
Didactic Speech Synthesizer: Acoustic Module
Formants Model
João Paulo Teixeira and Anildo P. Fernandes
Polytechnic Institute of Bragança, Bragança, Portugal
Keywords: Speech Analysis, Speech Synthesis, Text-to-Speech Conversion, Signal Processing, Formants Model.
Abstract: Text-to-speech synthesis is the main subject treated in this work. It will be presented the constitution of a
generic text-to-speech system conversion, explained the functions of the various modules and described the
development techniques using the formants model. The development of a didactic formant synthesiser under
Matlab environment will also be described. This didactic synthesiser is intended for a didactic
understanding of the formant model of speech production.
1 INTRODUCTION
The human desire to give talk to an object or
machine accompanies the civilization for a long
time. A computer system used for this purpose is
called a speech synthesizer, and can be implemented
in software or hardware (Saraswathi, 2010). In the
Decade of 1960, it was possible to generate speech
from text (Sproat, 1997).
A TTS (Text-To-Speech) conversion system is
capable of performing an automatic reading of a
text. It operates with two major blocks (see Figure
1).
Figure 1: Block diagram of a TTS system (withdrawal of
(Teixeira, 2012)).
2 PROSODIC AND LINGUISTIC
PROCESSING
This block determines two types of information
needed to provide acoustic processing data that is
possible to generate speech, the segmental and
suprasegmental information (Teixeira, 2012).
The segmental information is linked to the basic
sounds that make up the message.
The suprasegmental information is associated
with prosody (Teixeira et al., 2003). This
information usually comes coded through three
acoustic speech signal parameters:
The temporal evolution of the
fundamental frequency (F0);
Duration of sound segments that make
up the phrase;
Power curve of acoustic signal.
These two types of information are extracted by
a sequence of task (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: The tasks of the Prosodic and Linguistic
Processing (withdrawal of (Teixeira et al., 2003)).
356
Paulo Teixeira J. and P. Fernandes A..
Didactic Speech Synthesizer: Acoustic Module - Formants Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0004249603560359
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2013), pages 356-359
ISBN: 978-989-8565-36-5
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2.1 Pre-processing
The first task of linguistic processing is the
formatting of the text properly in its textual form
representing numbers, abbreviations, etc (Teixeira et
al., 2003).
2.2 Linguistic Analysis
After pre-processing is the linguistic analysis, that
includes the syntax analysis and semantic analysis
(Teixeira et al., 2003).
2.3 Morpho-syntactic and Prosodic
Analysis
This block aims, from the previous analysis, mark
the syntactic-prosodic (as the inclusion of pauses
and/or enlargement of syllables) borders and the
word accents (Teixeira, 95).
2.4 Phonetic Transcription
Phonetic transcription is performed usually by rules.
For the Portuguese language these rules are
particularly complex as regards transcription of
vowels, whereas, at the same natural alphabet vowel
match several phonetic alphabet vowel, depending
on their position in the word, accent and adjacent
phonemes (Teixeira, 1995).
2.5 Prosodic Processing
Prosodic processing collects the supra-segmental
and segmental information extracted from the last
steps, and translates it into changes in segmental
duration (rhythm), fundamental frequency
(intonation) and inserting pauses with appropriate
duration.
2.5.1 Modelling of Segmental Durations
The term duration refers to the time it takes a certain
segment of speech. The duration of the syllable can
be determined by the equation (Barbosa P. and
Bailly, 94):
exp
iii
Dur z
(1)
duration of the syllable
i
i
Dur
(2)
Where,
z
is the z-score of the syllable,
i
and
i
are, respectively, average and standard deviation
of the logarithm of the duration of segment i.
2.5.2 Modelling of Fundamental Frequency
Modelling the fundamental frequency curves is the
most important issue to convey naturalness in
synthetic speech. Different type of model have been
used to model the F0 parameter such as the ToBI
system (Pierrehumbert, 1980), the Tilt model
(Taylor, 2000), the INTSINT (
INternational
Transcription System for INTonation) – proposed
by Hirst and Di Cristo (1998), or the Fujisaki model
(Fujisaki, 1983); (Teixeira 2012), that is a
parametric and deterministic model that allows the
determination of the values of F0 for every instant of
time.
3 ACOUSTIC PROCESSING
In this block, the sequences of segments previously
determined are selected from a database containing
all possible segments, and concatenated successively
according to each type of acoustic model. A typical
block diagram for the acoustic processing is
represented in the following form: (see Figure 3)
Figure 3: Block diagram of acoustic processing.
