
FPGA Implementation of SOBI to Perform BSS in Real Time
Apurva Rathi
1,2
, Xun Zhang
2
and Francois Vialatte
3
1
VIT University, Vellore, India
2
ISEP, Paris, France
3
ESPCI, Paris, France
Keywords: EEG, BSS, SOBI, FPGA.
Abstract: Blind Source Separation (BSS) is an effective and powerful tool for source separation and artifact removal
in EEG signals. For the real time applications such as Brain Computer Interface (BCI) or clinical Neuro-
monitoring, it is of prime importance that BSS is effectively performed in real time. The motivation to
implement BSS in Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) comes from the hypothesis that the
performance of the system could be significantly improved in terms of speed considering the optimal
parallelism environment that hardware provides. In this paper, FPGA is used to implement the SOBI
algorithm of EEG with a fixed-point algorithm. The results obtained show that, FPGA implementation of
SOBI reduces the computation time and thus has great potential for real time.
1 INTRODUCTION
EEG is one of the most widespread brain mapping
techniques to date and is used extensively for
monitoring the electrical activity within the human
brain both for research and clinical purposes. The
raw EEG data represent a projection of a set of
signals, which are a mix of brain and artifact
information. BSS is the process of recovering the
source signals from a linear mixture of measured
signals.
There is no general consensus about any one
BSS Algorithm being the best. Each algorithm has
its unique set of pros and cons and makes certain
assumptions about the sources in order to
compensate for the lack of information about the
mixing matrix and to be able to process the signals
blindly. (Joyce et al., 2004; Fitzgibbon et al., 2007)
and (Hyvarinen et al.) can serve as good reads for
literature on Artifact detection and removal in EEG
signals. SOBI using time structure of signals has its
unique set of advantages to offer as mentioned in
(Delorme et al., 2007) and was the chosen algorithm
in this work.
SOBI assumes stationary sources with non-
identical spectra and considers components at
various time lags and focuses on decorrelating them
as much as possible. As mentioned earlier, SOBI
offers some unique advantages such as ability to
resolve correlated signals, ability to resolve more
than one gaussian sources, more robust behaviour in
adverse Signal to Noise ratio (SNR), need for fewer
data points implying shorter epoch length –
something which is must for real time processing.
The application and usefulness of SOBI in Brain
Computer Interface has been shown in (Wang et al.).
It was shown that SOBI converges after only a few
iterations thus proving it worthy for real time
applications. However, the computational
complexity and cost for SOBI is high which can be
partially taken care of by appropriate design of the
FPGA architecture. Also, when real time processing
is the main goal a little additional cost is justifiable.
In this paper, an FPGA implementation of the
SOBI algorithm of BSS model is presented with co-
simulation design concept based on the fixed-point
number representation. The BSS Model and SOBI
algorithm are introduced in Section 2. In section 3,
the FPGA implementation is described. The result
analysis and the conclusion are given in section 4
and 5.
727
Rathi A., Zhang X. and Vialatte F..
FPGA Implementation of SOBI to Perform BSS in Real Time.
