
Towards a CDN over ICN
Byungjoon Lee, Hongseok Jeon, Seunghyun Yoon and Hoyoung Song
SmartNode Research Team, ETRI, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Keywords: Information-Centric Networking (ICN), Content Delivery Network (CDN).
Abstract: The development of Information-Centric Networking (ICN) concepts is one of the significant results of
different international Future Internet research activities. In the approaches, the networking paradigm shifts
from the host-to-host communication to the information-based communication. The ICN concept is
receiving huge attention because of the increasing demand for highly scalable and efficient distribution of
information. Meanwhile, the Content Delivery Network (CDN) has been an important patch to the existing
IP network that enables the fast delivery of content. Though the CDN architecture relies on the traditional
host-to-host communication model, it has been widely deployed to solve the content availability and on-
time delivery issues. In this paper, we cover issues and requirements to implement CDN over ICN
technologies, and suggest an architecture called IICN which enables an easy transition from IP-based CDN
to ICN-based CDN. In IICN, it is possible to incrementally replace IP nodes with ICN-capable nodes. We
believe that IICN suggests an important ICN application that leads to an Information-Centric Internet.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to the Sandvine report (Sandvine, 2011),
Netflix traffic is 37.5% and YouTube traffic is
11.3% of the North America Internet traffic in year
2011. Cisco also forecasted that the video traffic will
be 91% of the total Internet traffic in year 2014,
including videos exchanged by P2P applications or
downloaded from Web (Cisco, 2011). It means that
the Internet is simply becoming a delivery network
of video files from the popular Over-The-Top (OTT)
service providers.
Normally, the OTT service providersplayers use
Content Delivery Network (CDN) technologies to
enhance the content availability and the content
delivery performance. For example, Netflix has used
Akamai, Level3, and Limelight CDN solutions to
build an ISP-independent content delivery network.
The key components of CDN are request routers,
and surrogates (Pathan and Buyya, 20058): a
request router forwards a client request for content
to its designated surrogate, and the surrogate takes
the role of acquiring and delivering the content.
Especially, surrogates play a role of in-network
cache to place content as close as possible to access
network. Thus, the surrogates provide better QoE by
making content travel on shorter path. Recently,
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are stepping
towards an Operator-CDN that incorporates CDN
capabilities in their networks.
Meanwhile, in the Future Internet research
context, there have been suggestions for a new
networking paradigm called Information-Centric
Networking (ICN). The ICN researchers have
realized that the traditional Internet has taken a host-
to-host communication model, which inherently
focuses users to care about the location of
information. On the contrary, current Internet users
only care about ‘what’ information they want. The
paradigm shift from where to what have accelerated
the dawn of new transport layers that handles the
communication between networking parties by the
identifiers of information, not by the address of the
information. Such research activities include CCN
(Jacobson et al., 2009), DONA (Koponen et al.,
2007), and PURSUIT (http://www.fp7-pursuit.eu/
PursuitWeb/).
Though the ICN research activities have
demonstrated that many of the Internet problems can
be resolved by introducing the identifier-based
transports, but they are still in their incubation stages.
To prove their effectiveness, the ICN technologies
need to be incorporated into the widely-adopted ‘real’
content delivery technologies. In that sense, we
envision a Future CDN that deals with a huge
number of information using ICN technologies.
46
Lee B., Jeon H., Yoon S. and Song H..
Towards a CDN over ICN.
DOI: 10.5220/0004125900460051
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Communication Networking, e-Business and Optical Communication Systems (DCNET-2012),
pages 46-51
ISBN: 978-989-8565-23-5
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Therefore, in this paper, we list considerations
and requirements for the CDN-ICN integration. In
addition, we give a quick overview of our suggestion
for an ‘Interim’ ICN architecture called IICN.
