
Economic Benefits of an ERP System to a Low Tech SME
Anoud I. Bani-Hani
1
, Chris Hinde
1
and Thomas W. Jackson
2
1
Department of Computer Science, Loughborough University, Loughborough, LE11 3TU, U.K.
2
Department of Information Science, Loughborough University, Loughborough, LE11 3TU, U.K.
Keywords: ERP, Barriers, Cost Benefit.
Abstract: This case study describes the potential economic benefits for installing enterprise resource planning system
in small to medium enterprises, using a study of a small enterprise in the UK. The motivation for the
research is to investigate the claim of ERP vendors that their ERP solutions increase the performance of
their customers, increase profitability and efficiency of work processes. The case study goes through three
years of ERP implementation and this paper discusses what effects the system has had on the company’s
overall performance, what the benefits up until now are, and where there could be an enhancement to SMEs
from the ERP system. The major benefits accrue from the more accurate estimates the system is able to
provide and the resulting improvement in quotes.
1 INTRODUCTION
A study in 1998 by the IDC looked at the growth of
ERP systems, expected it to grow at a rate equal to
or greater than the software industry for which it
caters. AMR Inc., which was then the leading
industry and market analysis organisation
specialising in enterprise enabling technologies,
predicted that the ERP software market would grow
annually at a rate of 37% of the next five years. Over
10 years later many large organisations have
implemented an ERP system and research studies
during that time have shown the difficulties they
have faced (Esteves and Pastor, 1999). However, the
uptake of ERP systems in low-tech, small to medium
enterprises has been low and very few research
studies have investigated the barriers these
enterprises face in trying to implement an ERP
system ((Sahran and Goni, 2010) (Esteves and
Pastor, 1999) (Laukkanen et al., 2005)). The most
important benefit that ERP would bring to the
organization is the improvement in internal
communications and the increase in efficiency of the
information flow. Law and Ngai (2007) stated that
ERP “allows seamless integration of information
flows and business process across functional areas
within a company”, which is an extension of the
benefits listed by Bocij. The view was further
extended by Lozinsky (2008) on “As ERP improved
on access of information, it will make possible
more agile decision making for better negotiating
with customers and suppliers”.
The transitions from paper work and excel sheets
to an ERP system has been causing a lot of issues to
employees in SMEs and have been causing delays to
companies when they start to use ERP. This research
discuses a case study, that has adopted an ERP
system after two previous trials with different
software, and has overcome the barriers of
implementing ERP in Small to medium enterprises
(SMEs) using some successfully modified methods
(Bani-hani, 2010). This research starts by describing
the advantages and disadvantages of SMEs in terms
of culture, human resources, employees and the
acceptance of the system. Describing the Common
mistakes SME’s do when installing the system,
barriers and what are the steps applied in this case
study to overcome them. Followed by the potential
economic benefits the system would bring to the
case study used in the research. Findings and a
summary are drawn at the end.
2 SME’s ADVANTAGE &
DISADVANTAGES
Small to medium enterprises usually have a few
numbers of employees between 20-250, and usually
in most of the organisations in UK SMEs are
285
I. Bani-Hani A., Hinde C. and W. Jackson T..
Economic Benefits of an ERP System to a Low Tech SME.
DOI: 10.5220/0004144502850289
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2012), pages 285-289
ISBN: 978-989-8565-31-0
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

companies that have around 50 employees and this
has its advantages where it will be much easier to
spread knowledge between employees. This is due
to the less formal strategies, which increase
communication of knowledge, speed of decision
making and improve informality, which improve
employee’s commitment and their receptiveness of
knowledge management changes. This will also
increase the ability to react faster to the market
changes requirements and knowledge changing to
satisfy the market needs (Rothwell and Dodgson,
1994).
SMEs have fewer layers of management, which
means that decision making takes less time but at the
same time it means less thinking, less searching and
less use of knowledge management strategies.
Ghobadian et al (1996) has mentioned that SMEs
have a structural advantage over other enterprises, as
they are less complex, which makes the ability to
change much easier than larger organizations, and
also increase cross-functional exchange, which
makes decision making more efficient, SMEs also
tend to have a more flexible culture than other
organisations, small numbers of people with same
beliefs and values, which makes it easier for smaller
organisations to change and spread knowledge
management, but SMEs have a problem when it
comes to human resources as they attract less skilled
people, as highly skilled employees tend to go to
larger organisations, where they will have higher
salaries, insurance, more stable situation and
bonuses (Bani-hani, 2010). Achanga et al (2006)
said that SMEs usually have a small number of staff
which makes training almost impossible and longer
as training means stopping daily work activities, and
training individuals is very expensive for SMEs and
usually cannot afford it. Large enterprises usually
have more funds than small enterprises so they can
afford a better ERP system, hardware and give
employees more training which helps in the
implementation phase of the ERP system.
