
Feature-based Ontology Mapping from an Information
Receivers’ Viewpoint
Fumiko Kano Glückstad
1
and Morten Mørup
2
1
Copenhagen Business School, Dept. of International Business Communication,
Dalgas Have 15, DK-2000 Frederiksberg, Denmark
2
Technical University of Denmark, DTU Informatics, Section for Cognitive Systems,
Richard Pedersens Plads, DK-2800 Kgs Lyngby, Denmark
Abstract. This paper compares four algorithms for computing feature-based
similarities between concepts respectively possessing a distinctive set of
features. The eventual purpose of comparing these feature-based similarity
algorithms is to identify a candidate term in a Target Language (TL) that can
optimally convey the original meaning of a culturally-specific Source Language
(SL) concept to a TL audience by aligning two culturally-dependent domain-
specific ontologies. The results indicate that the Bayesian Model of
Generalization [1] performs best, not only for identifying candidate translation
terms, but also for computing probabilities that an information receiver
successfully infers the meaning of an SL concept from a given TL translation.
1 Introduction
Accelerated by the recent internet revolution with its fast-paced globalization, cross-
cultural communication, e.g. between an Asian and a European, becomes inherently
challenging due to the lack of sufficient linguistic resources directly bridging remote
languages. This challenge is not only caused by the lack of linguistic resources, but
also by differences in human perception of similar concepts existing in diverse socio-
cultural communities. The MONNET on Multilingual Ontologies for Networked
Knowledge project [2] and the KYOTO project on Knowledge-Yielding Ontologies
for Transition-based Organization [3] are some typical major projects that deal with
such multilingual issues based on ontological methodologies. The approaches taken in
these major research projects are thoroughly analyzed in [4] based on three
dimensions: international (standardized) vs. culturally-influenced domains; functional
(conceptual) vs. documental (lexical) localization; and finally interoperable vs.
independent ontology. The work presented here challenges this multilingual issue by
mapping independent ontologies from a culturally-influenced domain in a functional
manner. The work is part of an overall framework for investigating how background
knowledge possessed by a Source Language (SL) communicator and a Target
Language (TL) reader should be represented and linked in light of various cognitive
processes involved in cross-cultural communication. Background knowledge is
considered as the average domain knowledge possessed by average citizens in a
Kano Glückstad F. and Mørup M..
Feature-based Ontology Mapping from an Information Receivers’ Viewpoint.
DOI: 10.5220/0004088200340043
In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Natural Language Processing and Cognitive Science (NLPCS-2012), pages 34-43
ISBN: 978-989-8565-16-7
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

specific socio-cultural community and assumed to be represented as domain ontology.
We employ a knowledge representation method known as Terminological Ontology
(TO) [5] by constructing two culturally-dependent TOs respectively representing the
Danish- and the German educational systems. A specific purpose is to identify the
most optimal algorithm of mapping culturally-influenced domain knowledge existing
in two cultures using taxonomically organized hierarchical feature-structures obtained
from these TOs. A candidate algorithm is the so-called Bayesian Model of
Generalization (BMG) [1], a novel cognitive model that considers the hierarchical
feature-structure as prior knowledge of an SL communicator or a TL audience,
depending on the assignment of variables to be explained in next section. More
specifically, the BMG computes asymmetric (uni-directional) similarities based on
feature values either from an SL communicator- or a TL audience’s viewpoint by
considering the prior knowledge as cultural bias. The asymmetric coordination in
communication is also well illustrated in the Relevance Theory of Communication
[6]. Accordingly, the BMG is compared against Tversky’s set-theoretic model [7] that
has previously been tested in [8].
In Section 2, the similarity measures applied here are further explained in detail.
Section 3 describes an experiment applying four different feature-based similarity
measures to data-sets obtained from the TOs, respectively representing concepts in
the educational systems in Denmark and Germany. Section 4 discusses the analysis of
the results followed by conclusions in Section 5.