This position paper is organized as follows. In
section 2, we review some of the key building
blocks of CDN, and list the features that an ICN
methodology should incorporate to be integrated
with an existing CDN infrastructure. In section 3, we
cover the issues for the ICN-CDN integration, and
suggest possible solutions. In section 4, we provide
the architecture of IICN and its supporting
arguments. In section 5, we cover a related work. In
section 6, we conclude this paper and give our future
research directions.
2 CDN BUILDING BLOCKS
As briefly mentioned, there are two key building
blocks in CDN: request routers and surrogates. A
request router maps a client and its content request
to a surrogate that services the request. Normally,
the request router determines a surrogate by its
regional proximity to the client. The chosen
surrogate looks up the requested content within the
local content cache. If there is, the cached content is
serviced. If not, the surrogate interacts with other
surrogates in the same CDN hierarchy or contacts to
the origin server of the Content Provider (CP) to
download the requested content. On beginning the
download, the surrogate starts to service the content
to the client.
Thus, we are able to identify following key
building blocks in implementing a CDN: (1) a
request-routing function that determines the location
of a surrogate by proximity, and (2) content service
functions to service various client terminals.
2.1 Request Routing
Basically, the request routing function of CDN is a
mechanism that delivers a user to its closest
surrogate (Pathan and Buyya, 20058). More
precisely, it covers following technologies: (1) a
technique that determines the ‘closest’ surrogate, (2)
a redirection mechanism which forwards a user
content request to the surrogate, (3) a technique
which forwards the request to another surrogate or
an origin server to resolve a cache miss.
Normally, to determine a surrogate by the client
proximity, CDN solutions use the DNS hierarchy; a
domain name within a URL which identifies a
specific content is recursively resolved to an IP
address of a service router which disguises itself a
surrogate. A service router manages a pool of
surrogates (caches) to service clients within the same
access network.
On receiving a HTTP GET request for the URL,
the service router directs the request to a surrogate
that is chosen from the pool of surrogates. Basically,
the service router chooses the most unutilized
surrogate.
If the chosen surrogate does not have the content,
it recursively forwards the HTTP request to another
surrogate by following the path to the origin of the
content. If the requested content is not in any of the
surrogates, the content request is finally forwarded
to the origin server. To determine an origin server,
the reverse proxy technique is usually used.
Basically, a reverse proxy maps a domain name to
an origin server. Thus, by inspecting the domain
name within a URL, a surrogate is able to determine
an origin server.
2.2 Content Service
Basically, content requests from end users are file
requests. For example, YouTube video client
software progressively downloads the video file
hosted by the YouTube origin servers and plays it.
Similarly, Netflix video client software adaptively
downloads the video files cached in the surrogates to
play the whole video.
One thing to note is that various HTTP Adaptive
Streaming Technologies (Adobe, HTTP; Apple,
HTTP Live Streaming; Microsoft) are currently
being used to enable fast download and client-side
video control. In essence, the HTTP Adaptive
Streaming solutions partition a video into segments
to be downloaded and played respectively. Therefore,
to download and play a video, a client sends a
sequence of HTTP GET requests for the segments
that comprises the video. If a delay is observed
while downloading a segment, the client chooses to
download another segment with a smaller bandwidth
footprint. In this way, a client adapts itself to
different network conditions.
3 CONSIDERATIONS FOR CDN
OVER ICN
To design an ICN methodology to replace the key
components of CDN, we should focus on CDN
service scenarios. For example, the HTTP Adaptive
Streaming technology inherently forces us to model
a video by the aggregation of all relevant video
Towards a CDN over ICN
47
segments and their manifest files. It means that
information is actually a group of information. Thus,
to enable end-users to access sub-information, we
should take that into account when designing the
ICN identification, or information naming scheme.
