
Managing Personality Influences in Dialogical Agents
Jean-Paul Sansonnet
1
and Franc¸ois Bouchet
2
1
LIMSI-CNRS, BP 133, 91403 Orsay Cedex, France
2
SMART Laboratory, McGill University, 3700 McTavish Street, Montreal, Canada
Keywords:
Cognitive Agent Modeling, Personality Traits, Conversational Agents.
Abstract:
We present in this article an architecture implementing personality traits from the FFM/NEO PI-R taxonomy as
influence operators upon the rational decision making process of dialogical agents. The objective is to separate
designer-dependent resources (traits taxonomies, influence operators, behaviors/operators links) from the core
part of the computational implementation (the personality engine). Through a case study, we show how
our approach makes it easier to combine various resources and to observe various scenarios within a single
framework.
1 INTRODUCTION
Designing virtual humans or agents to be used as
long-term companions require them to display a be-
lievable behavior which remains consistent over time.
In psychology, the concept of personality trait (Cattell
et al., 1970; Goldberg, 1990) is defined as an habit-
ual pattern of behavior or emotion, and therefore pro-
vides an appropriate theoretical foundation to build
upon to reach the aforementioned goal. Once person-
ality traits have been identified (or designed, in the
case of an artificial agent), it is possible to anticipate
(or define) their influence, in order to know extent
how one will usually react in a particular situation:
not only from an emotional perspective, with works
from (Ortony et al., 1988) often used to implement
psychological phenomena into artificial agents, but
also from a rational point of view (Damasio, 1994), as
studied for artificial agents by Rousseau and Hayes-
Roth (Rousseau, 1996; Rousseau and Hayes-Roth,
1996).
However, most research works on the computa-
tional implementation of psychological phenomena
(cf. discussion in Section 4) usually fail to take into
account two key notions: coverage, as they often fo-
cus only on a small subset of psychological phenom-
ena (e.g. considering few traits), and comprehensive-
ness, because they resort to procedural implementa-
tions (e.g. hard-coded rules) therefore excluding ex-
perts (i.e. psychologists) from the agent’s behavior
design process. The work presented in this paper aims
at addressing those two restrictions.
Coverage Issues. A key question regarding the prin-
ciple of influence lies in the actual extent of the
psychological influence over the reasoning. Typ-
ically, artificial agents focus on distinct subsets
of domain-dependent psychological notions (e.g. a
poker player (Findler, 1977)). However, the growing
interest in conversational agents (Cassell et al., 2000)
opens new perspectives where psychological notions
become first class citizens (e.g. a different approach
to poker player (Koda and Maes, 1996)), thus leading
to a need not only for larger psychological domains,
but also for a more generic way to handle them.
Research works in psychology offer several per-
sonality traits taxonomies, but because such tax-
onomies try to cover a large set of aspects of the per-
sonality of a person, they are in turn too general from
a computational viewpoint: Catell’s 16 personality
factors (Cattell et al., 1970), only 5 large classes in
a single level for the Five Factor Model (FFM) (Gold-
berg, 1992), and 30 bipolar classes in the two-level
Revised NEO Personality Inventory (FFM/NEO PI-
R), which extends FFM. It is therefore difficult
to define a precise interpretation of their classes in
terms of operators over the rational process of agents,
even for FFM/NEO PI-R, the most fine-grained of the
commonly used taxonomies. For example, this led
us (Sansonnet and Bouchet, 2010) to propose an ex-
tended version of FFM/NEO PI-R with a third level of
so-called behavioral schemes that increases the pre-
cision in terms of classes (69 bipolar schemes) and
lexical semantics (each scheme being defined by a set
of actual behaviors).
89
Sansonnet J. and Bouchet F..
Managing Personality Influences in Dialogical Agents.
DOI: 10.5220/0004249300890098
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2013), pages 89-98
ISBN: 978-989-8565-38-9
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Comprehensiveness Issues. Assuming that a well-
grounded and precise taxonomy of personality is
available, a second question follows: what kind
of influence operators over the agent’s process can
be elicited from and associated with the taxonomy
classes? Some works have proposed models describ-
ing how influences operators can be associated with
taxonomy classes (cf. examples in Section 4), proving
the feasibility of such an approach on case studies, but
they are usually based on small subsets of arbitrarily
chosen psychological behaviors. Therefore there is a
need for a more comprehensive approach to the sys-
tematic implementation of complete personality traits
domains (e.g. covering FFM) onto the rational process
of artificial agents
1
, with two main requirements:
– Computational implementation: no complete, or-
thogonal, and approved set of operators that would
apply to main agent frameworks (from different fields
such as artificial intelligence, multi-agents systems or
intelligent virtual agents) currently exists. A modular
and flexible approach is needed, to allow subsets of
operators to be implemented in distinct frameworks.
– Psychological relevance: we need a model of re-
lationships between classes and operators approved
by psychologists. It would require a declarative ap-
proach, where distinct models of relationships could
be shared by psychologists for experimentation and
discussion, thus excluding procedural encoding.
Managing Influences with Personality Engines.
We propose an approach in which resources are both
application-dependent and designer-dependent repre-
sentations, and where the personality engines com-
bine those resources to implement actual scenarios.
This concept of personality engine allows to easily
implement and test various psychological hypotheses
through resource combination, but also to apply them
to a wide variety of application domains for experi-
mentation and evaluation purposes.
This article is organized as follows: in section 2,
we introduce the enriched taxonomy of personality
we have chosen to use in this study, show how it can
be used on an example from the literature and intro-
duce the concepts necessary to define a personality
engine. Section 3 presents a case study using a sim-
plified world of dialogical agents, shows how those
agents can be provided with a personality engine af-
fecting the way they communicate with each other,
and demonstrates how it can be used to implement the
example from section 2. Section 4 compares our ap-
proach to other attempts at implementing personality
features in agents.
1
Complete coverage has been attempted for emotions,
as in OCC (Ortony et al., 1988).
Table 1: Two-level FFM/NEO PI-R taxonomy.
