
Multiagent Model to Reduce the Bullwhip Effect
Borja Ponte Blanco and David de la Fuente García
Escuela Politécnica de Ingeniería, Universidad de Oviedo, Campus de Viesques s/n, 33204, Gijón, Spain
Keywords: Bullwhip, Supply Chain, Multiagent System, Time Series Forecasting.
Abstract: There are several circumstances which, in recent decades, have granted the supply chain management a
strategic role in the search for competitive advantage. One of the goals is, undoubtedly, the reduction of
Bullwhip Effect, which is generated by the amplification of the variability of orders along the chain, from
the customer to the factory. This paper applies multiagent methodology for reducing Bullwhip Effect. To do
this, it considers the supply chain as a global multiagent system, formed in turn by four multiagent
subsystems. Each one of them represents one of the four levels of the traditional supply chain (Shop
Retailer, Retailer, Wholesaler and Factory), and it coordinates various intelligent agents with different
objectives. Thus, each level has its own capacity of decision and it seeks to optimize the supply chain
management. The problem is analyzed both from a non collaborative approach, where each level seeks the
optimal forecasting methodology independently of the rest, and from a collaborative approach, where each
level negotiates with the rest looking for the best solution for the whole supply chain.
1 INTRODUCTION
A supply chain encompasses all participants and
processes involved in satisfying customer demands
around some products. Analyzing it, Forrester
(1961) noted that small changes in customer demand
are amplified along the supply chain, leading to
larger variations in demand supported by the
different levels, as they are further away from
customer. This is called the Bullwhip Effect (or
Forrester Effect), which, according to the subsequent
research by Lee et al. (1997), is due to four main
causes: demand forecastings, order batching, price
fluctuations, and shortage gaming.
There have been several changes in the last two
decades in the macro environment of the companies
that have set up a new business perspective. From
this, the production function is considered to have a
strategic role as a source of competitive advantage,
so that the practices related to managing the supply
chain now represent one of the main concerns of
business. In these circumstances, it is especially
emphasized the importance of proper management
of the supply chain regarding different objectives.
One of them is undoubtedly reducing the Bullwhip
Effect. In fact, Disney et al. (2003) demonstrated
that the Bullwhip effect leads the supply chain to
unnecessary costs that can represent, in some cases,
more than 30% of the total costs thereof.
In this context, this paper proposes the
application of Artificial Intelligence techniques to
the problematic associated with the Bullwhip Effect,
in order to create a tool aimed at reducing variations
in the demands transmitted along the supply chain.
More specifically, Distributed Intelligence is applied
to the problem through a multiagent system. It
determines the optimal order policy based on the
best demand forecasting method for each one of the
different levels that make up the supply chain,
understanding the forecasting errors as the main
causes in the creation of the Bullwhip Effect.
The presented document is divided into four
sections besides this introduction. Section 2 shows a
review of the most relevant and recent literature in
terms of reducing the Bullwhip Effect, with special
emphasis on models based on Distributed
Intelligence. Section 3 describes the model created
with the different agents that compose it, the
structure which includes them and the relationships
among them, which is the way in which intelligence
has been introduced to the system. Section 4
presents the results, mainly related to reducing the
Bullwhip Effect, for which we have used time series
data from the literature. Finally, section 5 presents
the conclusions according to the planned objectives.
67
Ponte B. and de la Fuente D..
Multiagent Model to Reduce the Bullwhip Effect.
DOI: 10.5220/0004245600670076
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2013), pages 67-76
ISBN: 978-989-8565-38-9
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 BACKGROUND: REDUCING
THE BULLWHIP EFFECT
2.1 Traditional Solutions
Each supply chain has its own characteristics,
mainly conditioned by the type of product which is
offered to the final consumer and by the market
conditions in which it moves, and that
unquestionably complicates the analysis of valid
methodologies for reducing the Bullwhip Effect.
However, it is possible to find some common
problems to all of them, and several authors have
proposed general strategies to be adapted to each
particular supply chain. These traditional solutions
to Bullwhip Effect are mainly based on collaboration
among the various members of the supply chain,
often sharing some information.
Thus, some practices that are carried out in some
companies and which have been successful in
reducing the Bullwhip Effect are:
Use of Information Technology systems such
as electronic data interchange (Machuca and
Barajas, 2004).
Postponement, which is based on a redesign
of products with the aim that the
differentiation takes place in nodes near the
customer. (Chen and Lee, 2009).
Efficient Consumer Response (ECR). These
are associations of companies to synchronize
the supply chain. (Disney et al., 2002).
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI). The
supplier controls the inventory of the
consumer, deciding on delivery times and
quantities. (Holmström, 1997).
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting and
Replenishment (CPFR). It means that
members of the supply chain can develop, in
a collaborative way, business plans and
processes (Ji and Yang, 2005).
2.2 Multiagent Systems in the Supply
Chain Management
The supply chain management, including all that
related to the Bullwhip Effect, is a highly complex
problem, conditioned by multiple agents, each of
which has to serve a large number of variables. In
the last two decades, authors have looked for
different ways to optimize the management by using
new techniques based on Artificial Intelligence.
