
Towards Unifying Existing Requirements Engineering Approaches
into a Unified Model
Saidi Imed Eddine
1,2
, Taoufiq Dkaki
1
, Nacer Eddine Zarour
2
and Pierre-Jean Charrel
1
1
IRIT Laboratory, University Toulouse 2, Mirail Maison de la Recherche, 5 Allée Antonio Machado,
31058 Toulouse, Cedex 9, France
2
LIRE Laboratory, University Mentouri, BP 325, Route Ain El Bey, 25017 Constantine, Algeria
Keywords: Requirements Modelling, Requirements Engineering Process, Viewpoints, Scenario, Goal, Similarity,
Algorithms.
Abstract: Several approaches have been developed to clearly identify software system requirements that satisfy their
stakeholders and can be implemented, deployed and maintained. These approaches can be distinguished
from one another. Indeed, some of them focus on goals and how to achieve them, others focus on scenarios
and illustrations, others rely on stakeholders’ viewpoints, and so on. Nevertheless, these approaches rely on
more or less shared concepts. In this paper, we build graphs that represent some of these approaches. Then
we compare these approaches by computing and analysing similarities between the graphs vertices. As a
result, we put forward the core concepts needed in requirements engineering. This will pave the way for a
unified model that will provide flexible software requirements identification, management and changes.
1 INTRODUCTION
“Requirements engineering (RE) is the discipline
concerned with understanding and documenting
software requirements” (Kazmierczak, 2003).
Many RE approaches have been developed to
describe and manage upstream phases of software
projects. Several types categorize these approaches.
In this paper, we deal with four of them: goal
oriented approaches, viewpoint oriented approaches,
scenario oriented approaches and another type in
which the three concepts goal, scenario and
viewpoint are invoked. Some of them have been
complemented with computer aided tools.
This paper is organized in five sections. In
section two, we present and draw metamodels of
some current RE approaches as graphs. For each
approach, vertices are concepts and edges represent
the links between them according to the approach
specification. We explore I* as a goal-oriented
approach, semiotic and PREview as viewpoint-
oriented approaches, CREWS as a scenario & goal
oriented approach and MAMIE as an integrated
approach of goal, viewpoint and scenario. In Section
3 we compare these five RE approaches by
computing and analysing similarities scores between
their graph vertices and draw our conclusions about
what should be the core concepts of our unified
model. In section 4, we introduce the embryo of the
new unified model that uses the different concepts
used in these approaches and we combine them into
one unified model. Finally, we conclude and draw
perspectives of this work.
2 REQUIREMENT
ENGINEERING APPROACHES
AND RELATED GRAPHS
In this section we present the different RE
approaches and their graphs according to their basic
concepts and principles. We successively explore I*
as a goal oriented approach, CREWS as a goal &
scenario approach, semiotic and PREview as
viewpoint oriented approaches and MAMIE as an
integrated approach (goal, scenario and viewpoint).
For each graph, we highlight the basic concepts and
introduce them as vertices. Each vertex is colored
according to its type (Static or Dynamic). For a
given approach, static concepts are entities and
dynamic concepts represent elements of the RE
process. In the following, static and dynamic
vertices are respectively drawn in light and dark
gray. Furthermore, each graph vertex can be
characterized as initial (INdegree = 0),
311
Eddine S., Dkaki T., Zarour N. and Charrel P..
Towards Unifying Existing Requirements Engineering Approaches into a Unified Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0004172003110315
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2012), pages 311-315
ISBN: 978-989-8565-31-0
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
intermediate (INandOUTdegrees 0) or final
(OUTdegree = 0). We inspect the RE approaches
specification to point out links between concepts and
convert them into edges.
