
UCASFUM: A Ubiquitous Context-aware Semantic Fuzzy User
Modeling System
Hilal Tarakci and Nihan Kesim Cicekli
Middle East Technical University, Inonu Blvd., 06531, Ankara, Turkey
Keywords:
User Modeling, Ubiquitous User Model, Social Web Mining, User Profiles.
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a ubiquitous user modeling system which illustrates different aspects of the indi-
vidual’s interests and his/her current and future context. The user model is constructed by aggregating and
semantically enhancing the partial profiles obtained by mining socially enhanced online traces of the user on a
regular basis. Those traces include actions performed and relationships established in the social web accounts
in addition to the local machine traces such as bookmarks and web history. The semantical enrichment process
consists of two phases: constructing an overlay model by using concepts and hierarchical information from
external knowledge bases and creating links from the constructed user model concepts to supported ontolo-
gies. The former phase outputs a semantically enhanced user model whereas the latter enables interoperability
between applications which use the proposed system for personalization. Moreover, fuzzy membership val-
ues are computed for each interest and context item in the user model. In order to model the semantically
enhanced user profile and represent fuzziness values, fuzzy hypergraph is used as data structure. Fuzzy hy-
pergraph representation enables extraction of partial user profiles in the requested domains besides answering
user modeling queries such as the degree of the user’s interest for the given concepts. By extracting partial pro-
files by specifying domains, the proposed system can be used for personalization purposes in multi application
environments.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the advent of Web 2.0, users are allowed to ac-
tively participate in the web by creating content and
interacting with each other by means of social net-
working and tagging platforms (Silva et al., 2008).
Thus, the social web structures which link people to
several concepts and to other users has emerged. The
large scale data created in Web 2.0 reflects the in-
terests and preferences about the content contributors
and is an invaluable data source for personalization
purposes.
The goal of Web 3.0(Lassila and Hendler, 2007) is
to close the gap between reality and virtual world by
personalizing the web. In order to achieve this goal,
Web 3.0 focuses on the individuals and supports per-
vasive and ubiquitous computing. Ubiquitous appli-
cations should be capable of running on different de-
vices and should be aware of the preferences of the
individual and the context. An example of a ubiqui-
tous application scenario is presented in (Carmichael
et al., 2005). In this scenario, there is a locator ser-
vice which connects to the user if he is available or
declares the user is busy. In order to achieve this task,
the service is able to sense the location of the user,
and whether he is actively working on the computer
in addition to being aware of his priorities and distin-
guishes whether the situation requires to interrupt his
work.
In order to support such use cases, a ubiqui-
tous and context-aware semantically enriched user
model is essential. The model should be interoper-
able amongst applications, otherwise each applica-
tion has to manage its own user profile, thus increas-
ing the computation costs. In this paper, we propose
such a model which illustrates different aspects of the
individual’s interests and preferences besides his/her
current and future context. The user model is con-
structed by aggregating and semantically enriching
partial profiles obtained by mining socially enhanced
online traces of the user on a regular basis. Those
traces include actions performed and relationships es-
tablished in the social web accounts in addition to the
local machine traces such as bookmarks and web his-
tory.
The semantical enrichment process consists of
278
Tarakci H. and Kesim Cicekli N..
UCASFUM: A Ubiquitous Context-aware Semantic Fuzzy User Modeling System.
DOI: 10.5220/0004169702780283
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development (KEOD-2012), pages 278-283
ISBN: 978-989-8565-30-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

two phases: constructing an overlay model by us-
ing concepts and hierarchical information from ex-
ternal knowledge bases and creating links from the
constructed user model concepts to supported ontolo-
gies. The former phase outputs a semantically en-
hanced user model whereas the latter enables interop-
erability between applications which use the proposed
system for personalization. Moreover, fuzzy member-
ship values are computed for each interest and context
item in the user model.
The semantically enhanced user profile which is
enriched with fuzziness values are stored by utilizing
fuzzy hypergraph data structure. Fuzzy hypergraph
representation enables extraction of partial user pro-
file in the requested domains and output formats be-
sides answering user modeling queries such as the de-
gree of the user’s interest for the given concepts. By
extracting partial profiles by specifying domains, the
proposed system can be used for personalization pur-
poses in multi application environments.
