
Using Use Cases for Domain Modeling
Janis Osis, Armands Slihte and Asnate Jansone
Institute of Applied Computer Systems, Riga Technical University, Kalku iela 1, Riga, Latvia
Keywords: Model Driven Architecture, Meta-model, Topological Functioning Model, Use Cases.
Abstract: This paper demonstrates the Use Case Builder tool and discusses its purpose and design. Previous results
show that Use Cases can be analyzed by means of natural language processing (NLP) and rules can be
defined for validating use cases against a given Ontology. By using this approach it is possible to acquire
formally defined knowledge for transformation to a Computation Independent Model (CIM) in Model
Driven Architecture (MDA). Use Case Builder provides a facility to define the use cases according to the
integrated domain modeling approach, which is described in this paper. The goal is to provide a formal base
for generating CIM with the possibility of tracing the transformation from Use Cases to the corresponding
Topological Functioning Model (TFM).
1 INTRODUCTION
This research focuses on acquiring formal
knowledge in a resulting form of use cases in order
to use it for transformation to a Computation
Independent Model (CIM) for Model Driven
Architecture (MDA). We later describe the
integrated domain modeling approach, which is
combining the declarative and procedural knowledge
for the domain knowledge model. We show how
declarative and procedural knowledge complement
each other and can be compared for validation
purposes. This work continues research on domain
modeling and specifically on TFM for MDA started
in (Slihte, 2011), (Slihte, 2010a), (Slihte, 2010b) and
(Slihte, 2010c). TFM for MDA approach introduces
a way to acquire a formal CIM and provides the
necessary methods to construct the CIM from
domain knowledge (which can also be considered as
part of CIM) and further transform CIM to
PIM/PSM. Construction of the CIM is part of related
research (Slihte, 2010a) and (Slihte, 2010b).
Research (Slihte, 2010a) describes a way to use
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for defining
domain knowledge that can be further formally
analyzed. Research (Slihte, 2010b) shows how it is
possible to automatically acquire a CIM from
domain knowledge. An algorithm is introduced to
automatically derive the TFM from business use
cases. This algorithm utilizes the statistical parser to
analyze the syntax of use case sentences and identify
functional features for the TFM. The problem of
potential ambiguity and inconsistency of the
business use case steps can be resolved by using
ontology (Slihte, 2011).
Next step for this research is to design the use
case structure in detail and provide a supporting tool
for creating the corresponding use cases in a MDA
standard complying fashion. This tool needs to
integrate declarative and procedural knowledge, and
also give the possibility to validate them against
each other. When this is achieved a formal
transformation from knowledge model to a
corresponding Computation Independent Model
(CIM) is possible as shown in (Slihte, 2010a). This
tool has to support the TFM for MDA approach
described in related work and provide access to the
particular use case model so that it can be analyzed,
validated and transformed. Moreover, this tool needs
to be fully compatible with MDA standards in order
for it to be then integrated with other MDA tools and
used for further transformations. This paper shows
the results of Use Case Builder implementation with
Eclipse Modeling Framework (EMF). We have
developed a formal meta-model of the use cases and
implemented the Use Case Builder. We demonstrate
the functionality with examples later in this paper.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 1 is
describing the integrated approach for domain
modeling that the Use Case Builder tool is based on.
Section 2 defines the meta-model of use cases and
describes how use cases can be used as part of
224
Osis J., Slihte A. and Jansone A..
Using Use Cases for Domain Modeling.
DOI: 10.5220/0004090002240231
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (MDA&MDSD-2012), pages 224-231
ISBN: 978-989-8565-13-6
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

domain knowledge. Section 3 demonstrates and
application of the Use Case Builder tool for a
business example. Section 4 talks about further
research and conclusions.
2 RELATED WORKS
Use Cases are defined with natural language, so
natural language process (NLP) has to be used for
analysis. Approach discussed in (Fliedl, 2007) called
NIBA (natural language requirements analysis in
German) is addressing the same issues. Natural
language requirements specifications form the basis
for the subsequent phase of the information system
development process, namely domain modeling.
