
Data Mining based Methodologies for Cardiac Risk Patterns
Identification
V. G. Almeida
1
, J. Borba
1
, T. Pereira
1
, H. C. Pereira
1,2
, J. Cardoso
1
and C. Correia
1
1
Instrumentation Center (GEI-CI), University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
2
ISA-Intelligent Sensing Anywhere, Coimbra, Portugal
Keywords:
Data Mining, Artificial Neural Network, Clustering, Arterial Distension Waveform, Cardiovascular Diseases.
Abstract:
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death in the world. The pulse wave analysis provides
a new insight in the analysis of these pathologies, while data mining techniques can contribute for an efficient
diagnostic method. Amongst the various available techniques, artificial neural networks (ANNs) are well es-
tablished in biomedical applications and have numerous successful classification applications. Also, clustering
procedures have proven to be very useful in assessing different risk groups in terms of cardiovascular function
in healthy populations. In this paper, a robust data mining approach was performed for cardiac risk patterns
identification. Eight classifiers were tested: C4.5, Random Forest, RIPPER, Naïve Bayes, Bayesian Network,
Multy-layer perceptron (MLP) (1 and 2-hidden layers) and radial basis function (RBF). As for clustering pro-
cedures, k-means clustering (using Euclidean distance) and expectation-maximization (EM) were the chosen
algorithms. Two datasets were used as case studies to perform classification and clustering analysis. The accu-
racy values are good with intervals between 88.05% and 97.15%. The clustering techniques were essential in
the analysis of a dataset where little information was available, allowing the identification of different clusters
that represent different risk group in terms cardiovascular function. The three cluster analysis has allowed the
characterization of distinctive features for each of the clusters. Reflected wave time (T_RP) and systolic wave
time (T_SP) were the selected features for clusters visualization. Data mining methodologies have proven
their usefulness in screening studies due to its descriptive and predictive power.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to World Health Organization (WHO),
Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) represent 31% of all
global deaths, making them the leading cause of death
in the world (Mendis, 2011). The global impact of
CVDs has motivated the development of low-cost di-
agnostic tools to be used in early stages of CVDs de-
velopment (Mendis, 2011).
The assumption that arterial stiffness is a marker
of CVDs has gained much relevance and support
during the last years. Several studies have reported
its predictive value in cardiovascular (CV) mortality
(Laurent, 2006).
The arterial distension waveform (ADW) contains
a significant amount of physiological information hid-
den in its morphology. The development and subse-
quent validation of efficient non-invasive ADW acqui-
sition devices has gained significant importance in the
last years (Avolio et al., 2010). The use of piezoelec-
tric (PZ) sensors in ADW monitoring have been repo-
rted by some authors with good performance in in
vivo clinical trials (Almeida et al., 2011a; Clemente
et al., 2010). Augmentation Index (AI) and Pulse
Wave Velocity (PWV) are amongst the most impor-
tant features that can be extracted from the ADW.
Both of them have been widely studied by the sci-
entific community and proved their usefulness in as-
sessing local and regional arterial stiffness (Laurent,
2006).
Data mining techniques have attracted a great deal
of attention due to their ability in extract implicit
and potentially useful information from huge amounts
of data. Their feasible implementation in computer-
aided diagnosis methodologies has given new insights
for the development of innovative and effective deci-
sion support systems for CV premature risk assess-
ment.
Classification and clustering routines in CV risk
assessment have already been reported in the litera-
ture, with good results. Shah, et. al. (2011) proved
the usefulness and feasibility of assessing different
127
G. Almeida V., Borba J., Pereira T., C. Pereira H., Cardoso J. and Correia C..
Data Mining based Methodologies for Cardiac Risk Patterns Identification.
DOI: 10.5220/0004222701270133
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms (BIOINFORMATICS-2013), pages 127-133
ISBN: 978-989-8565-35-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

CV risk groups in a healthy population. Jovic et. al.
(2011) addressed the electrocardiogram (ECG) clas-
sification problem using the combination of several
features in the analysis of heart rate (HR) variability.
Tsipouras et. al. (2008) developed a fuzzy rule-based
decision support system for the diagnosis of coronary
artery disease. The dataset included several features,
including demographic, clinical, and vascular data.