2 RELATED WORK
In our study, we aim to exploit online traces of the
user on social networking and tagging environments
in order to construct the user model. Moreover, we
propose to mine the social web in a context-aware
manner and compute fuzziness values for the discov-
ered information about the individual during aggrega-
tion and semantic enrichment of partial profiles which
are obtained from different knowledge sources. The
constructed user model is able to extract partial user
profiles for specified domains in supported ontology
formats in order to provide personalization for multi
application environments. Therefore, our research
is related to cross system personalization, ubiquitous
user modeling process for multi application environ-
ments and fuzzy user modeling.
Cross system personalization is formulated in
(Mehta, 2009) and proved to be effective in cold start
problem in addition to providing a more robust user
profile. The nature of individual user profiles dis-
tributed on the social web is analyzed in (Abel et al.,
2011). In our study, we not only consider explicitly
stated form based information in social networks, but
also activities performed such as sharing or comment-
ing on a video about a certain topic and clicking the
‘like’ button on a sports team page etc. Moreover, we
consider check-in declarations on Facebook profiles
for current context of the user and events for his/her
possible future context. A generic user modeling li-
brary for the social semantic web which allows for
generating profiles that summarize the given stream
of messages according to domain and application spe-
cific requirements is proposed in (Gao et al., 2011).
Similarly, we aim to tailor the constructed user model
in accordance with the needs of the requester appli-
cations. Furthermore, we intend to manage whole life
cycle of an individual’s user model by considering not
only the construction of the profile but also the neces-
sary information updates to the profile.
In a multi-application environment, there are two
scenarios of constructing and consuming user pro-
files. In the first scenario, each application may con-
struct a partial user model and the challenge is reusing
built partial user models amongst applications. The
second scenario which we adopt, separates the user
model constructor and consumer applications. (Vi-
viani et al., 2010) classifies user modeling approaches
for multi application environments as standardization
based and mediation based user modeling. In stan-
dardization approaches, all participating applications
in the environment which are consuming the profile
are required to support the same user model. We pro-
pose a hybrid solution by constructing a user model
which is dynamically mapped to several well known
ontologies during construction phase. The proposed
user model is capable of exporting the required por-
tion of the profile partially in the form of the ontology
supported by the consumer application.
In (Kavcic, 2004), the uncertainty in the user’s
knowledge description is dealt with a fuzzy user
model in adapting educational hypermedia domain.
The uncertainty arises from vague boundaries be-
tween known and unknown concepts whereas in our
study the uncertainty is the problem of determin-
ing set memberships of the user profile items. In
(Vanekov and Vojts, 2009) partial preferences of the
user are combined by using monotone aggregation
function and stored in an ontology structure. How-
ever, in our system we are trying to determine the
confidence of the user profile item instead of setting a
preference ordering between profile items.
When the user model is semantically enhanced
and fuzzy membership values are taken into account,
more sophisticated user model structures are required,
since pairwise relations is not able to represent higher
order relations amongst concepts. (Ghoshal et al.,
2009) models folksonomies as tripartite graph struc-
tures.However, tripartite graphs are not able to rep-
resent relations with order 4 or higher. In order to
address this problem, (Tan et al., 2011) models higher
order relations in the social network as a unified hy-
pergraph and considers recommendation as a ranking
problem on the constructed hypergraph. Influenced
by this idea we employ unified fuzzy hypergraph(Roy
H. Goetschel, 1995) structure which is able to model
UCASFUM:AUbiquitousContext-awareSemanticFuzzyUserModelingSystem
279

high order relations naturally in addition to support-
ing applications with different data reliability require-
ments which is determined by fuzzy membership val-
ues.
3 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
UCASFUM system consists of two main components
which are responsible for partial and semantic pro-
file construction. The former includes submodules
for mining socially enhanced online traces of the user
in order to build separate and independent fuzzy user
profiles from each knowledge source, whereas the lat-
ter receives the built partial user profiles and activ-
ity streams from social web accounts, and extracts
the current and future context of the user besides
constructing fuzzy hypergraph profile by enriching
the user model semantically by exploiting external
knowledge bases. The context in this work consists
of place and time.
