
Visual Tracking with Similarity Matching Ratio
Aysegul Dundar
1
, Jonghoon Jin
2
and Eugenio Culurciello
1
1
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, U.S.A.
2
Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Tracking, SMR, Similarity Matching Ratio, Template Matching.
Abstract:
This paper presents a novel approach to visual tracking: Similarity Matching Ratio (SMR). The traditional
approach of tracking is minimizing some measures of the difference between the template and a patch from
the frame. This approach is vulnerable to outliers and drastic appearance changes and an extensive study
is focusing on making the approach more tolerant to them. However, this often results in longer, corrective
algorithms which do not solve the original problem. This paper proposes a novel approach to the definition
of the tracking problems, SMR, which turns the differences into probability measures. Only pixel differences
below a threshold count towards deciding the match, the rest are ignored. This approach makes the SMR
tracker robust to outliers and points that dramatically change appearance. The SMR tracker is tested on
challenging video sequences and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Visual tracking of objects in a scene is a very im-
portant component of a unified robotic vision sys-
tem. Robots need to track objects in order to inter-
act. As such as they move closer, robots and other
autonomous vehicles will have to avoid other moving
objects, humans, animals, as they operate in our ev-
eryday environment.
The human visual system object tracking perfor-
mance is currently unsurpassed by engineered sys-
tems, thus our research tries to take inspiration and
reverse-engineer the known principles of cortical pro-
cessing during visual tracking. Visual tracking is a
complex task, with neuroscience studies of cortical
processing painting an incomplete picture, and thus is
only partially able to guide the design of a synthetic
solution. Nevertheless a few key features arise from
studying the human visual system and its tracking
abilities: (1) the human visual system is not limited
to three-dimensional conventional objects in space,
rather is able to track a set of visual features (Blaser
et al., 2000). Thus object in this paper refers to a dis-
tinct group of features in the two-dimensional space.
(2) It is not necessary for humans to have knowledge
of the object class before visual tracking, and (3) hu-
mans can track an object after a very brief presenta-
tion. Even though the human visual system does not
operate with frames it is common to desire synthetic
systems to be able to track from a single frame.
Visual tracking in artificial systems has been stud-
ied for decades, with laudable results (Yilmaz et al.,
2006). In this paper we focus on bio-inspired visual
tracking systems that can be part of a unified neurally-
inspired vision system. Ideally, a unified visual model
would be able to parse and detect an object every
frame, but right now there is no bio-inspired model
that can do this in real-time (DiCarlo et al., 2012; Le-
Cun et al., 2004; Serre et al., 2007). Deep neural net-
works come close to this performancewhen trained to
look for a single object on a large collection of images
(Sermanet et al., 2011).
A bio-inspired synthetic visual tracker is gener-
ally thought of having two outputs of the same unified
stream: one is a deep neural network classifier that
is capable of categorizing object, another is a shal-
lower classifier that can group features into object-
ness. The first deep system is used to be able to con-
tinue tracking an object as it disappears and reappears
in the scene, while the second system provides rapid
grouping of local features, by tracking local maxima
in the retinal space. Such distinction might be neces-
sary as a deep system will need 100-200ms to process
one visual scene (Thorpe et al., 1996), while tracking
without predicting object movement, as the one re-
quired for the oculo-motor control of smooth-pursuit
(Wilmer and Nakayama, 2007), requires faster pro-
cessing of the visual stream.
Inspired by recent findings on shallow feature ex-
tractors of the visual cortex (Vintch et al., 2010), we
280
Dundar A., Jin J. and Culurciello E..
Visual Tracking with Similarity Matching Ratio.
DOI: 10.5220/0004288602800285
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2013), pages 280-285
ISBN: 978-989-8565-48-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Table 1: Properties of the video dataset used in this work (Kalal et al., 2010a).
Video Sequence
1. David 2. Jumping 3. Pedestrian1 4. Pedestrian2 5. Pedestrian3 6. Car
Camera Movement yes yes yes yes yes yes
Partial Occlusion yes no no yes yes yes
Full Occlusion no no no yes yes yes
Pose Change yes no no no no no
Illumination Change yes no no no no no
Scale change yes no no no no no
Similar Objects no no no yes yes yes
Table 2: Number of correctly tracked frames from the state-of-art trackers and the SMR tracker. Table is taken and modified
from (Kalal et al., 2010b).