Furthermore, the application of Artificial Neural Net-
works (ANNs) in the cardiac field reveals its potential
and affordability (Yang et al., 2012).
Previous established developments have con-
tributed for a non-invasive acquisition device that
can be a convenient and suitable solution to assess
the hemodynamic condition (Almeida et al., 2011a;
Almeida et al., 2011b; Almeida et al., 2011c). In
the present study, an approach of CVDs risk assess-
ment is presented by the analysis of interesting pat-
terns and relationships in the pulse wave morphology
using classification and clustering procedures.
This paper is organized as follows: section 2 de-
scribes all the classification and clustering algorithms.
Section 3 centers on the used methodology, including
ADW data acquisition and data pre - processing tasks.
Results and Discussion are presented in section 4, and
finally, Conclusions are reported in section 5.
2 DATA MINING ALGORITHMS
Among the many different definitions that are found
in the literature, data mining can be defined as the
automatic or semi-automatic process of discovering
patterns in huge amounts of data. When data mining
techniques are efficiently applied, new and potentially
useful information can be extracted from a dataset.
Classification is used to classify data into prede-
fined categorical class labels, where the class is the
attributed most important for the model characteriza-
tion. Clustering consists of grouping similar data into
clusters. A cluster is defined as a set of objects that
are closely related to each other, and less related to
objects outside the cluster.
A set of classification and clustering algorithms
are described below.
2.1 Classification Algorithms
2.1.1 Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are sophisticated
analytical techniques, inspired by the biological ner-
vous system. In an ANN, a set of connected input and
output units, in which each connection has a specific
weight associated to it. The network learns by adjust-
ing the weights so as to be able to predict the correct
class label of the inputs.
Even though ANNs need high computational re-
sources, need rigorous parameter tuning (for example,
the number of hidden neurons in MLP) and have poor
interpretability, they present advantages that make
their effectiveness undeniable, as their outstanding ac-
curacy in general, ability to work with continuous at-
tributes and above average tolerance to redundant at-
tributes.
The most popular ANN architecture is the multi-
layer perceptron (MLP), which consists of input units,
an output layer and one or more hidden layers deter-
mined by the user. It uses back-propagation as the
learning algorithm. After the network inputs pass
through the input layer, they are weighted and fed to
a second layer, the hidden layer. The outputs of the
hidden layer can be inputs to another hidden layer or
inputs to the output layer, which will emit the net-
work’s prediction for the given tuples. Another pop-
ular approach is the radial basis function (RBF) net-
work, in which every hidden unit implements a radial
activation function and each output unit implements a
weighted sum of hidden unit outputs (Haykin, 1998).
2.1.2 Decision Trees Induction
Decision trees are very popular classification meth-
ods, due to their simplicity and interpretability. They
also have no need of parameter tuning or high compu-
tational power while holding good accuracy in overall
(Kotsiantis, 2007).
Decision trees assume a flowchart structure,
where each internal node represents a test in an at-
tribute that need to be classified, and each branch rep-
resents a possible outcome of this test. Popular deci-
sion tree induction techniques are the Random Forest
(Breiman, 2001) and C4.5 (Quinlan, 1993).
2.1.3 Bayesian Classification
Bayesian classifiers are based on Bayes’ theorem, and
predict class membership probabilities, such as the
probability of a given tuple belonging to a particular
class. Usual Bayesian classifiers are the Naïve Bayes
and Bayesian networks.
The major advantage of the Bayesian classifiers
is their short computational time for training. They
also present good tolerance to missing values. How-
ever, their accuracy is usually lower than other classi-
fiers, which makes them good ’baseline’ classification
methods (Kotsiantis, 2007).
BIOINFORMATICS2013-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
128

Figure 1: Schematic representation of main tasks performed along this work: ADW acquisition (where, DAQ is the data
acquistion sytem), feature points selection and database storage.
2.1.4 Associative Classification
In associative classification, association rules are gen-
erated and analysed, showing strong associations be-
tween attributes - value pairs that occur frequently in
a given dataset. A typical associative classifier is the
RIPPER algorithm, which was proposed by Cohen
(1995) and is based on association rules with reduced
error pruning.