FFM Traits FFM/NEO PI-R facets (each symbol in-
cludes a + and a - (antonym) pole)
Openness Fantasy, Aesthetics, Feelings, Actions, Ideas, Val-
ues
Conscientious-
ness
Competence, Orderliness, Dutifulness,
Achievement-striving, Self-discipline, Deliberation
Extraversion Warmth, Gregariousness, Assertiveness, Activity,
Excitement-seeking, Positive-emotions
Agreeableness Trust, Straightforwardness, Altruism, Compliance,
Modesty, Tender-mindedness
Neuroticism Anxiety, Angry-Hostility, Depression, Self-
consciousness, Impulsiveness, Vulnerability
2 THE PERSONALITY ENGINE
2.1 An Enriched Personality Domain
2.1.1 The Traditional FFM/NEO PI-R Taxonomy
Several theoretical approach to study human person-
ality have been developed over years: Freudian psy-
choanalysis, types and traits, Maslow and Rogers’
humanistic psychology, Bandura’s social-cognitive
theory, etc. Among them, personality traits have
been widely used as a ground for studies in affec-
tive computing (Rizzo et al., 1997) and cognitive
agents (Gratch and Marsella, 2004). We will therefore
rely on them and focus on the FFM/NEO PI-R taxon-
omy (Goldberg, 1981), which is the most prominent
one in the context of computational studies (cf. (John
et al., 2008)). The FFM/NEO PI-R taxonomy is made
of five classes of psychological behaviors, also called
O.C.E.A.N. traits. Each FFM trait is divided into six
sub-classes (called facets) resulting in 30 bipolar
2
po-
sitions (Costa and McCrae, 1992), listed in Table 1.
The semantics of each facet is intuitively defined by
a unique gloss
3
, e.g. facet Fantasy is defined by “recep-
tivity to the inner world of imagination” and Aesthetics
by “appreciation of art and beauty”.
2.1.2 The Enriched FFM/NEO PI-R/BS
Taxonomy
The FFM/NEO PI-R taxonomy has the advantage of
being grounded on state of the art research in psychol-
2
Each facet has a positive (resp. negative) pole noted +
(resp. −) associated with the concept (resp. the antonym of
the concept). Facets are usually referred to using the name
of their + pole.
3
A gloss is a short natural language phrase defining in-
tuitively a lexical semantics sense, as found in dictionaries
or in WordNet synsets (Fellbaum, 1998).
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
90

ogy, which allows us to safely consider that it covers
a large part of the domain of a person’s personality
traits. However, when one is interested in the compu-
tational expression of psychological phenomena such
as personality traits, the facet definitions (based on a
unique gloss per facet as in the aforementioned exam-
ples) are too general from two complementary points
of view:
1) They can cover a large set of psychological behav-
iors so that scripting the psychologyof a character can
be imprecise. A third level, breaking down facets into
smaller subsets would facilitate an association with
more specific behaviors.
2) Definitions are so general that defining a precise
functional relation between facets and influence op-
erators can be difficult, which also encourages to go
towards breaking down facets into more specific psy-
chological behaviors.
These considerations led us to rely on an en-
riched three-level taxonomy of FFM/NEO PI-R, called
FFM/NEO PI-R/BS (Bouchet and Sansonnet, 2010)
and available on the Web
4
, in which each facet of
FFM/NEO PI-R, is decomposed in so-called behavioral
schemes (or schemes in short). It extends FFM/NEO
PI-R by associating glosses to the senses of a large
set of 1055 personality adjectives, using the WordNet
database (Fellbaum, 1998), completed and aligned
with 300 Goldberg’s questionnaire so-called q-items
5
,
and for each FFM/NEO PI-R position, glosses and
items have been clustered into sets
6
of congruent op-
erational behaviors: the schemes.
Quantitatively, FFM/NEO PI-R/BS taxonomy fea-
tures: N
facet
= 30, N
gloss
= 766, N
scheme
= 69,
N
glosses/facet
= 26 and N
schemes/facet
= 2.3.
2.1.3 Example: Defining a Personality Profile
into the FFM/NEO PI-R/BS Taxonomy
We propose to consider an example taken from
CyberCafe in Rousseau and Hayes-Roth (1996),
in which several characters who endorse the same
interactional role of a waiter (w
i
) have distinct
psychological profiles P(w
i
), entailing distinct psy-
chological behaviors B(w
i
) such as:
P(w
1
) realistic, insecure, introverted, passive, secretive
B(w
1
) Such a waiter does and says as little as he can
P(w
2
) imaginative, dominant, extroverted, active, open
B(w
2
) This waiter takes initiative, comes to the cus-
tomer without being asked for, talks much
4
http://perso.limsi.fr/jps/research/rnb/toolkit/taxo-glosses/taxo.htm
5
http://ipip.ori.org/newNEOKey.htm
6
Like facets, schemes are bipolar and are often referred
to by their +pole.
Considering the psychological profile P(w
1
) of
waiter w
1
, it can easily be transposed onto the
FFM/NEO PI-R/BS taxonomy in terms of scheme ac-
tivations (formal definition is given in Section 2.2.3):
P’(w
1
) = {
realistic ⇒ O-fantasy-PRACTICAL;
insecure ⇒ C-competence-INSECURE;
introverted ⇒ E*(-COLD, -NONGOSSIPMONGER, -SOLITARY,
-UNCOMMUNICATIVE, -UNCHARISMATIC,
-DISCRET, -SUBMISSIVE, -PLEADING, -
LANGUID, -APATHETIC, -ASCETIC, -BLASE);
passive ⇒ E-activity-APATHETIC;
secretive ⇒ A-trust-SECRETIVE
}
where elements of P(w
1
) are transposed in or-
der, separated by ’;’ in P’(w
1
). We can notice that
this profile mainly activates negative poles and that a
FFM/NEO PI-R/BS scheme can easily be found to cor-
respond to each P trait (which means that P traits are
more schemes than actual FFM traits or FFM/NEO PI-
R facets). The only exception is introverted, which is
associated to the whole FFM trait -Extraversion, thus en-
tailing 12 schemes, which adds precision. The same
remarks apply to P(w
2
) but for the activation of pos-
itive poles; it is actually likely that P(w
1
) and P(w
2
)
were hand-built.
