
Action Sequencing and Error Production in Stroke Patients
with Apraxia
Behavioral Modeling using Bayesian Logic Networks
Charmayne Mary Lee Hughes
1
, Moritz Tenorth
2
, Marta Bienkiewicz
1
and Joachim Hermsdörfer
1
1
Lehrstuhlfür Bewegungswissenschaft, Technische Universität München,
Georg-Brauchle-Ring 60-62, München, Deutschland
2
Intelligent Autonomous Systems Group, Department of Informatics, Technische Universtität Münche,
München, Deutschland
Keywords: Apraxia, Modelling, Bayesian Logic Networks, Activities of Daily Living.
Abstract: Individuals with Apraxia often suffer from cognitive impairments during the execution of activities of daily
living (ADL). In this study, we used a statistical relational learning approach (Tenorth, 2011) to model the
behavior of apraxic patients and neurologically healthy individuals (n = 14 in each group) during ADL
performance. Video analysis indicated that apraxic patients committed more errors than control participants,
typically committing omission, addition, and substitution errors. The results of the Bayesian Logic Network
(BLN) approach indicate that the relevance of the nodes (i.e., actions) differed between the control
participants and apraxia patients. Furthermore, there were more nodes in the patient group, which is likely a
result of addition and substitution errors, or by alternative ways of solving the task using a different set of
tools. Overall, the results of the present study highlight the variability inherent in ADL performance, which
need to be considered when developing action and error prediction models.
1 INTRODUCTION
Stroke is most frequent neurological disease (WHO
1978). After a stroke incident as many as 24% of
patients suffer from persistent impairments of praxic
functioning (Bickerton et al., 2012), which often
result in “deficits in the execution of learned
movement which cannot be accounted for by either
weakness, incoordination, or sensory loss, or by
incomprehension of or inattention to command”
(Geschwind, 1975, pp. 188). The most important
characteristic of apraxia is that patients often retain
sensorimotor functions and capabilities but their
cognitive ability to carry out previously familiar
tasks (e.g., dressing, preparing and eating meals and
grooming) is adversely reduced (Goldenberg and
Hagmann 1998).
The difficulty these patients experience in
sequencing everyday tasks places great strain on
patients’ individual independence, their families, and
the national healthcare systems which have to
provide continuous support and care (Sunderland
and Shinner, 2007).
In this paper, we present an approach for
modeling and recognizing partially ordered ADL in
healthy and apraxic populations. We apply statistical
relational learning techniques to extract the joint
probability distribution over the actions in an
activity, their properties, and their pairwise ordering
constraints. The resulting full-joint probability
distributions elucidate relevant and important actions
and ordering relations for a given task. We propose
that this model can be used to classify and verify
activities, identify relevant actions in an activity, and
infer missing data.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Apraxia
Limb apraxia is a cognitive-motor characterized by
impairment in the performance of skilled movement,
and is operationally defined as a neurological
disorder of learned purposive movement skill that is
not explained by deficits of elementary motor or
sensory systems (Rothi and Heilman, 1997), or by
193
Lee Hughes C., Tenorth M., Bienkiewicz M. and Hermsdörfer J..
Action Sequencing and Error Production in Stroke Patients with Apraxia - Behavioral Modeling using Bayesian Logic Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0004233001930200
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2013), pages 193-200
ISBN: 978-989-8565-37-2
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

patients’ inability to understand the tasks
(Goldenberg, 2008); (Rothi and Heilman, 1997);
(Liepmann, 1905). Apraxia is frequently caused by
relatively large lesions in the territory of the left
middle cerebral artery (MCA), resulting in plegia of
the contralateral right hand. In the case of right hand
plegia, the apraxia patient has the use of only the
ipsilateral left hand. Further, apraxia does not only
affect the side of the body opposite to the cerebral
lesion (contralateral limb), but also the ipsilateral
side.
2.2 Apraxia and Error Production
Research has demonstrated that apraxia patients
have difficulty performing many activities of daily
living, often committing errors during the action
planning and execution (Buxbaum et al., 1998);
(Schwartz et al., 1991; 1998). For example, apraxia
patients will often omit an action (e.g., turn on the
coffee maker without having inserted water) or use
an inappropriate object (using a knife to stir a cup of
tea) during the performance of ADL (Humpreys and
Forde 1998); (Schwartz et al., 1998).
