
Comparing Viral (HIV) and Bacterial (Staphylococcus aureus)
Infection of the Bone Tissue
Mohammad Ali Moni
1
, Pietro Li
`
o
1
and Luciano Milanesi
2
1
Computer Laboratory, Cambridge University, William Gates Building, 15 JJ Thomson Avenue, Cambridge CB3 0FD, U.K.
2
Institute for Biomedical Technologies, Via Fratelli Cervi, 93 20090, Segrate, Italy
Keywords:
Osteomyelitis, HIV, Staphylococcus aureus.
Abstract:
This paper focuses on the differences between S. aureus bacterial and HIV viral infection of the bone tissue.
Both of these infections alters the RANK/RANKL/OPG signalling dynamics that regulates osteoblasts and
osteoclasts behavior in bone remodelling. These infections rapidly lead to severe bone loss and it may even
spread to other parts of the body. Since both HIV and osteomyelitis cause loss of bone mass, we focused
on comparing the dynamics of these diseases by means of computational models. Firstly, we performed
meta-analysis on the gene expression data of normal, HIV and osteomyelitis bone conditions and compare
the effects of HIV and S. aureus infection. We mainly focused on RANKL/OPG signalling, the TNF and
TNF receptor superfamilies and the NF-kB pathway. Using information from the gene expression data, we
estimated parameters for a novel model of osteomyelitis. Then we develop another multi strain HIV ODE
model incorporating the HAART therapy. Our ODE modelling aims at investigating the dynamics of the
effects of osteomyelitis and HIV infection in bone remodelling.
1 INTRODUCTION
Bone remodelling is a cellular process conducted by
osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption
and by osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone for-
mation. Another type of cells, the osteocytes, are
trapped in the bone matrix and these cells play a rele-
vant role in the remodelling process. In normal bone,
the bone resorption and bone formation rate are all
relatively constant (Raggatt and Partridge, 2010). But
pathological conditions such as cancer, infection and
autoimmune diseases can alter the equilibrium be-
tween bone resorption and bone formation, reducing
bone density and increasing the risk of spontaneous
fractures.
The RANK/RANKL/OPG signalling pathway
plays an important role in bone metabolism. RANK
is a protein expressed by osteoclasts and it is a recep-
tor for RANKL, a protein produced by osteoblasts.
RANK/RANKL signalling triggers osteoclast dif-
ferentiation, proliferation and activation, thus it
prominently affects the resorption phase during bone
remodelling. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is a decoy
receptor for RANKL. It is expressed by mature
osteoblasts and it binds to RANKL, thus inhibiting
the production of osteoclasts. While under normal
circumstances, the ratio of RANKL/OPG is carefully
balanced and the increase of RANKL plays an essen-
tial role in favouring resorption through osteoclast
formation, function, and survival.
Osteomyelitis is characterized by severe and rapid
bone loss. It is a bone infection mainly caused
by the aggressive pathogen S. aureus. The action
of S. aureus increases RANKL expression and de-
creases OPG expression in osteoblasts in patients
with staphylococcal osteomyelitis. The increase in
RANKL is likely to trigger osteoclast-induced bone
resorption and bone destruction that may help to ex-
plain patients with osteomyelitis have significant bone
loss (Claro et al., 2011).
On the other hand, infection with the human im-
munodeficiency virus-1 (HIV) and the resulting ac-
quired immune efficiency syndrome (AIDS) affect
not only cellular immune regulation but also the bone
metabolism (Reem et al., 2011). It is observed that
significant number of HIV-1 infected patients exhibit
osteopenia and osteoporosis, leading to higher inci-
dence to develop weak and fragile bones during the
course of disease (Gibellini et al., 2008). Patients with
HIV infection have decreased numbers of osteoblasts,
decreased bone mineralization and increased risk of
fracture compared to age and sex matched HIV unin-
196
Ali Moni M., Liò P. and Milanesi L..
Comparing Viral (HIV) and Bacterial (Staphylococcus aureus) Infection of the Bone Tissue.
DOI: 10.5220/0004249801960201
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms (BIOINFORMATICS-2013), pages 196-201
ISBN: 978-989-8565-35-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

fected patients. However, the molecular mechanisms
behind these associations remain unclear (Cummins
et al., 2011).
