
Hemorrhage Control by Short Electrical Pulses
In Vivo Experiments
Guy Malki, Ofer Barnea and Yossi Mandel
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Keywords: Hemorrhage Control, Electrical Pulses, Liver Injury.
Abstract: An internal hemorrhagic shock is one of the leading causes of death in the battlefield and other trauma
events. However the application of direct pressure, as in the treatment of an external hemorrhage, is not
possible. Most common techniques to achieve vasoconstriction are through heat; yet heating causes
irreversible destruction of organ tissues. Therefore, there is a need for a non-thermal based technology for
hemorrhage control. The current research describes, for the first, an attempt to reduce the amount of
bleeding in animal model liver injuries by using electrical pulses treatment (EPT). In the experiments, which
were performed on 28 rats and 14 rabbits, a short (25µs and 50µs) EPT was applied to the treatment groups
and the amount of bleeding was compared to the non-treatment (NT) groups. A reduction of 60%, 36% and
44% in blood volume, was found in the 25µs-rats, 50µs-rats and 25µs-rabbits EPT groups, respectively
(P<0.001). Also, it was found that the hemorrhage control was not caused by the mechanical pressure
applied by the electrodes, and there was no evidence for thermal coagulation. Further research is needed to
fully expose the potential of this treatment and the modality for hemorrhage control in civilian and military
settings.
1 INTRODUCTION
Hemorrhage shock is one of the leading causes of
death in the battlefield and other trauma events.
Most battlefield hemorrhages are compressible, e.g.
they can be controlled by a tourniquet or other
means of direct pressure application. A recent
survey made by the US army demonstrated the
effect of early tourniquet application in increasing
survival rates while causing minimal damage (Kragh
et al., 2011).
However, bleeding occurring in internal cavities
(such as the chest or the retroperitoneal space) or in
solid organs (e.g. liver, spleen and kidneys) is
considered non-compressible and the application of
direct external pressure is not possible. Hemorrhage
control from solid organs is challenging even in the
setting of an operation theatre, because of their rich
vasculature and lack of supportive connective
tissues.
In order to cope with this important need, there
are several techniques that being researched for
hemorrhage control in solid organs, of which the
main ones are by mechanical pressure and thermal
coagulation. However, each of these technologies
has its drawbacks and currently none of them have
evolved into clinical devices. For example, High
Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) (Burgess et
al., 2007); (Vaezy et al., 1997), induces a rapid
temperature increase in tissue, and cavitation
formation, both leading to thrombosis and platelet
activation. This technique has some adverse
reactions such as an irreversible destruction of the
liver and blood vessels, and overheating.
Nevertheless, these techniques, as well as others, are
still under evaluation and were not proved to give
full answer the clinical need in the battlefield or in
the surgical theater. Thus, there is a need for a non-
thermal based technology which will cause
vasoconstriction, thrombosis and hemorrhage
control.
Thrombosis of a clamped blood vessel was
demonstrated by several authors by using a direct
current application device (Guarini, 1971);
(Hladovec, 1975). However, applying this technique
for clinical use in hemorrhage control is not practical
because of the expected injury to the tissue. The
effect of short electrical pulses on blood vessel
constriction and thrombosis was reported in several
papers (Gehl et al., 2002); (Matsushima et al., 1994);
103
Malki G., Barnea O. and Mandel Y..
Hemorrhage Control by Short Electrical Pulses - In Vivo Experiments.
DOI: 10.5220/0004190001030107
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices (BIODEVICES-2013), pages 103-107
ISBN: 978-989-8565-34-1
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

(Sersa et al., 1999); (Yu-ling et al., 1997), which
studied electrochemical therapy for tumors. These
papers demonstrated a significant temporary
reduction in blood flow after pulsing.
The specific characterization of various pulse
parameters on blood vessels constriction and
thrombosis was recently described by Palanker et al.,
(2008), which reported that the vasoconstriction
effect appeared shortly after 10 seconds of electrical
stimulation while thrombosis was achieved at 3
minutes. A pulse rate of 0.1Hz was sufficient for
maintaining vasoconstriction, yet there were
evidence of inflammation and necrosis. The authors
reported that the effect is probably non-thermal as
the temperature rise during the treatment did not
exceed 0.01
o
C. Nevertheless, the exact mechanism
for vessel constriction and thrombosis is still
unclear, thus a comprehensive study of these
mechanisms is necessary.
