
A Novel Pipeline for V(D)J Junction Identification using RNA-Seq
Paired-end Reads
Giulia Paciello
1
, Elisa Ficarra
1
, Alberto Zam
`
o
2
, Chiara Pighi
2
, Carmelo Foti
1
, Francesco Abate
1,3
,
Enrico Macii
1
and Andrea Acquaviva
1
1
Department of Computer Engineering, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy
2
Department of Pathology and Diagnostics, University of Verona, Verona, Italy
3
Department of Biomedical Informatics Center for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics,
College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University, New York, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Antibody, V(D)J Junction, RNA-Seq Data.
Abstract:
Immunoglobulin heavy and light chains are assembled respectively from germline V, D, J and V, J segments
within a process called V(D)J recombination involving the development of T and B lymphocytes. The discov-
ery that abnormal antibodies are often related to a wide range of pathologies conducted during the last years
to many studies inherent the immunoglobulin features. In particular the identification of the functional V(D)J
sequence of an antibody is considered fundamental since it could allow to understand the link between a par-
ticular disease and a specific recombination in a certain tissue and to promote the engineering of therapeutic
antibodies. Objective of the implemented pipeline consists in the identification of the so called ’main clone’
that characterizes a neoplastic tissue using paired-end RNA-Sequencing (RNA-Seq) reads.
1 INTRODUCTION
The finding that abnormal antibodies are in many
cases related to different pathologies, such as sys-
temic lupus erythematosus (Fraser, 2003), multiple
sclerosis (Hueber, 2002) and rheumatoid arthritis
(Huang, 1998), led during the last years to an in-
creasing interest in the study of one specific antibod-
ies feature that is the V(D)J junction and its char-
acterization. Thanks to the studies conducted since
the mid-century it is nowadays note that the vari-
able regions of the immunoglobulin heavy (IGH) and
light (IGL) chains are assembled respectively from
germline Variable (V), Diversity (D), Joining (J) and
V, J segments within a process called V(D)J recom-
bination involving the development of T and B lym-
phocytes (Jung, 2004), (Bassing, 2002). The afore
mentioned process is capable to account for the huge
variability of the immunoglobulin repertoire allowing
the immune response of the organisms to a wide range
of antigens. In particular, several different mecha-
nisms are involved in the production of heavy chain
variable region diversity with respect to V(D)J recom-
bination: The introduction of nucleotides by the ter-
minal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) (Alt, 1982)
that follows the deletion at the 3’ end of the V gene,
at the 5’ end of the J gene, and at both ends of the D
gene which recombine, or the introduction of short in-
verted sequences (palindromic-regions) at the V(D)J
junction, are well known examples.
The identification of the functional V(D)J se-
quence of an antibody is becoming fundamental since
it could allow to understand the link between a partic-
ular disease and a specific recombination in a certain
tissue and to promote the engineering of therapeutic
antibodies.
The present work is inspired from two main con-
cepts. First, the knowledge that neoplastic tumors of-
ten contain more than one type of cells called clones,
since descendent from a single progenitor cell, even
if they are strongly related to a specific type of cells,
the so called ’main clone’. The main clone is char-
acterized by the remarkable amplification of a spe-
cific rearrangement of the immunoglobulin gene or T-
cell receptor gene in comparison to that characteriz-
ing the other clones. Second, thanks to the evolution
of High Throughput Sequencing (HTS) technology it
is possible to sequence the RNA of neoplastic tissues
in less than a week. Thus, in principle it is possi-
185
Paciello G., Ficarra E., Zamò A., Pighi C., Foti C., Abate F., Macii E. and Acquaviva A..
A Novel Pipeline for V(D)J Junction Identification using RNA-Seq Paired-end Reads.
DOI: 10.5220/0004247601850189
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms (BIOINFORMATICS-2013), pages 185-189
ISBN: 978-989-8565-35-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

ble to identify the main clone that characterizes the
tissue of interest by detecting the most amplificated
VDJ rearrangement in the samples under study in a
short time, compatible with the development of fo-
cused therapies.
However, the analysis of V(D)J junction from
RNA-Seq data is challenging because of two main
problems: i) The recombination process makes most
of the RNA reads not correctly mapping on the ref-
erence genome - This is similarly to the gene fusion
detection problem (Abate, 2012), with the additional
complexity that the recombinant regions are three in-
stead of two and that they have a much smaller size
with respect to fused transcripts; ii) The large variabil-
ity of the junction, given by the introduction of nu-
cleotides in the region boundaries. Current state-of-
art tools, which are not based on RNA-Seq, are able
to analyse a single sequence at a time to determine
VDJ rearrangements. Hence, they cannot be used to
identify the main clone in a tissue sample.