DOI: 10.5220/0004182507270731
In Proceedings of the 4th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (SSCN-2012), pages 727-731
ISBN: 978-989-8565-33-4
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
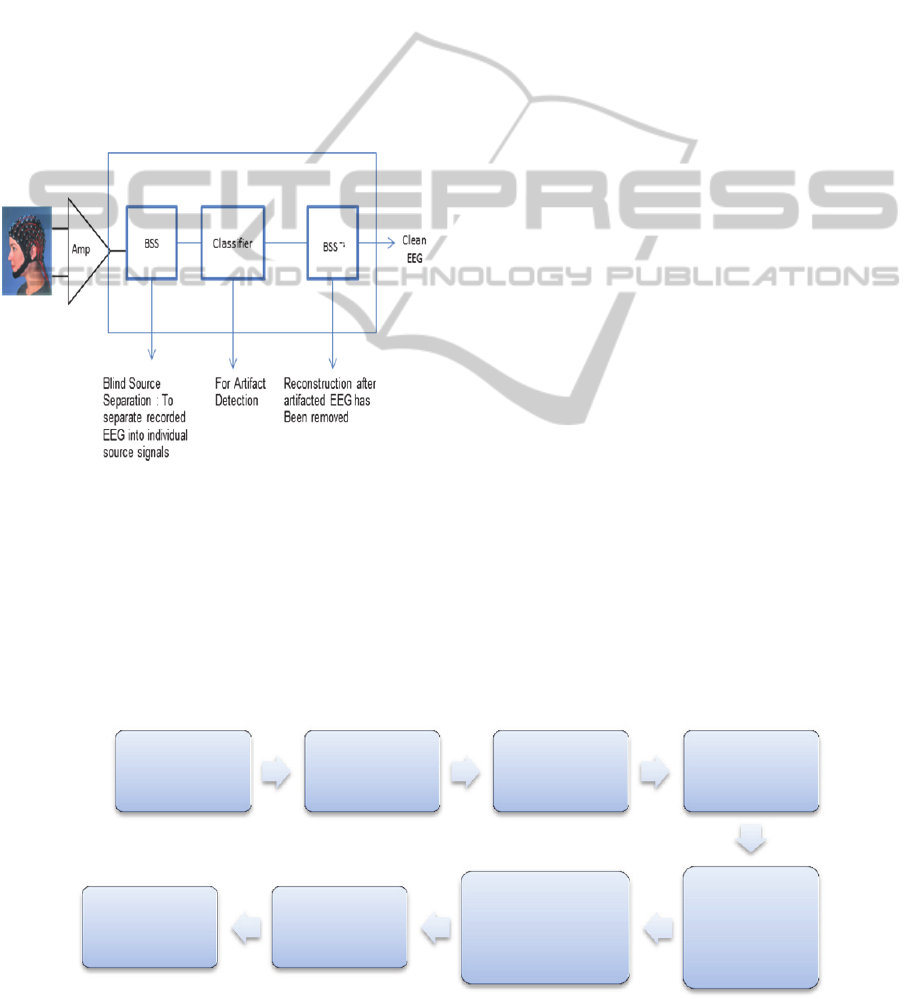
2 ALGORITHM AND PROBLEM
FORMULATION
2.1 BSS Model
BSS is the process of recovering the source
signalsfrom a linear mixture of measured signals.
There are three distinct steps required for removal of
artifact/noise from EEG using BSS: 1) separate
(unmix) the measured EEG into sources using a BSS
algorithm, 2) identify and discard artifact/noise
sources and retain brain sources, and 3) project the
retained brain sources back into sensor space
resulting in artifact/noise-free EEG as is illustrated
in Fig. 1
Figure 1: Artifact detection and removal using BSS.
Component estimation from EEG data can be
mathematically formulated as follows.
X = AS (1)
meaning that the sensor data X is rotated by an
unmixing matrix
, to arrive at the components S.
To clarify, all quantities in Equation 1 are matrices.
A is referred to as the mixing matrix, each column of
which describes signal propagation from an
individual source to each electrode site. The
meaning of “blind” is that both the original sources
(represented by matrix S) and the way the sources
were mixed (represented by A) are all unknown, and
only mixed signals or mixtures represented by X)
can be measured and observed.
2.2 SOBI Algorithm
SOBI was first introduced by Adel Belouchrani,
Karim Abed-Meraim, Jean François Cardoso and
Eric Moulins in the year 1997. The steps involved in
SOBI algorithm are illustrated in Figure 2 while the
detail explanation of the algorithm may be found in
(Belouchrani et al., 1997). As previously stated,
SOBI exploits the time coherence of the source
signals for source separation. As opposed to the
other approaches, it relies only on stationary second
order statistics. It was shown in (Tong et al., 1990;
Belouchrani et al., 1993) that blind identification is
feasible based on the eigen decomposition of spatial
covariance matrices. In (Belouchrani et al., 1997),
blind identification is achieved by performing joint
diagonalization of a set of spatial covariance
matrices. In (Belouchrani et al., 1997) it was also
shown that considering a set of matrices rather than
unique correlation matrix increases the robustness at
a low additional computing cost. SOBI exploits the
time coherence of the source signals and assumes
that the signals are uncorrelated in time. Also, for
the sake of simplicity the noise is modelled as
additive white noise. However, this assumption is
not crucial. The aim of BSS is to identify the
mixture matrix A and to recover the source signals s
(t) from the array output x (t) without any a priori
knowledge of the array manifold.
Figure 2: Schematic Representation of BSS using SOBI.