The potential application of the electrical pulsing
effect on blood vessels is studied by our group. Our
long term goal is to develop a portable device to
control internal non-compressible hemorrhage from
solid organs. The current research describes, for the
first time in vivo experiments, an attempt to reduce
the amount of bleeding caused in rat and rabbit liver
injury.
2 METHODS
In vivo experiments were performed on livers of 28
adult Sprague-Dawley rats and 14 New Zealand
rabbits. The experiment protocol was approved by
the Animal Rights Council of the Israel Ministry of
Health and conformed to guidelines for the humane
care of animals. Animals were supplied by Harlan
Laboratories Ltd., Jerusalem, at the age of 3 months.
Average animal weight is depicted in Table 1.
2.1 RAT Experiments
The animals were anesthetized with an IM injection
of Ketamine HCI (0.19ml/100 gram) and Xylazine
(0.03ml/100 gram) solution. The surgical operation
started 20 minutes after anesthetization to get an
initially uniform point for all animals, and until that
time the animal was weighed and placed on a
heating blanket to maintain its body core
temperature. Additional anesthetics were given
approximately every 20 minutes via titration. A
midline abdominal incision was performed and the
liver was gently exposed. The median lobe of the
liver was resected 13 mm from the lobe edge and the
removed part was weighed using portable scales
(Ohaus Company, model N2B110).
Following the liver injury, the animals were
divided into four groups. In the control group no
treatment (NT) was given after the liver injury.
Electrical pulses treatment (EPT) was performed to
2 groups, using a protocol which includes 100
electrical pulses of 500V at a pulse repetition of
1Hz, and pulse duration of 25µs and 50µs, for the
EPT25 and EPT50 groups, respectively. In addition,
in order to inspect the possibility of bleeding
decrease due to mechanical pressure exerted on the
liver lobe, a mechanical treatment (MT) group had
been defined, so that the electrodes were placed on
the median lobe for 200 seconds, as similar to the
EPT groups, however, no pulses were delivered.
For all the groups, except the NT, the rat’s
injured medial liver lobe was placed between two
customized copper electrodes, which were attached
to a commercial caliper (Figure 1a). The distance
between the 2 parallel slabs was adjustable, and
determined for each animal by its liver thickness
(mean electrode distance was 3.98±0.56 mm). A
series of electrical pulses were generated by a square
wave electroporation system (ECM 830, Harvard
Apparatus), which was operated in the mono-phasic
mode.
Following these interventions, the abdomen was
closed using continuous sutures and the rats were
maintained on heating blanket for 1 hour without
any further treatment. Total blood loss was
measured 60 minutes after liver injury, by soaking a
cotton wool in the peritoneal cavity; the same
method reported by previous authors (Hildreth et al.,
1996); (Holcomb et al., 1999); (Matsuoka and
Wisner, 1996). Blood loss for each animal was
normalized by its body weight. All surgical
interventions and measurements were performed by
the same investigators (GM, YM), to avoid variance
in the procedure, which could affect the results.
The liver was removed immediately after
euthanasia and fixed into formaldehyde 10%.
Histological slices were processed for H&E staining
in paraffin sections and then cut perpendicular to
liver edge in order to demonstrate the transition
between treated and untreated zones.
2.2 Rabbit Experiments
Animals were anesthetized with an intra-muscular
injection of Ketamine HCI (50 mg/kg) and Xylazine
(3.5 mg/kg) solution followed by maintenance
dosage, and 20 minutes following the administration
of anesthetic drugs, a midline abdominal incision
BIODEVICES2013-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
104

Table 1: Animal weight and excised liver weight (normalized to animal weight) in all groups.
Rat Rabbit
Group NT MT EPT50 EPT25 EPT25 NT
N
11 4 8 5 7 7
Animal weight [gr]
398.66±20.14 408.3±49.5 398±32.9 392.3±33.6 3196±448 3106±293
Normalized Excised
Liver Weight [%]
0.26±0.07 0.25±0.06 0.22±0.05 0.21±0.05 - -
was performed and the liver was gently exposed. In
this experiment set, different liver injury was
performed: 2 cuts of 5mm deep and 3cm long in
each front liver lobe (total 6 cuts in 3 lobes).