Among these methods, there are several authors who
have approached the supply chain as a network of
intelligent agents. These are called multiagent
systems.
Fox et al. (1993) were pioneers in the proposal
of the organization of the supply chain as a network
of cooperating intelligent agents. In their work, each
agent executes one or more functions of the supply
chain, coordinating their actions with other agents.
Later, Shen et al. (1998) developed the tool
MetaMorph II, which, through an agent-based
architecture, integrates partners, suppliers and
customers with a lead company through their
respective mediators within a supply chain network
via the Internet.
Kimbrough et al. (2002) studied whether a
structure based on agents could be valid for the
supply chain management, and they reached the
conclusion that the agents were able to effectively
play the well known Beer Game (Sterman, 1989),
reducing the Bullwhip Effect. Moyaux et al. (2004)
used a multiagent system for modeling the behavior
of each company in the supply chain. The paper
proposes a variant of the Beer Game, which they
called "Quebec Wood Supply Game”.
Liang and Huang (2006) developed, based on a
multiagent architecture, a model which allowed
predicting the order quantity in a supply chain with
several nodes, where each one of them could use a
different system of inventory. De la Fuente and
Lozano (2007) presented an application of
Distributed Intelligence to reduce the Bullwhip
Effect in a supply chain, based on a genetic
algorithm. Zarandi et al. (2008) introduced Fuzzy
Logic in the analysis.
Wu et al. (2011) applied the multiagent
methodology to establish a supply chain model and
to analyze in detail the Bullwhip Effect created
along the chain, considering the non existence of
information exchange among different members.
One of the last studies in that regard is the one by
Saberi et al. (2012), It develops a multiagent system,
and which links the various agents that form it,
emphasizing the collaborative aspect.
We can conclude that supply chain has become a
complex system that requires modern methodologies
for its analysis, seeking to optimize their
management.
3 CONSTRUCTION OF THE
MODEL
3.1 Global Multiagent System
To prepare the base model, we have considered a
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
68
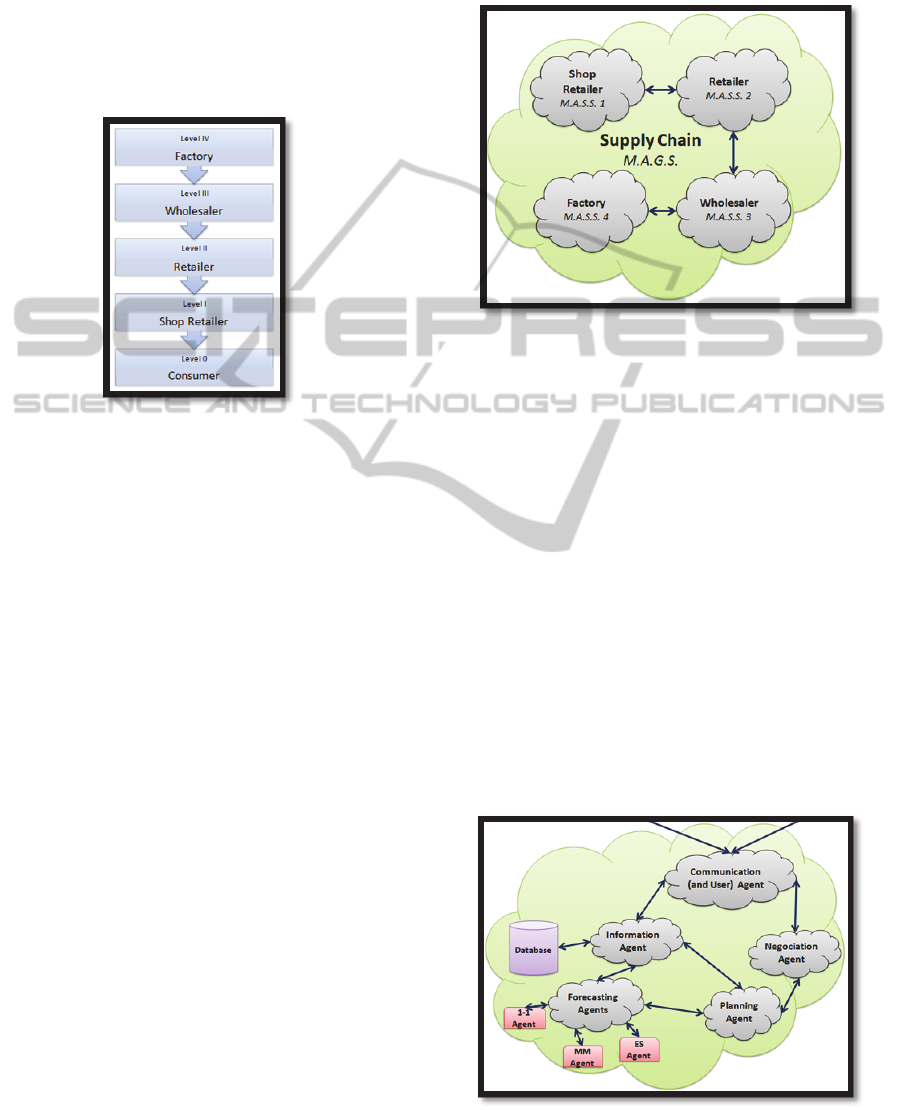
traditional supply chain with linear structure, which
consists of five main levels: Consumer, Shop
Retailer, Retailer, Wholesaler and Factory. Figure 1
shows the graphical representation of the levels,
indicating the materials flow, which occurs from the
top of the chain (Factory) to the lower levels
(Consumer). Therefore, it is called downstream
flow. The information flow is considered to be in the
opposite way, which is called downstream flow.