Research outlines that both, the textual and the
conceptual representations are not appropriate for
being thoroughly captured and validated by the
stakeholders. To introduce this link, first the textual
specifications are linguistically analyzed and
translated into a so-called conceptual predesign
schema. This formulated using an interlingua which
is based on a lean semantic model, thus allowing
users to participate more efficiently in the design
and validation process. After validation, the
predesign schema is mapped to a conceptual
representation (e.g. UML). The sequence of these
translation and transformation steps is described by
the ‘‘NIBA workflow’’ (Fliedl, 2007).
There have been other attempts to transform an
informal description to a formal model. Approach
proposed in (Francu, 2008) suggests generating
implementation from textual use cases. This
approach uses statistical parser on use cases and by
analyzing the parse trees compose so called Procases
for further use in implementation generation.
Procases can be thought of as a formal model of
requirements. In this method (Francu, 2008) the
generated system source code is being used to verify
system requirements, and also to use it as a
framework for further development of the system.
Corresponding tools have been developed for this
method and impressive results have been achieved
by acquiring source code of the system from use
cases of the system. The downside of this approach
is that it does not use existing MDA standards and
thus is not flexible or reusable.
Another approach ReDSeeDs (Kaindl, 2007)
defines software cases to support reuse of soft-ware
development artifacts and code in a model driven
development context. This approach is very formal
and it depends on writing the software cases very
precisely by adding specific meaning to every word
or phrase of software case sentences.
The Use Case Driven Development Assistant
(UCDA) tool’s methodology follows the IBM
Rational Unified Process (RUP) approach to
automate the class model generation (Subramaniam,
2004). First the requirements of the system are
analyzed identifying the use cases and actors of the
system. Using these artifacts the tool can generate
the UML use case diagram, class diagram,
communication diagram, and other artifacts. This
tool is utilizing natural language processing methods
for processing the requirements in textual form. The
downside of this approach is that this methodology
deals only with identifying use cases, but not how
they operate. This means that the main scenario of
the use cases or the flow of events has to be
manually defined by the system analyst.
Other related works include the research of
topological modeling with TFM (Osis, 2007a),
(Osis, 2007b), (Osis, 2008a), (Osis, 2008b), (Osis,
2008c) and (Osis, 2010). This defines the basis for
the domain modeling approach based on TFM,
which is used for the Use Case Builder tool. Recent
research on model-driven domain analysis and
software development using the TFM shows the
integration of TFM with MDA (Osis, 2011a), (Osis,
2011b), (Osis, 2011c), (Osis, 2011d), (Asnina, 2011)
and (Osis, 2011e).
3 THE INTEGRATED DOMAIN
MODELING APPROACH
This paper is considering the integrated domain
modeling approach described in previous research
(Slihte, 2011). This approach suggests starting the
system analysis process from formally defined
declarative and procedural knowledge with a
perspective of integration with MDA. We are
exploiting ontology and use cases for defining the
knowledge model for a business domain. The
ontology is constructed by a knowledge engineer
and use cases are constructed by a business analyst.
While doing so the use cases need to be validated in
order to correspond to the ontology. This is an
iterative process, because the ontology or the use
cases have to be modified until they correspond to
each other. This process requires a sufficient
supporting tool, so that the correspondence can be
automatically determined sequentially in each step
of the knowledge model development. This paper
discusses the design of this tool and demonstrates its
functionality.
UsingUseCasesforDomainModeling
225
The purpose of these tools would be to enable
users: 1) to construct or reuse a domain ontology; 2)
develop business use cases for this domain; 3) verify
these business use cases via controlled natural
language and the ontology defined previously; 4)
automatically generate the CIM for this domain in
form of a TFM; 5) verify the functional
requirements; 6) transform the CIM to PIM/PSM in
a form of UML. The users of this toolset would be
the knowledge engineer and the business analyst.
