
Towards Assistive Robotics for Home Rehabilitation
Elsa Andrea Kirchner
1,2
, Jan Christian Albiez
1
, Anett Seeland
1
, Mathias Jordan
1
and Frank Kirchner
1,2
1
Robotics Innovation Center, German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI),
Robert-Hooke-Straße 5, Bremen, Germany
2
Robotics Lab, University of Bremen, Robert-Hooke-Straße 5, Bremen, Germany
Keywords:
Cognitive Human-robot Interaction, Rehabilitation Robotics, Virtual Reality and Interfaces, Exoskeleton,
Psychophysiological Data.
Abstract:
In this paper, we want to point out the possibilities that arise from the latest advances in robotic exoskeleton
design and control. We show that approaches of artificial intelligence research and robotics that integrate
psychophysiological data analysis offer the possibility to assist disabled people in their everyday lives. Thus,
continuous long term rehabilitation training and daily support can be provided in the future to help them to
regain motor functions. We outline a possible scenario for fully embedded home rehabilitation and its com-
ponents. The presented work further investigates two challenges of the application of such a system in more
detail: (i) improvement of the interaction between the patient and the supporting interface and (ii) enhance-
ment of reliability of predictions made about the patients intention. In the experimental part we demonstrate
that the exoskeleton control can compensate for gravitational loads, imposed by the device itself. Further, we
present results that show that movement onset prediction can be made based on different psychophysiological
measures, and can be improved with respect to their reliability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Every year, more than 200.000 patients in Ger-
many suffer from neurological impairments due to
stroke (Platz and Roschka, 2009). They show ma-
jor loss of motor abilities which severely impairs their
ability to continue their lives both in private as in their
professional domains. Apart from the dramatic im-
pact on the individuals, a maior societal and financial
impact on the economy has to be considered since too
many of these individuals cannot be fully reintegrated
into the professional world, or may have to abstain
from a professional life altogether. When including
other impairments of the motor system than those in-
duced by stroke, an in-homogenous group of patients
with different demands have to be treated. Hence, re-
habilitation could be more efficient with rehabilitation
systems that are able to cover a wide range of patients.
Full recovery rate could further be increased by pro-
viding professional long term rehabilitation and sup-
port. Therefore, rehabilitation systems should allow
to increase the number of treatment sessions that is
so far limited due to the shortage of skilled therapists
and costs. To summarize, there is a big need for reha-
bilitation tools that transfer rehabilitation and support
in every day life.
In this paper we will outline a future fully em-
bedded home rehabilitation and support system and
pinpoint the technological developments needed to
achieve our vision. This is a fully integrated, daily
rehabilitation provided by a lightweight, comfortable-
to-wear upper body exoskeleton that has enough force
to move a plegic arm of a patient. By analysis of psy-
chophysiological signals, like the electroencephalo-
gram (EEG), the electromyogram (EMG) and gaze
direction, an artificial intelligence-based control ar-
chitecture is able to predict intentions of the user to
support self-initiated movements.
The support of self-initiated movements has a pos-
itive effect on rehabilitation (Clark and Smith, 1999).
The earlier a later supported movement is predicted
the more will the patient have the impression that he
himself is controlling his arm autonomously, although
the exoskeleton is actually moving it. Early predic-
tion of movements re-connects the movement plan-
ning phase of the brain with movement execution to
re-establish the capability of the patient for freely and
self-paced movements.
168
Andrea Kirchner E., Christian Albiez J., Seeland A., Jordan M. and Kirchner F..
Towards Assistive Robotics for Home Rehabilitation.
DOI: 10.5220/0004248501680177
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices (BIODEVICES-2013), pages 168-177
ISBN: 978-989-8565-34-1
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

To cover the need for rehabilitation systems which
are able to analyze and monitor the behavior of the
subject while operating in a familiar environment, the
patient should interact with a real or simulated ev-
eryday environment. All processing needed for the
support system should fit into a smartphone sized on-
board computing device.
In the long term vision, the patient should be able
to live at home without the help of others, receiving
rehabilitation sessions on demand and thus increas-
ing the chances for full recovery. Additionally, such
a system is in principle able to automatically proto-
col the success of rehabilitation. This can be done by
analyzing psychophysiological data and action force,
recorded by sensors that are integrated into the ex-
oskeleton.
To implement such a rehabilitation system some
challenges have to be dealt with, two of those are
investigated here: (i) to develop a control mecha-
nism that support the patient during interaction with
the support system, i.e., by compensating for gravi-
tational load of the exoskeleton, and (ii) to improve
the reliability of prediction made with respect to the
patients movement intention. Thus, the paper is
structured as follows: after presenting relevant re-
search (Sec. 2) in context of our technological ap-
proach for future home rehabilitation that is briefly
described in Section 3, we present results of three
studies conducted to deal with the before mentioned
challenges (Sec. 4), closing with a conclusions and
outlook (Sec. 5).
2 ROBOTIC REHABILITATION
Currently, there are already some robotic systems ap-
plied in rehabilitation. The conception of these sys-
tems is based on modern, evidence-based therapy ap-
proaches, such as repetitive task-orientated bilateral
and distal training as well as assist-as-needed and mir-
ror therapy (Hesse et al., 2009; Platz and Roschka,
2009). The main goal of these modern therapy ap-
proaches is to increase the neuroplasticity of the cen-
tral nervous system (Volpe et al., 2000; Takahashi
et al., 2008). Some examples from praxis show that
the usage can be reported as successful and that a re-
habilitation effect can be measured using these kinds
of system (Volpe et al., 2000).
Depending on the characteristic and severety of
symptom, different system designs are currently used.
This means that in praxis a certain system is only used
on a defined, usually small group of patients. For ex-
ample, the swiss company Hocoma
1
provides three
different rehabilitation systems (ArmeoPower, former
ARMin (Mihelj et al., 2007), ArmeoSpring, Armeo-
Boom) for upper limb rehabilitation which are based
on task-oriented training scenarios in a virtual envi-
ronment, which facilitates treatment of neurological
diseases of different severity. Even though there are
synergies between the rehabilitation systems (e.g., in
the software platforms, the visual feedback or assess-
ment tools) the physical systems are totally different,
which means in order to address the whole range of
possible patients, different physical systems are re-
quired.
