
Planning and Reactive Agents in Dynamic Game Environments
An Experimental Study
Roman Barták, Cyril Brom, Martin Černý and Jakub Gemrot
Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Malostranské náměstí 25, Praha 1, Czech Republic
Keywords: Action Planning, Dynamic Environments, Intelligent Virtual Agents, Comparison.
Abstract: Many contemporary computer games can be described as dynamic real-time simulations inhabited by
autonomous intelligent virtual agents (IVAs) where most of the environmental structure is immutable and
navigating through the environment is one of the most common activities. Though controlling the behaviour
of such agents seems perfectly suited for action planning techniques, planning is not widely adopted in
existing games. This paper contributes to discussion whether the current academic planning technology is
ready for integration to existing games and under which conditions. The paper compares reactive techniques
to classical planning in handling the action selection problem for IVAs in game-like environments. Several
existing classical planners that occupied top positions in the International Planning Competition were
connected to the virtual environment of Unreal Development Kit via the Pogamut platform. Performance of
IVAs employing those planners and IVAs with reactive architecture was measured on a class of game-
inspired maze-like test environments under different levels of external interference. It was shown that agents
employing classical planning techniques outperform reactive agents if the size of the planning problem is
small or if the environment changes are either hostile to the agent or not very frequent.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dynamic, real-time and continuous environments
pose a big challenge for the design of intelligent
virtual agents (IVAs). First person role-playing
(RPG) and shooter (FPS) games are canonical
examples of a subclass of such environments that are
motion-intensive while offering the agent only
limited options to interact with the environment and
with other agents. Many serious games also fit this
description.
One of the fundamental problems faced by an
IVA in such an environment is the action selection
problem – what to do next? In computer games, the
prevalent approach is using reactive techniques, the
most common being behaviour trees (Champandard,
2007) and finite state machines (FSMs) (Fu and
Houlette-Stottler, 2004). Although the reactive
techniques handle the dynamic aspects of the world
well, they have some limitations: their plans are
fixed and cannot be altered during runtime and they
require a large amount of authoring work as the
world gets more complex. There is however a
complementary approach to solve the action
selection problem – AI planning, which has a history
of over 40 years of academic research. Planning
could theoretically allow IVAs to act smarter while
easing the design burden. In this paper we focus on
the longest studied approach – classical planning as
solved by STRIPS (Fikes and Nilsson, 1971).
Unfortunately, the gap between game AI and
planning communities is still huge and only a few
attempts were made to employ classical planning for
controlling IVAs in dynamic environments. There
are also numerous issues to be addressed for
successful application of planning in complex
domains (Pollack and Horty, 1999). While planning
implementations in FPS-like domains do exist, we
are not aware of any rigorous comparison of
classical planning to reactive techniques in such
environments.
The goal of this paper is to determine the
conditions that allow AI planning to outperform
reactive techniques in controlling IVAs in game-like
environments. This is done by designing a class of
agent centric game-like motion-intensive test
environments that allow a smooth adjustment of
their dynamicity. Performance of agents (measured
by the solution time and the number of solved
problems) with reactive approach and agents
234
Barták R., Brom C.,
ˇ
Cerný M. and Gemrot J..
Planning and Reactive Agents in Dynamic Game Environments - An Experimental Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0004254202340240
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2013), pages 234-240
ISBN: 978-989-8565-38-9
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

controlled by planners is then compared under
different levels of external interference.
The rest of the paper starts with discussion of
related research. Afterwards the actual experimental
setup is introduced. Then the experimental results
are presented and the final part discusses the results
and points out possible future research.
2 RELATED WORKS
To our knowledge, the only published papers on
planning implementation in a commercial game
describe the work of Orkin on F.E.A.R. and the
GOAP system (Orkin, 2006) that dates back to
2004-2006. GOAP is a planning system derived
from STRIPS, but enhanced to better suite game
needs. GOAP was reportedly used in other games
(Orkin, 2012) and other planning systems for games
have likely been created. However, no research
papers have been published yet.
Vassos and Papakonstantinou (2011) tested the
BlackBox (Kautz and Selman, 1998) and Fast
Forward (Hoffmann and Nebel, 2001) planners on a
domain representing an FPS game. They show that
the planners are able to plan in sub-second time for
reasonably sized problems. However, the planning
component is not connected to any real simulation.
