
Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis based on Automatic Spontaneous
Speech Analysis
K. Lopez-de-Ipiña
1
, J. B. Alonso
2
, J. Solé-Casals
3
, N. Barroso
1
,
M. Faundez
4
, M. Ecay
5
, C. Travieso
2
,
A. Ezeiza
1
and A. Estanga
5
1
System Engineering and Automation Department, University of the Basque Country, Donostia 20008, Spain
2
Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, IDeTIC, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain
3
Digital Technologies Group, Universitat de Vic, Vic, Spain
4
Universitat Politècnica de Mataró (UPC), Tecnocampus, Mataró, Spain
5
Neurology Department CITA-Alzheimer Foundation, San Sebastian, Spain
Keywords: Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis, Spontaneous Speech, Emotion Recognition.
Abstract: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most prevalent form of progressive degenerative dementia and it has a high
socio-economic impact in Western countries, therefore is one of the most active research areas today. Its
diagnosis is sometimes made by excluding other dementias, and definitive confirmation must be done
trough a post-mortem study of the brain tissue of the patient. The purpose of this paper is to contribute to
im-provement of early diagnosis of AD and its degree of severity, from an automatic analysis performed by
non-invasive intelligent methods. The methods selected in this case are Automatic Spontaneous Speech
Analysis (ASSA) and Emotional Temperature (ET), that have the great advantage of being non invasive,
low cost and without any side effects.
1 INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer's Diseases (AD) is the most common type
of dementia among the elderly people and it is
characterized by progressive and irreversible
deterioration of higher brain functions or cognition,
with loss of memory, judgment and language. The
disease prevents the execution of daily life tasks,
giving rise to severe disability towards a full
dependence. An early and accurate diagnosis of AD
helps patients and their families to plan for the future
and offers the best opportunity to treat the symptoms
of the disease. Currently the only possible way to
diagnosis the disease with absolute certainty is by
exclusion of other dementias and making a post-
mortem brain tissue analysis. Thus for the diagnosis
of AD three distinctions are being used: possible,
probable and definite (Sociedad Española de
Neurología;Van de Pole, 2005). This paper presents
a new approach for early AD diagnosis based on two
non-invasive and low cost automatic methods: the
Automatic Spontaneous Speech Analysis and the
Emotional Temperature.
This paper is organized as follows: In the next
section some aspects of Alzheimer disease diagnosis
and speech features of the language are presented.
Resources and methods used are presented in
Section 3. In Section 4 we present experimental
results. Finally conclusions and future work are
depicted in section 5.
2 ALZHEIMER DISEASE
DIAGNOSIS
Eight cognitive domains are most often damaged in
AD (Morris, 1993; American Psychiatric Associa-
tion): memory, language, perception, attention,
constructional skills, counselling skills, problem
solving, and functional capabilities. The clinical
diagnosis is usually based on: Tests of memory and
other cognitive functions, behavioural changes
analysis; Neuroimaging (CT, SPECT, PET), and the
absence of other causes by other medical tests. The
greater the number of tests used in the detection, the
higher the reliability of the diagnosis.
698
López de Ipiña K., B. Alonso J., Solé-Casals J., Barroso N., Faundez M., Ecay M., Travieso C., Ezeiza A. and Estanga A..
Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis based on Automatic Spontaneous Speech Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0004188606980705
In Proceedings of the 4th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (SSCN-2012), pages 698-705
ISBN: 978-989-8565-33-4
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: Spectrogram of a control person during Spontaneous Speech.
Figure 2: Spectrogram of a control person during Spontaneous Speech.
Non-invasive Intelligent Techniques of diagnosis
may become valuable tools for early detection of
dementia and can be used by non-technologists in
the habitual environments of the patient without
altering or blocking their abilities. ASSA and ET are
some of them.
After the loss of memory, one of the major problems
of AD is the language (Figures 1, 2, 3, 4). The loss
of ability to express with language will affect two
types or two aspects: difficulty to speak and
difficulty to understand others, which difficult the
natural communication process with the
environment. We can find different communication
deficits in the area of language, such as (Buiza,
2010; Martinez et al, 2012):
• Aphasia: difficulty in speaking and
understanding
• Anomia: difficulty for recognizing and
naming things.