Today, some approaches of exoskeleton-based as-
sistance exist. The exoskeleton system HAL pre-
sented in (Otsuka et al., 2011) aims at expanding, in-
tensifying and supporting physical capabilities of hu-
mans during activities of daily living. In context of
an everyday task (meal assistance), the device is able
to guide and support the user during reaching move-
ments and thus facilitates the impaired subject to take
his meal independently. The overall system has 4
electrically actuated degrees of freedom (3 shoulder,
1 elbow) and offers a grasp-assistance mechanism,
which operates separated from the rest of the system.
HAL moves the user’s limb totally passive using a
minimum jerk control approach. Like ARMin (Mihelj
et al., 2007), HAL is fixed to a grounded support and
thus is massively restricted in his operational range.
Besides exoskeleton devices also end-effector-
based approaches can be found in modern therapy. A
good example is the InMotion Arm Robot (former:
MIT Manus (Hogan et al., 1992)) which assists pa-
tients by moving their totally passive arm or by sup-
porting an active movement coming from the patient.
This system simulates the classical hand-to-hand ther-
apy of a therapist with a continuous determination of
position and force applied to the arm of the patient.
It is also equipped with a visual feedback which al-
lows to address even complex tasks. A drawback is
that the system is stationary and restricted to planar
movements.
Independent of the physical system, the usage of
virtual reality scenarios is one important approach of
supporting patients within typical daily activities as
discussed in (Guidali et al., 2011). In their work,
an exoskeleton is combined with a virtual reality sce-
nario. The integration of daily purposeful activities in
rehabilitation sessions is thought to improve rehabili-
tation progress much more than artificial movements
could, since trained motor behaviors and brain path-
ways are addressed.
Another example for the usage of virtual reality
1
http://www.hocoma.com/en/products/armeo/
TowardsAssistiveRoboticsforHomeRehabilitation
169

is the PITS system (Villiger et al., 2011). This assis-
tance system is not applying physical therapy but al-
lows the realization of known therapeutical principals
and therapies, e.g., mirror therapy. The pathological
weak or plegic arm can behave in a virtual reality. The
therapeutic approach can differ depending on the state
of the patient, i.e., whether he is already able to carry
out own activity or not.
The integration of pyschophysiological measures
and stimulation of motor activity are future ap-
proaches that can help to improve rehabilitation. In
the Brain2Motion project
2
an exoskeleton shall be
combined with a textile-based surface motor neu-
roprosthesis. This neuroprothesis shall apply func-
tional electrical stimulation (FES). Besides, a non-
invasive EEG-based Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)
and an electrooculography (EOG) interface will be
integrated as well to support the whole system.
Other approaches integrate electromygraphic signals
alone (Lenzi et al., 2012) or both, EMG and EEG in
combination (Gancet et al., 2011).
To summarize, approaches reviewed here address
one or more of the three main fields of expertise: BCI
technologies, virtual reality, and exoskeleton. In some
systems, it is shown that the integration of at least two
of these fields into a support system can improve the
support of the user. However, they are very special-
ized in function and design, mostly stationary and can
only address certain pathologies according to the ther-
apy approach the individual developer groups are fol-
lowing.
3 TECHNOLOGICAL APPROACH
To combine different approaches, the proposed reha-
bilitation system (see Fig. 1) should be composed of
1) an exoskeleton which adapts to the body charac-
teristics of the user and supports or carries out in-
tended movements 2) a virtual (or real) environment
the user can move in and perform natural interactions,
and 3) integrated psychophysiological data analysis
for movement prediction of self-paced movements by
an 4) embedded processing module. In the following,
we give an overview of our technological approach
and the main components of the system.
3.1 Exoskeleton
The exoskeleton system presented is a 7 degrees-of-
freedom (DOF) haptic device, built around the human
2
http://hal.umh.es/brain2motion/description.html
everyday situation
⦁ movement preparation detection
⦁ possible motion trigger
⦁ prediction of users desire
⦁ motion path estimation
⦁ possible motion trigger in
very early rehabilitation
phase after brain lesion
⦁ user assistance / control
⦁ movement planning (fwd. kinematics)
⦁ active movement execution
⦁ force feedback application
⦁ physical movement detection
⦁ confirmation of eeg-based motion prediction
⦁ movement pattern prediction
⦁ possible motion trigger in later rehabilitation phase
⦁ full virtual immersion
⦁ visual feedback
⦁ force feedback computation
⦁ semantic control and supervision
Exoskeleton
Virtual scenario
Eye-tracking
EMG
EEG
Figure 1: Future home rehabilitation supported by an ex-
oskeleton, a virtual scenario and biosignal analysis.
body and worn by the user. It allows support of sub-
jects with impaired motor skills during activities of
daily life.
In the initial design phase, we identified the three
main goals for designing the system, described in the
following: 1) The exoskeleton has to be wearable by
the user and not to be fixed to a special support mech-
anism, 2) it should have multiple contact points to
the user’s body, allowing for the reflection of com-
plex force patterns to the user and thus enable precise
guidance of movements. 3) It has to be inherently
safe, which means that the subject always has to be
able to overcome any force the exoskeleton imposes
on the body of the operator during movement execu-
tion. The mechanical structure of an exoskeleton has
to be highly adaptive to be able to cope with differ-
ent human proportions (segment lengths & joint posi-
tion). In addition to that, human joints are not joints in
the sense of classical mechanical engineering. Often
axes are not fixed in space, but drift along trajecto-
ries (especially in the shoulder and the elbow) to opti-
mize the force of the muscle-tendon system. This has
to be captured by the exoskeleton through permanent
alignment of system axes to the corresponding human
joints.
Based on multiple literature studies on human
physiological and behavioral tests, a one arm ex-
oskeleton haptic device was developed (see Fig. 2).
The exoskeleton interacts via four points with the hu-
man, meassuring the forces by sensors integrated in
the structure. Another important factor is the opera-
tional workspace of the system coupled to the user.
Several experiments show that the exoskeleton does
not prevent the execution of the most important arm
movements with a coverage of about 60 % of the over-
all human arm workspace and up to 90 % of the nat-
ural manipulation workspace. The 7 active DOFs
are driven by an electro-hydraulic actuation concept,
BIODEVICES2013-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
170

Figure 2: (Left) The kinematics of the designed exoskeleton
with 7 active degrees of freedom and two passive measured
degrees. (right) The DFKI RIC exoskeleton worn by a user.
which encompasses a highly integrated low-pressure
fluid servo-valve that can be directly mounted on a
rotary vane actuator, resulting in a safe and dense ac-
tuation unit, operating at 30bar hydraulic supply pres-
sure. The entire control of the actuation is carried out
locally by a set of distributed µControllers, which run
a combination of model-based feed-forward and clas-
sical feed-back control approaches, and communicate
to a central control system via CANbus (Jordan et al.,
2012). On top of this inner loop of n low-level torque
controllers (n equal to the number of active DOF), the
overall control system of the exoskeleton is organised
in a multi-layer architecture, with a cascaded struc-
ture. The outer loop contains several elements (feed-
forward as well as feedback), which determine the
reference torque
~
τ
re f
for the controllers in the inner
loop. Within this context, a special gravity compen-
sation block deals with minimizing the impact of the
exoskeleton on the wearer by compensating for the
weight of the device.