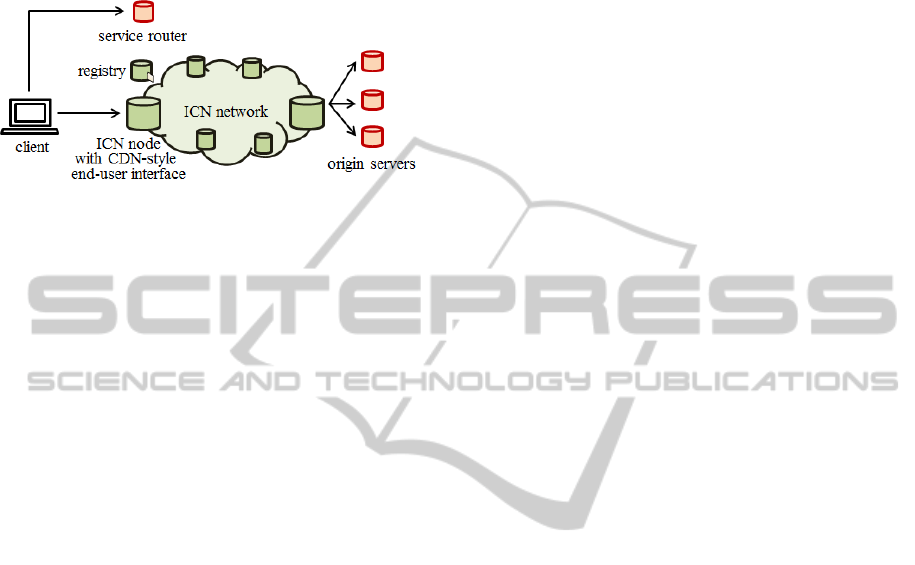
Figure 1: “CDN over ICN” Architecture.
In covering the considerations for an architecture
that implements CDN over ICN, we assume a
network provided in Figure 1. ICN nodes have the
same end-user interface with surrogates, but interact
with each other using ICN technologies. ICN nodes
have a built-in reverse proxy functionality to
interoperate with content origin servers. Registry
manages mappings between information identifiers
and their locations.
3.1 Request Routing
The service router is the first entity that receives a
HTTP GET request from end users. In CDN, it
chooses a surrogate and redirects the request to it. In
CDN designed over ICN, the service router selects
an ICN node, instead of a surrogate, to redirect the
HTTP GET request.
One thing to note is that most ICN
methodologies service the information request by its
identifier, not by the name of the file. It means that
the service router should convert a file name within
a URL into a sequence of identifiers. To handle the
conversion, the service router should manage or
interact with a database that maintains the mapping
between information metadata and identifiers. The
metadata (normally given inside of the URL) should
contain the description of the data, which is detailed
enough to be uniquely mapped to a sequence of
identifiers. The original HTTP GET request and its
URL are modified in result of the conversion, and
redirected to the most optimal ICN node, e.g., in
terms of proximity, which is able to service the
sequence of identifiers.
Because of the aggregate relationship between
information, the conversion result should be ‘a
sequence of’ identifiers. If we use a hierarchical
naming structure (Pathan and Buyya, 20058), this
sequence of identifiers can be flattened into a single
identifier. However, the hierarchical naming
structure makes it hard to predict the length of the
identifier. Therefore, it is more desirable to separate
an identifier into a routing identifier and its sub-
identifiers.
Normally, the routing identifier uniquely
identifies a single publication of information in the
ICN network. It is mainly used to route the
information request packets to their destinations.
The sub-identifiers of the identifier uniquely identify
one component of the publication. For example, we
might choose to use the identifier 0 to represent the
manifest file of a group of video files encoded by the
Microsoft IIS Live Streaming solution. Sub-
identifiers of each sub-identifier might be used to
specify a specific range of bytes of each file.
3.2 Origin Servers
In the traditional CDN, the interaction with the
origin servers is handled by the reverse proxies
(w3.org). In ICN, instead of using reverse proxies,
we might choose to place pseudo-publications
within ICN nodes. For example, let us assume that
one of the origin servers of Figure 1 request to
publish a file foo.mp4 in the ICN network. The
service router does the conversion between the file
name and a sequence of identifiers, and requests a
nearby ICN node of the origin server to publish an
entry <routing ID, URL to the origin server>. The
service router uses the information to choose an
optimal ICN node to service the file, and the ICN
node uses the information to pull down the file from
the origin server on receiving a request. At the same
time, the registry receives a message that represents
‘what’ content is published ‘where’.