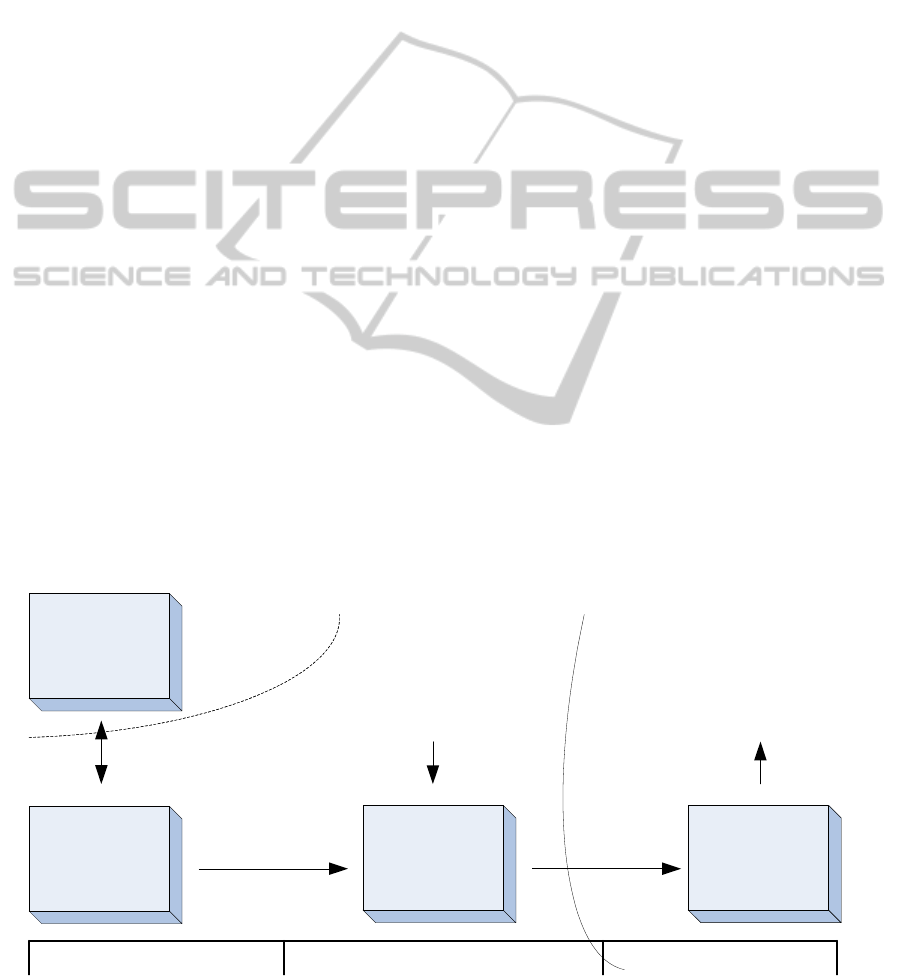
In figure 1 you can see that
TFM for MDA toolset
consists of: 1) Ontology Development tool – a tool for
defining ontology according to OWL standard; 2) Use
Case Builder – this tool will allow the user to
define the use cases for this domain and check if the
correspond to the ontology, and also do the
transformation from use cases to TFM for the
domain; 3) TFM Builder – will also allow to verify
the functional requirements, edit the TFM and do the
transformation from TFM to UML (which would be
represented by a 3rd party tool). Ontology
development tool has to support OWL standard, but
other than that it can be a 3rd party tool, i.e.,
Protégé. You can also see the distinction between
CIM and PIM/PSM that correspond to these tools
from perspective of MDA.
After the acquisition of a formal and verified
knowledge model the next step is to do a
transformation to the business model. It is possible
to generate the business model automatically using
the TFM generation algorithm. Nevertheless, TFM
will have to be validated as well. If any changes are
necessary, they will have to be done in the
knowledge model and then the TFM can be
regenerated. Additionally, within the business and
requirements models it is possible to derive the
Business Processes and UML Use Case diagram
from TFM. The next step of TFM for MDA lifecycle
is transforming CIM to PIM/PSM. The source for
this transformation is the business model (CIM) and
the target is the design model (PIM/PSM).
In earlier work (Slihte, 2010c) some suggestions
have been made what tool support would be
necessary for TFM for MDA approach. In this paper
we expand the toolset to support the new workflow
suggested in previous section. Advantage of using
MDA standards is that MOF compatible meta-
models can be created for business use cases using
XMI, as well as for a TFM. A statistical parser can
be used for analyzing the sentences of use cases, and
thus retrieving functional features for a TFM of the
system. To prevent incompleteness, redundancy or
inconsistency of the business use cases ontology and
controlled natural language is used. At last, for
retrieving the cause-effect relations between these
functional features the structure of the business use
cases is exploited.
