
Expertise Search in Unstructured Data in ECM using
S-BPM Approach
Alexander Gromoff, Julia Stavenko, Kristina Evina
and Nikolay Kazantsev
Institute National Research University, Higher School of Economics,
Faculty of Business Informatics, BPM Department,
Science & Education Center of Information Control Technologies, Moscow, Russia
Abstract. This article describes the application of currently most promising
methods of graph theory, content analysis and (3) subject-oriented approach to
business process modelling for creating and automation of innovative process
and therefore for maximization of ROI (return on investments) in intellectual
and social capital of enterprises. In a course of development, instant full-text
indexation takes place and taxonomic picture of different branches for such
community is formed. In due course system gathers the statistics and builds-up
maps of intercommunication with priority allocation of most discussed topics.
A group of predetermined experts begins discussion on development prospects
of this or that subject afterwards. The strategic map of investments into
innovative development that can be offered to group of investors for
competitive investments eventually turns out. In this process all steps except
final (gathering of experts) are human non-dependant, what increase efficiency
of the process in general.
1 Introduction
The most important property and feature of any information system is knowledge
management, its allocation, processing and transformation, production and
reproduction, transfer, storage and codification. Knowledge carriers are workers and
external advisors. Therefore, while discussing innovative processes it is necessary to
point out that not only ‘who knows what’ is important, but also ‘who knows who and
how comes that’ is an essential part of knowledge exchange between members of
social network. It is possible to talk about effective integration of employees into the
added value chain of knowledge exchange process only having realized a nature of
information as kernel element of the “doing by learning, learning by doing” approach
to the company’s activity.
How to create the corresponding information environment? Due to the researchers
position, the answer to this question lies in an integrated management of process
resources such as intellectual (people, information, and knowledge), and quality, and
risk as well. These relations are evident but not always accounted in realization of the
strategies. As long the knowledge is increased in a system, the quality of the
Gromoff A., Stavenko J., Evina K. and Kazantsev N..
Expertise Search in Unstructured Data in ECM using S-BPM Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0004104800940105
In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Modelling, Simulation, Verification and Validation of Enterprise Information Systems and 1st
International Workshop on Web Intelligence (WEBI-2012), pages 94-105
ISBN: 978-989-8565-14-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

corresponding processes is increased this in conjunction (K+Q) reduce the risk
(general and operational), and as a result entropy of that system either stabilized or
even reduced, because of the positive knowledge accumulation. And reversely, as
soon knowledge is stabilized (stagnate) or even starts to decrease, because of internal
or external processes destructing intellectual capital or potential of the system, at that
particular moment quality starts to fall down letting operational risk to raise and all
that in combination led immediately to increase of entropy of the system in general.
These relations are not un envying at all. In a big system with serious delay in
reaction on internal or external changes it often can lead to total system destruction or
dissimilation on subsystems till the level when each newly organized smaller system
will obtain its level of entropy stability or manageability. That management is
possible only by merging social and intellectual capital for obtaining the maximum
efficiency. In medias res,
‘social capital’ as net substance connects an intellectual
capital; these are interaction patterns, which create advantages to one social group,
and, perhaps, barriers to another one.
2 Main Problems in Enterprise Knowledge Management
2.1 Problem 1
The main problem, in this case, is that not all types of structures are suitable for
knowledge assignment. Everything rides on category of transferred knowledge.
Explicit, easily codified knowledge can be hanged over by means of an e-mail, FTP,
Internet or fixed in documents. Implicit knowledge, on the other hand, demands direct
interaction and experience exchange between two and more employees. For example,
presentations exchange, which are shown to employees, is usual practice, and here an
exchange of context and expertize, necessary condition for creating such presentation
(that has much higher intellectual value), not so simply occurs in companies because
of existing organizational and social barriers. For transferring implicit knowledge
direct connections with source of this knowledge, based on mutual understanding and
trust between the recipient and the sender (mentoring and training condition) has to be
established.
2.2 Problem 2
Next problem in network knowledge exchange is that the required knowledge is not
situated often in a zone of employee’s visibility, for example, in different clusters of
employees in social structure. Social networks have so-called horizon, which is
characterized by the degree of nods distance (managers, employees) from each other.
It was shown repeatedly that such horizon in social networks represents two distance
degrees – direct contacts of nod and their direct contacts of contacts [1]. On the third
degree of a distance both the manager and the employee don't understand any more
what is going on and this knowledge isn't available for them, except obvious well-
known information which is reachable in the public access.