Figure 1: Supply Chain Model.
The methodology used for the modeling and
analysis in this research is based on multiagent
systems. A multiagent system is a system composed
of multiple intelligent agents, which interact among
them. An agent can be defined as a computer
system, which is able to perform autonomous and
flexible actions that affect their environment
according to certain design goals.
Thus, the behavior of each one of the main levels
of the supply chain (Shop Retailer, Retailer,
Wholesaler and Factory) will be simulated using a
multiagent subsystem (which we will call MASS).
The four multiagent subsystems form a global
multiagent system (which we will call MAGS)
which represents the whole supply chain. In turn,
each subsystem will consist of several intelligent
agents which interact among them, seeking to satisfy
predefined objectives.
In our case, we consider static agents as they do
not travel through the network, which have an
internal symbolic reasoning model committed to the
planning and negotiation for coordination with other
agents. Thus, each agent has an incomplete
knowledge of the problem, with decentralized data,
so there is no overall control in the system.
All this means that each subsystem can represent
a member of the supply chain, so that the global
multiagent system has similar characteristics to the
overall supply chain as:
Autonomy: each level decides and executes
without external intervention.
Social skills: each level communicates with
the other ones.
Reactivity: each level modifies its behavior
depending on the environment.
Figure 2: General model of the global multiagent system.
Figure 2, by way of synthesis, shows a scheme of
the global multiagent system (MAGS) which
simulates the supply chain, formed in turn by four
local multiagent subsystems.
Thus, the supply chain management through a
multiagent system allows the creation of an agile
network which reacts in real-time to customer
demands, compared to traditional systems, where
everything is decided before the client makes the
request.
3.2 Multiagent Subsystems
Each multiagent subsystem replicates the behavior
of one of the levels of the supply chain. In turn, this
subsystem will consist of several interconnected
intelligent agents. Each multiagent subsystem will
have some set goals that it will try to meet as best as
possible, given certain conditions in its environment.
Figure 3: Detail of the multiagent subsystem on each level
of the supply chain.
MultiagentModeltoReducetheBullwhipEffect
69

Figure 3 shows the detail of the internal structure
of a multiagent subsystem. There, it is possible to
identify five types of agents: Communication Agent,
Information Agent, Planning Agent, Forecasting
Agents –which, in turn, include three agents
according to the used method of demand
forecasting– and Negotiation Agent. It also
highlights the existence of a database to store the
most relevant information for each subsystem.
3.2.1 Information Agent
The database associated with each multiagent
subsystem store a temporary data series for the level
of the supply chain partner. These mainly include:
Information on the demands received.
Information on demand forecasting to be
considered.
Information on the situation of inventory at
the beginning and at the end of periods to be
considered.
Information on deliveries to the lower level
of the supply chain.
Information about orders to the top level of
the supply chain.
Thus, the Information Agent’s main objective is the
mediation between the database and the other
agents. So, they do not see a database, but another
agent, and thus we achieve uniformity in the system.
The Information Agent will only respond to requests
for information from other agents and it will store
the data given to him.
3.2.2 Communication (and User) Agent
Communication (and User) Agent will be
responsible for carrying out the interactions of the
multiagent subsystem with the adequate agents. It
works, thus, as a spokesman. Communications
among the various levels of the supply chain will be
only through Communication Agents. Each one
works in two ways:
It transmits purchase orders received by the
agents of its own level to the top level of the
supply chain.
It collects the purchase orders received from
the lower level and it provides them to the
other agents at its level.
Furthermore, the Communication (and User) Agent
acts as an intermediary between the multiagent
subsystem and the user, so that the other agents do
not relates directly to the user. This agent
communicates with the user through a graphical
interface, with two objectives:
To allow the user to enter information that
may condition the environment of the agents.
To show the user the most relevant
information on the supply chain management.
3.2.3 Forecasting Agents
Forecasting Agents are the real core of the system.
Each one will carry out the calculations of demand
forecasting for future periods based on a
predetermined method. All forecasting methods will
make their decisions based on historical data,
received from the Information Agent.
Initially, the system consists of three agents, but
it is an open group, so that in future we can add new
forecasting methods, increasing its capabilities.
1-1 Agent forecasts using one-one method,
which is based on estimating the demand at any
period as the one in the previous period. It can be
expressed as follows:
(1)
Where
is the forecast of demand in period t,
and
is the demand received in period t.
MM Agent forecasts using the moving average
method of order n, which estimates the demand in
any period as the average of the latest n demands. It
can be expressed as:
1
⋯
(2)
Where
is the forecast of demand in period t, n
is the number of periods to be considered for the
moving average and
( ∈ 1, is the demand
received in period t-i.