4 USING USE CASES FOR
DOMAIN MODELING
A use case is a description of a process and its steps
in detail, and may be worded in terms of a formal
model. A use case is intended to provide sufficient
detail for it to be understood on its own. A use case
has been described as “a generalized description of a
set of interactions between the system and one or
more actors, where an actor is either a user or
Ontology
Development
(OWL)
Use Case
Builder
TFM Builder
Verification
Transformation Transformation
UML
CIM-Business/Requirements
PIM/PSM
3
rd
party
tool
CIM-Knowledge
Verify
functional
requirements
Generate
source code
3
rd
party
tool
Figure 1: This schema shows the toolset necessary for TFM for MDA approach.
ENASE2012-7thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
226
another system (Fliedl, 2007). There is no standard
way to write the content of a use case, and different
formats work well in different cases (Francu, 2008).
But there is a common style to use: 1) Title: "goal
the use case is trying to satisfy"; 2) Main Success
Scenario: numbered list of steps; 3) Step: "a simple
statement of the interaction between the actor and a
system"; 4) Extensions: separately numbered lists,
one per Extension; 5) Extension: "a condition that
results in different interactions from the main
success scenario". In the Unified Modeling
Language (UML), the relationships between all (or a
set of) the use cases and actors are represented in a
use case diagram or diagrams, originally based upon
Ivar Jacobson's Objectory notation (Francu, 2008).
In context of using use cases as domain
knowledge we don’t need to go as far as the UML
diagram, but it is necessary to define the format of
the use cases. This format is also considered for
generating CIM for a domain defined by procedural
knowledge in form of use cases.
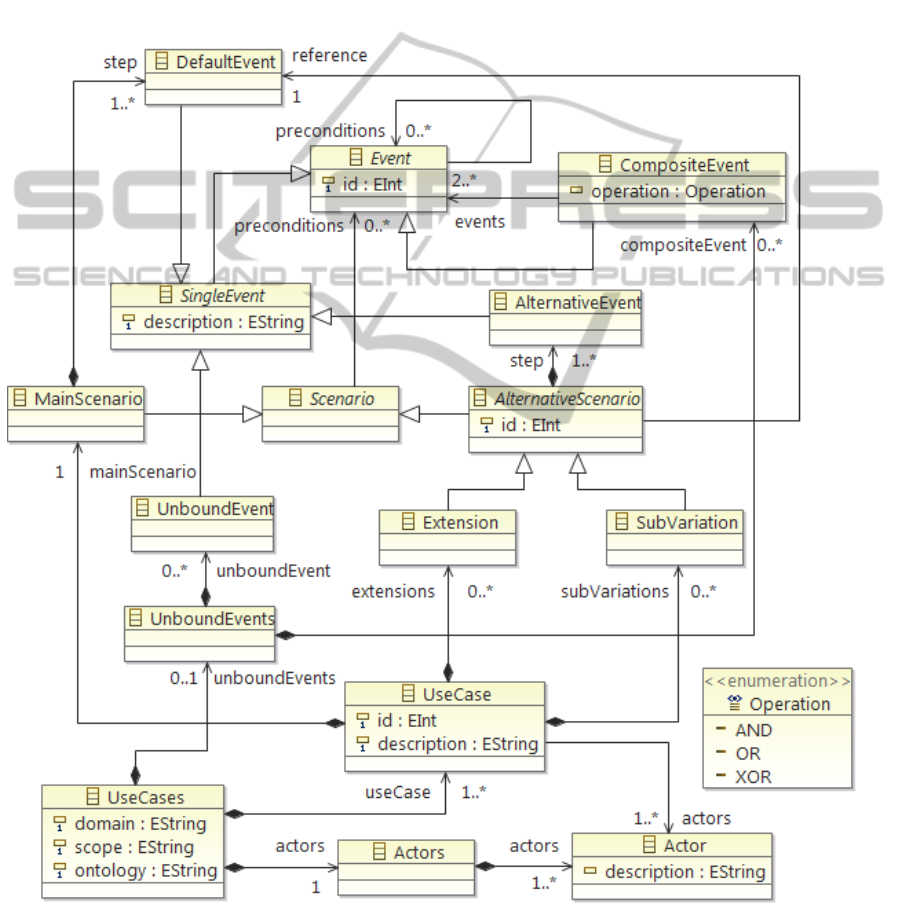
Main classes for the use cases model are Actor,
Figure 2: This figure shows a MOF-compatible metamodel of a set of use cases. A set of use cases consists of 1 or more use
cases, which have a main scenario, extensions and sub-variations, which consist of use case steps. Each use case has a title,
list of actors (at least 1 actor), and can have preconditions. Each use case step has its number description and can have a
precondition. For extensions and sub-variations the reference attribute is used. This shows which of the steps in the main
scenario it references, so for main scenario steps reference will be empty.
