
Constrained Minimum-Variance PID Control using Hybrid
Nelder-Mead Simplex and Swarm Intelligence
N. Pillay and P. Govender
Optimization Studies Unit, Dept. of Electronic Engineering, Durban Univeristy of Technology, Kwa-Zulu Natal,
Republic of South Africa
Keywords: Achievable Performance, Minimum Output Variance, Hybrid Optimization, PID Controller, SISO System.
Abstract: The paper proposes the use of an efficient hybrid optimization routine by combining Nelder-Mead simplex
with Particle Swarm algorithm (NMPSO) to synthesize a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) type
controller. The conceived controller is capable of providing the best possible performance for regulating
stochastic disturbances under closed loop conditions. A global optimal solution is found by exploiting the
process output variance expression in terms of its closed loop impulse response coefficients. The results of
which are used to define an achievable lower bound of the PID performance in terms of the output variance
of the closed loop system. Several simulation examples drawn from literature are used to demonstrate the
efficacy of the proposed methodology.
1 INTRODUCTION
Controller performance assessment (CPA) has
gained interest from researchers and academics
during the last two decades (Harris, 1989; Huang
and Shah, 1999; Hugo, 2006; Veronesi and Visioli,
2011). Seminal work conducted by Harris (1989)
sparked considerable interest in the field. This is
indicated by numerous CPA methods that have
emerged. Excellent reviews on the subject can found
in Jelali (2006) and Qin (1998). CPA is mainly used
to verify the health of a current control system by
clarifying whether it is operating optimally within
certain constraints such as delay time, disturbance
and process characteristics. In today's competitive
economic climate it has become crucial for
controllers to operate optimally in order to reduce
product wastage and provide minimal output
variance. In this paper, the structural constraint
imposed by PID type controllers is the focus as it
directly impacts on output variance and is widely
used for industrial control.
When stochastic disturbances affect the control
system, it is usually desired to achieve minimum
output variance (Harris, 1989). For time invariant
linear discrete time systems with time delay, which
have no finite zeros on or outside the unit circle,
minimum variance control (MVC) represents the
best possible control to alleviate the negative effects
of stochastic disturbances (
Åström, 1979). It is worth
noting that a practical implementation of the MVC
algorithm for process control would lead to
excessive wear on the final control element. This is
due to its wide bandwidth and noise amplification
which leads to the aggressive control action (Hugo,
2006). However these problems are not a deterrent
when using the algorithm for CPA. A controller
performance index (CPI) can thus be defined as one
that compares the current process output to the
output that would have occurred if some "optimal"
controller had been applied to the process such as
the technique proposed by Harris (1989) using
MVC. The methodology does present a serious
drawback however since it does not take controller
structure into consideration. Owing to this
limitation, the MVC performance benchmark is
unobtainable and highly optimistic for low order
controllers such as the PID type (Jelali, 2006). Since
PID type controllers are commonly used for
industrial control due to their transparent control
algorithm and cost versus benefit ratio they provide
its "achievable" performance is an important task
(Ko and Edgar, 2004; Sendjaja and Kariwala, 2009;
Agrawal and Lakshminarayanan, 2003).
Furthermore, a controller specific performance
bound provides valuable insight as to whether a
more advanced control algorithm is required to
330
Pillay N. and Govender P..
Constrained Minimum-Variance PID Control using Hybrid Nelder-Mead Simplex and Swarm Intelligence.
DOI: 10.5220/0004263403300337
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2013), pages 330-337
ISBN: 978-989-8565-39-6
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

achieve the desired control objective. A key
difficulty in characterizing achievable performance
for a restricted structure controller is the non-
convexity for the resulting optimization problem for
which no direct and simple global solution is
possible (Sendjaja and Kariwala, 2009).