95

Thus, the popular theory that all of us are living in a small world and are
connected by "six handshakes» is illusion. Six degrees of a distance are actually a
really «big world» for organization and our possibility to find knowledge inside it, is
very limited, therefore, in such a case knowledge is considered as inaccessible and
often it is necessary «to invent a bicycle» for the solution of the task.
Without deepen discussion the root of this problems is obtained in human being or
natural language uncertainty and redundancy, which accumulated with each transfer
and finally exceed a thread hold of content identification. That is why hierarchical
management structures with more than 3 levels are ineffective and extremely slow
reactable.
In our case neither manager nor employee can receive the necessary expertize due
to badly designed communications inside the company, mainly because of social and
cultural barriers between them. In one’s turn, it leads to occurrence of pseudo-
scientific discussions in blogs, and then transfer of these imaginations in information
flows and processes. Bert calls this situation «structural holes» in a network, meaning
the existence of communicative spaces that are not connected among themselves [2].
2.3 Ex-ante Conclusion
All this leads to the problem of social capital management and merger of semantically
close spheres of competences, which are burning issues in knowledge management as
a whole. Scientific community is seriously bothered about its own ideas and opinions
distribution and more specifically, implementation of these ideas in innovations that
should convert future from Value added to Quality added paradigm. The true
professionals, gained through the years of experience their unique knowledge, are
sure that this knowledge would never be reduced to the elementary business
implementation since it simply change a way of ‘traditionalism’ in business, and very
often reduce significantly cost adding chain, what became ‘immoral’ in modern
business world. Otherwise it’s impossible to explain the facts of decades delay in
implementation of evidently socially beneficial results of investigation in different
areas and countries, but this question exceed a frame of the current work.
3 Enterprises as Closed Systems
Before shifting to description of the above-mentioned problems, it is necessary to
formulate understanding of modern company as a system. Respectively, at first it is
necessary to consider it as a part of system of higher order (for example, knowledge
management system) and to allocate properties of this system and its subsystems from
the governmental and social points of view.
The most important property and feature of this system is knowledge
management, its allocation, processing and transformation, production and
reproduction, transfer, storage and codification, as been mentioned above.
Among set of definitions of "knowledge": «Knowledge is information that is
materialized in course of task or problem solution». There through, in definition of
knowledge it is emphasized that it should grow out of an action or some decision
96

p
rocess
d
could ha
v
p
rove of
i
Still
p
informat
i
self-orga
n
activity r
system c
o
knowled
g
which h
a
p
rocesse
s
knowled
g
b
etween
knowled
g
and envi
r
3.1 R
e
Recently
which ar
e
environ
m
on beha
v
derivativ
e
egocentr
i
from stat
u
position
(
that the
d
of salary
Exist
i
achieve
m
for defi
n
analysis
[
[8, 9] w
docume
n
d
edicated to
o
v
e, it become
s
i
ts existence,
p
redominates
i
on, instead o
f
n
izes, cooper
a
epresents int
e
o
nsists of int
e
g
e), quality a
n
a
ve certain in
p
s
have certa
i
g
e exchange
p
volumes of
i
g
e and risks
r
onmental fri
e
e
search Time
l
there was a
e
growing ou
t
m
ent. The gre
a
v
iour analysis
e
of its intel
l
i
c approach i
t
u
s and role p
(
social capita
l
d
egree of soci
a
[5], encoura
g
F
i
ng research
e
m
ents in this
q
n
ition of exp
e
[
7]. In other r
e
as realized
o
n
ts.
o
btaining me
a
s
evident tha
t
otherwise it’s
the understa
n
f
qualitative
e
a
tes with an e
n
e
raction of da
t
e
grated proce
s
n
d risks». It
fo
p
ut and targe
t
i
n nods and
p
rocess consi
i
nformation t
r
of updating,
e
ndliness (res
p
l
iness
set of resear
c
t
of their uni
v
a
test distributi
of certain p
e
l
igent actions
is possible t
o
o
sition of net
w
l
) point of vie
w
a
l capital of
e
ement from f
r
ig. 1. Current t
r
e
s on expert
i
q
uestion. For
e
rtise
p
rofile
e
search an ap
p
o
n the basis
o
a
surable resul
t
t
only applica
t
s
just ‘a mani
f
n
ding of kno
w
e
ssence, whi
c
n
vironment,
b
t
a carriers an
d
s
s manageme
n
f
ollows thenc
e
t
characterist
i
problem po
i
i
sts in necess
i
r
ansferred fo
r
commerciali
z
p
ect for the e
n
c
hes on the t
v
ersal exploit
a
i
on was recei
v
e
rson (netwo
r
and its inte
r
o
allocate the
t
work nod po
i
w
. For instan
c
e
mployee infl
u
r
iends and co
l
r
end in knowle
ise search i
n
example, so
m
of each nod
proach to ex
p
o
f co-author
s
t
. If to consi
d
t
ion of the p
a
f
estation of a
w
w
ledge as cer
t
c
h develops s
i
b
reeds and m
o
d
knowledge.
