
Soft Systems Methodology
A Conceptual Model of Knowledge Management Systems Initiatives in Malaysian
Public Universities
Nor Hasliza Md Saad
1
, Hasmiah Kasimin
2
, Rose Alinda Alias
3
and Azizah Abdul Rahman
3
1
School of Management, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800, Penang, Malaysia
2
Faculty of Economics and Management, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Selangor, Johor, Malaysia
3
Faculty of Computer Science and Information System, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Selangor, Johor, Malaysia
Keywords: Knowledge Management Systems, Soft Systems Methodology, Multiple Case Studies.
Abstract: The implementation of knowledge management systems (KMS) initiatives is recognized by its highly
complex situations and difficult to manage, involving a range of interrelated and overlapping components of
technology, organization and people. The objective of the study is to demonstrate how the Soft Systems
Methodology (SSM) approach can be applied to investigate the implementation of KMS initiatives in their
natural setting. The study is carried out through four case studies within Malaysian Public Universities
(MPUs) representing different characteristics of universities based on the year of their establishment. The
findings reveal the process of KMS initiatives contains six different kinds of activity through the
development of conceptual model. Furthermore, the analysis was conducted to identify factors influencing
the activities within the proposed conceptual model. In this sense, the application of SSM recommends the
advantage of a comprehensive analysis by integrating both the process and the factors influencing the
implementation of KMS initiatives in the higher education context, especially in the MPUs.
1 INTRODUCTION
The higher education (HE) sector involves
knowledge-based organisations where the role and
function of institutions is based on the ‘knowledge’
agenda (Oakley, 2003), (Cronin and Davenport,
2000). KMS initiatives should be implemented in
the HE sector to change its classical paradigm to
confront changes in the external environment change
and provide effective services to meet market
demand and enhance the organization (Serban and
Luan, 2002). A variety of different approach of
KMS initiatives can be introduced not only in the
areas of teaching and learning, but also in the area of
administration to support a wide range of business
processes. In the last decade, an increasing number
of HE sectors around the world have begun to
introduce KMS initiatives. However, there is little
knowledge on how MPUs implement KMS
initiatives and what challenges they confront.
Several studies that examine KMS initiatives in the
higher education sector in Malaysia have indicated
that public universities were slow to implement
KMS initiatives and most were at the initial stage of
implementation (Mohayidin et al., 2007); (Suhaimee
et al., 2005). The objective of the study is to
demonstrate how the SSM approach can be applied
to investigate the implementation of KMS
initiatives, especially the development of conceptual
model. Furthermore, the analysis identifies which
factors in the surrounding environment are
facilitating to the implementation of KMS initiatives
and which may impede the effectiveness of KMS
initiatives.
2 SOFT SYSTEMS
METHODOLOGY
The SSM emerged in response to the limitations of
the hard systems approach to adequately address
complex real world problems that involve human
issues. The emergence of a hard systems approach
was influenced by systems engineering and system
analysis, which use a systematic approach to
problem-solving in relation to the design,
development and operation of a machine to achieve
60
Md Saad N., Kasimin H., Alias R. and Abdul Rahman A..
Soft Systems Methodology - A Conceptual Model of Knowledge Management Systems Initiatives in Malaysian Public Universities.
DOI: 10.5220/0004139000600069
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2012), pages 60-69
ISBN: 978-989-8565-31-0
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

predefined objectives (Ingram, 2000). Thus, to solve
a problem they use reductionists concepts that divide
the problem into smaller pieces and manageable
fragments, without emphasising human or
organisational issues (Bennetts et al., 2000). This
approach is highly appropriate in clearly structured
and well-defined problems. In the early 1970s, the
soft systems methodology was incorporated into a
practical methodology by Professor Peter Checkland
in collaboration with his colleagues at Lancaster
University (Checkland, 1981). The approach used to
apply SSM to research can vary, but the basic
feature corresponding to the conceptual basis
remains constants. In general, this means that SSM
typically has three primary concerns in process of
improving problem situations. First, SSM is
concerned with examining complex problems
involving the socio-technical system, which involves
human intervention. A strong emphasis is placed on
understanding the different perceptions of multiple
stakeholders involved in the problem situations.
Second, SSM highlights the importance of creating a
purposeful human activity model relevant to the
problem situations as a device to identify appropriate
changes that could be made to improve the problem
situation. Finally, SSM strives to create a learning
system to identify methods for improvement by
providing with one or more alternative solutions
rather than an optimisation approach (Petkov et al.,
2007). In this research we will focus on the
particular strength of SSM in developing conceptual
model that identify the necessary pattern activities in
the process of KMS initiatives.