ES Agent, finally, determines forecasts
according to the simple exponential smoothing
method, which estimates the demand in any period
as the weighted average of the last period demand
and the forecast of demand in that period. It can be
expressed as follows:
∙
1
∙
(3)
Where
is the forecast of demand in period t,
is the forecast of demand in period t-1,
is
the demand received in period t-1, and ∈ 0,1 is
the exponential smoothing coefficient or weighing
of the forecasting error.
MM Agent evaluates all the moving averages
from n = 2 to n = 15 (for n = 1, it coincides with
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
70

one-one method), selecting, on the basis of available
data, the optimal moving average. The ES Agent
evaluates all the forecasts for coefficients from
α = 0.1 to α = 0.9, with jumps of 0.1, selecting the
optimal coefficient. In both cases, we choose the
optimal forecast according to the mean square error
criterion, which must be minimized, expressing it as
follows:
1
(4)
Where
is the forecast of demand in period t,
is the real demand in period t and m is the
number of available data.
3.2.4 Planning Agent
Planning Agent collects the forecasts made by the
Forecasting Agents, and it is the responsible of
deciding which one is the best, based on the
Bullwhip Effect generated in the supply chain. Many
authors quantify the Bullwhip Effect in supply chain
as follows:
(5)
Where
is the variance in consumer demand
for the product, and
represents the variance in
the rate of the factory production.
Likewise, the Bullwhip Effect generated at each
step can be defined as the ratio of the variance in
orders sent to the upper node of the supply chain,
and the variance in orders received from the bottom
node of the supply chain.
(6)
Where
represents the Bullwhip Effect
generated in the level i,
is the variance in orders
sent to the upper node of the supply chain, y
represents the variance in the orders received from
the lower node of the supply chain. This allows
expressing the Bullwhip Effect along the chain as
the product of the ratios that define the Bullwhip
Effect at each level.
In these circumstances, the Planning Agent will
select as the optimal forecasting method that which
minimizes the effect generated in that level, seeking
to reduce the effect generated in the chain, unless it
is activated Negotiation Agent, in which case the
selection of the optimal method is detailed later.
From there, the Planning Agent will be
responsible for providing the Information Agent the
necessary information on the node to complete the
database. This information, for each period,
includes:
The forecast of demand (
according to the
optimal method.
The initial inventory situation (
, which is
the sum of the final situation of the inventory
in the previous period (
and orders
received at the beginning of the period,
which, considering a unitary lead time, are
assumed to have been made during the
previous period (
.
(7)
The final situation of the inventory (
,
which is the difference between the initial
situation of the inventory (
and the
demand received in the current period (
,
so that negative values show stock-out.
(8)
The deliveries to the lower level of the supply
chain (
), which coincides with the demand
(
), unless it is impossible to satisfy it
completely.
min
,
(9)
The orders to be made to the upper level of
the supply chain (
, which can be
expressed as the difference between the
forecast of the demand (
and the final
situation of the inventory (
), or zero, if the
above difference is negative.
max
,0
(10)
3.2.5 Negotiation Agent
Negotiation Agent will be activated by the user,
when it is considered appropriate by the latter, from
the interface of the developed tool. When it is active,
it will allow the management of forecasting demand
in the supply chain in a coordinated way through
collaboration between Shop Retailer and Retailer, on
the one hand, and Wholesaler and Factory, on the
other.
Every Negotiation Agent will initiate a process
MultiagentModeltoReducetheBullwhipEffect
71

of discussion with the Negotiation Agent to which it
relates, through the Communication Agent. The
collaborative framework is mainly based on the
sharing of information between the agents with the
goal of finding a balance between a forecast
considered acceptable in local terms, and a forecast
which is profitable to the whole system, since both
terms can sometimes come into opposition.
Thus, the Negotiation Agent for each level
interacts with the Planning Agent, seeking the
optimal policy, which not only tries to minimize the
Bullwhip Effect generated in the node, but it also
seeks to minimize the global Bullwhip Effect
generated in the supply chain.
3.3 Implementation of the Model
To implement the model, we have used NetLogo
5.0.1. Figure 4, by way of example, shows a screen
shot of the interface of the implemented model in a
particular instant of a simulation.
Figure 4: Screenshot of the interface.
NetLogo is a programming environment created
by Uri Wilensky (1999) and continuously developed
by the Center for Connected Learning and
Computer-Based Model, which allows the
development of multiagent models for simulation
and analysis of phenomena of a different type.
4 NUMERICAL APPLICATION
4.1 Tests with Random Demands
First, we describe numerically some tests carried out
on the developed multiagent model, considering
random demands, which follow certain statistical
distributions. We have used samples with 30
temporary data.
Table 1 presents the results of the fifteen tests,
where the columns contain the following values: the
number of the test; the statistical distribution which
follows the demand, which can be normal N (μ, σ)
(where μ refers to the mean demand and σ refers to
its standard deviation) or Poisson P (μ) (where μ is
the mean of demand); the Bullwhip Effect generated
in the case that all levels use the one-one model
(BW1); the Bullwhip Effect generated by using the
developed tool without activating the Agent
Negotiation (BW2); and the Bullwhip Effect
generated by using the developed tool when
activating the Agent Negotiation (BW3).