2.2 Clustering Algorithms
2.2.1 k-Means Algorithm
The k-Means algorithm is a type of partitional cluster-
ing. It acknowledges the number of desired clusters
input k and partitions a set of n objects into k clusters,
so that the resulting intra-cluster similarity is high but
the inter-cluster similarity is low. Cluster similarity is
measured in regard to the mean value of the objects
contained in a cluster, which is, in fact, the cluster
centroid. The k-means algorithm is an iterative pro-
cess, and continuously iterates until a specific crite-
rion function (usually the square error) converges.
K-means clustering is relatively scalable and effi-
cient in processing large datasets. However, it cannot
handle categorical attributes and is unsuitable for dis-
covering clusters with non-convex shapes. Also, it is
quite sensitive to noise and outliers, so an efficient
pre-processing of the data could and should be per-
formed before applying the method (Han and Kam-
ber, 2006).
2.2.2 Expectation - Maximization
The expectation-maximization (EM) clustering algo-
rithm is a complex probabilistic extension of the k-
means method. Instead of assigning each object to a
cluster with which it is most similar, EM assigns each
object to a cluster according to a weight represent-
ing the probability of membership, which means that
there are no strict boundaries between clusters, and
new means are determined based on weighted mea-
sures (Han and Kamber, 2006).
3 METHODS
This section describes the used methodology, includ-
ing data acquisition procedures, feature selection, pre-
processing routines and respective data mining analy-
sis.
3.1 Data Acquisition
The non-invasive PZ probe was placed over the
carotid artery during data acquisitions performed at
sampling rate of 1kHz. The architecture of the acqui-
sition system is shown in Figure 1.
Age, gender, weight, height, smoking habits and
diabetes history were registered and Body Mass In-
dex (BMI) was later calculated for all of the subjects.
Systolic and diastolic blood pressure values (SBP and
DBP, respectively) and heart rate (HR) were measured
before the ADW recording with an automatic digital
DataMiningbasedMethodologiesforCardiacRiskPatternsIdentification
129

Table 1: Non-demographic attributes list.
Attribute Description Units
T_SP Upstroke time [ms]
T_RP Time at reflection point [ms]
T_DW Starting time of dicrotic wave [ms]
H_SP Systolic amplitude [-]
H_RP Reflected wave amplitude [-]
H_DW Dicrotic wave amplitude [-]
R1 Downstroke time between systolic and dicrotic wave [ms]
R2 Amplitude quotient between H_DW and H_SP [-]
R3 Amplitude difference between H_SP and H_RP [-]
R4 Amplitude quotient between H_SP and H_RP [-]
AI Augmentation Index [%]
FWHM Full width at half maximum [ms]
RMSE Root mean square error (RMSE) between each pulse and the av-
erage pulse
[%]
RMSSD Root mean square of successive differences (RMSSD) of SP,
DW and RP (T-time and A-amplitude)
[ms or amp (a.u.)]
oscillometric sphygmomanometer (Omron M6 Com-
fort, Kyoto, Japan).
The patient measurement protocol was mainly
based on the subject condition standardization of Van
Bortel, et. al., (2002) . All measurements were made
in a similar time of the day, at the same temperature
controlled room (22-23
◦
Celsius). Subjects remained
seated on a comfortable chair during the measure-
ments. At least 3 measurements of roughly 30-40 sec-
onds were made per subject. A morphological analy-
sis was performed to identify pulse artefacts caused
by voluntary and involuntary movements. Subse-
quently, the pulses were segmented and feature point
extraction by pulse wave analysis was performed.
The dataset is composed by tuples where each tu-
ple represents one segmented pulse. Each pulse con-
tains a maximum of 29 attributes. Most of these at-
tributes are numerical, but some of them are cate-
gorical/nominal attributes. All non-demographic at-
tributes are described in Table 1.
• Dataset I: This group is constituted by 25 healthy
(class 1) subjects and 25 unhealthy subjects (class
2). A set of 2947 pulses was analysed. The num-
ber of pulses is approximately equal for each class
(1425/1522). Eight classifiers were trained us-
ing this dataset. Demographic data (age, gender,
smoker, diabetes history, height, weight, BMI,
SBP, DBP, HR) were removed.
