
Data Mining Service Architecture
An Exploration on Self-organizing Software
Junpeng Bao, Bin Tao, Jie Su and Hui He
Department of Computer Science & Technology, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, P.R. China
Keywords: Software as a Service (Saas), Self-organizing Software (SOS), Data Mining, Service Composition, Service
Oriented Architecture (SOA).
Abstract: Software as a Service (SaaS) becomes a very important trend in software engineering. In order to practice
the principles of SasS and Service Oriented Architecture (SOA), we introduce a concept of Self-Organizing
Software (SOS) and a simple prototype implementation, called Data Mining Service Architecture (DMS
Arc) in the paper. SOS implies that the software will automatically build and accomplish the executive
entity according to the user requirements. The DMS Arc is a knowledge based service composition system
that aims to encapsulate basic Data Mining functions into meta services and automatically combine those
services according to the stored knowledge models to fulfil a specific Data Mining requirement. We present
some key issues that place in the SOS service cycle. The DMS Arc project is still on developing, and will be
published as a public facility in a Cloud Computing environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is a significant problem to increase automatic level
in the software engineering and reduce those
repeated work assigned to human. A computer can
not originally create software by itself, but it can
automatically fulfill some task again and again by
some rules. We present the concept of
Self-Organizing Software (SOS) in order to develop
an automatic software product scheme by means of
assembling a group of basic software service to
accomplish the given requirements. SOS is a model
driven auto-build software process that
automatically constructs software from basic
software units according to user requirement models
and stored knowledge models. SOS pursues the
principles of Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)
and Software as a Service (SaaS) (Papazoglou et. al,
2007; Gold et. al, 2004; Staab et. al. 2003). The
contributions of SOS are that the basic services can
be assembled automatically according to preserved
rules in the system. However, those basic services
will originally developed by human, but them will
be cyclically used automatically.
In this paper, we introduce a SOS prototype,
named as Data Mining Service Architecture (DMS
Arc). Obviously, The DMS Arc encapsulates some
basic steps and functions of Data Mining so as to
combine them to support some simple Data Mining
applications. The DMS Arc is designed for Cloud
Computing environment. The basic services can be
deployed at the different computing nodes, and the
whole architecture will develop to a piece of Data
Mining service cloud that will be published as a
public facility.
2 DATA MINING SERVICE
ARCHITECTURE
2.1 Service Architecture
The DMS Arc uses Service Knowledge Model to
drive service composition. A hypothesis is that it is
not difficult to search a service, and all services are
registered in a unified Service Registration Center
(SRC). The system fetches service requirements in
terms of the knowledge model and user’s
description. Indeed, a service is directly searched in
the SRC by matching the service description with
the user’s requirement description. The user
requirements may match multiple candidate services
so that the DMS Arc has to select the optimal
service composition.
In the traditional architecture, a user has to bind
with the service supplier. It implies that the user is
463
Bao J., Tao B., Su J. and He H..
Data Mining Service Architecture - An Exploration on Self-organizing Software.
DOI: 10.5220/0004126504630467
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends (ICSOFT-2012), pages 463-467
ISBN: 978-989-8565-19-8
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
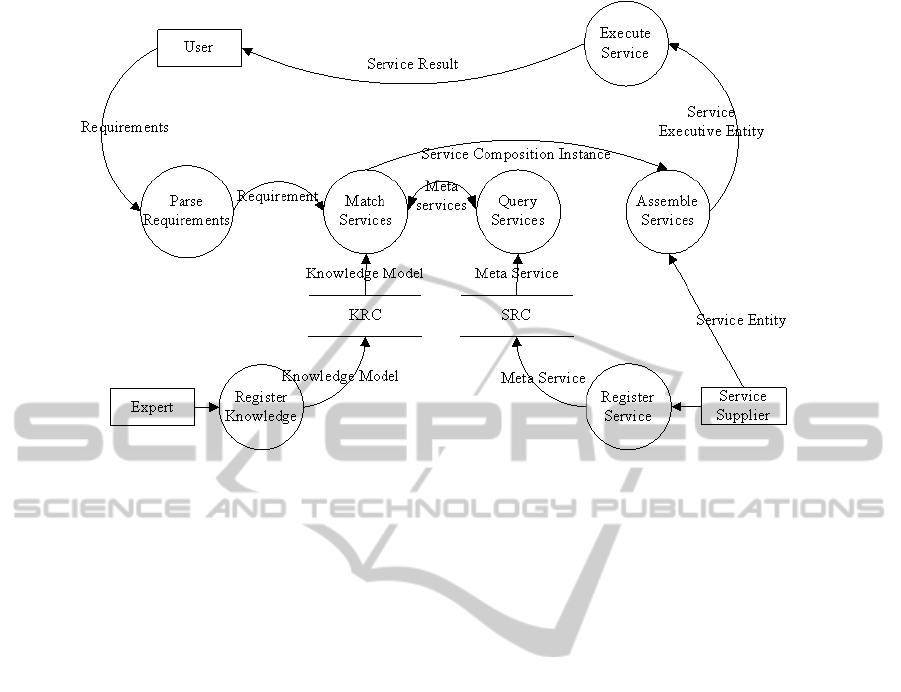
Figure 1: The data flow diagram of the software service process in the DMS Arc.