P’(w
1
) offers a more systematic positioning in
FFM/NEO PI-R and a more precise behavioral defi-
nition because the definition B(w
1
) is replaced with
the glosses associated with the activated schemes in
FFM/NEO PI-R/BS. For example, -PRACTICAL is defined
by the WordNet glosses (N
i
) and Goldberg’s q-items
(Q
i
) associated to it:
N618 guided by practical experience and observation rather than theory
N626 aware or expressing awareness of things as they really are
N788 freed from illusion
N1232 concerned with the world or worldly matters
N795 sensible and practical
Q6 Spend time reflecting on things
Q7 Seldom daydream
Q8 Do not have a good imagination
Q9 Seldom get lost in thought
In summary, FFM/NEO PI-R/BS offers a pre-
cise grounding for personality description: not
only it covers the eight classes proposed in Cyber-
cafe (Rousseau, 1996), but it also enables a more pre-
cise and practical behavioral description, which justi-
fies our decision to use it in the following sections.
2.2 Architecture of a Personality Engine
2.2.1 Personality Engine Structure
We define a personality engine
PE
as a 5-tuple such as
PE
= h
O
,
W
,
T
,Ω
W
,
M
i where:
–
O
is a personality ontology that enables precise de-
ManagingPersonalityInfluencesinDialogicalAgents
91

scriptions of personalities. We will use in this pa-
per the set Σ of bipolar schemes from FFM/NEO PI-
R/BS (described in Section 2.1.2), thus |Σ| = 69. The
subset of positive (resp. negative) positions is de-
noted +Σ (resp. −Σ), and their union is ±Σ such as
±Σ = +Σ ∪ −Σ and |±Σ| = 138;
–
W
is an agent world model that includes: their inter-
nal structure
W
s
; their external communication proto-
cols
W
c
; their rational decision making process
W
r
. For
example, a BDI-based model or a more specific one,
such as the one defined in Section 3.1.1;
–
T
is an application topic enabling the instantiation
of
W
in a particular case;
– Ω
W
is a set of influence operators over
W
r
∪
W
c
=
W
rc
;
–
M
is an activation matrix, establishing a relation over
±Σ× Ω
W
.
O
,
W
and
T
are considered as given resources,
whereas Ω
W
and
M
must be elicited from the resources,
as explained in 2.2.2 and 2.2.3.
2.2.2 Influence Operators Elicitation
Given an agent model
W
, influence operators are meta
rules ω ∈ Ω
W
controlling or altering the non structural
parts of
W
, i.e.
W
rc
.
Example. Let us consider some plan in
W
r
contain-
ing the expression e = PAR[a
1
,a
2
,a
3
], which is a set
of three actions to be executed in no particular or-
der (like operator PAR of CSP). One can define the
rule ω
1
= PAR → SEQ which, applied to e, can intu-
itively stand for an indication to an agent to execute
its actions routinely (and correctly). On the contrary,
a rule ω
2
= SEQ → PAR could stand for a disorderly
agent (and sometimes lead to incorrect executions of
the plan).
This simple example shows that whenever, for-
mally, any rule over
W
rc
is an influence operator, only
those that could be interpreted in terms of psycho-
logical behaviors are actually relevant. Consequently,
one has to consider operator elicitation as an opera-
tion from
W
rc
×
O
7−→ Ω
W
rather than
W
rc
7−→ Ω
W
.
The definition of an algorithm that takes a cou-
ple of resources
W
and
O
and automatically produces
the
7
set Ω
W
is still an open question. For the time be-
ing, we have to restrict to hand-built operators sets,
which are de facto designer(s)-dependent. The no-
tion of personality engine makes it possible to handle
the management of this diversity (e.g. distinct propo-
sitions
PE
i
, based over the same
W
and/or
O
, can be
tested and systematically compared). An example of
operator elicitation is detailed in Section 3.2.1.
7
using ‘the’ raises issues of existence (no possible in-
fluences found) and unicity (several distinct sets found thus
prompting an order relation).
Operators Intensity and Direction. Operators like
PAR and SEQ, are activated straightforwardly: they
are applied or not. However, various operators can
be activated in more complex manners through argu-
ment passing. We will consider two frequent cases:
– An intensity is given, cf. activation levels in Table 3;
– Operators also working in reverse or antonym mode
can be given a direction (e.g. operator ω
−safe
in Sec-
tion 2.3.1).
2.2.3 Activation Matrix Elicitation
Once given the set schemes σ ∈ ±Σ and a set of influ-
ence operators ω ∈ Ω
W
, the designer(s) of a particular
processing engine must elicit how ±σ
i
are linked to
ω
i
, that is which schemes activate which operators.
This relation, which is again designer-dependent, is
established by a multi-valued matrix
M
of so-called ac-
tivation levels λ
i, j
such that
M
= ±Σ × Ω
W
. Elements
λ
i, j
of
M
have the following values and conventions:
2 activate operator with strong force
1 activate operator with moderate force
0 the operator is deactivated
-1 activate antonym operator (if it exists) with
moderate force
-2 activate antonym operator (if it exists) with
strong force
2.3 Instantiating Personality Engines
Once given a particular personality engine
PE
0
, one
has a symbolic structure that can be instantiated into
actual situations varying from two main points of
view: application topics and personality profiles.
2.3.1 Application Topics
Let
T
0
be a particular topic providing a set of available
actions α
i
∈
A
(
T
0
). The topic also provides influence
operators of
PE
0
with application-dependent informa-
tion about α
i
. For example, let ω
+safe
be an oper-
ator that sorts a set of actions from the safest to the
least safe : ω
+safe
.
= Sort({α
i
},≺
danger
). To be oper-
ational, operator ω
+safe
requires topic
T
0
to provide a
measure function µ
danger
:
A
(
T
0
) 7−→ [0,1]. Operator
ω
+safe
has an antonym, ω
−safe
, that sorts actions in
reverse order.