n
t of resourc
e
e
knowledge
e
i
cs according
i
nts. The m
a
i
ty for searc
h
r
understandi
n
z
ation, a pri
o
n
vironment) o
f
o
pic of anal
y
a
tion, both in
v
ed by the eg
o
r
k nod), expl
r
action with
o
direction of
i
nt of view a
n
c
e, the carrie
d
u
ences his pr
o
l
leagues [6].
d
ge manageme
n
a social
n
m
e researcher
s
in a networ
k
p
er
t
-oriented
s
s
hip analysis
d
er any kno
w
a
rticular kno
w
w
ill without p
o
t
ain number
o
milar to live
o
difies: «Prac
t
Optimal con
t
e
s (people, in
f
e
xists only in
to the purpo
s
a
nagement i
n
of continuo
u
n
g, quality o
f
ritization, so
c
f
knowledge.
y
sis of social
corporate an
d
o
centric appr
o
a
ining social
o
ther people
(
s
ocial networ
k
n
d from com
m
d
-out research
e
o
motion [3, 4
]
n
t.
n
etwork cont
a
s
use text cla
s
k
by means
o
earch in soci
a
of employe
e
w
ledge one
w
ledge is a
otention’.
o
f definite
organism,
t
ically any
t
rol of
t
his
f
ormation,
processes
s
es. These
n
tegrity in
u
s balance
f
resultant
c
ialization
networks,
d
in social
o
ach based
reality as
(nods). In
r
k analysis
m
unicative
e
s showed
]
, increase
t
ain many
ssification
o
f citation
a
l network
e
s in their
97

3.2 Motivation, Methodology, Research Questions
3.2.1 Research Aim
In this current research the main objective is the creation of innovative process in
companies which is based on automation of knowledge exchange between employees.
The approach is based on egocentric analysis of a social network and detection of
manager and employee competences, in other words, definition of their expertize
level.
Accordingly, some kind of virtual community communicating among itself on
different topics is created; it is adhered to knowledge exchange process, for example,
webinars on various subjects. These workshops are formed at once with a sight on
receiving innovative and significant result, at its final stage the mechanism of
investors competition takes place.
3.2.2 Methodology
On first stage the service of expertize search is developed by means of search inquiry
creation on corporative portal or in e-mail, as a result the relevant list of experts (the
indicator of intellectual capital of the company) is shown. Besides the list of relevance
it is necessary to understand, whether this or that expert (employee/manager) is
available to communication and adjustment of communication (the indicator of social
capital of the organization). Merger of these two functionalities allows to create the
two-factor indicator of expertize based on measurement of its intellectual and
personal contribution.
On second stage the elimination of communication gaps between experts and
efficient knowledge exchange by means of free ideas circulation in company on basis
of internal communications. In other words the creation of convenient information
environment in order to receive return from employee in form of a relevant
independent expert appraisal of problem area. Such environment can be created
through the virtue of subject-oriented approach application to automation of
innovative processes in organization, where the main emphasis is placed on
employees (subjects) reflexivity, in other words on ability to creative potential and
self-analysis activization.
3.2.3 Research Questions
Research Question 1
Expert’s identification on user demand (according to concepts in inquiry).
Research Question 2
Expert’s social capital measurement in intra corporate expert network for employees
ranking.
Research Question 3
Innovative process management of expertize transfer from one employee to another.
98

4 Research Description
Empirical base of this research is based on real correspondence data of managers and
employees for the chosen period of time and unique communications base in the real
processes, kindly provided by IT Co. for this particular work. E-mail can give a real
backbone for semantic information observation and information on real social
network. Implicit expert knowledge contains in text documents which employees
exchange and describes their competences.
Essentially, any message in a network, in process of communications, directly or
indirectly relating to business activity or business process execution, possesses the
value for the analysis. This value can have various aspects as from point of view of
solved in this work task (allocation of expert community), and from sociology,
psychology and psychoanalysis point of view, besides, certain interest to results of
this survey inevitably arises at enterprises security departments (including
information security). Unavoidably, there should raise a question of private life rights
protection of analyzed community, however, authors of this work would like to evade
from discussion on “private life” existence within official duties or business
processes.
However, it should be noted that the received results can be used by wide range of
experts who are engaged in researches of organized communities for concrete result
achievement.