Following liver injury, rabbits were divided into
two groups. EPT25 group received 200 pulses
(500V, 1Hz) that were given with pulse duration of
25µs and NT group received no treatment. In the
EPT25 group, the rabbit liver was treated with
customized electrodes comprised of two copper
plates of 4mm wide and 29mm long, and spaced
apart by 7.2mm (Fig 1b). Following each liver cut,
the electrodes were positioned on the liver surface
while the cut is in equal distances between the
electrodes and a series of electrical pulses were
given, similarly to the treatment described for rat
liver injury. In addition, thermal images have been
taken using a thermal camera (model A40, FLIR)
before and immediately after the treatment, in order
to distinguish if there is temperature increase during
the electrical treatment.
Following these interventions, rabbit’s abdomen
was closed using continuous sutures and the animals
were maintained on heating blanket for 1 hour
without any further treatment. Total blood loss was
measured 60 minutes after liver injury in the same
method as described for rats. All surgical
intervention and measurements for all experiments
were performed by the same investigator (GM).
3 RESULTS
Average animal weight and excised liver weight in
rats (normalized to the animal weight) are reported
in table 1. Both parameters were not significantly
different between all animal groups (p>0.1). These
results indicate that the injury protocol was pretty
much the same, and therefore could not affect the
blood loss results.
Blood loss weight can be observed in Figure 2,
as a box plot chart of normalized bleeding weight for
all animal groups. On each box, the black circle is
the mean value, the central line is the median, the
edges of the box are the 25
th
and 75
th
percentiles, and
the lines outside the box are the most extreme data
points (minimum and maximum).
In contrast to the normalized excised liver
weight, the blood loss amount in the EPT50 and
EPT25 rat groups was significantly reduced by 36%
and 60%, respectively, as compared to the NT group
(p<0.001 for both groups). Blood loss in the EPT25
group was significantly lower than in the EPT50
group (p=0.025), suggesting that the pulse duration
can affect the molecular processes of the electrical
treatment (which are not known yet) in becoming
faster and/or more efficient. Blood loss in the MT
group did not differ significantly from the NT group
(p=0.43), and this finding is probably indicates that
the mechanical pressure is not the reason for the
reduced bleeding from the injured liver.
Similar results were found for the rabbits (Fig 2),
where blood loss in the electric pulse treatment
group was smaller by more than 44% as compared to
the NT group (p=0.004).
4 DISCUSSION
The results, which were achieved by in-vivo animal
experiments, demonstrated that short electrical
pulses of 25µsec and 50µsec decreased the amount
of hemorrhage from a rat liver injury by 60% and
36%, respectively, and a rabbit liver injury by 44%.
Apparently, the effect was not caused by the
mechanical pressure applied by the electrodes per-
se, but by the electrical field applied on the tissue,
because there was no significant different in the
measured bleeding amount between the NT group
and the MT group.
The distinction between the treatment effective
between the rats and the rabbits can be explained by
the difference in the electrode configuration. In the
rabbits’ case the treatment was on the surface area,
so the electric field was not enough deep. On the
other hand in the rats’ case the electrodes were in the
two sides of the wound, so the electric field was
stronger in the injury site, and increase the treatment
effective.
Another potential cause for hemorrhage
reduction could be a thermal coagulation caused by
the increased temperature rise in response to pulse
HemorrhageControlbyShortElectricalPulses-InVivoExperiments
105
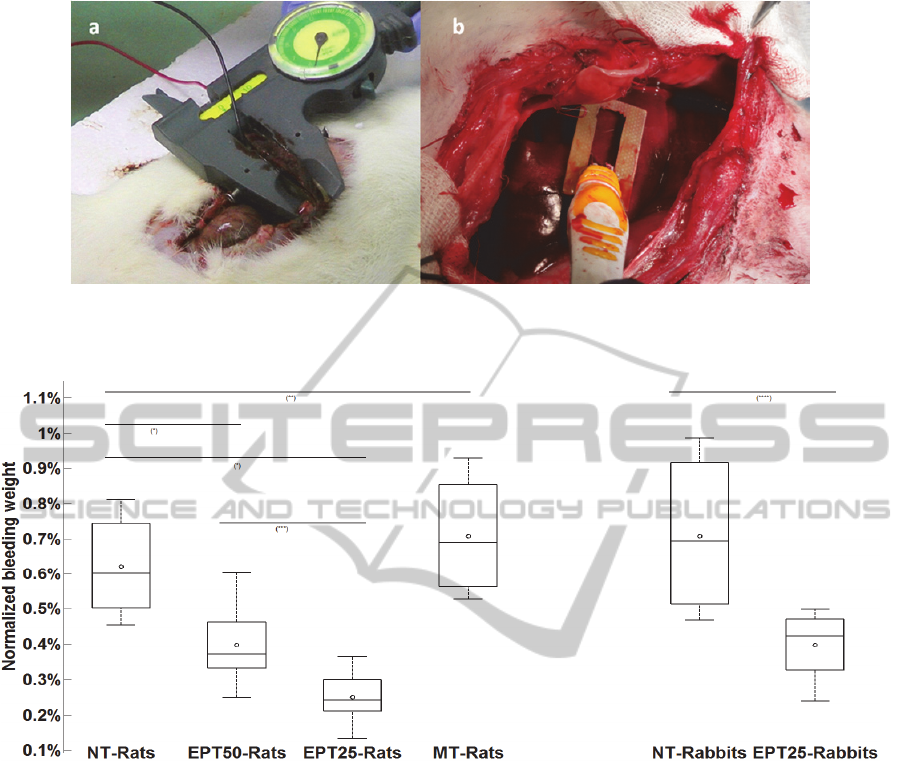
Figure 1: Experimental setup of rat (a) and rabbit (b) liver. Rat liver was treated with two parallel plate electrodes mounted
on a hand caliper adjusting for liver thickness. Rabbit liver injury was treated by fix parallel plates electrodes positioned at
two sides of the wound.