• Dataset II: This dataset consists of 93 healthy and
young subjects between 18-30 years. A set of
4471 pulses was analysed. The full list of 29 pa-
rameters was used for clustering procedures.
3.2 Data Pre-processing
Before applying the desired data mining techniques,
all data must be rigorously pre-processed to avoid
low-quality mining results. Usual data cleaning rou-
tines were executed to discover and correct discrepan-
cies in data, consequently ensuring high-quality data.
These routines include missing value removal, outlier
identification, irrelevancy and redundancy analysis.
Data normalization procedures to transform the at-
tributes into a 0 to 1 range were applied to the data
used in ANN classification tasks, due to their need of
standardized inputs to perform efficiently.
3.3 Data Mining
The Weka (Waikato Environment for Knowledge
Analysis) free machine learning system was selected
as the data mining tool for use during classification
and clustering analysis due to its comproved effi-
ciency, versatility and affordability (WEKA, 2012).
3.3.1 Classification
Classification methods can be evaluated according
to their general accuracy, computation cost, robust-
ness, scalability and interpretability (Han and Kam-
ber, 2006). The selected classification algorithms
were: C4.5, Random Forest, RIPPER, Naïve Bayes,
Bayesian Network, MLP (1HL), MLP (2HL) and
RBF. Accuracy (ACC), sensitivity (SST), specificity
(SPT) and precision (PRC) measures were deter-
mined with the number of true positives (TP), true
BIOINFORMATICS2013-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
130
negatives (TN), false positives (FP) and false nega-
tives (FN). Training speed was also measured, accord-
ing the following rank: * [>60s], ** [20-60s], ***
[10-20s], **** [2-10s], ***** [0-2s]. The classifica-
tion task was performed in Weka using 10-fold cross-
validation.
3.3.2 Clustering
Clustering methods can be evaluated by their vi-
sual interpretability, scalability, dimensionality, ro-
bustness and ability to deal with different types of
attributes. A wide range of clustering methods ex-
ists on the literature. K-means clustering (using Eu-
clidean distance) and expectation-maximization (EM)
were the algorithms selected to test. Reflected wave
time (T_RP) and systolic wave time (T_SP) were the
selected features for clusters visualization.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Dataset I
Results from the classification performance are ex-
pressed in Table 2. All classification methods ex-
cept Bayesian based - classification exhibited accu-
racy values >95%. Random forest was the best
classifier, in overall, by having the highest accuracy
and sensitivity. Comparing with the other classifiers,
ANN methods require high computational resources,
as they can take more than 30 seconds to be trained.
However, ANN algorithms have shown superior re-
sults in terms of specificity, which means that the FP
error rate is low. The three classifiers with highest
accuracy scores were: random forest, 1-hidden layer
MLP and 2-hidden layers MLP.