Thompson and Levine (2009) compared a
performance of an agent employing a classical
planner on several runs in static and dynamic
versions of the same environment. The paper is
however focused on the agent architecture and the
performance comparison is very brief.
Long (2007) run a set of matches in Unreal
Tournament between bots controlled by FSMs and
bots controlled with GOAP. Bots controlled with
GOAP win the matches more often, but no fine-
grained statistical analysis has been done.
We know no other performance comparison of
classical planning techniques in game-like domains.
There are however other related papers where
different planning approaches are included.
Two of the alternative approaches to classical
planning are the hierarchical task networks (HTN)
formalism and Markov decision processes (MDP).
The reader is referred to works by Hawes (2004) and
by Hoang, Lee-Urban, and Muñoz-Avila (2005) for
evaluations of HTN in game-like environments and
to works by Balla all Fern (2009) and Nguyen et al.
(2011) for MDP evaluations.
Overall, the aforementioned papers show that
planning in dynamic real-time environments is
feasible and performs well against various baselines,
but the papers either do not provide a rigorous
comparison or do not compare planners directly to
reactive techniques. This paper addresses this gap by
deep comparison of classical and reactive planners.
3 EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
Comparing reactive techniques to planning is a
multi-faceted problem and there are many possible
design options. Since the area of planning in
dynamic game-like domains is not well studied, it is
important to focus on a well-defined problem with a
limited number of parameters first. The dynamicity
of environment was chosen as the most important
factor for this paper, while all the other factors were
either left out completely or kept as simple as
possible. Still there are many ways how dynamicity
may be achieved. Thus it may be useful to
investigate the nature of dynamicity present in
games first.
In most game-like environments, the changes are
continuous while planning, as other symbolic AI
approaches, is discrete by nature. A natural way to
discretize the dynamics is to consider only
“important” changes, i.e., the changes that would
affect a chosen discrete representation of the world.
On a very abstract level, discrete dynamics may be
considered as interference to the initially static state
of the (symbolic) world. Interference may be
broadly categorized with three general parameters:
delay – mean delay between two successive
changes;
impact – the scope of the impact of a single
change to the state of the environment; and
attitude – whether hostile or friendly changes
are dominant. The hostile changes interfere with
agent’s goals, while the friendly changes open
new possibilities for the agent to reach its goals.
Table 1: Comparison of game situations by their
interference profile.
Situation Delay Impact Attitude
FPS shootout 0.5 - 2s Small Hostile
Quest in a RPG, no combat > 5s Medium Balanced
Getting food in The Sims 1 – 5s Small Friendly
Navigating through
a spaceship falling apart
1 – 3s Large Hostile
Table 1 summarizes a few game situations with
respect to the above parameters. However the reader
should keep in mind that such summary necessarily
involves a large amount of subjective interpretation
PlanningandReactiveAgentsinDynamicGameEnvironments-AnExperimentalStudy
235

and therefore is by no way definitive.
It is beneficial if the test environment covers the
complete spectrum of interference parameters,
because such an environment may be considered as
an abstract model of a whole class of games. While
most of the previous work in this area focused on
performing matches between two classes of agents,
we let the agents in our work to solve a common
problem individually. This should mitigate the
influence of implementation details of the agents on
overall result trends. It is also important that the
problem is not overly complex, so that there is not
much room for improvement of reactive techniques
by fine-tuning of the reactive plans by hand.
To keep the focus area small, we expect the
world to be fully observable and the actions
available to the agent to be deterministic.
3.1 Test Environment
The proposed game environment consists of rooms
on a grid that are connected by corridors. There is a
door in the middle of each corridor. On both ends of
the corridor, there is a button. A button may open
one or more doors and/or close one or more doors all
over the map. Initially, all doors are closed. The
agent starts at a predefined room and has a goal
room to reach. The agent is aware of all effects of all
buttons. See Figure 1 for an example scenario in
such an environment. The shortest solution to go
from A1 to C2 is to: 1) Push the east button at A1. 2)
Go to B1. 3) Push the west button at B1. 4) Go to A2
(through A1). 5) Push the north button at A2. 6) Go
to C1 (through A1 and B1). 7) Push the west button
at C1. 8) Go to C2 (through B1 and B2), which is
the goal,
Figure 1: Example of a map.