3.3 Streamers
Usually, information within the ICN network is
serviced by streamers. These days, because of the
port-80 issue, HTTP-based streamers are commonly
used, including the HTTP Adaptive Streaming
engines. The streaming engines lookup the file
system for information to service.
One of the key considerations for integrating
ICN to this end-user interface is that we should not
modify the existing streamer implementations which
service information to end users. It means that (1)
we need an ICN-abstraction layer which provides
the streamer with a virtual read-only file system, and
(2) a conversion rule which translates a file name
into a sequence of identifiers. The conversion rule
DCNET 2012 - International Conference on Data Communication Networking
48

should be consistent with the conversion rule that we
have mentioned on Section 3.1.
The file system implementation might be
complicated if we use a chunk-based ICN transport
such as CCN which limits the size of the content-
exchanging packets (Pathan and Buyya, 20058).
4 IICN ARCHITECURE
Following the observations in the previous sections,
we have defined an ICN architecture called IICN,
which is designed to facilitate the CDN-ICN
integration. In this section, we list our architectural
decisions step-by-step with detailed usage scenarios.
4.1 Publication of Information
Figure 2: Publication Procedure for a Content Provider.
A Content Provider (CP) expresses its intention for
publishing content to the service provider by sending
a URL and metadata. The URL points to the origin
server for accessing the content and metadata
describe the content. The metadata include
information such as the name of content, a
description, the total size of the content, CP
identifier, etc. From the metadata, the service router
generates a routing identifier.
Then the service router sends the publication
result (the identifier and the URL) to the ICN node.
The recipient ICN node saves the mapping between
the identifier and the URL, and sends a registration
message to a registry. The registration message
contains the routing identifier and the address of the
ICN node. The registry maintains the records which
maps an identifier to its actual locations. IICN
implements its control plane using the registry.
One thing to note is that, in IICN, potentially all
ICN nodes can play the role of reverse proxy
(sometimes called content acquirer (Cisco, http://
www.cisco.com/)).
4.2 Information Routing
IICN follows the request-response communication
model of CCN; a consumer of information expresses
an ‘Interest’ on the information and a producer of
the information sends a response to the Interest.
However, while CCN requires a proactive and a
priori deployment of the FIB entries to forward the
Interest packets, we take a rather different approach
of ‘querying’ the location of information before
sending Interests, and relying on IP FIB entries to
forward the Interests to the destination.
Figure 3: Client sends a HTTP GET request.
First, a HTTP GET request for content is
delivered to the service router, via the traditional
CDN request routing mechanism. On receiving the
request, the service router looks up its database and
converts the HTTP GET request to include the
identifier of the content. Then, the modified request
is redirected to the nearby IICN node, and its
streamer. To service the request, the streamer looks
up the requested file in the virtual file system. The
file system converts the file lookup to Interests, and
expresses the Interests to the network.
Figure 4: Interest routing.
In IICN, to send an Interest for X, a node first
queries its location to the registry (Figure 4). If there
is a published content X in the network, the registry
replies its address y. The address y is embedded into
the Interest packet to be used as a routing hint by all
intermediate IICN nodes in the same path to the
destination of the Interest. As all IICN nodes are
OSPF-capable, each node is able to calculate the
address of the next-hop IICN node by consulting the
OSPF FIB entries. Before forwarding the Interest
packet, each IICN node replaces the destination IP
address of the packet with the next-hop address.
Towards a CDN over ICN
49

On receiving an Interest, each IICN node checks
if it has the requested content X. If there is a cached
chunk of X, it is replied. If not, the node keeps
forwarding the Interest to the next-hop IICN node. If
the Interest reaches the final destination y, the
destination node looks up its file system for X. If
there is no such content in its file system, the node
tries to download the content from the origin server
by consulting the reverse proxy records. On
downloading the content, the IICN node sends a
reply (Data packet) to the Interest Packet. Basically,
the Data packet forwarding scheme is the same with
the Interest packet forwarding scheme.