3.2 Home Rehabilitation
To start therapy, the usage of a virtual environment al-
lows controlled interaction of the patient with objects
in known scenarios. A controlled retrieval of certain
simple and complex movements through a therapist,
who is controlling the scenario and is designing the
therapy for the subject, is easily possible. By this,
one can make use of the positive and motivating ef-
fect of having a patient interacting in known scenar-
ios that replicate possible activities in normal life, like
preparing breakfast in the kitchen, while still control-
ling the patients activity by, e.g., setting a jar of jam
in different positions in the interaction space (Fig. 1)).
A virtual scenario can further easily be used to predict
the intention of a patient. An intended behaviour of a
patient can – in the simplest approach – be pre-defined
by the semantic content of a fixated object in a virtual
scenario. For example, if the subject is fixating a jar
of jam in a shelf (Fig. 1) it is likely that the patient
wants to grab it. If the jar of jam is already standing
in front of him on the table, he might want to open it.
If it is already open, he may likely want to get a spoon
to scoop out some jam for his slice of bread etc.. Fur-
ther, movement direction and even the target position
can be determined and used to calculate movement
direction to be executed by the exoskeleton. Thus, by
making use of the semantic context, intended move-
ment directions can be computed during the patient’s
interaction with a virtual environment.
In real environments, object recognition and con-
text analysis would further be required, which puts
greater demands onto the whole system and its artifi-
cial intelligence. However, by extending the system
to be able to deal with real environments, a transfer
of the rehabilitation system from its usage for therapy
into daily support is possible.
3.3 Psychophysiological Data
To enhance human-machine interaction for the pur-
pose of rehabilitation, it is not enough to equip robotic
systems with sensors that allow to react on the human
behavior, but to predict his behavior with the goal to
adjust the support of the robotic device to the current
and upcoming requirements of a patient.
In our approach, a movement is initiated by move-
ment onset prediction based on EEG or EMG. In case
some data is disturbed, as it is likely the case for EEG
and EMG data recorded from stroke patients, move-
ments can still be triggered by means of eye tracking.
Hence, interruption of the motor-sensor loop due to
different kinds of disorders can be compensated very
flexible by the system to allow psychophysiologically
adapted guidance of an exoskeleton. This allows the
application of one rehabilitation device to a number
of different disorders and even to patients with paretic
limbs, while being situated in an every day environ-
ment.
For any kind of adaptation of the exoskeleton con-
trol by psychophysiological data, one has to assure
that malfunction due to misclassification is avoided.
This can be assured by combining and weighting pre-
dictions made on the basis of different types of data,
e.g., to predict movements based on EEG data while
using EMG signals to assure that the subject wants
to move and did not just imagine a movement, or to
predict movement by EEG data and use force sensors
integrated in the exoskeleton to trigger the onset of
the movement (Folgheraiter et al., 2012). When eye
tracking is used to control for, e.g., movement direc-
tion, even a weak EEG or EMG signal can be used to
TowardsAssistiveRoboticsforHomeRehabilitation
171

FPGA
embedded Linux
RAM
Cache
Network USB UART
Flash DSP/ML Timer
CPU
System Bus
Figure 3: Design for system on chip for processing of psy-
chophysiological data.
assure that the patient wants to use his gaze to trigger
a movement, as shown for a BCI application (Zan-
der et al., 2010). Hence, the combination of differ-
ent kinds of psychophysiological data enables differ-
ent kinds of control and adaptation of the exoskeleton
with respect to the requirements of the patient and the
state of rehabilitation to support correct function.
3.4 Embedded Processing
For a full integration of our approach into the daily
life of a patient, not only the sensors but also the
data analysis hardware has to be embedded into the
rehabilitation system. Reconfigurable, application-
specific hardware components can be a solution re-
alized by using field-programmable gate arrays (FP-
GAs) which become increasingly popular for DSP
techniques (Meyer-B
¨
ase, 2007). So far only few
approaches had applied embedded analysis for psy-
chophysiological data (e.g., (Shyu et al., 2010)). A
special embedded computational systems is currently
developed that allows to combine a generic processor
for software-specific tasks and application-specific
parallel DSP architectures, as shown in Fig. 3.
4 EXPERIMENTAL PART
In the following, we present and discuss results of a
study investigating the capability of the developed ex-
oskeleton to compensate for gravitational loads. This
is especially important in order to keep the device as
transparent as possible to the user during training ses-
sions and extend the application time of the device.
Further, compensation of gravitational loads prevents
user fatigue, by relieving the subject from additional
load, and helps to successfully fulfill the rehabilita-
tion task (Beer et al., 2008). A second study was con-
ducted to develop a procedure that improves perfor-
mance in the prediction of movement planning based
on EEG single trial analysis (see Sec. 4.2). In fu-
ture, EMG signals could alternatively or additionally
to EEG signals be used to predict movement onset.
Further, EMG signals can be used to confirm move-
ment onset earlier than it can be done when using
force sensors integrated into the exoskeleton as dis-
cussed in (Folgheraiter et al., 2012)). Hence, in a
third study EMG onset activity during different types
of movements that may occur during rehabilitation of
arm movements are investigated with respect to the
earliness and reliability of detection (see Sec. 4.3).
For this paper, offline EEG and EMG analysis were
both performed on a standard PC.