2 Feature-based Similarity Algorithms
The first three similarity measures are derived from Tversky´s ratio model. This
model is defined as follows [7]:
(
,
)
=1/[1+
∗
(
−
)
+∗
(
−
)
(
∩
)
]
(1)
In equation (1), X and Y, respectively, represent feature sets of objects x and y, and
is considered as additive function.(Y⋂X) represents common features present in both
Y and X, (Y-X) denotes distinctive features existing in Y but not in X, and (X-Y)
denotes distinctive features in X but not in Y. α and β are free parameters which
enables one to compute an asymmetric similarity relationship between object x and y.
Accordingly, three combinations of parameter values are assigned in the previous
study [8]: A) α=1 and
β
=1: which corresponds to the Jaccard Similarity Coefficient
[9] that represents a symmetric similarity relationship between object x and y; B) α=1
and
β
=0: which only computes distinctive features present in Y, not in X; and C) α=0
and
β
=1: which only computes distinctive features present in X, not in Y.
As briefly stated above, a key point is to clarify which variable is defined as a
concept in an SL- or a TL culture. According to Tversky [7], if sim(y,x) is interpreted
as the degree to which y is similar to x, then y is the subject to the comparison and x
is the referent. This definition should be applied to all three parameter settings
defined in here. Keeping this definition in mind, an additional key point is that
Tenenbaum & Griffiths [1] demonstrate that Tversky’s model C) is formally
corresponding to the following equation which forms the basis of the BMG explained
35

below. Equation (2) computes the conditional probability that y falls under C
(Consequential region) given the observation of the example x [1]. The consequential
region C in our work indicates the categorical region where a subject y belongs.
(
∈
|
)
=1/[1+
∑
(ℎ,)
:∈,∉
∑
(ℎ,)
:,∈
]
(2)
In equation (2), a hypothesized subset h is defined as the region where a concept
belongs to h, if and only if, it possesses feature k [1]. Thus, P(h, x) = P(x|h)P(h) in
equation (2) represents the weight assigned to the consequential subset h in terms of
the example x. Accordingly, the BMG - algorithm D) - is considered as a model
where the weight P(h, x) is - based on the strong sampling scheme defined in [1] -
specifically assigned to Tversky’s model C). The weight is defined as follows [1]:
(
|
ℎ)=
1
|ℎ|
∈ℎ
0ℎ
(3)
Here, |h| indicates the size of the region h [1]. In our work, the number of objects
possessing the k
th
feature in the referent ontology is considered as the size of the
region h. [1] explains that the prior P(h) is not constrained in their analysis so that it
can accommodate arbitrary flexibility across contexts. Hence in this work, we set
P(h) = 1. In the following experiments the BMG is compared against the three
parameter settings defined for Tversky’s Ratio model.
3 Experiment
3.1 Data Preparation
Data Source: The data-sets used in [8] have been used as original data sources. They
are based on document corpora obtainable from the Eurydice web-site published by
the Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency under the EU commission.
These documents describe the German- and Danish educational systems both in
English and in the original languages based on the ISCED classification. Hence, it is
feasible to identify terminological expressions in the original language from these
documents and eventually identify translation equivalences linking between German
and Danish. Hence, language-dependent terms and their definitions describing the
educational systems in the two cultures have manually been extracted from the
respective English corpora for developing TOs. The reason that these non-remote
European languages are employed in this work is that these documents are written in
accordance with the standardized template defined by the Eurydice, which may better
provide for a well controlled experiment for assessing the similarity measures.
One of the key principles for developing the TOs is that a concept automatically
inherits all feature specifications of its super-ordinate concepts [5]. A dimension of a
concept is an attribute occurring in a non-inherited feature specification of one or
more of its sub-ordinate concepts. The values of the dimension allow a distinction
among sub-concepts of the concept in question. For example, a dimension of the
concept “pre-primary education” is [AGE] whose values are [0-3 | 3-6]. These
36

dimension values distinguish the sub-concepts: “nursery” and “kindergarten”. The
dimension can only occur on sister concepts and a given value can only appear on one
of these sister concepts. In this way, a concept must be distinguished from each of its
nearest super-ordinate concepts as well as from each of its sister concepts by at least
one feature specification [5]. These principles enable us to generate well-structured
feature sets that are assumed to be useful for the feature-based similarity
computations. Tables 1 and 2 show examples of the expressed feature structures.
