
Extending Recognition in a Changing Environment
Daniel Harari
and Shimon Ullman
Department of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, The Weizmann Institue of Science, Rehovot, Israel
Keywords: Object Recognition, Video Analysis, Dynamic Model Update, Unsupervised Learning, Bayesian Model.
Abstract: We consider the task of visual recognition of objects and their parts in a dynamic environment, where the
appearances, as well as the relative positions between parts, change over time. We start with a model of an
object class learned from a limited set of view directions (such as side views of cars or airplanes). The
algorithm is then given a video input which contains the object moving and changing its viewing direction.
Our aim is to reliably detect the object as it changes beyond its known views, and use the dynamically
changing views to extend the initial object model. To achieve this goal, we construct an object model at
each time instant by combining two sources: consistency with the measured optical flow, together with
similarity to the object model at an earlier time. We introduce a simple new way of updating the object
model dynamically by combining approximate nearest neighbors search with kernel density estimation.
Unlike tracking-by-detection methods that focus on tracking a specific object over time, we demonstrate
how the proposed method can be used for learning, by extending the initial generic object model to cope
with novel viewing directions, without further supervision. The results show that the adaptive combination
of the initial model with even a single video sequence already provides useful generalization of the class
model to novel views.
1 INTRODUCTION
The world around us is a dynamic environment, and
a robust visual recognition system should therefore
be able to detect and interpret objects as they change
over time. The dynamic changes are useful, since
they provide cues for both segmentation and 3D
structure, but also challenging, as both the
appearance and the relative positions of visual
features may change over time. A recognition
system should be able to learn the multiple
appearances and structures of a class of objects from
a dynamic input, and ideally accomplish this with
little or no supervision that provides labeling of the
objects and their parts.
In this paper we deal with a specific aspect of
dynamic recognition. We assume an initial model
that can detect an object and its parts from a limited
set of views (such as side views of cars or airplanes).
Given an input video, the model successfully detects
the object and its parts at some time t
. The goal is
to continue to detect the object as its images changes
in the video at later times tt
, and to use the
dynamically changing views to extend the model
and allow it to classify novel objects under new
views which the original model fails to recognize.
We describe a learning process that can efficiently
combine the initial model with the novel dynamic
input and obtain a significant extension of the
original model based on even a single object
instance, as illustrated in figure 1.
A main contribution of our approach is
constructing the object model at time tt
by
combining two sources of information: compatibility
with the measured optical flow and similarity to the
object model at an earlier time.
2 RELATED WORK
We follow the paradigm of detecting and localizing
objects by their constituent parts. Part-based object
recognition has been successfully demonstrated in
many recognition problems, mainly for detecting
objects in static images (Agarwal et al., 2004;
Crandall et al., 2005; Epshtein and Ullman, 2007;
Felzenszwalb and Huttenlocher, 2005; Fergus et al.,
2005). Object parts can be obtained manually
(Felzenszwalb and Huttenlocher, 2005) or
automatically (Agarwal et al., 2004; Ullman et al.,
2002) during training from a set of sample images of
the object. Each part is characterized by a visual
632
Harari D. and Ullman S..
Extending Recognition in a Changing Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0004281106320640
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2013), pages 632-640
ISBN: 978-989-8565-47-1
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: Approach outline. Given an initial generic model of the class object in a certain view (a), an object instance and its
parts are detected in a dynamic scene at some time t
. The model continues to detect the parts for as long as possible, while
adapting to novel views of the object at times tt
(b). The updated model is extended to cope also with general class
object instances in novel views without external supervision (c).