Filter Buffer Normalizer Whitening
Calculate
theCorrelation
Matrices
Joint
Diagonalization
Estimating
SourceSignals
PostProcessing
IJCCI2012-InternationalJointConferenceonComputationalIntelligence
728

The first pre-processing step is Normalization so
as to ensure that the source signals have unit
variance. The next step is Whitening which is
achieved by Singular Value Decomposition of the
mixture matrices. Whitening reduces the
dimensionality of the BSS problem, following which
the mixing matrix A may be defined as
A =
#
U (2)
Where W is the whitening matrix and U is a unitary
matrix. It is shown in (Belouchrani et al., 1997) that
the whitening matrix is determined from covariance
matrix at t = 0 (R (0)), provided the noise covariance
matrix is known or can be estimated. The Unitary
factor U may be thought of as a unitary matrix that
simultaneously diagonalizes a set of covariance
matrices considered at various time lags. A detailed
analysis of SOBI algorithm can be found in
(Belouchrani et al., 1997). Though SOBI has not
been implemented in hardware before, (Huang et al.,
2008; Shyu et al., 2008; Li and Lin, 2005 and Du
and Qi, 2004) can be good references for literature
on hardware implementation of other BSS
algorithms.
3 DESIGN AND
IMPLEMENTATION
3.1 Design Methodology
Fig 2 illustrates the basic flow of the SOBI
Algorithm. As is evident, Whitening i.e. Singular
Value Decomposition, Correlation i.e. determining
the correlation matrices and Joint Diagonalization of
the correlation matrices; comprise of the major part
of the algorithm. Firstly, a SIMULINK model was
developed and the results were compared to those
obtained from the MATLAB code. The SIMULINK
model was built in order to be able to perform
Hardware Co-simulation, which is an intermediate
stage between software and hardware
implementation. This intermediate approach is
expected to gauge the benefits of both software and
hardware and thus could provide a better solution.
This is based on the belief that it is not always
prudent and economical to implement the entire
system in hardware. Instead, implementing only
those blocks which allow certain amount of
parallelism and / or for which the computational
time is to be reduced, could turn out to be more
economical and better solution.
The three approaches to develop a Co-simulation
between SIMULINK/ MATLAB and XILINX ISE
are as mentioned below:
1) Using System Generator
2) Using HDL Coder and EDA Simulator Link
3) Using EDA Simulator Link and a Black Box
containing the hand coded VHDL code.
In the first two approaches, the VHDL code is
automatically generated from a MATLAB code or a
SIMULINK model. However, there are several
restrictions on what all MATLAB functions can be
directly mapped onto a VHDL code. In view of
these limitations and after several failed attempts
with the first two approaches, it was decided to hand
code the VHDL code. Also, hand coded VHDL code
offers the advantage that it can be optimized as per
the need.
Thus, VHDL code for three of the most
important blocks – Singular Value Decomposition,
Correlation and Joint Diagonalization - of the SOBI
model were written and simulation results were
obtained for the same. The next step was to
synthesize the blocks. The code for which
simulation results were obtained was written using
real data type, which is not synthesizable. Thus, the
code for Correlation block was rewritten using
Floating point representation and simulation results
were obtained for the same. However, as the floating
point package (Bishop, 2005), (that need to be used
since floating point was not an inbuilt data type until
VHDL 2008) integrated in VHDL 2008 is not yet
officially supported by Xilinx XST13.4, several
synthesis issues were encountered. Thus, the
correlation Block was finally synthesized using
signed number representation. Finally, the synthesis
report was generated and the parameters were
modified so as to optimize the performance.
3.2 Proposed Architecture for
Correlation Block
The Figure 3 denoted below represents the process
to determine a single Correlation matrix. n such
processes may be run in parallel to determine the n
correlation matrices at various time lags. However,
running the processes in parallel would imply more
hardware resources being used.