Table 1. Example of german data source (terms and feature sets).
ID Term Feature-values
G2 preschool education {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED0}
G5 kindergärten {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED0, child welfare, 3-6y.o.}
G7 schulkindergärten & vorklassen {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED0, preparation}
G10 primary education {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1}
G11 primary school {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1, <6-10y.o.<}
G13 secondary education { ISCED97, children & young, ISCED2+3}
G14 lower secondary level {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED2+3, <10-16y.o.<}
G15 school offering one single course {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED2+3, <10-16y.o.< , single}
G16 hauptschule {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED2+3, <10-16y.o.< , single , general basic, 5-9
th
grade}
G18 gymnasium {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED2+3, <10-16y.o.< , single, intensified, 5-12/13
th
grade}
G19 schools offering several courses {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED2+3, <10-16y.o.< , several}
Table 2. Example of danish data source (terms and feature sets).
ID Term Feature-values
D2 pre primary {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED0}
D4 kindergarten {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED0, 3-6y.o.}
D6 single structure {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2}
D7 alternative structure {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, alternative}
D8 home tuition { ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, alternative, compulsory, 6-16y.o}
D9 efterskole or youth school {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, alternative, compulsory, <14-18y.o.<}
D10 efterskole {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, alternative, compulsory, <14-18y.o.<, boarding school, approved
by state}
D11 youth school {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, alternative, compulsory, <14-18y.o.<, day-to-day, public
municipal council}
D14 municipal school {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, formal teaching, municipality}
D16 0-9
th
form {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, compulsory}
D17 0
th
form {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, compulsory, preparation}
D18 1-9
th
form {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, compulsory, general basic}
D19 10
th
form {ISCED97, children & young, ISCED1+2, optional}
Creation of Feature-term Matrices: In order to compute similarities, matrices
referring to the German- and Danish educational systems which, respectively, consist
of 58 and 52 terms are manually generated from the feature sets. Feature value
columns are defined in the following way:
1. All feature values existing in the Danish and German data sources are registered in
both matrices.
2. If feature values in the Danish and German matrices are completely overlapping
(e.g. “ISCED0-pre-primary” in DK and “ISCED0-pre-primary” in GE), the feature
columns in question should be merged into one column.
3. If a feature is possessed by a term, the numeric value should be “1”, otherwise “0”
in the matrices.
4. If a feature value in one matrix is completely included in a feature value in the
other matrix (e.g. “ISCED1+2” in DK and “ISCED1” in GE), a term possessing the
feature that includes the other feature (e.g. Danish “ISCED1+2”) should have numeric
value “1” in both feature columns (e.g. “ISCED1+2” in DK and “ISCED1” in GE). It
means that a term possessing a feature value that is included in the other feature (e.g.
37

German “ISCED1”) should have numeric value “1” only in the feature column in
question.
5. If feature values in the Danish and German matrices are partly overlapping (e.g.
“ISCED1+2” in DK and “ISCED2+3” in GE), a dummy column referring to the exact
overlapping feature value (e.g. “ISCED2” for both DK and GE) is created. In this
example, a Danish term possessing a feature “ISCED 1+2” should have numeric value
“1” in both “ISCED 1+2” and “ISCED2” columns, but not in the “ISCED2+3”
column.
In this way, we create the German matrix consisting of 58 terms x 117 feature values
and the Danish matrix consisting of 52 terms x 117 feature values.
3.2 Similarity Computation
The basic idea of similarity computation here is to identify a translation candidate
from concepts existing in a TL culture. Assuming that SL communicators and TL
information receivers have general conceptualization of culturally-dependent domains
- in this case the educational system in each country - all combinations of similarities
between TL- and SL terms are computed. When computing similarities based on the
three settings of Tversky’s model and the BMG described in Section 2, the variables:
“terms subject to comparison” and “referent terms” are consistently defined across the
four feature-based similarity algorithms: A) Tversky: α=1 and
β
=0 (Jaccard); B)
Tversky: α=1 and
β
=0; C) Tversky: α=0 and
β
=1; and D) the BMG.