3 METHODOLOGY
This research adopts a multiple case study approach
to investigate four MPUs representing two major
characteristics of the higher education environment
in Malaysia: the older universities established before
1990, where generally larger in size; the newer
universities established after 1990, where commonly
representing smaller in size. An interpretive
approach is used as a mode of inquiry to allow the
researcher to establish meaning from the complex
problem of the real-world situation. Data collection
came mainly from interviews and document
analysis, and each of these methods offers important
insights and understanding into the cases. First, the
interviews were held with the KMS champions who
were highly involved in major activities in the
implementation of KMS initiatives at the university
level. They included IT Directors, IT Managers,
Chief Librarians and other related administrative
director. Second, relevant documents were collected
from government publications, annual reports,
institutional websites, business manuals and slide
presentations. Data were collected on the issues
related to (i) the champion of KMS initiatives; (ii)
the process involved; and (iii) the influencing factors
of the implementation of KMS initiatives.
4 FINDINGS
This section compares the findings of the four cases,
highlighting the similarities and differences to find
the common patterns of activities in a conceptual
model for implementing KMS initiatives. The
analysis revealed that this conceptual model has six
related activities, as depicted in Figure 1.
The four cases were divided into two groups for
the purposes of comparison and contrast. One group
consists of University A(UA) and University B(UB),
which are categorised as older universities. The
other group consists of University C(UC) and
University D(UD), which represent newer
universities. In general, MPUs are slowly
undergoing changes to embrace the challenge of the
implementation of the KMS initiative. The cases
differ in their priority and scope of bringing the
KMS initiative to the university context. However,
they have common activities that indicate they are
operating in the similar context of MPUs.
4.1 Activity 1: Gain Awareness and
Appreciation of KMS Initiatives by
Top Management
This activity deals with the awareness of and
appreciation for KMS initiatives by top
management. In each case, the appreciation of KMS
initiatives by top management was found to be
crucial for creating more formal and conscious
attempts to implement KMS initiatives at the
university level. They were important instruments
for bringing KMS initiatives to the forefront of the
university agenda (Soliman and Spooner, 2000);
(Singh and Kant, 2008). The universities’ decision to
implement KMS initiative is generally triggered by a
specific event or circumstance, which they are taken
place. In general, the summary of activity 1 is listed
in Table 1.
According to the findings of the analysis, the
primary factor influences for this activity is
environmental Pressure. The external environmental
context within the social contexts of the MPU
SoftSystemsMethodology-AConceptualModelofKnowledgeManagementSystemsInitiativesinMalaysianPublic
Universities
61

Figure 1: The Conceptual Model of KMS initiatives in MPUs.
represents the influence of various factors that
contributed to the implementation of KMS
initiatives. In all cases, the government agenda stood
out as one of the most important external factors for
bringing KMS initiatives into universities. Many
respondents recognised the contribution of this
factor in influencing top-level decision makers.
Another external factor that emerged from the data
analysis concerns advances in technology. All of the
case universities struggle to keep pace with rapid
rate of technological changes. In several cases,
external recognition seems to be an effect of
continuously maintaining the effective utilisation of
technology for facilitating KMS initiatives. Awards
and public recognition have been possible incentives
for influencing the implementation of KMS
initiatives. An example of external recognition is the
government rewards for excellent utilisation of
technology in improving business performance. The
university’s interest in the KMS initiatives also
arises because of its desire to follow other MPUs
that are already embarking on KMS initiatives.
Table 1: The summary of activity 1.
Influencing
Factor
Key Issues Highlighted Case
External
pressure
Government agenda,
competitive and global
education environment, and
rapid technological change
UA, UB,
UC, UD
External recognition UB,UC
Peer community pressure UC, UD
4.2 Activity 2: Identify and Assign
KMS Champions to Spearhead the
KMS Initiatives
In activity 2, it is important to consider that the
university’s top management contributed strongly to
the selection and assignment of KMS champions.
The university’s top management plays a critical
role in identifying specific KMS champions with
multidisciplinary expertise and representatives from
the core business departments that would enhance
the implementation. A summary of activity 2 is
listed in Table 2.
According to the findings of the
analysis, the primary influences for this activity can
be classified as follows:
a) Identification of KMS Champion. With regards
to the characteristics of the KMS champions, an
interesting element has emerged. In all of the cases,
the two main domains of expertise have emerged in
making the KMS initiatives successful: the technical
professionals from the IT department and
information management professionals from the
library domain.
The KMS champions contribute their expertise to
support KMS initiatives. The IT department is more
strongly driven by their efforts in preparing for the
advanced technical requirements of KMS initiatives.
The library is concerned with upgrading traditional
library services and information resources into a
more digital environment. The selection of KMS
champions should be based on expertise that can
KMIS2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
62

Table 2: The summary of activity 2.