FPGAImplementationofSOBItoPerformBSSinRealTime
729
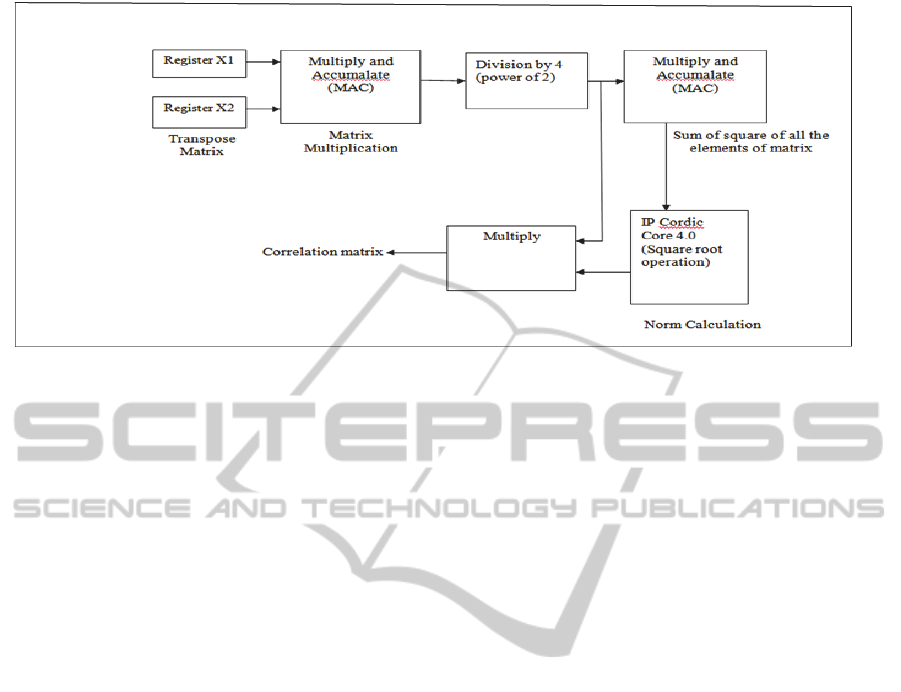
Figure 3: Proposed architecture for implementation of Correlation Block.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Simulation Results
As mentioned earlier, the simulation results for SVD
block (using real data type), correlation Block (using
real, floating point and signed numbers data type)
and Joint Diagonalization block (using real and
floating point data type) were obtained considering a
2 x 4 input matrix, that is, 2 channels and 4 data
points. The parameter p which determines the
number of correlation matrices to be considered, was
set to 2. Several observations were made which are
listed below.
If it is intended to write a synthesizable code, real
data type should not be used. The use of Logic cores
to implement mathematical functions such as square
root, does introduce a bit of latency and thus some
hand coded functions should be developed instead.
Also, though it is easy to program in Floating Point
it is certainly not a hardware Engineer’s choice as it
utilizes a lot of hardware resources.
Both the Joint Diagonalization and SVD block
involved the calculation of eigen values and vectors.
Based on the simulation results, it was concluded
that the power method should be used only when the
largest eigen value and the corresponding eigen
vector is to be calculated. While it worked well in
the Joint Diagonalization block, it didn’t produce
accurate results for the SVD block which involved
calculation of eigen values and vectors of a 2 x 2
matrix. Thus, the Jacobi method should be used
instead.
4.2 Synthesis Results
Using the signed integer data type, the synthesis of
the correlation block was made possible and the
synthesis report was generated. The mapping
procedure failed due to the over utilization of IOBs
(Bounded input output). However, the synthesis
report generated does provide some insight into the
synthesis of the code. The timing report shows a
minimum delay of 12.795 ns which corresponds to a
Maximum frequency of 78.155 Mhz. This is higher
than the maximum frequency of 64 MHz achieved in
(Huang et al., 2008). Although, in (Huang et al.,
2008) the entire algorithm was implemented while in
our case only a part of it is implemented. As
observed by changing a few parameters, it may be
concluded that there is a lot of scope for
optimization.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Thus, the synthesis results obtained for the
Correlation Block, do verify that the computation
time could be reduced by implementing the SOBI
algorithm in FPGA. Also, there is scope for a lot of
optimization that can be done to achieve higher
speed. Also, as was observed while working on the
codes, SOBI does offer a lot of scope for parallelism
and pipelining as there are a lot of matrix operations
involved and thus it seems only wise to implement it
in FPGA. Once, the major blocks of Correlation,
Joint Diagonalization and Singular Value
Decomposition are made synthesizable, it might be
IJCCI2012-InternationalJointConferenceonComputationalIntelligence
730

interesting to perform Co-simulation between
MATLAB - Xilinx and make a comparison between
Software, Hardware and Hardware Co-simulation.