As for IT, Large enterprises have an IT
department who is dedicated mainly for ERP
implementation and training, etc... SMEs on the
other hand usually have part time IT person who is
responsible for IT support along with the ERP
installation, implementation, maintenance, training
and everything, which can lead to project delays, or
sometimes abandoning the system in case of IT
person leaving the company as it will be hard to find
a replacement (Snider et al 2008), which was
illustrated at the case study when replacing two
different ERP systems with the change of the
developer working on them. However, SMEs also
has some disadvantages that make it difficult to use
computer based knowledge management systems,
Egbu has discussed the disadvantages are the
inability to fund long-term and risky knowledge
management programmes, weaknesses in
technological competencies, which make use of
knowledge difficult, as it needs an IT system to
spread knowledge easier, faster, and more cost
effectively, and a weakness in giving training and
education to employees (Egbu, 2001).
Another disadvantage identified by Rothwell &
Dodgson (1994) “SMEs have little management
experience”, and that applies because usually the
manager of an SME is the owner of the organisation
which makes decision making less formal and less
professional.
One of the problems employees at SMEs have is
being unable to refer to each other’s work, if
information was transferred effectively from one
employee to another through an organized system,
then problems would be solved easier, and learning
will be in a better place in the organisation. Most of
this work is tacit knowledge; knowledge that has
been gained from project experience that needs to be
transferred from one employee to another and here is
where the conversion techniques need to be used, as
this problem is sorted in bigger organization and
need to be converted to suit smaller ones, for that
studies have been undertaken to investigate the
correlation between ERP and the size of the
organization.
The following section will talk about the barriers
found at the case study and how the size of the
enterprise would affect ERP implementation
process.
3 BARRIERS OF THE ERP
IMPLEMENTATION FOUND AT
CASE STUDY
Barriers found at case study from were as follow:
1. Low tech SME’s usually attract people with
low educational skills.
2. Unskilled employees, make it difficult to
implement an ERP system, as it requires
many hours of training to bring them up to
just a basic level of IT understanding.
3. Lack of motivation for employees to endorse
the new system.
4. Lack of training due to financial costs and
lack of time.
5. Lack of process mapping.
KMIS2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
286
6. Lack of knowledge (awareness) about the
implementation process.
7. Lack of interest from the Top Management.
8. Inadequate project resources, as information
are not updated regularly.
9. Resistance to change.
10. Unrealistic expectations.
11. Lack of project planning.
12. Fear of losing an authority/ job insecurity.
13. Lack of transaction time and cost during
implementation of ERP.
14. SMEs are less disciplined when it comes to
process definition and improving practices.
Those barriers have been overcome through
applying change management techniques to
employees at the case study (Bani-Hani 2010), and
action research, but what are the benefits of ERP and
what are the economic benefits found at case study.
4 BENEFITS OF AN ERP SYSTEM
Bocij et al (2006, p605) stated that the benefits an
information system brings to the company are often
harder to quantify as these benefits are often
intangible in nature, like improving customer
services, improving management of information,
internal and external communication in the
company. It will also support core business function
and improve product quality. However the
quantifiable benefit is the reduction in cost.
Lozinsky (1998) stated that operating cost will be
reduced which will lead to the increase of return on
investment. Bendoly and Schoenherr (2005) have
also stated the benefits from implementing an ERP
would include the elimination of redundant or
unnecessary processes to improve resources
allocation and system wide standardizations.
5 POTENTIAL BENEFITS OF
IMPLEMENTING ERP SYSTEM
IN SMEs
The MD of the company’s main concern is the
financial status of the company, how much they
gain, lose, ROI, etc. For that a study of the financial
benefit of ERP to assure the MD was needed in
order to prove how the system is more accurate than
the manual estimates.