There are several types of models to perform the
acoustic processing. The Formant model (Klatt, DH,
1987) stores the frequency components of segments
in the frequency domain (the formant frequencies
and respective bandwidths). It allows a complete
separation of information about source (F0) and
vocal tract (formants and bandwidths).
3.1 Formant Model
This type of synthesis simulates the transfer function
of the vocal tract by circuit connection resonators, in
series or parallel, with their respective frequencies
and bandwidths used as input parameters of this
synthesizer (Klatt, 1987).
In figure 4 it is a schema representation of a
synthesizer of formants.
DidacticSpeechSynthesizer:AcousticModule-FormantsModel
357
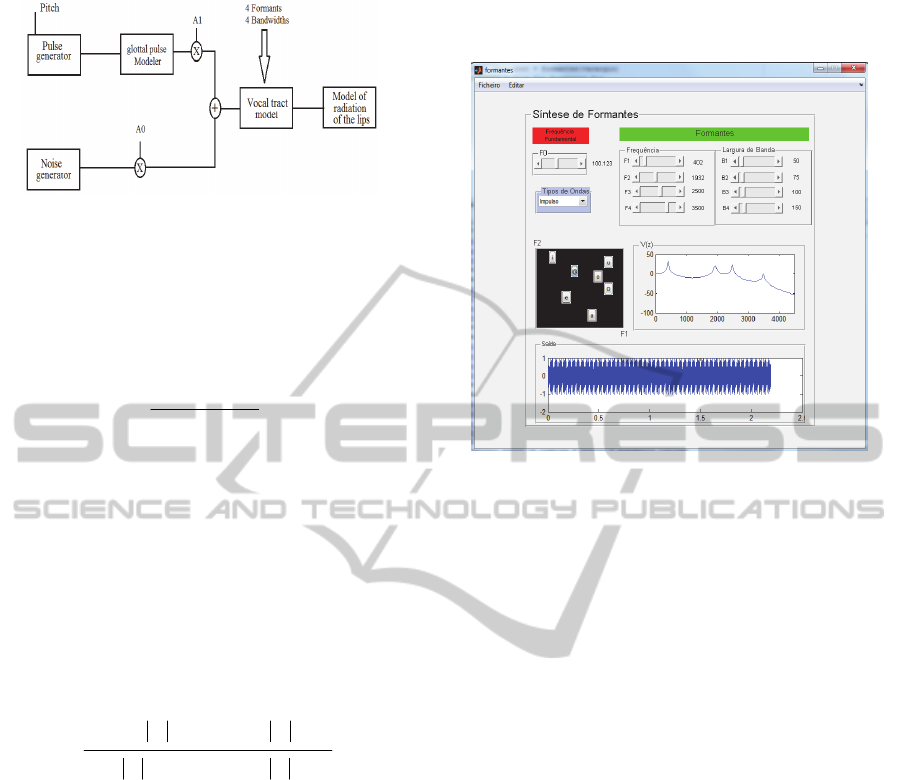
Figure 4: Formants synthesis scheme (withdrawal of
(Barros, 2002)).
The glottal pulse model block produces a
sequence of pulses spaced by the fundamental period
desired. The transfer function is given by (Teixeira,
95):
1
2
1
ln
()
1
ae a z
Gz
az
(3)
a
is the parameter that represents the timbre of
the voice, and 0.9 is the optimal value.
For unvoiced sounds excitation model is simpler.
The resonances of the speech, modelled by
formants, correspond to the poles of transfer
function V(z). An all-pole model is a very good
representation of the effects of the vocal tract for
most speech sounds. The frequency response of one
resonator (k) of the vocal tract can be given by
(Teixeira, 95):
2
2
12
12 cos2
()
12 cos2
kkk
k
kkk
zFTz
Vz
zFTzzz
(4)
For model the air pressure in the lips, the effects
of radiation should be included. The pressure is
related with the volumetric speed of the air through
the lips and is modelled by a high pass filter
operation. In fact at low frequencies it can be said
that the pressure is derived from the volumetric
velocity. The effect of radiation is expressed as
(Teixeira, 95):
1
0
() 1Rz R z
(5)
3.1.1 Development of the Didactic
Synthesizer
The synthesizer is developed using the graphical
interface known as Guide (done in Matlab), as
presented in Figure 5. It represents the information
source (F0) and type of excitation signal in the upper
left side, below the F1-F2 formants plane for the
vowels. In the upper right side is the information
about vocal tract namely the formats and their
frequency response.
Figure 5: Interface to the formants model. Labels are in
Portuguese.