In this paper we present an algorithm that ad-
dresses these issues, enabling the use of RNA-Seq to
determine the main clone recombinant alleles occur-
ring in a given tissue sample. The algorithm is based
on two steps, for VJ and D alleles identification re-
spectively. In the result section we report the details
of the analysis conducted on two samples of MCL
(Mantel Cell Lymphoma), highlighting the support-
ing reads for the most amplificated clones. Validation
is performed by comparing the V(D)J recombinations
obtained by the proposed pipeline against the V(D)J
regions obtained using state-of-art approaches applied
to the sequence of the main clone (known a priori) ob-
tained in laboratory via Polymerase Chain Reaction
(PCR).
2 STATE OF THE ART
Numerous tools have been developed with the pur-
pose of finding the best match between a rearranged
sequence and the V, D and J germlines, but all of
them are characterized by a different approach to the
problem for what is concerning the starting point of
the analysis. They try indeed to assign a specific V,
D and J alleles to a unique sequence, extracted in
laboratory via PCR or via High-throughput sequenc-
ing (HTS) experiments (Prabakaran, 2011), (Jackson,
2012), rather than identify, using a set of reads, the
main clone recombinant alleles.
IMGT/V-QUEST (Giudicelli, 2004) is the first au-
tomatic tool developed to align both Immunoglobulin
(IG) and T-cell receptor (TCR) sequences belonging
to different species with the germline IG and TCR
gene and allele sequences of the IMGT reference di-
rectory. Being based on Blast algorithm (Altschul,
1990) the tool results satisfying in aligning sequences
in the Varable Heavy (VH) and Joining Heavy (JH)
regions where large areas of sequence similarity can
be found, but not in the shorter D region due to the
role of the enzymatic processes in introducing or mu-
tating bases.
JOINSOLVER (Souto-Carneriro, 2004) tries to go
over this problem using a different scoring system
to match D segments that gives a higher score for
longer matches, being based upon consecutive nu-
cleotide matches, whereas searches for two relatively
conserved motifs ’TAT TAC TGT’ and ’C TGG GG’
to find the extreme points of the Third Complemen-
tary Region (CDR3).
Also IMGT/JunctionAnalysis (Monod, 2004) tries
to overcome the problems related to the identifica-
tion of the D allele and the nucleotides mutated or
introduced by the specific processes proper of the
V(D)J recombination. The junction is here defined
as the region starting at the second conserved cysteine
(CYS) of the V-region at position 104 and ending with
the conserved tryptophan (J-TRP for IGH chains)
or the conserved phenylalanine (J-PHE for the IG
light chains) at position 118. IMGT/JunctionAnalysis
searches the constitutive regions of the junction by
comparing the user sequence with the IMGT refer-
ence directory, but since the nucleotide sequences of
3’-V region and 5’ J-region are too short to be identi-
fied by the tool, V and J allele names have to be given.
SoDA (Volpe, 2006) is another tool developed for
deciphering IG and TCR gene segments composition.
Initially the set of possible V, D and J segments is
chosen thanks to independent unconditional pairwise
alignments between the target gene and each candi-
date gene segments, in particular for what is concern-
ing D segments each candidate is evaluated by align-
ment against the part of the target sequence between
the V conserved cysteine and the J conserved trypto-
phan or phenylalanine. In the second phase of the pipe
all the segments are at the same time aligned against
the previous identified sets.
Programs such as VDJSolver (Ohm-Laursen,
2006) and iHMMune-align (Gaeta, 2007) apply in-
stead statistical models to obtain the best fitting of the
given sequence on the V, D and J alleles: Even if these
methods represent an alternative way to identify the
rearrangement the good performances of the tools are
strictly linked to the quality and diversity of training
datasets.