In the literature, researchers have proposed using
gradient-based methods (Agrawal and
Lakshminarayanan, 2003; Ko and Edgar, 2004) and
solving a series of non-convex programs using sums
of squares (SOS) programming (Sendjaja and
Kariwala, 2009) for determining the optimal
solution. Recently, the use of DividingRECTangles
(DIRECT) algorithm was proposed by Veronesi and
Visioli, 2011. Also, Shahni and Malwatkar, 2011
suggested using a ring of iterations based on the
M
ATHWORKS
®
Optimization Toolbox. In this paper
we propose using a hybrid optimization strategy for
determining achievable PID performance.
The paper is arranged as follows: Section II gives a
review of the derivation of the objective function as
given by (Shahni and Malwatkar, 2011). The global
minimization of which would provide the best
possible PID control. It is important to note that
their derivation is given in terms of the controller
gains which is later exploited in the subsequent
sections by the proposed algorithm; Section III
describes the hybrid optimization algorithm; Section
IV shows the use of the proposed algorithm to
determine the global optimal solution; Section IV
also discusses the simulation experiments that were
conducted and compares the results to the methods
of Huang and Shah (1999) and Sendjaja and
Kariwala (2009). An analysis of the results is also
given in this section; Section V concludes the study.
2 PROBLEM FORMULATION
We consider the typical closed loop single-input
single-output (SISO) feedback control system shown
in Figure 1. The process output variable is given
as
()yt
, with the controller signal denoted by
()ut
and the disturbance driving white noise being
represented by
()at
.
t
is the sample interval. The
process output is given as
11
() ( ) () ( ) ()yt gq ut hq at
(1)
where
1
()
g
q
and
1
()hq
represent the process and
disturbance transfer functions respectively. The
symbol
1
q
represents the backshift operator. For
the sake of brevity and convenience, the backshift
operator
1
q
and sample time
t
will be omitted in
the subsequent sections unless circumstances
necessitate its presence. It is worth noting that the
control system set-point
()rt
does not vary in this
study since the focus is for regulating stochastic
disturbances. Hence for regulatory control of the
SISO system shown in Figure 1 the transfer between
y
and
a
is:
(2)
We make the following assumptions for the closed-
loop system
G
(Sendjaja and Kariwala, 2009).
1.
Process (g) and disturbance (h) transfer
functions are stable, causal and contain no
zeros on or outside the unit circle except at
infinity due the time delay.
2.
a
is a random white noise sequence.
The output variance is defined as:
(3)
where is the H
2
norm.
Figure 1: Discretized single loop feedback control scheme.
The minimum variance (MV) benchmark can be
obtained by (Huang and Shah, 1999):
(4)
where
d represents the process delay time and d
m
is
the
th
m
discrete impulse response of the disturbance
model
d . Since we are determining an achievable
lower performance benchmark for PID type
controllers, Eq. (4) may not be attainable for this
controller structure. In order to reduce output
variance in terms of the PID structure limitation the
following expression requires solving:
2
()at
1
()kq
1
()
g
q
1
()hq
()yt
()rt
()ut
1
yh
G
agk
1
2
0
d
M
Vm
m
yh
2
2
()Var y G
ConstrainedMinimum-VariancePIDControlusingHybridNelder-MeadSimplexandSwarmIntelligence
331

(5)
Now the structure of a digital version of the PID
controller which can be found published in many
textbooks on process control is (Ko and Edgar,
2004).
(6)
where
, and represent the proportional, integral
and derivative gains of the PID controller
respectively. Eq. (3) can be written as
(7)
where
i
G
represents the closed loop impulse
response system. Now the
th
m
element of may
be defined by which gives the
closed loop impulse response coefficients for the
system . . In this paper the
number of the closed loop impulse response
coefficients is limited to
4md . This ensures that
the closed loop impulse response converges and
computational power is not exhausted unnecessarily.
It is assumed that since the system converges and
approximately equals to zero at the
th
m
element;
. Eq.(7) can now be written as
(8)
Once the controller parameters are known the
coefficients of can easily be determined using
the "impulse" function in the M
ATHWORKS
®
MATLAB
®
software package. However determining
the controller gains that provide a global optimal
solution is a non-trivial task. Details of the
optimization algorithm used in this regard are
discussed in the next section.