involved in the service process so that is not fit for
thoroughly automatic service composition and
execution. The traditional architecture is useful for
the human-computer interactive applications, such as
Web Game, Social Network. But the Data Mining
services focus on large scale data processing that
usually does not expect human involvement.
Therefore, in the DMS Arc, the actions of a user are
only submitting requirements and waiting for service
results.
There are 3 extern roles in the architecture: the
service requester (i.e. the user), the knowledge model
expert and the service supplier. The inner roles have
2: the Service Registration Center (SRC) and the
Knowledge Registration Center (KRC). The user
submits the requirements and take the final service
results. The expert input knowledge into the KRC.
The service supplier registers the meta service in the
SRC with detail service information. Hence, the
Service Composition Center is an intelligent agent,
which automatically assembles meta services into an
executable entity according to knowledge models and
accomplishes the entire service process.
In the DMS Arc, a user submits requirements so
as to trigger a system service action. The DMS Arc
will parse the user requirements at the first step. That
needs some respective knowledge models in order to
infer the set of candidate meta services that satisfy
the user requirements. At the reasoning step, the
system will find out not only meta services, but also
the assembling pattern of those meta services (i.e. the
service composition model). Since the number of the
satisfied meta services may be more than one, the
system has to retrieve all eligible meta service and
then selects the optimal service composition
according to the service composition model. After
input the service data, the service combining is over.
At last, the system starts the respective service,
administrates those services’ life cycle. When the
whole service procedure is finished, the results will
be sent to the user, and the service executive entities
are dismissed. This is an entire life cycle of a SOS
service, as shown in the figure 1.
2.2 Design of the DMS Arc
2.2.1 Key Issues
The DMS Arc faces the following 7 issues in a SOS
service cycle.
(1) To define and parse the user requirements;
(2) To define and register a knowledge as well as
the organization of the knowledge repository;
(3) To define and register a meta service as well
as the organization of the meta service repository;
(4) To reason and match a knowledge;
(5) To query and match a service;
(6) To compose and verify services;
(7) To execute and administrate services.
When all of these issues are thoroughly settled,
the DMS Arc will be completely built. Now, the
project is just at the beginning, and we would like to
introduce our ideas and a draft implementation of the
DMS Arc in this paper.
ICSOFT 2012 - 7th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
464

2.2.2 User Requirement Definition
It is natural for a user to describe requirements in a
natural language but it is very hard for a computer to
precisely understand and parse the semantic
information from natural language texts. Now a user
has to fill a detail form to define a requirement that
includes:
R=(Name, Des, Pre, In, Exp, Qos, K)
where R denotes a requirement. Name is a name
of the requirement. Des is a short description of the
requirement content. Pre is the pre-condition that has
to be satisfied before the requirement. In presents the
input data. Exp presents the expectation of the result.
Qos is the quality of the service, which is a reserved
interface and not considered at the present. K is the
knowledge model about the service composition. In
order to avoid any ambiguous understanding about
the semantic information of the requirement, the user
has to explicitly choose a rule from the knowledge
repository as the start of the inference.
2.2.3 Knowledge Model Definition
A knowledge model in the DMS Arc is a Directed
Acyclic Graph that defines a transition process
among a set of meta services. In a knowledge model,
a node presents a meta service that is a component of
a combined complex service, an edge presents the
link between two meta services, i.e. the transition of
messages from one meta service to the other. A
knowledge model is used to indicate which service is
deployed and how to assemble those services in order
to fulfil a specific task. A knowledge model is
explicitly defined as follows:
K=(Name, Des, Pre, In, Af, Ao, Out, Post, Qos,
DAG)
Where K is a knowledge model. Name is a name
of the knowledge. Des is a short description of the
knowledge. Pre is the pre-condition that has to be
satisfied before the knowledge is used. In denotes the
input data. Af denotes the effect of the knowledge.