In all cases, it is considered that the initial
inventory at all levels of the supply chain coincides
with the average of the corresponding statistical
distribution.
Table 1: Results of tests with random demands.
Test Demand BW1 BW2 BW3
1 N(100,10) 266.42 12.64 2.37
2 N(100,10) 234.88 10.17 2.79
3 N(100,10) 256.26 26.16 3.33
4 N(100,5) 692.59 12.70 2.41
5 N(100,5) 699.37 30.54 3.33
6 N(100,5) 649.15 30.29 3.49
7 N(100,1) 1399.00 25.43 3.11
8 N(100,1) 2717.60 13.87 2.16
9 N(100,1) 2010.94 7.51 1.97
10 P(100) 323.64 16.68 2.18
11 P(100) 259.36 2.19 1.48
12 P(100) 396.19 19.96 3.09
The results presented in Table 1 show, broadly
speaking, the huge efficiency of the multiagent
model developed in this paper versus one-one
model. In all cases, the achieved results, in terms of
Bullwhip Effect, improve the performance of the
one-one model in several orders of magnitude.
In these circumstances, the shown results
demonstrate the poor performance of the model 1-1
when the demand for a particular product can be
estimated through a Poisson or normal distribution.
In the case of normal distribution, the Bullwhip
Effect generated along the supply chain considerably
increases when the standard deviation of consumer
demand decreases. In this case, the variance in
orders along the supply chain will also decrease, but
the variation will be smaller in relative terms.
So, with such a degree of randomness, the
approximation of the demand in a certain period
according to the demand in the previous period is a
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
72
bad alternative. In fact, the model tends to select
moving averages of a large number of periods. In the
same vein, the model determines that the best
solutions with exponential smoothing are offered by
very low parameters, in order to minimize the effect
of the latest demands in the forecast.
In the referred cases with high randomness, it is
necessary to use other methods of forecasting, and a
system based on intelligent agents is, in view of the
data, a good way to coordinate them. The collected
results show that using simple forecasting methods,
such as moving averages or exponential smoothing,
allows reaching great results in reducing the
Bullwhip Effect.
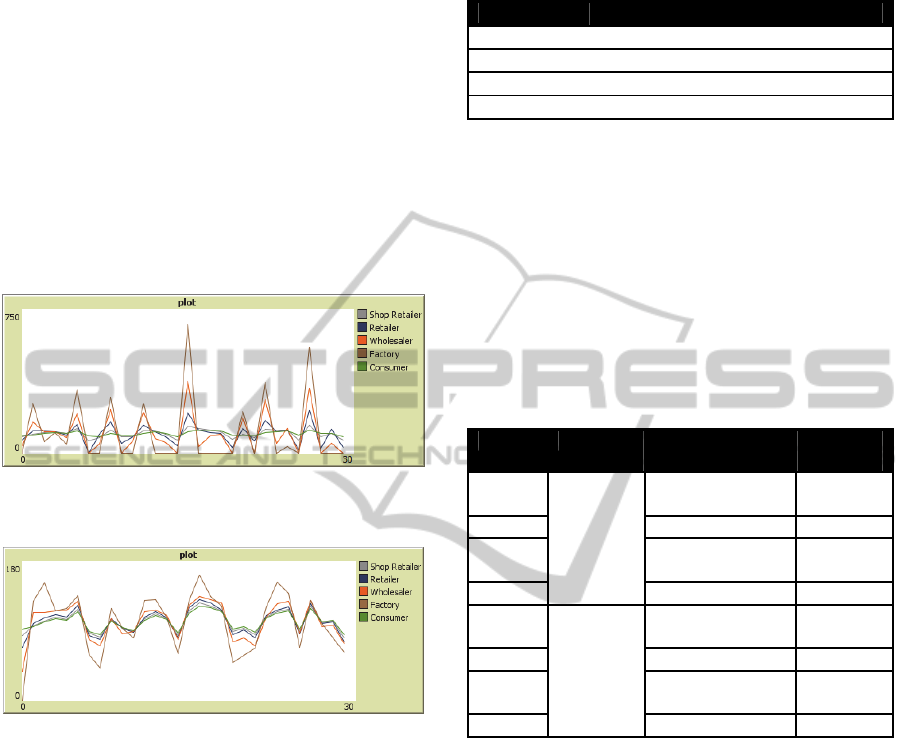
Figure 5: Variation of orders along the supply chain in the
test 1 with One-One model.
Figure 6: Variation of orders along the supply chain in the
test 1 with the developed multiagent model.
By way of example, Figures 5 and 6 show
variations of purchase orders made by the four levels
of the supply chain in test 1, as well as consumer
demand, obtained from a normal distribution with
mean 100 and standard deviation 10. It is clearly
seen how the consumer demand, which is the same
in both cases, is much more amplified in the case of
one-one model that in the case of multiagent system.
Table 2 shows, in each case, the optimal policy for
each level of the supply chain.