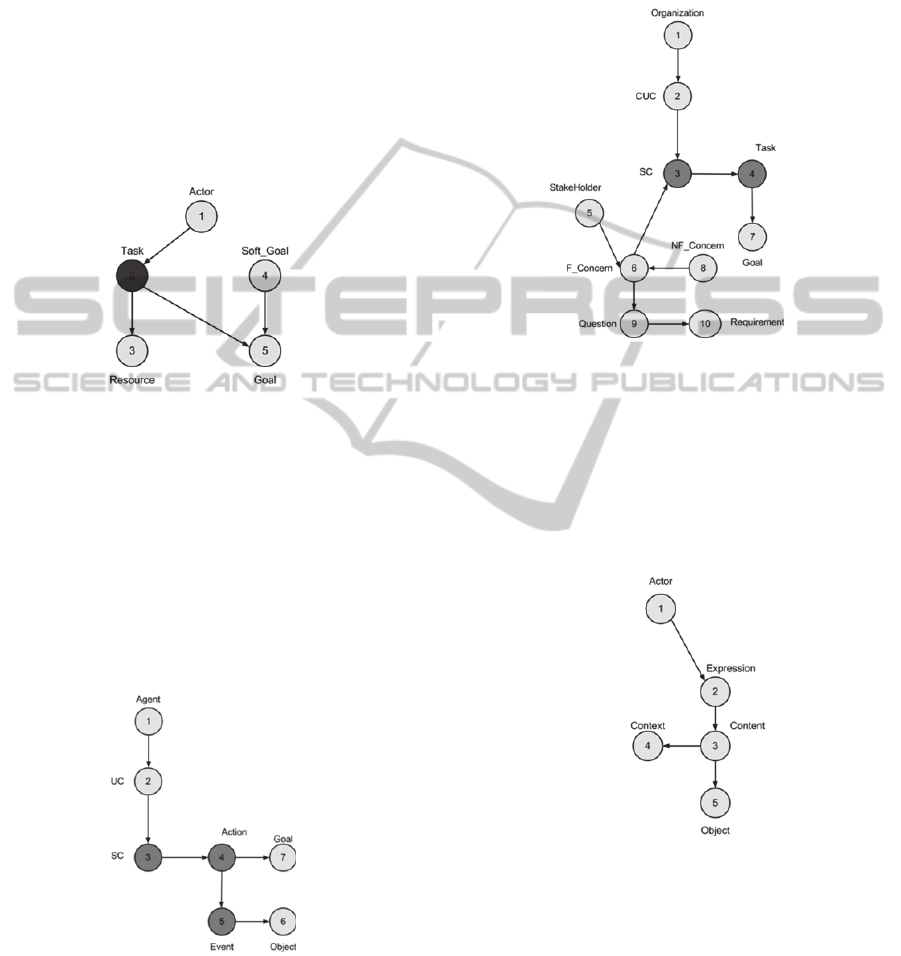
2.1 A Goal Oriented Method: I*
i* (I star, for intentions) is a goal-oriented approach
proposed by Eric Yu (Yu, 1995). i* includes two
basic models (Jaelson, 2011): Strategic
dependencies (SD) and Strategic Rationale (SR).
Figure 1 illustrates the graph that represents i*
concepts and the links between them.
Figure 1: I* Concepts visualization.
2.2 A Goal and Scenario Oriented
Approach: CREWS
CREWS (Cooperative Requirements Engineering
With Scenario) is a requirements engineering
approach using both Scenario and Goal developed in
the framework of an ESPRIT Project (European
Reactive Research Project) (Alistair et al., 1998).
Figure 2 illustrates the graph that represents CREWS
concepts and the links between them.
Figure 2: CREWS Concepts Visualization.
2.3 A Combined Method: MAMIE
MAMIE (from MAcro to MIcro requirements
elicitation) is a requirements engineering approach
that integrates the three concepts: goal, viewpoint
and scenario to elicit requirements for an inter-
company Co-operative information system
(Bendjenna, 2010). Figure 3 illustrates the graph that
represents MAMIE concepts and links between
them.
Figure 3: MAMIE Concepts visualization.
2.4 The Semiotic based Approach: A
First Viewpoint Oriented Approach
The semiotic approach is a viewpoint-oriented
approach proposed by P. J. Charrel (Charrel, 2002).
Figure 4 illustrates the graph of Semiotic concepts
and links between them.
Figure 4: MAMIE Concepts visualization.
2.5 PREview: A Second Viewpoint
Oriented Approach
PREview method (Process and Requirements
Engineering Viewpoints) (Sommerville et al., 1997)
has been developed in a research and development
project called REAIMS. It is a multi-perspective
approach that identifies and separates different
system viewpoints. Figure 5 presents the graph of
PREview concepts and links between them.
KMIS2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
312

Figure 5: PREview Concepts Visualization.
3 SIMILARITIES BETWEEN
GRAPHS: RE APPROACHES
COMPARISON
In this section, we compare the above approaches by
computing structural similarities (Blondel et al.,
2004) between the vertices of their graphs. To
understand the concept of similarity between
vertices of directed graphs, let A and B two RE
approaches, G
and G
their graphs and n
and
n
their respective number of vertices. The
similarity matrix can be obtained as the limit of the
normalized even iterates of:
=
The comparison between I* and PREview gives the
matrix illustrated in the figure 6.
Figure 6: Matrix of similarities between I* and PREview.
The expression ‘
concept of A is similar to
concept of B’ is denoted by AC
=BC
. For
example:
∗
= ,
We set to nil values when the two concepts are not
of the same type (Static or Dynamic). We don’t take
into account the results when the two concepts have
not the same type. For example, we reject:
=
∗
.