The problems that the patients have for
communicating according to the stage of the disease
and how it can help would be:
• First Stage: Difficulty for finding the right
word in the spontaneous speech. Of-ten it is
not detected.
• Second Phase: impoverishment of language
and vocabulary for everyday use.
• Third stage: Answers sometimes are very
limited and with very few words.
Moreover, the emotional response in Alzheimer's
patients becomes impaired and seems to go through
different states. In the early stages appears social and
even sexual disinhibition, behavioural changes (be
angry and not being able to perform common tasks,
not to express or not remembering) (Shimokawa et
al, 2001; Goodkind et al, 2010; Cadieux and Greeve,
2000). However, the emotional memory remains...
And they cry more easily to be aware that caregivers
of stroke. They gratefully acknowledge the caresses,
smiles and hugs. The Alzheimer's patient reacts
aggressive on things that, for healthy people, are
harmless. Perceives a threat or danger where does
not exist. In more advanced stages of Alzheimer's
patients often may seem shy and apathetic,
symptoms that often are attributed to memory
AlzheimerDiseaseDiagnosisbasedonAutomaticSpontaneousSpeechAnalysis
699
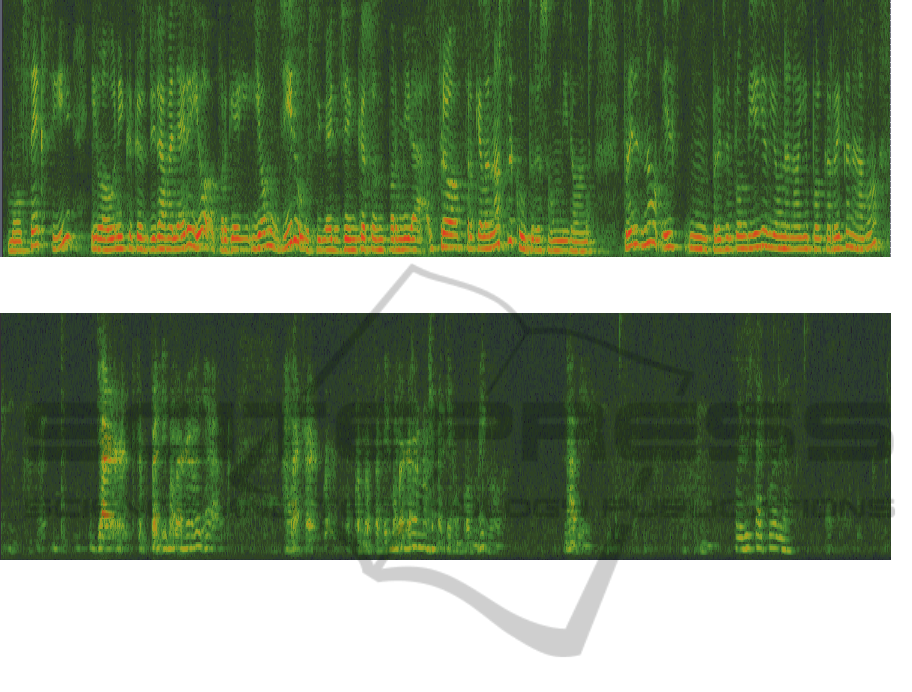
Figure 3: Spectrogram of a control person during Spontaneous Speech.
Figure 4: Spectrogram of a person with AD during Spontaneous Speech.
problems or difficulty for finding the right words.
Some responses are likely to be magnified due to an
alteration in perception. Other research suggests,
moreover, that the patients in this progressive brain
disorder, in advanced stages, may also have a
reduced ability to feel emotions due to loss of
memory and memories. Then it appears apathy and
sometimes depression.
3 METHODS
There are different elements that are part of social
life, intellectual and personnel that constitute the
individual, and one of the most important is spoken
language. This allows us to speak, to communicate
with others, share knowledge, express well with
cultural and personal identity. Spoken language is
the most spontaneous, natural, intuitive and efficient
communication way among people. Therefore, the
analysis by automatic methods of Spontaneous
Speech, the freer and more natural expression of
communication could be a useful noninvasive way
for early diagnosis by combining it with other
methodologies. In this study we analyze
Spontaneous Speech fluency through measures of
voice segment length, pause length, speech
development, libraries, short time energy, centroid
(Napp, 1980).