So considering the both S. aureus and HIV infec-
tion, we develop a hybride modelling framework for
combining and untangling the relationships of phys-
iological and molecular data. We then apply the
methodology to determine disease related abnormal-
ities of the key osteogenesis molecular network. We
believe that this framework could easily be adapted to
model also other bone diseases like multiple myelo-
mas or Paget’s disease, and that could help in bet-
ter understanding the disruptions of cellular and sig-
nalling mechanisms that underlie such bone patholo-
gies.
2 METHODS
2.1 Data Analysis and ODE Models
For our meta analysis, we have considered 5 different
human microarray data sets from the Gene Expression
Omnibus (htt p : //www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/),
accession numbers are GSE16129, GSE6269,
GSE11907, GSE11908, and GSE18464 (Ardura
et al., 2009; Ramilo et al., 2007). We observe that
RANKL, RANK, OPG and NF-kB proteins impact
more on the bone remodelling for osteomyelitis and
osteoporosis (Ramilo et al., 2007; Ardura et al.,
2009). For this reason to understand the effect of
S. aureus and HIV on osteomyelitison bone remod-
elling, we have taken in account all the genes TNF
and TNF receptor superfamilies including the genes
related to the proteins RANKL, RANK, OPG and
NF-kB proteins. We have selected samples of 48
infected and 27 healthy controls for S. aureus. In case
of HIV infection, we choose 22 data samples of low
viral loads (LVL, <= 10,000 RNA copies/ml), 22
data samples of high viral loads (HVL, => 10,000
RNA/copies/ml) and 11 healthy controls. The data
sets contain data from people of different age and
sex. Here, normalization procedures and statistical
analysis are performed by using Bioconductor R
packages (Gentleman et al., 2004). Standard anova
and Box plots representation were used to analyze
and visualize the expression levels of these genes
for the S. aureus and HIV infection conditions. For
presenting the signaling and interaction pathways
of the genes, we used cytoscape for data integration
and network visualization (Smoot et al., 2011) and
reactome functional interaction (FI) cytoscape plugin
for knowledge base of human biological pathways
and network processes (Joshi-Tope et al., 2005).
We have implemented the ODE models in C++,
R, and using the bioconductor package FME pack-
age (Soetaert et al., 2010) to analyse parameter sen-
sitivity and robustness. We have used MATLAB for
steady states and ODE calculation using state of art
numerical routines. In our models, most of the param-
eters are from biological literature and from the gene
expression data. Even parameters from the mathemat-
ical modelling literatures are estimated from biologi-
cal experimental studies.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Bioinformatics of S. aureus and HIV
Since that both S. aureus and HIV cause loss of bone
mass, we decided to cross-compare the gene expres-
sion data sets of both pathogens infection. We have
compared the expression levels of genes involved in
S. aureus causes osteomyelitis, HIV infection and
healthy controls using the box plots and polar his-
togram (see Figure 1 and 2).
From the analysis of our gene expression data
(GSE16129, GSE6269, GSE11907, GSE11908), we
observe that few genes, related to TNF, TNF receptor
superfamilies including RANKL, RANK, OPG and
NF-kB have statistically different levels of expression
in osteomyelitis and or HIV infection compare to the
healthy controls. We observe that, with respect to
control cases, TNFSF10, TNFSF12, TNFSF13, TN-
FRSF10B, TNFRSF10C, TNFRSF1A, TNFRSF1B,
NFKB2, REL and RELB genes related to RANKL,
RANK, OPG, NF-kB proteins, TNF and TNF recep-
tor superfamilies are over expressed and TNFRSF14,
TNFRSF25, TNFSF11, NF-kB1 and RELA genes are
down regulated in S. aureus caused osteomyelitis (see
Figure. 1).
From the meta analysis of the HIV infection, we
observe that TNF, TNFSF4, TNFSF13, TNFRSF8,
TNFRSF10A, TNFRSF21, TNFAIP3 and TNFAIP6
genes are up regulated and TNFSF13B, TNFSF18,
TNFSF11, TNFRSF10C, TNFRSF10D, TNFAIP8
and TNFAIP8L2 are down regulated (see Figure. 2).