Video Sequence
1. David 2. Jumping 3. Pedestrian1 4. Pedestrian2 5. Pedestrian3 6. Car
Number of Frames 761 313 140 338 184 945
(Lim et al., 2004) 17 75 11 33 50 163
(Collins et al., 2005) n/a 313 6 8 5 n/a
(Avidan, 2007) 94 44 22 118 53 10
(Babenko et al., 2009) 135 313 101 37 49 45
(Kalal et al., 2010b) 761 170 140 97 52 510
SMR (this work) 761 313 140 236 66 510
postulate that simple tracking processes are based on
a shallow neural network that can quickly identify
similarities between object features repeated in time.
We propose an algorithm that can track and extract
motion of an object based on the similarity between
local features observed in subsequent frames. The lo-
cal features are initially defined as a bounding box
that defines the object to track.
Our work uses a modified template matching algo-
rithm butoffers an advantageovertraditional template
matching algorithms. Traditional template matching
algorithms define the tracking problem as follows:
We are given two images, F(x, y) and G(x, y), which
represent the pixel values at each location (x, y).
G(x, y) is the template, representing the object that
wanted to track, that may come from the user selec-
tion or an automatic detection algorithm, and F(x, y)
is the new image that comes from a camera. The goal
is to find the new location of the object (h
1
, h
2
) by
minimizing some measures of the difference between
F(x + h
1
, y + h
2
) and G(x, y) in different configura-
tions.
In our work we change this definition of tracking
and propose a novel approach, Similarity Match Ra-
tio (SMR). This approach is more robust to appear-
ance change, disappearance and outliers because in-
stead of trying to minimize some measures of differ-
ence between F(x+h
1
, y+h
2
) and G(x, y) as a whole,
we want to find (h
1
, h
2
) that gives the best match ratio
between F(x+ h
1
, y+ h
2
) and G(x, y). To do this, we
are turning pixel differences between F(x+h
1
, y+h
2
)
and G(x, y) into probability values and accumulat-
ing them for every pixel that has a good match. If
there is no good match between some pixels, these
pixels provide zero probabilities because we are not
interested in how badly the two pixels match. The
method is tested on challenging benchmark video se-
quences which include camera movement, partial/full
occlusion, illuminance change, scale change and sim-
ilar objects. State-of-the-art performance is achieved
from these video sequences.
2 PREVIOUS WORK
Most popular trackers that are based on the tra-
ditional definition of the tracking problem (e.g.
Sum-of-Squared-Distances (SSD), Sum-of-Absolute-
Differences (SAD), Lucas-Kanade tracker) try to find
distance vector (h
1
, h
2
) that minimizes the difference
between F(x + h
1
, y + h
2
) and G(x, y) either on the
grayscale or color image. However, the template
G(x, y) may be including outliers or some parts that
VisualTrackingwithSimilarityMatchingRatio
281

dramatically change or disappear, which cause track-
ing failure. The common approach to overcome these
tracking failures is that trackers should not treat all
pixels in a uniform manner but eliminate outliers from
the computation.
Some studies (Comaniciu et al., 2003; Shi and
Tomasi, 1994) propose using a weighted histogram as
a measure to minimize for tracking an object. By as-
suming that pixels close to the center are the most re-
liable, these methods weigh them higher, since occlu-
sions and interferences tend to occur close to bound-
aries. However, a dramatical change in the appear-
ance can occur even in the center, which cannot be
handled by this method.
There are studies that aim to detect outliers and
suppress them from the computation. (Hager and Bel-
humeur, 1998) uses the common approach that out-
liers produce large image differences that can be de-
tected by the estimation process (Black and Jepson,
1998). Residuals are calculated iteratively and if the
variations of the residual are bigger than a user de-
fined threshold they are considered outliers and sup-
pressed. (Ishikawa et al., 2002) uses the spatial coher-
ence property of the outliers which means that outliers
tend to form a spatially coherent group rather than be-
ing randomly distributed across the template. In that
work the template is divided into blocks and constant
weights are assigned for each block. If the image dif-
ferences of the blocks between the frames are large,
it means these blocks include a significant amount of
outliers. The method excludes the blocks that contain
outliers from the computation of minimization. These
methods are more robust to outliers. However, they
are computationally expensive.
(Kalal et al., 2010b) proposes forward backward
error which is based on the fact that correct track-
ing should be independent of the direction of time-
flow. Firstly, points are tracked in the forward direc-
tion. Then, backward tracking is applied to validate
the trajectories. This method enables trackers to avoid
tracking points that disappear from the camera view
or change appearance drastically. Before our work,
Kalal’s tracker was the state-of-the-art.