3.3 Results
Figure 1 shows the most typical patterns of similarity scores obtained from the
aforementioned four algorithms from top to bottom: A), B), C), and D). Figure 1-a
indicates that algorithms A) and B) are relatively identical, showing that rather
general German terms, such as G2 and G46, score higher similarities. On the other
hand, algorithms C) and D) show that the terms from G2 to G9, all of which are
within the category of preschool education in Germany, score the highest. Especially,
the BMG clearly identifies the series of German preschool educations, all of which
are targeted for children under the school age categorized as ISCED0. Since - in the
simplified formulae of the BMG - the sum of distinctive features possessed by
referent (variable: x) but not subject to comparison (variable: y) and common features
possessed by both x and y become denominator, the eventual score results in the value
“1”. From a communicator’s viewpoint, it is reasonable to consider that, based on
prior knowledge of Danish SL concepts, all the German TL terms that possess feature
ISCED0 targeted for children under the school age are categorized as objects
belonging to D2.
In Figure 1-b, algorithm B) identifies general German terms such as G1, G2 and
G46 as the most similar terms to D4: kindergarten. On the other hand, all other
algorithms indicate that term G5: “kindergärten” has the highest similarity in terms of
D4. Especially, the BMG clearly points out this implication selecting G5 as the most
similar concept to D4, because the size principle weights the feature value, “3-6 years
38
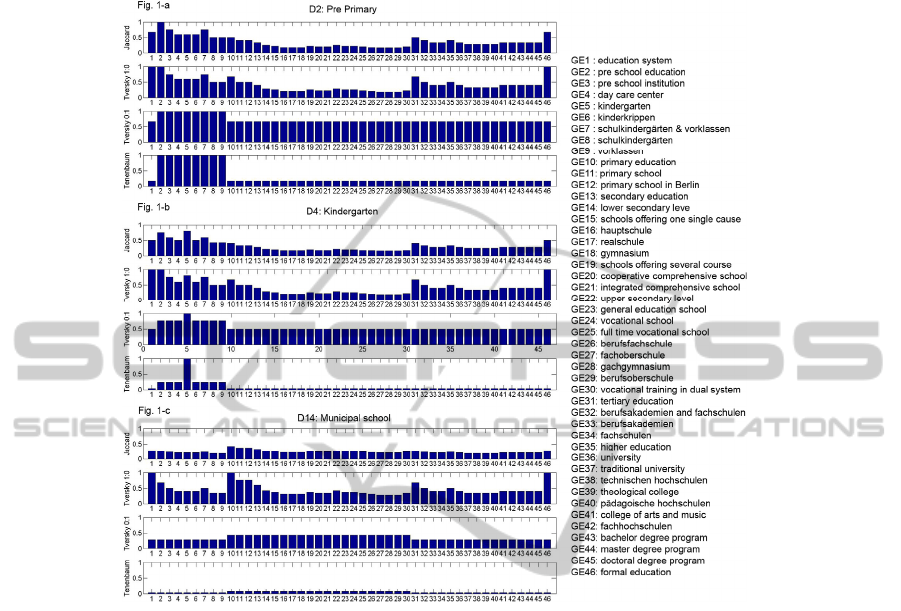
old”, which is possessed only by D4 and G5, heavier than other features.
Fig. 1. Similarity scores: German as variant, Danish as referent.
Figure 1-c for the algorithms C) and D) show that the series of terms referring to
the German primary- and secondary education have slightly higher similarity scores
than other terms. However, the scores in the BMG are particularly low. When
inspecting the feature values of D14, it becomes clear that D14 contains two
distinctive features (“formal teaching” and “municipality”) that are not possessed by
any German terms. In addition, the fully- and partly overlapping common features are
possessed by many terms in both German and Danish, which result in assigning lower
feature weights due to the size principle of the BMG [1]. It should be noticed that,
when contrasting the feature set of D14 with the definition from the text corpus: a
comprehensive school covering both primary and lower secondary education, i.e. one
year of pre-school class, the first (grade 1 to 6) and second (grade 7-9/10) stage basic
education, or in other words it caters for the 6-16/17-year-olds, it turns out that no
decisive features (age, grade etc.) that describe D14 are included in the feature set.