Based on the results, it can be decided as to what
actually to implement in FPGA. This way an
economical use of Hardware resources can be made.
In the near future, when the floating and fixed point
packages are officially supported by Xilinx XST for
synthesis purpose, the same work can be
implemented using Fixed or Floating point
representation, which unlike integers is a descent
way of representing real life EEG data.
This work is the first initiative taken to
implement SOBI to perform BSS in Real time and
thus is just at a preliminary stage. The project
provides a global view of the implementation, while
considering the Correlation block in-depth. This
work could be used to make a choice of the methods
to implement various blocks, as an analysis of the
methods for each block has been made in this
project. A lot of work needs to be done further.
However, the work does provide hope that SOBI
could serve as a potential candidate for real time
BSS. Thus, it could pave a way for on-line
processing required in applications like Brain
Computer Interface.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
SIGMA Laboratory, ESPCI, Paris Tech
ISEP, Paris
Gerard Drefus, ESPCI, Paris
Yohei Tomita, SIGMA Lab, ESPCI, Paris
Parvaneh Adibpour, SIGMA Lab, ESPCI, Paris
Antoine Gaume, SIGMA Lab, ESPCI, Paris
REFERENCES
Carrie A. Joyce, A Irina F. Gorodnitsky, B And Marta
Kutasb,c, “Automatic removal of eye movement and
blink artifacts from EEG data using blind component
separation”, Psychophysiology, 41 (2004)
S. P. Fitzgibbon,* D. M. W. Powers,† K. J. Pope,† C. R.
Clark*, “Removal of EEG Noise and Artifact Using
Blind Source Separation”, J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007
Jun;24(3):232-43.
A textbook by Aapo Hyvarinen, Juha Karhunen, Erki Oja,
“Independent Component Analysis”
Arnaud Delorme1,2, Terrence Sejnowski1, Scott Makeig2,
“Enhanced detection of artifacts in EEG data using
higher-order statistics and independent component
analysis”, NeuroImage 34 (2007) 1443–1449
Yan Wang1, Matthew T. Sutherland2, Lori L.
Sanfratello2, Akaysha C. Tang234, “Single-Trial
Classification Of Erps Using Second-Order Blind
Identification (Sobi)”,
Wei-Chung Huang1, Shao-Hang Hung1, Jen-Feng
Chung1,2, Meng-Hsiu Chang1, Lan-Da Van2, and
Chin-Teng Lin1,2, “FPGA Implementation of 4-
Channel ICA for On-line EEG Signal Separation”,
Biomedical Circuits and Systems conference, 2008.
BIOCAS.2008.IEEE
Kuo-Kai Shyu, Member, IEEE, Ming-Huan Lee, Yu-Te
Wu, and Po-Lei Lee, “Implementation of Pipelined
FastICA on FPGA for Real-Time Blind Source
Separation”, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,
vol. 19, No. 6, June 2008
Zhongfeng Li and Qiuhua Lin, “FPGA Implementation of
Infomax BSS Algorithm with Fixed-Point Number
Representation ”, Neural Networks and Brain, 2005.
ICNN&B ’05 An International Conference on 13 – 15
Oct. 2005
Hongtao Du and Hairong Qi, “An FPGA Implementation
of Parallel ICA for Dimensionality Reduction in
Hyperspectral Images”, Geoscience and Remote
Sensing Symposium, 2004. IGARSS ’04 . Proceedings.
2004 IEEE International
L. Tong, V. C. Soon, R. Liu, and Y. Huang, “AMUSE: A
new blind identification algorithm,” in Proc. ISCAS,
New Orleans, LA, 1990.
A. Belouchrani, K. Abed Meraim, J.-F. Cardoso, and E.
Moulines, “Second-order blind separation of
correlated sources,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Digital Signal
Processing, Cyprus, 1993, pp. 346–351.
Adel Belouchrani, Member, IEEE, Karim Abed-Meraim,
Jean-François Cardoso, Member, IEEE and Eric
Moulines, Member, IEEE, “A Blind Source
Separation Technique Using Second-Order Statistics”,
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 45, no.
2, February 1997
David Bishop, “Fixed and Floating Point packages for
VHDL”, http://www.vhdl.org/fphdl/Float_ug.pdf
FPGAImplementationofSOBItoPerformBSSinRealTime
731