The proposed system is also equipped with a
query engine module which enables extracting par-
tial profiles on requested domains in specified output
formats and answering user modeling queries such as
’To what extent is the user interested in having a vaca-
tion in Switzerland’. Answering this query requires a
fuzziness computation on the model by using vacation
and Switzerland concepts unless ’having a vacation in
Switzerland’ is already explicitly modeled. The sys-
tem components are visualized in Figure 1.
3.1 Partial Profile Builders
In the proposed work, the information which is re-
quired in order to construct the holistic user profile
is synthesized from two main sources: (i) distributed
user profiles embedded in the social accounts and (ii)
the traces left on the devices of the individual. The
former is the main knowledge source for extracting
user interests and preferences and by analyzing the
social bits and social bytes. A social bit is defined
as an atomic data unit which is acquired from a per-
son’s online social activity and indicates the presence
or absence of a single feature. Assembling social bits
into groups to represent a single unit of information
produces a social byte.For instance, a YouTube video
which is shared on the Facebook page of an individ-
ual is a social byte whereas the attributes about the
video such as its genre, number of likes or comments
are its social bits. The latter knowledge source which
is the devices owned by the individual is optional and
requires the user to install a client application to ana-
lyze his web usage data and bookmarked web sites.
In the proposed system Facebook, Twitter and
LinkedIn social web accounts are mined besides the
user’s personal and work pc and his/her smart phone.
However, the system can be easily scaled for other
social web accounts or personal devices.
3.2 Semantic Profile Builder
The semantic profile builder component aggregates
the separate partial user profiles constructed by partial
profile builders and processes the incoming activity
streams from the social web accounts of the individ-
ual. This module is responsible for two main tasks:
extracting user’s current and future context and build-
ing the fuzzy hypergraph user model by aggregating
the partial profiles.
The context extractor module searches for user’s
check-in declarations in order to determine his/her
past and current context, whereas the events are ex-
ploited to extract possible future context for the indi-
vidual. In this work, place and time information is
used to model context. However, the system can be
modified to exploit other context such as the weather,
people in vicinity etc.
A hypergraph is the generalization of an ordinary
graph by introducing hyperedges which are nonempty
subsets of the vertex set. Nodes of a hypergraph rep-
resents the entities to be modeled such as users and
concepts in social networking domain. Hyperedges
represent the high order relations between those en-
tities. In this study, we assign the node which speci-
fies the category of other nodes as the type of the hy-
peredge. For instance, a hyperedge connecting a user
with type footballer and nodes Messi and Arda Turan
models the situation that Messi and Arda Turan are
amongst favorite footballers of the user. In a fuzzy
hypergraph, each vertex in the hyperedge is assigned
a fuzziness value in the range [0,1] representing the
reliability of the entity belonging to the relation mod-
eled by the hyperedge.
The fuzzy hypergraph profile builder aggregates
the partial profiles in order to construct a holistic user
model. During aggregation process, the raw user in-
terest profiles are semantically enriched by construct-
ing an overlay model by using concepts and hierarchi-
cal information from external knowledge bases. The
primary vocabulary used to construct such model is
selected as Wikipedia categories as in (Ramanathan
and Kapoor, 2009) and (Min and Jones, 2011) due to
the maturity of the ontology and its ease of use with
the help of DBPedia. The secondary knowledge base
is Wordnet, and is used when the concept can not be
located under Wikipedia categories.