The results obtained also show that close
negotiation and collaboration in the supply chain
between Factory and Wholesaler, on the one hand,
and Shop Retailer and Retailer, on the other, is a
very appropriate strategy for the reduction of the
Bullwhip Effect. Collaboration significantly
improves the performance of multiagent model,
achieving amazing results.
Table 2: Optimal Policy for each level of the supply chain
in test 1.
Level Optimal Forecasting Method
Shop Retailer
Exponential Smoothing with .
Retailer
Exponential Smoothing with .
Wholesaler
Moving Average with
Factory
Moving Average with
4.2 Tests with Real Demands
For further analysis, some tests with real data on
developed multiagent model will be shown. We
have chosen eight time series obtained from
databases. Table 3 shows, for each one of the eight
series, the series name; the database which contains
the information; the content of the information; and
the number of data which comprise the series.
Table 3: Data on the time series used to test the multiagent
model.
Series Database Content Number
of data
AL03
Abraham
(1983)
Electricity
Consumption
106
AL04 Car sales 108
AL09 Mortgage – Loan
Differences
159
AL11 Gas Consumption 106
BJ02
Box –
Jenkins
(1976)
Price of IBM
shares
369
BJ06 Wolfer sunspots 100
BJ08 Airline company
passengers
144
BJ15 Warehouse sales 150
Table 4 presents the results of applying the genetic
algorithm on the eight series, where the columns
contain the following values: the number of the test;
the used series; the Bullwhip Effect generated if all
levels of the supply use the one-one model (BW1);
the Bullwhip Effect generated by using the
developed tool without activating the Agent
Negotiation (BW2); and the Bullwhip Effect
generated by using the developed tool by activating
the Agent Negotiation (BW3).
As in the case of random demands, it is
considered that the initial inventory, in all cases,
coincides with the demand of the first period.
The obtained results again demonstrate the
effectiveness of multiagent model in reducing
Bullwhip Effect generated along the supply chain. In
all cases, the results generated by the one-one model
are improved, although the difference is more
relevant in some cases than in other ones.
MultiagentModeltoReducetheBullwhipEffect
73

Table 4: Results of tests with real demands.
Test Series BW1 BW2 BW3
1 AL03 65.90 1.54 1.22
2 AL04 48.70 1.32 1.11
3 AL09 29.93 3.29 2.61
4 AL11 13.74 6.00 2.88
5 BJ02 4.20 1.12 1.05
6 BJ06 15.41 4.18 3.35
7 BJ08 12.28 1.25 1.18
8 BJ15 2.75 1.13 1.03
This situation evidences again that the use of
simple forecasting methods, coordinated through a
multiagent system allows a great improvement, in
terms of Bullwhip Effect, comparing to the results of
the one-one model. There is not clear proportionality
between the result provided by the multiagent
system and the result provided when all agents use
the one-one model, which indicates again that the
fitness of each forecasting method depends on the
characteristics of the time series.
When analyzing the results, it is more
appropriate to do it from a relative point of view that
from an absolute one. When considering a larger
number of data, and since the series in some cases
have definite trends, the values of the Bullwhip
Effect are significantly lower than in the cases
analyzed with random demands.
AL09 time series is a clear example where the
results of the multiagent system significantly
improve the results of the one-one model. Without
introducing Negociation Agent, the Bullwhip Effect
is divided by 9 when using the model. Figures 7 and
8 show variations of purchase orders made by the
four levels of the supply chain. Comparing the
vertical scale of both graphs, it is possible to see the
huge difference. Table 5 shows, in each case, the
optimal policy for each level of the supply chain.
Figure 7: Variations in orders along the supply chain for
the AL09 series with the one-one model.
Figure 8: Variations in orders along the supply chain for
the AL09 series with the multiagent model.
Table 5: Optimal Policy for each level of the supply chain
for the AL09 series.
Level Optimal Forecasting Method
Shop Retailer
Moving Average with
Retailer
Moving Average with
Wholesaler
Moving Average with
Factory
Moving Average with
A reverse situation is the one for the time series
AL11. Figures 9 and 10 show the variations of
purchase orders made by the four levels of the
supply chain. With these data, the multiagent system
is not able to produce such a high improvement over
the one-one method, given the strongly stationary
character in the series.
Figure 9: Variations in orders along the supply chain for
the AL11 series with the one-one model.
The results obtained in the analysis also suggest that
collaboration in the supply chain is an appropriate
solution for reducing the Bullwhip Effect.
Figure 10: Variations in orders along the supply chain for
the AL11 series with the multiagent model.
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
74
4.3 Application of Advanced
Forecasting Methods
Finally, after having demonstrated the effectiveness
of the multiagent model, we consider the
introduction of advanced forecasting methods, such
as the autoregressive integrated moving average
(ARIMA models). The objective is to assess the
extent whether these techniques can help for
reducing the Bullwhip Effect. Then, we use the same
series as in section 4.2, but considering that the first
stage of the supply chain (Retailer) performs the
demand forecasting using ARIMA techniques.