3 HYBRID OPTIMIZATION
ALGORITHM
The basis of integrating the Nelder-Mead (NM)
simplex routine and Particle Swarm Optimization
(PSO) is merely to combine their distinct
advantages. It will be shown later that this proves to
yield an efficient search routine capable of
determining high quality solutions for the problem
discussed in the previous section. This section
introduces the individual search procedures of NM
and PSO, followed by a description of the hybrid
NMPSO.
3.1 Nelder-Mead Simplex Search Method
The Nelder-Mead simplex algorithm (Nelder and
Mead, 1965) is a widely used numerical method for
solving nonlinear unconstrained optimization
problems. This computationally compact
optimization routine can be invoked in MATLAB
®
Optimization Toolbox 5.0 using the function
"fminsearch". The optimization function attempts to
minimize a real-valued function
()
f
x
using only
function values without any derivative information
(explicit or implicit) (Lagarias et al., 1998). Four
key scalar operations form the basis of rescaling the
simplex based on the local behavior of the objective
function. These are: reflection (
), expansion (
),
contraction (
) and shrinkage (
). Through these
procedures the simplex can successively improve
itself and approach on the optimum. Universal
choices used in the standard NM algorithm are
(Lagarias et al., 1998):
1, 2, 0.5, 0.5
A review of the steps to the search routine as
described by Lagarias et al. is given below:
1.
Initialization. The minimization of function
()
f
x for
n
x
begins with a generation of
vertices located at points in
n
. The simplex
points are generated around the initial guess
0
x
of
1n
points for
n
-dimensional vectors
x
.
For
2n
, three points construct a triangle and
3n
, four points generate a tetrahedron and so
forth. Iteration
k
begins by ordering and
labeling these vertices as
() () ()
12 1
...
kk k
n
f
ff
,
where
()k
i
f
denotes
()
()
k
i
f
x
.
()
1
k
f
is referred to
P
K
012
...
i
GGGGG
I
K
D
K
() ( )
T
ii
Var y G G
(0,1,...,)
m
Gm
i
G
imi
GG
min ( ) min( )
PID
PID
T
mi mi
k
k
Var y G G
mi
G
12
12 3
1
1
PID
kkq kq
k
q
1
P
ID
kKKK
2
(2)
P
D
kKK
3
D
kK
2
2
min ( ) min
PID PID
kk
Var y G
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
332

as the best function value and
()
1
k
n
f
as the worst
function value. Similarly
()
1
k
x
is referred to as
the best point and
()
1
k
n
x
as the worst point in
n
.
At each step in the iteration, the algorithm
discards the current worst point
()
1
k
n
x
, and
replaces it with another point into the simplex.
For the sake of convenience, superscript
k
is
omitted.
2.
Reflection. A reflection point
r
x
is computed
from
(9)
where
1
n
i
i
x
X
n
is the centroid of the
n
best
vertex points except
1n
x
. Evaluate
()
rr
f
fx
.
If
1 rn
f
ff
, accept the reflected point
r
x
and
terminate the iteration.
3.
Expansion. If
1r
f
f , compute the expansion
point,
(10)
Evaluate
()
ee
f
fx
. If
er
f
f
, accept
e
x
and
terminate the iteration, otherwise if
er
f
f
accept
r
x
and terminate the iteration.
4.
Contraction. If
rn
f
f
generate contraction
between
X and the better of
1n
x
and
r
x
.
a.
An outside contraction is performed if
1nrn
f
ff
and computed by
(11)
Evaluate
()
cc
f
fx
. If
cr
f
f
, accept
c
x
and
terminate the iteration, otherwise go to shrink
operation in step 5.
b.
An inside contraction is done if
1rn
f
f
and
calculated by
11
()(1)
cc n n
x
XXx Xx
(12)
Evaluate
()
cc cc
f
fx
. If
1cc n
f
f
, accept
cc
x
and terminate the iteration, otherwise go to
shrink operation in step 5.
