
GENERALIZED NET MODEL FOR TELECOMMUNICATION
PROCESSES IN TELECARE SERVICES
Velin Andonov, Todor Stojanov, Krassimir Atanassov
Dept. of Bioinformatics and Mathematical Modelling Inst. of Biophysics and Biomedical Engineering,
Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad. G. Bonchev Str., Block 105, Sofia-1113, Bulgaria
velin_andonov@yahoo.com, todor@clbme.bas.bg, krat@bas.bg
Peter Kovachev
National Institute of Geophysics, Geodesy and Geography,
Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Acad. G. Bonchev Str., Block 3, Sofia-1113, Bulgaria
pkov@abv.bg
words: telecare services, generalized nets.
Abstract: In (Andonov et al., 2012) a Generalized Net (see (Atanassov, 2003, 2007)) model of processes, related to
tracking the changes in health status of adult patients has been presented. The contemporary state-of-the-art
of the telecommunications and navigation technologies allow this model to be extended to the case of active
and mobile patient. This enforces the inclusion of patient's current location as a new and significant variable
of the model. Various opportunities are considered for the retrieval of this information, with a focus on the
optimal ones, and a refined Generalized Net model is proposedt.
.
1 INTRODUCTION
Let us take a look into life sensors attached to a
person's body and one other type of sensors.The
sensors can be divided into two main groups. The
first group is the group of the stationary sensors.
They are placed in the rooms to monitor for CO,
CO
2
concentration, temperature and other
parameters which can endanger one's life. These
types of sensors are patient independent and can
work autonomously. They are connected to the
server with internet connection (WiFi or LAN).Their
alarm events in most of the cases are True positive,
can be recognized and a decision can be easily
taken.
The second type of sensors are looking for
biomedical parameters e.g. ECG signal, SPO2. They
collect the biomedical signals, analyze them and
consequently take the most expected decision.
Alarm message is sent sent to the server and, if
necessary, part of untypical biomedical signal or
parameter value. The server can send requests to the
sensor to confirm the alarm event or resend
biomedical signal or parameter. In these sensors we
can have the False positive event. For this reason the
server has to have very smart filter for False positive
removing or translate the alarm event to human
operator if the case is complicated.
The second type of sensors can work with a
cheap smart module for connecting to the GSM
network. Because this network allows more
flexibility and the patient is free to go wherever he
wants. These sensors can make communication to
smart phone by Bluetooth or direct cable
communication. Nowadays, the existing GSM
network has enough speed and possibility for data
translation via e.g. network type 3G and 4G too.
Also these GSM modules can have the GPS module.
This GPS module is necessary in case that the
medical center has to localize the person in urgent
cases such as earthquake, fires, etc. The smart
module can send the GPS coordinates to the rescue
center for easy localization of the person or persons.
In order to carry out the connection between
GSM networks, the sensor should have a GSM
module or a smart module. Another requirement to
prevent connection break is that the GSM module
158
Andonov V., Stojanov T., T. Atanassov K. and Kovachev P.
GENERALIZED NET MODEL FOR TELECOMMUNICATION PROCESSES IN TELECARE SERVICES.
DOI: 10.5220/0005415301580162
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Telecommunications and Remote Sensing (ICTRS 2012), pages 158-162
ISBN: 978-989-8565-28-0
Copyright
c
2012 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

has to be connected to at least two networks
available or a WiFi network connection should be
accessible.
2 LOCATION TECHNOLOGIES
There are three most commonly used location
technologies: stand-alone (typical stand-alone
technology is dead reckoning), satellite-based and
terrestrial radio-based.
2.1 Satellite-based Systems
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) are
systems of satellites that provide autonomous geo-
spatial positioning with global coverage.
Only the
United States NAVSTAR Global Positioning
System (GPS) (Hofmann-Wellenhof) and the Russian
GLONASS are fully globally operational GNSSs.