4.2 Dataset II
4.2.1 Two Clusters
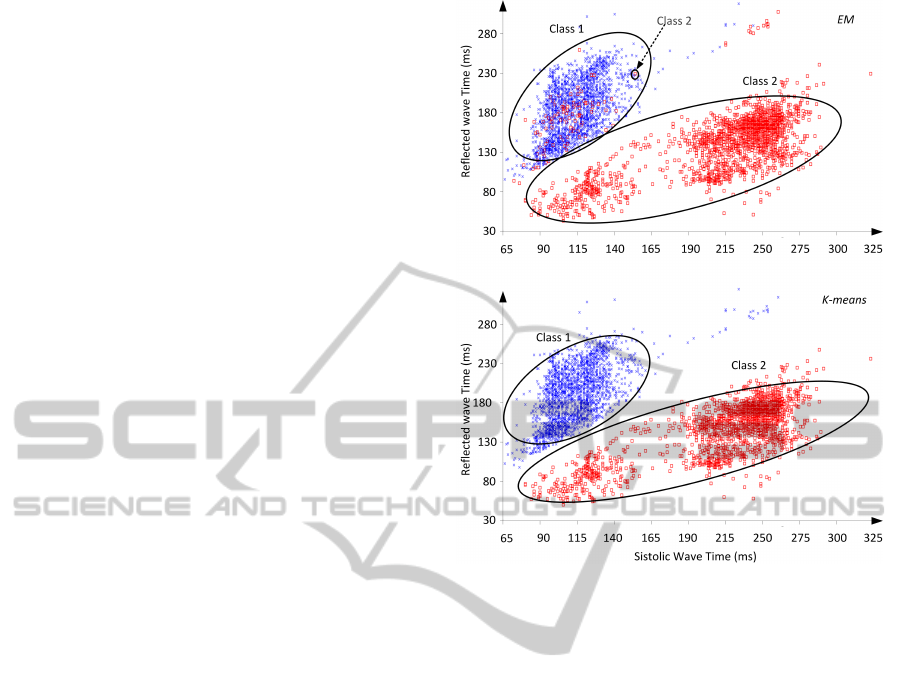
Figure 2 displays the clusters performance for EM
and k-means algorithms by the RP time and SP time
analysis. Different colored points represent different
pulse labels (blue = class 1; red = class 2). Categor-
ical features (gender, smoker) were eliminated in the
k-means clustering method due to its limitations with
categorical attributes.
The EM plot presents unsatisfactory splitness be-
tween the two classes, as visible by the dashed ar-
row that indicates a point from class 2 inside the class
1 group. Visually, the results of k-means clustering
are more desirable and satisfying, as it partitioned
Figure 2: Clusters performance obtained for EM (top) and
k-means algorithm (bottom) using two clusters, Cluster
1=blue, Cluster 2=red.
the dataset in two perfectly homogeneous risk groups.
For both EM and k-means, the blue group (class 1)
presents itself as a more healthier partition than the
red group (class 2), as it represents the cases where
the reflection wave arrives after the systolic point, and
class 2 represents a group with higher risk for CV
complications due to the early RP time.
4.2.2 Three Clusters
The k-means clustering was the chosen algorithm
for three risk group clustering, due to its better per-
formance in two-cluster analysis in comparison with
EM.
During the clustering procedures, RMSSD_RPT
negatively interfered in primary cluster measure-
ments. For this reason, this parameter was removed
from the subsequent analysis alongside categorical
features. The clustering groups are presented in Fig-
ure 3. The dataset is split in three clusters, which are
not completely split due to clusters 2 and 3. This
could be due to irrelevant features taking part in the
clustering process.
It can be noted by Table 3 that cluster 3 (green ho-
mogeneous zone in Figure 3) is mostly represented by
ADW type C pulses, where T_RP > T_SP. Adding to
DataMiningbasedMethodologiesforCardiacRiskPatternsIdentification
131

Table 2: Classifier selection results.
Classifier ACC SST SPT PRC Training Speed
C4.5 95.72 95.58 95.86 95.58 ****
Random Forest 97.15 97.47 96.85 96.66 ****
RIPPER 95.72 95.72 95.34 95.07 ***
Naïve Bayes 88.05 88.05 86.60 89.42 *****
Bayesian Network 89.01 84.60 92.90 91.80 *****
MLP (1 HL) 96.98 96.84 97.11 96.91 **
MLP (2 HL) 96.74 96.56 96.91 96.70 *
RBF 96.23 96.23 95.23 96.93 ***
Figure 3: Clusters performance obtained for k-means algo-
rithm using three clusters, Cluster 1=blue, Cluster 2=red,
Cluster 3=green.
that, the mean AI of the cluster centroid is negative (-
11.2%), which represents cluster 3 as a low CVD risk
group. Cluster 2 (red points) pulses are mostly type
B pulses, where T_SP > T_RP. Cluster 2 represents
an intermediate group in terms of CV risk. Cluster 1
pulses (blue points) represent the less homogeneous
group, as the are also scattered in the cluster 2 area.
These pulses are mainly ADW type A pulses, with
some ponctual type B pulses. This group has higher
CV risk in comparison with Cluster 2 and 3.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In the current paper, data mining techniques were ap-
plied to the analysis of ADW features using classifi-
cation and clustering techniques.