5.
Shrink. Evaluate
f
at the
n
points
11
()
ii
vx xx
,
2,..., 1in
. The vertices
of the simplex at the next iteration is
12 1
, ,...,
n
x
vv
.
The algorithm is terminated until a stopping criterion
is satisfied. An example of a possible terminating
criterion can be maximum number of iterations. In
the case of equal function values being evaluated,
the points need to be ordered according to tie-
breaking rules. Further details of these rules can be
found in (Lagarias et al., 1998). The main
shortcoming of this search methodology is that it can
only find local minimums which depend entirely
upon the initial simplex starting point
0
x
.To find
different local minimums, the algorithm must start
with different and appropriate initial simplex
guesses.
3.2 Particle Swarm Optimization
Algorithm
The PSO technique, developed by Kennedy and
Eberhart (1995), is a computational based
optimization technique for dealing with problems in
which a best solution can be represented as a point
or surface within an n-dimensional search space.
The PSO concept is based on an analogy of the
social interaction that exists in flocking birds and
swarming bees. The technique, much like a genetic
algorithm (GA), is stochastic in nature and is
population based. However a major difference
between the PSO and GA is that the latter employs
genetic operators which filter out poor performing
individuals through natural selection. A key
distinguishing feature of the PSO is that all
individual particles are retained where members of a
group tend to follow the lead of the best in the
group. Each particle or agent also has a memory to
remember the best position that it has visited and the
knowledge of how the other agents around it have
performed. The procedure of PSO is reviewed
below.
1.
Initialization. Randomly generate agents within
the search space in which each particle
represents a potential solution. Each particle is
assigned an initial random velocity.
11
()(1)
rn n
x
XXx Xx
() ( )(1)
11
xX xXX Xx X x
er
nn
11
() ( )(1)
cr n n
x
XxXX Xx X x
ConstrainedMinimum-VariancePIDControlusingHybridNelder-MeadSimplexandSwarmIntelligence
333

2.
Velocity Update. Each agent flies through the
search space dynamically adjusting its velocity
and positional trajectories. These adjustments
are based on the personal experiences of the
agent in question, plus its knowledge of how its
companions have performed. The agents
position and velocity for the
th
i
particle within
an
n
-dimensional space are updated by the
following equations:
(13)
(1) () (1)
,,,
kkk
in in in
s
sv
(14)
pi ,...,2,1
qn ,...,2,1
With regards to (13) and (14):
()
,
k
in
v
= velocity of
agent i at iteration k,
= constriction factor,
1
c
=
cognitive acceleration,
2
c
= social acceleration,
()rand
= random number between 0 and 1,
p
best
=p-best of agent i,
gbest
= g-best of the
group,
()
,
k
in
s
= current position of agent i at iteration k,
p = number of agents, q=number of dimensions to
the optimization problem. Some popular variants of
the PSO algorithm include the inertia weight and the
constriction actor approach. In this study we have
used Clerc’s Type 1 constriction factor algorithm to
limit each agent’s velocity (Clerc, 1999). This
ensures a robust global convergence as each agent’s
velocity trajectory decreases when approaching the
best solution (Clerc, 1999). The constriction factor is
computed by
(15)
where,
12
(, )cc
.
It is worth noting that
must be greater than 4 to
ensure a proper value for
. A commonly used
value for
is 4.1 which gives a constriction factor
constant of
0.7298
. This constant multiplier
value was used in all the experiments.