Note that while this map is very small, it
demonstrates that the problem at hand cannot be
solved in the most straightforward way – the
solution requires the agent to move away from the
goal room twice. Also there is a dead end: if the
agent performs Steps 1 – 4 and then pushes the east
button at A2 to get to B2, he traps himself and is no
longer able to reach the goal.
An easy and efficient way for introducing
interference into the environment is to repeatedly
choose a subset of doors at random and alter their
state. The interference parameters are then
implemented in a straightforward way: the impact is
the fraction of the total door count that is affected
(on average) by a single interference. The attitude is
represented by the friendliness parameter, which is
the probability that a single door is set to open state
when it was chosen for interference.
3.2 Agent Action Selection
The agents have only two classes of actions to
choose: move to an adjacent room and push a button
in the current room. The details of execution of the
actions are delegated to an abstract interface to the
virtual world, which is the same for all agents.
Apart from the main action selection mechanism,
there are two kinds of planning heuristics available
to the agents:
(H1) If there is a clear path to the goal location, then
follow that path.
(H2) If there is a button in the same room as the
agent that will open an unopened door and will
not close any open door, then push the button.
Heuristic actions have a higher priority than the
agent logic – if the conditions are met, they are
always triggered.
Preliminary experiments have shown that
heuristic H1 is beneficial for all agents, while H2 is
beneficial for most tested reactive agents but its
effect on the planning agent performance is
questionable and the planning agents were not
employed with it in the consecutive tests. To
implement heuristics and reactive behaviour, agents
have a pathfinding module. From the experiment
point of view the total time spent in pathfinding was
negligible.
3.3 Agent Types
Initially, three reactive agent types were examined
with different heuristics. After a set of preliminary
experiments one instance of each type was chosen
for the final comparison. Two were chosen for their
high performance and one was chosen as a baseline:
Inactive – the agent performs only actions
triggered by heuristic H1 (baseline agent).
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
236

Random – in every round, the agent chooses a
reachable button at random moves to its
location and pushes it. The agent uses both
heuristics H1 and H2.
Greedy – if it is possible to move to a place
closer to the goal, the agent moves there. The
agent does not push any buttons, unless it is a
heuristic action; both heuristics are used.
Note that if there is interference and it is not
extremely unfriendly, the Greedy agent is likely to
eventually succeed in solving a map if the agent is
given enough time. However it is also likely that this
agent will produce “plans” far away from the
theoretical optimum.
The planning agent translates the actual state of
the world into the PDDL modelling language (Fox
and Long, 2003) and sends it to the planner. Until
the planner responds, the agent initiates no action.
When the plan is received, it is executed sequentially
and it is continuously checked for validity. If the
check fails or a heuristic action is triggered or if an
action fails to execute, the current plan is discarded
and the planner is called to yield a new one. All
planning agents used H1 as their only heuristic.
3.4 Chosen Planners
Out of the four fastest planners at the International
Planning Competition (IPC) 2011 three were based
on the Fast Downward platform (Helmert, 2006),
including the winner. The winning planner – LAMA
2011 (Richter et al., 2011) was chosen to represent
this platform. The second fastest planner at IPC
2011 was the Probe (Lipovetzky and Geffner, 2011)
and so it was chosen too. Apart from the two very
recent planners, three older planners, which have
earned reasonable respect in the past years, were
chosen. The first is SGPlan 6 (Hsu and Wah, 2008),
which won IPC 2006. The Fast Forward (FF)
planner (Hoffmann and Nebel, 2001), a top
performer at IPC 2002, was also chosen. All four
aforementioned planners are based on forward state
space search. The last included planner is the
BlackBox (BB) (Kautz and Selman, 1998) that
constructs a planning graph for the problem and
converts it into a SAT problem.
3.5 Technical Details
The experiments were carried out in the virtual
environment of Unreal Development Kit (UDK)
(Epic, 2012). The agents were written in Java using
the Pogamut platform (Gemrot et al., 2009). Moving
from one room to an adjacent one takes
approximately one second, while approaching and
pushing a button takes about 200ms.