appearance and by relations relative to other object
parts. (Felzenszwalb and Huttenlocher, 2005) have
suggested a pictorial structure representation using a
collection of parts arranged in a deformable
configuration. They model the appearance of each
part separately, and represent the deformable
configuration with spring-like connections between
pairs of parts. (Crandall et al., 2005) have extended
this approach by introducing a class of statistical
models for part-based object recognition that are
explicitly parameterized according to the degree of
spatial structure they can represent. These models,
called k-fans, provide a way of relating different
spatial priors that have been used for recognizing
generic classes of objects, including joint Gaussian
models and tree-structured models. (Felzenszwalb et
al., 2010) combined the powerful histogram of
gradients (HoG) features of (Dalal and Triggs, 2005)
into the part-based recognition framework. Their
approach uses a star-structured part-based model
consisting of HoG filters (representing the object
"root" and constituent parts), and associated
deformation models. To cope with multiple views
the algorithm splits the training set and learns a
mixture of models, each corresponding with a
different view. In this learning process the number
of models (views) should be manually defined, and
the training set should consist of enough samples for
each view.
Object and part detections were also considered
when applied to dynamic visual input, mainly for
tracking. (Dalal et al., 2006) have combined
differential optical flow descriptors with their
holistic object HoG descriptors for the task of
detecting and tracking humans in video sequences.
However, appearance and motion features are
learned only during training and cannot be updated
to cope with novel appearances and motion when
observed. (Ramanan et al., 2007) suggested to learn
specific appearance models of class objects from
detections of a generic model in the input video
sequence. These models are then used to track the
object instances in the analyzed video. However, this
approach is not suitable for online adaption of the
model to the input dynamics.
Other approaches such as (Cehovin et al., 2011;
Godec et al., 2011; Kwon and Lee, 2009; Lim et al.,
2005) introduce online learning and model adaption
under the tracking-by-detection paradigm for robust
object tracking under heavy deformations and
occlusions. These approaches maintain a specific
object model of the tracked object, while adapting to
changes in the object appearance and geometry
throughout the tracking period. However, as the
target goal of these methods is tracking of a specific
object instance, they do not aim to generalize to
other class object instances, or maintain past object
configurations over time. Recently, (Kalal et al.,
2011) have suggested a system for long-term
tracking of a human face in unconstrained videos.
The system is built on tracking-learning-detecting
approach using an off-line trained generic detector
and an online trained validation mechanism for
pruning incorrect detections. A multi-view model of
the target is automatically learned from a single
frontal example and the unlabeled dynamic visual
input. Nevertheless, although past configurations of
the tracked object are maintained over time, the
ExtendingRecognitioninaChangingEnvironment
633

model does not generalize to other class object
instances, as it is still targeted toward tracking.
In this paper we present an adaptive parts
detection model for a dynamic environment, that can
provide a recognition system with a simple and
efficient unsupervised learning mechanism that
updates the model over time. The suggested scheme
is a natural extension of state-of-the-art part
detection methods in static images. Our scheme
combines the structure of the model at time t with
the optical flow between time t and
t∆t
. Using
both motion and spatiotemporal consistency, the
model adapts online to dynamic changes of the
observed object, both appearance and structure.
Using statistical kernel density estimation (KDE)
and approximate nearest neighbors (ANN) tools, our
model provides a simple and efficient mechanism
for extending a generic object model to cope with
novel object views, via adaption to dynamic visual
input and without external supervision. The rest of
this paper is organized as follows: in section 3 we
describe the model and our probabilistic framework;
in section 4 we present an experimental performance
study; and in section 5 we discuss and conclude our
insights from this work.
3 METHODS
3.1 Overview
The adaptive model is initially a static, single-image
parts detection model of an object class (such as cars
or airplanes), with a star-like geometric structure
similar to (Crandall et al., 2005; Epshtein & Ullman,
2007; Felzenszwalb et al., 2010; Fergus et al., 2005).
This model is learned from a limited set of view
directions (such as side views). When applied to
video sequences, the model acts as a standard static
classifier on each frame until an instance of the
object class is successfully detected at frame t
. The
model is then applied to every two consecutive
image frames t and
t∆t
of the video sequence,
as long as the object is reliably detected.
Parts interpretation (identity and location) at time
t∆t
is obtained by combining two sources: the
model M
t
at time t, and the optical flow between
the frames. The model is then updated to M
t∆t
to be used in the subsequent frame. The updated
model at each frame is an adapted instance of the
initial model, based on the two corresponding views.