The information-routing scheme suggested in
this section is interoperable with legacy IP routers
because each IICN node switches the destination IP
address field in the packet header to the address of
next-hop IICN node. To the legacy IP routers, all the
IICN packets are just plain IP packets. Therefore,
IICN enables legacy IP routers to be incrementally
replaced with IICN nodes.
4.3 Virtual File System
In the previous section, we mentioned a virtual file
system which converts a file request to a sequence of
Interests. The virtual file system that the IICN node
provides is a read-only user-space file system
implemented on FUSE (http://fuse.sourceforge.net/).
The file system plays an important role in IICN
architecture because it enables the interoperation
between the streamer and the IICN networking layer
without any modification of the streamer source
codes.
The modified URL that an IICN node receives
(Figure 3) contains a modified file name that
includes a routing ID (for example, a file name
‘avatar.ism’ is replaced into ‘2325234_avatar.ism’
where 232534 is a routing ID). To process a ‘file
open’ request from the streamer, the file system
extracts the routing identifier from the file name and
sends a query message to the registry. If there is no
such content in the network, the file system responds
an error for the file open request.
To process a ‘file read’ request, the file system
first converts the file name into a sequence of
identifiers. For example, a request to read a byte
sequence (offset x, size sz) from the file
2325234_2750000_avatar.ismv is processed by
following procedure:
1. Extract the routing identifier: 2325234
2. extract the first sub-identifier: 2750000
(bitrate)
3. calculate the third sub-identifier: from
floor(x/M) to floor((x+sz)/M) where M is the
IICN chunk size
Thus, the request is converted to a sequence of
Interests that request content chunks by the
identifiers from (2325234, 2750000, floor(x/M)) to
(2325234, 2750000, floor((x+sz)/M)). By sending
the Interests to the network, the virtual file system is
able to retrieve all the bytes to service.
Figure 5: IICN Virtual File System.
5 RELATED WORK
The most closely related research project to IICN is
CCN (Pathan and Buyya, 20058). CCN defines a
named data networking transport. CCN names are
hierarchically organized to facilitate the expression
of ‘interests’. For example, a user who wants a first
video chunk of the video ‘resume.avi’ published by
CareerCup.com expresses the interest by the name
‘/CareerCup.com/resume.avi/_s0’. In response to the
interest, the CCN network returns a data. Because
the CCN chunk size is very small (close to the link
MTU), a user should keep expressing interests until
downloading the whole video.
To service a specific interest, CCN uses FIB
entries that guide interest packets to their destination.
To deploy FIB entries to each CCN node, it is
generally assumed that OSPF-like routing protocol
is used to enable a distributed FIB calculation.
Mapping information between names and their
actual locations are disseminated via the protocol.
One of the problems of CCN is the cost to
process the name. The length of the names might put
a negative impact on the overall performance of
CCN routers. For example, D. Perino et al (Perino
and Varvello, 2011) have pointed out that
contemporary memory technologies are not good
enough to support CCN.
Another problem of CCN is the volume of the
router states. The number of FIB entries is
proportional to the number of named data in the
network. It means if there is huge number of data,
the network cannot guarantee the correct operation.
DCNET 2012 - International Conference on Data Communication Networking
50

To solve the issue of the identifier length, we
have separated a routing identifier from the name
and fixed its size. All IICN routers use only the
routing identifier to make forwarding decisions. This
greatly simplifies the complexity of the forwarding
logic of IICN nodes. Thus, IICN is much more
feasible solution to implement.
To solve the router state explosion issue, we
choose to use IP routing without modification rather
than to devise a new routing mechanism. To use the
IP routing, we have separately built an identifier-
address mapping system (that is, registry) outside of
the IICN data layer, and have made all IICN nodes
OSPF-capable. As all the information that incurs the
state explosion issue is shifted to an external system,
we are able to define the IICN data layer on top of
IP without scalability issues.
