Automated Classification of Therapeutic Face Exercises using the Kinect
Cornelia Lanz
1
, Birant Sibel Olgay
1
, Joachim Denzler
2
and Horst-Michael Gross
1
1
Neuroinformatics and Cognitive Robotics Lab, Ilmenau University of Technology, Ilmenau, Germany
2
Computer Vision Group, Friedrich Schiller University Jena, Jena, Germany
Keywords:
Facial Expressions, Curvature Analysis, Point Signatures, Line Profiles, Therapeutic Exercises.
Abstract:
In this work, we propose an approach for the unexplored topic of therapeutic facial exercise recognition us-
ing depth images. In cooperation with speech therapists, we determined nine exercises that are beneficial for
therapy of patients suffering from dysfunction of facial movements. Our approach employs 2.5D images and
3D point clouds, which were recorded using Microsoft’s Kinect. Extracted features comprise the curvature
of the face surface and characteristic profiles that are derived using distinctive landmarks. We evaluate the
discriminative power and the robustness of the features with respect to the above-mentioned application sce-
nario. Using manually located face regions for feature extraction, we achieve an average recognition accuracy
of about 91% for the nine facial exercises. However in a real-world scenario manual localization of regions
for feature extraction is not feasible. Therefore, we additionally examine the robustness of the features and
show, that they are beneficial for a real-world, fully automated scenario as well.
1 INTRODUCTION
Facial expressions are key to interpersonal commu-
nication. Diseases like stroke or mechanical injury
of the facial nerve can lead to a dysfunction of fa-
cial movements. These impairments of facial expres-
sions may have various consequences that can con-
strain daily life and can lead to social isolation. Exam-
ples for these consequences are eating difficulties, im-
paired appearance of the face, and misunderstandings
in face-to-face communications due to ambiguous fa-
cial expressions. Similar to rehabilitation exercises
that help to regain body functions, there are exercises
for the recovery of facial expressions. Besides prac-
tising under supervision of a speech therapist, patients
additionally have to conduct unattended exercises on
their own. However, the incorrect conduction of exer-
cises can impede the training success or even lead to
further impairment. An accompanying training plat-
form could enrich unsupervised training exercises by
tutorial, feedback and documentation functions. Tu-
torial functions can support correct exercise conduc-
tion by providing text and video instructions. A feed-
back function could give advice regarding mistakes
or inaccuracies during training. The documentation
in form of videos or feedback enables the therapist to
review the past unsupervised training units, if neces-
sary. The conception and implementation of such a
training platform is a challenging and complex task
that comprises several subtasks. In this work we will
focus on one subtask, that is, the evaluation of fea-
tures. However, to enable a better understandig of the
context of our work, we give a short overview of the
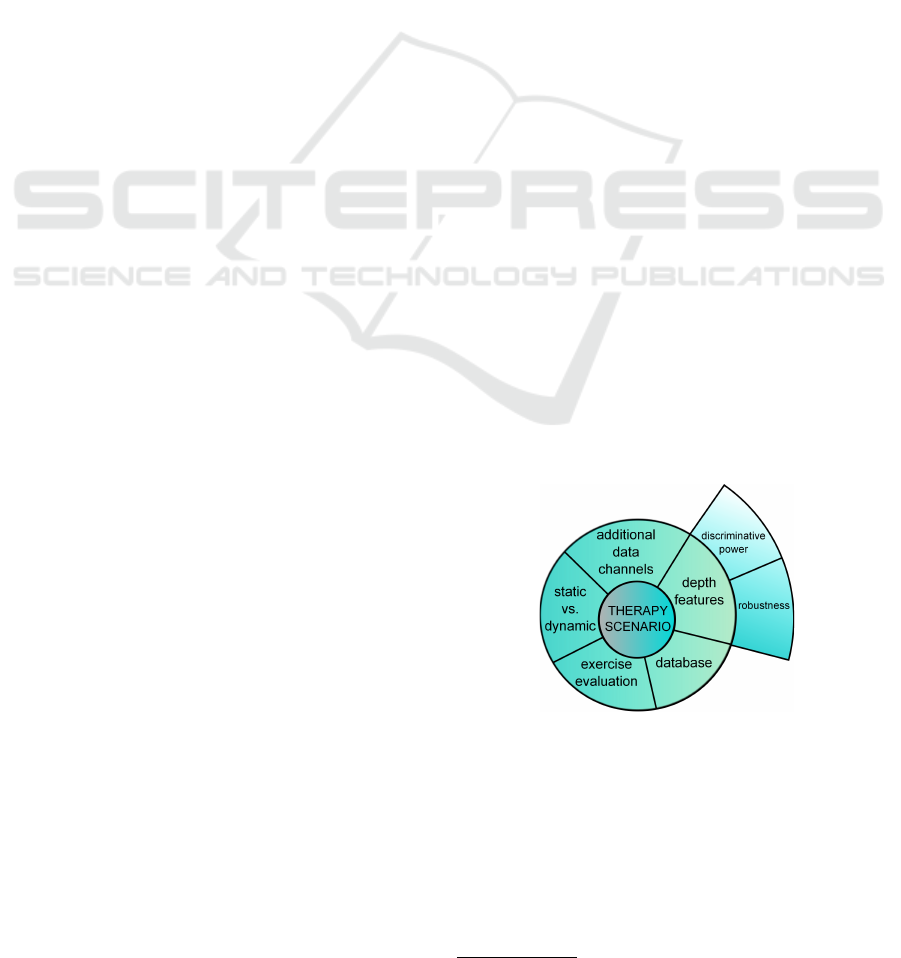