Satellite navigation systems that provide
enhanced accuracy and integrity monitoring usable
for civil navigation are classified as follows: the
combination of existing satellite navigation systems
(GPS and GLONASS), with
Satellite Based
Augmentation Systems (SBAS) or Ground Based
Augmentation Systems (GBAS) (2010 FEDERAL
RADIONAVIGATION PLAN)
. In the United States,
the satellite based component is the
Wide Area
Augmentation System (WAAS), in Europe it is the
European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service
(EGNOS) (
Gauthier,2001; Filip, 2001), and in Japan it
is the
Multi-Functional Satellite Augmentation
System (MSAS). Ground based augmentation is
provided by systems like the
Local Area
Augmentation System (LAAS).
2.2 GPS Receivers
There are three types of GPS receivers which are
available in today's marketplace. Each of the three
types offers different levels of accuracy.
To this
point, the discussion in this paper has focused on
Coarse Acquisition (C/A code) GPS receivers. The
two remaining types of GPS receiver are Carrier
Phase receivers and Dual Frequency receivers. C/A
Code receivers typically provide 1-5 meter GPS
position accuracy with differential corrections (Filip,
№5/2001). C/A Code GPS receivers provide a
sufficient degree of accuracy to make them useful in
most GIS and emergency applications. A GPS
tracking unit is a device that uses the Global
Positioning System to determine the precise location
of a vehicle, person, to which it is attached and to
record the position of the asset at regular intervals.
The recorded location data can be stored within the
tracking unit, or it may be transmitted to a central
location data base, or internet-connected computer,
using a cellular, radio, or satellite modem embedded
in the unit. This allows the asset's location to be
displayed against a map backdrop either in real time
or when analyzing the track later, using GPS
tracking software
http://www.liveviewgps.com/.
GPS personal tracking devices assist in the care of
the elderly and vulnerable. Devices allow users to
call for assistance and optionally allow designated
carers to locate the user's position, typically within 5
to 10 meters. Their use helps promote independent
living and social inclusion for the elderly. Devices
often incorporate either 1-way or 2-way voice
communication which is activated by pressing a
button. Some devices also allow the user to call
several phone numbers using pre-programmed speed
dial buttons. GPS personal tracking devices are used
in several countries to help in monitoring people
with early stage of dementia and Alzheimer
http://www.eurogps.eu/bg/world-news/tracking/99-
gps-tracking-alzheimer.
2.3 Positioning in 3G Networks
• Mobile-based technologies: Cell-ID, time
advance;
• Network-based technologies: TDOA (time
difference of arrival), AOA (angle of
arrival);
• Mobile-assisted technologies: A-GPS
(assisted GPS), AFLT (advanced forward
link trilateration),
E-OTD (enhanced
observed time difference),
U-TDOA;
These technologies typically use base stations,
satellites or devices emitting radio signals to the
mobile receiver to determine the position of its user.
Signals can also be emitted from the mobile device
to the base. Commonly studied techniques are angle
of arrival (AOA) positioning, time of arrival (TOA)
positioning, and time difference of arrival (TDOA)
positioning. All these methods require radio
transmitters, receivers, or transceivers. To determine
the location, these methods generally have the
assumption that one end of the positioning system is
fixed and the other end is moveable such as a mobile
phone. However, the location determination
capability can be either at the fixed end or at the
mobile end. For performance improvement,
hybridmethods (various combinations of the
techniques) are possible (
Overview of 2G LCS
Generalized Net Model for Telecommunication Processes in Telecare Services
159

Technnologies and Standards, London, UK, January
2001
).