Errors of action can be broadly divided into errors of
omission (the failure to execute critical actions or
sequence of actions), and errors of commission
(performing an action in an incorrect or
inappropriate way) (Schwartz et al., 1991). The
errors in the latter category can be further segmented
into sequence errors (performing an action in the
wrong order), additions (adding an extra component
action), semantic errors (using a semantically related
object instead of the correct one), perseverations
(repeating an action or action sequence), and quality
or spatial errors (using an inappropriate amount of
ingredients or failing to use tools). A summary of
the most common errors is shown in Table 1.
Several case studies have shown that some error
types are more frequent than others (Morady and
Humphreys, 2009); (Schwartz, 1995); (Schwartz et
al., 1991; 1995; 1998); (Forde et al., 2004); (Morady
and Humphreys, 2011); (Forde and Humphreys,
2000; 2002); (Humphreys and Forde, 1998). For
example, patients with left- hemisphere stroke
(LCVA; Buxbaum et al., 1998), right hemisphere
stroke (RCVA; Schwartz et al., 1999) and patients
with Action Disorganization Syndrome (ADS;
Humphreys and Forde, 1998) general omit more
steps and make more sequence errors during ADL
performance. By comparison, addition errors,
perseveration errors, quality or spatial errors, and
semantic errors are less frequently observed than the
more prominent errors.
3 MODELLING ACTION
SEQUENCING AND ERROR
PRODUCTION
Given the deficits in action sequencing and the
errors in the movement quality in apraxic
populations a model needs to be able to describe
both low-level motor defects, (e.g., grasping an
object with an inappropriate grip), and high-level
errors (e.g., performing a task in a wrong sequence).
A model should also be able to compare
performance with prior observations of the same
subject or to a reference group. The former
comparison can be used to detect changes in the
performance of an individual, whereas the latter
comparison could be used to assess performance
relative to individuals with similar (i.e., apraxic) or
dissimilar (i.e., neurologically healthy) features.
3.1 Partially-ordered Tasks
Many of today’s approaches for activity recognition
are using sequence-based methods like Hidden
Markov Models (HMMs; Patterson et al., 2005),
Conditional Random Fields (CRFs; Vail et al., 2007)
or Suffix Trees (Hamid et al., 2007). These models
directly describe the observed sequences by local
action transitions, and are based on the Markov
assumption that the transition to the next action only
depends on the current action.
However, there exists a great deal of freedom in
how an ADL task can be performed, such that the
same goal can be reached by significantly different
action sequences. In these tasks, subsequent actions
depend not only on the previous one, but on all
actions that have already been performed, since they
determine which other ones are still needed to
complete the task at hand.
One example of a system that is able to model
such a partial ordering among actions is the work of
Shi and colleagues (Shi et al., 2004) that uses
manually specified Dynamic Bayesian Networks to
model behavior when calibrating a blood glucose
monitor. However, this approach does not describe
action properties (e.g., which object is manipulated,
or which grasp is used) and as such does not allow
for reasoning beyond the partial order of action
types.
The model described in this paper differs from
the aforementioned approaches in that it is able to
describe complex tasks (including the partial order,
but also other action properties like the types of
manipulated objects), and is capable of learning a
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
194

Table 1: Summary of action errors often committed by apraxic individuals. Examples are drawn from the task of preparing
two cups of tea used in the current experiment.
Error Type Definitions Example
Addition
Adding an extra component action that is not
required in the action sequence
Adding instant coffee to the cup
Omission
An action sequence in which one step or subtask
is not performed, despite the lack of any intention
to omit the step or subtask
Turning on the kettle on without having
inserted water
Perseveration The unintentional repetition of a step or subtask Adding more than one tea bag to a cup
Mislocation
An action that is appropriate to the object in hand
but is performed in completely the wrong place
Pouring some liquid from the bottle
onto the table rather than into the glass
Substitution
An intended action carried out with an unintended
object
Pouring coffee grounds instead of sugar
into the cup
Misestimation
Using grossly too much or too little of some
substance
Pouring half of the milk jug contents
into the cup
model from observed data. This latter point is
especially important in the context of cognitive
rehabilitation. Clinicians would be able to compare
performance before and after rehabilitation to
evaluate changes in the performance of individual
apraxic patients, and contrast this to performance of
apraxic patients with similar neurological
backgrounds.