Figure 2: Box plot of normalized bleeding weight in all animal groups (rats and rabbits). Control groups were not treated,
EPT50 and EPT 25 were treated by 200 pulses of 50 and 25 µs, respectively, in a repetition rate of 1 Hz. Unpaired t-test
results for various comparisons are as follows: (*) p<0.001, (**) p=0.43, (***) p=0.025, (****) p=0.004.
treatment. However, thermo-coagulation is usually
expected at temperatures of above 60-70
O
C (Graham
et al., 1998); (Matsuoka et al., 2004), and were
probably not achieved in these experiments, even at
the longer pulse duration [According to a parallel
theoretical study in our group, which investigated
the shape of the electric field and the heating that
accompanying to the electrical treatment in different
configurations of electrodes, through mathematical
models and computer simulations in COMSOL and
MATLAB].
Further, there was no evidence for thermo-
coagulation and temperature rise in the histological
sections and the thermal images, respectively.
Interestingly, we found that 25µsec pulses were
significantly more effective in reducing hemorrhage
volume compared to 50µsec pulses. One possible
explanation may be related to a local increase in
liver perfusion in response to the relative
temperature rise in the case of 50µsec pulses, as
reported in previous studies (Precup et al., 2010). It
could be hypothesized that such a local increase in
perfusion could cause a relative increase in blood
loss, partially reducing the effect of treatment.
We hypothesize that the hemorrhage control
observed in this study is associated to endothelial
layer damage, leading to irreversible vessel
constriction and forming a thrombus. A similar
effect was reported in other electrochemical therapy
studies (Gehl et al., 2002). Ramirez et al., (1998)
reported that electrical pulses of 850 V/cm and 100
microseconds long, caused a decrease in blood
perfusion to the spleen and mesenteric arteries, and
also reported that electrical pulsing of the liver
BIODEVICES2013-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
106

caused a decrease in perfusion, as was demonstrated
by a color test. Sersa et al., (2008) found that 3
minutes following tumor electric pulsing, blood flow
decreased by about 80 percent, and histological
evaluation of the endothelial cells showed that they
were rounded and swollen causing narrowing of the
blood vessels lumen.
Our study has several limitations to be
considered. First, blood pressure and pulse were not
measured or controlled during the experiments. This
could theoretically increase variance in the amount
of bleeding. Second, in this preliminary study we did
not address the effect of treatment in the case of
traumatic coagulopathy, which is expected in cases
of severe liver trauma. This issue calls for future
research. Other issues to be studied in larger animals
are the design of the electrodes in order to optimize
electric field geometry, optimize pulse parameters to
achieve finer results, better control of tissue
temperature, and the possible use of changes in the
electrical properties of the tissue for measuring
treatment effect.
In conclusion, in this preliminary research we
demonstrate that short electric pulses can
significantly reduce the amount of bleeding from
injured liver in a rat model. The effect is probably
non thermal and possibly related to the effect on
blood vessels’ endothelial layer. Further research is
needed in order to fully expose the potential if this
treatment modality for hemorrhage control in
civilian and military settings.
