
EEG Discrimination with Artificial Neural Networks
S
´
ergio Daniel Rodrigues
1
, Jo
˜
ao Paulo Teixeira
1
and Pedro Miguel Rodrigues
2
1
Polytechnic Institute of Braganc¸a, Braganc¸a, Portugal
2
University of Porto, Porto, Portugal
Keywords:
Electroencephalogram, Alzheimer’s Disease, Artificial Neural Network.
Abstract:
Neurodegenerative disorders associated with aging as Alzheimer’s disease (
AD
) have been increasing signifi-
cantly in the last decades.
AD
affects the cerebral cortex and causes specific changes in brain electrical activity.
Therefore, the analysis of signals from the electroencephalogram (
EEG
) may reveal structural and functional
deficiencies typically associated with
AD
. This study aimed to develop an Artificial Neural Network (
ANN
) to
classify
EEG
signals between cognitively normal control subjects and patients with probable
AD
. The results
showed that the EEG can be a very useful tool to obtain an accurate diagnosis of AD. The best results were
performed using the Power Spectral Density (
PSD
) determined by Short Time Fourier Transform (
ST FT
) with
a
ANN
developed using
Levenberg − Marquardt
training algorithm,
Logarithmic Sigmoid
activation function
and 9 nodes in the hidden layer (correlation coefficient training: 0.99964, test: 0.95758 and validation: 0.9653
and with a total of: 0.99245).
1 INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s disease(
AD
) is a progressive degenerative
neurological disorder of brain that leads to irreversible
loss of neurons (Blennow et al., 2006). Lesions usu-
ally start in the hippocampus (which is an important
structure in memory formation) and in the cerebral
cortex (Blennow et al., 2006; Feldman and Woodward,
2005). In AD patients brain can be observed senile
plaques formed by amyloid plaques and neurofibril-
lary tangles. Amyloid plaques are found outside the
neurons, neurofibrillary plaques are found inside the
neurons and result in the death of the cells. Gradually,
the neurons degenerate and a generalized collapse of
brain tissue occurs (Feldman and Woodward, 2005).
The aging process increases the incidence of
AD
which
is typically diagnosed in aging people (Moreira and
Oliveira, 2005).
Researchers estimate that 1 in every 85 people may
have
AD
in the next 35 years and this disease may
affect about 100 million people by 2050 (Stahl, 2008).
It is therefore necessary to reach a correct diagnosis
of
AD
before significant loss of memory appears, be-
cause early diagnosis enables the treatment conditions
(Blennow, 2005). A tool suitable for assisting
AD
diagnosis is the EEG (Hort et al., 2010).
One of the most frequently observed abnormalities
in
EEG
activity of
AD
patients is an increase in power
at low frequency bands and a decreased power in the
higher frequency bands(Baker et al., 2008; Rodrigues
and Teixeira, 2011). The deceleration of
EEG
signal
usually occurs in intermediate and severe stages of
AD
(Jeong, 2004).
In the present study we intend to develop an Ar-
tificial Neural Network (
ANN
) to discriminate
EEG
signals between cognitively normal control subjects
(Cs) and AD patients.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Selection of Patients and
Controls/EEG Recording
We had the collaboration of thirty four subjects (14
Controls and 20 of
AD
).
EEGs
were recorded from
the international system 10-20 of 19 electrodes. The
frequency sample was 200 Hz. Then,
EEGs
were
organized in 5 s artifact-free epochs (1000 samples)
(Rodrigues and Teixeira, 2011). It should be noted that
all recordings were digitally filtered with a band-pass
filter between 1 Hz and 40 Hz.
236
Daniel Rodrigues S., Paulo Teixeira J. and Miguel Rodrigues P..
EEG Discrimination with Artificial Neural Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0004249702360241
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2013), pages 236-241
ISBN: 978-989-8565-36-5
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2.2 EEG Signal Processing
Fourier transform (FT ) allows us to represent the sig-
nal in the frequency domain. It is the spectral
EEG
signal processing currently used (Rioul and Vetterli,
1992).