We utilize adaptive ANN search, combined with
statistical KDE, for efficient online updating of the
model, using the dynamically changing views to
extend the initial object model as described below.
3.2 Probabilistic Model
The initial static object detector is based on the
representation of the object and its constituent parts
following (Epshtein and Ullman, 2007), with a
graphical model similar to the one shown in figure 2,
excluding spatiotemporal variables. The appearances
of parts and their geometric configurations are
learned from positive static image samples which
contain the class object (one instance roughly
centered in the image) and negative image samples
which do not contain the class object. The learning
process may be in a fully supervised manner.
However, we prefer the weakly supervised learning
approach of object parts (Agarwal et al., 2004)
which is more realistic, and automatically selects the
parts from a large set of image fragments according
to their mutual information with the object class
(Vidal-Naquet and Ullman, 2003). For each selected
part, a set of appearances of equivalent parts
together with their geometric configuration (relative
offset from the object center in our settings) is
extracted from the positive training images by
similarity matching.
The probabilistic framework of the adaptive
spatiotemporal model is a natural extension of the
initial static object detector and is defined as
follows. At time frame
t∆t
we define a random
variable C to represent the object center location in
the image, and a set of random variables denoted by
X
X
to represent the image locations of N
object parts. The observed appearances of object
parts in the image are represented by a set of random
variables, which are image feature descriptors
F
F
. The image locations of the interpreted
object and parts in the previous frame t are
represented by the random variables C
and
X
X
respectively. The observed
velocities of the object and parts are derived from
the optical flow between frame t and
t∆t
, and
are represented by the random variables V
and
V
V
respectively. The representation can
be described by the graphical model shown in figure
2. The full interpretation of object and parts at frame
t∆t
is given by the joint probability as in
equation 1.
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
634

Figure 2: Probabilistic graphical representation of the
adaptive model. Similar to the initial static model, the
latent variables Cand
X
represent the image locations of
the object and its parts in the current frame. The observed
appearance of the parts in the current frame is represented
by
F
which are image features. Spatiotemporal
information is represented by observed image positions of
the object and its parts at the previous frame C
and
X
respectively, and their measured velocities V
and
V
respectively (derived from the optical flow between the
frames).
N
i
iiii
p
iii
c
p
c
pp
c
XFPVXXPVPCXP
C,VCPVPCP
,,C,,V,C,P
1
,
XVFX
(1)
⁄
: We use a non-parametric representation
for the probability
P
F
X
⁄
of the observed
appearance of an object part
conditioned on its
image location. For given image positions, we use
SIFT descriptors (Lowe, 2004) as appearance
features of the image patches centered at these
positions. Given a set of appearance features for part
, the probability of a new appearance feature F
is
obtained using a Gaussian KDE over the
distances of
F
from a subset of k nearest neighbors
(
k-NN)
Y
Y
among the original set as
shown in equation 2. For efficiency we use
approximate nearest neighbors search as in (Arya &
Mount, 1993).
k
j
j
i
ii
h
YF
hk
XFP
1
2
2
exp
2
1
(2)
Using this non-parametric representation for the
conditional probability of observed appearances,
allows us to control the online adaption of the
appearance model, by changing the set of known
appearances at each time frame as follows. At the
update phase of the two-frame scheme, the
appearance of the successfully interpreted object
part
at the previous frame, is added to the current
set of known appearances of this part, thus allowing
a gradual adjustment of the appearance model via
the
k-NN approach. Furthermore, by memorizing
previously observed appearances of the object part,
this approach provides a robust online adaption
mechanism which can recover from possible
erroneous interpretations. Based on initial
experiments, we manually determined the number of
nearest neighbors (
25) and the bandwidth
parameter (
0.27), which remain the same in all
our experiments.