Besides, because IICN is defined on IP, we can
incrementally deploy IICN nodes in the network.
IICN packets are forwarded hop-by-hop between
IICN nodes and all the legacy IP network elements
are simply ignored.
6 CONCLUSIONS
CDN, a network consists of IP network elements and
data surrogates, is designed to provide network users
with better QoE by reducing the number of hops that
a data packet should travel to reach clients.
ICN is a networking methodology which tries to
redesign the network data layer to support identifier-
based communication. ICN focuses on achieving a
scalable and efficient architecture that is able to
handle a huge number of information.
In this paper, we have suggested a new ICN
architecture, IICN. The architecture is targeting on
easy transition from IP-based CDN to ICN-based
CDN. We believe the integration between CDN and
ICN (actually, CDN over ICN) can demonstrate the
effectiveness ICN.
For that purpose, we have introduced one
possible integration scenario of CDN over ICN, and
explained the overall architecture of IICN. IICN
adopts the existing IP routing and forwarding
mechanism without modification to guarantee the
interoperability with legacy IP network elements.
Further, we have defined interfaces to streamers and
CP origin servers to facilitate the easy transition
from IP-based CDN to ICN-based CDN. In addition,
we have tried to solve many issues of existing ICN
solutions, such as CCN. In this paper, we have
argued that the hierarchical naming structure of
CCN is not effectively implemented, and it causes
the routing state explosion problem. In designing
IICN, we have used only the routing identifier for
forwarding, and separated the mapping between
identifiers and their locations from the data layer. In
result, we believe that we have achieved a better
architecture in scalability.
For the future work, we are planning to do many
feasibility tests on the IICN architecture. The more
thorough architectural description of IICN and
evaluation results will be covered in the next version
of this paper.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the IT R&D program of
KCC/KCA (11911-05003: R&D on Smart Node
Technology for Cloud Networking and Contents
Centric Networking).
REFERENCES
Sandvine White Paper, Global Internet Phenomena Report,
Spring 2011.
Cisco White Paper, Entering the Zettabyte Era, June 2011.
A. K. Pathan and R. Buyya, A Taxonomy of CDNs,
Content Delivery Networks, R. Buyya, M. Pathan, and
A. Vakali (Eds.), Springer-Verlag, Germany, 2008.
V. Jacobson, D. K. Smetters, J. D. Thornton, M. F. Plass,
N. H. Briggs, and R. L. Braynard, Networking named
content, In Proceedings of the 5th international
conference on Emerging networking experiments and
technologies (CoNEXT), pp. 1-12, 2009.
T. Koponen, M. Chawla, B. Chun, A. Ermolinskiy, K. H.
Kim, S. Shenker, and I. Stoica, A data-oriented (and
beyond) network architecture, SIGCOMM Comput.
Commun. Rev. 37, 4 (August 2007), pp.181-192.
Publish-Subscribe Internet Technology, http://www.fp7-
pursuit.eu/PursuitWeb/
Adobe, HTTP Dynamic Streaming, http://www.adobe.com
/products/hds-dynamic-streaming.html
Apple, HTTP Live Streaming, https://developer.apple
.com/resources/http-streaming/
Microsoft, IIS Smooth Streaming, http://www.iis.net/
download/SmoothStreaming
w3.org, ESI invalidation protocol 1.0, http://www.w3.
org/TR/esi-invp
Cisco, Cisco Content Delivery Applications for Internet
Streaming Version 2.5, http://www.cisco.com/
en/US/prod/collateral/video/ps7191/ps7127/product_d
ata_sheet0900aecd806a40f3.html
FUSE: Filesystem in Userspace, http://fuse.source
forge.net/
D. Perino, and M. Varvello, A Reality Check for Content
Centric Networking, In Proceedings of the ACM
SIGCOMM Workshop on Information-Centric
Networking (ICN), pp. 44-49, 2011.
Towards a CDN over ICN
51