FT
constitutes a disadvantage of not being able
to provide information both in time and frequency of
signal characteristics. Indeed, in signal transformation
from the time domain to the frequency domain there
is a lost of information about the temporal location
(Blennow,2005). Thus, by observing the
FT
of a sig-
nal is impossible to say where a particular event is
located, since what is obtained is only the frequen-
cies that compose the signal throughout the whole
time interval considered. If a signal is stationary this
drawback is irrelevant. However, if a signal contains
many non-stationary or transient characteristics (char-
acteristics which are usually the most important parts
of a
EEG
signal)
FT
can not detect such processes
(Blennow,2005). Seeking a solution to this problem it
is common to use the Short-Time-Fourier-Transform
(
ST FT
).
ST FT
maps a signal using a bidimensional
function defined in time and frequency and represents
a form of compromise between representation both in
time and frequency of this signal. Although the
ST FT
provides information on time and frequency, there is a
disadvantage when choosing a particular size for the
window that will go through the signal, because this
window remains the same for all frequencies. It turns
out that many signals have a window of variable length
which allows a more precise location of a particular
event both in time and frequency, because in most
cases it is impossible to determine an optimal window
size that can find events with enough resolution at very
different frequencies(Blennow, 2005). So,
ST FT
also
presents limitations. To overcame the problem, we
used the
ST FT
because it uses a constant time win-
dow and therefore we can analyze the
EEG
signal in
short time stationary periods. Thus, we calculated the
power spectral density (
PSD
), functions that had the
force of power variations as a frequency function. The
PSD
(
S
x,w
[k]
) was calculated by the autocorrelation
function (
R
xx
(u)
) of
ST FT
of the signal, as can be
seen in the follow equations (Rodrigues and Teixeira,
2011).
R
xx
[u] =
(
1
N
·
∑
N−m−1
n=0
x[n] · x[n + u] , u ≥ 0
R
∗
xx
[−u] , u < 0
(1)
(2)
S
x,w
[k] =
1
N
· DFT S
R
xx
[u]
=
1
N
·
2N−1
∑
u=0
R
xx
[u] · e
− j·
2πk
2N−1
·u
,
where, k = 0, ..., 2N − 1.
The
PSD
was normalized to the scale 0 to 1 and it
was designated
PSD
n
(Rodrigues and Teixeira, 2011),
as can be observed in the next equation.
PSD
n
[m, k] =
S
x,w
[n]
∑
k
2
n=k
1
S
x,w
[n]
, m = 0, ..., N
t
− 1 (3)
where k
1
and k
2
represent discrete cutoff frequencies.
2.3 Feature Extraction
The relative power (
RP
) in
EEG
conventional frequen-
cies bands was obtained by the sum of the components
of the
PSD
n
in the conventional frequency bands: delta
(
δ
, 1-4 Hz), theta (
θ
, 4-8 Hz), alpha (
α
, 8-13Hz), beta1
(
β
1
, 13-19 Hz), beta2 (
β
2
, 19-30 Hz) and gamma (
γ
,
30-40 Hz).
RP(δ) =
4Hz
∑
f =1Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (4)
RP(θ) =
8Hz
∑
f =4Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (5)
RP(α) =
13Hz
∑
f =8Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (6)
RP(β
1
) =
19Hz
∑
f =13Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (7)
RP(β
2
) =
30Hz
∑
f =19Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (8)
RP(γ) =
40Hz
∑
f =30Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (9)
Four spectral ratios were used to resume the de-
celeration of the EEG as defined in (Rodrigues and
Teixeira, 2011).
r
1
=
RP(α)
RP(θ)
(10)
r
2
=
RP(α) + RP(β
1
) + RP(β
2
) + RP(γ)
RP(δ) + RP(θ)
(11)
r
3
=
RP(β
1
) + RP(β
2
)
RP(δ)
(12)
r
4
=
RP(β
2
)
RP(δ)
(13)
In order to achieve a through analysis of the spec-
tral characteristics of the
EEG
records of the patients
diagnosed with probable Alzheimer’s disease and
Cs
EEGDiscriminationwithArtificialNeuralNetworks
237

in this study the following parameters were calculated
using the PSD.