Hence, the result in Figure 1-c could potentially be significantly improved if the
quality of data source is reconsidered.
As described in Section 2, the BMG can, by exchanging assignment of variables x
and y, also compute probabilities that a TL audience generalizes a source concept
39
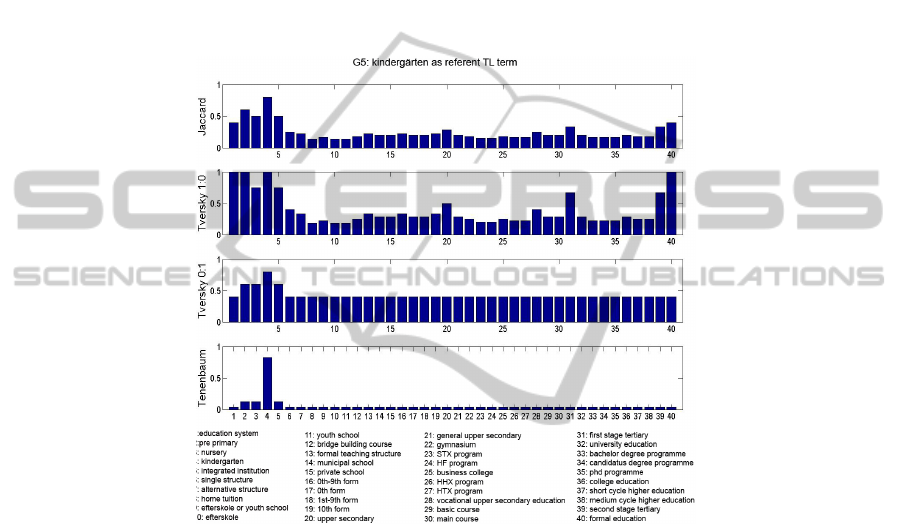
from a stimulus presented by an SL communicator. Hence, in Figure 2, Danish SL
concepts are defined as subjects to comparison and German TL terms as referent. This
computes probabilities, from a German TL reader´s viewpoint, that he/she possibly
infers the meanings of Danish SL concepts based on his/her prior knowledge of the
German educational concepts when a German TL term is given as translation.
Although Figure 2 shows that all four algorithms scored the highest for D4, it
demonstrates that, due to the assigned feature weights, the BMG clearly indicates that
a German TL audience will, from the given TL stimulus G5, likely infer D4. Another
noteworthy point is that similarity relations between D4 and G5 are not symmetrical,
e.g. the BMG result in Figure 2 is 82.3%, while it is 100% in Figure 1- b.
Fig. 2. Generalization probabilities: Danish as variant, German as referent.
4 Discussions
By inspecting similarity scores of all combinations between Danish and German
concepts, the results obtained from the BMG seem to reasonably identify optimally
specific translation candidates if the structured feature sets are properly prepared.
For further analyzing the performance of the BMG, Figures 3 outlines
corresponding relationships between the Danish SL concepts and the German TL
terms from a Danish communicator’s viewpoint. The corresponding relationships are
depicted by the three patterns: 1) solid thick arrows, when the probability scores are
70% or higher; 2) transparent thick arrows, when the probability scores are 40% or
higher and below 70 %; and 3) thin arrows, when the probability scores are 20% or
higher and below 40%.