Influencing Factors Key Issues Highlighted Case
a) Identification of KMS Champion
D
iversity of expertise domains (IT department and
L
ibrary).
UA,UB,U
C,UD
b) Formalisation of the Organisational
Structure
Clear specialized department (KM center) and create new
r
ole(CIO/CKO).
UA, UC
L
ack of clear specialized department and create new role. UB,UD
c) RelationshipbetweenKMS
Champions
Close collaboration between KMS champions UC,UD
L
ack of collaboration between KMS champions UA,UB
effectively assist in ensuring better implementation.
Many studies on KMS initiatives within the HE
context have reported that either the library or the IT
department indeed play a major role in the projects
and activities of KMS (Cain et al., 2008); (Chan et
al., 2005); (Chang, 2003), (Cronin and Davenport,
2000).
b) Formalisation of the Organisational Structure.
The concern for this activity is to specify a clear role
and responsibility of the KMS champion for KMS
initiatives. The top management is in a position of
authority to delegate responsibility and the setting of
the organisational structure. The presence of an
organisational structure setting by creating specific
positions and structure would help to make KMS
initiatives highly visible organization (McDermott
and O’Dell, 2001), as demonstrated in the case of
UA and UC. Daft (2007) argued that a lesser degree
of formalisation of the organisational structure, such
as creating a task force function and responsibility,
seems to solve the short-term problem and lack of
sustainability. However, the issue of a lack of a clear
organisational structure emerged in the other two
cases. These cases were concerned with establishing
a taskforce to address KMS initiatives rather than
adjusting their existing organisational structure.
c) Relationship between KMS Champions. The
coordination of the relationship of KMS champions
was another common issue that drew attention in the
analysis of the four cases. From the findings,
collaboration between KMS champions is critical to
achieve a comprehensive and unified direction to
support university-wide KMS initiatives. This need
is often due to the normal practice of these KMS
champions, which have different business practices
and services. The close relationships among these
key players were achieved by the skilful
coordination and monitoring of the university’s top
management. The close relationship of KMS
champions in the case of UC was able to contribute
to the standardisation of the KMS project and
initiatives;hence, they utilised the scarce resources
available in the most efficient manner to support the
project. This accomplishment is achieved through
coordination by top management (Cain et al., 2008),
and without this formality, the management of
collaboration is unlikely.
4.3 Activity 3: Establish a Strategy for
the KMS Initiatives
This activity is considered to be very crucial that
would serve as a platform to effectively guide the
overall implementation of KMS initiatives. A
strategy needs to be established to decide what
important elements should be included in the KMS
initiatives, as presented in Table 3.
According to the findings of the analysis, the
primary influences for this activity can be classified
as follows:
a) Knowledge Resource. The central issue for
initiating KMS is to identify the types of potential
knowledge resources that can offer strategic value
and outcomes to the organisation. The essence of
this activity is to make knowledge resources more
accessible and available online. In all of the cases,
priority was according to leveraging explicit
knowledge resources that exist in terms of business
documents and reports or reside in various
resources, including in the core databases.
In addition, this knowledge resource is somehow
lacking in a standardisation procedure to manage. To
make this matter more problematic, knowledge is
scattered across the university and exists in a variety
of formats. However, most cases demonstrated less
effort to leverage tacit knowledge sources from
human experience and business activities. This tacit
knowledge is usually considered to be more difficult
to leverage than explicit knowledge, and there is
poor understanding of the proper way to manage
tacit knowledge.
b) Policies and Procedures. In most cases, the KMS
champions are concerned with the lack of policies
and procedures for clearly regulating and controlling
the related activities. Furthermore, it is clearly stated
that very little effort has been made by top
management to put appropriate policies and
SoftSystemsMethodology-AConceptualModelofKnowledgeManagementSystemsInitiativesinMalaysianPublic
Universities
63
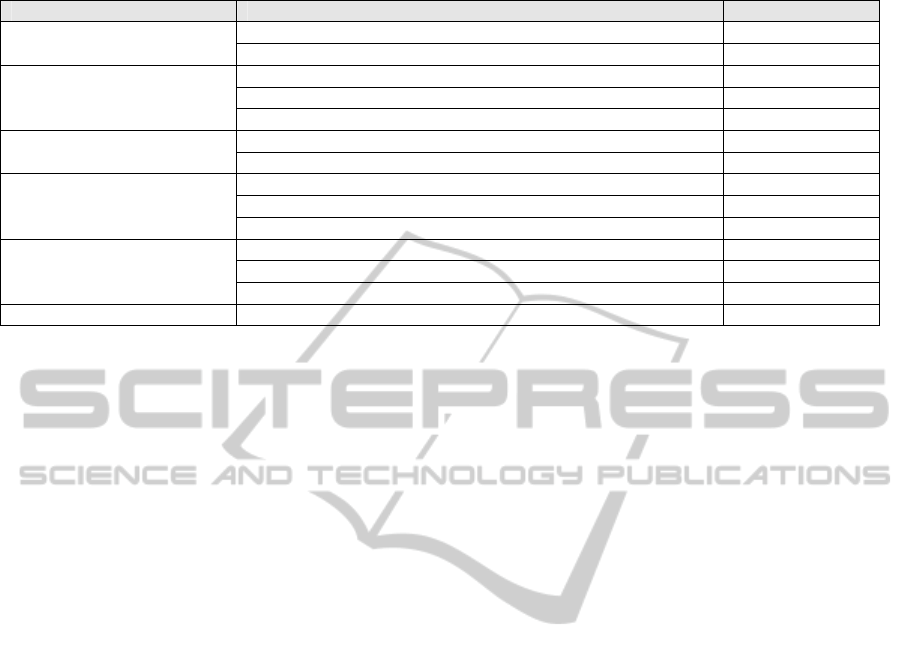
Table 3: The summary of activity 3.