3 SIMILARITY MATCHING
RATIO (SMR) TRACKER
The SMR tracker uses a modified template-matching
algorithm. In this algorithm, we look for similarity
between a template G(x, y) and patches of a new video
frame F(x+ h
1
, y + h
2
). The SMR computes the dif-
ference between the template and the patches at each
pixel. Templates are moved convolutionally on the
Figure 1: (Top) The red box is the SMR tracker’s output,
the blue box is the SAD tracker’s output. The ground-truth
from the first frame is used as a template which is shown
on the left top corner of the frame. (Bottom) The absolute
differences for each pixel between the template and result
from the SMR tracker are mapped on the left and from the
SAD tracker on the right. Dark values (close to zero) report
a better match. Note that even though there are higher dif-
ferences, the SMR tracker is able to find the correct patch.
new video frame, and stepped by one pixel. If this
difference is lower than a threshold, it is summed to
the output after negative exponential distance conver-
sion. This thresholding eliminates outlying pixels, in
such a way that they do not appear in the final output.
The SMR algorithm is as follows:
1. The search area, (h
1
, h
2
), is limited to the neigh-
borhood of the target’s previous position.
2. For each pixel in the template G(x, y), the method
is checking if the condition |F(x + h
1
, y + h
2
) −
G(x, y)| ≤ α is satisfied, where α is a dynamic
threshold defined in 6.
3. If satisfied, we are interested in how close the
match is, so the pixel difference is converted into
a probability value p by p = exp(−|F(x+ h
1
, y+
h
2
) − G(x, y)|). If not these pixels are ignored.
4. The probability values are summed up for
each patch. The algorithm finds the (h
1
, h
2
)
that gives the highest similarity matching ratio,
argmax
h
1
,h
2
∑
p.
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
282
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7
number of pixels
pixel difference between the template and the patch
SMR
(a)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7
number of pixels
pixel difference between the template and the patch
SAD
(b)
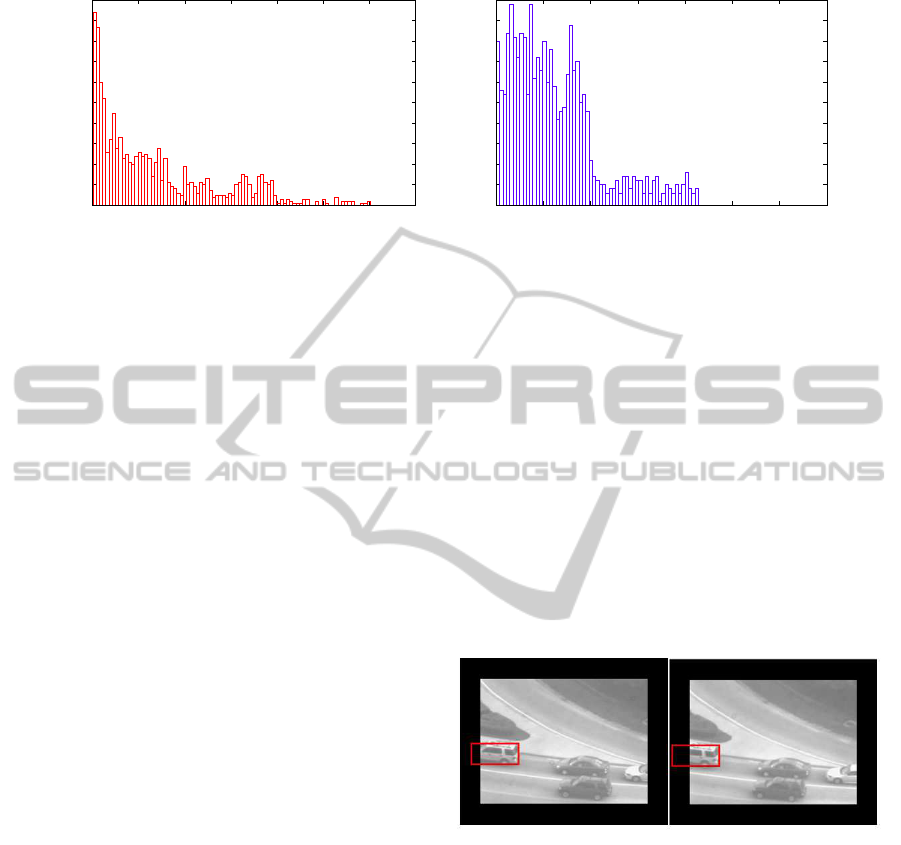
Figure 2: Histogram of the pixel differences that were mapped in Figure 1. (a) Map between the template and result from
the SMR tracker and (b) result from the SAD tracker. The SAD tracker minimizes the number pixels with large differences,
whereas the SMR tracker maximizes the number of pixels that have small differences.