⁄
: The structure of object parts is represented
as a geometric star-like model. The probability
P
X
C
⁄
of an object part conditioned on the object
center location is modeled as a mixture of
Gaussians. The first component is the geometric
configuration of the initial static object detector for
part
, represented by a Gaussian distribution over
spatial offsets between the object center locations
and part locations (in the training set images). The
second component is a Gaussian kernel over spatial
offsets between recently interpreted object and part
locations in the input video, which are being updated
online during the update phase of the two-frame
scheme. (We used the 3 most recent interpretations
in our experiments.) The weights of the mixture
components may be adjusted according to the
interpretation confidence levels. However, in our
experiments we used constant uniform mixing
weights.
,
⁄
,
,
⁄
: Spatiotemporal
consistency and motion constraints for the object
and parts between two time frames, are represented
via the conditional probabilities
,
⁄
and
,
⁄
respectively. For every two time
frames we calculate the velocity of the whole object
and interpreted part
at the previous frame . These
velocities are calculated as a weighted average of the
optical flow at every pixel location within the
object’s and part’s image regions respectively,
utilizing a dense optical flow algorithm (Black &
Anandan, 1996). The velocities imply Gaussian
distributions for the location of the object and part at
the current time frame
∆
given their
interpreted locations at the previous frame
(equation 3). The parameters
σ
and σ
are set
relative to the object size and part size respectively
(we used a factor of 0.5 in our experiments).
C
1
X
2
X
N
X
1
F
2
F
N
F
p
C
p
X
1
p
X
2
p
N
X
c
V
1
V
2
V
N
V
ExtendingRecognitioninaChangingEnvironment
635

Figure 3: Image samples from the image and video datasets. (a,b) Training images of the initial model of side-view cars and
airplanes (Fei-Fei et al., 2007; Fergus et al., 2003). (c,d) Video sequences of cars and airplanes changing their viewing
directions. (e) Non-class video sequences (Ferryman, 2009). (f) Test images of cars at novel viewing directions (Cornelis et
al., 2006).
2
2
2
exp,
2
exp,
i
i
p
ii
ii
p
i
c
c
p
c
p
tVXX
VXXP
tVCC
VCCP
(3)
We assume uniform prior distributions for the
object center among all image pixel locations
.
4 PERFORMANCE STUDY
We demonstrate the performance of the adaptive
object and parts detection model on two object
categories: cars and airplanes. For each category, an
initial model of the object class from a side-view is
learned from a training set consisting of positive
class images and negative background images. We
then apply the algorithm to sets of video sequences
containing instances of the class object in various
dynamic environments, starting at roughly the
known side viewing direction. We analyze the
adaption of the model while the object and
background dynamically change throughout the
video sequences. Finally, we show how the updated
model extends the initial model to cope with novel
viewing directions of general object class instances,
even after exposure to a single video sequence.
4.1 Datasets
For training initial object class models, we used 123
side-view images of cars from the Caltech101
dataset (Fei-Fei et al., 2007) to learn a car detector
with 8 parts, and 473 side-view images of airplanes
from Caltech dataset (Fergus et al., 2003) to learn an
airplane detector with 10 parts. 467 natural images
not containing the object classes were used as
negative examples.
For testing the initial and the updated models, we
used car images at different views from ETHZ
dataset (Cornelis et al., 2006) (476 images from a
side view, 154 images at roughly
30
°
, and 120
images at around
60
°
), and 103 validation images of
airplanes from the Caltech dataset (Fergus et al.,
2003). The models were also applied to more than
200 background images (extracted from the
PASCAL'09 dataset, Everingham et al., 2009),
which do not contain instances of the two object
classes.
For dynamic inputs we used 3 videos of cars
taken from a stationary video camera, 4 videos of
airplanes from the internet, and 4 videos of people
walking (not containing cars or airplanes) from
(Ferryman, 2009). The car sequences, consisted of
75 frames each, and depicted 3 different cars making
a left turn at a junction, starting from a side-view,
and ending at a view of about
60
°
70
°
. The
airplane sequences consisted of more than 100
frames each, and depicted 4 different planes
changing their viewing direction during taxi and
takeoff. The walking people sequences did not
contain any car or airplane instances, and were used
to evaluate the classification performance of the
initial and updated models. Sample images from the
different image and video datasets are shown in
figure 3.