Other methods based based on measuring the
signal strength or measuring the signal characteristic
patterns and multipath characteristics of radio
signals arriving at a cell site from a caller. For
measuring the signal strength, it employs multiple
cell sites to find the location. For measuring the
signal characteristic patterns, it identifies the unique
radio frequency pattern or "signature" of the call and
matches it to a similar pattern stored in its central
database (
Shu Wang, Jungwon Min, Byung K. Yi, 2008;
Y. Zhao, 2000).
TOA and TDOA are time-based measurement
technologies. They can be implemented either based
on the forward (down) link signal or reserved (up)
link signal. In addition, the location determination
capability can reside either at the network side or at
the mobile phone. In order to locate several base
stations or cell sites, the sensitivity of the mobile
phone may need to be increased. These methods also
require software modification on the mobile phone
and additional location determination units and
related software in the network. As discussed above,
the mobile phone needs to listen to the signals of at
least three base stations or cell sites. The visibility
and geographical locations of these base stations will
affect the availability and the accuracy of the
location determination (
Overview of 2G LCS
Technnologies and Standards, London, UK, January
2001).
The performance of the satellite-based GPS
receiver is getting better and better while the
receiver size and price keep going down. To develop
an assisted GPS (A-GPS) solution for the mobile
phone requires software and hardware modifications
of both the mobile phone and its communications
network.
The A-GPS use a GPS reference network (or a
wide-area DGPS network) whose receivers have
clear views of the sky and can operate continuously.
This reference network is also connected with the
cellular infrastructure, and continuously monitors
the real-time constellation status and provides
precise data such as satellite visibility, ephemeris
and clock correction, Doppler, and even the
pseudorandom noise code phase for each satellite at
a particular epoch time. At the request of the mobile
phone or location-based application, the assist data
derived from the GPS reference network are
transmitted to the mobile phone GPS receiver (or
sensor) to aid fast start-up and to increase the sensor
sensitivity. Acquisition time is reduced because the
Doppler versus code phase uncertainty space is
much smaller than in conventional GPS due to the
fact that the search space has been predicted by the
reference receiver and network. This allows for
rapid search speed and for a much narrower signal
search bandwidth which enhances sensitivity. Once
the embedded GPS receiver acquires the available
satellite signals, the pseudorange measurements can
be delivered to network-based position
determination entity (PDE) for position calculation
or used internally to compute position in the handset.
Additional assisted data, such as DGPS
corrections, approximate handset location or cell
base station (BS) location, and other information
such as the satellite almanac, ionospheric delay,
universal time coordinated (UTC) offset can be
transmitted to improve the location accuracy,
decrease acquisition time, and allow for handset-
based position computation. Several schemes have
been proposed in the standards which reduce the
number of bits necessary to be exchanged between
the handset and the network by using compression
techniques such as transmitting only the non-
redundant or the changes to parameters instead of
the raw parameters themselves. Other satellite
systems could be used, such as the Russian
GLONASS system, but none of the standards have
made provision for anything except GPS and the
GPS Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS)
signals. Besides adding a GPS reference network
and additional location determination units in the
network, the mobile phone must embed, at a
minimum, a GPS antenna and RF down converter
circuits, as well as make provision for some form of
digital signal processing software or dedicated
hardware (
Overview of 2G LCS Technnologies and
Standards, London, UK, January 2001). Аll the radio-
based technologies discussed can be affected by
interference, blockage, and multipath.
3. GENERALIZED NET MODEL
In our model, we consider n patients. The i-th patient
has i
k
different sensors. The sensors for the i-th
patient are represented by the tokens δ
i,1
, δ
i,2
, ... ,δ
i,ik .