Ao denotes the objects that will be affected by the
knowledge. Out denotes the output data. Post is the
post-condition of the knowledge model. Qos is the
quality of the service, which is a reserved interface
and not considered at the present. DAG is the
directed acyclic graph of the knowledge model,
which is defined as follows:
DAG=(Start, End, [From1, To1], [From2,To2]…)
where Start denotes the start service. End denotes
the end service. [From1, To1] denotes an edge from
the node From1 to the node To1. Every node in the
DAG describes a meta service.
At present, all knowledge models are created and
maintained by expert. They are described in Xml and
stored in the KRC.
2.2.4 Knowledge Matching
If a user does not appoint the start knowledge in the
requirement definition, the system will parse the user
requirement so as to find an appropriate knowledge
model from the KRC to satisfy the requirement. That
is the knowledge matching process. Now we use a
simple matching principle:
R.PreK.Pre R.InK.In R.ExpK.Out
R.QosK.Qos
Where R denotes a user requirement and K
denote a knowledge model. R.PreK.Pre means the
pre-condition of the knowledge can be inferred from
that of the requirement. R.InK. means the input
data of the requirement covers the input of the
knowledge. R.ExpK.Out means the output of the
knowledge contains the expectation result of the
requirement. QosK.Qos means the quality
constraints of the knowledge satisfies that of the
requirement.
2.2.5 Meta Service Definition
There are many widely used service description
scheme, such as Web Services Description Language
(WSDL) (Kona et. al, 2007), Service Composition
Description Language (SCDL) (Yue et. al. 2007) and
Web Ontology Language (OWL)(Ren et. al., 2011).
WSDL is supported by many compile and browser
tools, but it lacks of attributes description, constraint
of service behaviour and context of the service
composition. SCDL supports the context description
of service composition, pays attention on the
constraint of Web service behaviour, but it lacks of
some non-functional properties including quality of
the se
The Xml structure encoding service encodes a
well-formed xml text into a rvice. OWL uses an
explicit computer-understanding markup language to
describe Web service, tries to realize automatic and
intelligent service composition according to semantic
description and logic reasoning.
In DMS Arc, we use QWSDL(Hu et. al, 2005) to
define and describe a meta service. QWSDL is a
modified WSDL, which absorbs some features of
SCDL and expands its capabilities to define a service
with more precise description. In fact, a meta service
is explicitly defined as follows:
Data Mining Service Architecture - An Exploration on Self-organizing Software
465

S=(Name, Des, Pre, In, Af, Ao, Out, Post, Qos)
where S is a meta service. Name is a name of the
service. Des is a short description of the service. Pre
is the pre-condition that has to be satisfied before the
service is used. In denotes the input data. Af denotes
the effect of the service. Ao denotes the objects that
will be affected by the service. Out denotes the
output data. Post is the post-condition of the service.
Qos is the quality of the service, which is a reserved
interface and not considered at the present.
2.2.6 Service Querying and Matching
Service querying is the process to find all meta
services that can satisfy the requirement. Since the
number of eligible services may be more than one.
Service matching is the process to select the optimal
meta services from those candidate services
according to the knowledge model. Then the selected
meta services will be combined to a whole complex
service to fulfil the user’s task.
In a knowledge model DAG, each node is a
service description so that a node will match a
registered meta service. If a service Ks that is
described in a knowledge model DAG’s node is
matched with a registered meta service Sr, they must
satisfy the follows:
Ks.PreSr.Pre Ks.InSr.In Ks.Af=Sr.Af
Ks.Ao=Kr.Ao Ks.OutSr.Out
Sr.PostKs.Post Ks.QosSr.Qos
The DMS Arc service adapter will find the
optimal registered meta service for each node in a
knowledge model.
3 A TEST CASE
3.1 Xml Similarity Detection
We have implemented a simple Xml similarity
detection application to test the DMS Arc prototype.