Emotions arise from the need to face a changing
and partially unpredictable world which makes
necessary to any intelligent system (natural or
artificial) the development of emotions to survive
(Plutchnik, 1980; Cowie, 2001). Emotions are
closely linked to learning and understanding process.
Emotions are cognitive processes related to the
architecture of the human mind (decision making,
memory, attention, etc.).
Human interaction includes emotional
information about partners that is transmitted
through language explicitly and implicitly through
nonverbal communication. The nonverbal informa-
tion, which is often spread by corporate-cultural
gestures, attitudes, modulations of voice, facial
expressions, etc., it essential in human communica-
tion as it has a high effect on the communication
provision of the partners and on the intelligibility of
speech. Human emotions are affected by the
environment, the direct interaction with the outside
world but also by the emotional memory emerged
from the experience of individual and cultural
environment, the so called socialized emotion.
Emotions use the same components subjective,
cultural, physiological and behavioral that the
IJCCI2012-InternationalJointConferenceonComputationalIntelligence
700
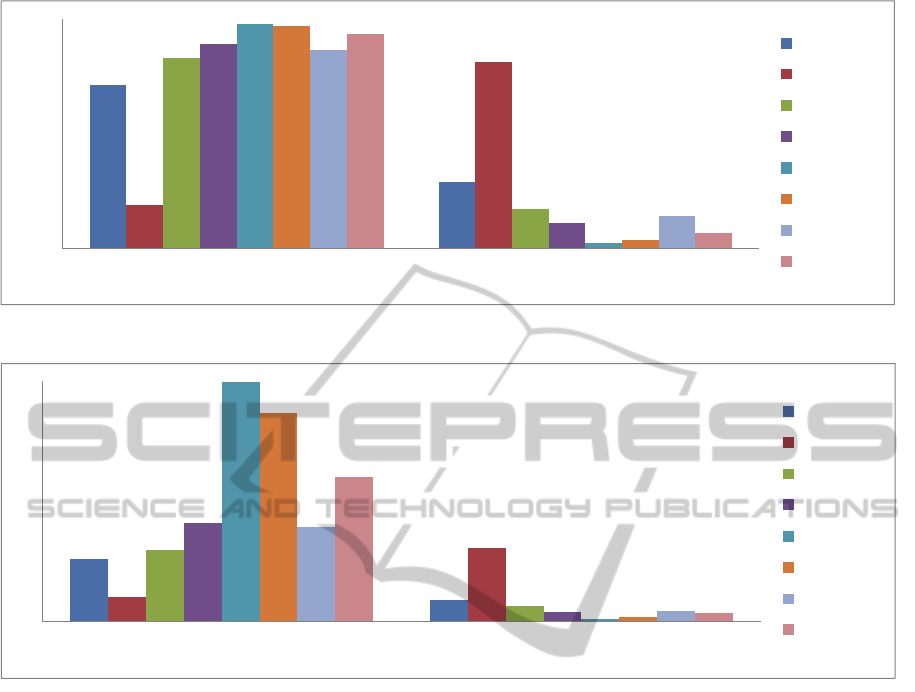
Figure 5: Voiced/unvoiced Percentage in the Spontaneous Speech.
Figure 6: Voiced/unvoiced Segment Average.
individual's perception express with regard to the
mental state, the body and how it interacts with the
environment. The emotions, far from being an
obstacle in understanding the universe, they describe
it clearly.
Therefore, we will use the measure called
Emotional Temperature (Alonso et.al, 2001) in our
study. This method proposes a new strategy based
on a few prosodic and paralinguistic features set
obtained from a temporal segmentation of the speech
signal. Next it is described the steps to estimate the
value of the measure "emotional temperature". The
speech signal is windowed by a hamming window of
0.5 seconds overlapped 50%
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The database for the experimentation is composed
by about 10 hours of Spontaneous Speech from
videos where people tell enjoyable personal stories
divided in about 30 minutes of people with AD
diagnosis and about 9 hours of control people. The
recording atmosphere is relaxed and non-invasive.
The speech is divided into segments of 60 seconds.
Finally it is obtained a database of about 600
segments of Spontaneous Speech. The database is
multicultural and multilingual and with a wide range
of ages. In this experimentation 4 control people of
middle age (ME-NAD) (2 males and 2 females), 3
people with AD (ELD-AD) diagnosis and one elder
person without pathology (ELD-NAD) will be used.