The Mean Frequency (
MF
) is defined as the fre-
quency comprising of
50%
of the power (Rodrigues,
2011).
0.5
40Hz
∑
1Hz
PSD
n
( f ) =
MF
∑
1Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (14)
The
PSD
shows the highest peak at the
α
band. So
we can calculate a parameter entitled Individual Alpha
Frequency (
IAF
) in the extended
α
band between 4Hz
and 15 Hz (Rodrigues, 2011).
0.5
15Hz
∑
4Hz
PSD
n
( f ) =
IAF
∑
4Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (15)
The Spectral Edge Frequency (SEF95%) is calcu-
lated as the frequency that comprises 95% of the power
spectrum (Rodrigues, 2011).
0.95
40Hz
∑
1Hz
PSD
n
( f ) =
SEF95%
∑
1Hz
PSD
n
( f ) (16)
Finally, the Spectral Entropy (
SE
) is a measure of
disorder that can be used as an irregularity estimate
of the
EEG
as we can see on the equation below (Ro-
drigues, 2011):
SE = −
40Hz
∑
1Hz
PSD
n
( f ) · Log[PSD
n
( f )] (17)
3 METHODOLOGY
We developed an
ANN
in order to discriminate
EEG
signals between
Cs
and
AD
patients. It was created the
input
P
matrix with
EEG
data of the subjects in study.
This input matrix consists in one column for each seg-
ment of 5 s for all subjects (controls and patients). The
lines of the matrix consist in the 14 features defined
above (6
RP
, 4 spectral ratios -
r
,
MF
,
IAF
,
SEF95%
and
SE
) for the 19 electrodes, in a total of 14
∗
19=266
lines. In the future we intend to reduce this number
of input nodes by a selection process. It was found
that some electrodes presented probable noise, due to
bad conduction during the acquisition process. These
electrodes were identified by observation of the spec-
tral components because they had similar energy in
all bandwidth. To reduce that noise we proceeded to
the average of electrodes without noise belonging to
the same group of the subject involved, including the
damaged electrode. For example, if the electrode 8 of
a control subject presented noise we proceeded to the
substitution of the data of this electrode by the average
of all electrodes of
Cs
without noise in any electrode,
including the electrode 8. This method allowed to re-
move electrodes with wrong data. To identify noise
moments we have used the
sur f
function of
Matlab
software, which allowed to create a three-dimensional
shaded surface from
PSD
components of signals of
all five segments seconds presented in the electrode
signal, which would allow the visualization of some
useful information to create the P matrix.
Thus, in a first phase it was checked whether there
were significant oscillations between electrodes posi-
tioned at the same position either
Cs
or
AD
patients
and, if oscillations in subjects belonging to the same
group were significant. It was found limited relevance
for the identification by visualization, because differ-
ences were observed in electrodes of subjects belong-
ing to the same group.
In a second phase we tried to find out if there were
amplitude variations along the electrode segments and
if the peaks were determinative. It was found that
AD
patient 4 presented small variations along the segments
in frequency (view Figure 1), compared to other cases
where there were no large amplitudes of the electrodes
and that presented a greater distribution of the am-
plitudes per electrode. It has been assumed that
AD
patient 4 was in an advanced phase of the AD. As in
patient 4, also the patient 10 and 38 and control subject
17 exhibited large variations with small amplitudes of
energy in a restricted range of frequencies. It should
be noted the fact that in the universe of 14
Cs
the only
one who showed higher accumulations of energy in a
restricted range of frequencies of electrodes was the
control subject 17.
Figure 1: EEG signal Amplitude of successive segments
(right axis) of one electrode along frequency (left axis).
In a third and last stage we look for noise existence
in
AD
patients and
Cs
and we confirmed noise in elec-
trode 8 of the patient 5, in electrodes 8 and 9 of the
control subject 7, in electrodes 8 and 16 of the control
subject 13, in electrode 16 of patient 25 and in the
electrodes 8,9 and 17 of the patient 50.