remaining subtasks. Figure 1 presents five of the in-
volved subtasks, which will be discussed in the fol-
lowing.
Figure 1: Different subtasks of the conception and imple-
mentation of an automated therapeutic exercise platform.
Facial movements cause changes of the face sur-
face, which can be captured by depth image sen-
sors like Microsoft’s Kinect
1
or Time-of-flight Cam-
eras
2
,
3
. The extraction of depth features allows to
examine the face surface, independently from skin
colour and lighting conditions. Although there exist
other systems that are capable of recording depth data
1
http://www.xbox.com/en-US/kinect
2
http://www.pmdtec.com/
3
http://www.mesa-imaging.ch/
556
Lanz C., Olgay B., Denzler J. and Gross H..
Automated Classification of Therapeutic Face Exercises using the Kinect.
DOI: 10.5220/0004294005560565
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2013), pages 556-565
ISBN: 978-989-8565-47-1
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

with much higher depth resolution than the Kinect
(e.g. (Grosse et al., 2011)), we decided to use this sen-
sor because of its moderate price. This makes such
an application suitable for widespread use in low-cost
training platforms. Furthermore, the Kinect allows to
capture additional data channels such as intensity
images in parallel to depth images. These might be
helpful if depth information is not suitable to describe
certain facial movements. For example, it can hardly
be determined whether the eyes are closed by solely
employing depth information.
The nine therapeutic face exercises that we focus
on in this paper are rather static. The pace of the ex-
ercise conduction from neutral face to final state, e.g.
both cheeks puffed, is not important. It is more rel-
evant that the exercises final states are retained for
some seconds. Nevertheless, it is likely that additional
information, obtained by examining the dynamics of
an exercise instead of single static snapshots, may
contain valuable information. Additionally, it is pos-
sible to reduce the amount of noise in the data by
smoothing over time.
The evaluation of the exercises, which is essen-
tial for a feedback functionality, is a complex task.
Besides the choice of appropriate technical tools, it is
necessary to define, in which cases an exercise is per-
formed correctly and in which it is not. Additionally,
we need to assess how feedback should be communi-
cated in order to be most beneficial for a patient.
Furthermore, it is necessary to collect a database
of training and test images that contain the exercises
performed by healthy people as well as the exercise
conduction by people with dysfunction of facial ex-
pression abilities. In our experiments, nine therapeu-
tic facial exercises are employed that have been de-
fined in cooperation with speech therapists. We only
employ training and test data recorded from exercises
of healthy persons. We omit data recorded from per-
sons with dysfunction of facial expressions, as we ex-
pect their ground-truth to be ill-defined. This is due
to the circumstance, that incorrect conduction of an
exercise may resemble other exercises, as shown in
Figure 2.