The ARIMA model, introducing the seasonality,
can be defined by:
,,
,,
Where p (P) is the order of the autoregression, d
(D) is the order of differentiation and q (Q) is the
order of the moving average. Lowercase parameters
are nonseasonal, while uppercase parameters are
seasonal, where n is the order of seasonality.
To carry out the analysis, we use IBM SPSS
Statistics 19. Table 6 contains the proposed model
for each one of the eight time series.
Table 6: ARIMA models of the time series.
Series Database ARIMA Model
AL03
Abraham
(1983)
0,0,1
0,1,1
AL04
2,0,0
0,1,0
AL09
1,0,0
AL11
1,0,0
0,1,1
BJ02
Box –
Jenkins
(1976)
0,1,0
BJ06
0,0,2
1,0,0
BJ08
0,1,1
0,1,1
BJ15
1,1,1
Table 7 is an extension of table 3 but adding a
column with the results when considering the
ARIMA models to forecast demand in the first level
of the supply chain (BW4). Furthermore, we show
the reduction achieved in each case.
The results presented show that the use of
advanced forecasting methods leads to the reduction
of Bullwhip Effect. Thus, the inclusion of ARIMA
models at the lowest level of the supply chain
provides very interesting results, and it can
significantly reduce, in many cases, the Bullwhip
Effect. In these circumstances, we consider to
incorporate them to the multiagent model, through a
new agent within the Forecasting Agents.
Table 7: Results of the tests using ARIMA models.
Test Series BW2 BW4 Reduction
1 AL03 1.54 1.52 1.30%
2 AL04 1.32 1.28 3.03%
3 AL09 3.29 2.54 22.80%
4 AL11 6.00 3.89 35.17%
5 BJ02 1.12 1.13 0.89%
6 BJ06 4.18 3.45 17.46%
7 BJ08 1.25 1.23 1.60%
8 BJ15 1.13 1.12 0.88%
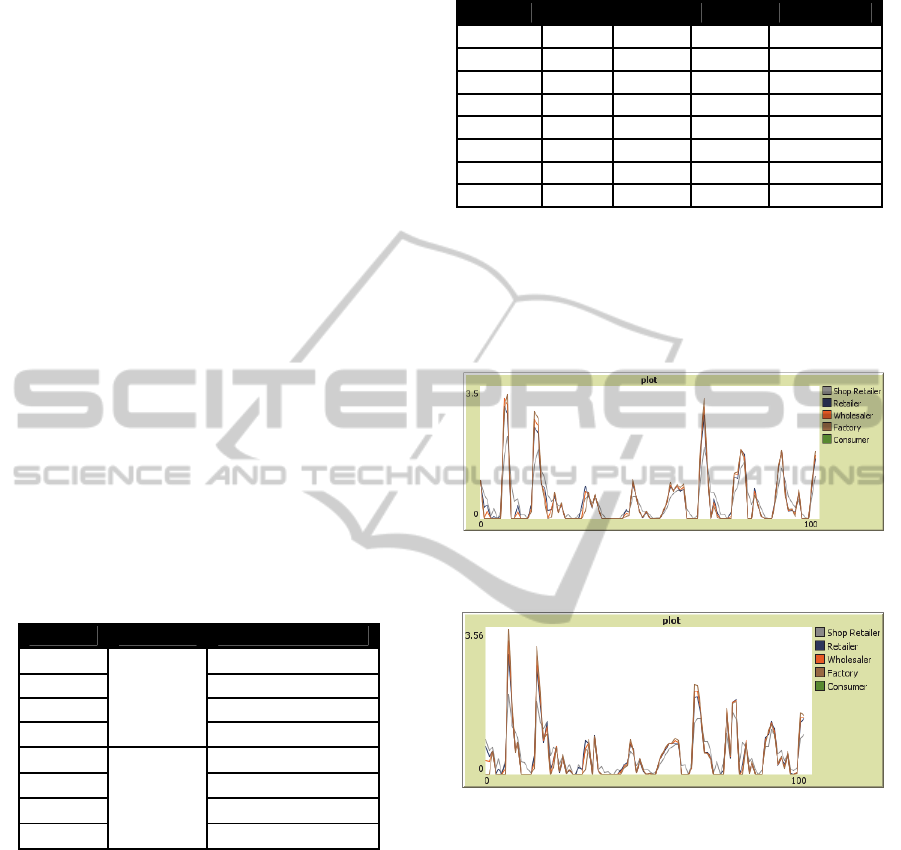
Figures 11 and 12 depict, by way of example, the
results obtained for the two cases to compare, in the
series BJ06. It is possible to see how the use of
ARIMA models significantly reduces, above 15%,
the variability of orders along the supply chain.
Figure 11: Variation of orders along the supply chain for
the BJ06 series with multiagent model.
Figure 12: Variation of orders along the supply chain for
the BJ06 series with multi-agent model, sing ARIMA
forecasts in the lower level of the supply chain.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The paper describes an application of multiagent
methodology aimed at reducing the Bullwhip Effect
in a supply chain. This is represented as a global
multiagent system, itself composed of four
subsystems multiagent. Each of them refers to one of
the levels of the supply chain (Shop Retailer,
Retailer, Wholesaler and Factory).