BIOSIGNALS2013-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
238

The matrix P was split into three randomly exclu-
sive subgroups:
• Subset 1: Training set.
• Subset 2: Validation set.
• Subset 3: Test set.
The subset 1 presented the most part of the
P
ma-
trix for training. It was about 80% of the
P
matrix.
Therefore, this subset had the remaining segments for
each subject in study. The subset 2 and 3 showed about
10% of the
P
matrix, respectively, and they had three
segments of each subject randomly selected, from the
34 subjects in study. The size of each subset can be
observed in table 1.
Table 1: Dimension of Training, Test and Validation Sets.
Total Dimension of matrix P=266x1066
Training Set Validation Set Test Set
266x862 266x102 266x102
In this work a feed-forward architecture of
ANN
was employed with 266 nodes input layer and 1 node
in the output layer. The output node codes if the data
features correspond to a control subject or in oppo-
sition corresponds to a patient. Different number of
nodes in the hidden layer has experimented. For all
ANN
architectures, two learning algorithms were used,
the Resilient Back-Propagation (
trainrp
) and the Lev-
enberg - Marquardt (
trainlm
) and two Transfer Func-
tions in the hidden layer were also used, Logarithmic
Sigmoid (
logsig
) and the Tangential Sigmoid (
tansig
).
Several nodes variations on the hidden layers were
utilized and the
purelin
was the transfer function of
the output layer. The best
ANN
results were obtained
with
trainlm
,
logsig
and 9 nodes on the hidden layer,
as can be seen by the autocorrelation coefficient (R)
of the training, test and validation sets and overall
P
matrix presented in the table 2.
Once the output of the ANN is a linear function
between 0 and 1 and we considered 0 for controls and
1 for
AD
patients a threshold value of 0.5 of output
was considered. Therefore values
>
0.5 of the output
are interpreted as
AD
patients and values
<
0.5 are
considered as Cs.
3.1 Train with Resilient
Back-propagation Algorithm
Next will be showed the best results for regression and
for the performance of
ANN
obtained with
trainrp
al-
gorithm (Riedmiller and Braun, 1993),
logsig
transfer
function and 14 nodes in the hidden layer (view Figure
2 and Figure 3). It must be noted that the result of the
correlation coefficient in Test Set has the highest value
for this
ANN
. The
tansig
transfer function had no-
ticed great results but not so greatest as
logsig
transfer
function.
Figure 2: Regression Plot with trainr p algorithm.
Figure 3: Performance Plot with trainrp algorithm.
3.2 Train with Levenberg-Marquardt
Back-propagation Algorithm
Next will be showed the best results for regression and
for the performance of
ANN
obtained with
trainlm
al-
gorithm (Marquardt, 1963; Hagan and Menhaj, 1994) ,
logsig
transfer function and 9 nodes in the hidden layer
of entrance in the neural network (view Figure 4 and
Figure 5). This
ANN
was the performance with the
best correlation coefficient of the
P
matrix and of the
Training and Validation Sets. Similar to the
trainrp
algorithm, the
tansig
activation function had noticed
equally great results but not so greatest as
logsig
acti-
vation function.