All the final experiments were run on a dedicated
computing server with two AMD Opteron 2431
processors (6 cores each, 2.4GHz, 64bit) and 32GB
RAM, running CentOS (Linux core version 2.6).
Five experiments at a time were run. This setup did
allow each planner instance and each environment
simulation to have its own core to run on and left a
big margin of free RAM so that the experiments did
not compete for resources.
3.6 Experiment Scale
Since the simulations run in real-time, the
experiments are very time consuming, especially for
large maps (up to 15 minutes per run). Therefore the
number of maps was limited. Table 2 summarizes
the four map types used. The number of actions
refers to the number of grounded “push button” and
“move to adjacent room” actions. The actual maps
were generated at random.
The interference parameters were set based on
the estimates from Table 1 and observations from
the preliminary experiments. The delay values were
chosen as 0.5, 1.5 and 3 seconds. The impact
(fraction of the doors changed at once) values were
0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 and the friendliness (probability a
door opens) values were 0, 0.15, 0.3, 0.5 and 0.7.
More focus was kept on hostile environments since
reactive agents clearly dominated with friendliness
0.3 and higher. For each combination of map, agent,
and interference parameters three experiments were
run with different random seeds for interferences.
This led to a total of 29 295 experimental runs
taking over 50 days of computing time.
Table 2: Map classes and domain sizes (grounded actions).
Map Class/Size
Number of
Maps
Domain Size
(atoms/actions)
Small (55) 9 65 / 90 - 160
Medium (77) 9 133 / 190 - 336
Large (1010) 9 280 / 390 - 720
1313 4 481 / 650 - 1248
4 RESULTS
The primary metric is the success rate. It measures
whether the agent managed to reach the goal before
a specified timeout elapsed. The timeout was set
(separately for each map size) to 5 times the time
needed by all planning agents on average to reach
PlanningandReactiveAgentsinDynamicGameEnvironments-AnExperimentalStudy
237

the goal without interference. Statistical results for
the success rates are assessed using multiple
comparisons of means with Tukey contrasts
(Hothorn et al., 2008) over an ANOVA fit with a
first order generalized linear model.
In the preliminary runs, the LAMA 2011 planner
performed very poorly (worse than Random and
only slightly better than Inactive). The main reason
is that the Fast Downward platform carries out a
quite costly translation of the PDDL input to
different formalism before starting the actual
planning. The pre-processing of our domains took
from several hundred milliseconds to several
seconds, which is a big performance hit, considering
the interference delays. To save computing time,
LAMA 2011 was removed from further
experiments.
4.1 Overall Performance
In total results (see Table 3) FF, BB, SGPlan 6 (SG)
and Greedy are indistinguishable (all p > 0.88),
while all the other differences are significant (all
p < 10
-3
). On small maps, differences among
planners are not significant, while all other
differences are (all p < 10
-3
). Although the actual
results differ, similar p-values hold for medium and
large maps except that Probe–BB difference
becomes significant (p < 10
-3
). On 13x13 maps,
Greedy is significantly better than the rest (all
p < 10
-3
) and SG with FF are better than Inactive
(p < 10
-3
and p = 0.01 respectively). Other
differences are not significant. The Inactive baseline
bot showed that in many cases no smart acting is
required to complete a map.
While the success rate of planning agents
decreases with the growing map size, the success
rate of Greedy and Inactive behaves differently. This
is due to the different timeout values – in small,
medium and large maps Inactive and Greedy agent
reached the goal shortly before the respective
timeout in many runs, indicating that the success rate
is likely to grow if they were given more time. For
1313 maps, most of the runs finished long before
the timeout.
An important metric is also the time the agent
spent solving the problem – the solution time. The
solution time is considered only for the runs where
the agent actually reached the goal. To analyse the
solution time, a linear model is fitted to the data with
solution time log transformed to be closer to normal
distribution, and Tukey’s HSD test (McKillup,
2006) is performed to reveal significant differences
between agent pairs.