Since each of the above-mentioned subtasks con-
sists of diverse aspects, we focus on the extraction and
evaluation of depth features in this publication. Our
depth features are extracted from 2.5D images and 3D
point clouds recorded by the Kinect Sensor. We refer
to 2.5D images as 2D images that contain the object-
to-camera distance instead of the object’s intensity
value. We analyse the facial surface by extraction of
curvature information and surface profiles. Surface
profiles comprise line profiles and point signatures.
Line profiles are based on paths that connect two land-
mark points, whereas point signatures are based on
radial paths around single landmark points.
We examine the features’ discriminative power
with respect to the classification of nine therapeutic
exercises and their robustness regarding varying fea-
ture extraction regions. In the targeted real-time sce-
nario regions and points for feature extraction need to
be determined automatically. We expect that this step
leads to variations from manually located face regions
and landmarks. Therefore it is necessary that the fea-
tures are robust against these deviations.
Figure 2: Patient with facial paresis on his right side. Left
image: The exercise right cheek puffed is conducted cor-
rectly because the bulge of the cheek is a passive process as
reaction of a higher air pressure inside the mouth and a con-
traction of the buccinator on the left facial side. Right im-
age: The exercise left cheek puffed is conducted incorrectly.
The lack of contradiction in the right buccinator leads to the
bulge of the right cheek.
2 RELATED WORK
Automated recognition of therapeutic face excercises
is an unexplored research field. In practice, there are
already tools that support the patient with regard to
exercising that is not supervised by a therapist. These
tools are videos and programs that give instructions
to the patient, with respect to correct exercise con-
duction (LogoVid
4
), and, to some extent, allow for
a documentation of exercise frequency and success
(CoMuZu
5
). The documentation, however, is done by
the patient himself, which is often impractical or even
questionable. At the moment, there are no commer-
cial solutions available that automatically recognize a
performed therapeutic exercise.
(Nakamura et al., 2003) evaluated the success
of facial exercises to prevent synkinesis after facial
paresis. Synkinesis is an involuntary associated facial
movement such as eye closure during smiling. They
manually measure the eye opening width by using an
image editing software. (Gebhard et al., 2000) pre-
sented a system for the diagnosis support of patients
4
http://www.comuzu.de
5
http://www.logomedien.de/html/logovid7a.html
AutomatedClassificationofTherapeuticFaceExercisesusingtheKinect
557

with facial paresis using 2D colour images. There-
fore, they analysed facial asymmetries in the eyes,
nose and mouth regions.
At present, there are no publications known to us
that focus on the automated recognition of therapeu-
tic facial exercises using depth information. Never-
theless, we can utilize approaches from works on face
detection, as well as person and emotion recognition.
(Colombo et al., 2006) use curvature of the surface of
a 2.5D image to detect salient face features like eyes
and nose. A triplet consisting of a candidate nose and
two candidate eyes is processed by a classifier that is
trained to discriminate between faces and non-faces.
Based on curvature information estimated on a 3D tri-
angle mesh model, (Wang et al., 2006) classify 3D
faces according to the emotional state that they repre-
sent.
Point signatures were developed by (Chua and
Jarvis, 1997) as an approach for 3D object recogni-
tion. They presented an enhanced algorithm for face
recognition based on point signatures in (Chua et al.,
2000). (Wang et al., 2002) extracted point signatures
in 2.5D images and Gabor filter responses in gray-
level images and employed their combination for face
recognition.
In this work we orient on the method of (Wang
et al., 2006) to create histograms of curvature types.
We utilize the face recognition algorithm from (Chua
et al., 2000) for the classification of our nine thera-
peutic exercises and supplement it with a similar ap-
proach that employs line profiles instead of radial pro-
files. In contrast to (Wang et al., 2006), where manu-
ally placed landmarks are used, we additionally eval-
uate our results with automatically located landmark
positions.
3 METHOD
In the following, we briefly review the determination
of surface curvature (section 3.1) as far as it is neces-
sary to understand the basic principles of our curva-
ture feature types (section 3.2). For detailed informa-
tion we refer to (Besl and Jain, 1986). In sections 3.3
and 3.4 the extraction of line profiles and point signa-
tures is presented. In the last section, we focus on the
automation of the feature extraction process.