In spite of low speed during training, ANNs al-
gorithms have shown high performance in terms of
successfully assessing correct classes (MLP (1-HL)
and MLP (2-HL)). Random Forest also presented su-
perior results in terms of accuracy and sensitivity. The
better training speed was achieved by Bayesian clas-
sifiers, but, on the other hand, they presented low per-
formance.
In future trials, the use of multiple classifiers in the
Table 3: Three clusters features mean.
Attribute
Cluster
1 2 3
Pulses 458 1550 2463
Age 21.6 21.0 21.7
Weight (Kg) 63.0 55.4 63.2
Height (m) 1.7 1.6 1.7
BMI (Kg/m
2
) 21.3 20.8 21.8
SBP (mmHg) 109.9 106.1 108.6
DBP (mmHg) 69.6 70.3 68.9
HR (bpm) 72.8 67.5 72.9
SPT (ms) 172.7 234.4 117.1
RPT (ms) 103.0 143.2 179.9
DWT (ms) 240.3 306.4 274.4
SPA (amp) 1.0 1.0 1.0
RPA (amp) 0.8 0.9 0.9
DWA (amp) 0.8 0.8 0.7
R1 (-) 67.6 72.0 157.3
R2 (-) 0.8 0.8 0.7
R3 (-) 0.2 0.1 -0.1
R4 (-) 0.8 0.9 -0.9
AI (%) 21.0 12.6 -11.2
RMSSD_SPT (ms) 34.9 25.5 21.7
RMSSD_SPA (amp) 0.0 0.0 0.0
RMSSD_RPA (amp) 0.5 0.0 0.2
RMSSD_DWT (ms) 54.2 18.5 42.8
RMSSD_DWA (amp) 0.1 0.1 0.1
FWHM (ms) 459.0 450.6 466.3
RMSE (%) 0.1 0.0 0.1
development of predictive models as, for example, a
weighted multiple classifier predictive methodology
as suggested by Gorunescu et. al. (2011) could be an
interesting approach to develop.
In clustering methods, more than the usefulness
when there is no, or little, information available, the
information that is extracted from them can be cru-
cial in fully understanding the data. The three cluster
analysis has allowed the characterization of distinc-
tive features for each of the clusters. It is also im-
BIOINFORMATICS2013-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
132

portant to focus the number of pulses in each one of
the clusters. Cluster 1 presents only 458 pulses, a re-
duced value in comparison with pulses in cluster 2
and 3, 1550 and 2463, respectively. However, this
fact occurs due to the population characteristics, only
young subjects between 18 and 30 years. Clustering
methodologies can be further improved by perform-
ing a progressive attribute removal for a subsequent
visual correction.
The developed methodology has proven its usage
in screening studies due to its descriptive and predic-
tive power. The successful application of data mining
techniques can help to predict under-diagnosed pa-
tients, and identify and classify at-risk people in terms
of health with the goal of reducing healthcare cost.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge Fundação para a Ciência e
Tecnologia for funding SFRH/BD/61356/2009 and
PTDC/SAU-BEB/100650/2008, project developed
under the initiative of QREN, funding by UE/FEDER,
through COMPETE-Programa Operacional Factores
de Competitividade. The authors also thanks to Coim-
bra University Hospital Centre (C.H.U.C.) and Dr.
Rui Providência, SCDSOS-Sudden Cardiac Death
Screening of Risk factors, for the support in clinical
trials.
REFERENCES
Almeida, V. G., Pereira, H. C., Pereira, T., Figueiras, E.,
Borges, E., Cardoso, J. M. R., and Correia, C. (2011a).
Piezoelectric probe for pressure waveform estimation
in flexible tubes and its application to the cardiovas-
cular system. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical,
169(1):217–226.
Almeida, V. G., Pereira, T., Borges, E., Pereira, H. C., Car-
doso, J. M. R., and Correia, C. (2011b). A real time
cardiac monitoring system-arterial pressure waveform
capture and analysis. Proceedings of the PECCS 2011.
Algarve, Portugal.