3.2 Bayesian Logic Networks
The Intelligent Autonomous Group (IAS) at the
Technical University of Munich (TUM) has
developed a model of action recognition that can
handle the high degree of variation often observed in
ADL tasks (Tenorth, 2011). The model is able to
learn the partial ordering of actions in these ADL
tasks using Bayesian Logic Networks (BLNs; Jain et
al., 2009). By learning the models, they extract the
joint probability distribution over the actions in an
activity, their properties, and their pairwise ordering
constraints. The results are statistical relational
models that describe the partial order imposed on all
actions in a task, as well as the general relations
between consecutive actions and their properties.
From training data, partially-ordered models can
learn which actions are relevant and which ordering
relations are important, such that actions that occur
in all observations of a task are considered more
relevant than those that are only rarely observed, and
ordering relations that consistently hold are also
more likely to be important. Thus, the advantage of
this approach is that the system is capable of
learning such a model that is able to describe
complex tasks including their partial order from
observed data.
3.3 Modelling Partially-ordered Tasks
In this paper, we use Bayesian Logic Networks
(BLNs; Jain et al., 2009) to represent and model the
behavior of healthy and apraxic patients during ADL
performance. Given space limitations we refer the
reader to Jain et al., (2009) for more detailed
methodological information.
In general, BLNs are statistical relational models
that combine the expressiveness of first-order logics,
necessary to describe the complex interactions
between actions and the parameters associated with
these actions, with the representation of probability
in a probabilistic logical language.
The tasks and actions in the system are formally
represented as follows. A set of tasks is denoted by
T, which is described by a set of actions, A
t
, a
possibly empty set of action properties P
t
, and an
ordering relation O
t
among the actions.
T = {T
t
| T
t
= A
t
, P
t
, O
t
)}
Observation action sequences, S, are instances
created by performing the task. A task model
describes the partial order inherent in a given
activity, and action sequences are the sequential
samples following this partial order. Action
sequences are described as:
S = {S
T
s
| S
T
s
= a
0
, a
1
,…)}
Observed actions in an action sequence are denoted
with the subscript index a
i
, the prototypical actions
in a task model have a superscript a
i
. Action
sequences are related to tasks via the activityT
predicate.
activityT(S
T
) = T
ActionSequencingandErrorProductioninStrokePatientswithApraxia-BehavioralModelingusingBayesianLogic
Networks
195
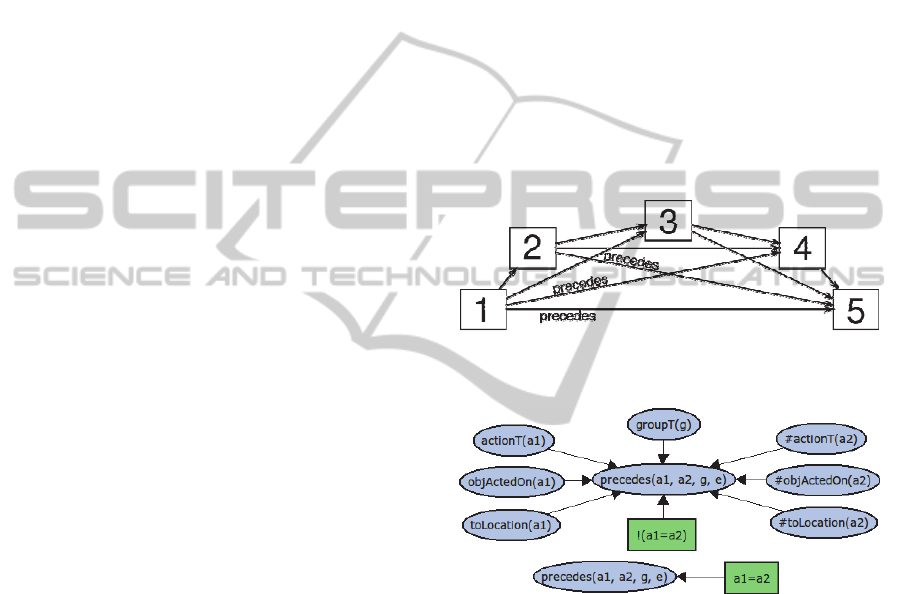
Each task model comprises of a set of n actions,
which have one of m different types A
0
, … A
m
.