Greedy performed clearly the best among the
reactive agents. The results of Greedy and planning
bots are presented in Table 4. On small maps, all
differences are significant (all p < 10
-3
) except for
SG-BB (p = 0.2) and Probe–FF (p = 0.99). On both
the large and the medium maps, all planners beat
Greedy (all p < 10
-5
), while the only significant
difference between the planners is Probe–BB
(p < 0.01, other p > 0.14). On 1313 maps, all
differences except for FF–SG and BB–Greedy are
significant (all p < 2·10
-5
).
Table 3: Average success rates over all experiment runs.
Best results in each row are highlighted.
Map BB FF Probe SG Greedy Rand Inactive
Small 0.80 0.80 0.76 0.80 0.61 0.64 0.25
Medium 0.69 0.66 0.63 0.67 0.57 0.52 0.30
Large 0.51 0.48 0.46 0.48 0.56 0.40 0.32
1313 0.40 0.43 0.42 0.44 0.68 0.42 0.38
Total 0.60 0.59 0.57 0.60 0.61 0.50 0.31
Table 4: Average solution times [s] with std. deviation (in
brackets). Best results in each row are highlighted.
Map BB FF Probe SG Greedy
Small 23.3 (13) 28.2 (19) 28.1 (15) 24.7 (14) 32.4 (19)
Medium 42.7 (27) 46.0 (30) 50.2 (31) 46.2 (30) 58.6 (38)
Large 72.1 (46) 75.7 (49) 85.6 (51) 78.5 (49) 96.5 (58)
1313 214 (188) 167 (144) 206 (167) 181 (172) 253 (218)
While the results for solution time are favourable
to the planners, they should be interpreted with
caution, since the number of successful runs is very
different among the agents (see Table 3). Thus the
longest times – the ones where the agent failed to
reach the goal – are effectively not included.
For reactive agents, the time spent deliberating is
almost negligible – less than 0.2% of the solution
time, the planning agents however spent on average
from 25% to 33% of solution time deliberating. SG
showed the least growth of time for single planning
execution with the growing map size.
4.2 Performance and Dynamicity
While all the dynamicity parameters have
statistically significant impact on the agent
performance (for both metrics), the interference
impact has smaller effect than the interference delay.
This is most likely due to the fact, that the effect of a
change in interference impact is much more
dependent on the friendliness setting. There is
indeed a high interaction factor between the two.
Interestingly, the effect of the interference impact is
least visible on the reactive agents.
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
238
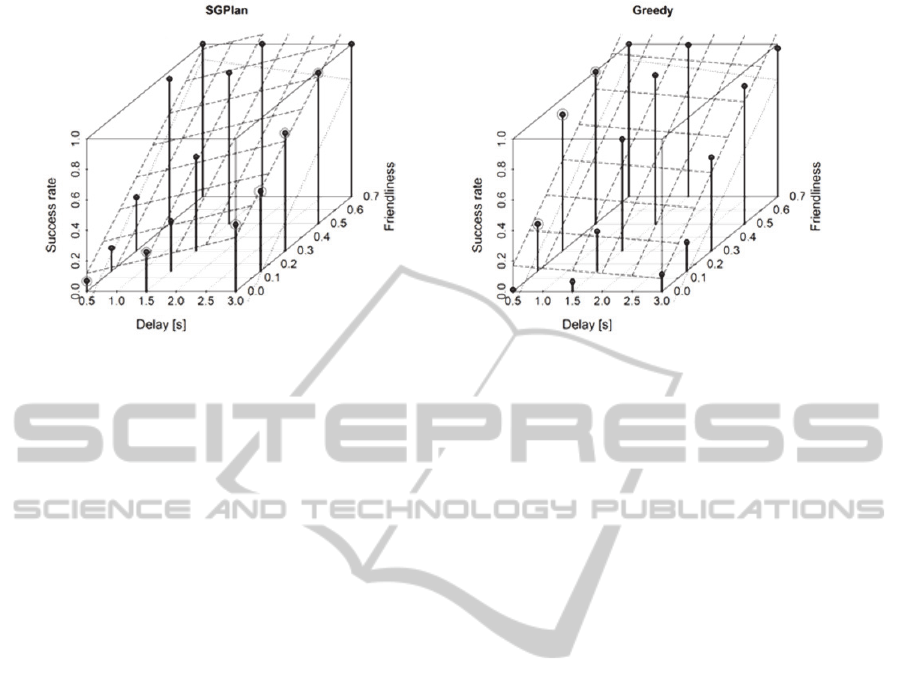
Figure 2: Success rates of SGPlan and Greedy bots in different dynamic conditions. The dotted lines show a plane fitted to
the results of the Inactive bot. Planes are fitted to the averaged results and they are intended only as a visual cue. Gray
circles mark points where the respective agent is significantly better than the other (all p < 0.01).