To evaluate both object and parts detections in
the videos, a human observer was presented with
sample appearances of the class object and its parts
(as learned during the training of the initial static
model), and was asked to manually annotate the
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
636

Figure 4: Examples of object parts adaption in dynamic scenes. Top: A car video sequence at frames 1, 30, 40, 50, 60.
Bottom: An airplane video sequence at frames 1, 50 and 100.
positions of the object and parts at every frame of
the video sequences. (It should be noted that the
exact interpretation of the object and its parts during
a change of view may be somewhat subjective even
for human judgment.)
4.2 Adaptive Part Detection
Our algorithm first detects an object class instance in
the video input based on its initial static model. We
compared the performance of our initial model with
a state-of-the-art object detector (Felzenszwalb et
al., 2010) using the same training data of side-view
images of cars and airplanes. Performance
evaluation was conducted similar to the PASCAL'09
detection challenge, were detections are considered
correct if the area of overlap between the predicted
bounding box and ground truth bounding box
exceeds 50%. Our initial model yields an average
precision (AP) of 98% on the cars category and 87%
on the airplanes category, compared with the
detector by (Felzenszwalb et al., 2010), which yields
77% AP on cars and 97% on planes. The results
demonstrate satisfying recognition capabilities of the
initial model, which are comparable with state-of-
the-art performance.
Once the object is reliably detected by the initial
model, our model is applied to every two
consecutive frames of the input video sequence,
while adapting to the dynamic changes in viewing
directions of the object and its parts. To evaluate the
quality of the adaption process, we analyzed the
localization error of the detected object and parts at
each frame with respect to ground truth positions,
which were manually annotated. We compared the
results of the updated model with the localization
error yielded by the initial static model when applied
to each video frame. Table 1 shows the average
localization error across changing views for a car
video sequence and an airplane video sequence. For
object parts of size
32 32
pixels a reasonable
localization error is around 15 pixels. The table
shows that the model reliably adapts to roughly
60
°
Table 1: Adaptive parts detection. Object and parts average localization error and standard deviation (in pixels) across
changing views in two video sequences of turning car and airplane. The analysis is performed for both the initial static
model and the adaptive model. The object detection error is averaged over time frames between views, while the parts
detection error is averaged also over all object parts (8 parts for the car and 10 parts for the airplane).
Car
Adaptive
model
Object
41 2
0.5 5
2 10
5 378
Parts
53 8
6 9
9 15
16 3541
Initial
model
Object
31 4
1 6
1 43
55 1367
Parts
63 10
9 19
16 56
50 13246
Airplane
Adaptive
model
Object
52 2
1 3
2 16
6 262
Parts
65 10
8 14
40 53
113 75133
Initial
model
Object
112 2
2 13
2 19
9 5122
Parts
64 8
6 20
42 57
106 84121
ExtendingRecognitioninaChangingEnvironment
637

Table 2: Is a detection prior enough for successful detection? Detection performance evaluation of the initial model, when
applied to 2 video sequences of the cars category. The detection threshold is reduced by a fixed rate after every successful
detection, implying an increasing confidence level of finding the object at subsequent frames. Performance results are
compared with the average precision rate of the adaptive model when applied to these videos.
Detection
threshold
decay rate
Static model with
detection prior
Adaptive
model AP
rate
Precision Recall
Cars
sequence 1
0% 100% 12.9%
71%
1% 56.3% 20.5%
2% 42.9% 43.2%
Cars
sequence 2
0% 100% 26.7%
72%
1% 95.5% 36.2%
2% 50.4% 53.5%
change in viewing direction for cars and
45
°
for
airplanes, within this localization error limit of all
object parts. The initial model however, violates this
localization error limit already at around
20
°
change
from the known side-view for both object categories.
The increase in performance was obtained for the
whole object as well as the individual parts.
Examples of parts adaption in input video sequences
are shown in figure 4 for both cars and airplanes.