A
t
= { a
0
, a
1
,…, a
n
}
∀i ∈ [0, n] : actionT (a
i
) ∈ { A
0
, A
0
, …, A
m
}
Actions may have different properties like the object
manipulated or the hand used to manipulate the
object. P
t
assigns a probability values to each
property π ∈ ᴨ of each action a
i
:
P
t :
A
t
× ᴨ →
ᴨ = { π
0
, π
1
,… π
p
}
P
ij
= P(π
j
(a
i
) = True)
For action sequences, this reduces to a simple
indicator matrix that, for each action-property-pair,
contains a probability value that this combination is
present. In the case of reliable observations, this
probability will be 1, in other cases it reflects the
observation uncertainty. For tasks, P
t
is more
complicated and depends on the properties of the
problem at hand.
The ordering relation O
t
for a task T describes
the probability that an action a
i
is executed before an
action a
j
in the respective task context. The relative
ordering of two actions is expressed using the
precedes predicate defined as
∀a
i
, a
j
∈ S
s
: (I < j) ⇔ precedes (a
i
, a
j
, S
s
)
Figure 2 illustrates how a sequence 1-2-3-4-5 is
translated into a set of pairwise ordering constraints.
Sequences of observed actions are described by
giving the types of actions (actionT), their ordering
(precedes) and optionally their parameters (e.g.,
objectActedOn). For example
activity(Act
0
) = MakeTea
˄ actionT (N
1
) = N
1
˄ objectActedOn (N
1
, O
1
)
˄ actionT (O
1
) = O3
˄ actionT (N
2
) = N
3
˄ actionT (N
3
) = N4 …
˄ precedes (N
1
, N
2
, Act
0
) = True
˄ precedes (N
1
, N
3
, Act
0
) = True ˄ …
˄ precedes (N
1
, N
2
, Act
0
) = True ˄ …
From training data represented as such logical
equations, the system learns Bayesian Logic
Networks (BLN) using the implementation in the
ProbCog statistical relational learning library.
A BLN is defined as a tuple B = (D, F, L) which
consists of the declarations of types and functions D,
a set of fragments of conditional probability
distributions F, and a set of hard logical constraints
L as formulas in first-order logic. The fragments F
describe dependencies between abstract random
variables. Similar to the manner in which predicate
logic abstracts away from the concrete entities in
propositional logics, BLNs represent generic
relations between classes of entities, as opposed to
common Bayesian networks that represent
probabilistic dependencies between concrete entities.
While the structure of the conditional probability
fragments is defined manually, the value domains
and probabilities are learned from data. Due to the
relational nature, the fragments become very
compact and generic. The BLN fragment, consisting
of random variables (oval nodes) and preconditions
for the respective fragments to be applicable
(rectangular nodes), that has been used in our
experiments is shown in Figure 3. The fragment
describes the dependencies between precedes(a
i
, a
j
,
S
s,
, e ,g), actionT(a
i
),objActedOn(a
i
), toLocation(a
i
),
and the group (patients or control).
Figure 2: Describing the partial order in the sequence 1-2-
3-4-5 by pairwise precedence relations.
Figure 3: Model structure of the data with dependencies as
conditional probability distribution fragments.
This fragment serves as a template for the
construction of a ground network. For a given set of
entities (i.e., observations of actions), the template is
instantiated into a ground mixed network, expanding
the abstract relations with the concrete domains of
actions of objects. Learning BLNs requires
determining the conditional probability tables in the
fragments in F, which reduces to simply counting
the relative frequencies of the relations in the
training set.
4 EVALUATION
Fourteen patients (age = 55.86 y, SD = 12.94, 7
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
196

men, 7 women) with lesions following a single
cerebrovascular accident (CVA) participated in the
study. There were 3 left-handed and 11 right-handed
patients. Fourteen healthy participants served as the
control group (age = 38.53 y, SD = 14.74, 6 men, 8
women). None of the control participants had any
history of neurological disorders or any constraints
of upper limb movements. Eleven control
participants were right-handed, and three control
participants were left-handed.