The semantic enrichment process consists of two
KEOD2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
280
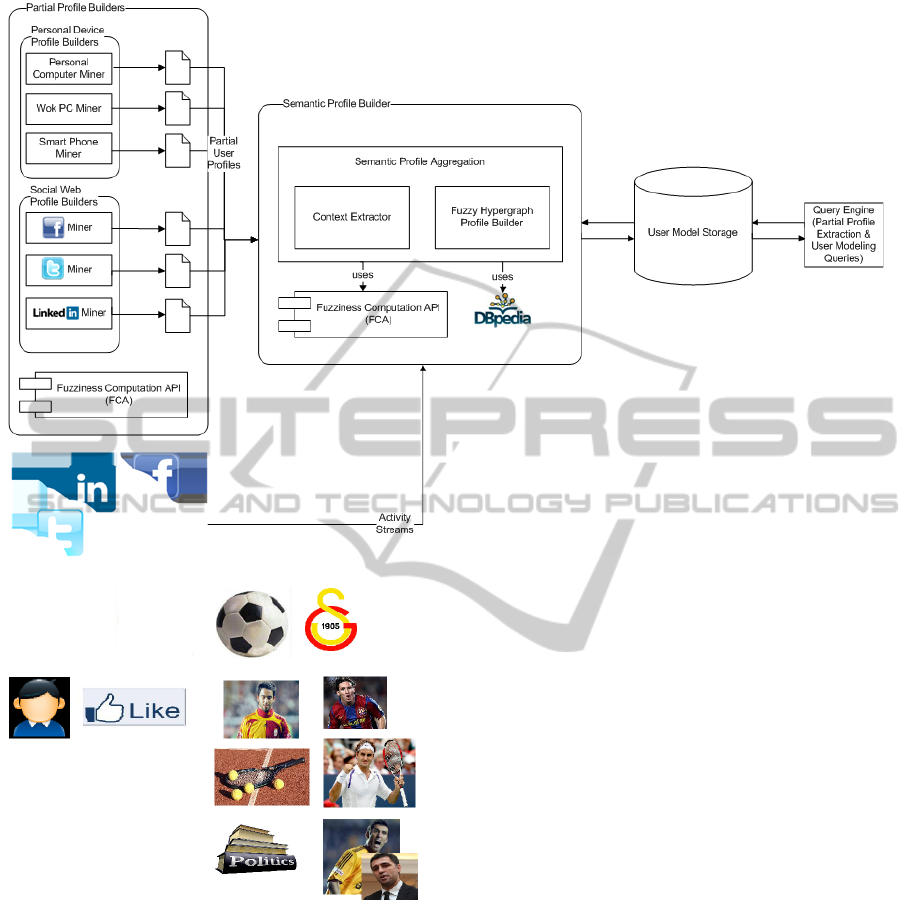
Figure 1: UCASFUM System Overview.
Figure 2: Raw User Profile for the user Feride.
phases. The first phase constructs an overlay model
by using concepts and hierarchical information from
external vocabularies, revises fuzzy membership val-
ues and outputs a semantically enhanced user model.
The second phase creates links from the constructed
user model concepts to supported ontologies enabling
interoperability between applications which use the
proposed system for personalization.
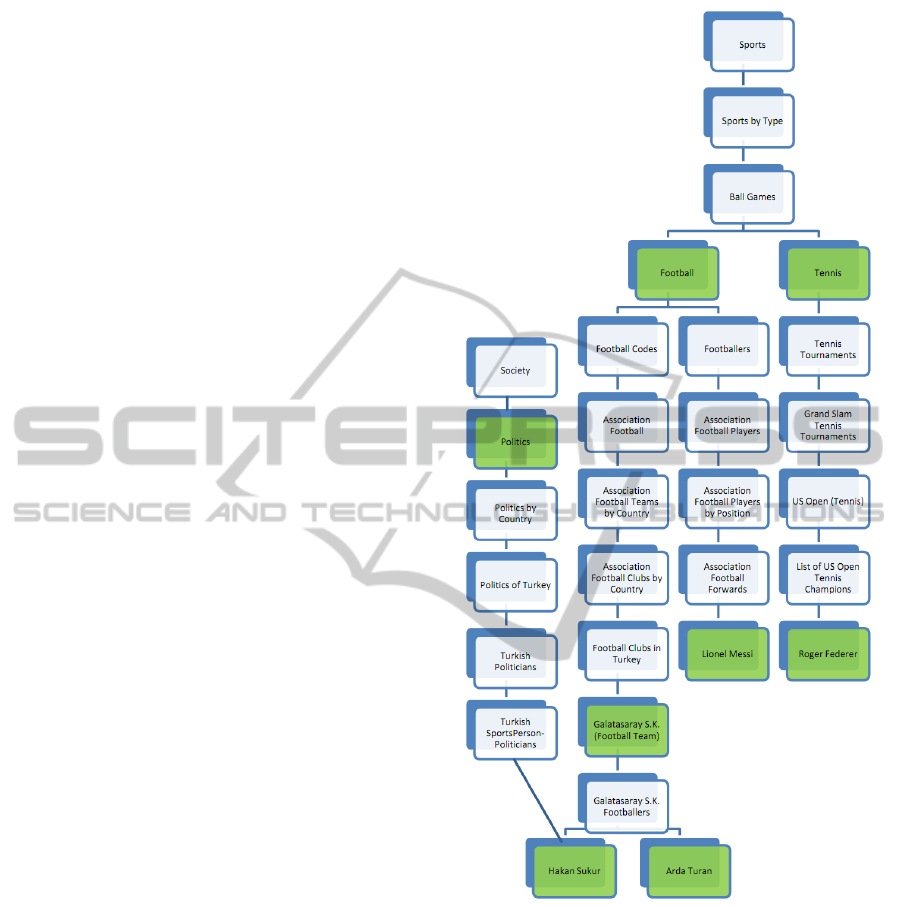
The first phase is illustrated with an example. The
simplified raw user profile which is assumed to be
obtained after aggregation of partial profiles is illus-
trated in Figure 2. According to her raw profile,
Feride likes football, Galatasaray which is a Turk-
ish football team, Arda Turan who was a Galatasaray
football player, Lionel Messi who is a famous football
player, tennis, Roger Federer who is a tennis cham-
pion, politics and a Turkish politician Hakan Sukur
who used to be a Galatasaray football player. In or-
der to semantically enhance the example raw pro-
file, Wikipedia categories are searched in order to
discover a super category for interest items. A par-
tial Wikipedia category tree which spans the interest
items in the sample profile is presented in Figure 3.
Creating other spanning trees for profile items is pos-
sible, since the same item may be categorized under
more than one category in Wikipedia category tree.
The categories that match the example raw profile
items are shaded in the figure. The constructed se-
mantic user model is as follows:
Hyperedge {
type: Ball Games,
nodes:
Hyperedge {
type: Football
nodes:
Hyperedge {
type: Football Clubs in Turkey,
nodes:
Hyperedge {
type: Galatasaray S.K. (Football Team)
nodes:
Hyperedge {
type: Galatasaray S.K. Footballers,
nodes: Arda Turan, Hakan Sukur }
UCASFUM:AUbiquitousContext-awareSemanticFuzzyUserModelingSystem
281
}
}
Hyperedge {
