, A., Zhang, C., Mann, S., Fourquet, E., Hahn, M., Kinnear, K., Lam, M.
and Cowan, W. (2009) An Evaluation of Shape/Split Grammars for Architecture, Research
Report CS-2009-23, David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science, University of Water-
loo, Ontario.
10. Ilčík, M., Fiedler, S., Purgathofer, W. and Wimmer, M. (2010) Procedural Skeletons: Kin-
ematic Extensions to CGA-Shape Grammars, SCCG, Budmerice, May 13, 2010.
11. Lee, H. (2006) The Development of Parametric Shape grammars Integrated with an Interac-
tive Evolutionary System for Supporting Product Design Exploration, PhD Thesis Project,
Industrial Design, Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
12. Lee, H. C. and Tang, M. X. (2009) Evolving Product Form Designs Using Parametric Shape
Grammars Integrated with Genetic Programming, Artificial Intelligence for Engineering De-
sign, Analysis and Manufacturing, Cambridge University Press, vol. 23, pp. 131-158.
13. Liddy, E. D. (2001) Natural Language Processing, In Encyclopaedia of Library and Infor-
mation Science, 2
nd
Ed., NY., Marcel Decker, Inc.
14. Mori, M. (1970) Bukimi no Tani [The Uncanny Valley] (K. F. MacDorman and T. Minato.
Trans.) Energy, 7(4), pp. 33-35.
15. Nitzberg, K. (2008) Traveling Through Time and the Consideration of Design, Smithsonian
Cooper-Hewitt, National Design Museum.
16. Preda, M., Salomie, I. A., Preteux, F. and Lafruit, G. (2005) Virtual Character Definition
and Animation within the MPEG-4 Standard, 3D Modelling and Animation: Synthesis an-
dAnalysis Techniques for the Human Body, IRM, Sarris N., Strintzis, M.G., Ed.
17. Renner, G. and Ekrárt, A. (2003) Genetic algorithms in computer aided design, Computer-
Aided Design, vol. 35, pp. 709-726.
18. Scheider, E., Wang, Y. and Yang, S. (2007) Exploring the Uncanny Valley with Japanese
Video Game Characters, Tokyo: The University of Tokyo, September, 2007, pp. 546-549.
19. Stiny, G. and Gips, J. (1972) Shape Grammars and the Generative Specification of Painting
and Sculpture, Proceedings of IFIP Congress, vol. 71, pp. 1460-1465.
20. Toch, E. (1977) The Shaping Forces in Music: An Inquiry into the Nature of Harmony –
Melody – Counterpoint – Form, Dover publications, Inc., New York.
21. Trescak, T., Esteva, M. and Rodriguez, I. (2009) General Shape Grammar Interpreter for
Intelligent Designs Generations, Sixth International Conference on Computer Graphics,
Imaging and Visualisation, cgiv, pp. 235-240.
22. Woodbury, R. (2010) Elements of Parametric Design, Routledge, New York.
23