The first set of tests consists of ASSA
experiments. Results (Fig. 5, 6, 7) show significant
fluency loss in people with AD with regard to the
voiced/unvoiced percentage in the speech (Fig. 5)
and to the length of voiced/unvoiced segments (Fig.
6)
Fig 7 (a) along the time (consecutive segments
(S2:S6) shows that people with AD disease tend to
decrease the length of voice segments and the
fluency by increasing the unvoiced segment number
and decreasing the length of voice segments. Results
show a decreasing slope in the evolution of
0
20
40
60
80
100
Voice Unvoice
ELD1‐AD
ELD2‐AD
ELD3‐AD
ELD4‐NAD
ME1‐NAD
ME2‐NAD
ME3‐NAD
ME4‐NAD
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
VoiceSegmentAverage UnvoiceSegmentAverage
ELD1‐AD
ELD2‐AD
ELD3‐AD
ELD4‐NAD
ME1‐NAD
ME2‐NAD
ME3‐NAD
ME4‐NAD
AlzheimerDiseaseDiagnosisbasedonAutomaticSpontaneousSpeechAnalysis
701
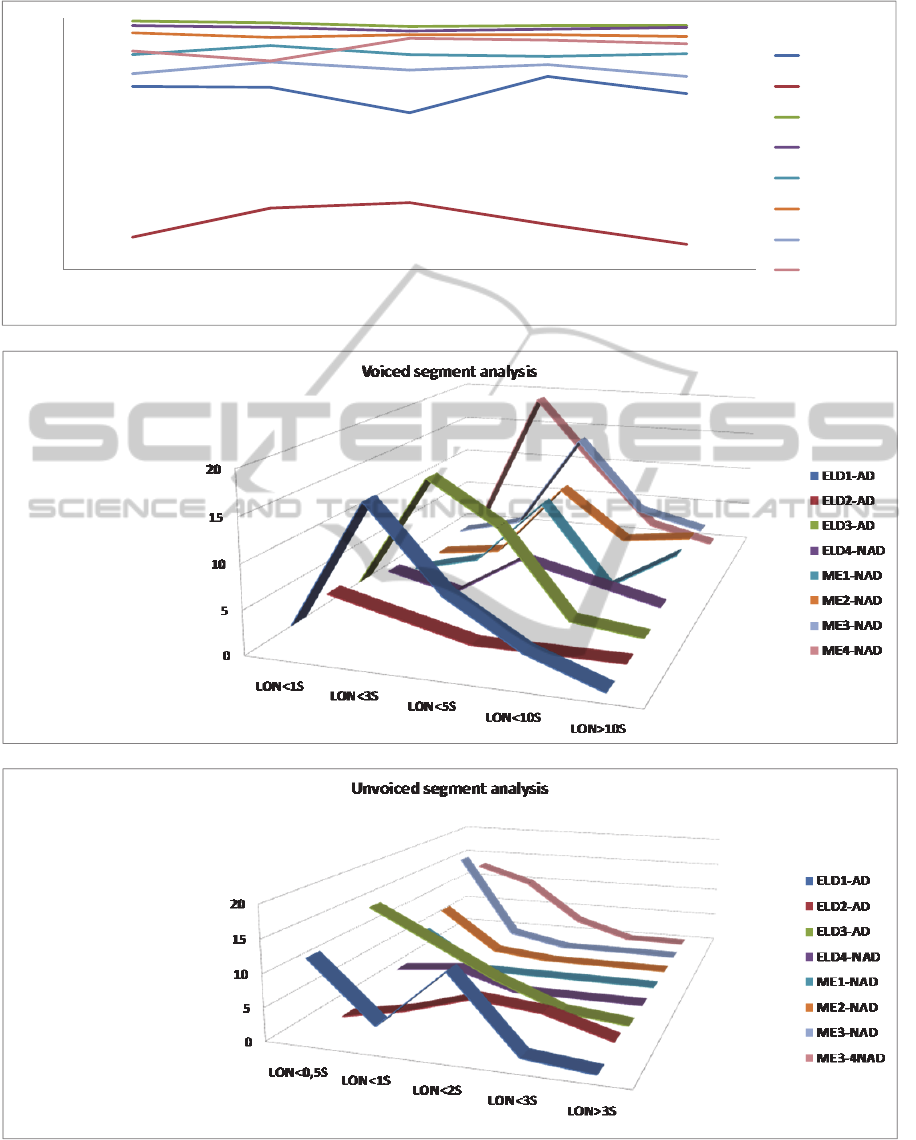
Figure 7: (a) The Spontaneous Speech Evolution with regard to the Speech Percentage along the time, for the consecutive