Figure 4: Experimental set up.
Subjects sat at a table with a dimension of 100
cm x 60 cm. The arrangement of the objects on the
table is shown in Figure 4, with a total of 14 objects
located on the work surface. Each participant was
asked to perform a 2 cup tea making task, in which
one cup of tea required milk and two sweeteners,
and the other cup of tea required lemon and one
sugar cube. Subjects were informed that all the
things required to make the tea are on the table, and
that they were to inform the experimenter if they
required help stabilizing an object. Two trials were
performed. Actions were recorded by a video
camera (Panasonic HDC-SD909) located 45° to the
right side of the table.
After data collection, the video data was
annotated using a custom made visual labelling tool
(Tenorth, 2011) and entered into the BLN learning
tool in order to learn the conditional probabilities
and domains of random variables from a given
training database and the fragment network. Specific
methodological information can be found in section
3.3.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Learning the Partial Order
Figure 5 depicts the conditional probabilities inside
the precedes-node of the BLN. The visualizations
contain all nodes that have a probability of at least
2E-6. The ellipse dimensions are proportional to the
product of the marginal probabilities of the action
components, the thickness of the edges is
proportional to the conditional probability of the
target given the origin times the probabilities of the
target and origin nodes. Note that the node
dimensions do not reflect the probability of the
action/object/location combination in the task, which
is why e.g. the node "Pour water to kettle" is smaller
than the "Pour water to cup2" node (since "kettle" is
less likely than "cup2").
In order to improve clarity, the redundant
relations between actions have been pruned. That is
to say, in instances in which P(precedes(A;B)) = 1,
P(precedes(A;C)) = 1 and P(precedes(B;C)) = 1, the
edge A - C was not drawn. As can be seen, the
algorithm is able to successfully recover the partial-
order structure from the data obtained from both
healthy and patient populations. The nodes in Figure
2 have been arranged in a way that the more
prominent ordering relations are pointing
downwards.
The results of the BLN approach show that the
relevance of the nodes (i.e., actions) is different
between the two groups, indicated by the different
sizes. There are more nodes in the patient group,
which were caused by addition or substitution errors
or by alternative ways of solving the task using a
different set of tools. There are some very consistent
orderings for apraxic patients, which can be seen by
the very bold arrows between some of the actions. In
total, however, there is more variation in how they
perform the actions, which is visible by the heavily
interconnected nodes. In comparison, control
participants mostly added the ingredients before
pouring water into the cups (indicative of a strong
ordering relation), but the order in which the
ingredients were added was not consistent (i.e.,
weak ordering relations). In total, they were much
more consistent in how they performed the task and
mostly completed the task without errors.
5.2 Error Types and their Frequency
Control participants successfully completed the task
in 86% of trials (total 6 errors). Three errors were
considered to be omission errors, where the
ActionSequencingandErrorProductioninStrokePatientswithApraxia-BehavioralModelingusingBayesianLogic
Networks
197

Figure 5: Learned dependencies in fourteen healthy controls (left) and apraxia patients (right).
participant failed to add sugar into cup2, and milk
into cup1. Two errors were classified as substitution
errors, where participants added two sugar cubes to
cup2 and one sweetener to cup1. One error was
classified as addition, where an extra sugar cube was
added to cup2.
Figure 6 shows the proportions of errors during
the tea making task for apraxic patients. Apraxia
patients committed errors in 60% of trial, with a
total of 38 errors recorded. Patients produced
omission errors in 47% of error trials. Examples of
omission errors include failing to pour water from
the jug into the kettle, put tea bags into one or both
cups, or adding sweetener to the cup that required it.
Errors of addition were also frequently
committed (16% of errors), with patients adding
coffee to a cup of tea, or putting sugar or lemon into
the cup that did not require it. Patients committed
substitution errors in 13% of trials, and typically
added coffee instead of a teabag into either cup1 or
cup2. There were also a small number of trials in
which patients committed quality (11%),
anticipation (8%), and mislocation (5%) errors.