2.3.2 Personality Profiles
Intuitively, personality profiles are often defined as
sets of adjectives/adverbs describing the behavior of
a person. For instance, in the Cybercafe example (cf.
Section 2.1.3), personality profile P(w
1
) was first de-
fined with a set of common words: {realistic, inse-
cure, introverted, passive, secretive}. The research
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
92

about personality trait taxonomies enables more pre-
cise definitions that use a mapping in terms of sets of
well-grounded concepts, like P’(w
1
). Using FFM/NEO
PI-R/BS prompts the following definition:
Given an individual x, its personality pro-
file P(x) can be defined as a set of |Σ| functions
p(σ
i
) : Σ −→ {+,≍,−} where:
≍ means that with regard to scheme σ
i
, person x’s
behavior is not significantly deviant from an aver-
age behavior;
+ means x’s behavior is deviant from average ac-
cording to +pole;
− means x’s behavior is deviant from average ac-
cording to -pole.
Notation. When one considers the 69 schemes of Σ,
people tend to exhibit an average behavior for most
of them. Consequently P(x) is often a scarce vector
with most elements valued with ≍, so P(x) is prefer-
ably given as a set of non ≍ schemes. For example,
Paul’s personality will be denoted in short: P(Paul) =
{-HARDWORKER, -ATTENTIVE, HARMLESS, EMPATHIC, -SHOWY}, ig-
noring the 64 other schemes for which his behavior
doesn’t stand out.
3 CASE STUDY
In this section we present a case study showing how
personality engines can be defined, then instantiated
in actual situations. To support the eliciting process
of influence operators, one must chose an application
model, for example, to focus on agents’ communica-
tion, well-used KQML, ACL-FIPA or BDI with logics
(KGP, 2APL, Golog-based etc.).
3.1 TALKINGS: a Typical World of
Dialogical Agents
We consider here a simplified model, called TALK-
INGS (a simple world of agents interacting through
message passing), that allows a comprehensive pre-
sentation of our approach. For this example, we have
chosen to focus on conversational agents, a fast grow-
ing application domain. Consequently, we will con-
sider traits and operators associated with social and
dialogical aspects of the agents, which cover about
55% of the FFM/NEO PI-R/BS schemes(Sansonnetand
Bouchet, 2010). The process described here is com-
plementary to non-dialogical aspects of the agents
studied in (Bouchet and Sansonnet, 2011)).
3.1.1 Agent Model
Let TALKINGS be an actual world composed of phys-
ical or abstract entities, which is accessed through a
representation of its entities into a symbolic model
M . An entity e
i
∈ M is defined in L
M
, its associated
language of description, as a set of rule-based defini-
tions of the general form D
i
= le ftpart 7→ rightpart
such that ∀e
i
∈ L
M
; e
i
= {D
i
}.
Agents a
i
∈ A represent dialogical entities of M that
can perform practical reasoning. An agent a
i
∈ A is
defined as a 5-tuple hid,K,S, Φ,Ψi where:
– id is a string providing a unique identifier for the
agent;
– Knowledge base K = k
i
∈ L
k
is a set of propositions
over M ;
– Social base S is the set of roles endorsed by the
agent (over TALKINGS, or relatively to another agent
of TALKINGS);
– Feature base Φ is the set of physical attributes of the
agent (to simplify, Φ will not be considered further);
– Psychological base Ψ = Ψ
T
∪ Ψ
M
is a set of static
traits Ψ
T
and dynamic moods Ψ
M
(dynamic moods
are out of scope here since we focus on personality
associated with static traits).
3.1.2 Message Structure
Collectives c
i
of TALKINGS agents support the oper-
ation SEND[t, a,{b
i
},m] enabling the transfer of mes-
sage m at turn t between the sender agent a and one
or more receiver agents {b
i
}. In the following, we re-
strict this definition to interactions between the cou-
ple of agents a ⇔ b (in the following, a denotes the
so-called speaker and b its interlocutor) hence con-
sidering operations of the form SEND[t, a,b,m]. A
message m into such SEND operations contains four
expressions, explicitly stated by speaker agent a to-
wards interlocutor agent b:
m = hReaction, Proaction, Forces, Contenti
Reaction is the attitude that a adopts, and expresses
explicitly, in reaction to its own evaluation of the pre-
vious message from b at turn t − 1. Reactions are or-
ganized on a -/+ scale, ranging from total disagree-
ment (noted No) to total agreement (noted Yes). The
first message of the first turn of a session has an empty
reaction (noted –).
Proaction is the main attitude stated by a towards b.
Two main proactive attitudes are considered, accord-
ing to the direction of the intention of a:
– Ask, represented as a
A Content
←−−−−− b, where agent a
sends a query to b about Content;
– Propose, represented as a
P Content
−−−−−→ b, where agent
a sends a proposition to b about Content.
ManagingPersonalityInfluencesinDialogicalAgents
93
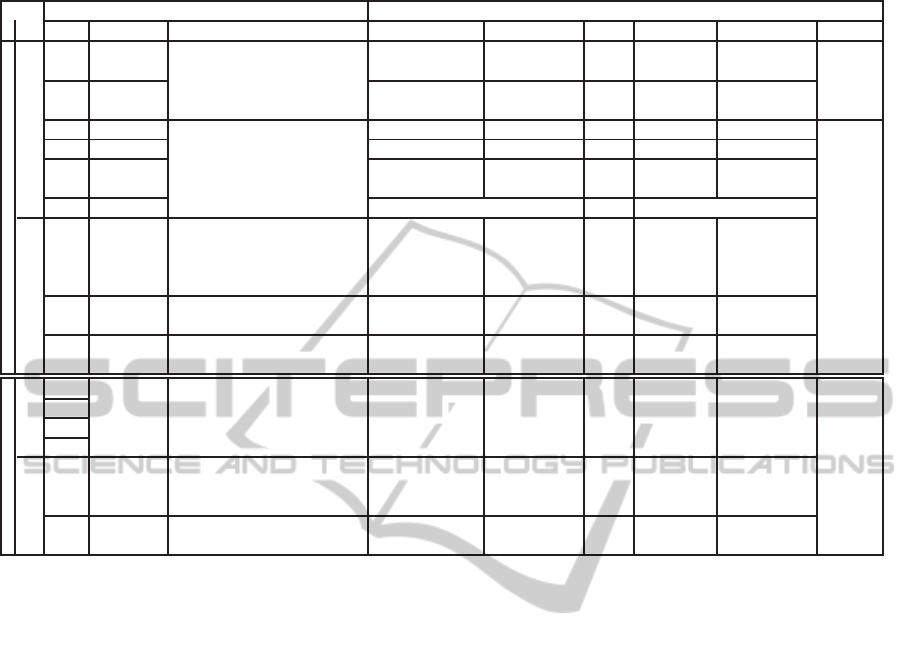
Table 2: Intuitive semantics of the levels of activation of the message operators.