For this reason some comparisons were needed
to take place, such as:
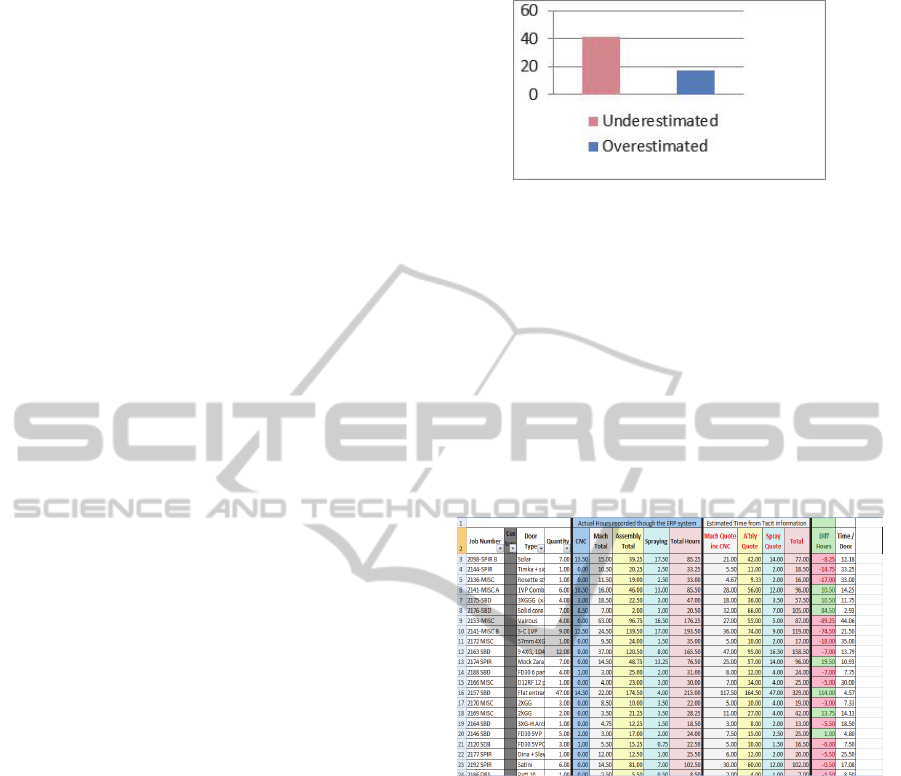
Figure 1: 41 Jobs, 70.6% of the tracked jobs were
underestimated at the quote stage. 16 or 29,4% of the jobs
were overestimated at the quote stage.
The number of hours actually quoted for a door
(Job tracker), recording hours to the system through
the ERP from the shop floor work, live hours were
collected, and the results were gathered after a test
phase that lasted for more than a year. It was found
that out of 60 jobs tracked, 41 were quoted wrong,
underestimating how long it actually takes on the
shop floor to be made. Products have been taking
more time in manufacturing than the charge to
customers.
Figure 2: Job tracker comparison between ERP recorded
hours and estimated hours.
Material updates (Purchase orders), as the MD
uses prices from his own tacit knowledge, the
company lost money on some jobs because they
were using old prices, or losing customers because
they were overpricing a number of quotes due to
incorrect estimation.
Some of the results found were at the quotation
stage, the ones sent to the customer, and it was
found that in 2011 the case study has won 266
(39.87%) quotes and lost 379 (60.13%) quotes, 82 of
them were due to overpriced products. Out of the
(60.13%) 2011 lost quotes (31%) from them are lost
due to prices, (3%) for long lead times and (3%) for
changing needed specifications, (20%) due to high
delivery charges and the other (43%) were lost due
to customers changing their minds some for needing
a third party to do all measurements, or for fittings,
EconomicBenefitsofanERPSystemtoaLowTechSME
287

and sometimes just because they lost a site contract
or other reason.
In money terms, they have won £1,210,698.84
worth of quotes this year and lost £6,443,682.82
worth of quotes, £1,438,105.66 of them due to
inaccurate pricing, which were taken over by our
competitors’. Analysing the lost quotes due to
prices, and redoing them again through the ERP
system, a number of errors were found, but most
importantly out of 82 quotes lost due to prices, 56
were estimated with lower prices from what the
estimator sent to customer, 17 were underestimated
due to un tracking the price changes, and 9 quotes
files were unfound. No patterns were found for the
results because of the un-systematic approach the
estimator use, and asking the estimator, it was found
that some quotes were raised in price to make a
balance in some other lost jobs or mistakes done in
jobs, the exact example was: “I was quoting a
customer’s quote and I received a phone call about a
door at a customer site with a faulty meaning we
have to remake the door from scratch and to make it
up for the loss I’ve added around £200 to this
quote”, Company MD. This unsystematic approach
has been causing the company losses in both quotes
stage and job stage of the company work process.
6 FINDINGS FROM CASE STUDY
There are few questions to be asked in order to
verify the results of the implementation:
Can you observe productivity in your planning
area few months after ERP implementation? Do
things which have been assumed as complex before
implementation seem very simple after
implementation? Can you now control your budget,
stocks etc? Have you not stopped your and
customer's production lines because of material
shortage due to better planning system?
A successful ERP implementation in any case
study needs to fulfil these arguments. At the case
study, live prices are used for quotes, which if
accepted and turned into sales orders, transferring
them easily into a job that can automatically alert the
purchasing department of what needs to be
purchased for this jobs, updating quantities,
scheduling a job for the shop floor, tracking it
through the work, being able to determine job stages
and update customers, has been accomplished, and
made creating a job file much easier than previously
as each file use to be typed manually into excel
sheets, paper work. The case study was able to
overcome a number of barriers to the
implementation and can feel a financial difference in
the quotes sent to customers, which help in losing
fewer customers and with increasing the
productivity of the company.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
A successful ERP implementation is based on the
understanding and clarity of the processes and work
flow through the various departments in the
organization. It also depends on the support
employees get when using the system, especially
from top management. There were many barriers to
successful implementation, many of which were not
predicted. Bani-Hani et al. described these focusing
on the difficulty of persuading many of the
employees that the ERP system could make their job
easier and more successful.