UsingUseCasesforDomainModeling
227

Event, Scenario and UseCase, which ties the
previous objects together. Use cases class is the root
class for the model and has attributes domain, scope
and ontology. Ontology attribute will hold the
technical name of the ontology for the domain,
which will be uploaded via use cases tool. As shown
in the metamodel, use cases model consist of actors,
unbound events and use cases.
Actors are included in this model to organize the
actors involved in the use cases, so that it would be
possible to choose form already existing actors or
add new ones. Class Actors is a container for actors
in the use cases model, so both actors references are
containment. Actor has a description, describing
what this actor represents in this domain. There is
only 1 container in a use case model, but there can
be many actors. There has to be at least 1 actor in the
use cases model.
Events are all the steps in the use case and also
all preconditions. Event is an abstract class with an
id as attributes. Attribute id has to be unique in
scope of all events, so that it is possible to
unambiguously reference an event. Each event can
have 0 or many preconditions, which are also events.
Class Event has 2 sub-classes: SingleEvent and
Composite Event. SingleEvent is an abstract class
representing a single event. It has a description
attribute and 3 sub-classes: DefaultEvent,
AlternativeEvent and UnboundEvent. Class
DefaultEvent represents an event that occurs in the
default sequence of events of a use case. Class
AlternativeEvent represents an event that occurs in
an alternative sequence of events of a use case. So
the main scenario uses the default events as steps
and extensions and sub-variation use the alternative
events as steps. Class UnboundEvent represents an
unbound event that is not used in any scenario, but is
used as a precondition. All preconditions for events
or scenario steps also have to be events, but some
events will not be part of a scenario in the use cases
model. For this kind of events we have the unbound
event container. Class UnboundEvents is a container
for unbound events in the use cases model.
Composite events are represented with the class
CompositeEvent. This kind of event let’s you
reference other events (at least 2) with a
corresponding operation. Operations are defined in
an enumeration Operation, which defines AND, OR
and XOR operations. This way it is possible to
define sequences of events with operations.
Moreover, these sequences can also contain other
composite events. Composite events will also be
held by the unbound events container.
Scenarios hold the preconditions and the order of
the events that occur if these preconditions are true.
Class Scenario is an abstract class, which has 2 sub-
classes MainScenario and AlternativeScenario.
MainScenario is a container for the default sequence
of events happening for a particular use case,
therefore main scenario can have 1 or more default
event objects. There can be only 1 main scenario for
a single use case. AlternativeScenario is an abstract
class, which represents a possible alternative
sequence of events (alternative to the main
scenario). Alternative scenarios have an id attribute,
because there can be 0 or more than 1 alternative
scenarios in a single use case. There are 2 possible
alternative scenarios – extension or sub-variation of
the main scenario.
Use case holds the references to the scenarios
and actors. There has to be at least 1 use case in a
use cases model. Class UseCase also has an id and a
description as attributes. Each use case must have 1
main scenario and it may or may not have extensions
or sub-variations.