3.1 Curvature Analysis
Our aim is the classification of faces according to
the therapeutic exercises a patient performs. Facial
movement leads to a change of the face surface. We
analyse the surface by extracting curvature informa-
tion from 2.5D range images and 3D point clouds.
The parametric form of a surface in 3D is s(u, v) =
[x(u, v) y(u, v) z(u, v)]
T
, with u and v denoting the axes
of the parameter plane (Figure 3). On the basis of this
function, we can determine the first and the second
fundamental forms, which uniquely characterize and
quantify general smooth shapes. The elements of the
first fundamental form I are:
I =
s
u
· s
u
s
u
· s
v
s
u
· s
v
s
v
· s
v
. (1)
The subscripts denote partial differentation. The ele-
ments of the second fundamental form J are:
J =
s
uu
· n s
uv
· n
s
uv
· n s
vv
· n
, (2)
with n being the unity normal vector of the tangent
plane in the point with parameters (u, v). Although
both fundamental forms are a unique representation
of the surface, more common for surface character-
ization are combinations of both, because they allow
for an intuitive interpretation. Using I and J, the shape
operator matrix W can be computed by:
W = I
−1
· J. (3)
The mean curvature H gives information about the di-
rection of the curvature (convex, concave) and is de-
termined by:
H =
1
2
tr [W] , (4)
with tr [W] being the trace of the shape operator W.
The Gaussian curvature K contains the information
whether curvatures that are orthogonal to each other
point in the same or in different directions (Figure 4).
It is computed as follows:
K = det [W]. (5)
Opposed to the general parametric representation, the
parametrization of a 2.5D range image takes a very
simple form s(u, v) = [u v z(u, v)]
T
. Because a 2.5D
image is spanned by two axes that generate a discrete
(pixel) grid the derivation of s with respect to u and
v is simplified and results in s
u
= [1 0 z
u
]
T
and s
v
=
[0 1 z
v
]
T
. Therefore, for the computation of H and K
only the partial derivatives of z are relevant:
H =
z
uu
+ z
vv
+ z
uu
z
2
v
+ z
vv
z
2
u
− 2z
u
z
v
z
uv
(1 + z
2
u
+ z
2
v
)
3
2
, (6)
K =
z
uu
z
vv
− z
2
uv
(1 + z
2
u
+ z
2
v
)
2
. (7)
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
558

uv - Parameter Plane
n
Surface in R³
s(u,v)
s
u
s
v
(u,v)
Figure 3: Surface in 3D with the corresponding parameter
plane (image according to (Besl and Jain, 1986)).
Figure 4: Two surfaces with orthogonal maximum and min-
imum curvatures that point in different (upper surface: hy-
perbolic convex) and in the same directions (lower surface:
elliptic convex).
3.2 Extraction of Curvature
Information
Prior to feature extraction, we smooth the face sur-
face using an average filter. On a subset of the data,
we performed tests with different filter sizes and fil-
ter parameters, which showed that adequate low-pass
filtering has strong impact on the success of classi-
fication. For example, Gaussian filtering was tested
but resulted in lower classification results compared
to average filtering.
We extract the mean and Gaussian curvature for
each pixel, respectively 3D-point, to obtain informa-
tion about the facial surface. This results in around
2 × 8000 to 2 × 13000 values per face, depending on
the face-to-camera distance. In order to reduce the
dimensionality of the feature space, we summarize
the curvature values with a histogram (Wang et al.,
2006). To maintain spatial information, we define
four regions (A-D) from which histograms are ex-
tracted (Figure 5). Each histogram is weighted with
the number of pixels of the region described by it.
The selected cheek regions are axially symmetric, due
to the fact that some of the therapeutic exercises are
asymmetric and each face side contains valuable in-
formation. Two additional regions, in which high fa-
cial surface variation among all exercises is visible,
were determined. Further refinement of the regions
was omited to maintain a certain robustness in case of
automatically determined regions.
The curvature type histogram feature is obtained
by extraction of mean curvature H and Gaussian cur-
vature K for every 2.5D pixel, respectively 3D point
according to equations (4)-(7). In the next step, both
values are combined to discrete curvature types as
1
2
3
4
B
A
C
D
5
Figure 5: Regions A-D are employed for curvature fea-
ture extraction. Region borders are derived from landmark
points 1-5. The determination of the landmark points is ex-
plained in sections 3.5 and 4.1.
shown in Table 1 (Colombo et al., 2006). Subse-
quently, the discrete curvature types of each region
are summarized with histograms. The concatenation
of these histograms forms the feature vectors that are
subjected to the classification process. For each image
a 32 dimensional feature vector is extracted (8 curva-
ture type histogram bins per region).