4.1 Exoskeleton Inverse Dynamics
As described, inside the exoskeleton control system a
gravitation compensation block exists, which aims at
minimizing the impact of the exoskeleton to the user,
by compensating for the weight of the device. This
was realized via a feed-forward controller based on
the inverse dynamic model of the haptic device, which
is updated at a frequency of 100Hz. Briefly, inverse
dynamics is establishing the following relationship:
τ
grav
(t) = f (q
act
(t), m) (1)
The function describing Eq. 1 defines, according to
the actual pose of the exoskeleton in the joint space
q
act
, the torque τ
grav
for each active joint of the de-
vice, which is necessary to compensate for gravi-
tational effects caused by the following mechanical
structure (gravitation compensation). For this pur-
pose, a mass model of the active exoskeleton sys-
tem m was developed and integrated into the real-time
control loop. The resulting reference values are com-
municated via CANbus to the distributed joint con-
trol system, which is directly located at the mechani-
cal structure of the exoskeleton and running at a fre-
quency of 2kHz. Due to the fact that the compensation
of gravitational loads is always active, the remain-
ing control structure includes permanent knowledge
about the dynamic behaviour of the system, which is
advantageous (Kelly, 1997).
Experimental Setup. To verify the capability of the
exoskeleton system to compensate for gravitational
loads caused by the device itself, 15 subjects with
different anthropometric measurements were asked to
wear the system and perform voluntary movements in
space. Within the test, alternation between wide and
small motions was encouraged in order to cover the
full-body working range. This enabled us to record
data during long transitional movements as well as
short, precise movements. Furthermore subjects were
asked to state how much the exoskeleton influenced
BIODEVICES2013-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
172
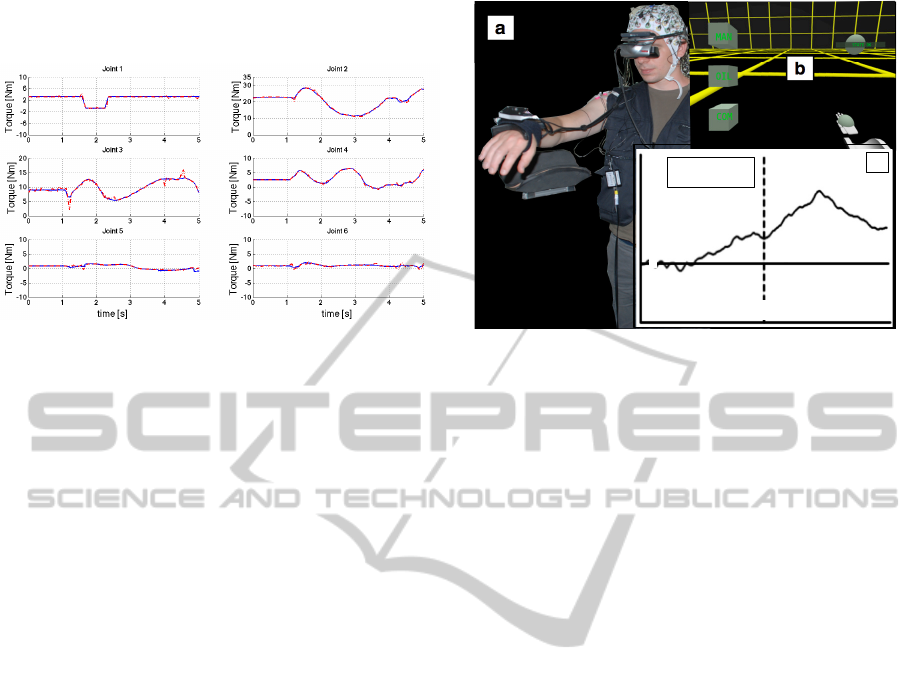
them during operation, in order to get a subjective
feed-back of the comfort of the device.
Figure 4: Movement associated joint torques for active
degrees of freedom of the exoskeleton; (blue) reference
torque; (red) actual torque.
Results. Fig. 4 shows experimental results for the
desired and actual joint torques of all actuated
degrees-of-freedom during a voluntary movement of
one subject in combination with the exoskeleton sys-
tem. It is obvious that the torque control system of the
device is able to track the desired reference torques
very well. Small errors occur mainly when the user
changes the direction of movement of a joint. These
errors cannot be further reduced due to the fact that
the control frequency of the torque controller is lim-
ited by the control frequency of the valves (11Hz).
Presented results are representative for all tested sub-
jects. Nonetheless, even with detectable small er-
rors, all subjects reported that the exoskeleton appears
transparent to them, especially during small move-
ments.
4.2 Reliability of EEG-based Movement
Predictions
Directed motor action requires planning by the brain.
Several parts of the brain are involved in motor plan-
ning including the primary motor cortex. Its activ-
ity can be recorded with the help of EEG systems.
Changes in EEG activity are expressed in the fre-
quency range (Leeb et al., 2006) as well as in event-
related potential (ERP) activity, especially in the Lat-
eralized Readiness Potential (LRP) (Kornhuber and
Deecke, 1965; Santucci and Balconi, 2009). By de-
tecting those differences in brain activity, it is gen-
erally possible not only to predict the execution of
movements but also which side (right or left body
side) and which part of the body (arm or leg) will be
moved (Leeb et al., 2006).
In a pilot study published in (Folgheraiter et al.,
2011), we investigated whether ERP activity can be
a
b
2
-2
4
-4
0
ms
c
-300
-600
300 600
-6
µV
Difference curve
of C3/C4
0
Figure 5: (a+b) Experimental setup (details see text). (c)
Averaged difference curve between electrodes C3 and C4.
used to predict upcoming movements by applying su-
pervised classification techniques. The prediction can
be transferred into a continuous score to prepare an
exoskeleton for movement onsets. The study pre-
sented here was performed in a similar setup. We in-
vestigated the reliability of movement prediction dur-
ing complex arm movements. As extension of the first
study, a multi-task condition was created to simulate
a more realistic situation, where subjects’ concentra-
tion is shared among different activities. The main
goal of the study was to investigated the effect of the
number of training windows (used to train a classifier)
onto the stability of movement prediction.
Experimental Setup. Four male subjects (between
25 and 31 years, right-handed, and normal or
corrected-to-normal vision) were situated in a virtual
scenario (see Fig. 5). Subjects had to move their right
arm from a rest position, supported by an armrest (see
Fig. 5 a), to a target position visualized by a virtual
target ball (see Fig. 5 b, upper right corner). After
entering the target ball, the subjects returned to the
rest position while the next target ball appeared. Par-
ticipants had to stay in the rest position for at least 5
seconds before starting the next movement. The num-
ber of movements out of the rest position differed in
each run from 116 to 159. While performing this task,
subjects had to respond to three different seldom, im-
portant messages that were presented together with
unimportant information in a ratio of 1:20 (Fig. 5 b,
all types of information were projected in front of the
target ball). To respond, subjects had to touch one par-
ticular response cube out of three possible ones that
were displayed in the virtual environment (Fig. 5 b,
left side). For each subject, 3 runs were conducted on
the same day and merged for data analyses.