Notably, no adaptations are made to the initial
model, when the algorithm is applied to the walking
people video sequences which do not contain
instances of the object class.
Our online update algorithm is gradual in the
sense that the adapted model combines the old and
current parts appearances and object geometries. The
mixture is obtained by adding the appearance and
displacement from the current model to the ANN
structure. We compared this mixed adaptation with
an alternative where the current-frame model
(appearance and geometry of the detected object)
completely replaces the previous model. The
evaluation for the detection performance of the
object and parts was done on a car video sequence.
Our adaptive algorithm yielded 70% AP for the
detection of the whole object and 60% AP for the
detection of the individual parts. The replacement
alternative yielded 58% AP for the detection of the
whole object, but only 40% AP for the detection of
the parts, which is similar to the performance of the
initial static model of 44% AP for the object
detection and 39% AP for the parts detection. These
results demonstrates the benefit of using a mixture
of the initial model with the novel input, even in
dealing with views not included in the original
model.
As temporal consistency of the dynamic visual
input is an important source of information for the
recognition process, it may be argued that a static
object model alone may suffice, if we increase the
prior for detecting the object after each successful
detection. To examine this possibility, we evaluated
the detection of the static object detector on test
video sets, while decreasing the initial detection
threshold by a fixed rate after each frame when the
object was successfully detected. Table 2 shows the
evaluation results for 2 video sets of the cars
category. We used threshold decreasing rates of 1%
and 2%, and compared the performance with a non-
decreasing (0%) threshold. The initial threshold was
obtained at equal precision-recall rates of the static
object detector during training. As the threshold
decreasing rate goes up, recall rates increase as well,
but precision drops rapidly, and the overall
performance is inferior to the adaptive model.
4.3 Learning New Views
Our algorithm, when applied to dynamic visual
input, adapts to changes in viewing directions of the
object and extends the initial model to cope with
novel views of the class object. In this experiment
we show that the adaptive combination of the initial
model with even a single video sequence already
provides useful generalization of the class model to
novel views. To evaluate the detection performance
of the updated model, we tested the car model that
was adapted to a turning car, on a set of car images
seen from 3 different views: a side-view, roughly
30
°
view and about 60
°
view (Cornelis et al., 2006).
Each image contains a different car instance, none of
which was already observed by the model (neither
during the training of the initial model, nor in the
video sequences). For comparison, we also tested a
state-of-the-art object detector by (Felzenszwalb et
al., 2010), that was trained on side-view car images.
The results in figure 5 show that the updated model
generalizes to the new viewing directions of 30
°
and
60
°
without losing the performance on the initial
side-view. Example part detections images are
shown in figure 6.
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
638
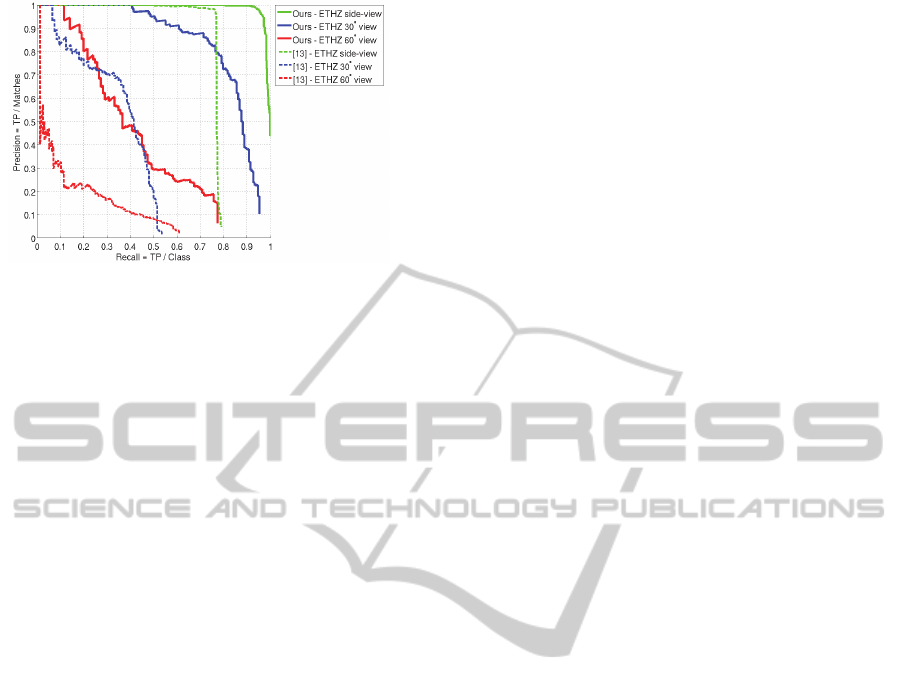
Figure 5: Learning novel views. Object detection
precision-recall graphs for different views of cars. Shown
in solid is the detection performance of our adaptive
model after it was applied to a single video sequence of a
turning car. The colors indicate the 3 views of car images