It is notable only TNFSF13 is up-regulated in both
types of diseases and TNFSF11 (RANKL genes) is
down regulated in the both osteomyelitis and HIV in-
fection.
Interestingly we found that, despite of increasing
RANKL gene expression in osteomyelitis, OPG gene
expression become more deregulated in osteomyeli-
tis. Therefore we report that gene expression in HIV
and osteomyelitis could generate an unbalance be-
tween RANKL and OPG, but also other genes, re-
ComparingViral(HIV)andBacterial(Staphylococcusaureus)InfectionoftheBoneTissue
197
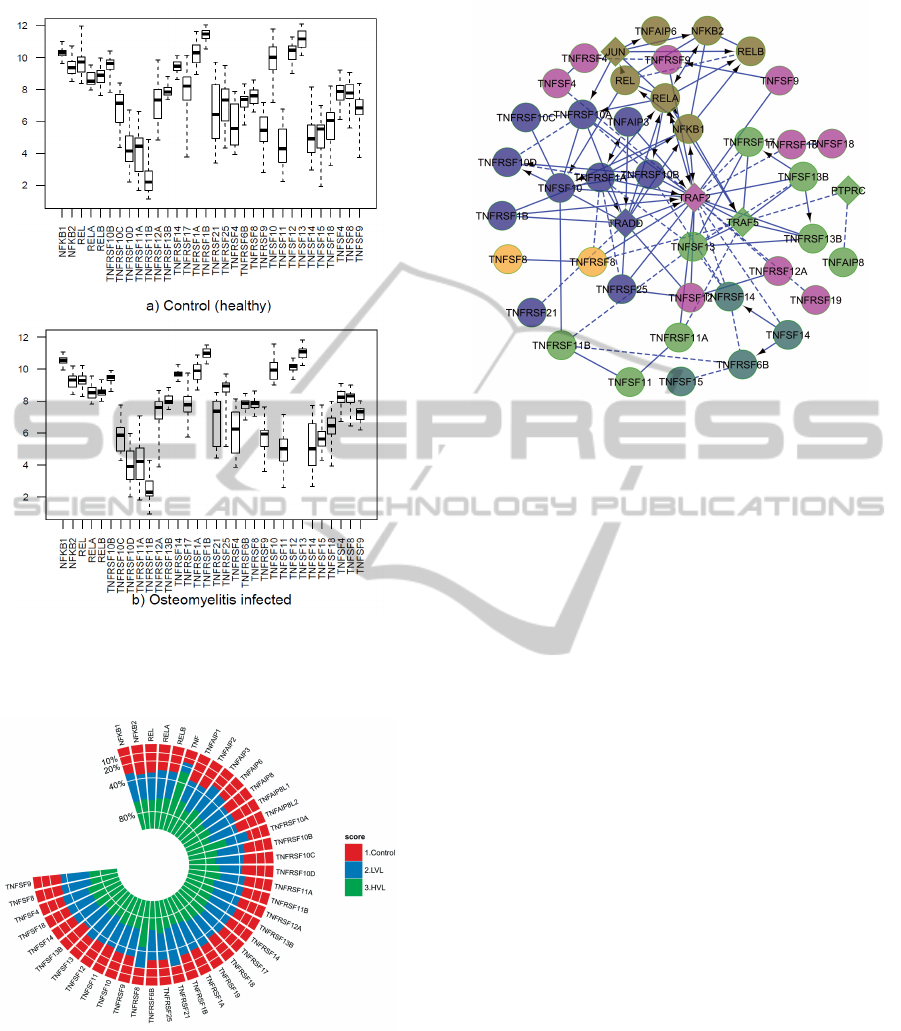
Figure 1: Expression level (y axis) of the 32 genes (x axis)
of the human osteoclasts corresponding to a) 27 healthy
controls and b) 48 S. aureus caused osteomyelitis infected
patients.
Figure 2: Average expression level of the genes are com-
pared among healthy control, low viral level and high viral
level infected patients.
lated to TNF, TNF receptor superfamilies and to NF-
kB may be involved. Finally, we showed signaling
pathways of these genes and grouped based on their
interaction pathways (see Figure. 3).