5 DEMONSTRATION OF THE
USE CASE BUILDER
This section shows the functionality of the Use Case
Builder tool. For this demonstration of the Use Case
Builder tool an example Library business is
considered. To create a use cases model it is
necessary to do the following steps: 1) create a new
use cases model with use cases as root node; 2)
create actors container and actors for the use cases;
3) create unbound events container and define the
unbound events for the use cases; 4) create each use
case for the business domain; 5) create the main
scenario and define the corresponding steps for each
use case; 6) create the sub-variations and define the
corresponding steps for each use case; 7) create
extensions and define the corresponding steps for
each use case.
For this particular example the use cases model
is “Library client management and book lending”.
There are 2 actors Librarian and Client. There are 4
use cases – “Going to the library”, “Registering”,
“Requesting a book” and “Returning a book”. Let’s
take a closer look at the “Requesting a book” use
case, which is shown in figure 4.
The main scenario shows the default sequence of
ENASE2012-7thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
228
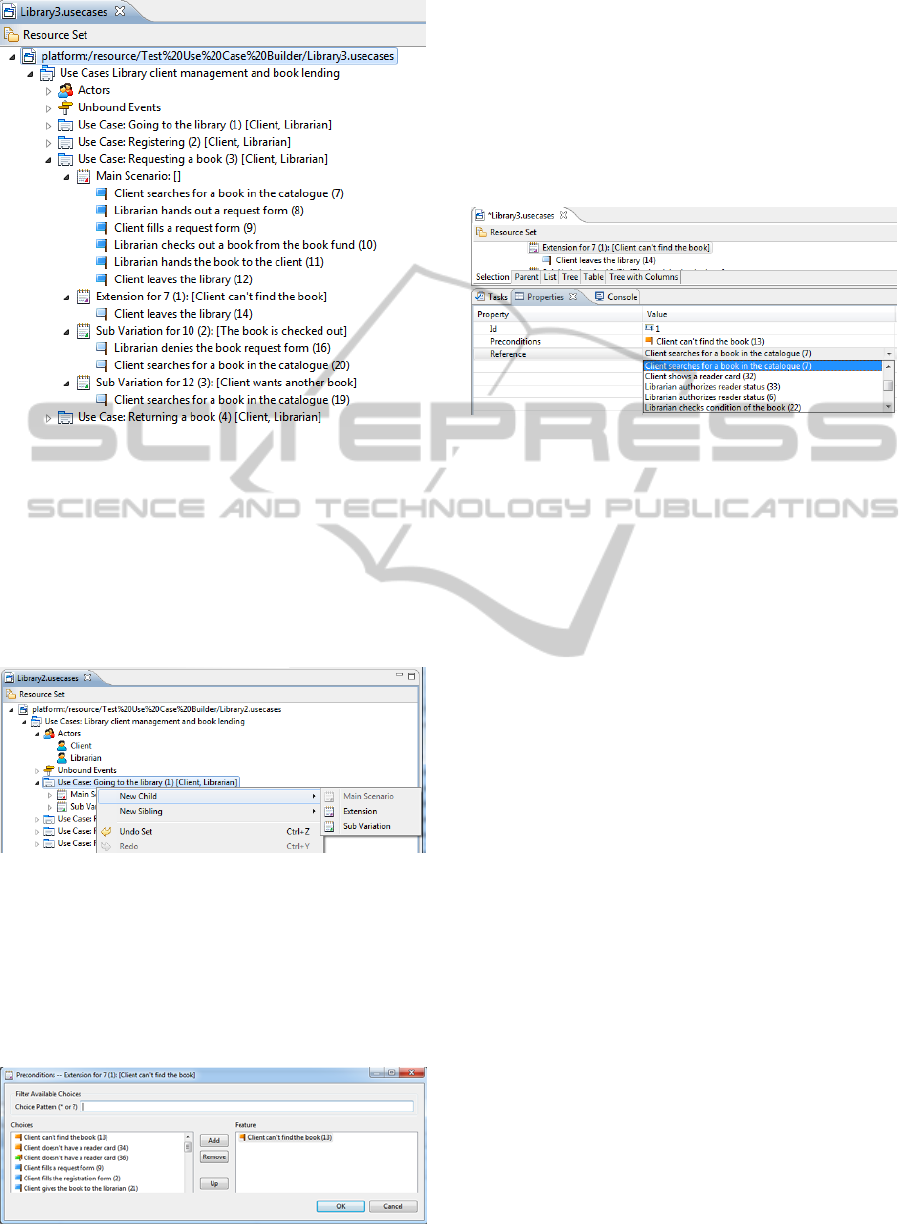
Figure 3: Use Case “Requesting a book”.
events when client is requesting a book. There are
no preconditions for this use case. The main scenario
starts with client searching for a book, and ends with
the client receiving the book and leaving the library.