levels Operators Activation levels λ
1 2 CODE Label Definition -2 -1 0 1 2 Range
Proaction
Explicit
A Ask
probability for the agent to tend
to use Ask or Propose
- - none ask if
needed
ask even if not
needed
J0,2K
P Propose - - none propose if
needed
propose even if
not needed
D Dominance
probability for the agent to use
the force or its antonym
inferior supporter none equal superior
J−2,2K
F Feeling aggressive cold none polite warm
M Motivation show false motive hide motive none motive if
needed
motive even if
not needed
I Incentive menace none promise
Implicit
G Guess capacity of the agent to perceive
other agents in terms of their
rational processes, their mental
states, etc.
perceive false do not perceive none perceive if
explicit
perceive even
if not explicit
C Conflict attitude of the agent about risking
to provoke conflicts
like conflicts accept con-
flicts
none dislike con-
flicts
avoid any con-
flict
S Sincerity sincerity of the agent about all
parts of a sent message
tell false facts actively hide
facts
none frank very/too frank
Reaction
Explicit
A+
Reaction
typical reaction to an Ask or
Propose depending on the global
evaluation by b of the Forces
expressed by a
always no
yes but with
protest
none
yes but
can be
conditional
always yes
J−2,2K
A-
P+
P-
Implicit
B Bond reaction to results of G (e.g. per-
ceiving a is sad, b will: +) feel
sad; 0) not care; -) feel happy)
bond to reverse do not bond none bond if
needed
bond even if
not needed
N Negotiate reaction in the management of
conflicts existing and explicit
increase sustain none settle always yield
Note: level 2 (resp.-2) includes level 1 (resp.-1), i.e. it can exhibit behaviors of level 1 (resp.-1)
Forces are optional modalities of proaction operators
(A|P), explicitly expressed by a, in order to contribute
to the expected success of the message. A message
from a is considered successful when in reply from b,
the reaction of b is positive and the proaction of b is
relevant to a. We consider four distinct forces, each
organized as a bipolar -/+ scale:
– Dominance ranges from force -submissive to +dom-
inant, which can modalize operators A|P, e.g. A -
submissive can be viewed as begging and A +dominant
as requesting.
– Feelings ranges from force -aggressive to +affective,
which can accompany operators A|P.
– Motivation ranges from force -hide to +open. An
agent using open force explains clearly and frankly
the rational motive(s) of the sending. Conversely, the
agent can try to hide its rational motives or even to
express untrue motives.
– Incentive ranges from force -menace to +promising.
An agent a using +promise force attempts at facilitat-
ing the success of its message by providing rational
positive reasons for b to react positively to it, or by ad-
dressing direct rewards. Conversely, a can try to ob-
tain agreement from b through-menace (e.g.by stating
rational negative outcomes for b if it disagrees) or by
addressing direct threats.
Content is the body of the message, that is the object
of the proaction. Five main classes of objects are con-
sidered:
– Knowledge is a fact k
i
∈ L
k
;
– Action is an operation upon the world. For example,
A a(x) means a asks b to execute a(x), while P a(x)
means a intends to execute a(x);
– Resource is an entity in the world that can be pos-
sessed and transferred;
– Norm describes rights or duties of agents in a given
collective c
i
;
– Emotion describes a personal mental state (e.g.
mood) or an interpersonal affective relationship.
With these definitions, the structure of a message m
can be represented as:
− |Yes|No × A|P × [D][F][M][I] × k|a|r|n|e
where | separates alternatives, [] embraces op-
tional forces, k,a, r,n,e are the five types of con-
tent and × is the Cartesian product, thus defin-
ing the message domain. A turn t is a couple
hSEND[t, a,b,m], SEND[t,b,a,m
′
]i where m
′
is the re-
ply to m. A simple interactional session is a sequence
of turns; more complex sessions can include sub-
sessions (called threads) e.g. in case of conditional
reactions.
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
94

Table 3: Excerpt from Activation matrix
M
TALKINGS
. When λ
i, j
=
/
0 then λ
i, j
=GenericAgent
j
.
Proaction Reaction
Operator code A P D F M I G C S A+ A- P+ P- B N
Value range 02 02 2-2 2-2 2-2 2-2 2-2 2-2 2-2 2-2 2-2
Generic agent 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 -1 1 -1 1 1 Waiters
T Facet Scheme w
1
w
2
O fantasy -PRACTICAL *
O fantasy +IDEALISTIC 2 2 2 2 -1 2 2 2 0 *
O fantasy +CREATIVE 2 2 -2 *
C competence -INSECURE 2 0 -2 2 0 2 1 1 2 *
E warmth +FRIENDLY -1 2 2 2 2 2 *
E warmth -COLD -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 *
E assertiv. +DOMINEER. 2 2 -1 0 -1 -1 -1 -2 -2 -1 *
E activity +ACTIVE 2 -1 2 2 -1 *
E activity -APATHETIC 0 0 -2 0 0 0 1 1 -1 2 *
A trust -SECRETIVE 0 -1 0 -1 -2 0 *
-PRACTICAL is the antonym pole of scheme +IDEALISTIC resp. +FRIENDLY/-COLD, +ACTIVE/-APATHETIC.