Tests performed on the raw data show that the
one-one method greatly amplifies demand variability
of end consumer throughout the supply chain,
especially when the demands have a high degree of
MultiagentModeltoReducetheBullwhipEffect
75

randomness. In this context, the application of
multiagent model, with other forecasting methods,
markedly reduces the Bullwhip Effect generated.
To develop the tool, we have considered only
simple forecasting methods, such as moving
averages and exponential smoothing, so that each
level of the chain uses the best one that suits the
demand it should deal with. With them, it is possible
to achieve great results in reducing Bullwhip Effect.
Even so, we have also shown that the inclusion of
more advanced forecasting methods (ARIMA
models) allows an even better system performance.
Lastly, we have analyzed the effect of
negotiation and collaboration among different levels
of the supply chain, verifying that it is an adequate
solution in reducing the Bullwhip Effect.
REFERENCES
Abraham, B., Ledolter, J. (1983): Statistical Methods for
Forecasting. New York Weley.
Box, G. E. P., Jenkins, G. M. (1976): Time Series Analysis:
Forecasting and Control. San Francisco: Holden Day.
Chen, L., Lee Hau, L. (2009): Information Sharing and Order
Variability Control Under a Generalized Demand Model.
Management Science. Vol. 55(5), pp. 781-797.
De la Fuente, D.; Lozano, J. (2007) “Application of
distributed intelligence to reduce the bullwhip effect”.
International Journal of Production Research. Vol.
44(8), pp. 1815-1833.
Disney, S. M., Towill, D. R. (2002): Transfer function
analysis of forecasting induced bullwhip in supply
chain. International Journal of Production Economics.
Vol. 78, pp. 133-144.
Disney, S. M., Towill, D. R. (2003): The effect of Vendor
Managed Inventory (VMI) dynamics on the Bullwhip
effect in supply chain. International Journal of
Production Economics. Vol. 85, pp. 199-215.
Disney, S. M., Towill, D. R. (2003): On the Bullwhip and
inventory variance produced by an ordering policy.
Omega. Vol. 31, pp. 157-167.
Forrester, J. W. (1961): Industrial dynamics, MIT Press.
Cambridge, MA.
Fox, M. S., Chionglo, J. F., Barbuceanu, M. (1993): The
Integrated Supply Chain Management System.
Internal Report, Univ. of Toronto.
Holmström, J. (1997): Product range management: a case
study of supply chain operations in the European
grocery industry. Supply Chain Management. Vol.
2(3), pp. 107–115.
Ji, Y. F., Yang, H. L. (2005): Bullwhip Effect Elimination
in Supply Chain with CPFR. Proceedings of the 2005
International Conference on Management Science &
Engineering. Vol 1-3, pp. 737-740.
Kimbrough, S. O., Wu, D. J., Zhong, F. (2002): Computer
the beer game: can artificial manage supply chains?
Decision Support Sytems. Vol. 33, pp. 323-333.
Lee, H. L., Padmanabhan, V., Whang, S. (1997): The
bullwhip effect in supply chains. Sloan Management
Review. Vol. 38(3), pp. 93-102.
Liang, W. Y., Huang, C. C. (2006): Agent-based demand
forecast in multi-echelon supply chain. Decision
Support Systems. Vol. 42(1), pp. 390-407.
Machuca, J. A., Barajas, R. (2004): The impact of
electronic data interchange on reducing bullwhip
effect and supply chain inventory costs.
Transportation Research Part E. Vol. 40, pp. 209-228.
Moyaux, T., Chaib-draa, B., D'Amours, S. (2004): An
agent simulation model for the Quebec forest supply
chain. Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence. Vol.
3191, pp.226–241.
Saberi, S., Nookabadi, A. S., Hejazi, S. R. (2012):
Applying Agent-Based System and Negotiation
Mechanism in Improvement of Inventory Management
and Customer Order Fulfilment in Multi Echelon
Supply Chain. Arabian Journal for Science and
Engineering. Vol. 37(3), pp. 851-861.
Shen, W., Xue, D., Norrie, D. H. (1998): An Agent-Based
Manufacturing Enterprise Infrastructure for
Distributed Integrated Intelligent Manufacturing
Systems. In Proceedings of the Practical Application of
Intelligent Agents and Multi-Agent Systems
PAAM'98, London, UK.
Sterman, J. D. (1989): Modelling managerial behaviour:
Misperceptions of feedback in a dynamic decision
making experiment. Management Science. Vol. 35(3),
pp. 321-339.
Wilensky, U. (1999): NetLogo. Northwestern University,
Evanston, IL: The Center for Connected Learning and
Computer - Based Modeling. Retrieved from
http://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/
Wu, S. N., Gan, W. H., Wei, F. M. (2011): Analysis on the
Bullwhip Effect Based on ABMS. Procedia
Engineering. Vol. 15.
Zarandi, M. H. Fazel; Pourakbar, M.; Turksen, I. B.
(2008): A fuzzy agent-based model for reduction of
bullwhip effect in supply chain systems. Expert
systems with applications. Vol. 34(3), pp. 1680-1691.
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
76