type: Association Football Forwards S.K. Footballers,
nodes: Lionel Messi }
}
Hyperedge {
type: Tennis,
nodes:
Hyperedge {
type: List of US Open Tennis Champions,
nodes: Roger Federer}
}
}
Hyperedge {
type: Society,
nodes:
Hyperedge {
type: politics,
nodes:
Hyperedge {
type: Turkish Sports-person Politicians,
nodes: Hakan Sukur}
}
}
3.3 Query Module
The query module is responsible for two tasks: (i)
providing extraction of partial user profile for the re-
quested domains in the specified output format and
(ii) answering user modeling queries. The first task
enables personalization of multi application environ-
ments by parameterizing user profile requests in three
dimensions: a list of domains concerning the re-
quester application, the desired output format which
must be one of the supported ontologies by the sys-
tem and a reliability threshold specified according to
reliability requirements of the application. The fuzzy
hypergraph structure enables extraction of partial pro-
files on requested domains by using types of hyper-
edges and external vocabularies. When requested
domains match types of hyperedges, those hyper-
edges are sent to the requested application as partial
user profile. For instance, an application which is
about football requests a partial user profile limited
to football domain, whereas a more specific applica-
tion which sells Galatasaray products wants a partial
profile on Galatasaray. The partial profiles which are
sent to the requester applications are hyperedges with
type football and Galatasaray S.K. (Football Team)
respectively.
If a requested domain does not match any of the
hyperedge types, the domain is located on the ex-
ternal knowledge bases and the semantic user model
is searched for the domain’s subcategories. For in-
stance, if the requested domain is sports, no matching
Figure 3: Wikipedia Category Tree for interests of the User
Feride.
hyperedge could be found in the semantic user model
for the sample user Feride. However, when sports
domain is located in the Wikipedia category tree and
subcategories are examined, Ball games hyperedge is
sent as partial user profile.