It was already noted that concerning the success
rate, the Greedy bot performed the best on average.
However, in hostile environments (friendliness = 0)
and in less dynamic environments (delay = 3s), the
planners prevailed.
Figure 2 shows a plane fitted through the average
success rates of SG and Greedy bots, depending on
the environment friendliness and the interference
delay. It shows the principal difference between the
reactive and planning approaches in handling
dynamicity. While the success rate of the Greedy
agent grows with shorter interference delays, the
success rate of SG decreases quite steadily. There is
a minor exception to this rule at the friendliness
level 0, because in such a setting the environment
dynamics cannot bring the reactive agent any new
opportunity. Note that the Inactive agent has similar
properties to Greedy, while Rand is similar to
planning agents.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The most important conclusion is that in small or
hostile or less dynamic domains, the contemporary
planning algorithms are fast enough to provide
advantage over the reactive approaches. The
perceived limits of real-time applicability (planning
faster than 1s) of contemporary planners are
somewhere above one hundred atoms and two
hundred ground actions.
While it is still improbable that AI in a
commercial game would be allowed to consume a
whole processor core, it is likely that given today’s
gaming devices, solving problems with tens of
predicates and actions in real-time will be easily
manageable. Performance could be improved by a
tighter integration of the planning component.
Moreover, all tested planners return only optimal
(shortest) plans. In most game scenarios, suboptimal
plans would be sufficient which could greatly speed
the search process up.
On the other hand, the results also explain why
planning is not the first choice in IVA design.
Unless the environment is either changing slowly or
in an extremely hostile way, even a simple reactive
approach might prove reasonably efficient. While
planning is most effective for smaller domains, it is
also easier to write specialized reactive agents for
such domains. This reduces the possible gain from
implementing a planning algorithm. It is also useful
to know that the planner performance depends more
on the interference delay than on the interference
impact.
There are nevertheless some limitations to the
applicability of results of this paper to the general
case. Despite all measures taken to the contrary, the
environment is still quite specific. The design of
interferences made waiting in front of a door until it
opens by chance – which is an important part of
Greedy agent operation – a viable choice. But this is
not a typical feature of a game scenario. It is also
possible that the simplicity of the environment (only
two kinds of actions, simple goals) affected the
results in some major way.
An important side part of work on this paper was
to connect classical planners to Java and the
Pogamut platform with one universal API through
the development of an open source library
Planning4J (Černý, 2012b). We hope that this tool
PlanningandReactiveAgentsinDynamicGameEnvironments-AnExperimentalStudy
239

will help other researchers cross the gap between
planning and IVAs.
Multiple possibilities for future research are
available. It would be interesting to see if the given
results scale to more extreme parameter values,
larger maps and more complex domains.
Another research direction is to tightly integrate
the planner with the agent. Interleaving planning and
execution as well as meta-reasoning about the
planning process and explicit handling of
uncertainty in the world might bring a significant
performance boost.
A more detailed discussion of the experiment
design and complete results are described in author`s
thesis (Černý, 2012).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by the student research
grant GA UK 655012/2012/A-INF/MFF, by the SVV
project number 265 314 and by the grant P103/10/1287
from GAČR .
REFERENCES
Balla, R.-K., Fern, A., 2009. UCT for Tactical Assault
Planning in Real-Time Strategy Games. in
Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Pp. 40-45.
Černý, M., 2012. Comparing Reactive Techniques to
Classical Planning for Intelligent Virtual Agents.
Master Thesis, Charles University in Prague.
Černý, M., 2012b. Planning4J. Available at
Http://Code.Google.Com/P/Planning4j/
Champandard, A. J., 2007. Understanding Behavior Trees.