The tokens δ
i,1
, δ
i,2
, ... ,δ
i,ik
enter the net in place l
2
with initial characteristics:
"name of the patient; sensor's parameters"
The criterion for the correctness of the signal
detected by the sensors is represented by the token α
which stays permanently in place l
7
with initial
characteristic:
"criterion for the corectness of the signal"
The tokens d
i,1
, d
i,2
, ... ,d
i,ik
stay permanently in
First International Conference on Telecommunications and Remote Sensing
160
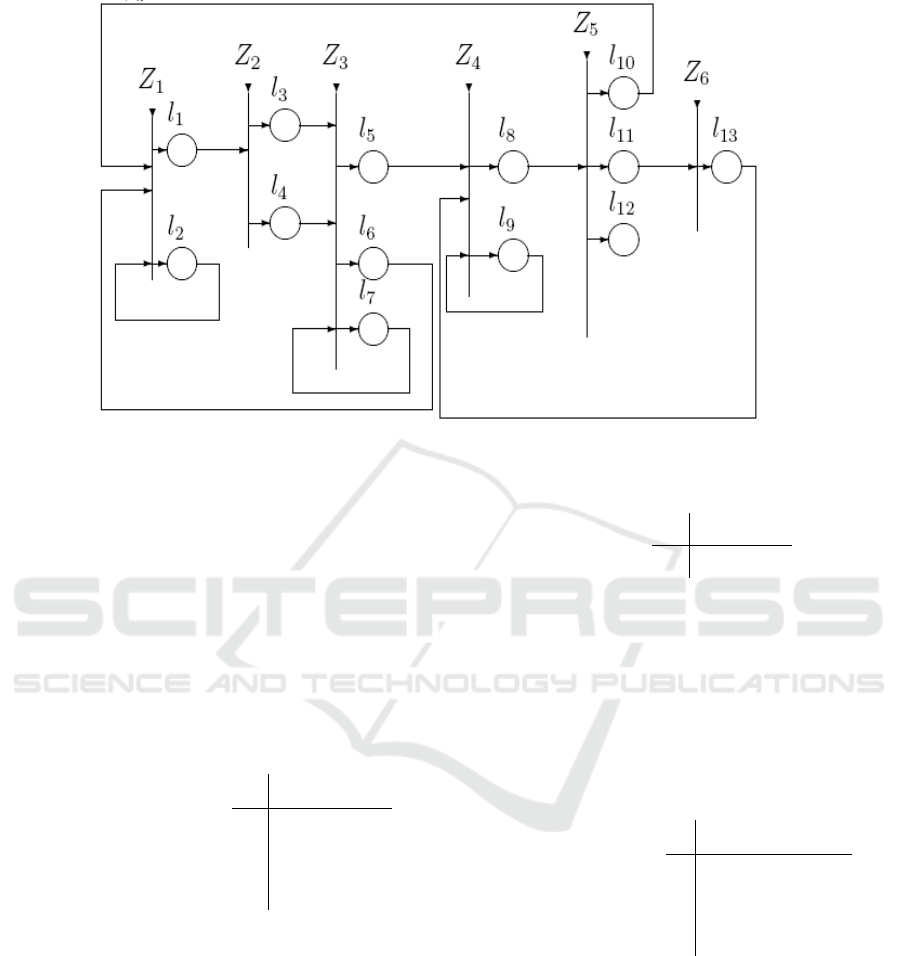
Figure 1: Generalized Net
place l
9
with initial characteristic:
"name of the patient; previously recorded sensor
data and respective action taken"
We use the tokens d
i,,j
to keep record of the sensor's
data which can be used in future to decide whether
the patient should be sent to a medical doctor.
Below is a formal description of the transitions
of the net.
l
1
l
2
Z
1
=<{l
1
, l
6
, l
10
},{l
1
,l
2
},
l
2
W
2,1
W
2,2
> ,
l
6
false true
l
10
false true
where
W
2,1
= ”the sensor detected the patient's body
signals”,
W = ¬ W ,
2,2 2,1
where ¬ P is the negation of the predicate P.
When the truth-value of the predicate W
2,1
=true
the token δ
i,j
enters place l
1
with characteristic:
“signal of the sensor about the current patient”
When the truth-value of the predicate W
2,2
=true the
token δ
i,j
enters place l
2
without a new characteristic.
l
3
l
4
Z
2
= <{l
1
},{l
3
,l
4
},
l
1
W
1,3
W
1,4
>,
where
W
1,3
= ”the signal comes from a stationary
sensor”,
W
1,4
= ¬ W
1,3
.