BIOINFORMATICS2013-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
186
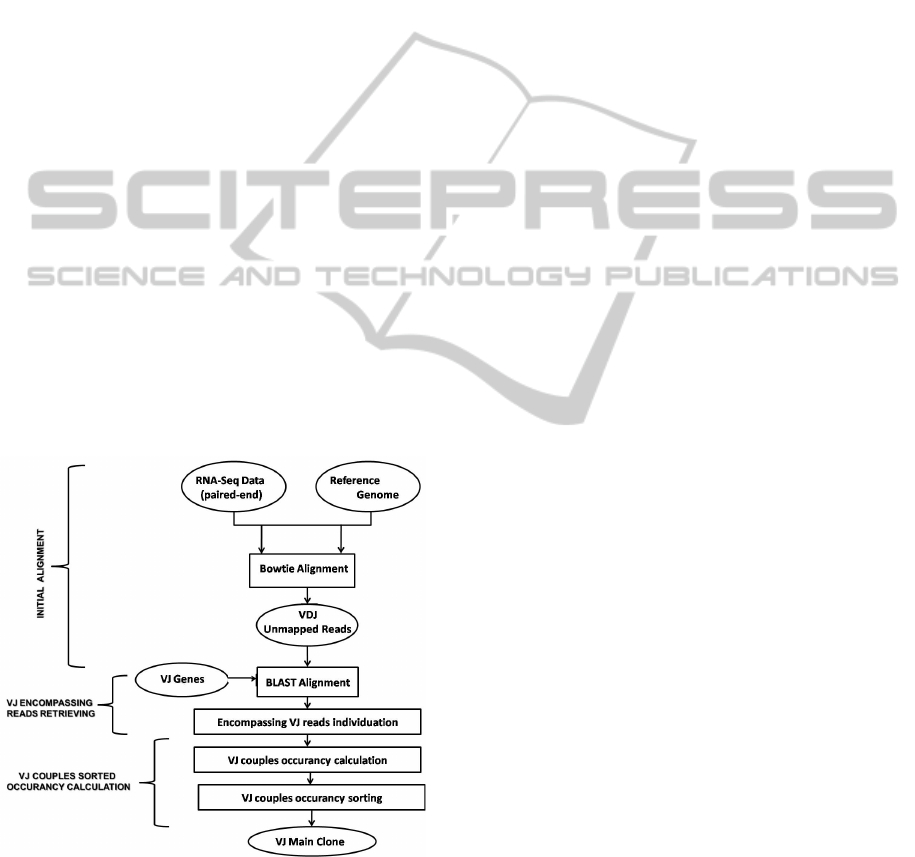
3 METHODS
The main clone identification is conducted in two
phases within the proposed workflow.
The first, that we will call in the following VJ al-
leles individuation shown in Figure 1 aims to detect
the V and J gene segments from which the variable re-
gions of the different clones are arranged and to score
each VJ rearrangement on the basis of the number of
reads supporting it.
The second, we will call D alleles individuation
which purpose is to recognize for the most supported
VJ couple identified before, the D allele introduced
during the recombinational process. The proposed
pipeline was applied to 2 samples of MCL for which
the quality was previously assessed. RNA was
extracted using Allprep QUIAGEN Columns and
then sequenced in 100 bp paired-end reads using an
Illumina HiSeq1000. For these samples the VDJ
rearranged sequence of the main clone was retrieved
in laboratory via PCR.
3.1 VJ Alleles Individuation
The individuation of the V and J alleles involved in
the main clone rearranged sequence is performed
during this step following the activities depict in
Figure 1 and detailed below .
Figure 1: VJ alleles individuation.
Initial Alignment. The starting point for determin-
ing the list of the VJ rearrangements is the alignment
of short RNA-Seq paired-end reads to the reference
genome (hg19). The alignment is performed using
Bowtie (0.12.8) (Langmead, 2009) in order to retrieve
from the initial set of data only those reads that don’t
map on the genome due to splicing events that poten-
tially could involve also V, D and J alleles in the pro-
cess called V(D)J recombination. We will call these
reads VDJ Unmapped Reads.
VJ Encompassing Reads Retrieving. The reduced
dimension of the new dataset, allows in this step for
performing a more accurate mapping of the VDJ Un-
mapped Reads on the V and J alleles using Blast
(2.2.25) (Altschul, 1990) with default parameters.
Objective of the this alignment is to retrieve from the
VDJ Unmapped Reads only those mates mapped on
the 272 V alleles or on the 16 J alleles proper of the
IGH locus. We define in this step a VJ recombination
if, given a read, a mate is mapped on a V allele and the
other on a J allele: We call these reads Encompassing
VJ Reads. It is worth noting that the remarkable poly-
morphism occurring among the considered genes, in
addition to homology (Li, 2002), conduct the same
read to define different VJ couples.
VJ Couples Sorted Occurancy Calculation. Based
on the number of reads supporting the recombina-
tion, each of the identified VJ couples is scored. Be-
cause of homologies inside the same allele, the reads
that present multiple matches are removed. A sort-
ing based on the number of Encompassing VJ Reads
supporting the recombinations is so performed. A list
containing all the identified clones is given at the end
of this phase: The most supported VJ couple is here
defined as that characterizing the main clone.