TowardsAssistiveRoboticsforHomeRehabilitation
173
Data Processing. During the experiment, EEG was
continuously recorded from 124 electrodes (extended
10-20 system, actiCap, Brain Products GmbH, Mu-
nich, Germany), referenced to FCz and amplified us-
ing four 32-channel DC amplifiers (Brain Products
GmbH, Munich, Germany) and filtered with a low
cutoff of 0.1 Hz and high cutoff of 1000 Hz. Sig-
nals were digitized with a sampling rate of 5000 Hz.
Impedance was kept below 5 kΩ.
To train the classifier and evaluate experimental
results, a movement marker was added to the EEG
stream whenever the subjects moved their arm 5 cm
away from the rest position. According to this marker,
windows of 1000 ms length were cut out. 13 differ-
ent training windows for the “movement preparation”
class were analyzed, i.e. [−1600, −600], [−1550,
−550], . . . , [−1000, 0]. For the “resting state” class,
training windows of an equal length were cut out ev-
ery 1000 ms, if no other marker was stored in the data
stream 1000 ms before or 2000 ms after that window.
In the test case, windows were cut out every 50 ms
independent of the class label. Each window was
standardized channel-wise (subtraction of mean and
division by standard deviation). A decimation was
applied with a finite impulse response (FIR) filter to
reduce the sampling rate of the data from 5000 to
20 Hz. Next, a FFT band-pass filter with a passband
of 0.1 to 4 Hz was applied and the last 4 values of
each channel were used as features. Finally, normal-
ized features were classified by a support vector ma-
chine (SVM) with a linear kernel. In each training
run, SVM parameters were optimized with an inter-
nal 5-fold cross validation using a pattern search al-
gorithm (Nocedal and Wright, 1999). To calculate
a performance measure the labeling of the continu-
ous instances (i.e., windows in the test case) was re-
quired. Since the onset of the LRP cannot exactly be
determined for single trials, we defined an uncertain
area (from −600 to −350 ms) which was left out for
metric calculation. Also, predictions made based on
windows ending at −150 to 0 ms were excluded due
to the fact that the actual movement onset had hap-
pened before the movement marker was stored. The
balanced accuracy (Brodersen et al., 2010), i.e., the
mean of true positive and true negative rate, was used
as performance measure.
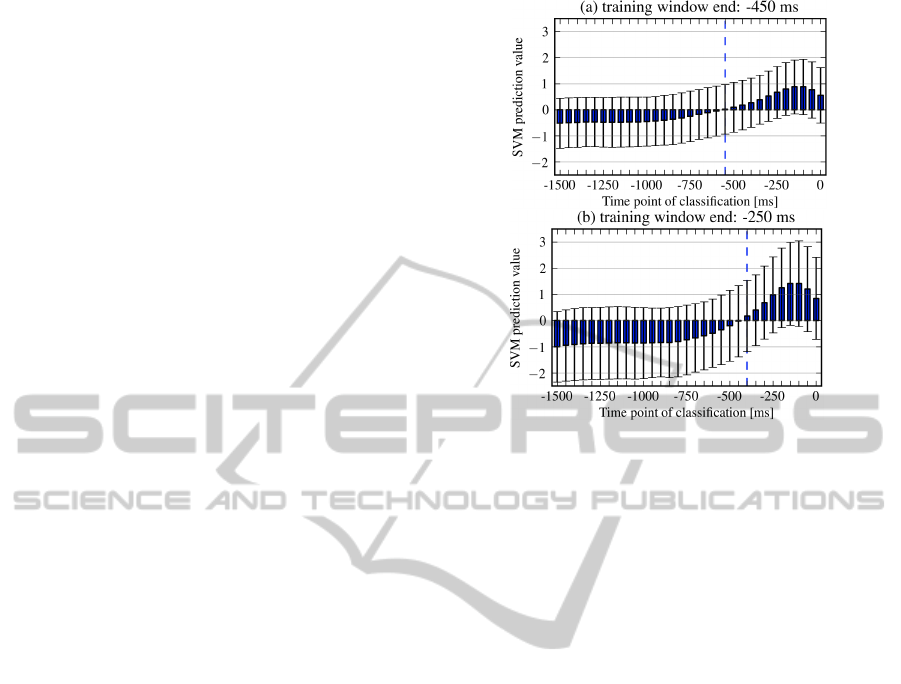
To investigate the effect of the number of train-
ing windows an iterative procedure was applied. In
each iteration, the training window with best perfor-
mance on the training data was calculated and used
for the next iteration. This led to an increased num-
ber of training windows in each iteration until all
training windows were used. Parts of test data per-
formances were analyzed for individual subjects by
Figure 6: Mean (bars) with SD (error bars, n = 8600) of
SVM prediction values for consecutive classified instances.
The dashed line illustrates the time point when the mean
prediction value exceeds zero.
repeated measures ANOVA with number of training
windows as a within-subjects factor.
Results. Fig. 6 illustrates the trade-off between
training on an early window (−450 ms, Fig. 6 a) com-
pared to training on a later window (−250 ms, Fig. 6
b): a classifier based on the later window learned a
later prediction (compare crossing of zero), but yield
higher prediction scores.