EEGDiscriminationwithArtificialNeuralNetworks
239
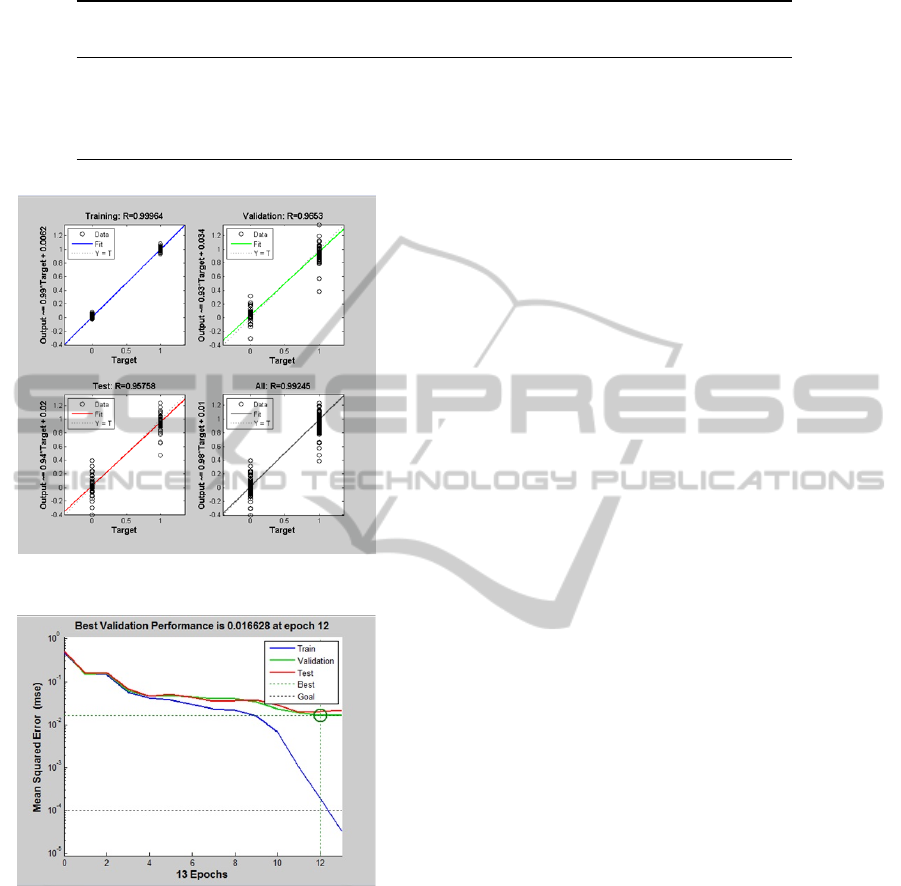
Table 2: Classification results.
Training Transfer Nodes of the Training Test Set Validation P Matrix
Algorithm Function Hidden Layer Set (R) (R) Set (R) (R)
TrainRP Logsig 14 0.98341 0.96138 0.96171 0.97932
TrainLM Logsig 9 0.99964 0.95758 0.9653 0.99245
TrainRP Tansig 11 0.97885 0.93211 0.95087 0.97173
TrainLM Tansig 9 0.99807 0.91164 0.95555 0.98622
Figure 4: Regression Plot with trainlm algorithm.
Figure 5: Performance Plot with trainlm algorithm.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
AD
keeps on defying medical research, even despite
the progress achieved in better knowledge of the com-
plex processes of deterioration of memory levels, this
disease still remains with no prospect of a cure. There-
fore, it is very important to have an early diagnose
of disease in order to avoid their evolution. In this
paper we developed a model based on
ANN
to discrim-
inate between
Cs
and
AD
patients. A set of 14 features
for each electrode was used in the input of the
ANN
.
These features are based in the
PSD
determined with
the
ST FT
. The features consists in the Relative Power
of the
PSD
in the bandwidths of delta, theta, alpha,
beta1, beta2 and gamma, four spectral ratios, the Mean
Frequency, the Individual Alpha Frequency, the Spec-
tral Edge Frequency and the Spectral Entropy. The
output consisted in a binary to classify
Cs
or
AD
pa-
tients. Several
ANN
were experimented with different
number of nodes in the hidden layer and activations
functions. The Resilient Back-Propagation and the
Levenberg-Marquardt training algorithms were also
experimented. The best results give a correlation co-
efficient of 0.961 in the test set. Once the data of this
set were never seen during the training process we
may consider it as a very competitive result compared
with similar previous works. Namely, the obtained
classification results can be compared with the stud-
ies presented in (Vialatte et al., 2005a; Vialatte et al.,
2005b; Vialatte et al., 2008; Rodrigues et al., 2011;
Rodrigues and Teixeira, 2011; Rodrigues, 2011; Melis-
sant et al., 2005).
For a future work we intend to reduce the number
of features used in the input of the
ANN
and identify
electrodes that can be removed due to low discrimi-
native power. Experiment the use of the
PSD
deter-
mined using the Wavelet Transform as presented by
Rodrigues in (Rodrigues, 2011; Rodrigues and Teix-
eira, 2011; Rodrigues et al., 2011).