40
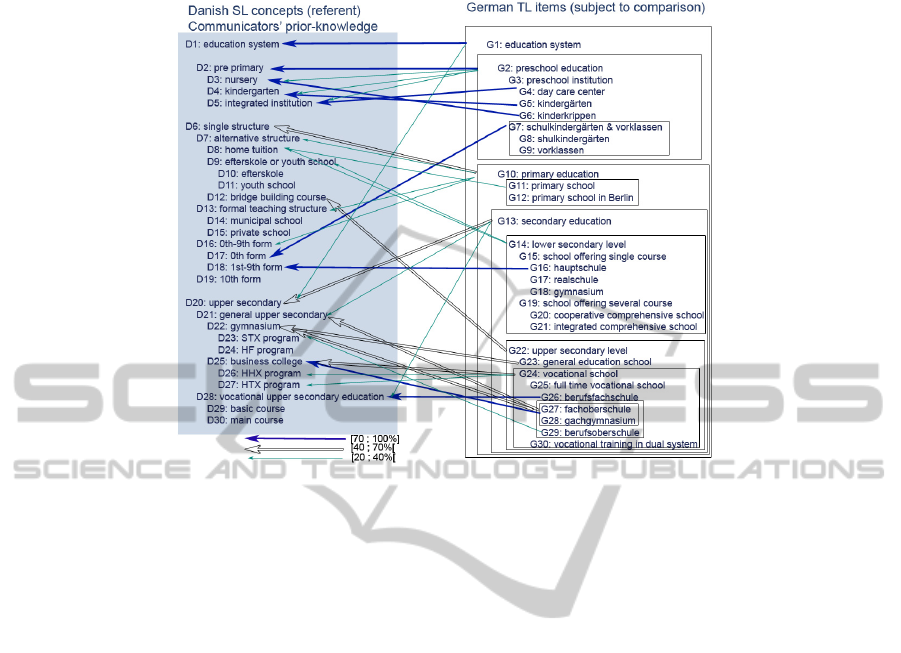
Fig. 3. Ontology mapping overview: from a Danish communicator’s viewpoint.
Figure 3 also indicates that a communicator who has prior-knowledge of the
Danish educational system (gray filled square box) observes each German TL concept
as translation candidate and assess whether each German TL concept falls under the
class of each Danish SL concept. A more concrete and imaginable picture would be
that a communicator whose mother tongue is Danish seeks for a translation candidate
in his/her non-native language (German). For example, in a situation where a Danish
communicator looks for a German translation candidate for a concept D2, all of the
German terms within the relevant transparent square box, from G2 to G9, respectively
falls under the class D2 with the probability range [70 ; 100].
On the other hand, Figure 4 illustrates that a German TL information receiver
possibly generalizes the meanings of Danish SL concepts from a given German TL
translation as stimulus based on his/her prior knowledge of the German educational
concepts (gray filled square box). For instance, if he/she observes a German stimulus,
G3, he/she will likely infer some of the Danish source concepts within the relevant
transparent square box, from D2 to D5, with the probability range [40 ; 70[ that is
lower than the case of the German stimulus, G2 with the probability range [70 ; 100].
Although the BMG [1] can be quite useful as algorithm for linking multilingual
culturally-specific concepts existing for two cultures, there are still some
unsatisfactory results that have been identified in this study. For example, in both
Figures 3 and 4, the German concept, G11, has relations with D8. According to our
intuitive assessment based on the basic domain-knowledge, G11 should rather be
relevant to some of the concepts among D13-D18. When inspecting the feature sets of
G11 and D8/ D13-D18, it becomes obvious that, while G11 contains a feature “[10-16
y.o.]”, D13-D18 which refers to the Danish formal primary education for children 6-
16 years old does not contain features referring to age range. Instead, D8 contains the
41
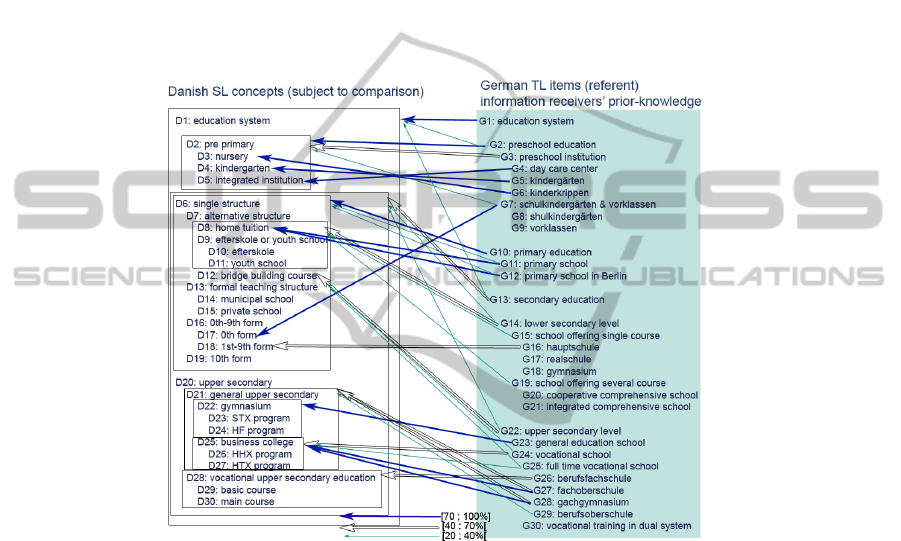
important definitional feature about the age. This problem has been caused, not by the
BMG, but by the particularly strict principles for constructing TOs which may risk
causing the elimination of important features. This issue indicates that, if some
decisive features are lacking or some irrelevant features are included, the results
obtained from the BMG can immediately be affected. Hence, a future attempt would
be to investigate how to generate appropriate feature sets, that is, a more flexible
taxonomic organization of feature structures based on terms and definitions identified
in domain-specific parallel corpora. This may improve the mapping of culturally-