Figure 3: Network of the 44 genes related to the NF-kB, tnf
and tnf receptor super families including RANKL, RANK
and OPG. The network includes both up and down regulated
genes, on the basis that both will potentially appear in a
single differentially expressed pathway. Circular nodes are
genes in the microarray data sets, while diamond shaped
nodes are linkers, that were determined programmatically to
connect the circular nodes in a network. The whole network
is clustered based on the signaling pathways and showed
each pathway using individual color.
3.2 Cell Interaction Models
Although gene expression and actual protein abun-
dance are only loosely correlated, taking into account
the results of gene expression data, we modified the
autocrine and paracrine parameters of the existing
mathematical model based on Komarova model (Ko-
marova et al., 2003). We considered more appropri-
ate to incorporate into the model the algebraic rela-
tionship of positive and negative regulators (such as
RANKL and OPG) than just the RANKL change.
On the basis of this consideration we developed
new models for reproducing osteomyelitis conditions.
Then we developed a multistrain HIV model includ-
ing the RANKL and OPG gene expression level with
condition.
3.2.1 Bacterial Infection Model
We develop a differential equation model for describ-
ing the dynamics of bone remodelling and of bone-
related pathologies at a multicellular level. The model
describes the continuous changes and the interactions
between populations of osteoclasts and osteoblast.
Our cellular-level model is based on the work by Ko-
marova et al (Komarova et al., 2003), where they
developed an important model for bone remodelling
BIOINFORMATICS2013-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
198
based on experimental results described in Parfitt’s
work (Parfitt, 1994) which has inspired many other
similar models.
The ODE model for bone remodelling describes
the dynamics of osteoblasts’ (Ob) and osteoclasts’
(Oc) population and calculates the bone density as
a function of Ob and Oc. The model describes the
autocrine and paracrine relationships between osteo-
clasts (Oc) and osteoblasts (Ob).
Here the parameters g
i j
describe the effective-
ness of autocrine and paracrine regulation, g
11
de-
scribes the osteoclast autocrine regulation, g
22
is the
osteoblast autocrine regulation, g
21
is the osteoblast-
derived paracrine regulation, and g
12
is the osteoclast
paracrine regulation. The autocrine signalling has a
positive feedback on osteoclast production (g
11
> 0),
and paracrine signalling has a negative feedback on
osteoclast production (g
21
< 0). The autocrine signal-
ing has a positive feedback on osteoblast production
(g
22
> 0), and paracrine signalling has a positive feed-
back on osteoblast production (g
12
> 0). The overall
regulatory circuit should lead to a positive mineral-
isation balance (z) which could be described by the
expression
dz
dt
= −k
1
O
c
+ k
2
O
b
where k
1
and k
2
are
the resorption and formation rates, respectively. The
bone density is determined by the difference between
the actual resorption and formation activity when os-
teoclasts and osteoblasts exceed their steady levels.
Therefore bone density is calculated as a function of
z. Moreover, we introduced the regulation factors
in order to model an increased RANKL expression
by osteoblasts, which results both from the analysis
performed on gene expression data and from exper-
imental evidences (Morabito, 2004). In our model
g
21
is the result of all the factors produced by os-
teoblasts that activates osteoclasts and as explained
in (Komarova et al., 2003), g
21
= RANKL − OPG
where RANKL is the effectiveness of RANKL sig-
nalling while OPG is the effectiveness of OPG sig-
nalling.
Starting from this, we consider the progressing of
osteomyelitis induced by the S. aureus (variable B).
Since several evidences show that the dynamics of the
bacterial population follows a Gompertz curve, we
consider an equation of the form
dB
dt
= γ
B
B · log(
s
B
),
where γ
B
is the growth rate of bacteria, and s is the
carrying capacity, i.e. the maximum population size.