Almeida, V. G., Santos, P., Figueiras, E., Borges, E.,
Pereira, T., Pereira, H. C., Cardoso, J. M. R., and
Correia, C. (2011c). Hemodynamic features extrac-
tion from a new arterial pressure waveform probe.
Proceedings of the BIOSTEC (BIOSIGNALS 2011).
Rome, Italy.
Avolio, A. P., Butlin, M., and Walsh, A. (2010). Ar-
terial blood pressure measurement and pulse wave
analysis–their role in enhancing cardiovascular as-
sessment. Physiol Meas, 31(1):R1–47. Avolio, Al-
berto P Butlin, Mark Walsh, Andrew England Physiol
Meas. 2010 Jan;31(1):R1-47. Epub 2009 Nov 26.
Bortel, L. M. V., Duprez, D., Starmans-Kool, M. J., Safar,
M. E., Giannattasio, C., Cockcroft, J., Kaiser, D. R.,
and Thuillez, C. (2002). Clinical applications of arte-
rial stiffness, task force iii: Recommendations for user
procedures. AJH, 15:445–452.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning,
45:5–32.
Clemente, F., Arpaia, P., and Cimmino, P. (2010).
A piezo-film-based measurement system for
global haemodynamic assessment. Physiol Meas,
31(5):697–714. Clemente, Fabrizio Arpaia, Pasquale
Cimmino, Pasquale England Physiol Meas. 2010
May;31(5):697-714. Epub 2010 Apr 16.
Gorunescu, F., Gorunescu, M., Saftoiu, A., Vilmann, P., and
Belciug, S. (2011). Competitive/collaborative neural
computing system for medical diagnosis in pancreatic
cancer detection. Expert Systems, 28(1):33–48.
Han, J. and Kamber, M. (2006). Data Mining:Concept and
Techniques. Elsevier, San Francisco.
Haykin, S. (1998). Neural Networks - A Comprehensive
Foundation. Pearson education, India.
Jovic, A. and Bogunovic, N. (2011). Electrocardio-
gram analysis using a combination of statistical, ge-
ometric, and nonlinear heart rate variability features.
Artif Intell Med, 51(3):175–86. Jovic, Alan Bo-
gunovic, Nikola Netherlands Artif Intell Med. 2011
Mar;51(3):175-86. Epub 2010 Oct 25.
Kotsiantis, S. B. (2007). Supervised machine learning:
A review of classification techniques. Informatica,
31:249–268.
Laurent, S., e. a. (2006). Expert consensus document on ar-
terial stiffness:methodological issues and clinical ap-
plications. European Heart Journal, 27:2588–2605.
Mendis, S. e. a. (2011). Global Atlas on Cardiovascular
Disease Prevention and Control. World Health Orga-
nization, Geneva.
Quinlan, J. R. (1993). C4.5: Programs for Machine Learn-
ing. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Mateo, Cali-
fornia.
Shah, A. S., Dolan, L. M., Gao, Z., Kimball, T. R., and
Urbina, E. M. (2011). Clustering of risk factors: a
simple method of detecting cardiovascular disease in
youth. Pediatrics, 127(2):e312–8.
Tsipouras, M. G., ThemisP.Exarchos, Fotiadis, D. I., Kot-
sia, A. P., Vakalis, K. V., Naka, K. K., and Michalis,
L. K. (2008). Automated diagnosis of coronary
artery disease based on data mining and fuzzy mod-
eling. IEEE Transactions On Information Technology
In Biomedicine.
WEKA (2012). Weka 3: Data mining software in java.
Yang, J., Singh, H., Hines, E. L., Schlaghecken, F., Iliescu,
D. D., Leeson, M. S., and Stocks, N. G. (2012). Chan-
nel selection and classification of electroencephalo-
gram signals: An artificial neural network and ge-
netic algorithm-based approach. Artif Intell Med,
55(2):117–26. Yang, Jianhua Singh, Harsimrat Hines,
Evor L Schlaghecken, Friederike Iliescu, Daciana D
Leeson, Mark S Stocks, Nigel G Netherlands Artif In-
tell Med. 2012 Jun;55(2):117-26. Epub 2012 Apr 12.
DataMiningbasedMethodologiesforCardiacRiskPatternsIdentification
133