Influencing Factors Key Issues Highlighted Case
a) Strategic direction
Lack of clear strategy direction UA,UB,UD
Clear strategy direction and comprehensive UC
b) Management of
Knowledge resource
Systematic procedure to manage knowledge resource UC
Lack of systematic procedure to manage knowledge resource UA,UB,UD
Less emphasis on leveraging tacit knowledge UA,UB,UC,UD
c) Policies and procedures
Lack of clear policies and procedures UA,UB,UD
Clear policies and procedures UC
d) Outsourcing
consideration
Speed up project development UA, UC
Gain knowledge and skills UA,UC
Avoid bias decision UA
e) Financial support
Insufficient financial support UA, UB
Sufficient financial support UC
Constraints in financial planning UA,UB
f) Incentives and rewards Lack of incentive and reward UA,UB, UD
procedures in place to support KMS initiatives. It is
particularly challenging for KMS champions to
induce participating departments to participate in
their KMS initiatives because the introduction of
KMS initiatives somehow changes the current
practice of business processes to encourage the
adoption of IT applications and enhance knowledge-
sharing activities. However, only the case of UC
provided policies and procedures to guide all
departments within the university to ensure the
adoption of KMS initiatives. Notwithstanding, a
number of studies have discussed the importance of
creating well-documented policies and procedures to
address core activities in the process of KMS
initiatives (Ronald D. F and K., 2007); (Sharifuddin
and Rowland, 2004); (Patricia Ordóñez de Pablos,
2004).
c) Outsourcing Consideration. The role of KMS
champions is ultimately to be responsible for
managing KMS initiatives according to the plan.
Some of the cases naturally underestimated the
complexity of preparing and managing KMS
initiatives to be completed according to the project
schedule and desired outputs. Unfortunately, these
cases did not consider effective decisions in gaining
the benefits of outsourcing (e.g., expertise, cost, and
time). Among the four institutions, two cases
stressed the importance of employing outsourced
support. They believed that this approach might
influence the process of KMS initiatives in a
positive way. These two cases highlighted their
conscious decisions to hire external consultants
during the initial stage of introducing KMS
initiatives. This effort was particularly considered to
be a method for gaining the advantage of the
specialised skills of the consultants and to accelerate
project development.
d) Financial Support. The issue of financial support
appeared to have an important influence on the
selection and development of new technological and
innovative solutions at the institutional level. The
first primary concern brought up in all of the cases
was the time constraint related to financial IT
planning. The three cases agreed that to continue
updating the system to keep abreast of rapid rate of
technological change, they needed to upgrade the
comprehensive archival systems and introduce new
systems to keep them in compliance with their
current technological functions. The problem of
allocation financial support for KMS initiatives is
many facetted, especially is in the long term and
involved various interrelated projects. The allocation
of financial support tended to be concerned with
priorities need to be addressed. According to Wong
(2005), decision maker(s) should develop a realistic
scope of the project, according to available financial
support.
Incentive and Reward. Reward and incentive are
another important consideration for effective KMS
initiatives. The focus of this activity is to encourage
participation in KMS initiatives. One case identifies
the importance of preparation incentives and
rewards to KMS champions and staff participants
which found that the incentives help individuals to
increase their willingness to participate and feel
appreciated for their contribution. Many studies have
posited that the essence of incentives and rewards is
to support changes to employee attitudes and
behaviours such that they will contribute and
participate in KMS initiatives (Sing and Kant, 2008).
KMIS2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
64

Table 4: The summary of activity 4.