5. G(x, y)
t+1
= F(x + h
1
, y + h
2
)
t
The patch is ex-
tracted in every detection and assigned as new
template.
6. Dynamic threshold α = max(G(x, y)
t
−
G(x, y)
t+1
) · k where k = 0.25 is a constant
determined experimentally.
The biggest advantage of the SMR is that pixel
differences above α are not contributing to the match-
ing similarity output. These pixels may be outliers or
points that dramatically change appearance, and thus
should not affect the matching similarity. Outlying
pixels usually only increase the error and cause fail-
ure, so we chose to ignore them in this method. This
way, only reliably matching pixels contribute to the
output of each matching step.
4 RESULTS
This approach is tested on a challenging benchmark:
the TLD (Kalal et al., 2010a) dataset. From this
dataset six videos with different properties were se-
lected as displayed in Table 1. Each video contains
only one target. The metric used is the number of cor-
rectly tracked frames. For this test, color videos are
converted to grayscale. State-of-the-art performance
is achieved and results are presented in Table 2.
To illustrate how the qualitatively different way of
defining the tracking problem of the SMR tracker pro-
vides better results than the traditional approach, we
will compare the SMR tracker with the SAD tracker
in the present section.
Figure 1 shows the detections from the SAD
tracker and the SMR tracker where they have used
the same template. Points that dramatically changed
appearance cause the SAD tracker to fail whereas the
SMR tracker correctly detects the object. For illustra-
tion purposes, the differences for each pixel between
the template and the patches the SAD tracker and the
SMR tracker detected are mapped in Figure 1. The
patch the SMR tracker detected has a bigger sum of
absolute differences. However, that is because of the
region that dramatically changed appearance. That
patch has many close matches with the template as
can be seen in Figure 2. As such, the SMR tracker
is able to detect it. Again, with the same principle
the SMR tracker is able to track the object when it is
going out of the scene as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: The red boxes are the SMR tracker’s outputs. The
video frame is extended and padded by zeroes. The SMR
tracker is able to track when the target is going out of the
frame. The template update is ceased in these situations
which prevents the drifting from the object.
The SMR tracker is more robust to outliers than
the traditional approach. As can be seen in Figure
4, outliers cause the SAD tracker to drift away from
the object, whereas the SMR tracker (Figure 4) finds
the target. Ideally, the bounding box should be en-
tirely filled with the target. However, during long-
term tracking, the object may move back and forth
and rotate which causes some background pixels to
be included in the next template. A tracker does not
know which pixels belong to the object and which
ones belong to the background. On the other hand,
VisualTrackingwithSimilarityMatchingRatio
283

Figure 4: (Top) The red boxes are the SMR tracker’s outputs. (Bottom) The blue boxes are the SAD tracker’s outputs.
Outlying pixels cause the SAD tracker to drift, whereas the SMR tracker is not affected by them.
the SMR tracker has a higher probability of rejecting
background pixels, as they tend to change more.
The SAD tracker from the 2nd frame to 3rd in Fig-
ure 4 (bottom) drifts away from the object, because
the pixels from the background have become included
in the bounding box and they propagate to the tem-
plate. When the face moves right, the SAD tracker
does not move and drifts away from the object be-
cause the background, which has high contrast, gives
big differences if the bounding box shifts to a new po-
sition. Therefore, the traditional approach gives pri-
ority to preventing big differences when it is making
a decision, even if these pixels are not the majority of
the template. On the other hand, the SMR tracker is
focusing on the number of pixels that have small dif-
ferences with the template, which is a human face in
this case (Figure 4 top).