When the truth-value of the predicate W
1,3
=true
the token δ
i,j
enters place l
3
and does not obtain any
new characteristic. When the truth-value of the
predicate W
1,4
=true the token δ
i,j
enters place l
4.
l
5
l
6
l
7
Z
3
= <{l
3
, l
4
, l
7
},{l
5
,l
6,
l
7
},
l
3
true false
false
>,
l
4
W
4,5
W
4,6
false
l
7
false false true
where
W
4,5
= ”the criterion shows that the signal of the
sensor is correct and it must be further evaluated
whether a medical doctor's reaction is necessary”,
W
4,6
= “the criterion shows that the current signal
must be confirmed”.
When the current δ
i,j
token enters places l
5
or l
6
it
does not obtain any new characteristics.
Generalized Net Model for Telecommunication Processes in Telecare Services
161

l
8
l
9
Z
4
= <{l
5
, l
9
, l
13
},{l
8
,l
9
},
l
5
true false
>,
l
9
false true
l
13
false true
When the current δ
i,j
token enters place l
8
it
obtains the characteristics of the respective d
i,j
token.
In place l
9
the token d
i,j
obtains as characteristic the
signal parameters of the respective δ
i,j
token and the
decision that has been made. In place l
13
the current
δ
i,j
token splits into two tokens, the original δ
i,j
token which continues to stay in place l
13
and a new
token d’
i,j
with the same characteristics which enters
place l
9
. and it unites there with the respective d
i,j
token.
where
W
8,10
="the history shows that the signal should
be confirmed",
W
8,11
= "there is no similar sensor data in the
history or the history suggests that the patient should
be sent to a medical doctor"
W
8,12
= "the history suggests that no action
should be taken",
l
13
Z
6
= <{l
11
},{l
13
},
l
11
true >,
When the current δ
i,j
token enters place l
13
it
obtains the characteristic:
"send the patient to a medical doctor"
REFERENCES
Andonov, V., et al. Generalized Net Model for Telecare
Services, IEEE Conf. “Intelligent Systems”< Sofia, 6-
8 Sept. 2012 (in press).
Atanassov, K. Generalized nets, World Scientific,
Singapore, 1991.
Atanassov, K., On Generalized Nets Theory, “Prof. Marin
Drinov” Publishing House of the Bulgarian Academy
of Sciences, 2007.
Hofmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., GPS Theory
and Practice, ISBN 3-211-82839-7 4
th
d. Springer-
Verlag Wien New York
2010 Federal Radionavigation Plan, Published by
Department of Defense, Department of Homeland
Security, and Department of Transportation, This
document is available to the public through the
National Technical Information Service, Springfield,
Virginia 22161DOT-VNTSC-RITA-08-02/DoD
4650.05
Gauthier, L., P. Michel, J. Ventura-Traveset, J. Benedicto.
EGNOS: The First Step in Europe’s Contribution to
the Global Navigation Satellite System. ESA bulletin
105 February 2001, p. 35-42
Filip, A., H. Mocek, L. Bazant. GPS/GNSS Based Train
Positioning for Safety Critical Application.
Signal+Draht, (93) №5/2001, p. 51-55
Filip, A., H. Mocek, L. Bazant. GPS/GNSS Based Train
Positioning for Safety Critical Application.
Signal+Draht, (93) №5/2001, p. 51-55
3GPP TSG SA2 LCS Workshop LCS-010019, Overview
of 2G LCS Technnologies and Standards, London,
UK, January 2001, 11 – 12, Source: Motorola, Inc.
Location Based Services (LBS) for mobiles:
Technologies and Standards – WCNC/ICC 2008, Shu
Wang, Jungwon Min, Byung K. Yi, LG Electronics
Mobile Research, USA
Zhao, Y., “Mobile Phone Location Determination and Its
Impact on Intelligent Transportation Systems”, IEEE
Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,
vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 55-64, Mar. 2000.
l
10
l
11
l
12
Z
5
= <{l
8
},{l
10
,l
11,
l
12
},
l
3
W
8,10
W
8,11
W
8,12
>,
First International Conference on Telecommunications and Remote Sensing
162