Influencing Factors Key Issues Highlighted Case
a) IT infrastructure and
platform
Lack of coordination and standardization UA,UB,UD
Effective Coordination and standardisation UC
Complexity of maintaining the mixture of legacy and new
technology
UA,UB
Robust IT infrastructure UC
b) Knowledge repository
Lack of coordination and standardization UA,UB,UD
Complexity of managing large amounts of databases UA,UB,
Large collection of resources involved in digitalising UA,UB,
Lack of information security control UA,UB,UD
Complexity of digital document categorisation UA,UB,UC,UD
Less complexity of managing a small amount of resources. UC
c) System application
development
Isolated development and focus on departmental needs UA,UB,UD
Integrated and interoperable UC
d) Network performance and
reliability
Extensive network security threats and poor performance. UA,UB
Lack of network interruption UD,UC
4.4 Activity 4: Identify the Necessary
IT Support for the KMS Initiatives
This activity concerns efforts to decide on and
prepare the necessary IT solutions to support the
desired KMS initiatives’ objectives, as listed in
Table 4. This activity is essential for effective
implementation of KMS initiatives. In this activity,
the IT professional provides a crucial role in
identifying and guiding on the requirements for IT
capabilities and functionality that can support and
enhance the process for capturing, storing and
disseminating knowledge (Tseng, 2008).
There are five major component issues that
should be addressed for effective KMS initiatives.
a) IT Infrastructure Platform. In each case, IT
infrastructure influenced the preparation of
technology requirements for KMS initiatives. There
are two major barriers experienced by several cases
for moving towards the mission of preparing IT
platforms for facilitating KMS initiatives. The first
barrier is the lack of a standard and common IT
infrastructure; current platforms are heterogeneous
and controlled by different departments. Within this
situation, the equipment and infrastructure are often
poorly managed, which leads to inefficient use of
resources. Another concern regarding IT
infrastructure is the maintenance of insufficient
technical requirements that are outdated or lack
capable technologies. This issue reflects concerns
about the challenge of preparing an appropriate IT
infrastructure in which some components of the
installation-based infrastructure are subject to
upgrades or replacement. The other potential
problem raised was incompatibility and complexity
with the installation-based infrastructure. The well
preparation of IT infrastructure was especially
apparent in the case of UC, especially with well-
planned state-of-the-art technology in providing a
coordinated and standardised approach. This factor
seems to facilitate better technology management
without much concern for the various conflicts of
multiple standards of equipment and outdated
technology. The development of a well-planned
architecture of an IT infrastructure for the entire
university environment is an important consideration
to facilitate coordination, management, and
connectivity among different departments(Zakareya
Ebrahim, 2005).
b) Knowledge Repository. In all cases, database
resources, with their various challenges and
opportunities, were brought into play because they
are considered to be at the heart of the knowledge
resources that can be better utilised. There are six
major barriers that were experienced by these cases
in moving towards the mission of preparing
technology platforms for facilitating KMS
initiatives. First, a lack of coordination and
standardisation of database resources has a negative
influence on the complex process of data integration,
data availability and data accessibility. The cause of
the problem was identified as being either the
incompatibility of heterogeneous platforms or that
the database resources were placed at dispersed
locations that often lacked common data definitions
and poor data documentation. On the contrary, UC
had an encouraging experience with enterprise
database solutions and centralised data management
for the entire knowledge repository.Within this
scope, this university acknowledged that this
database approach was designed to enforce
consistency and facilitate database management
SoftSystemsMethodology-AConceptualModelofKnowledgeManagementSystemsInitiativesinMalaysianPublic
Universities
65

across different resources.
Second, the huge amount of database resources
has also increased the complexity of managing a
knowledge repository for the cases of UA and UB.
These universities have undertaken the task of
collecting their archive resources together with
current data resources into a more manageable
effort. Third, they also have large collections of
databases resources and paper-based documents
requiring effective electronic management to make
them more accessible and available. Fourth,
throughout the four cases, the lack of systematic
categorisation of digital documents is widely
recognised as one of the earliest and most crucial
efforts in managing digital documents. Finally, the
issue of information security was the most pressing
concern in all of the cases. There is a crucial need
for better information security in terms of user
access control and document confidentiality.
c) System Application Development. According to
the cross-case analysis, there is a significant
difference between UC and the other three
universities. In many cases, the continuing effort to
develop multiple applications for different purposes
in an uncoordinated manner worsens the lack of
information shared and increases duplication efforts.
UC attempted to take advantage of offering
integrated and interoperable applications for
business usage. The benefit of this approach is that it
would tremendously streamline business processes,
enhance information flow across departments, and
reduce the usage of paper. Cain et al.(2008)
suggested that universities should focus on
applications for supporting the streamlining of
business processes by understanding and developing
integration to meet the range of business function
needs. Furthermore, many cases focus on user-
friendly applications but ignore the importance of
customisation and personalisation of the user
interface.
d) Network Performance and Reliability. The issue
of network performance concerns the network speed
and connectivity of system applications. The major
current network issues emphasise the concern
regarding threats from hackers, intruders or viruses.