Additionally, we introduced four parameters f
i j
used
to model the effects of the infection on the autocrine
and paracrine regulation factors g
i j
. The resulting
equations are:
dO
c
dt
=α
1
O
g
11
(1+ f
11
B
s
)
c
O
g
21
(1− f
21
B
s
)
b
− β
1
O
c
, (1)
dO
b
dt
=α
2
O
g
12
/(1+ f
12
B
s
)
c
O
g
22
− f
22
B
s
b
− β
2
O
b
, (2)
dz
dt
= − k
1
max(O
c
−
¯
O
c
,0) + k
2
max(O
b
−
¯
O
b
,0)
(3)
dB
dt
=(γ
B
−V )B · log(
s
B
). (4)
b
Time [days]
c) Bone
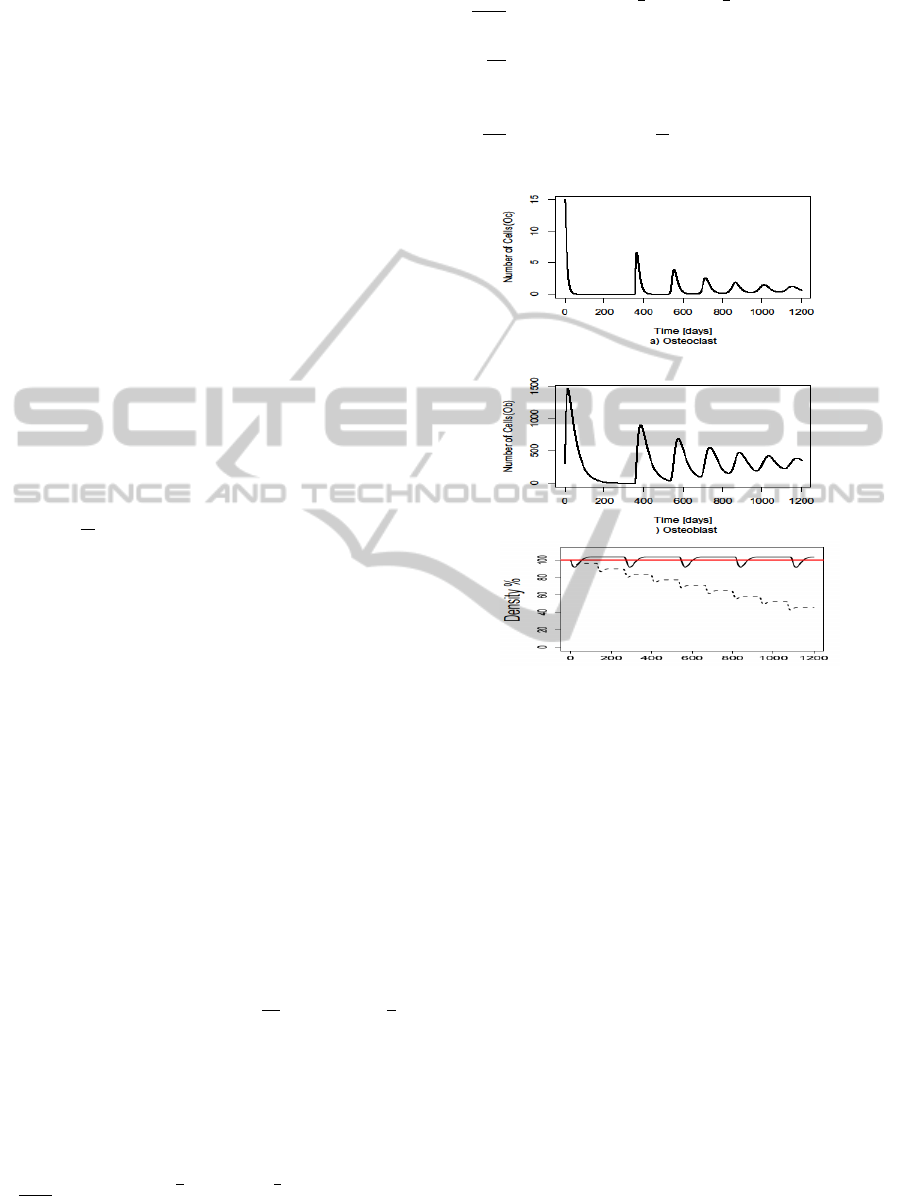
Figure 4: Simulation results of the ODE model. The os-
teomyelitis condition affects the osteoclast, osteoblast pat-
terns and bone density. In x axis time in days and y axis the
local cell density. In case of bone density figure, red line
represents the steady state, black line represents the healthy
condition and dashed line is the effect of osteomyelitis.