specific concepts applying the BMG. Another key point is that the analysis performed
here is a rather subjective assessment. Hence, for future undertakings, it is necessary
to identify an appropriate method based on assessments using human subjects.
Fig. 4. Ontology mapping overview: from a German audience’s viewpoint.
5 Conclusions
In this work, the Bayesian Model of Generalization [1] and Tversky’s set-theoretic
model [7] have been applied to data-sets consisting of culturally-specific concepts and
of features extracted from data sources based on Terminological Ontologies [5]. The
results indicate that, if input data-sets consisting of culturally-specific concepts and of
feature-values in two cultures are properly prepared, the BMG [1] can be uniquely
used not only for identifying a TL translation candidate, but also for estimating
probabilities of how a TL information receiver generalizes an SL concept from a
given TL translation. To successfully promote the next step for an overall framework,
a human based assessment of concept mappings as well as an improvement of the
method to create highly appropriate feature sets, will be required.
42

References
1. Tenenbaum, J. B., Griffiths, T. L., 2001. Generalization, Similarity, and Bayesian
Inference. In: Behavioral and Brain Sciences 24, 629-640.
2. Declerck, T. et al., 2010. Ontology-based multilingual access to financial reports for
sharing business knowledge across Europe. In: Rooz, J., Ivanyos, J. (Eds.) Internal
Financial Control Assessment Applying Multilingual Ontology Framework, Budapest:
HVG Press, 67-76.
3. Vossen, P. et al., 2008. KYOTO: A system for mining, structuring and distributing
knowledge across languages and cultures. In: Proc. The 6
th
International Conference on
Language Resources and Evaluation, Morocco, 1462-1469.
4. Cimiano, P. et al., 2010. A Note on Ontology Localization. In: Journal of Applied Ontology
Vol. 5, No. 2, IOS Press, 127-137.
5. Madsen, B. N., Thomsen, H. E., Vikner, C., 2004a. Principles of a system for
terminological concept modelling. In: Proc. The 4
th
International Conference on Language
Resources and Evaluation, ELRA, 15-19.
6. Tversky, A., 1977. Features of Similarity. In: Psychological Review 84, 327-352.
7. Sperber, D., Wilson, D., 1986. Relevance: Communication and Cognition. Oxford:
Blackwell
8. Glückstad, F. K., 2011. Asymmetric Similarity and Cross-Cultural Communication Process.
In: 9th International Conference on Terminology and Artificial Intelligence: Proceedings of
the Conference. 8-10 November 2011, Paris, France. Paris : Institut National des Langues et
Civilisations Orientales , 2011. p. 59-65.
9. Jaccard, P., 1901. Étude comparative de la distribution florale dans une portion des Alpes et
des Jura. Bulletin de la Société Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles 37: 547–579.
43