This focus is due to a lack of coordination in
controlling fragmented server locations across the
university and frequent service interruptions.
Network performance is another concern that
supports the effectiveness of KMS initiatives,
particularly in the cases of UA and UB. Specifically,
network connection problems, such as network
failure or a slow connection, tend to erode the
efficiency of information flow and decrease user
satisfaction. Centralised policy management and
network interface provisioning are powerful
strategies to regulate the network and control traffic
load for performance, efficiency and security (Joshi
et al., 2001).
4.5 Activity 5: Prepare Support
Programs for the KMS Initiatives
The preparation of appropriate support programs is
another important stage to address in the process of
implementing KMS initiatives. Each case study has
its own way to make not only KMS champions but
also participating departments aware of the current
KMS initiatives being conducted and to attempt to
clearly spread KMS initiatives. The summary of the
activity 5 is listed in Table 5.
a) Motivation and Commitment of KMS
Champions. In the three cases, motivation emerged
as an influencing factor that encouraged the key
players to effectively implement the KMS
initiatives. The motivating factors might be in terms
of the sponsorship of required resources and
leadership from top management in pursuing the
wider scope of KMS initiatives across the university.
For these KMS champions, the top management was
fundamental in its position of authority to set the
direction of KMS initiatives and to delegate
resources to drive the KMS initiatives forward.
Motivation and commitment of the KMS champions
influences the effectiveness of KMS initiatives
(Holsapple and Joshi, 2000).
This study found that the KMS champions perform
an important role in distributing KMS messages and
activities consistently across the university. In
addition, the three cases also demonstrated that the
KMS champions were motivated to spearhead KMS
because they perceived that KMS initiatives would
provide a new opportunity to enhance business
processes and decision making. In the majority of
the cases, it was clear that there was a problem with
the process of firmly understanding the concept of
KMS initiatives. Many studies have identified that
understanding the concept of KMS plays a major
role in preparing and identifying effective
approaches to supporting KMS initiatives (Pieris et
al., 2003); (Ajmal et al., 2010). Furthermore, the
KMS champions need to be equipped with IT
knowledge and skills that will help them make
decisions or develop effective IT support. Several
studies have revealedthat public sector is confronted
by a severe technology skills deficit, mostly in the
form of a lack of proper training.(Moon, 2002);
(Norris et al., 2001).
KMIS2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
66

Table 5: The summary of activity 5.
Influencing Factors Key Issues Highlighted Case
a) Motivation and
commitment of
KMS champions
Lack of clear understanding of the KMS concept UA,UB,UD
Lack of IT skills and knowledge UA,UB,UC,UD
Perceived benefit AU,UB,UC
Lack of top management support UD
b) Motivation and
commitment of
participatory
departments
Lack of perceived benefit of the project UA,UB,UD
Prefer an individual department approach UA,UB,UD
Lack of trust and confidence UA,UB,UD
Perceived benefit of the project UC
Communication between KMS champions and business departments UC
Trust and confidence to share their information UC
Table 6: The summary of management activity.
Influencing Factors Key Issues Highlighted Case
Coordination approach
Lack of standard coordination approach UA,UB,UD
Standard coordination approach UC
Measure progression Lack of performance measurement UA,UB,UC, UD
b) Motivation and Commitment of Participating
Departments. The key objective of this activity is to
create awareness about KMS initiatives over the
entire university and attract other departments’
participation. The finding indicates that the
involvement and participation of the business
departments is crucial to give appreciation to their
ideas and comments, including creating a sense of
ownership and perceived benefit of the project. In
many cases, they were concerned about the lack of a
knowledge-sharing culture due to a lack of
communication and connectivity among the various
business departments because of differences in their
operations and services. Furthermore, the KMS
champion faces another problem concerning a lack
of trust and confidence in the information security
flow in the digital environment. This issue was
partly due to the absence of a formal approach and
procedural guidelines to deal specifically with this
problem. Thus, it became difficult for KMS
champions to stimulate and motivate the various
departments to have a favourable attitude towards
knowledge sharing. This finding is consistent with
the literature on IT project development, which
found that the key players of a project should not
underestimate the stakeholder’s capacity to influence
either the escalation or failure of the project
(Markus, 1983); (Walsham, 1993).
4.6 Management Activity: Monitoring
and Controlling the
Implementation of the KMS
Initiatives
The management activity is also considered a very
important activity in SSM, as it has become essential
to monitor and control with the issues that prevent
effective KMS initiatives. A summary of
management activity is shown in Table 6.