4.1 Research Question 1
The first task is expert’s identification on user demand (according to concepts in
inquiry). Experts search (people possessing high qualification (competence) of subject
domain uses the proved hypothesis that person’s qualification strongly correlates with
set of characteristic concepts which he uses; these terms are specific to concrete area.
In this respect, subject domain for each set of terms can be different and is not
connected with cognitive subject domains that is realized by person and is not
allocated as separate essence. Now therefore, expert is the person who with high
probability understands questions mentioned in the text. In order to separate
significant terms from common ones, how it is described above, it is possible to
formulate hypothesis that characteristics of rank distribution possess not only
dependence on rank from frequency of word usage in the text (Tsipf's law), but also
dependence on rank from relative frequency of term usage by the author. For this
purpose it is necessary to count up statistics of relative frequency of term
usage for
all texts written by the specific employee
,
=
,
∑
,
(1)
where
,
is number of utilization of term
by person
; total number уof
utilization of all terms by person
in denominator
It is possible to assume that significant terms should have strong non-uniform
distribution of relative frequency of usage among employees, and common ones –
approximately identical relative frequency of usage. Let's construct similar
99

depende
n
employe
e
Fig. 2. D
e
double lo
g
It is i
n
"grant" i
s
are notio
n
in the ch
o
employe
e
significa
n
namely
d
In co
n
higher v
a
allows di
that on t
h
occurren
c
corporat
e
formatio
n
most co
m
corporat
e
How
e
to get s
t
"normal"
ones. W
h
range of
e
discussio
factor).
The
f
distributi
o
concrete
distributi
o
number
o
distributi
o
1
The empir
i
n
ces in doubl
e
e
s texts
1
:
e
pendence of
r
g
arithmic scale.
n
tuitively cle
a
s
the specific
n
al in narro
w
o
sen subject
d
e
is approxi
m
n
t words an
d
d
ispersion in
o
n
sequence o
f
a
lues of dispe
r
stinguishing
s
h
e basis of di
c
e algorithm
e
experts sea
r
n
of limited
l
m
petent in t
h
e
expert netw
o
e
ver, receivin
g
t
able result.
O
are approxi
m
h
ether this
m
e
xperts, cate
g
n of the holi
d
f
ollowing al
g
o
n and to c
l
"closeness"
o
ns by calc
u
o
f used wor
d
o
n vector o
f
i
cal base of the r
e
e
logarithmic
s
r
elative freque
n
a
r that such t
e
term of subj
e
w
range of ex
p
d
omain beca
u
m
ately the sa
m
d
general m
e
bservable dis
t
the experim
e
r
sion of relati
v
s
ignificant ter
m
spersion calc
u
it is possibl
e
ch which is
b
l
ist of emplo
y
h
is or that q
u
o
rk is formed.
g
one assesse
d
O
n this figu
r
m
ately equal
m
eans that the
g
orically "no"
d
ays season a
n
g
orithm allo
w
l
arify its sp
e
processes
d
u
lating perce
n
d
s employed
f
personal "c
l
e
search was base
d
s
cale for vari
o
n
cy of term u
s
e
rms as "gran
t
e
ct domain, «
m
p
erts. Terms
"
u
se probabilit
y
m
e. Analyzi
n
e
aning word
s
t
ribution of r
e
e
nt, it is poss
ve frequency
m
s from the
c
u
lation of rel
a
e
to reveal e
x
b
ased on tex
t
y
ees (experts
)
u
estion. On
t
d
value on dis
p
r
e the disper
s
but are they
e
y should be
as these con
c
a
nd condition
s
w
s to essenti
a
e
cifics. Usin
g
d
efinition of
n
t of words
b
by the em
p
loseness" of
d
on the docu
m
e
n
o
us terms (se
e
s
age written b
y
t
" and «mish
u
m
ishustin» is
"
project", "in
f
y
of its utiliz
a
n
g the diagra
m
s
the distrib
u
e
lative freque
n
ible to draw
of term usag
e
c
ommon ones
a
tive frequen
c
x
perts for pr
t
s analysis. T
h
)
working at
t
he basis of
p
ersion migh
t
s
ion value f
o
are displace
d
defined as c
o
c
epts were all
o
s
of its car
r
yi
n
a
lly extend t
h
g
exper
t
-dete
r
each specif
i
b
elonging to
loyee, finall
y
each emplo
y
n
ts from the e-m
a
fig. 3) chose
n
y
the author fr
o
u
stin» are sig
n
the proper n
o
f
o
r
mation" ar
e
a
tion by each
m
it is visibl
u
tion charact
e
n
cies of terms
c
onclusion t
h
e
is that crite
r
.