from the ETHZ dataset (Cornelis et al., 2006) at side-
view, 30
°
and 60
°
. The results show that the adapted
model generalizes to the new views with high precision
rates, while maintaining high precision-recall rates for the
initial side-view. Dashed lines indicate for comparison the
performance of a state-of-the-art detector by
(Felzenszwalb et al., 2010) trained on side-view car
images.
5 DISCUSSION
This paper presents an approach to adaptive object
and parts detection in a dynamic environment.
Starting with an initial model of an object class
covering a limited set of views, our algorithm is
applied to a video input which contains the object
moving and changing its viewing direction. Once the
object is detected at some time
t
, the goal is to
continue to detect the object as its images change in
the video at later times
tt
, and to use the
dynamically changing views to extend the model,
and allow it to classify novel objects under new
views, which the initial model fails to recognize.
The dynamic changes are challenging, since both the
appearance of object parts as well as their relative
positions may change considerably over time.
We combine two sources of information in
constructing the object model at time
t∆t
:
compatibility with the measured optical flow
between time frame
t and
t∆t
, and similarity to
the object model at time
t. These sources of dynamic
visual information are well studied in human vision
and known as motion and spatiotemporal
consistency. Our approach also provides a simple
general method of dynamically updating an object
model: by combining approximate nearest neighbors
search with kernel density estimation, the model
update is obtained by an adaptive mixture of old and
new instances, which allows efficient gradual
adaption to the changing appearance and structure.
Unlike tracking-by-detection methods, which
focus on the tracking of a specific object target over
time rather than building a general class model, the
results demonstrate how the proposed method can be
used for learning, by extending an initial generic
object model, to cope with a new set of viewing
directions of the object class, without further
supervision. The results show that the adaptive
combination of the initial model with even a single
video sequence already provides useful
generalization of the class model to novel views.
While current state-of-the-art methods such as
(Felzenszwalb et al., 2010) learn multiple
configurations of an object class from a set of
limited viewing directions in a supervised manner,
the suggested approach allows the automatic
acquisition of novel views, by extending known
configurations via adaptive parts detection in
dynamic scenes. The adaption is incremental and the
model is updated with every new input. A future
extension of the current work could be to use a large
set of videos to automatically construct a final model
that covers a large set of viewing directions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work was supported in part by the European
Research Council (ERC) Advanced Grant “Digital
Baby” to SU.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, S., Awan, A., & Roth, D. (2004). Learning to
detect objects in images via a sparse, part-based
representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell,
26(11), 1475–1490.
Arya, S., & Mount, D. N. (1993). Approximate nearest
neighbor queries in fixed dimensions. Proc ACM-
SIAM Symp on Discrete Algorithms, 271–280.
Black, M. J., & Anandan, P. (1996). The Robust
Estimation of Multiple Motions: Parametric and
Piecewise-Smooth Flow Fields. Computer Vision and
Image Understanding, 63(1), 75–104.
Cehovin, L., Kristan, M., & Leonardis, A. (2011). An
adaptive coupled-layer visual model for robust visual
tracking. Proc IEEE Int Conf Computer Vision, 1363–
1370.