The proposed system is able to provide partial user
profiles in the supported ontologies by using the exter-
nal links constructed during Phase2 of Semantic En-
richment Algorithm. The fuzzy membership values
assigned to each user profile item enables filtering the
user profile items according to their reliability.
KEOD2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeEngineeringandOntologyDevelopment
282

4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we propose a ubiquitous user model for
multi application environments which is constructed
by mining the user’s activities on social web accounts.
Furthermore, we anticipate that computing fuzziness
values, modeling the user in a context-aware manner
and semantically enriching the constructed model will
reinforce the reliability of the user profile. In order
to accomplish this, fuzzy hypergraph data structure,
which naturally represents high order relations and
defines fuzzy membership values for each element of
hyperedges, is used to model the user. In future work,
we perform extensive analysis on social web mining
methodology by providing several fuzziness compu-
tations, context-awareness and semantic enrichment
approaches in order to evaluate the effect of fuzziness,
semantic enhancement and context-awareness on the
reliability of the ultimate user profile.
REFERENCES
Abel, F., Herder, E., Houben, G.-J., Henze, N., and Krause,
D. (2011). Cross-system user modeling and personal-
ization on the social web. User Modeling and User-
Adapted Interaction, Special Issue on Personalization
in Social Web Systems:1–42.
Carmichael, D. J., Kay, J., and Kummerfeld, B. (2005).
Consistent modelling of users, devices and sensors in
a ubiquitous computing environment. User Modeling
and User-Adapted Interaction, 15(3-4):197–234.
Gao, Q., Abel, F., and Houben, G.-J. (2011). Genius: A
generic user modeling library for the social semantic
web. In Proceedings of Joint International Semantic
Technology Conference. Springer.
Ghoshal, G., Zlatic, V., Caldarelli, G., and Newman, M.
E. J. (2009). Random hypergraphs and their applica-
tions. Phys.Rev.E, 79(6).
Kavcic, A. (2004). Fuzzy user modeling for adaptation in
educational hypermedia. Systems, Man, and Cyber-
netics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, IEEE Trans-
actions on, 34(4):439–449.
Lassila, O. and Hendler, J. (2007). Embracing web 3.0.
IEEE Internet Computing, 11(3):90–93.
Mehta, B. (2009). Cross System Personalization: Enabling
Personalization Across Multiple Systems. VDM Ver-
lag, Germany.
Min, J. and Jones, G. J. (2011). Building user interest pro-
files from wikipedia clusters. In In the Workshop on
Enriching Information Retrieval (ENIR 2011) at SI-
GIR 2011. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Ramanathan, K. and Kapoor, K. (2009). Creating user pro-
files using wikipedia. In Conceptual Modeling - ER
2009, pages 415–427. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Roy H. Goetschel, J. (1995). Introduction to fuzzy hy-
pergraphs and hebbian structures. Fuzzy Sets Syst.,
76(1):113–130.
Silva, J. M., Rahman, A. S. M. M., and Saddik, A. E.
(2008). Web 3.0: A vision for bridging the gap be-
tween real and virtual. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM
international workshop on Communicability design
and evaluation in cultural and ecological multimedia
system, pages 9–14. ACM.
Tan, S., Bu, J., Chen, C., Xu, B., Wang, C., and He, X.
(2011). Using rich social media information for music
recommendation via hypergraph model. ACM Trans.
Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl., 7S(1):22:1–
22:22.
Vanekov, V. and Vojts, P. (2009). Fuzziness as a model
of user preference in semantic web search. In
IFSA/EUSFLAT Conf., pages 998–1003.
Viviani, M., Bennani, N., and Egyed-Zsigmond, E. (2010).
A survey on user modeling in multi-application en-
vironments. In Advances in Human-Oriented and
Personalized Mechanisms, Technologies and Services
(CENTRIC), 2010 Third International Conference on,
pages 111–116.
UCASFUM:AUbiquitousContext-awareSemanticFuzzyUserModelingSystem
283