The basic steps of similarity detection include: Data
Cleaning, Text Encoding, Feature Selecting and
Similarity Calculating. Obviously, there are many
optional algorithms at each step. The detection
strategy is various according to different algorithm
combination. So we cut the whole similarity
detection process into 4 services, i.e. one step one
service. Then a variety of algorithms is encapsulated
into different meta services. As a result, these
services are ready to be published in the Cloud
Computing environment and will be a public facility
to easily rebuild a new detection approach or
compare with different methods.
The DMS Arc is running on the Apache Axis2
framework, which is the second SOAP engine with a
new Xml processing kernel named AXIOM (AXIs
Object Model). In order to expand the flexibility and
scalability of the DMS Arc as well as quick service
development, we use several languages to implement
different services. In fact, the cleaning services are
written in Java, encoding services are written in
Python, the feature selecting services and similarity
calculating services are written in Matlab. There
meta services are deployed on 2 servers. Our meta
services also comply with OSGi (Open Service
Gateway Initiative) specification because it is helpful
to system stability and efficiency.
There is only one knowledge model in the Xml
similarity detection application. The knowledge
defines the basic services (i.e. steps) and their
relationships in the detection process.
Table 1: A Xml structure encoding service.
Attribute
Value
Name
S_Xml_Structure_Encoding
Des
This service encodes a well-formed
Xml document into a sequence of
code by means of multi-level
encode method according to the
Xml document’s structural
information.
In
Set(Xml document)
Out
Set(code sequence)
Af
Method= Multilevel_Encoding
Ao
Null
Pre
Xml document is well-formed
Post
Null
Qos
Null
3.2 A Meta Service Example
The Xml structure encoding service encodes a
well-formed xml text into a sequence of code
according to the Xml structure information. Namely,
this service converts a Xml document into a code
series so that some series analysis methods, such as
Fourier Transform and Wavelet Transform (Su and
Bao, 2012), can be applied to Xml documents. There
is a variety of structure encoding methods, for
example, Trivial Encoding, Multilevel Encoding,
Pairwise Encoding and Linear Encoding.
ICSOFT 2012 - 7th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
466

4 CONCLUSIONS
SaaS is a very important trend in the software
engineering. We introduce an ongoing project of a
SOS system prototype to practice the principles of
SaaS. The ideas of the DMS Arc are that the basic
functions in Data Mining are encapsulated into meta
services and a service composition route is defined
by a knowledge model. As a result, services can be
extracted from a user requirement and automatically
combined into a complete executive process
according to the stored knowledge model. We
believe that the DMS Arc will develop to a real SOS
system when the knowledge models and meta
services are enriched enough in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by National Natural
Science Foundation of China (Grant 60903123), the
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central
Universities and the Baidu Theme Research Plan on
Large Scale Machine Learning and Data Mining.
REFERENCES
C. Atkinson, P. Bostan, O. Hummel, D. Stoll, 2007. A
Practical Approach to Web Service Discovery and
Retrieval. IEEE ICWS 2007, Salt Lake City, Utah,
USA. pp. 241-248.
N. Gold, A. Mohan, C. Knight, M. Munro, 2004.
Understanding service-oriented software. IEEE
Software, 21(2):71-77.
J. Q. Hu, P. Zou, H.M. Wang, B. Zhou, 2005. Research on
Web Service Description Language QWSDL and
Service Matching Model. Chinese Journal of
Computers. 28(4):505-512.
S. Kona, A. Bansal, G. Gupta, 2007. Automatic
Composition of Semantic Web Services. IEEE ICWS
2007, USA, pp. 150-158.
M. P. Papazoglou, W. J. Van Den Heuvel, 2007. Service
Oriented Architectures: Approaches, Technologies and
Research Issues. VLDB Journal, 16(3):389-415.
K. J. Ren, N. Xiao, J. J. Chen, 2011. Building Quick
Service Query List Using WordNet and Multiple
Heterogeneous Ontologies toward More Realistic
Service Composition. IEEE Transactions on Services
Computing. 4(3):216-229.
J. Su, J. P. Bao, 2012. A Wavelet Transform Based
Structural Similarity Model for Semi-structured Texts.
Advance in Intelligent and Soft Computing.
135:159-167.
S. Staab, et. al. 2003. Web Services: Been There, Done
That? IEEE Intelligent Systems, 18:72-85.
K. Yue, et. al. 2007. SCDL: An Object-Oriented Web
Services Composition Description Language. Journal
of Yunnan University, 29(1):24-31.
Data Mining Service Architecture - An Exploration on Self-organizing Software
467