Cornelis, N., Leibe, B., Cornelis, K., & Van Gool, L.
(2006). 3D City Modeling Using Cognitive Loops.
Proc Int Sym 3D Data Processing, Visualization, and
ExtendingRecognitioninaChangingEnvironment
639

Figure 6: Parts detection examples of the adaptive model after it was applied to a single video sequence of a turning car. Car
images are from the ETHZ dataset (Cornelis et al., 2006): (a) at side-view, (b) at 30
°
view, (c) at around 60
°
view.
Transmission, 9–16.
Crandall, D., Felzenszwalb, P., & Huttenlocher, D. (2005).
Spatial priors for part-based recognition using
statistical models. Proc IEEE Conf Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition, 10–17.
Dalal, N., & Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of Oriented
Gradients for Human Detection. Proc IEEE Conf
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 886–893.
Dalal, N., Triggs, B., & Schmid, C. (2006). Human
Detection Using Oriented Histograms of Flow and
Appearance. Proc IEEE Int Conf Computer Vision,
428–441.
Epshtein, B., & Ullman, S. (2007). Semantic Hierarchies
for Recognizing Objects and Parts. Proc IEEE Conf
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1–8.
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I., Winn,
J., & Zisserman, A. (2009). The PASCAL Visual
Object Classes Challenge 2009 (VOC2009) Results.
Retrieved from http://www.pascal-
network.org/challenges/VOC/voc2009
Fei-Fei, L., Fergus, R., & Perona, P. (2007). Learning
generative visual models from few training examples:
An incremental Bayesian approach tested on 101
object categories. Computer Vision and Image
Understanding, 106(1), 59–70.
Felzenszwalb, P. F., Girshick, R. B., McAllester, D., &
Ramanan, D. (2010). Object Detection with
Discriminatively Trained Part-Based Models. IEEE
Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 1–20.
Felzenszwalb, P. F., & Huttenlocher, D. P. (2005).
Pictorial structures for object recognition. Int J
Computer Vision, 61(1), 55–79.
Fergus, R., Perona, P., & Zisserman, A. (2003). Object
class recognition by unsupervised scale-invariant
learning. Proc IEEE Conf Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, 2, 264–271.
Fergus, R., Perona, P., & Zisserman, A. (2005). A sparse
object category model for efficient learning and
exhaustive recognition. Proc IEEE Conf Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1, 380–387.
Ferryman, J. M. (2009). Workshop on Performance
Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance. Retrieved
from http://www.cvg.rdg.ac.uk/PETS2009
Godec, M., Roth, P. M., & Bischof, H. (2011). Hough-
based tracking of non-rigid objects. Proc IEEE Int
Conf Computer Vision, 81–88.
Kalal, Z., Mikolajczyk, K., & Matas, J. (2011). Tracking-
Learning-Detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach
Intell, 34(7), 1409–1422.
Kwon, J., & Lee, K. M. (2009). Tracking of a non-rigid
object via patch-based dynamic appearance modeling
and adaptive basin hopping monte carlo sampling.
Proc IEEE Conf Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, 1208–1215.
Lim, J., Ross, D., Lin, R., & Yang, M. (2005). Incremental
learning for visual tracking. In L. Saul, Y. Weiss, & L.
Bottou (Eds.), Advances in Neural Inform Process Syst
(Vol. 7, pp. 793– 800). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from
scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Computer Vision,
60(2), 91–110.
Ramanan, D., Forsyth, D., & Zisserman, A. (2007).
Tracking People by Learning Their Appearance. IEEE
Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 29(1), 65–81.
Ullman, S., Vidal-Naquet, M., & Sali, E. (2002). Visual
features of intermediate complexity and their use in
classification. Nature Neuroscience, 5(7), 682–687.
Vidal-Naquet, M., & Ullman, S. (2003). Object
recognition with informative features and linear
classification. Proc IEEE Int Conf Computer Vision,
281–288.
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
640