3.1.1 D Alleles Individuation
In order to identify for the most supported VJ couple
the recombining D allele, only those mates belonging
to a VJ encompassing read that don’t map totally on
the V or J allele are retrieved.
These mates are aligned using Shrimp aligner
(2.2.2) (Stephen, 2009) on the D genes.Once again
a sorting based on the occurancy of each D allele is
performed and the most supported allele considered
as the recombined allele for the specific VJ couple.
4 RESULTS
In Figure 2 are shown the results obtained applying
our pipeline on the two samples under study. Subfig-
ure A and B are respectively relative to the five clones
most supported by reads detected in Sample 1 and in
Sample 2. On the x-axis is reported the number of
supporting reads for the recombinations indicated on
ANovelPipelineforV(D)JJunctionIdentificationusingRNA-SeqPaired-endReads
187

Figure 2: Supporting reads for the five clones most supported by reads. Subfigure A and B report respectively for
Samples 1 and 2 on x-axis the number of reads supporting the VJ recombinations detected (darker bar) and the identified D
allele (lighter bar) for the recombinations indicated on y-axis. The rectangular box highlights the main clone detected by the
developed pipeline.
Table 1: V(D)J recombinations identified by different tools for the sequence of the main clone obtained via PCR in
laboratory. Table a and b report respectively for Samples 1 and 2 the V, D and J assignments given by different tools to the
sequence obtained in laboratory via PCR for the main clone.
(a) Sample 1
Tool V(D)J recombination
IMGT/Junction IGHV3-34*01 IGHD3-22*01 IGHJ4*02
JOINSOLVER IGHV3-34*01 IGHD3-22*01 IGHJ4*02
VDJsolver IGHV3-34*01 IGHD3-22*01 IGHJ4*02
SoDA IGHV4-34*01 IGHD3-22*01 IGHJ4*02
(b) Sample 2
Tool VDJ recombination
IMGT/Junction IGHV1-8*01 IGHD1-26*01 IGHJ6*03
JOINSOLVER IGHV1-8*01 IGHD1-26*01 IGHJ6*03
VDJsolver IGHV1-8*01 IGHD1-26*01 IGHJ6*03
SoDA IGHV1-8*01 IGHD1-26*01 IGHJ6*03
the y-axis. In particular the darker bar represents the
number of mates supporting the VJ rearrangements
whereas the other the number of mates supporting the
D allele detected for the considered recombination.
The main clone for each of the sample has been
correctly identified as the one with the maximum
number of supporting reads (see the rectangular boxes
in Figure 2 A and B). Furthermore it can be no-
ticed that for each of the analysed sample, the re-
ported recombinations involve alleles belonging to the
same V, D and J immunoglobulin subgroup. The ob-
served feature allows to affirm that all the recombina-
tions pointed out in Sample 1 and 2 describe in real-
ity the same clone: The noticed behaviour, expected
since the first alignment performed, can be indeed ex-
plained considering polymorphisms and homologies
occurring in IGH genes (Li, 2002). Both polymor-
phisms and homologies introduce a bias in the align-
ment leading the same mate to be mapped on different
genes.
In Samples 1 and 2 (see Figure 2 A and B) the J
allele involved in the five most supported recombina-
tions belongs respectively to IGHJ4 and IGHJ6 sub-
group: In particular two specific members of these
families can be distinguished that are IGHJ4*02 for
Sample 1 and IGHJ6*03 for Sample 2. IGHV4 and
IGHV1 subgroup are instead the reported alignments
for the two analysed Samples. The D allele reported
in each of the presented graphic is that characterized
by the highest score for the specific recombination af-
ter Shrimp alignment: The other D alignments were
indeed supported by a not considerable number of
reads. In both the Samples the D specific allele and
not only a D subgroup is maintained along all the re-
BIOINFORMATICS2013-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
188

combinations detected: IGHD3-22*01 for Sample 1
and IGHD1-26*01 for Sample 2.
In order to validate our identified main clone se-
quences, highlighted with a rectangular box in Figure
2 A and B, we verify if our V, D and J rearranged
alleles were the same as those obtained by insert-
ing the main clone PCR sequence in different online
tools. We perfomed this comparison against four free
available tools: IMGT/JunctionAnalysis (Monod,
2004), JOINSOLVER (Souto-Carneriro, 2004), VDJ-
solver (Ohm-Laursen, 2006) and SoDA(Volpe, 2006).