The formant and bandwidth parameters for each
vowel were previously recorded. The synthesis was
performed using this recorded parameters and a half
Hanning windows was applied in the beginning of
the speech signal and the other half Hanning
window has used in the end of the speech signal in
order to avoid abrupt onset and offset of speech.
The vocal tract filter was implemented with the
equation 4 for each formant and bandwidth. Initially
the glottal function is invoked to create the glottal
pulses vector. Then this signal is filtered in a cycle
of 4 iterations with the correspondent frequency
response filter of equation 4 and using the values of
the first formant and bandwidth in the first iteration
and the second, third and fourth formants/bandwidth
pairs in following iterations.
The result is stored into a vector for the
concatenation. To implement the radiation of the lips
the signal was filtered using the filter of equation 5.
Then, the two half Hanning windows were applied
to the beginning and end of the signal. Finally, the
signal is represented in the lower window and the
sound speech is reproduced.
The database with the parameters of the formants
and respective bandwidths for the vowels were built
using the Praat program (Boersma and Weenink).
To get the parameters, we have to choose the
vowel and record it. Then we analyse it carefully, so
we can take correct information to be used in the
synthesizer (Figure 6).
BIOSIGNALS2013-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
358

Figure 6: How to have the information of the Formants
and bandwidths using Praat.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
DEVELOPMENTS
This paper described the basic mechanism of human
speech production and the engineering models used
to develop a TTS system. The main objectives of the
blocks were explained. The acoustic module
methods were also referred and a special attention
was taken to the formant model because it was the
model used in this development.
A didactic acoustic module based in the Formant
model was developed for the purpose of
demonstration of the self Formant model. The
application fulfils its purpose and the synthesis
results with quality enough for understanding, once
only a single vowel or a sequence of vowels are
reproduced in this version. The application allows
the synthesis of any speech sound because the user
can select the vowel or the formant and bandwidth
parameters. The user can also experiment different
types of source excitation, from a sampled glottal
wave, to a synthetic glottal wave between sinusoidal,
triangular or rectangular wave formats.
An evolution of this version is under
development in the way of a speech synthesizer. At
this moment the acoustic module is build lacking the
complete development of the formant and
bandwidths of diphones database. This version will
allow the user to insert the phoneme sequences to be
reproduced.
REFERENCES
Barbosa P., Bailly G. (1994). Characterisation of rhythmic
patterns for text-to-speech synthesis, in Speech
Communication, 15: 127-137.
Barros, M. J., (2002). "Estudo Comparativo e Técnicas de
Geração de sinal para Síntese de Fala ". Master
dissertation, Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade
do Porto.
Boersma, Paul and Weenink, David. Praat: doing
phonetics by computer. Phonetic Sciences, University
of Amsterdam. http://www.fon.hum.uva.nl/praat/
Fujisaki, H.. (1983). Dynamic characteristics of voice
fundamental frequency in speech and singing. In
MacNeilage. In P. F., Editor. The Production of
Speech, pages 39-55. Springer-Verlag.
Hirst, D. and Di Cristo, A.. (1998). Intonation Systems – A
Survey of Twenty Languages. Cambridge University
Press.
Klatt, DH (1987). Review of text-to-speech conversion for
English - Journal of the Acoustical Society of
America, 82 (3) - 1987. Pages 737-793.
Pierrehumbert, J. B. (1980). The Phonology and Phonetics
of English Intonation. PhD thesis, Massachusetts
Institute of Technology.
Saraswathi, S., (2010). Design of Multilingual Speech
Synthesis System. Academic journal article from
Intelligent Information Management, Vol. 2, No. 1.
Sproat, Richard W. (1997). Multilingual Text-to-Speech
Synthesis: The Bell Labs Approach. Springer.
Taylor, P. (2000). Analysis and Synthesis of Intonation
using the Tilt Model. Journal of the Acoustical Society
of America. vol 1073, pp. 1697-1714.
Teixeira, J. P. (2012). Prosody Generation Model for TTS
Systems - Segmental Durations and F0 Contours with
Fujisaki Model. LAP LAMBERT Academic
Publishing ISBN-13: 978-3-659-16277-0.
Teixeira, J. P., (1995). "Modelização Paramétrica de
Sinais para Aplicação em Sistemas de Conversão
Texto-Fala." Master Dissertation, FEUP – Porto.
Teixeira, J. P.,Barros, M. J. and Freitas, D., (2003).
"Sistemas de Conversão Texto-Fala." Procedings of
CLME, Maputo.
DidacticSpeechSynthesizer:AcousticModule-FormantsModel
359