REFERENCES
Burgess, S., Zderic, V., & Vaezy, S. (2007). Image-guided
acoustic hemostasis for hemorrhage in the posterior
liver. Ultrasound in medicine & biology, 33(1), 113-9.
Gehl, J., Skovsgaard, T., & Mir, L. M. (2002). Vascular
reactions to in vivo electroporation: characterization
and consequences for drug and gene delivery.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1569(1-3), 51-8.
Graham, J., Bronskill, & Henkelman, (1998). Time and
Temperature Dependence of MR Parameters.pdf. MR
Parameters and Thermal Coagulation, 39, 198-203.
Guarini, S. (1971). Model of Arterial Thrombosis in Rats,
8719(96).
Hildreth, J., Wisner, D. H., Matsuoka, T. (1996).
Uncontrolled Hemorrhage from Parenchymal Injury :
Is Resuscitation Helpful ? The Journal of Trauma:
Injury, Infection, and Critical Care, 40(6), 915-922.
Hladovec J. (1975). A quantitative model of venous stasis
thrombosis in rats. Physiol Bohemoslov., 24(6), 551-4.
Holcomb, J. B., Pusateri, a E., Harris, R. a, Charles, N. C.,
Gomez, R. R., Cole, J. P., Beall, L. D., et al., (1999).
Effect of dry fibrin sealant dressings versus gauze
packing on blood loss in grade V liver injuries in
resuscitated swine. The Journal of trauma, 46(1), 49-
Kragh, John F., Jr, MC, U. C. M., Dubick, Michael A. ,
PhD David G. Baer, PhD James Johnson, P., &
Blackbourne, Lorne H. , MC, U., (2011). New
Tourniquet Device Concepts for Battlefield
Hemorrhage Control. THE ARMY MEDICAL
DEPARTMENT JOURNAL, 38-48.
Matsuoka, T., & Wisner, D. H., (1996). Resuscitation of
uncontrolled liver hemorrhage: effects on bleeding,
oxygen delivery, and oxygen consumption. The
Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical
Care, 41(3), 439-45.
Matsuoka, Ishida, M. and Konishi, (2004). Numerical
study of temperature distribution in tissue for
thermalcoagulation therapy..pdf. Journal of
Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 272-276, 2426-
2427.
Matsushima Y, Takahashi E, Hagiwara K, Konaka C,
Miura H, Kato H, K. Y., (1994). Clinical and
experimental studies of anti-tumoral effects of
electrochemical therapy (ect) alone or in
combinationwith chemotherapy. Eur J Surgery,
574(59-67).
Palanker, D., Vankov, A., Freyvert, Y., & Huie, P.,
(2008). Pulsed electrical stimulation for control of
vasculature: temporary vasoconstriction and
permanent thrombosis. Bioelectromagnetics,
29(2),
100-7.
Precup, C. G., Gonganau-Nitu, D., Scurtu, R. R.,
Dindelegan, G., Biro, A., Soritau, O., Crişan, C., et al.,
(2010). Assessement by laser Doppler of the
peripheral tumour perfusion after radiofrequency
ablation for colorectal liver mestasis--experimental
study. Chirurgia (Bucharest, Romania : 1990), 105(1),
71-6.
Ramirez, Orlowski, Bindoula, Dzodic, Ardouin, Bognel,
Jr, B., et al. (1998). Electrochemotherapy on liver
tumours in rabbits. British Joumal of Cancer, 77(12),
2104-2111.
Sersa, G., Jarm, T., Kotnik, T., Coer, a, Podkrajsek, M.,
Sentjurc, M., Miklavcic, D., et al., (2008, January 29).
Vascular disrupting action of electroporation and
electrochemotherapy with bleomycin in murine
sarcoma. British journal of cancer.
Sersa, G. Parkins, C. . ., & Chaplin, D. J., (1999). Tumour
Blood Flow Changes Induced by Application of
Electric Pulses. European Journal of Cancer, 35(4),
672-677.
Vaezy, S., Martin, R., Schmiedl, U., Caps, M., Taylor, S.,
Beach, K., Carter, S., et al., (1997, January). Liver
hemostasis using high-intensity focused ultrasound.
Ultrasound in medicine & biology.
Yu-ling Xin, Fu-zhou Xue, Bing-sheng Ge, Feng-rui
Zhao, Bin Shi, and W. Z., (1997). Electrochemical
Treatment of Lung Cancer. Bioelectromagnetics, 18,
8-13.
HemorrhageControlbyShortElectricalPulses-InVivoExperiments
107