When combining training windows, Fig. 7 a)
shows that adding a second window during train-
ing significantly increased performance for each sub-
ject. Using more than two training windows showed
no significantly higher performance. The perfor-
mance does even decrease significantly when combin-
ing more than nine windows (Fig. 7 b). Our results are
consistent with (Blankertz et al., 2006) who stated to
train a classifier on two training windows to obtain a
somewhat time shift invariant classifier for online ap-
plication. Highest improvement of performance could
be shown for subject 4 which obtained clearly low-
est performance with a single training window. How-
ever, by adding training windows, the total amount
of training data is also increased. Hence, we ensured
that the found effect is not just a result of an enlarged
amount of training data by comparing different train-
ing set sizes (150 vs. 160,.. . , 350 examples). Results
showed no training set size effect (p = n.s. for all pair-
wise comparisons). The decrease in performance can
be explained by the increase in variation due to the
high number of different training times. Although all
BIODEVICES2013-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
174
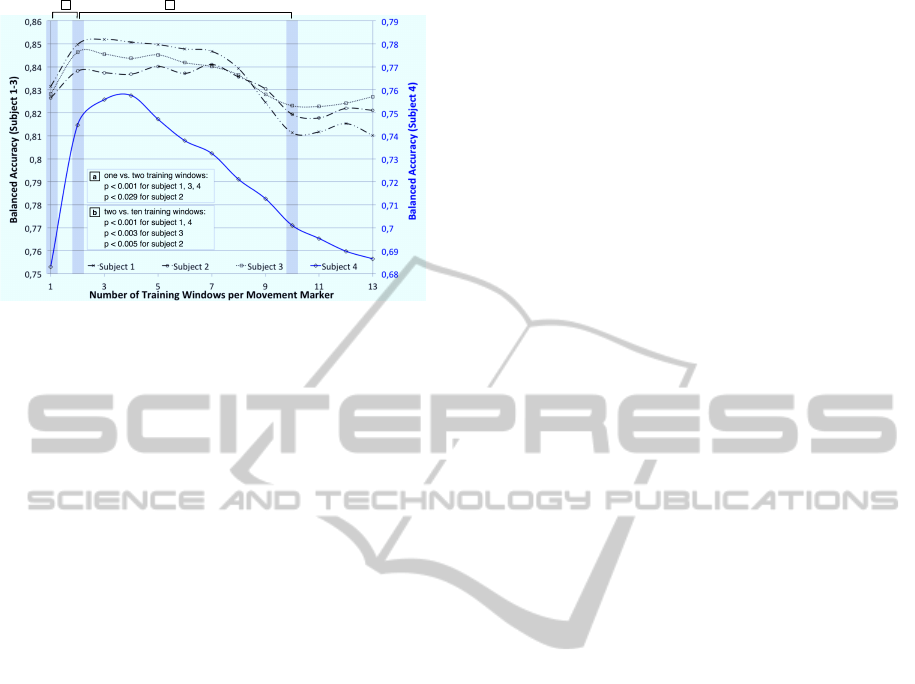
two vs. ten training windows:
p < 0.001 for subject 1, 4
p < 0.003 for subject 3
p < 0.005 for subject 2
one vs. two training windows:
p < 0.001 for subject 1, 3, 4
p < 0.029 for subject 2
a
b
a
b
Figure 7: Movement prediction performance of a 5×2-fold
cross validation for a greedy addition of training windows.
Statistical comparison for each subject of a) one and two
training windows, b) two and ten training windows.
of the 13 training windows under investigation can be
counted as “movement preparation” instances (Fig. 5
c), likely not the same discriminative information is
contained. Evaluation constraints (depending on the
application, e.g., the time when a movement at least
has to be detected) may have an impact on final per-
formance as well.
4.3 EMG-based Movement Prediction
For rehabilitation, EMG is typically used to actively
control devices by detecting movement onset or clas-
sifying the kind of movement, e.g., type of hand
movement (Arvetti et al., 2007). However, EMG can
also be used to predict movement onset since some
time is required to transfer the electrical signal mea-
sured at the muscle into a contraction of the mus-
cle, also known as electromechanical delay. Thus,
we investigated whether EMG can be used to predict
movement onset. In our proposed rehabilitation sys-
tem (see Fig. 1) EMG could further be used to detect
movement onset earlier in time than the force sensors
that are integrated in the exoskeleton to trigger lock-
out (Folgheraiter et al., 2012). Hence, by means of
reliable EMG onset detection the force required for
interaction could possibly further be reduced. Results
of a study investigating reliable prediction and detec-
tion of movement onsets by means of EMG analysis
are presented and discussed in the following.
Experimental Setup. Eight male subjects (right-
handed, and normal or corrected-to-normal vision)
participated. Arm movement was executed imme-
diately or with a delay based on a cue, or self-
determined. Each of the different movements were
performed slowly (movement duration of at least
1000 ms), in normal speed and fast (individual move-
ment duration of at most 120 to 275 ms). For each
of the nine conditions 120 movements had to be per-
formed with two short breaks after 40 and 80 tri-
als. EMG was recorded bipolar with 8 channels
positioned at muscles M. brachioradialis, M. biceps
brachii, M. triceps brachii, M. deltoideus using a
bipolar amplifier (Brain Products GmbH, Munich,
Germany) with a sampling rate of 5000 Hz (low cutoff
of 0.1 Hz and high cutoff of 1000 Hz). The physical
movement onset was recorded with a motion track-
ing system (ProReflex1000, Qualisys AB, Gothen-
burg, Sweden) sampled at 500 Hz using an infrared
sensitive marker placed on the hand of the subject.
The signal was synchronized with the EEG data and
allowed a position estimation of 0.15 mm.
Data Processing. The output of all four EMG chan-
nels as well as the mean of all four channels was used
as input for the movement onset detection. For evalu-
ation of movement prediction, a classified movement
onset was counted as true positive (TP) in case it was
detected 500 to 0 ms before the physical movement
(Fig. 8 a). For evaluation of movement detection,
all classified movement onsets 500 ms before and up
to 500 ms after the physical movement onset were
counted as TPs (Fig. 8 b). Movements that could
not be detected within the given time were counted
as false negative (FN). Movements that were detected
outside of the given time were counted as false pos-
itive (FP) (see Fig. 8). As performance metric, the
balanced accuracy was used. To detect the movement
onset, EMG was preprocessed to enhance the signal-
to-noise ratio by calculating the variance (VAR) and
an adaptive threshold (Equ. 2) was applied to dis-
tinguish the two classes “movement onset” and “no
movement” (Tabie and Kirchner, 2013):
threshold(t) = ¯x
N
(t) + p ∗ σ
N
(t), p ∈ N (2)
where t is the current time point, ¯x
N
(t) and σ
N
(t)
are the mean and standard deviation of a window of
length N ending at time point t and p is a sensitiv-
ity factor. A grid search approach was used to opti-
mize all parameters for classification: EMG electrode
(EMG1, EMG2, EMG3, EMG4, mean of EMG1-
EMG4), window length for VAR (20, 50, 100 ms), p
(0 to 19), window length N (1, 2, 3, 4 s) and the re-
quired interval of data points exceeding the threshold
(0, 4, 10, 20, 40 ms).
Results. Best performance was obtained with
EMG2 (M. biceps brachii), a window length of 20 ms
for VAR, p = 5, N = 2 s, and a 20 ms interval dur-
ing which data points had to exceed the threshold.