segments (S2:S6). (b) Voiced segment analysis with the regard to segment length (c) Unvoiced segment analysis with the
regard to segment length.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
S2 S3 S4 S5 S6
ELD1‐AD
ELD2‐AD
ME1‐NAD
ME2‐NAD
ME2‐NAD
ME2‐NAD
ELD3‐AD
ELD4‐NAD
IJCCI2012-InternationalJointConferenceonComputationalIntelligence
702
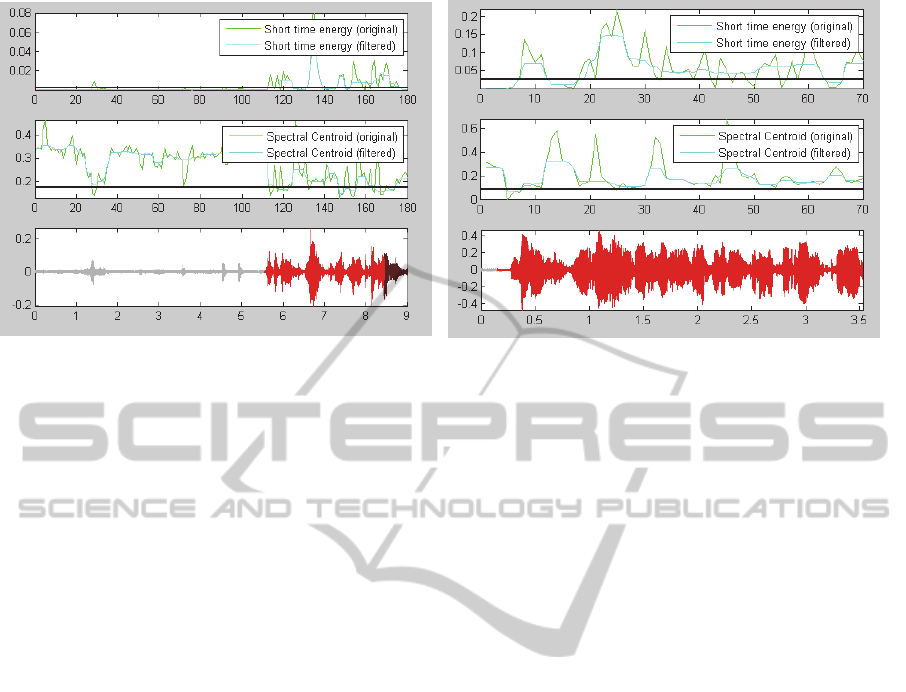
Figure 8: Plots of Speech Signal, Short Time Energy and Spectral Centroid.
Spontaneous Speech for people with AD. The
analysis of voiced and unvoiced segments with
regard to length segments (Figure 7. b, c) shows a
tendency of people with AD disease to use more and
shorter voiced segments. They can´t stand Speech
Fluency for a long time. In their Spontaneuous
Speech usually don´t appear segment longer than 10
second. With regard to unvoiced segments along the
speech they use more and longer segments than
control people. Figure 8 shows also lower Short
Time Energy also for this people and lower Spectral
Centroid for AD. The Spontaneous Speech
Evolution with regard to the Speech Percent-age.