Figure 6: The distribution of errors by error type for
patients with apraxia.
In sum, the error production results are
consistent with previous research (Buxbaum et al.,
1998); (Schwartz et al., 1998) demonstrating that
omission errors are the most commonly committed
type of errors during ADL. In addition, errors did
Omission
(47%)
Addition
(16%)
Substitution
(13%)
Quality
(11%)
Anticipation
(8%)
Mis loc ation
(5%)
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
198

not appear to be related to the laterality of lesion,
hemiparesis, or aphasia type. Future research into
error production in apraxic populations will continue
to examine this issue, in order to ascertain the
variables that correlate to error production.
Analysis also indicated that distractor objects
located in the workspace influenced ADL behavior
in 23.7% of trials. Interestingly, of the three
distractor objects (i.e., jar of coffee, dessert spoon,
fork), only the coffee jar influenced behavior, with
patients adding coffee into a cup instead of a tea bag
(substitution error) or adding coffee and a tea bag
into a cup (addition error). This finding
complements previous research (Moores et al.,
2003); (Schwartz et al., 1998) suggesting that
semantically related distractors compete for
selection with appropriate target objects for action.
More detailed analysis on a larger group of apraxia
patients is needed to ascertain how the semantic
relatedness of distractors influences action
sequencing and error production during ADL
performance.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we presented a statistical relational
learning approach to model the behavior of apraxic
patients during ADL performance. Congruent with
previous research (Buxbaum et al., 1998); (Schwartz
et al., 1998) we found that apraxic patients
committed more errors than control participants. The
most frequently committed errors were omission,
addition and substitution errors. These errors are
recognizable by the nodes (i.e., actions) located in
the upper left corner of the apraxic patient learned
dependency visualizations (Figure 5).
The results of the BLN approach indicated that
the relevance of the actions (i.e., nodes) differed
between the controls and apraxics, with more nodes
in the apraxic patient group. The larger number of
nodes is due to errors associated with addition and
substitution. The high degree of variation in action
sequencing for this task resulted in a highly
interconnected task graph.
Overall, control participants showed a strong
ordering relation between some actions in the task.
That said there was some flexibility in the order in
which the ingredients were added. For example, in
some trials participants first added the sugar and
then lemon to cup2, and on other trials participants’
added lemon and then sugar. This finding indicates a
weak ordering relation between those actions.
Control patients usually added milk at the very end
of the task, both groups filled the kettle with water
first.
The results of the present paper highlight the
variability inherent in ADL performance, and
indicate that the BLN approach is able to describe
the partial order imposed on all actions in a task,
including the general relations between consecutive
actions and their properties. The presented models
have been learned from annotated data and represent
a joint probability distribution over not only the
ordering, but also the types and properties of actions
in the task. This distribution allows various
inference tasks including classification into
patient/control group, error prediction, inference of
likely properties and types of individual actions, etc.
We plan to investigate these possibilities in our
future work and consider this a promising approach
to behavioral modelling for use in cognitive
rehabilitation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank Georg Goldenberg for
access to patients, Saskia Steinl and Rhoia
Neidenbach for help with data collection, Alexander
Matschl for help with data analysis, and the
CogWatch cooperation partners for their insightful
comments. This study was supported by a grant from
the European Commission (FP7-ICT-2011-288912).
REFERENCES
Bickerton, W., Riddoch, M. J., Samson, D., Balani, A.,
Mistry, B., and Humphreys, G. W., (2012). Systematic
assessment of apraxia and functional predictions from
the Birmingham Cognitive Screen. Journal of
Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 83, 513-
521.
Buxbaum, L. J., Schwartz, M. F., and Montgomery, M.
W., (1998). Ideational apraxia and naturalistic action.
Cognitive Neuropsychology, 15, 617-643.
Forde, E. M. E., Humphreys, G. W., and Remoundou, M.,
(2004). Disordered knowledge of action order in
action disorganisation syndrome. Neurocase, 10, 19-
28.
Geschwind, N., (1975). The apraxias: neural mechanisms
of disorders of learned movements. American
Scientist, 63, 188-195.