TowardsAssistiveRoboticsforHomeRehabilitation
175
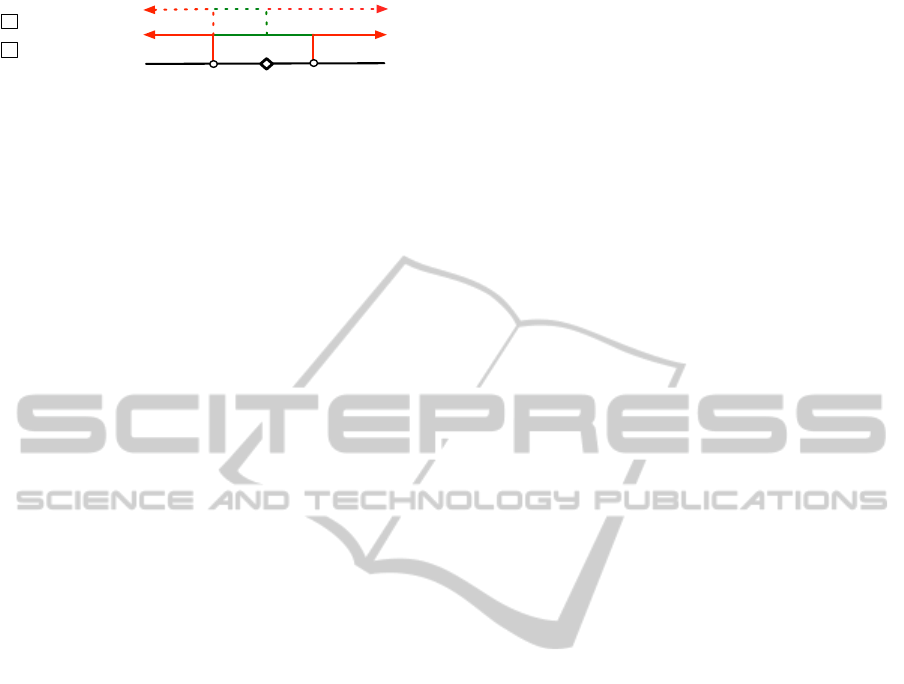
physical
movement onset
FP
500 ms500 ms
TP
TPFP
movement prediction
movement detection
a
b
FP
FP
Figure 8: False positives (FP) and true positives (TP) in
EMG based movement prediction (a) and detection (b).
EMG onset could be detected with a high mean per-
formance (BA = 0.88). Movement prediction showed
only a slightly but significant lower mean perfor-
mance of BA = 0.81 [mean difference = 0.075, SE
= 0.007; F(1,213) = 129.73, p = 0.001]. To quantify
how early a prediction of upcoming movements was
possible, we further calculated the mean time differ-
ence between physical movement onset and our pre-
diction which was 95.26ms (SE = 27.76). Results
clearly show that movement onset can be predicted
based on EMG data, i.e., before the physical move-
ment onset.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
OUTLOOK
We presented results of an experiment, which inves-
tigated the performance of our control approach of
a multi-contact-point and wearable exoskeleton with
respect to the interaction between human and ex-
oskeleton. It could be shown that the exoskeleton
behaves transparent to the user and thus can act as
a guidance and support system for human arm move-
ment without impeding the person wearing it. The
presented exoskeleton so far only supports one arm.
In the design decisions for a full upper body rehabil-
itation that covers a wide range of patients, it is use-
ful to consider both arms and the torso. Hence, the
kinematics of a new exoskeleton has to take into ac-
count both shoulders and the spine. We are currently
designing a new upper-body system which focuses on
full-force feedback and a comfortable way to wear the
system.
Results of studies presented in Sec. 4.2 and 4.3
showed that upcoming movements can be predicted
by EMG and EEG analysis with a similar high per-
formance. Reliability of EEG-based prediction can
be enhanced by appropriate combination of training
data. This should help when analyzing data contain-
ing less information, e.g., in case of neuronal impair-
ment. Currently we are planning studies that allow to
record EMG and EEG data during supported move-
ments on different groups of patients to further in-
vestigate possible improvements during data process-
ing and classification and by combining psychophys-
iological measures, e.g., EMG and EEG data. The
integration of gaze control into real and virtual sce-
narios using eye tracking based on technical devices
(eye tracker) is the next step, that will allow interac-
tion within the virtual scenario even in case of mas-
sive neuronal and muscular impairment.
By adapting the support to the requirements of the
patients, not only in respect to the severity of neu-
ronal and muscular impairment but also in respect to
the progress of rehabilitation, support can be mini-
mized by time based on the progress in rehabilitation.
Automatically recorded and analyzed psychophysio-
logical and interaction data of the patient can be a
good indicator for progress in rehabilitation. This and
the parallel analysis and integration of different psy-
chophysiological data raises high requirements on the
effectiveness of computational devices regarding cal-
culation capacity and time as well as power consump-
tion. Hence, to accomplish rehabilitation that is fully
integrated into the people’s everyday life and adapts
to the patient’s state requires further research and de-
velopment in software and hardware design.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by the German Ministry of
Education and Research, (grant no. 01IW07003 &
01IW10001) and by the German Ministry of Eco-
nomics and Technology (grant no. 50RA1011 &
50RA1012). We want to thank Su Kyoung Kim,
Marc Tabie, Hendrik W
¨
ohrle, Niels Will, Jan Hen-
drik Metzen and Johannes Teiwes for their help with
the manuscript and data analysis.
REFERENCES
Arvetti, M., Gini, G., and Folgheraiter, M. (2007). Classi-
fication of EMG signals through wavelet analysis and
neural networks for controlling an active hand pros-
thesis. In Proc. 2007 IEEE 10th Intern. Conf. on Re-
habilitation Robotics, pages 531–536, Noordwijk.
Beer, R., Naujokas, C., Bachrach, B., and Mayhew, D.
(2008). Development and evaluation of a gravity com-
pensated training environment for robotic rehabilita-
tion of post-stroke reaching. In Conf. on Biomed.
Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob-2008), pages
205–210, Scottsdale.
Blankertz, B., Dornhege, G., Lemm, S., Krauledat, M., Cu-
rio, G., and M
¨
uller, K.-R. (2006). The Berlin Brain-
Computer Interface: Machine learning based detec-
tion of user specific brain states. J. of Universal Com-
puter Science, 12(6):581–607.
Brodersen, K., Ong, C., Stephan, K., and Buhmann, J. M.
(2010). The balanced accuracy and its posterior dis-
BIODEVICES2013-InternationalConferenceonBiomedicalElectronicsandDevices
176

tribution. Proc. 20th Intern. Conf. on Pattern Recog-
nition, pages 3121–3124.