We associate concepts from B to those of A by
reading similarity values from each line and by
getting the most important related column (concept
from A). If a concept from graph A is related to
none of the concepts of graph B, we associate to it
concepts from B by reading similarity values from
its column and by getting the most important related
line.
4 UNIFIED REQUIREMENT
ENGINEERING MODEL:
GRAPH COMPOSITION
In this section, we analyse results of similarities
obtained in the section 3 in order to point out the
concepts of the future unified model, build the
corresponding graph and draw the meta-model.
4.1 Graph Composition
Let UREM (Unified Requirement Engineering
Model) our future unified model and G
its
graph. G
is composed of three parts: initial
vertex, intermediate vertices and final vertex. There
are six types of cases regarding comparisons
between vertices: initial to initial, initial to
intermediate, intermediate to intermediate of both
static and dynamic types, intermediate to final, final
to final. Dynamic concepts are only observed in
intermediate to intermediate case.
The three following steps describe the
composition process:
4.1.1 Similarities Scores Grouping
The first step of G
composition consists to
group similarities results in three groups according
to its three parts.
4.1.2 Degree of Consensuality
In this step, for each case in a group, we compute the
Degree of Consensuality (DC) of each concept in the
comparisons. DC is the number of times that the
concept appears in similarities results. For example
in the initial node group, the initial to initial case, we
have found that the Agent concept of CREWS
approach finds its counterpart in the four others RE
approaches. We denote:
#
=4
The initial to Intermediate case vertices will be
integrated either in the initial or the intermediate
vertices in
according to the max value of DC.
The final to intermediate case vertices will be
integrated either in the final or the intermediate
vertices in
.
TowardsUnifyingExistingRequirementsEngineeringApproachesintoaUnifiedModel
313
4.1.3 Graph Composition
In this step we analyse and group results obtained
from the previous step. For each concept, its DC
appears as an exponent.
- Initial vertex of
is presented in the
following format:
=
∪
We have obtained:
=
,
,
,
,
,
,
∪
,
,
,
We integrate similar concepts in one concept and
give it the name of the max DC value of the
integrated concepts.
=
∪
,
,
,
- Intermediate nodes of G
is presented in
the following format:
=
∪
∪
∪
=
,
,
,
,
,
∪
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
∪
,
,
,
∪
,
,
,
,
Regarding dynamic concepts we keep using Task,
Action and Event in our UREM to handle operations
within the requirement engineering process. We set
Task as a set of Actions and each action has a start
and an end event as defined in CREWS. For the
intermediate to intermediate static concepts, we
integrate concepts into one concept which is
Requirement and we obtain:
=
, ,
∪
∪
6
,
2
,
1
,
1
∪
4
,
3
,
2
,
1
,
1
- Final node in the format:
=
∪
We get the results:
=
∪
,
,
,
,
Actor is now the initial vertex of
and
Goal its final vertex, Requirement is an intermediate
vertex. Remaining vertices are integrated and used
according to the high value of DC. History,
Question, Expression, Name, Focus will be
integrated as intermediate vertices. UC will be
integrated in the initial vertex. To build the graph,