5 FAILURE MODE
Even though the SMR tracker updates the template
at every frame in this presented work, drifts caused
by the accumulation of small errors during each de-
tection are not observed by applying this method on
the benchmark dataset. However, when an object be-
comes occluded very slowly, updating the template at
every frame causes the template to include foreground
pixels that do not belong to the object. An example
can be seen in Figure 5. A better template update
mechanism will prevent this kind of failure. This will
most probably require the use of a classifier, which is
out of the scope of the work in this paper. Another
limitation of this method is the inability of updating
the template size. This may become a problem when
the object goes further away from the camera. In that
Figure 5: Red boxes are the SMR tracker’s results. The
every-frame template update causes the outlying pixels to
propagate to the templates. When outlying pixels dominate
the template, the SMR tracker fails.
case, the object will get smaller and may become a
minority of the pixels within the bounding box which
would cause the failure of the tracker.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposed a novel approach of tracking: the
Similarity Matching Ratio (SMR). The SMR tracker
is more robust to outliers than the traditional ap-
proaches because it is not collecting differences be-
tween the template and the frame for each pixel. In-
stead, it is collecting probabilities from the pixels
that have small differences from the template. The
SMR tracker tries to find a region which maximizes
the good match instead of minimizing the differences
for the whole template. The SMR tracker is tested
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
284

on challenging video sequences and achieves state-
of-the-art performance (See Table 2). These results
show that SMR is a superior approach.
REFERENCES
Avidan, S. (2007). Ensemble tracking. Pattern Analy-
sis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on,
29(2):261–271.
Babenko, B., Yang, M., and Belongie, S. (2009). Vi-
sual tracking with online multiple instance learning.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009.
CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on, pages 983–990.
IEEE.
Black, M. and Jepson, A. (1998). Eigentracking: Robust
matching and tracking of articulated objects using a
view-based representation. International Journal of
Computer Vision, 26(1):63–84.
Blaser, E., Pylyshyn, Z., Holcombe, A., et al. (2000).
Tracking an object through feature space. Nature,
408(6809):196–198.
Collins, R., Liu, Y., and Leordeanu, M. (2005). Online se-
lection of discriminative tracking features. Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transac-
tions on, 27(10):1631–1643.
Comaniciu, D., Ramesh, V., and Meer, P. (2003). Kernel-
based object tracking. Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on, 25(5):564–577.
DiCarlo, J., Zoccolan, D., and Rust, N. (2012). How does
the brain solve visual object recognition? Neuron,
73(3):415–434.
Hager, G. and Belhumeur, P. (1998). Efficient region track-
ing with parametric models of geometry and illumina-
tion. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE
Transactions on, 20(10):1025–1039.
Ishikawa, T., Matthews, I., and Baker, S. (2002). Efficient
image alignment with outlier rejection. Citeseer.
Kalal, Z., Matas, J., and Mikolajczyk, K. (2010a). P-N
Learning: Bootstrapping Binary Classifiers by Struc-
tural Constraints. Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition.
Kalal, Z., Mikolajczyk, K., and Matas, J. (2010b). Forward-
backward error: Automatic detection of tracking fail-
ures. In Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2010 20th Inter-
national Conference on, pages 2756–2759. IEEE.
LeCun, Y., Huang, F., and Bottou, L. (2004). Learning
methods for generic object recognition with invari-
ance to pose and lighting. In Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, 2004. CVPR 2004. Proceedings
of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on,
volume 2, pages II–97. IEEE.
Lim, J., Ross, D., Lin, R., and Yang, M. (2004). Incremen-
tal learning for visual tracking. Advances in neural
information processing systems, 17:793–800.
Lucas, B. and Kanade, T. (1981). An iterative image regis-
tration technique with an application to stereo vision.
In Proceedings of the 7th international joint confer-
ence on Artificial intelligence.
Sermanet, P., Kavukcuoglu, K., and LeCun, Y. (2011).
Traffic signs and pedestrians vision with multi-scale
convolutional networks. Snowbird Machine Learning
Workshop.
Serre, T., Wolf, L., Bileschi, S., Riesenhuber, M., and Pog-
gio, T. (2007). Robust object recognition with cortex-
like mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach.
Intell., 29:411–426.
Shi, J. and Tomasi, C. (1994). Good features to track.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1994.
Proceedings CVPR’94., 1994 IEEE Computer Society
Conference on, pages 593–600. IEEE.
Thorpe, S., Fize, D., Marlot, C., et al. (1996). Speed
of processing in the human visual system. nature,
381(6582):520–522.
Vintch, B., Movshon, J. A., and Simoncelli, E. P. (2010).
Characterizing receptive field structure of macaque v2
neurons in terms of their v1 afferents. Annual meeting
in Neuroscience.
Wilmer, J. and Nakayama, K. (2007). Two distinct visual
motion mechanisms for smooth pursuit: Evidence
from individual differences. Neuron, 54(6):987–1000.
Yilmaz, A., Javed, O., and Shah, M. (2006). Object track-
ing: A survey. Acm Computing Surveys (CSUR),
38(4):13.
VisualTrackingwithSimilarityMatchingRatio
285