Here, we introduced four parameters: f
i j
used to
model the effects of the infection on the autocrine and
paracrine regulation factors g
i j
. The bacterial param-
eters f
11
, f
12
, f
21
, f
22
are all nonnegative.
¯
O
c
and
¯
O
b
denote the steady states of O
c
and O
b
, respec-
tively. The S. aureus-induced infection affects the
normal remodelling activity by reducing osteoblasts’
growth rate and increasing RANKL and decreasing
OPG expression. The parameter V describes the ef-
fectiveness of the antibiotic treatment as a factor de-
creasing the growth rate γ
B
of bacteria. Two dif-
ferent kinds of treatment can be distinguished: bac-
teriostatic treatments that stop bacteria proliferation
(V = γ
B
); and bacteriocide treatments which kill bac-
teria (V > γ
B
). Simulation results for osteoclasts, os-
teoblasts and bone density are compared in Figure 4.
ComparingViral(HIV)andBacterial(Staphylococcusaureus)InfectionoftheBoneTissue
199
3.2.2 HIV Infection Model
Here, our work is based on the evolution of a multi-
strain ode model of HIV-1 dynamics, firstly appeared
in (Sguanci et al., 2007). These models are well pre-
sented and take specific biological reality into account
and the effect of the RANKL, which is the main issue
for osteomyelitis and bone remodelling. Furthermore,
we have introduced an abstract representation of the
HAART therapy treatment by including the necessary
parameters that rule the dynamics of our model ac-
cording to the known effects of the treatment. Muta-
tion parameter µ generates additional strains of virus
from existing phenotype strains. Here, we have con-
sidered k different strains of viral particles and in-
fected cells.
The interactions among the immature T cells (U),
uninfected mature T cells (T ), infected cells (I), viral
strains (V ) and RANKL signaling (G) are translated
into following system of ordinary differential equa-
tions (ODEs):
dU
dt
=λ − δ
ut
U −δ
u
U
∑
k
V
k
− δ
ug
UG (5)
dT
i
dt
=δ
ut
U −
∑
k
(1 − η
RT
)β
k
V
k
T
i
− δ
t
T
i
− α
ti
T
i
I
k
(6)
dI
k
dt
=
∑
k
0
µ
kk
0
(1 − η
RT
)β
k
0
V
k
0
∑
i
T
i
− δ
i
I
k
+ α
ti
T
i
I
k
(7)
dV
k
dt
=(1 − η
PI
)πI
k
− δ
v
V
k
(8)
dG
dt
=σ
∑
k
V
k
(9)
Equation (5) describes the constant production of
immature T cells by the thymus at rate λ and their
transformation into mature T cells at rate δ
ut
. For
RANKL immature T cells are cleared at a rate δ
ug
and immature T cells are also cleared more at a rate
δ
u
.
Equation (6) describes how uninfected mature T
cells are produced at fixed rate δ
ut
by the pool of im-
mature T cells. These cells interact with any strain of
the virus, V
k
and become infected at rate β
k
= β ∀k.
The infectiousness parameter, β, is not constant over
time, but depends on the interplay between viruses. In
addition, T -cells are cleared out at fixed rate α
ti
.
Equation (7) describes the infection of mature
CD4+ T cells. Infected cells of strain k arise upon
the interaction of a virus of strain k with any of the
mature T cell strains. The infected cells, in turn, are
cleared out at rate δ
i
. In addition, the infected cells
are added for cell to cell spreading of viruses at fixed
rate α
ti
.
Equation (8) describes the production of viral
strains from infected cells at fixed rate π, viruses are
cleared out at fixed rate δ
v
.
Equation (9) describes the production of RANKL
for HIV at fixed rate σ.