3.2 Building a Personality Engine in
T
ALKINGS
3.2.1 Eliciting Influence Operators
Considering the previous agent’s model (i.e.
W
=
TALKINGS), it is possible to associate with the model
a set of influence operators Ω
TALKINGS
that define meta
control over the rational decision making process of
the agents
W
r
and over the message passing process
W
c
. We will focus here on the operation of build-
ing and sending messages, i.e. on
W
c
. Browsing the
model, described in section 3.1.1, we can define 15
operators organized in a 2×2 ontology, mirroring the
model structure: at the first level of the ontology, in-
fluence operators on message passing can be divided
into two main classes, proaction and reaction, and at
the second level, we can distinguish for each class im-
plicit and explicit operators. We therefore distinguish:
– Explicit proaction operators, which are expressed
into messages.
– Implicit proaction operators, which are not explic-
itly expressed in messages but can influence the way
messages are built and are related to the social capac-
ities of the agent.
– Explicit reaction operators, which are expressed
into messages, in terms of Yes/No reactions.
– Implicit reaction operators, which mirrors implicit
proaction.
Table 2 gives a list of exhibited message operators
together with an abridgment of their semantics asso-
ciated with their activation levels λ, ranging on scales
with discrete positions defined in Section 2.2.3.
While we have used a simplified communicat-
ing agent model, together with the description of the
FFM/NEO PI-R/BS schemes, it was possible to exhibit
12 operators, defined and organized as in Table 2. In
comparison, the eight “types of behaviors” similar to
our operators (Perceiving, Reasoning, Learning, De-
ciding, Acting, Interacting, Revealing, Feeling) given
in Cybercafe (Rousseau and Hayes-Roth, 1996) re-
main rather general, although some can be directly
mapped onto TALKINGS operators such as Perceiv-
ing and Guess, Learning and Ask, Revealing and Motivation.
Feeling would not be handled here since we consider
interactions only and not internal emotions.
3.2.2 Establishing an Activation Matrix
Given the set ±Σ and the set Ω
TALKINGS
of elicited
operators in the case study TALKINGS, it is possible
to define an activation matrix
M
TALKINGS
, which estab-
lishes the relationships between the schemes and the
operators. Table 3 shows an excerpt of a proposition
for
M
TALKINGS
(from the 138 schemes of ±Σ, we dis-
play only the 10 schemes used in the example of Sec-
tion 3.2.3). Not to overload Table 3, activation val-
ues λ
i, j
that are associated with an average behavior
are factorized in headline “Generic agent” and repre-
sented as empty cells.
3.2.3 Example of Personality Scripting
As an example of instantiation of the personality
engine defined for TALKINGS, we consider P’(w
1
)
from the Cybercafe example (cf. Section 2.1.3). For
simplification purposes, the 12 schemes associated
with adjective ‘introverted’ are coerced into a sin-
gle one Ewarmth-COLD (first arbitrarily chosen) thus
prompting a new profile: P”(w
1
) = { Ofantasy-PRACTICAL;
ManagingPersonalityInfluencesinDialogicalAgents
95

Ccompetence-INSECURE; Ewarmth-COLD; Eactivity-APATHETIC; Atrust-
SECRETIVE }. Respectively, for waiter w
2
we have:
P”(w
2
) = { Ofantasy+CREATIVE; Eassertiveness+DOMINEERING;
Ewarmth+FRIENDLY
8
; Eactivity+ACTIVE; Efantasy+IDEALISTIC
9
}.
Values of activation levels associated with P”(w
1
)
and P”(w
2
) in
M
TALKINGS
are given in Table 3. For ex-
ample, crossing Tables 2 and 3, it is possible to iden-
tify the influences of one of the schemes of P”(w
1
)
e.g. Atrust-SECRETIVE (last line of Table 3):
A/0 don’t ask explicitly (while average behavior would be
1: ask if needed by the rational process)
P/0 don’t propose explicitly (idem)
F/0 no sensibility to inner feelings activated (idem)
M/-1 hide one’s own motives
I/0 usage of positive or negative incentives over others
deactivated
A-/-2 react explicitly always by a rejection when asked
with a force considered negative
A+/-1 react explicitly positively but with protest, when
asked with a force considered positive
B/0 no bond positive or negative is activated (while the
average behavior would be 1: bond if needed by the
rational process e.g. in social condolences)
Operators A, P, F, I, B are controlled via deactivation (λ =
0). Actually average behavior often uses (λ = 1)
One can make the following remarks:
R1. Over the set of 12 operators in Table 3, scheme
+PRACTICAL is not distinct from Generic agent. This is con-
sistent with the fact that Bratman’s agents implement
an implicit personality close to scheme +PRACTICAL and
be viewed as a particular case.
R2. All lines of Table 3 are distinct, entailing that
all schemes are distinct concepts with distinct sets of
influences.
R3. It happens that profiles of the Cybercafe wait-
ers, P”(w
1
) and P”(w
2
) activate exclusive schemes
(*). Their definition is not always consistent, mean-
ing that some schemes are activated by contradictory
levels e.g. 1 and -2. In theory, when a personality is
scripted, nothing prevents from defining conflicting
activations of the same operator: our approach makes
it easier to automatically check for such cases and to
handle them manually or automatically, according to
an order relation possibly provided by psychologists.
3.3 Discussion
Relevance and Completeness of the Operators.
The process of operator elicitation ensures that all
operators defined in trait Conscientiousness are rele-
vant. For example, in the case study above, because
8
First scheme chosen with same rule in P”(w
1
).
9
Again, first scheme of trait Open chosen.
they are synthesized from scheme glosses, they are
activated in a non trivial manner at least once
10
(i.e.
∀σ ∈
M
TALKINGS
,∃ j such that λ
i, j
6= generic-agent (i)).