It has to be
m
c
y distributio
n
o
gram servic
h
is analysis i
s
the enterpris
e
expert’s lists
t
not be enou
g
o
r words "au
d
towards "s
i
o
ncepts for t
h
o
cated at the
e
n
g out (so-ca
l
h
e definition
r
mined taxon
o
i
c employee
taxonomy,
f
y
, we will r
e
y
ee concerni
n
a
ils of IT Co.
n
from the
o
m rank in
n
ificant so
o
un which
e
common
enterprise
l
e that for
e
r differs,
usage.
h
at exactly
r
ion which
m
entioned
n
of terms
c
e of intra
s
used for
e
who are
the intra
g
h in order
u
gust" and
i
gnificant"
h
e narrow
e
xpense of
l
led social
of expert
omies for
to these
f
rom total
e
ceive the
n
g all (or
100

allocated
)
static or
employe
e
The
f
employe
e
The
a
this fra
m
4th of J
u
employe
e
Such
“intellec
t
circles
a
tradition
a
unessent
i
p
otential
inevitabl
y
p
otential
4.2 R
e
The sec
o
expert
n
p
rovisio
n
p
sycholo
g
means o
f
edges re
p
with eac
h
Mess
a
interacti
o
individu
a
In or
centralit
y
b
ased o
n
main ind
i
• Betw
e
other no
d
)
processes i
n
constant, m
o
e
or change o
f
f
ollowing cha
e
within a yea
Fig. 3.
C
a
nalysis of ch
a
m
ework. It is
p
u
ne correspon
e
.
distributions
t
ual prints”.
D
a
re develope
d
a
l is that till
s
i
al that emer
g
innovative p
r
y
will be fixe
for develop
m
e
search Ques
t
o
nd research
t
n
etwork for
n
s of modern
g
y. Commun
i
f
graph G =
(
p
resent conne
h
other.
a
ges exchan
g
o
n – as bigrap
h
a
l in network
i
der to meas
u
y
. Centrality
–
n
number of
i
i
cators of cen
t
e
enness – sh
o
d
s in network.
n
corporation.
o
reover, it i
s
f
his personal
r
t (Fig.3) de
p
r
.
C
hanges in acti
v
a
nging intere
s
p
ossible to n
o
d
s to the firs
t
are unique
D
istributions
d
analogical
l
s
ome particul
a
g
ence of sim
i
r
ocess. Emerg
d but this wi
l
m
ent and what
t
ion 2
t
opic is expe
r
employees
r
theory of n
e
i
cations can
b
(
V, E) where
ctions betwe
e
g
e among em
p
h
. Positionin
g
i
s defined by
i
u
re social ca
p
–
is indicatio
n
i
ts communic
t
rality:
o
ws what infl
u
If network i
s
It is note-wo
r
s
possible to
ambitions, in
t
p
icts change
o
v
ity of concrete
s
ts or prioritie
o
te only that
t
t
return wee
k
and can be
of new subj
l
y; their ba
s
a
r period of
t
i
lar innovatio
n
ence of new
w
l
l be questio
n
is language e
v
r
t’s social ca
p
r
anking. Me
t
e
tworks, mat
h
b
e presented i
n
set of V-top
s
e
n employees
p
loyees can
b
g
isn't satisfie
d
i
ts relations t
o
p
ital it is off
e
n
of how high
c
a
t
ions with
o
u
ence the no
d
s
designed in
s
r
thy, that this
judge adap
t
t
erests etc. fr
o
o
f accents in
employee wit
h
s for this dist
r
t
he distributio
k
from fortni
g
in many res
p
ects, new co
s
ic differenc
e
t
ime they jus
t
n
gives the
e
w
ords, jargon
s
n
of an expert
v
olution.
p
ital measure
m
t
hodological
h
ematical lin
g
n
form of soc
i
s
represent e
m
, expressed i
n
b
e presented
a
d
by spatial d
i
o
other positi
o
e
red to calcu
is the emplo
y
o
ther networ
k
d
has for con
n
s
uch a manne
r
representatio
n
t
ability of th
e
o
m speed of it
s
activity of t
h
h
in a yea
r
.
r
ibution rema
i
n
"anomaly"
g
ht business t
r
p
ects compa
r
n
cepts, and
d
e
from sign
i
haven’t occ
u
e
vidence that
s
, new politic
a
assessment
w
m
ent in intra
base of res
e
g
uistics, soci
o
i
al system de
s
m
ployees, an
d
n
their comm
u
a
s network st
r
i
stance. Any
p
ns.
l
ate indicato
r
y
ees social c
a
k
nods. There
n
ection of gap
r
that there ar
n
won't be
e specific
s change.
h
e specific
i
ns behin
d
falling on
r
ip of this
r
able with
d
iscussion
ificant or
u
rred. It is
there is a
a
l subjects
w
ha
t
has a
corporate
earch are
o
logy and
s
cribed by
d
set of E-
u
nications
t
ructure of
p
osition of
r
s of nods
a
pital, it is
e
are three
p
s between
r
e no other
101

ways of interaction of other nods except through this nod, it will have the maximum
influence. Removal of nod which has big betweenness indicator will cause break of
information flow and will lead to network [10] fragmentation. Such nods act as
brokers or doorkeepers as they supervise information flows [11].