Goldenberg, G., (2008). Apraxia. In: Goldenberg, G. and
Miller B. (Eds.), Handbook of Clinical Neurology -
Neuropsychology and Behavior (pp. 323-338).
Edinburgh: Elsevier.
Goldenberg, G., and Hagmann, S., (1998). Therapy of
activities of daily living in patients with apraxia.
ActionSequencingandErrorProductioninStrokePatientswithApraxia-BehavioralModelingusingBayesianLogic
Networks
199

Neuropsychological Rehabilitation, 8(2): 123-141.
Hamid, R., Maddi, S., Bobick, A., and Essa, I., (2007).
Structure from statistics-unsupervised activity analysis
using suffix trees. IEEEI, 206, 7.
Humphreys, G. W. and Forde, E. M. E., (1998).
Disordered action schema and action disorganisation
syndrome. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 15, 771-811.
Jain, D., Waldherr, S., and Beetz, M., (2009). Bayesian
Logic Networks. Technical report, IAS Group,
Fakultät für Informatik, Technische Universität
München.
Liepmann, H., (1905). Ueber Störungen des Handelns bei
Gehirnkranken. Berlin: Karger.
Moores, E., Laiti., L., and Chelazzi, L., (2003).
Associative knowledge controls deployment of visual
selective attention. Nature Neuroscience, 2, 182-189.
Morady, K.., and Humphreys, G., (2009). Comparing
action disorganization syndrome and dual-task load on
normal performance in everyday action tasks.
Neurocase, 15, 1-12.
Morady, K., and Humphreys, G., (2011). Multiple task
demands in action disorganization syndrome.
Neurocase, 17, 461-472.
Patterson, D., Fox, D., Kautz, H., and Philipose, M.
(2005). Fine-grained activity recognition by
aggregating abstract object usage. In Ninth IEEE
International Symposium on Wearable Computers,
Proceedings, 44-51.
Rothi, L. J. G., and Heilman, K. M., (1997). Apraxia: The
Neuropsychology of Action. East Sussex (UK):
Psychology Press.
Schwartz, M. F., (1995). Re-examining the role of
executive functions in routine action production.
Structure and Functions of the Human Prefrontal
Cortex, 769, 321-335.
Schwartz, M. F., Buxbaum, L. J., Montgomery, M. W.,
Fitzpatrick-DeSalme, E., Hart, T., Ferraro, M., Lee, S.
S., and Coslett, H. B., (1999). Naturalistic action
production following right hemisphere stroke.
Neuropsychologia, 37, 51-66.
Schwartz, M. F., Montgomery, M. W., Buxbaum, L. J.,
Lee, S. S., Carew, T. G., Coslett, H. B., Ferraro, M.,
Fitzpatrick-DeSalme, E., Hart, T., and Mayer, N.,
(1998). Naturalistic action impairment in closed head
injury. Neuropsychology, 12, 13-28.
Schwartz, M. F., Reed, E. S., Montgomery, M., Palmer,
C., and Mayer, N. H., (1991). The Quantitative
Description of Action Disorganization After Brain-
Damage - A Case-Study. Cognitive Neuropsychology,
8, 381-414.
Schwartz, M. F., Montgomery, M. W., Fitzpatrick-
desalme, E. J., Ochipa, C., Coslett, H. B., and Mayer,
N. H., (1995). Analysis of a disorder of everyday
action. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 12, 863-892.
Shi, Y., Huang, Y., Minnen, D., Bobick, A., and Essa, I.,
(2004). Propagation networks for recognition of
partially ordered sequential action. cvpr, 02, 862–869.
Sunderland, A. and Shinner, C., (2007). Ideomotor apraxia
and functional ability. Cortex, 43, 359-367.
Tenorth, M., (2011). Knowledge processing for automous
robots. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Technische
Universität München, München, Deutschland.
Vail, D. L., Veloso, M. M., and Lafferty, J. D., (2007).
Conditional random fields for activity recognition. In
AAMAS ’07: Proceedings of the 6
th
international joint
conference on Autonomous agents and multiagent
systems, 1-8. New York, NY, USA: ACM.
World Health Organization, (1978). Cerebrovascular
disease: a clinical and research classification, Offset
Series No. 43. Geneva: World Health Organization.
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
200