Conversely, the elicitation process does not ensure
that all possible operators are found; from a psycho-
logical point of view this is not yet attainable. Ac-
tually this issue is in support of our approach that is
based on the state of the art of the coverage of the
domain of the psychology of a person, that is to say
trait taxonomies, in particular FFM/NEO PI-R. More-
over, the refined version FFM/NEO PI-R/BS, grounded
on large ascertained lexical resources (e.g. WordNet),
covers according to the state of current literature, the
effective behaviors that are associated with personal-
ity traits, hence restricting the risk of silence.
Validation of Activation Matrix Values. Weights
λ
i, j
∈
M
TALKINGS
are set by annotators. This results
in 1) inter annotator quantitative differences that can
be partly controlled with statistic tools acting over
the annotating group; 2) qualitative controversies be-
tween computer science experts and psychologists.
The proposed approach has the virtue of putting into
light the essential issue of those qualitative controver-
sies, usually embedded in the programming process
of the procedural approaches, listed in Section 4. In
our case, the use of a declarative method, through a
matrix of activation levels instead of procedural rules,
increases the comprehensiveness and the tracking of
the traits/behaviors association. Moreover, the declar-
ative approach clarifies the discussions with psychol-
ogists, who in fine must validate the decisions.
Evaluation of the Model. In this paper we propose
an approach for handling the phenomena, stated in
the literature, of personality traits influence over plans
and actions. Our purpose is not the direct evaluation
of a particular model (composed of: a specific ratio-
nal model, a specific set of influence operators and
a specific set of activation levels) through an experi-
mentation. Here we pursue a double objective:
1. present a proof of concept of the principle of influ-
ence: ‘points of influence’ actually exist in the ratio-
nal decision making process;
2. propose a method that is a) generic i.e. not de-
signed for a small set of specific traits but covering
a large domain of the personality of a person; and b)
declarative i.e. using explicit levels instead of embed-
ded rules.
For example, a consequence is that Table 2 and Ta-
ble 3 must be viewed as instances of our approach. As
10
Except for first line of table 3 (O fantasy -practical),
which is similar to a line generic-agent as this trait can be
viewed as Bratman’s notion of practical reason (1987).
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
96

such, they need to be evaluated through proper exper-
iments, but which are beyond the scope of this paper.
4 RELATED WORKS
Since works of Rousseau and Hayes-Roth (1996) , ex-
tensive research has been undertaken, especially re-
cently, involving both psychological phenomena and
artificial agents in at least four communities: rational
agents, multi-agents systems, conversational agents
and affective computing.
Gratch and Marsella (2004) have implemented a
psychological model, mainly dedicated to emotions,
based on traditional SOAR architecture, but most au-
thors have proposed improvements of BDI architec-
tures exhibiting both rational reasoning modules and
psychological reasoning modules (Lim et al., 2008).
For example, the eBDI model (Jiang et al., 2007)
implements emotions in a BDI framework, in which
they give a good introduction about the necessity to
implement emotions into rational agents. Indeed,
BDI architectures offer an open and flexible engine
(the deliberation cycle), for example using tools like
2APL (Dastani, 2008), which is why we rely on it for
the support of the framework that underlies this study.
However our approach is distinct from most stud-
ies using BDI engines, mainly because in those stud-
ies the psychology of the agent is based on dynamic
mental states (like moods and affects, as in Sec-
tion 3.1.1), which influence the bodily (facial and ges-
tural) expression of emotions, but they have no or lit-
tle impact upon the decision making process of the
agent, especially for controlling conversational strate-
gies. Instead, in our approach the static features of
the personality of an agent are expressed through its
influences upon operational behaviors.
Using the BDI platform JACK (Howden et al.,
2001), CoJACK (Evertsz et al., 2008) provides an ad-
ditional layers which intends to simulate physiologi-
cal human constraints like the duration taken for cog-
nition, working memory limitations (e.g. “loosing a
belief” if the activation is low or “forgetting the next
step” of a procedure), fuzzy retrieval of beliefs, lim-
ited attention or the use of moderators to alter cogni-
tion. A similar approach is taken for conversational
agents in PMFserv (Silverman et al., 2006).
However, in these studies, authors focus on the in-
fluence of physical or cognitive capacities over the de-
liberation cycle but not on actual psychological phe-
nomena like moods or traits.
Closer to our work, Malatesta et al. (2007) use
traits to create different expressions of emotions, es-
pecially by influencing the appraisal part of the OCC
theory (Ortony et al., 1988). They focus on how
agents evaluate the results of their actions and of ex-
ternal events, whereas we focus on the way they per-
form a task. In the same way, Rizzo et al. (1997) have
shown that goals and plans can be used to represent a
character’s personality in an efficient way, by attribut-
ing specific behaviors to the pursuit of each goal. Per-
sonality traits are used to choose between the multi-
ple goals of a BDI agent (i.e. traits influence Desires).
Once chosen, goals are planned and executed directly.
However, in our case, traits operate on already
planned goals (i.e. traits influence Intentions). This
remark also applies to (McRorie et al., 2009),
based on the architecture of conversational agent
GRETA (Pelachaud, 2000), which involves models
of personality for the expression of emotions (face,
gesture, etc.) and to the FATIMA architecture (Doce
et al., 2010) stemming from (Pelachaud, 2000), which
implements personality traits.
Finally, all these studies share the same approach
to psychology, each of them focusing on particular
capacities or particular traits. They do not attempt to
cover a whole domain, hence they are not concerned
with managing and comprehensiveness issues.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We have shown in this article an approach based on
personality engines which provides three main advan-
tages: firstly, it reduces and reifies author/designer-
dependent parts in only three main kinds of resources:
trait ontologies, sets of influence operators and acti-
vation matrices. Secondly, it defines a process for
designing the resources and for implementing, in a
declarative way (activation matrix), personality influ-
ences in dialogical agents. Finally, it proposes an ar-
chitecture where these resources can be flexibly com-
bined (cf. section 3.2) and easily observed (cf. section
3.2.3).
We intend to extend this work in two main di-
rections: by eliciting operators over outstanding BDI
agent frameworks to demonstrate its independence
over the framework used, and by experimenting with
scenarios supervised by psychologists. The percep-
tion of the implemented agent’s personality by hu-
man users could be evaluated post-interaction with
questionnaires such as the Agent Persona Instru-
ment (Baylor and Ryu, 2003).