• Closeness shows possibility of fast access to information; it is inversion of sum of
the shortest distances between each nod and each different nod in network. The fewer
the intermediary nods between the current nod and other nods, the lower is the
closeness indicator and the higher is the closeness degree[12]. This position is quite
advantageous at communications implementation.Than less than intermediary nods
between the flowing nod and other nods, the indicator of closeness and subjects is
lower than subjects degree of closeness [12] is higher. This position is very
advantageous at communication implementation.
• Centrality degree – this characteristic shows who the most active nod in network
is. In compliance with networks theory a large number of interactions of nod can not
only change nod position in network, but also change positions of other nods. The
individual indicator of centrality shows, in what degree the nod is connected by other
knots, that is how closely it is connected with group [13].
• Centrality as indicator of centrality of own vector (eigenvector centrality) — nod
importance in network [14]. The indicator estimates relative measures for all nods
inside network based on to whom nod neighbors have connection.
• Clustering coefficient [15] - degree of nods connectivity in network. This
cofficient characterizes tendency to formation of groups of interconnected nods, so-
called cliques.
4.3 Research Question 3
The third task is innovative process management of expertize transfer from one
employee to another.
Thesis 1: The innovative system should possess ability to support interaction
between innovators and experts for carrying out expertize of an innovation.
Thesis 2: The most expedient way of creation and automation of innovative process
is application of subject-oriented approach to innovative process management. In such
case there are all necessary conditions for realization process and network
communities ad hoc and also for brightest development of reflection while creating
new knowledge.
For specification of above-mentioned theses let’s consider how S-BPM realization in
tool system Metasonic (former jCOM1) S-BPM Suite looks.
The model of innovative process in «Process Manager» is designed in such a
manner that the subject "Initiator" (the founder of innovation) sends the message
"Innovation" to the subject «Experts Search Service» (it not the person but the
element of system which is processing information). «Experts Search Service»
possesses profiles of enterprise staff, in reply to the demand sends the message to the
initiator with candidates of potential investors of intellectual capital and their profiles.
Having analyzed recommendations and profiles of candidates initiator sends the
invitation to potential investors «Request for Community Creation» and receives
102
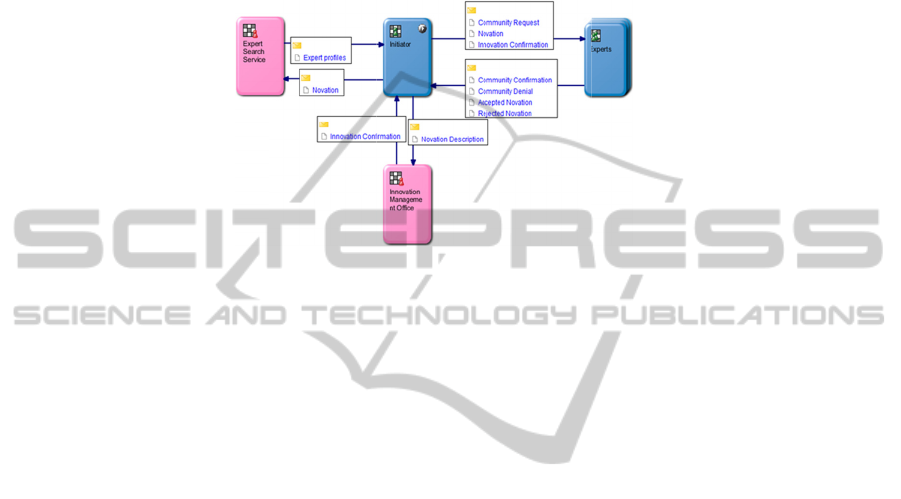
approbat
i
commun
i
who ha
v
p
rocess
w
p
articipa
n
all com
m
Fig. 4. E
x
Innovatio
n
4.4 R
e
In cours
e
irrelevan
c
informat
i
workflo
w
adequate
coding,
p
The
d
connecti
o
informat
i
an innov
a
mature p
h
who are
r
5 Con
c
The carri
1) Intell
e
authors
a
concepts
,
subject
d
each oth
e
domain).