There is 1 extension and 2 sub-variations. The
functionality of creating extensions and sub-
variations is demonstrated in figure 5.
Figure 4: Creating an extension or sub-variation.
The extension is for the case when the client
can’t find the book he is looking for. For this there is
an unbound event defined “Client can’t find the
book”. The functionality of adding a precondition to
the extension is shown in figure 6. There can be
multiple preconditions.
Figure 5: Adding a precondition to a scenario.
Every alternative scenario need to have the
reference defined, which determines the step in the
main scenario it is alternative to. For this extension,
the extended step is “Client searches for a book in
the catalogue”. The functionality of defining the
reference is shown in figure 7. Alternative scenario
can contain only 1 reference, which is the event
from the main scenario of the use case.
Figure 6: Defining the reference of alternative scenario.
The first sub-variation is for the case when the
book that client is looking for has already been
checked out. In this case client has to look for
another book he would like to request. This scenario
references the step “Librarian checks out a book
from the book fund”, which will be substituted with
this alternative scenario. The second sub-variation is
for the case when the client wants to order another
book. This alternative scenario references the step
“Client leaves the library” from the main scenario.
So instead of leaving the library client can also
search for another book. The steps of these
alternative scenarios are shown in figure 4.
6 FURTHER RESEARCH
AND CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we focus on the Use Case Builder tool
in context of the integrated domain modeling
approach. A MOF-compatible meta-model of the use
cases has been discussed in detail and used for the
Use Case Builder implementation. The integrated
domain modeling approach was described, which
shows the context of the role of this tool.
In current state the tool is able to support the use
case development process, but it is still lacking the
functionalities of uploading ontology and use case
validation. This functionality is considered for
further research and will be implemented as follows.
Stanford Statistical Parser will be used for each use
case step’s description to analyze the grammatical
syntax. This parser has a Java library that can be
UsingUseCasesforDomainModeling
229

used for this purpose, with a tree class for analyzing
the syntax trees. OWL API will be used for
uploading OWL ontology file and analyzing it for
use case verification. OWL API provides Java
library that will be used in Use Case Builder. There
is an OWLOntology class that will contain the
ontology to be compared to the use case step syntax
trees provided by Stanford Statistical Parser. For use
case validation the EMF Validation Framework will
be used.
Use Case Builder tool is an important step
towards the integrated domain modeling approach.
On top of this tool the rest of the necessary
functionality can be built. We have demonstrated
how the tool can be applied today, but the main
achievement is that the use case models developed
with this tool are compatible with MDA standards
and can be further used in transformations.
REFERENCES
Moore, R., Lopes, J., 1999. Paper templates. In
TEMPLATE’06, 1st International Conference on
Template Production. SciTePress.
Smith, J., 1998. The book, The publishing company.
London, 2
nd
edition.
Slihte, A., Osis, J., Doniņš U., 2011. Knowledge
Integration for Domain Modeling, Proceedings of the
3rd International Workshop on Model-Driven
Architecture and Modeling-Driven Software
Development, China, Bejing, 8.-11. June, 46-56.
Slihte, A., 2010. Transforming Textual Use Cases to a
Computation Independent Model. MDA & MTDD
2010, Greece, Athens, 22.-24. July, 33–42.
Šlihte, A., 2010. The Specific Text Analysis Tasks at the
Beginning of MDA Life Cycle. In: Data-bases and
Information Systems Doctoral Consortium, Latvia,
Riga, 5.-7. July, 11–22.
Slihte, A., 2010, Implementing a Topological Functioning
Model Tool. In: Scientific Journal of Riga Technical
University, 5. series., Computer Science, Vol. 43,
Riga, 68–75.