3.3 Hybrid Nmpso
The task of the hybrid search is to find the absolute
best set of controller parameters that satisfy the
objective function under certain constraints. In order
to ensure positive values of the controller parameters
the following inequalities are considered:
1
0k
,
2
0k
,
3
0k
. Values that violate these constraints
are penalized with a very large number resulting in a
poor cost function. It is worth noting that for a PI
controller the search space is given by two
dimensions (
2n
) whereas for a PID controller
three dimensions (
3n
) are created. Hence for a PI
controller each agent has a starting point of
0
[0;0]x
and for a PID controller the agent’s
initial position is given by
0
[0;0;0]x
. During the
PSO routine of the hybrid search the fitness function
defined by Eq. 8 is minimized and the best controller
parameters are saved. If after several unsuccessful
consecutive attempts the PSO algorithm fails to
improve on the current
gbest
position then the
search automatically switches over to the NM
optimization. The
gbest
position found by the PSO
algorithm is used as the starting point for the NM
search. The same fitness function (Eq. 8) is used for
the NM search. If a better
gbest
is found then this
new point is used in the PSO search and the
procedure is repeated until convergence is reached.
If the NM search is unsuccessful in determining a
better position then the algorithm terminates when a
terminating condition such as maximum number of
iterations is satisfied. The procedure for the hybrid
NMPSO search is presented in Figure 2.
It should be noted however that the proposed
algorithm is applied to known system transfer
functions. Thus the assumption is made that the
algorithm is applied on accurate models of process
and disturbance dynamics. Several examples
showing the effectiveness of the hybrid NMPSO
routine is given the next section.
4 ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLES
4.1 Preliminaries for the Experiments
Several simulation examples taken from literature
are used to verify the usefulness of the proposed
algorithm. These examples were taken from
(Sendjaja and Kariwala, 2009; Ko and Edgar, 2004
and Agrawal and Lakshminarayanan, 2003). All
simulations were conducted using the PC based test
platform with specifications given in Table 1.
Process (
g
) and disturbance ( h ) transfer functions
used in the simulation models are shown in Table 2.
(1) () () ()
,,1 ,,2 ,
[ ()( ) ()( )]
kk k k
in in in in n in
v v c rand pbest s c rand gbest s
2
2
24
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
334

1. Initialization. Generate a
population of size
p
with each
agent having a starting point
0
[0;0]x
for PI or
0
[0;0;0]x
for
PID.
Repeat
2. PSO method. Apply PSO to randomly
generate
p
number of particles in
the
n
-dimensional search space.
2.1 Fitness Function. Using the
agent’s current position
compute its fitness
according to Eq. (8).
Agents that violate the
constraints:
1
0k
,
2
0k ,
3
0k are penalized
with a large fitness
factor.
2.2 Selection. Select the global
best;
gbest
from the
population.
2.3 Velocity Update. Apply
velocity and position
updates to each agent
using Eqs. (13) and (14).
2.4 Stall. If after several
successive attempts the
algorithm does not improve
on
gbest
, go to Step 3
otherwise go to Step 2.
3. NM method. Simplex generated
around initial point given
by
gbest
.
3.1 Fitness Function. Evaluate
each simplex point
function using Eq.
(8).Order simplex points
from lowest function value
()
1
k
f
to highest
()
1
k
n
f
.
3.2 NM operators. Compute
reflection (
), expansion
(
), contraction (
) or
shrinkage (
) according
to Eqs. (9)–(12).
3.3 Global update. If a lower
global minimum is found
update position for
gbest
and go to Step 2.
Otherwise continue until some
termination condition is satisfied.
Figure 2: Hybrid NM-PSO algorithm.
When NMPSO algorithm fails to improve on the
current solution after ten consecutive attempts it
automatically terminates and the best solution is
saved. The maximum number of iterations is set to
100 as an additional exit condition. The swarm
parameters used are:
12
2.05cc
with population
size of
20p
. Table 3 and Table 4 give the results
of the minimum variance PI and PID respectively
for the proposed method. The overall performance
of the NMPSO search is compared to that of the
SOS programming method of Sendjaja and Kariwala
(2009) and MV lower bound (Huang and Shah
1999). It is worth noting that the proposed NMPSO
optimisation algorithm provides accurate repeatable
solutions. Each example shown in Table 2 was
tested for ten trial runs and the results indicate the
stability and consistency of the proposed search
algorithm. The stochastic nature of the PSO is useful
in determining globally optimal regions within the
search space whilst the NM provides a finer search
in locally optimal regions. The proposed algorithm
is efficient and has the ability to find high quality
solutions in relatively short times even though the
algorithm written in MATLAB
®
has room for
considerable improvement.