Available at: Http://Aigamedev.Com/Open/Article/Bt-
Overview/ Accessed 2012-04-11.
Epic Games Inc., 2012. Unreal Development Kit.
Available at Http://Udk.Com/ Accessed 2012-04-10.
Fikes, R. E., Nilsson, N. J. , 1971. Strips: a New Approach
to the Application of Theorem Proving to Problem
Solving. Artificial Intelligence 2:189–208, 1971.
Fox, M., Long, D., 2003. PDDL2.1: an Extension to
PDDL for Expressing Temporal Planning Domains.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 20: 61-124.
Fu, D., Houlette-Stottler, R., 2004. the Ultimate Guide to
Fsms in Games. AI Game Programming Wisdom II,
Pp. 283-302. Hingham, Massachusetts: Charles River
Media.
Gemrot, J., Kadlec, R., Bída, M., Burkert, O., 2009.
Pogamut 3 Can Assist Developers in Building AI (Not
Only) for Their Videogame Agents. Agents for Games
and Simulations, LNCS 5920, Pp. 1-15.
Hawes, N., 2004. Anytime Deliberation for Computer
Game Agents, Ph.D. Diss., School of Computer
Science, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK.
Helmert, M., 2006. the Fast Downward Planning System.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 26: 191-246.
Hoang, H., Lee-Urban, S., Muñoz-Avila, H., 2005.
Hierarchical Plan Representations for Encoding
Strategic Game AI. Proceedings of the First Artificial
Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment
Conference, Pp. 63-68.
Hoffmann, J., Nebel, B., 2001. the FF Planning System:
Fast Plan Generation through Heuristic Search.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 14: 253-
302.
Hothorn, T., Bretz, F., Westfall, P., 2008. Simultaneous
Inference in General Parametric Models. Biometrical
Journal 50(3): 346–363.
Hsu, C.-W., Wah, B. W., 2008. The Sgplan Planning
System in IPC-6. in Proceedings of the Sixth
International Planning Competition, Pp. 5-7.
Kautz, H., Selman, B., 1998. BLACKBOX: a New
Approach to the Application of Theorem Proving to
Problem Solving. in Working Notes of the Workshop
on Planning as Combinatorial Search, Pittsburgh.
Lipovetzky, N., Geffner, H., 2011. Searching for Plans
with Carefully Designed Probes, in Proceedings of the
Twenty-First International Conference on Automated
Planning and Scheduling, Pp. 154-161.
Long, E., 2007. Enhanced NPC Behaviour using Goal
Oriented Action Planning, Master Thesis, School of
Computing and Advanced Technologies, University of
Abertay Dundee, Dundee, UK.
Mckillup, S., 2006. Statistics Explained: an Introductory
Guide for Life Scientists, Cambridge: Cambridge
University Press.
Nguyen T.-H.D. Et Al., 2011. CAPIR: Collaborative
Action Planning with Intention Recognition. in
Proceedings of the Seventh AAAI Conference on
Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital
Entertainment, Pp. 61-66.
Orkin, J., 2012. Personal Web Page. Accessed
2012-04-11. Available at
Http://Web.Media.Mit.Edu/~Jorkin/Goap.Html
Orkin, J., 2006. Three States and a Plan: the AI of
F.E.a.R.. in Proceedings of the Game Developer's
Conference.
Pollack, M. E., Horty, J. F., 1999. There’s More to Life
than Making Plans. AI Magazine 20(4): 71-83.
Richter, S., Westphal, M., Helmert, M. 2011. LAMA 2008
and 2011. in Seventh International Planning
Competition (IPC 2011), Deterministic Part, Pp. 50-
54.
Thompson, T., Levine, J., 2009. Realtime Execution of
Automated Plans using Evolutionary Robotics. in
IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and
Games, Pp. 333-340.
Vassos, S., Papakonstantinou, M., 2011. the Simplefps
Planning Domain: a PDDL Benchmark for Proactive
Npcs,” Proceedings of the Non-Player Character AI
Workshop (NPCAI-2011) of the Artificial Intelligence
& Interactive Digital Entertainment (AIIDE-2011)
Conference, Stanford CA, USA
.
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
240