This activity is very important, as once the
process of implementing KMS initiatives is
underway, it becomes essential to constantly monitor
and control the progress and performance of KMS
initiatives. It is interesting to note that the finding
indicates that most cases do not have institutional
monitoring and controlling mechanisms of the
implementation of KMS initiatives at the university
level. The central coordination of monitoring and
controlling KMS would provide a more unified and
collaborative approach. There is a need to develop a
monitoring and controlling system that would
constantly assess the implementation processes
(Baudoin, 2003).
5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
The SSM is presented as a tool for analyzing and
understanding unstructured problems that deal with
the complexity of social, culture, and political issues
in studying process of implementation of the KMS
initiatives. This approach proved to be suitable for
analyzing the KMS initiatives, since their
implementation are not only concerned about IT, but
also put emphasis on the contextual environment in
with they are embedded. Based on this
comprehensive analysis, the pattern of the common
process in KMS initiatives together with the
SoftSystemsMethodology-AConceptualModelofKnowledgeManagementSystemsInitiativesinMalaysianPublic
Universities
67

influencing factors were identified and highlighted.
It is clear that each activity has a different
influencing factor that can be classified into multiple
perspectives analysis. Activities 1, 2 and 3 and
management activity were concerned with the
influential factors of the organizational perspectives.
Consequently, activity 4 was influenced by technical
perspectives. Activity 5 was affected by personal
perspectives. The age of the university indicated that
the older MPUs have more challenging issues in
dealing with the technical, organisational, and
personal perspectives, compared to the newer
MPUs. From the technical perspectives, the
existence of several established technologies acts as
a barrier for the older MPUs because they must be
considered if they want to utilise newer
technologies. In addition, the size of these old
universities makes them more complex and more
costly to maintain compared to newer universities. It
is important for older universities to consider
changing IT in a slow and incremental process rather
than choosing a radical change (Ronnback and
Holmstrom, 2007). The analysis of organizational
perspectives shows that the older MPUs appear to be
more challenging of developing unified strategic
direction, managing of large knowledge resource,
creating appropriate policies and procedures, and
getting adequate financial support. The older the
organisation, the more stable the structure and have
a greater number of departments and thus generally
exhibit greater complexity in managing change
(Barnir et al., 2003); (Cranfield and Taylor, 2008).
In many cases, the older MPUs were more strongly
affected by personal perspective constraints than
were newer MPUs. The factors for this trend were
knowledge-sharing attitudes among KMS
champions and business departments. The older
organisations have more established organizational
behaviour that has become institutionalised and
business activities that have become routinised
compared to newer MPUs (Hannan and Freeman,
1984) In this way, the proposed conceptual model of
KMS initiatives can be used as an analytical tool to
guide the analysis of the process of implementing
KMS initiatives in higher education and can also be
applied as a guideline to support the introduction of
KMS initiatives, especially in the context of MPUs.
REFERENCES
Ajmal, M., Helo, P. & Keka, T., 2010. Critical Factors For
Knowledge Management In Project Business. Journal
Of Knowledge Management,, 14, 156-168.
Barnir, A., Gallaugher, J. M. & Auger, P., 2003. Business
Process Digitization, Strategy, And The Impact Of
Firm Age And Size: The Case Of The Magazine
Publishing Industry. Journal Of Business Venturing,
18, 789-815.
Baudoin, P., And Branschofsky, M., 2003. Implementing
An Institutional Repository: The Dspace Experience
At Mit. Science & Technology Libraries, 24, 31-45.
Bennetts, P., Wood-Harper, A. & Mills, S., 2000. An
Holistic Approach To The Anagement Of Information
Systems Development:A Review Using Soft Systems
Approach And Multiple Viewpoints. Systemic
Practice And Action Research, 13, 189-205.
Cain, T. J., Branin, J. J. & Sherman, W. M., 2008.
Knowledge Management And The Academy:
Strategies And Solutions At The Ohio State University
Are Changing How Expertise And Knowledge Are
Documented And Shared. Educause Quarterly, 31, 26-
33.
Chan, D. L. H., Kwok, C. S. Y. & Yip, S. K. F., 2005.
Changing Roles Of Reference Librarians: The Case Of
The Hkust Institutional Repository. Reference Services
Review, 33, 268-282.
Chang, S.-H., 2003. Institutional Repositories: The
Library's New Role Oclc Systems & Services, 19, 77-
79(3).
Checkland, P., 1981. Systems Thinking, Systems Practice,
Chichester, John Wiley & Sons.
Cranfield, D. J. & Taylor, J., 2008. Knowledge
Management And Higher Education: A Uk Case
Study. The Electronic Journal Of Knowledge
Management.