The second set of tests, consist of experiments of
Emotional Temperature. Support vector machines
(SVM) (Chang) have been used to quantify the
discriminative ability of the proposed measures. We
have used a freely available implementation named
LIBSVM (Chang) in our implementation, where a
radial basis kernel function was used. Classification
targets are: speakers without neurological pathol-
ogies and speakers diagnosed with Alzheimer. To
estimate the measure “emotional temperature”, first
of all each temporal frame is classified using a SVM
(also using a threshold that is obtained from EER in
the training step) and next, the percentage of
temporal frame that are classify as no pathological is
calculated, where this value is the "emotional
temperature" measure. Besides, normalization is
made to the measure "emotional temperature", for
that the measure "emotional temperature" has a
value 50 in the threshold of EER estimated in the
training step (Figure 9).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper new approaches for Alzheimer Disease
diagnosis based on Automatic Spontaneous Speech
Analysis and Emotional Temperature have been
presented. The purpose of the work is to contribute
to improve early diagnosis of dementia and severity
from automatic analysis, performed by non-invasive
automated intelligent methods. The selected
methods in this case are Automatic Spontaneous
Speech Analysis (ASR) and Emotional Temperature
(ET). These methodologies have the great advantage
of being non invasive, low cost methodologies and
have no side effects. The research on multicultural
and multilingual population shows some
encouraging results both in terms of the ASSA and
the Emotional Temperature, showing tendencies to
explore with a broader population. In future work we
will integrate the described methodologies with
automatic analysis methods of drawing and
handwriting as well as with automatic analysis of
facial features. We will extend also the analysis
population as well as the type of pathology.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by
SAIOTEK from the Basque Government. Dr. Solé-
Casals also acknowledges the partial support of the
University of Vic under the research grant R0904.
AlzheimerDiseaseDiagnosisbasedonAutomaticSpontaneousSpeechAnalysis
703
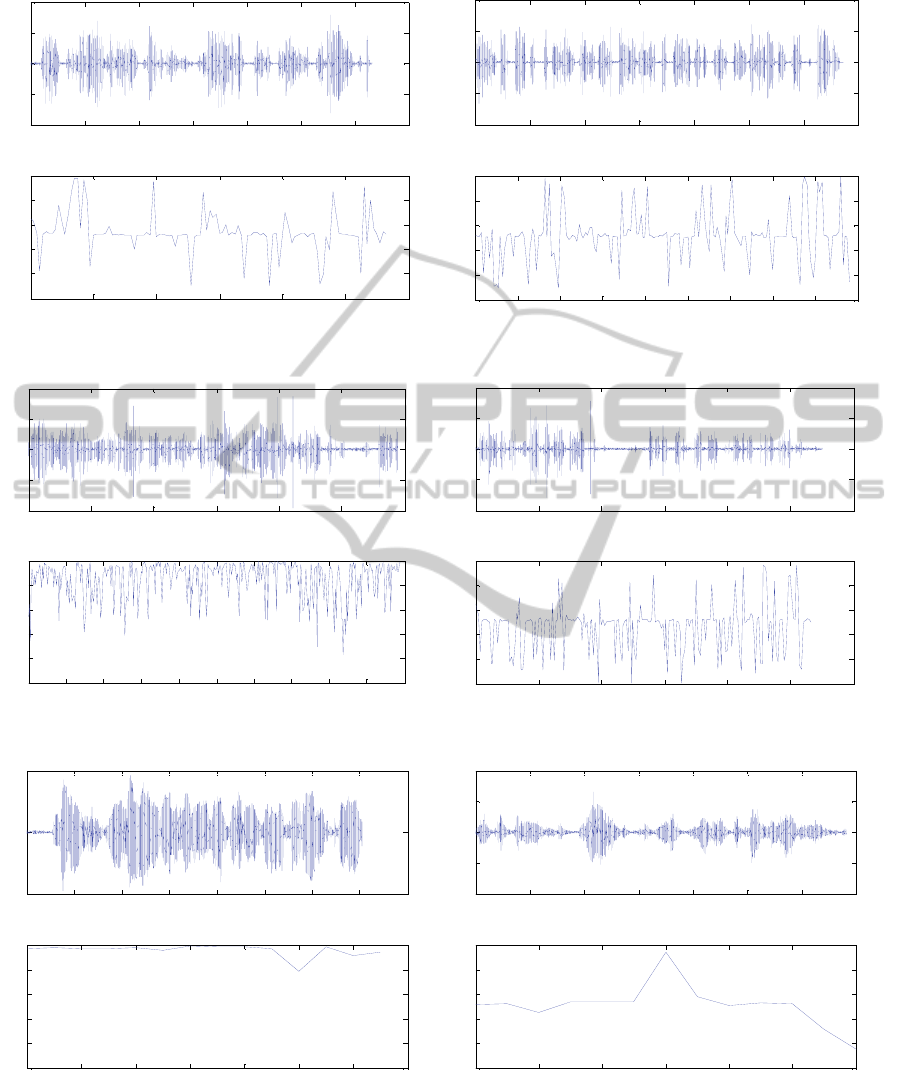
Figure 9: Emotional Temperature for, ELD4-NAD, ELD3-AD, ME3-NAD, ELD1-AD and a control person ME1-NAD
and a person with AD, ELD1-AD in a segment of 3 seconds.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
Tiempo (seg)
fichero: MAR01.wav
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Tiempo (seg) /Solo parte sonora
Temperatura Emocional: 59.6693
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
Tiempo (seg)
fichero: PAK01.wav
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Tiempo (seg) /Solo parte sonora
Temperatura Emocional: 46.169
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
Tiempo (seg)
fichero: LP2MNAD01.wav