Clark, M. and Smith, D. (1999). Psychological correlates of
outcome following rehabilitation from stroke. Clinical
Rehabilitation, 13(2):129–140.
Folgheraiter, M., Jordan, M., Straube, S., Seeland, A., Kim,
S. K., and Kirchner, E. A. (2012). Measuring the Im-
provement of the Interaction Comfort of a Wearable
Exoskeleton. Intern. J. of Social Robotics, 4(3):285–
302.
Folgheraiter, M., Kirchner, E. A., Seeland, A., Kim, S. K.,
Jordan, M., W
¨
ohrle, H., Bongardt, B., Schmidt, S.,
Albiez, J., and Kirchner, F. (2011). A multimodal
brain-arm interface for operation of complex robotic
systems and upper limb motor recovery. In Proc.
4th Int. Conf. Biomed. Electronics and Devices, pages
150–162, Rome.
Gancet, J., Ilzkovitz, M., Cheron, G., Ivanenko, Y.,
van der Kooij, H., van der Helm, F., Zanow, F., and
Thorsteinsson, F. (2011). MINDWALKER: A Brain
Controlled Lower Limbs Exoskeleton for Rehabilita-
tion. Potential Applications To Space. In 11th Symp.
on Adv. Space Techn. in Robotics and Automation,
pages 12–14.
Guidali, M., Duschau-Wicke, A., Broggi, S., Klamroth-
Marganska, V., Nef, T., and Riener, R. (2011). A
robotic system to train activities of daily living in a
virtual environment. Med. and Biol. Engineering and
Computing, 49(10):1213–1223.
Hesse, S., Werner, C., and Brocke, J. (2009). Maschinen-
und Robotereinsatz in der Neurorehabilitation. Or-
thop
¨
adie-Technik, 2:74–77.
Hogan, N., Krebs, H., Charnnarong, J., Srikrishna, P., and
Sharon, A. (1992). MIT-MANUS: a workstation for
manual therapy and training I. In Proc. Intern. Works.
on Robot and Human Comm., pages 161–165.
Jordan, M., Benitez, L. M. V., Schmidt, S., Folgheraiter,
M., and Albiez, J. (2012). Model-Based Control and
Design of a Low-Pressure Fluid Actuation System for
Haptic Devices. In Proc. 13th Intern. Conf. on New
Actuators (Actuator-12), pages 295–298, Bremen.
Kelly, R. (1997). PD Control with Desired Gravity Com-
pensation of Robotic Manipulators: A Review. The
Intern. J. of Robotics Research, 16(5):660–672.
Kornhuber, H. H. and Deecke, L. (1965). Hirnpoten-
tial
¨
anderungen bei Willk
¨
urbewegungen und passiven
Bewegungen des Menschen: Bereitschaftspotential
und reafferente Potentiale. Pfl
¨
uger’s Archiv f
¨
ur die
ges. Phys. des Menschen und der Tiere, 284(1):1–17.
Leeb, R., Keinrath, C., Friedman, D., Guger, C., Scherer,
R., Neuper, C., Garau, M., Antley, A., Steed, A., and
Slater, M. (2006). Walking by thinking: the brain-
waves are crucial, not the muscles! Presence: Teleop-
erators and Virtual Environments, 15(5):500–514.
Lenzi, T., De Rossi, S., Vitiello, N., and Carrozza, M.
(2012). Intention-based EMG Control for Powered
Exoskeletons. IEEE Transa. on Biomed. Engineering,
59(8):2180–2190.
Meyer-B
¨
ase, U. (2007). Digital Signal Processing with
Field Programmable Gate Arrays. Springer-Verlag,
Berlin, Heidelberg, 3rd edition.
Mihelj, M., Nef, T., and Riener, R. (2007). ARMin II -
7 DoF rehabilitation robot: mechanics and kinemat-
ics. In 2007 Intern. Conf. on Robotics and Automa-
tion, pages 4120–4125.
Nocedal, J. and Wright, S. (1999). Numerical Optimization.
Springer Series in Operations Research. Springer-
Verlag, New York.
Otsuka, T., Kawaguchi, K., Kawamoto, H., and Sankai, Y.
(2011). Development of Upper-limb type HAL and
Reaching Movement for Meal-Assistance. In Proc.
2011 IEEE Intern. Conf. on Robotics and Biomimetics
(ROBIO-11), pages 883–888.
Platz, T. and Roschka, S. (2009). Rehabilitative Therapie
bei Armparese nach Schlaganfall. Neurol. Rehabil.,
15(2):81–106.
Santucci, E. and Balconi, M. (2009). The multicompo-
nential nature of movement-related cortical potentials:
functional generators and psychological factors. Neu-
ropsychological Trends, (5):59–84.
Shyu, K.-K., Lee, P.-L., Lee, M.-H., Lin, M.-H., Lai, R.-J.,
and Chiu, Y.-J. (2010). Development of a Low-Cost
FPGA-Based SSVEP BCI Multimedia Control Sys-
tem. IEEE Transa. on Biomed. Circuits and Systems,
4(2):125–132.
Tabie, M. and Kirchner, E. A. (2013). EMG Onset
Detection—Comparison of different methods for a
movement prediction task based on EMG. In BIOSIG-
NALS. SciTePress. Accepted.
Takahashi, C. D., Der-Yeghiaian, L., Le, V., Motiwala,
R. R., and Cramer, S. C. (2008). Robot-based hand
motor therapy after stroke. Brain, 131(2):425–437.
Villiger, M., Hepp-Reymond, M.-C., Pyk, P., Kiper, D.,
Eng, K., Spillman, J., Meilick, B., Estevez, N., Kol-
lias, S. S., Curt, A., and Hotz-Boendermaker, S.
(2011). Virtual reality rehabilitation system for neu-
ropathic pain and motor dysfunction in spinal cord in-
jury patients. In 2011 Intern. Conf. on Virt. Rehab.
(ICVR), pages 1–4.
Volpe, B., Krebs, H., Hogan, N., Edelstein, O., Diels, C.,
and Aisen, M. (2000). A novel approach to stroke
rehabilitation: robot-aided sensorimotor stimulation.
Neurology, 54(10):1938–1944.
Zander, T. O., Gaertner, M., Kothe, C., and Vilimek, R.
(2010). Combining eye gaze input with a brain–
computer interface for touchless human–computer in-
teraction. Intern. J. of Human-Computer Interaction,
27(1):38–51.
TowardsAssistiveRoboticsforHomeRehabilitation
177