Cronin, B. & Davenport, E., 2000. Knowledge
Management In Higher Education. In: Bernbaum, G.
(Ed.) Knowledge Management And The Information
Revolution Educause Leadership Strategies Series.
San Franciso, Ca: Josey-Bass Inc.
Daft, R. L., 2007. Organization Theory And Design, Ohio,
Thomson Higher Education.
Hannan, M. T. & Freeman, J., 1984. Structural Inertia And
Organizational Change. American Sociological
Review, 49, 149--164.
Holsapple, C. W. & Joshi, K. D., 2000. An Investigation
Of Factors That Influence The Management Of
Knowledge In Organisations. Journal Of Strategic
Information Systems, 9, 235-261.
Ingram, H., 2000. Using Soft Systems Methodology To
Manage Hotels: A Case Study. Managing Service
Quality, 10, 6-10.
Joshi, J., Ghafoor, A., Aref, W. & Spafford, E., 2001.
Digital Government Security Infrastructure Design
Challenges. Ieee Computer, 34, 66-72.
Markus, M. L., 1983. Power, Politics And Mis
Implementation. Communications Of The Acm, 26,
430-444.
Mcdermott, R. & O’dell, C., 2001. Overcoming Cultural
Barriers To Sharing Knowledge. Overcoming Cultural
Barriers To Sharing Knowledge, 5, 76-85.
Mohayidin, M. G., Azirawani, N., Kamaruddin, M. N. &
Margono, M. I., 2007. The Application Of Knowledge
KMIS2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
68

Management In Enhancing The Performance Of
Malaysian Universities. The Electronic Journal Of
Knowledge Management, 5, 301-312.
Moon, M. J., 2002. The Evolution Of E-Government
Among Municipalities: Rhetoric Or Reality? Public
Administration Review, 62, 424-433.
Norris, D. F., Fletcher, P. D. & Holden.S., 2001. Is Your
Local Government Plugged In? Highlights Of The
2000 Electronic Government Survey. Available:
Www.Umbc.Edu/Mipar/Final_Draft/Pdfs/E-Gov.Icma
.Final-4-25-01.Pdf.
Oakley, A., 2003. Research Evidence, Knowledge
Management And Educational Practice: Early Lessons
From A Systematic Approach. London Review Of
Education, 1, 21-33.
Patricia Ordóñez De Pablos, 2004. Measuring And
Reporting Structural Capital: Lessons From European
Learning Firms. Journal Of Intellectual Capital, 5,
629-647.
Petkov, D., Petkova, O., T, A. & T, N., 2007. Systems
Thinking Techniques For Decision Support In
Complex Situations. Decision Support Systems, 43,
1615-1629.
Pieris, C., David, L. & William, M., 2003. Excellence In
Knowledge Management: An Empirical Study To
Identify Critical Factors And Performance Measure.
Measure Business Excellence, 7, 29-45.
Ronald D. F & K., U., 2007. Knowledge Management
Capability: Defining Knowledge Assets. Journal Of
Knowledge Management, 11, 94-109.
Serban, A. M. & Luan, J., 2002. Knowledge Management:
Building A Comparative Advantage In Higher
Education, Jossey-Bass.
Singh, M. D. & Kant, R., 2008. Knowledge Management
Barriers: An Interpretive Structure Modeling
Approach. International Journal Of Management
Science And Engineering Management, 3, 141-150.
Soliman, F. & Spooner, K., 2000. Strategies For
Implementing Knowledge Management: Role Of
Human Resources Management. Journal Of
Knowledge Management, 4, 337-345.
Suhaimee, S., Abu Bakar, A. Z. & Alias, R. A.:
Knowledge Management Implementation In
Malaysian Public Institution Of Higher Education. In:
In Proceedings Of The 2nd International Conference
On Intellectual Capital, Knowledge Management And
Organisational Learning, 2005 Dubai.
Syed Omar Sharifuddin, S. I. & Rowland, F., 2004.
Benchmarking Knowledge Management In A Public
Organisation In Malaysia. Benchmarking: An
International Journal,
11, 238-266.
Tseng, S., 2008. The Effects Of Information Technology
On Knowledge Management Systems. Expert Systems
With Applications, 35, 150-160.
Walsham, G., 1993. Interpreting Information Systems In
Organizations, Wiley, Chichester.
Wong, K. Y., 2005. Critical Success Factors For
Implementing Knowledge Management In Small And
Medium Enterprises. Industrial Management And
Data Systems, 105, 261-279.
Zakareya Ebrahim, Z. I., 2005. E-Government Adoption:
Architecture And Barriers. Business Process
Management Journal, 11, 589-611.
SoftSystemsMethodology-AConceptualModelofKnowledgeManagementSystemsInitiativesinMalaysianPublic
Universities
69