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Tiempo (seg) /Solo parte sonora
Temperatura Emocional: 94.9333
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
Tiempo (seg)
fichero: ALF07.wav
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Tiempo (seg) /Solo parte sonora
Temperatura Emocional: 41.298
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
-0.5
0
0.5
Time (seg)
File: NuriTxiki3.wav
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Time (seg) / Only voiced frames
Emocional Temperature: 100
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
Time (seg)
File: AlfredoTxiki3 modificado.wav
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Time (seg) / Only voiced frames
Emocional Temperature: 46.56
IJCCI2012-InternationalJointConferenceonComputationalIntelligence
704

REFERENCES
Alonso J., De León J., Alonso I., Ferrer MA. Automatic
detection of pathologies in the voice by HOS base
parameters. Journal on Applied Signal Processing.
2001; 4:275-284
American Psychiatric Association, 2000. Diagnostic and
Statistical Manual of Mental disorders, 4th Edition
Text Revision. Washington DC
Buiza Cristian. Evaluación y tratamiento de los trastornos
del lenguaje, Psicóloga. Gerontóloga. Unidad de
Memoria y Alzheimer. Matia Fundazioa. Donostia,
2010
Cadieux N. and Greeve K. Emotion processing in
Alzheimer's disease, Journal of the International
Neuropsychological Society, 1997, 3: 411-419, The
International Neuropsychological Society, DOI:
(About DOI) Published online: 2000.
Chang CC, Lin CJ. LIBSVM: a library for support vector
machines; 2001. Available from: http://www.csie.
ntu.edu.tw/ ~cjlin/libsvm.
Cowie, E. et al. ‘Emotion Recognition in Human-
Computer Interaction’. IEEE Signal Processing
Magazine, Vol 18(1). Pp. 32-80 (2001).
Goodkind MS, Gyurak A, McCarthy M, Miller BL,
Levenson RW., Emotion regulation deficits in
frontotemporal lobar degeneration and Alzheimer's
disease., Psychol Aging. 2010 Mar;25(1):30-7. PMID,
20230125, PMCID: PMC2841311
Knapp M. L.. Essentials of nonverbal communication.
Holt, Rinehart & Winston (1980).
Martinez-F., Garcia J., Perez, E. CarroJ., Anara,. J.M.
Patrones de Prosodia expresiva en pacientes con
enfermedad de Alzheimer, Psicothema, Vol. 24 , nº 1 ,
pp. 16-21, 2012.
Morris JC, The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current
version and scoring rules. Neurology, 1993. 43: p.
2412b-2414b.
Plutchnik, Emotion: A psychoevolutionary synthesis’New
York,Harper and Row (1980).
Shimokawa, A., Yatomi, N., Anamizu, S., Torii, S., Isono,
H., Sugai, Y., & Kohno, M. (2001). Influence of
deteriorating ability of emotional comprehension on
interpersonal behaviour in Alzheimer-type dementia.
Brain and Cognition, 47, 423-433.
Sociedad Española de Neurología, http://www.sen.es/
Van de Pol, L.A., et al., The effects of age and
Alzheimer's disease on hippocampal volumes, a MRI
study. Alzheimer's and Dementia, 2005. 1(1,
Supplement 1): p. 51.
AlzheimerDiseaseDiagnosisbasedonAutomaticSpontaneousSpeechAnalysis
705