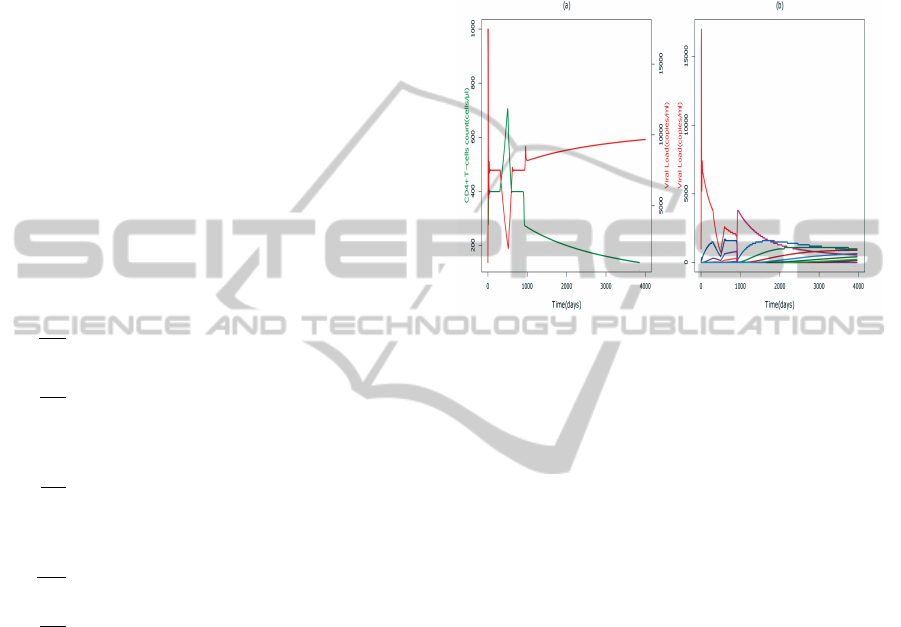
Figure 5: Therapy implemented from 200 days to 400 days
a) CD4 +T cells count -green color (cells/ml) and corre-
sponding viral load -red color (copies/ml) b) Effect on indi-
vidual strain based viral load (copies/ml).
By using this model, it is possible to predict some
scenarios of HAART treatment. HAART is one of
the ways suppressing viral replication in the blood
while attempting to prevent the virus rapidly devel-
oping resistance to the individual drug. The effect of
the HAART treatment is simulated by an interval of
time from 200 days to 400 days is reported in Fig-
ure. 5. Our results suggest that the drug treatment is
able to increase the concentration of healthy CD4+ T-
cells and decrease the concentration of virus and in-
fected cells in the blood. So, with implementing the
HAART therapy also changes the expression levels of
RANKL, that effects on the bone remodelling. How-
ever, it is observed that after discontinuing the treat-
ment, viral load increases again and hence concen-
tration of CD4+ T-cells decreases. Moreover, we ob-
served that short HAART treatments have small effect
if administrated when CD4 +T cells count is above
200 and they have even smaller effect when CD4+ T
cells counts are below 200.
4 CONCLUSIONS
From the meta analysis of gene expression data, we
observe that like S. aureus, HIV-1 increases the os-
teomyelitis that impact on bone remodeling. HIV-
1 virus upregulated and down regulated expression
BIOINFORMATICS2013-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
200

level of some genes in the similar pattern of S. aureus.
It is notable that the most important gene, RANKL,
is down regulated in the both S. aureus and HIV in-
fections. So we developed models for the bone re-
modeling including the effect of S. aureus caused os-
teomyelitis and HIV progression incorporating the ef-
fect of the RANKL that helps to gain better insight
of the complexity of the disease progression. Ac-
cording to our model, HAART therapy can substan-
tially decrease viral load and significantly increase
CD4+ T cells, but it cannot eradicated virus com-
pletely even after implementing the therapy for a long
time. From a methodological point of view this mod-
elling approach has led to the proposal of considering
additional estimators of the bone pathologies as diag-
nostic tool. That could also inspire the ideal situa-
tion in which a personalised model is generated from
(personalised) data and the comparison between clin-
ical data obtained during periodic medical check-up
is compared with the computer predictions. There-
fore our work is meaningful in perspective of a clin-
ical bioinformatics characterized by a close coupling
between clinical measures and modeling prediction.