Actor must be linked with dynamic concepts: Task,
Action and Event. These dynamic concepts must be
combined with static concepts in order to produce
results at the end of the requirement engineering
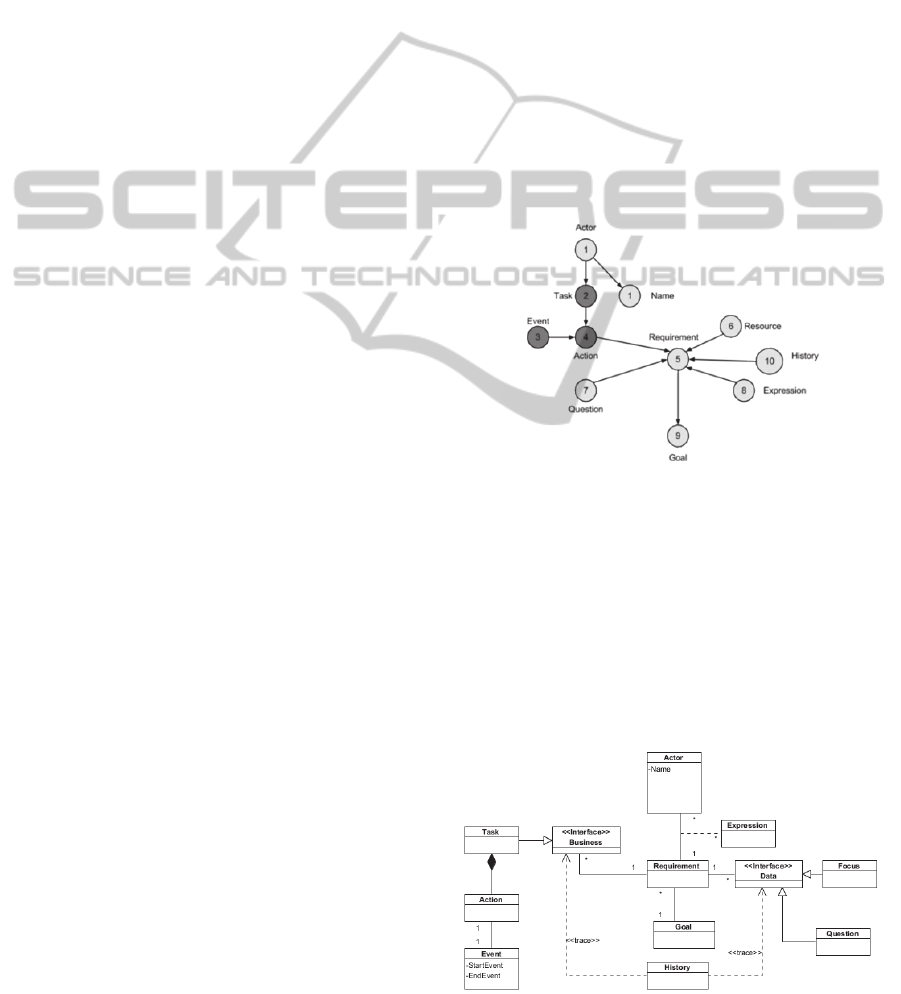
process. Figure 8 illustrates the graph proposed for
UREM.
Figure 8: UREM Graph
4.2 UREM Meta Model
In this subsection we draw a meta-model for UREM
from the graph proposed in figure 8. We add two
wrappers Business and Data to separate between
dynamic and static aspects of the model. Some
concepts will be defined as classes, others as their
attributes. The first version of UREM model is given
in figure 9:
Figure 9: UREM Meta-Model.
KMIS2012-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
314

5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has presented different requirements
engineering approaches. This allowed us to put
forward core underlying concepts. We noticed that
these concepts aren’t all simultaneously present in
the approaches. This points out the issue of
incompleteness of these approaches and call for a
new approach that embed all the core concepts. Our
paper is a first attempt to fulfill this need. We have
presented approaches concepts and links between
them as graphs. Then, we have compared concepts
by computing similarities scores (Blondel et al.,
2004) between their graphs vertices. Finally, we
have composed these vertices in order to obtain a
new unified requirement engineering model. Our
model needs more enhancements because we have
focused in this paper on structural similarities. As a
next step, we plan to add semantics analysis
regarding concepts to get a flexible approach,
implement this approach and propose an interactive
exploratory tool which aims to enrich the
requirements visualization.
REFERENCES
Bendjenna, H., Zarour, N. E., Charrel, P. J., 2010.
Eliciting Requirements for an inter-company
cooperative information System. Journal of Systems
and Information Technology (JSIT), Vol 12 n°4,
Emerald Group Publishing, pp. 305-333,
Castro, J., Goal Oriented Requirements Engineering i*,
Fifth International Conference on Research
Challenges in Information Science, May 2011.
Charrel P. J. 2002. The viewpoint paradigm: a semiotic
based approach for the inelligibility of a cooperative
designing process. Australasian Journal of
Information Systems, Vol. 10 No. 1, pp 1-10.
Kazmierczak E. 2003. Requirements Engineering 433-
641E, Course-work Masters The University of
Melbourne First Semester.
Sommerville I., Sawyer P. 1997. Viewpoints: principles,
problems and a practical approach to requirements
engineering. Computing Department, Lancaster
University, Lancaster LA1 4YR, UK, Annals of
Software Engineering 3.
Sawyer P., Sommerville I., Viller S. 1996. PREview:
Tackling the Real Concerns of Requirements
Engineering. Cooperative Systems Engineering
Group, Technical Report.
Sutcliffe A. G, Maiden N., Shailey M., Darrel M. 1998.
Supporting Scenario-Based Requirements
Engineering, IEEE Transactions on software
engineering, Vol. 24, NO. 12.
Vincent D. B., Anahi G., Maureen H., Pierre S., Paul V.
D. 2004. A Measure of Similarity between Graph
Vertices: Applications to Synonym Extraction and
Web Searching. Society for Industrial and Applied
Mathematics
Yu E., Modelling strategic Relationships for Process
Reengineering. PhD thesis, university of Toronto
Canada, 1995.
TowardsUnifyingExistingRequirementsEngineeringApproachesintoaUnifiedModel
315