As it is possible to note from Table 1, despite
methods and algorithms implemented by the differ-
ent tools are different, all of them agree about the V,
D and J allele assignments of the sequence obtained
in laboratory via PCR. The main clone detected by
the above mentioned tools is for both the Samples the
same we identified applying our pipeline.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The arising interest in understanding the correlation
between a specific pathology and the detection of ab-
normal antibodies with the main purpose of promote
the engineering of therapeutic antibodies conducted
us to develop a new approach to the analysis of the
V(D)J junction of mature B cells. Differently from
the other available tools our pipeline aims at identify
the recombinant V, D and J alleles by starting from
a set of RNA-Seq paired-end reads rather than from
a single sequence. The results obtained on two Sam-
ples of MCL, confirmed by several available tools on
the main clone PCR validated sequence, conducted
us to affirm that the implemented pipeline is capable
to manage the typical sequence features characteriz-
ing V, D and J alleles in other words homologies and
polymorphisms.
Future works will aim at validate the developed
flow on other neoplastic datasets and than at identify
the specific main clone sequence by considering all
the enzymatic processes above mentioned acting dur-
ing the VDJ recombination. We also intend to opti-
mize the proposed algorithm in order to identify and
characterize subclones or divergent clones in a neo-
plastic population and follow them up over time since
it is worth noting that during lymphoma development
the B cell repertoire can evolve.
REFERENCES
Abate, F. (2012). Bellerophontes: A rna-seq data analysis
framework for chimeric transcripts discovery based on
accurate fusion model. Bioinformatics.
Alt, F. W. (1982). Joining of immunoglobulin heavy chain
gene segments: implications from a chromosome with
evidence of three d-jh fusions. Proceedings of the Na-
tional Academy of Sciences.
Altschul, S. F. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool.
Journal of Molecular Biology.
Bassing, C. H. (2002). The mechanism and regulation of
chromosomal v(d)j recombination. Cell.
Fraser, N. L. (2003). The vh gene repertoire of splenic b
cells and somatic hypermutation is systemic lupus ery-
thematosus. Arthritis Res Ther.
Gaeta, B. A. (2007). ihmmune-align: hidden markov
model-based alignment and idedntification of
germline genes in rearranged immunoglobulin gene
sequences. Bioinformatics.
Giudicelli, V. (2004). Imgt/v-quest, an integrated software
program for immunoglobulin and t cell receptor v-j
and v-d-j rearrangement analysis. Nucleic Acids Re-
search.
Huang, S. (1998). Vh usage and somatic hypermutation in
peripheral blood b cells of patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol.
Hueber, W. (2002). Autoantibody profiling for the study
and treatment of autoimmune disease. Arthritis Res
2002.
Jackson, K. J. L. (2012). Divergent human populations
show extensive shared igk rearrangements in periph-
eral blood b cells. Immunogenetics.
Jung, D. (2004). Unraveling v(d)j recombination; insights
into gene regulation. Cell.
Langmead, B. (2009). Ultrafast and memory-efficient align-
ment of short dna sequences to the human genome.
Genome Biology.
Li (2002). Genetic diversity og the immunoglobulin heavy
chain vk region. Immunology Review.
Monod, M. Y. (2004). Imgt/junctionanalysis: the first tool
for the analysis of the immunoglobulin and t cell re-
ceptor complex v-j and v-d-j junctions. Bioinformat-
ics.
Ohm-Laursen (2006). No evidence for the use of dir, d-d
fusions, chromosome 15 open reading frames or vh
replacement in the peripheral repertoire was found on
application of an improved algorithm, jointml, to 6329
human immunoglobulin h rearrangements. Immunol-
ogy.
Prabakaran, P. (2011). Expressed antibody repertoires
in human cord blood cells: 454 sequencing and
imgt/high v-quest analysis of germiline gene usage,
junctional diversity, and somatic mutations. Immuno-
genetics.
Souto-Carneriro, M. M. (2004). Characterization of the hu-
man ig heavy chain antigen binding complementarity
determining region 3 using a newly developed soft-
ware algorithm, joinsolver. The Journal of Immunol-
ogy.
Stephen, M. (2009). Shrimp: Accurate mapping of short
color-space reads. PLoS Computational Biology.
Volpe, M. J. (2006). Soda: implementation of a 3d align-
ment algorithm for inference of antigen receptor re-
combinations. Bioinformatics.
ANovelPipelineforV(D)JJunctionIdentificationusingRNA-SeqPaired-endReads
189