Table1: Test PC platform specifications.
Processor
Intel ® Core™ i5 CPU 650 @
3.20GHz
Motherboard XCPI x64
RAM 4.00 GB
Software
MATHWORKS
®
MATLAB
®
7.10.0
(R 2010a)
4.2 Discussion of Results
The proposed method is applied to find the lower
bound of the minimum variance PI/D for several
examples taken from literature. Some significant
observations for the examples are given below.
1.
With regards to the results provided in Table 3
it is surprising to note that example 3 took the
shortest time (29.9 seconds) to solve even
though the process transfer function has the
largest dead time from the set of experiments.
Overall results for the time taken indicate that
PID controller's takes longer time to solve.
This is expected since the PID controller adds
another dimension to the problem as an
additional variable (
3
k
) is involved.
ConstrainedMinimum-VariancePIDControlusingHybridNelder-MeadSimplexandSwarmIntelligence
335
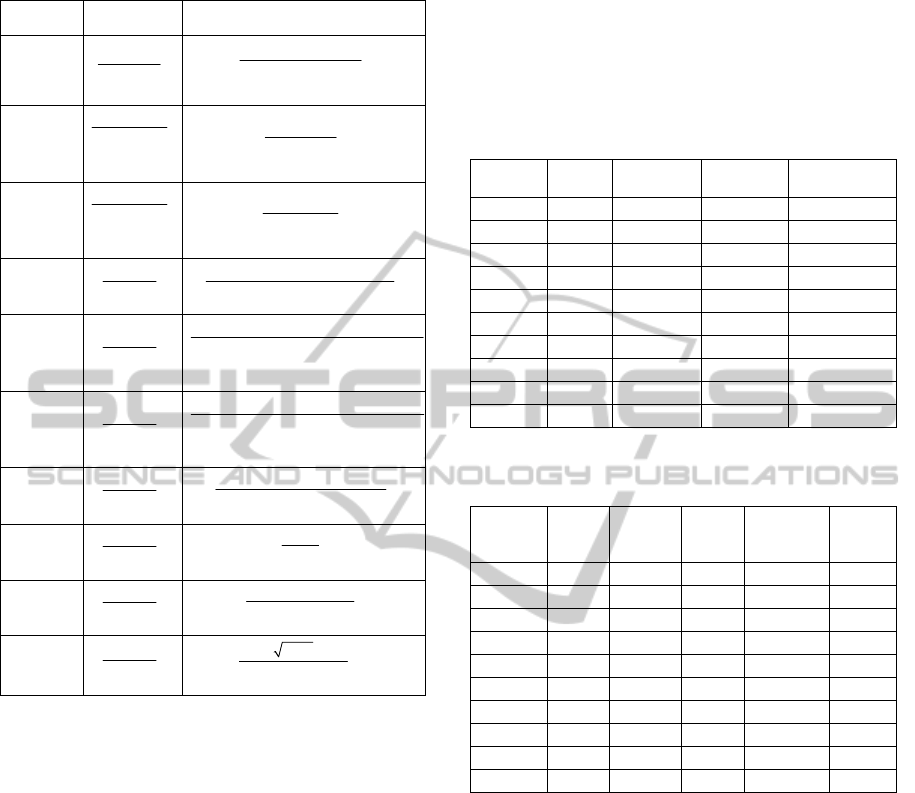
Table 2: Simulation models used in the experiments.