ManagingPersonalityInfluencesinDialogicalAgents
97

REFERENCES
Baylor, A. and Ryu, J. (2003). The api (agent per-
sona instrument) for assessing pedagogical agent per-
sona. In World Conference on Educational Multi-
media, Hypermedia and Telecommunications, volume
2003, pages 448–451.
Bouchet, F. and Sansonnet, J. P. (2010). Classification
of wordnet personality adjectives in the NEO PI-R
taxonomy. In Fourth Workshop on Animated Con-
versational Agents, WACA 2010, pages 83–90, Lille,
France.
Bouchet, F. and Sansonnet, J. P. (2011). Influence of person-
ality traits on the rational process of cognitive agents.
In The 2011 IEEE/WIC /ACM International Confer-
ences on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Tech-
nology, Lyon, France.
Bratman, M. E. (1987). Intentions, Plans, and Practical
Reason. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Cassell, J., Sullivan, J., Prevost, S., and Churchill, E., edi-
tors (2000). Embodied Conversational Agents. MIT
Press.
Cattell, R. B., Eber, H. W., and Tatsuoka, M. M. (1970).
Handbook for the sixteen personality factor question-
naire (16 PF). Champain, Illinois.
Costa, P. T. and McCrae, R. R. (1992). The NEO PI-R pro-
fessional manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assess-
ment Resources.
Damasio, A. R. (1994). Descartes error: Emotion, reason
and the human brain. New York: G.P. Putnam’s Sons.
Dastani, M. (2008). 2APL: a practical agent programming
language. In AAMAS ’08:The seventh international
joint conference on Autonomous agents and multia-
gent systems, volume 16, pages 214–248, Estoril, Por-
tugal. Springer-Verlag.
Doce, T., Dias, J., Prada, R., and Paiva, A. (2010). Creating
individual agents through personality traits. In Intelli-
gent Virtual Agents (IVA 2010), volume 6356 of LNAI,
pages 257–264, Philadelphia, PA. Springer-Verlag.
Evertsz, R., Ritter, F. E., Busetta, P., and Pedrotti, M.
(2008). Realistic behaviour variation in a BDI-based
cognitive architecture. In Proc. of SimTecT’08, Mel-
bourne, Australia.
Fellbaum, C. (1998). WordNet: An Electronic Lexical
Database. MIT Press.
Findler, N. V. (1977). Studies in machine cognition using
the game of poker. Commun. ACM, 20(4):230–245.
Goldberg, L. R. (1981). Language and individual differ-
ences: The search for universal in personality lexi-
cons. Review of personality and social psychology,
2:141–165.
Goldberg, L. R. (1990). An alternative description of per-
sonality: The big-five factor structure. Journal of Per-
sonality and Social Psychology, 59:1216–1229.
Goldberg, L. R. (1992). The development of markers for the
big-five factor structure. Psychological Assessment,
4:26–42.
Gratch, J. and Marsella, S. (2004). A domain-independent
framework for modeling emotion. Journal of Cogni-
tive Systems Research, 5(4):269–306.
Howden, N., Rannquist, R., Hodgson, A., and Lucas, A.
(2001). Intelligent agents - summary of an agent in-
frastructure. In Proc. of the 5th International Confer-
ence on Autonomous Agents, Montreal.
Jiang, H., Vidal, J. M., and Huhns, M. N. (2007). eBDI:
an architecture for emotional agents. In AAMAS ’07:
Proceedings of the 6th international joint conference
on Autonomous agents and multiagent systems, pages
1–3, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
John, O. P., Robins, R. W., and Pervin, L. A., editors (2008).
Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research. The
Guilford Press, 3rd edition.
Koda, T. and Maes, P. (1996). Agents with faces: the effect
of personification. pages 189–194.
Lim, M., Dias, J., Aylett, R., and Paiva, A. (2008). Im-
proving adaptiveness in autonomous characters. In
Prendinger, H., Lester, J., and Ishizuka, M., editors,
Intelligent Virtual Agents, volume 5208 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 348–355. Springer.
Malatesta, L., Caridakis, G., Raouzaiou, A., and Kar-
pouzis, K. (2007). Agent personality traits in vir-
tual environments based on appraisal theory predic-
tions. In Artificial and Ambient Intelligence, Lan-
guage, Speech and Gesture for Expressive Charac-
ters,achie AISB’07, Newcastle, UK.
McRorie, M., Sneddon, I., de Sevin, E., Bevacqua, E., and
Pelachaud, C. (2009). A model of personality and
emotional traits. In Intelligent Virtual Agents (IVA
2009), volume 5773 of LNAI, pages 27–33, Amster-
dam, NL. Springer-Verlag.
Ortony, A., Clore, G. L., and Collins, A. (1988). The Cog-
nitive Structure of Emotions. Cambridge, UK, cam-
bridge university press edition.
Pelachaud, C. (2000). Some considerations about em-
bodied agents. In Int. Conf. on Autonomous Agents,
Barcelona.
Rizzo, P., Veloso, M. V., Miceli, M., and Cesta, A.
(1997). Personality-driven social behaviors in believ-
able agents. In AAAI Symposium on Socially Intelli-
gent Agents, pages 109–114.
Rousseau, D. (1996). Personality in computer characters.
In AAAI Technical Report WS-96-03, pages 38–43.
Rousseau, D. and Hayes-Roth, B. (1996). Personality in
synthetic characters. In Technical report, KSL 96-21.
Knowledge Systems Laboratory, Stanford University.
Sansonnet, J. P. and Bouchet, F. (2010). Extraction of
agent psychological behaviors from glosses of word-
net personality adjectives. In Proc. of the 8th Euro-
pean Workshop on Multi-Agent Systems (EUMAS’10),
Paris, France.
Silverman, B. G., Cornwell, M., and O’Brien, K. (2006).
Human behavior models for agents in simulators and
games. In PRESENCE, volume 15, pages 139–162.
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
98