REFERENCES
Ardura, M., Banchereau, R., Mejias, A., Di Pucchio, T.,
Glaser, C., Allantaz, F., Pascual, V., Banchereau, J.,
Chaussabel, D., and Ramilo, O. (2009). Enhanced
monocyte response and decreased central memory t
cells in children with invasive staphylococcus aureus
infections. PLoS One, 4(5):e5446.
Claro, T., Widaa, A., O’Seaghdha, M., Miajlovic, H., Fos-
ter, T., O’Brien, F., and Kerrigan, S. (2011). Staphylo-
coccus aureus protein a binds to osteoblasts and trig-
gers signals that weaken bone in osteomyelitis. PloS
one, 6(4):e18748.
Cummins, N., Klicpera, A., Sainski, A., Bren, G., Khosla,
S., Westendorf, J., and Badley, A. (2011). Human im-
munodeficiency virus envelope protein gp120 induces
proliferation but not apoptosis in osteoblasts at physi-
ologic concentrations. PloS one, 6(9):e24876.
Gentleman, R., Carey, V., Bates, D., Bolstad, B., Dettling,
M., Dudoit, S., Ellis, B., Gautier, L., Ge, Y., Gentry,
J., et al. (2004). Bioconductor: open software devel-
opment for computational biology and bioinformatics.
Genome biology, 5(10):R80.
Gibellini, D., De Crignis, E., Ponti, C., Cimatti, L., Borderi,
M., Tschon, M., Giardino, R., and Re, M. (2008). Hiv-
1 triggers apoptosis in primary osteoblasts and hobit
cells through tnfα activation. Journal of medical vi-
rology, 80(9):1507–1514.
Joshi-Tope, G., Gillespie, M., Vastrik, I., D’Eustachio, P.,
Schmidt, E., de Bono, B., Jassal, B., Gopinath, G.,
Wu, G., Matthews, L., et al. (2005). Reactome: a
knowledgebase of biological pathways. Nucleic acids
research, 33(suppl 1):D428–D432.
Komarova, S., Smith, R., Dixon, S., Sims, S., and Wahl, L.
(2003). Mathematical model predicts a critical role for
osteoclast autocrine regulation in the control of bone
remodeling. Bone, 33(2):206–215.
Morabito, N. e. a. (2004). Osteoprotegerin and RANKL in
the Pathogenesis of Thalassemia-Induced Osteoporo-
sis: New Pieces of the Puzzle. Journal of Bone and
Mineral Research, 19(5):722–727.
Parfitt, A. (1994). Osteonal and hemi-osteonal remodeling:
The spatial and temporal framework for signal traffic
in adult human bone. Journal of cellular biochemistry,
55(3):273–286.
Raggatt, L. and Partridge, N. (2010). Cellular and molecular
mechanisms of bone remodeling. Journal of Biologi-
cal Chemistry, 285(33):25103.
Ramilo, O., Allman, W., Chung, W., Mejias, A., Ar-
dura, M., Glaser, C., Wittkowski, K., Piqueras, B.,
Banchereau, J., Palucka, A., et al. (2007). Gene
expression patterns in blood leukocytes discriminate
patients with acute infections. Blood, 109(5):2066–
2077.
Reem, A., Manisha, H., Gary, D., Riana, C., Sohrab, D.,
Nora, G., Natasha, I., Nicole, M., Linda, P., Amy, G.,
et al. (2011). Osteoimmunopathology in hiv/aids: A
translational evidence-based perspective. Pathology
research international, 2011.
Sguanci, L., Bagnoli, F., and Lio, P. (2007). Modeling hiv
quasispecies evolutionary dynamics. BMC Evolution-
ary Biology, 7(Suppl 2):S5.
Smoot, M., Ono, K., Ruscheinski, J., Wang, P., and Ideker,
T. (2011). Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data in-
tegration and network visualization. Bioinformatics,
27(3):431–432.
Soetaert, K., Petzoldt, T., et al. (2010). Inverse modelling,
sensitivity and monte carlo analysis in r using package
fme. Journal of Statistical Software, 33(3):1–28.
ComparingViral(HIV)andBacterial(Staphylococcusaureus)InfectionoftheBoneTissue
201