Fliedl, G., Kop, C., Mayr, H. C., Salbrechter, A.,
Vohringer, J., Weber, G., Winkler, C., 2007. Deriving
static and dynamic concepts from software
requirements using sophisticated tagging, Data &
Knowledge Engineering, Vol. 61, Iss. 3, 433-448.
Francu, J., Hnetynka, P., 2008. Automated Generation of
Implementation from Textual System Requirements,
Proceedings of the 3
rd
IFIP TC 2 CEE-SET, Brno,
Czech Republic: Wroclawskiej, 15-28.
Kaindl, H., 2007. Structural Requirements Language
Definition, Defining the ReDSeeDS Lan-guages,
January. Available: http://publik.tuwien.ac.at/files/
pub-et_13406.pdf [Ac-cessed: Mar 27, 2012]
Subramaniam, K., Liu, D., Far, B., Eberlein, A., 2004.
UCDA: Use Case Driven Development Assistant Tool
for Class Model Generation, Proceedings of the 16th
SEKE. Canada: Banff. Available: http://enel.
ucalgary.ca/People/eberlein/publications/SEKE-
Kalaivani.pdf [Accessed: Mar 27, 2010]
Osis, J., Asnina, E., Grave, A., 2007. Computation
Independent Modeling within the MDA. Proceedings
of the IEEE International Conference on Software
Science, Technology and Engineering, Herzlia, Israel,
IEEE Computer Society Nr. E3021, 30.-3. October,
22-34.
Osis, J., Asnina, E., Grave, A., 2007. Formal Computation
Independent Model of the Problem Domain within the
MDA. Information Systems and Formal Models,
Proceedings of the 10th International Conference
ISIM’07, Silesian University in Opava, Czech
Republic, 47-54.
Osis, J., Asnina, E., Grave, A., 2008. Computation
Independent Representation of the Problem Domain
in MDA. e-Informatica Software Engineering Journal,
Volume 2, Issue 1, 29-46.
Osis, J., Asnina, E., 2008. A Business Model to Make
Software Development Less Intuitive. Proceedings of
the 2008 International Conference on Innovation in
Software Engineering, Vienna, Austria. IEEE
Computer Society CPS, Los Alamitos, USA, 1240-
1246.
Osis, J., Asnina, E., Grave, A., 2008. Formal Problem
Domain Modeling within MDA. Communications in
Computer and Information Science (CCIS), Vol. 22,
Software and Data Technologies, Springer-Verlag
Berlin Heidelberg, 387-398.
Osis, J., Donins, U., 2010. Formalization of the UML
Class Diagrams. Evaluation of Novel Approaches to
Software Engineering. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Heidelberg, New York, 180-192.
Osis, J., Asnina, E., 2011. Model-Driven Domain Analysis
and Software Development: Architectures and
Functions. IGI Global, Hershey - New York, 487.
Osis, J., Asnina, E., 2011. Is Modeling a Treatment for the
Weakness of Software Engineering? In: Model-Driven
Domain Analysis and Software Development:
Architectures and Functions. IGI Global, Hershey -
New York, 1-14.
Osis, J., Asnina, E., 2011. Topological Modeling for
Model-Driven Domain Analysis and Software
Development: Functions and Architectures. In: Model-
Driven Domain Analysis and Software Development:
Architectures and Functions. IGI Global, Hershey -
New York, 15 – 39.
Asnina, E., Osis, J., 2011. Topological Functioning Model
as a CIM-Business Model. In: Model-Driven Domain
Analysis and Software Development: Architectures and
Functions. IGI Global, Hershey - New York, 40 – 64.
Osis, J., Asnina, E., 2011. Derivation of Use Cases from
the Topological Computation Independent Business
Model. . In:
Model-Driven Domain Analysis and
Software Development: Architectures and Functions.
IGI Global, Hershey - New York, 65 – 89.
ENASE2012-7thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
230

Osis, J., Asnina, E., Grave, A., 2007c. MDA Oriented
Computation Independent Modeling of the Problem
Domain. Proceedings of the 2
nd
International
Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to
Software Engineering (ENASE 2007), Spain,
Barcelona, 66 -71.
UsingUseCasesforDomainModeling
231