i
on «Confir
m
i
ty for innov
a
v
e accepted
t
w
ill occur in
e
n
ts of innova
t
m
unity partici
p
x
ample of des
c
n
Process Man
a
e
search Conc
l
e
of innovati
v
c
e of utilized
i
on selection,
w
system th
e
access to re
l
p
reservation a
n
d
escribed ap
p
o
n to both:
i
on and vario
u
a
tive process
h
ases of self-
r
r
esponsible f
o
c
lusions
ed-out resear
c
e
ctual capital
a
nd possessi
n
,
which relat
i
d
omain. Char
a
e
r (which me
a
m
ation of A
c
a
tion develo
p
t
he inquiry t
a
xpert’s com
m
t
ive process.
A
p
ants develop
m
c
ribing an inte
r
a
gement (S-BP
M
l
usion
v
e creativity
information.
which is rele
v
e
connection
l
evant infor
m
n
d access to p
roach on the
multiple s
e
u
s DBMS wit
h
m
anagement
r
ealization ca
n
r innovative
d
c
h solves thre
e
assessment:
e
n
g high qua
i
ve frequenc
y
a
cteristic term
a
ns high pro
b
c
cedence to
p
ment is aut
o
ake part. A
f
m
unity. The p
o
After accum
u
m
ent of innov
raction of act
o
M
point of vie
w
the most ess
Continuous
u
v
ant to solvi
n
wi
t
h infor
m
m
ation from
u
p
roble
m
-struc
t
S-BPM plat
f
e
rvices of i
n
h
access to d
a
system archi
t
n
be correcte
d
d
evelopment
p
e
problems:
e
xperts searc
h
a
lification (c
o
y
of mention
m
s can be in r
e
b
ability of re
f
Community
»
o
matically cr
e
f
te
r
wards the
o
tential inves
t
u
lation of int
e
ation takes pl
a
o
rs in the subj
e
w
).
ential risk fa
u
pdating of a
n
g task, is req
u
m
ation servi
c
u
nstructured
s
t
ured informa
t
f
orm allows
r
n
formation
a
a
ta at level of
f
t
ecture autoge
d
and analyze
d
p
rocesses.
h
(people regi
s
o
mpetence)
o
allows to c
o
e
lation of ont
o
f
erence of the
or denial.
e
ated where
a
innovation
d
or and expert
s
e
llectual inve
s
a
ce (Fig. 4).
e
ct-oriented m
o
c
tor is uncer
t
n
alyzed infor
m
u
ired. Theref
o
c
es providin
g
ources and s
e
t
ion are neces
s
r
ealization of
c
cess to u
n
f
ields. There
b
n
eration whi
c
d
by the expe
s
tered in syste
f subject d
o
o
nnect it wit
h
o
logical
p
rox
i
s
e terms to o
n
The new
a
ll experts
d
iscussion
s turn into
s
tments of
o
del of the
t
ainty and
m
ation and
o
re, except
g
reliable,
ervices of
sary.
f
operative
n
structured
b
y, there is
c
h in more
e
rts groups
e
m as texts
o
main) by
h specific
i
mity with
n
e subject
103

2) Social capital assessment: metrics calculation allowing estimation of
communication efficiency among experts.
3) Innovative process management: innovations creation and distribution process
automation in companies at the expense of independent expertize founded by experts
search service and assessment of employees information interaction.
At the moment there already exist solutions of automatic experts search. The HelpNet
tool uses information generated by users for creation of an expert profile [16]. One
more similar tool is Expert Locator which uses a representative collection of technical
documentation written by the employee for creation of expert indexes [17]. Recently
NASA's agency presented the Expert Finder [18] solution which uses substances
(keywords) allocation for publications submission summaries of user and then builds
experts rating in process of inquiries relevance. One more similar system is I-Help
[19] – agent system which models user’s characteristics for the other employee search
who might help him. Vector model is used for the most suitable employee selection
from the stated inquiry of allocated information.
The main problem of above-listed options is that they represent the subjective
value of employees competence and assume structured information utilization which
is created, collected, classifed and exchanged by employees. However, the majority of
organizations do not structure information but it actually contains answer to the
question who is the expert finally.
Novelty of the current research lie in creating means for automatic detection of
person who is an expert in what area, effective search of such expertize, informing
who from the identified experts is in network and means of communication with him.
All this will allow strengthening and accelerating innovative processes in
organizations at the expense of favorable information environment creation which
simplifies information exchange between employees and allows accumulating,
generalization and classification of advanced knowledge.