This paper was able to identify the costs and
benefits from the ERP system, and what difference it
can make to the financial status of the company if
used properly. In fact the improvement in accuracy
played a major part in convincing the management
of the value of the system. It was also clear that
there is a critical mass of support that is necessary to
persuade management to adopt the improved
procedures.
REFERENCES
Esteves J. M., Pastor J. A. (1999) “An ERP Life-Cycle-
based Research Agenda”, First international
workshop in Enterprise management and resource
panning: Methods, Tools and Architecture _
EMRPS’99, Venice, Italy.
Shahnorbanun Sahran, Feybi Ariani Goni, Muriati
MukhtarSahran, (2010) “ERP Implementation
Challenges in Small and Medium Enterprise: A
Framework and Case Study”, Advanced Materials
Research (Volumes 139 - 141).
Sanna Laukkanen, Sami Sarpola, Petri Hallikainen (2005),
“ERP System Adoption - Does the Size Matter?”
Proceedings of the 38th Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences – 2005.
Chuck C. H. Law, Eric W. T. Ngai (2007), “ERP systems
adoption: An exploratory study of the organizational
factors and impacts of ERP success”, Information &
Management, Volume 44, Issue 4, June 2007, Pages
418-432.
Paul Bocij, Andrew Greasley, Simon Hickie (2006)
“Business information systems: technology,
development and management” Book By Paul Bocij,
Andrew Greasley, Simon Hickie
KMIS2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
288

Lozinsky, S., (1998), “Enterprise-Wide Software
Solutions: Integration Strategies and Practices, first ed.
Addison- Wesley”, Reading, MA. Mabert, V. A., Soni,
A., Venkataramanan, M. A., 2000. Enterprise
resource planning surveyof US manufacturing firms.
Production and Inventory Management 41 (2), 52–58.
(2008).
Bani-Hani, A. I., Jackson, T. W. and Hinde, C. J.,
''Barriers to Knowledge Management in Small Low
Tech Enterprises'', Software Quality Management
XVIII, Dawson, R., Ross M. and Staples G.,
Southampton Solent University, Southampton,
Software Quality Management XVIII, BCS London,
April 2010, pp 41-52, ISBN: 978-0-9557300-8-5.
Rothwell, R. and Dodgson, M. (1994). “Innovation and
Size of Firm”, In M. Dodgson & R. Rothwell,
R.Handbook of Industrial Innovation.
Nicholas O’Regan, Abby Ghobadian, (2002) "Effective
strategic planning in small and medium sized firms",
Management Decision, Vol. 40 Iss: 7, pp.663 – 671.
Pius Achanga, Esam Shehab, Rajkumar Roy, Geoff
Nelder, (2006) "Critical success factors for lean
implementation within SMEs", Journal of
Manufacturing Technology Management, Vol. 17 Iss:
4, pp.460 – 471.
Brent Snider, Giovani J. C. da Silveira and Jaydeep
Balakrishnan (2008) “ERP implementation at SMEs:
analysis of five Canadian cases” Haskayne School of
Business, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada,
International Journal of Operations & Production
Management, Vol. 29 No. 1, 2009, pp. 4-29q Emerald
Group Publishing Limited 0144-3577, DOI
10.1108/01443570910925343.
Bani-Hani, A. I., Jackson, T. W. and Hinde, C. J.,
''Knowledge Management, Sharing and ERP Systems
in a Small Company'', Proceedings of International
Conference on Information & Communication
Systems, Jordan University of Science & Technology,
International Conference on Information &
Communication Systems, Irbid, Jordan, June 2011,
pp.24-27, ISBN:978-1-4507-8208-1
Lee, C. C. T., Egbu, C. O., Boyd, D., Xiao, H. and
Chinyo, E. 2005, Knowledge management for small
medium enterprises: capturing and communicating
learning and experiences, in: 4th Triennial CIB W99
Safety Health Environment Quality Conference, 17th -
20th May 2005, Port Elizabeth, South Africa.
Elliot Bendoly, Tobias Schoenherr, (2005) "ERP system
and implementation-process benefits: Implications for
B2B e-procurement", International Journal of
Operations & Production Management, Vol. 25 Iss: 4,
pp.304 – 319.
EconomicBenefitsofanERPSystemtoaLowTechSME
289