REFERENCES
Baker, M., Akrofi, K., Schiffer, R., and Michael, W. O. B.
(2008). Eeg patterns in mild cognitive impairment
(mci) patients. Open Neuroimag J., 2:52–55.
Blennow, K. (2005). Amesterd
˜
ao: European College of
Neuropsychopharmacology. ECNP.
Blennow, K., Leon, M., and Zetterberg, H. (2006).
Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet, 368:387–403.
Feldman, H. and Woodward, M. (2005). The staging and
assessment of moderate to severe alzheimer disease.
Neurology, 65:10–17.
Hagan, M. T. and Menhaj, M. (1994). Training feedfor-
ward networks with the marquardt algorithm. IEEE
Transactions on Neural Networks, 5:989–993.
BIOSIGNALS2013-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
240

Hort, J., O’Brien, J. T., Gainotti, G., Pirttila, T., Popescu,
B. O., Rektorova, I., Sorbi, S., and Scheltens, P. (2010).
Efns guidelines for the diagnosis and management of
alzheimer’s disease. European Journal of Neurology,
17:1236–1248.
Jeong, J. (2004). Eeg dynamics in patients with alzheimer’s
disease. Clin. Neurophysiol, 115:1490–1505.
Marquardt, D. (1963). An algorithm for least-squares es-
timation of nonlinear parameters. SIAM Journal on
Applied Mathematics, 11:431–441.
Melissant, C., Ypma, A., Frietman, E., and Stam, C. (2005).
A method for detection of alzheimer’s disease using ica-
enhanced eeg measurements. Artif Intell Med, 33:209–
222.
Moreira, P. and Oliveira, C. (2005). A Doen
c¸
a de Alzheimer e
outras Dem
ˆ
encias em Portugal, chapter Fisiopatologia
da doen
c¸
a de Alzheimer e de outras dem
ˆ
encias., pages
41–60. Lisboa: Lidel Edic¸
˜
oes T
´
ecnicas.
Riedmiller, M. and Braun, H. (1993). A direct adaptive
method for faster backpropagation learning: The rprop
algorithm. Proceedings of the IEEE International Con-
ference on Neural Networks, 1:586–591.
Rioul, O. and Vetterli, M. (1992). Wavelets and signal pro-
cessing. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 8:14–38.
Rodrigues, P. (2011). Diagn
´
ostico da doen
c¸
a de alzheimer
com base no electroencefalograma. Master’s thesis,
Instituto Polit
´
enico de Bragan
c¸
a - Escola Superior de
Tecnologia e Gest
˜
ao.
Rodrigues, P. and Teixeira, J. (2011). Artificial neural net-
works in the discrimination of alzheimer’s disease.
Communications in Computer and Information Sci-
ence, 221:272–281.
Rodrigues, P., Teixeira, J., Hornero, R., Poza, J., and Car-
reres, A. (2011). Classification of alzheimer’s elec-
troencephalograms using artificial neural networks and
logistic regression. Japan - Portugal Nano-Biomedical
Engineering Symposium 2011, 1(ISBN-4-904157-20-
6):33–34.
Stahl, S. (2008). Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology.
Neuroscientific Basis and Practical Applications. Cam-
bridge University Press, third edition.
Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A., Dreyfus, G., Musha, T., Rutkowski,
T., and Gervais, R. (2005a). Blind early detection of
alzheimer’s disease by blind source separation and
bump modelling of eeg signals. Lectues Notes in Com-
puter Science, 3596:683–692.
Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A., Dreyfus, G., Musha, T., Shishkin,
S., and Gervais, R. (2005b). Early detection of
alzheimer’s disease by blind source separation, time
frequency representation, and bump modeling of eeg
signals. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 3696:683–
692.
Vialatte, F., Maurice, M., and Cichocki, A. (2008). Why
sparse bump models? Neuroimage, 41:159.
EEGDiscriminationwithArtificialNeuralNetworks
241