Example
g
h
1
5
0.2
1
10.8
q
q
1
11
(1 )(1 0.4 )qq
2
12
1
0.08919
1 0.8669
q
q
1
0.08919
1 08669q
3
28
1
0.5108
1 0.9604
q
q
1
0.5108
1 0.9604q
4
6
1
10.8
q
q
1
111
10.6
(1 0 .5 )(1 0 .6 )(1 0.7 )
q
qqq
5
6
1
10.8
q
q
1
1111
10.2
(1 )(1 0.3 )(1 0.4 )(1 0.5 )
q
qqqq
6
6
1
10.8
q
q
1
1111
10.6
(1 )(1 0.5 )(1 0.7 )(1 0.6 )
q
qqqq
7
5
1
0.1
10.8
q
q
111
0.1
(1 )(1 0.3 )(1 0.6 )qqq
8
3
1
0.1
10.8
q
q
1
1
1 q
9
6
1
0.1
10.8
q
q
11
0.1
(1 )(1 0.7 )qq
10
3
1
0.1
10.8
q
q
12
0.001
(1 )(1 0.2 )qq
2. The proposed algorithm gives solutions that are
in agreement with the SOS programming
method of Sendjaja and Kariwala (2009) for
all the cases shown in Table 5. The
dimensionless values provided in Table 5
represent the closed loop variance. As noted
by Sendjaja and Kariwala (2009) the
controller structure imposes severe
limitations on controller performance as
shown in examples 6, 7 and 9 for PI control.
This indicates for these cases that the MV
lower bound presents a highly optimistic
benchmark for a low order PI control
structure. There are no controller structure
limitations for examples 2, 4 and 10
operating under PID control as there is little
difference between MV lower bound and
PID-MV for these examples.
3.
Improved achievable lower bounds are given by
the proposed NMPSO algorithm when
compared to the SOS programming method
for examples 3 and 6 for PI control and
examples 1, 7, 8 and 9 for PID control.
Table 3: NMPSO simulation results for minimum variance
PI controller.
Example
1
k
2
k
Iterations
Time taken
(s)
1 1.1175 -0.9891 23 49.49
2 0.3246 -0.3257 19 34.05
3 0.0333 -0.0334 19 29.90
4 0.0248 -0.0250 19 45.96
5 0.2101 -0.1880 31 78.03
6 0.2499 -0.2274 19 65.70
7 2.8056 -2.5376 27 64.77
8 3.4225 -2.9821 35 59.52
9 2.2861 -2.0495 35 67.91
10 3.3609 -2.9233 24 51.97
Table 4: NMPSO simulation results for minimum variance
PID controller.
Example
1
k
2
k
3
k
Iterations
Time
taken
(s)
1 2.8724 -4.4735 1.7873 47 114.56
2 1.8485 -3.4099 1.5627 47 110.00
3 0.0367 -0.0369 0.000 101 135.01
4 0.1383 -0.2598 0.1220 61 168.31
5 0.7382 -1.2336 0.5322 47 162.55
6 0.8743 -1.4796 0.6487 68 236.25
7 8.4515 -13.869 5.9375 62 161.29
8 6.6043 -9.4092 3.4838 54 100.23
9 8.5550 -14.389 6.295 83 187.76
10 6.2277 -8.7216 3.1414 59 124.83
5 CONCLUSIONS
A hybrid optimization routine which combines the
efficient global and local search capabilities of PSO
and NM respectively has been proposed. The
methodology was used to determine achievable
lower performance bounds for restricted structure
PI/D controllers. It is obvious that the achievable
PI/D performance bounds can be employed in a
performance monitoring context to evaluate the
performance of PI/D controllers operating in real-
world control loops. Future work will include
streamlining the hybrid NMPSO algorithm for use
on real-world process control loops. This would
include the use of a suitable online system
identification procedure to work in conjunction with
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
336

Table 5: Performance comparison of proposed methodology for minimum variance PI and PID controllers.