Quantity of efforts, which have to be made in order to organize innovative process
in organization depends on number of factors, such as organization size, automation
level, force of social communications in organization and etc. The developed service
can be applied as the tool to the solution of experts search problems on corporate
portals, in ECM – system and in any other IS accumulating publications data of
employees.
The further approaches and results of these studies may be used afterwards for
improvement of the incumbent companies as well as for processing and transferring
of the complicated unstructured information content within the Enterprise 2.0, joined
ventures or modern vertical integrated organization.
Acknowledgements
The given research was held in a frame of the contract № 13.G25.31.0096 with the
Ministry for Education and Science of Russian Federation «Creation of hi-tech
manufacture of unstructured information processing in cross-platform system on the
open-source software basis in order to increase management efficiency of innovative
activity of enterprises in modern Russia.
104

References
1. Noah E., Friedkin & Eugene C. Johnsen: Social Influence Network Theory: A Sociological
Examination of Small Group Dynamics (Structural Analysis in the Social Sciences),
Cambridge University Press; 1 edition edition (2011)
2. Burt R., 2001. The Social Capital of structural holes // Guillen M.F., Collins R., England P.,
Meyer M. (eds.). New Directions in Economic Sociology. N.Y.: Russel Sage Foundation:
201-246.
3. Fernandez, R. M., Castilla, E. J., & Moore, P. 2000. Social capital at work: Networks and
employment at a phone center. American Journal of Sociology, 105: 1288-1356.
4. Granovetter, M. [1974] 1995. Getting a Job: A Study of Contacts and Careers. Chicago, IL:
The University of Chicago Press.
5. Seidel, M. D. L., Polzer, J. T. & Stewart, K. J., 2000. Friends in high places: The effects of
social networks on discrimination in salary negotiations. Administrative Science Quarterly,
45:1-24.
6. Adler, P. S. & Kwon, S. W., 2002. Social capital: Prospects for a new concept. Academy of
Management Review, 27: 17-40.
7. Xiaodan Song, Belle L. Tseng, Ching-Yung Lin and Ming-Ting Sun, "ExpertiseNet:
Relational and Evolutionary Expert Modeling", Intl. Conf. on User Modeling, Edinburgh,
UK, July 2005.
8. Jing Zhang, Jie Tang, Juan-Zi Li: Expert Finding in a Social Network. In Proceedings of
DASFAA'2007. pp.1066~1069.
9. Yupeng Fu, Rongjing Xiang, Yiqun Liu, Min Zhang, Shaoping Ma: Finding Experts Using
Social Network Analysis 2007 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web
Intelligence.
10. Borgatti, S. P. & Everett, M. G., (2006). A Graph-Theoretic Perspective on Centrality.
Social Networks, 28(4), 466-484.
11. Wang, J., & Chen, C., (2004). An Automated Tool for Managing Interactions in Virtual
Communities - Using Social Netwrok Analysis Approach. Journal of Organizational
Computing and Electronic Commerce, 14(1), 1-26.
12. Wasserman, S. & Faust, K., (1994). Social Network Analysis: Method and
Applications.Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
13. Ahuja, M., Galletta, D. & Carley, K., (2003). Individual Centrality and Performance in
Virtual R&D Groups: An Empirical Examination. Management Science, 49(1).
14. P. Bonacich, Factoring and weighting approaches to status scores and clique identification,
Journal of Mathematical Sociology, 2 (1972).
15. Watts, D. J.: Collective Dynamics of «Small-world» Networks // Nature / Ed. by
S.H.Strogatz. 1998. Vol. 393.
16. Maron, M. E., Curry, S., Thompson, P.: An Inductive Search System: Theory, Design and
Implementation. IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 16(1) (1986), 21–28.
17. Steeter, L. A., Lochbaum, K. E.: An Expert/Expert Locating System based on Automatic
Representation of Semantic Structure. In Proc. of the Fourth IEEE Conference on Artificial
Intelligence Applications: San Diego, CA, (1988), 345–349.
18. Staab, S.: Human language technologies for knowledge management. Intelligent Systems,
16(6): (2001), 84–94.
19. Bull, S., Greer, J., McCalla, G., Kettel, L., Bowes, J.: User Modelling in I-Help: What,
Why, When and How. In Proc. of the 8th International Conference on User Modeling,
Sonthofen, Germany, July, (2001), 117-126.
20. Alexander Gromoff, Valery Chebotarev, Kristin Evina and Yulia Stavenko: An Approach
to Agility in Enterprise Innovation S-BPM One Learning by Doing - Doing by Learning
Third International Conference, S-BPM One 2011: Springer, 2011.
105