Example
MV
(Huang and
Shah, 1999)
PI controller
SOS programming method
(Sendjaja and
Kariwala,2009)
(lower bound, upper bound)
PID controller
SOS programming method
(Sendjaja and
Kariwala,2009)
(lower bound, upper bound)
Proposed
NM-PSO method
(PI-MV)
Proposed
NM-PSO method
(PID-MV)
1 2.9427 (3.5154, 3.5186) (3.0730, 3.0730) 3.5179 3.0679
2 0.0310 (0.0313, 0.0314) (0.0310, 0.0310) 0.0314 0.0310
3 3.0112 (3.1703, 3.1706) (3.0492, 3.0495) 3.1502 3.0493
4 3.4004 (3.4408, 3.4408) (3.4065, 3.4065) 3.4399 3.4059
5 11.9528 (17.7044, 17.7477) (13.6341, 13.8243) 17.7414 13.7207
6 58.3406 (122.4089, 123.6037) (83.5605, 89.6983) 117.4932 85.9108
7 0.2978 (0.5856, 0.5884) (0.4278, 0.4278) 0.5608 0.4166
8 3.0000 (3.7002, 3.7050) (3.2093, 3.2093) 3.7030 3.1923
9 0.3144 (0.5949, 0.5968) (0.4288, 0.4288) 0.5964 0.4199
10 0.0023 (0.0027, 0.0027) (0.0024, 0.0025) 0.0027 0.0024
the proposed algorithm to determine minimum
variance PI/D controllers.
REFERENCES
Agrawal, P., Lakshminarayanan, S., 2003. Tuning
Proportional-Integral-Derivative Controllers using
Achievable Performance Indices, Ind. Eng. Chem.
Res., Vol. 42, pp. 5576-5582.
Åström K.J., 1979. Introduction to Stochastic Control
Theory, Academic Press, London.
Clerc, M., 1999. The swarm and the queen: towards a
deterministic and adaptive particle swarm
optimisation, In proceedings of the congress on
evolutionary computation, Washington DC, United
States of America, pp. 1951-1957.
Eberhart, R.C., Kennedy, J., 1995. A new optimiser using
particle swarm theory. In proceedings of the sixth
international symposium on micro machine and
human science, Nagoya, Japan, pp.39-43.
Harris, T.J., 1989. Assessment of Control Loop
Performance, The Canadian Journal of Chemical
Engineering, Vol. 67, pp. 856-861.
Huang, B., Shah, S.L., 1999. Performance Assessment of
Control Loops: Theory and Applications, Springer-
Verlag, London, UK.
Hugo, A.J., 2006. Performance assessment of single-loop
industrial controllers, Journal of Process Control,
Vol.16, pp.785-794.
Jelali, M., 2006. An overview of control performance
assessment technology and industrial applications,
Control Engineering Practice, vol. 14, pp. 441-466.
Ko, B.S., Edgar, T.F., 2004. PID Control Performance
Assessment: The Single-Loop Case, AIChE Journal,
Vol. 50, No.6, pp.1211-1218.
Lagarias, J.C., Reeds, J.A., Wright, M.H., Wright, P.E.,
1998. Convergence properties of the Nelder-Mead
Simplex method in low dimensions, Society for
Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Vol.9 No.1, pp.
112-147.
Nelder, J. A., Mead, R., 1965. A simplex method for
function minimization, Computer Journal, Vol.7,
pp.308-131.
Qin, S. Joe., 1998. Control performance monitoring – A
review and assessment, Computers in Chemical
Engineering, vol. 23(2), pp. 173-186, 1998.
Sendjaja, A.Y., Kariwala, V., 2009. Achievable PID
performance using sums of squares programming,
Journal of Process Control, Vol.19, pp.1061-1065.
Shahni, F., Malwatkar, G.M., 2011. Assessment
minimum output variance with PID controllers,
Journal of Process Control, Vol. 21, pp. 678-681.
Veronesi, M., Visioli, A., 2011. Global Minimum-
variance PID Control ,18
th
International Federation of
Automatic Control (IFAC), pp. 7891-7896.
ConstrainedMinimum-VariancePIDControlusingHybridNelder-MeadSimplexandSwarmIntelligence
337