3.3 Extraction of Line Profiles
Although curvatures are extracted from each pixel,
their combination in a histogram blots out some of
the local information. Line profiles, in contrast, con-
tain local information by describing paths along the
face surface. Instead of using 2.5D images, line pro-
files are extracted from a point cloud, which lies in
a three-dimensional space. Each of the three dimen-
sions is expressed in metre. For a 2.5D image the two
dimensions are given in pixel units. However, the real
world distance that is described by the difference of
one pixel depends on the person-to-camera distance.
The smaller the distance of an object to the camera is,
the more pixels does this object cover on a 2.5D im-
age. As a result, comparison of different line profiles
is more difficult, when using 2.5D images.
In total, we extract nine line profiles from the 3D
point cloud of the face. Every line profile connects
two defined landmark points. Figure 6 shows the
paths of the profile lines. Seven profiles start at the
nose tip, connecting it in radial direction to silhouette
points. Two line profiles are horizontally located and
link two silhouette points.
The paths over the face consist of N equidistant
points p
n
(x, y, z), with n = 1...N. Nearest-neighbour
interpolation is employed in order to calculate miss-
ing points. The L2-norm of the position vectors of
every 3D point p
n
already creates a distinctive curve
as can be seen in Figure 7. However, in order to
achieve invariance with respect to the viewpoint (i.e.,
translation and rotation operations of the facial point
cloud), relative central differences between the 3D
points are calculated (left image of Figure 8). The im-
ages show, that the curves consist of 70 samples. This
AutomatedClassificationofTherapeuticFaceExercisesusingtheKinect
559

Table 1: Curvature type definition using mean and Gaussian curvature (H, K).
K < 0 K = 0 K > 0
H < 0 hyperbolic concave cylindric concave elliptic concave
H = 0 hyperbolic symmetric planar impossible
H > 0 hyperbolic convex cylindric convex elliptic convex
Figure 6: 3D face with marked paths of the nine line pro-
files.
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
0.66
0.67
0.68
0.69
0.7
0.71
0.72
0.73
0.74
Original line profile
point index
vector lengths (in metre)
Figure 7: Line profile from nose tip to the point of the chin
for the exercise A-shape.The curve shows the length (in me-
tre) of the position vector of each point p
n
. The opening of
the mouth, resulting in higher values, in the middle of the
curve and the chin shape on the right are visible.
0 20 40 60 80
0
2
4
6
8
x 10
−3
Distance line profile
point index
central difference (in metre)
0 5 10 15
0
0.005
0.01
0.015
Reconstructed distance line profile
point index
central difference (in metre)
Figure 8: Left: Distance line profile. Right: The recon-
structed line profile using the first 12 dct-coefficients.
p
ref
p
0
d
eye
Figure 9: Landmark points and line segments that are em-
ployed for the extraction of point signatures.
value may vary because the size of the head (subject-
specific) or the length of the curve (exercise-specific)
may change. To get an identical size of the curve
for every subject and every exercise and to reduce
the amount of feature dimensions we conduct a dis-
crete cosine transform (Salomon, 2004) on the curves
and build our feature vector using the first 12 dct-
coefficients. The right image of Figure 8 shows, that
the inverse discrete cosine transform with 12 coeffi-
cients yields a reasonable reconstruction of the origi-
nal curve. We derived the line profiles from the point
signature approach presented in the following section.
3.4 Extraction of Point Signatures
Similar to line profiles, point signatures are paths on a
surface (Chua and Jarvis, 1997). Instead of connect-
ing two landmark points the curve runs radial around
a distinctive point p
0
of a 3D point cloud. As can be
seen in Figure 9, in our approach the point p
0
is lo-
cated on the tip of the nose. In order to obtain the
point signature, a sphere is centered into the point p
0
of the 3D point cloud. The intersection of the sphere
with the facial points forms a curve Q in the three-
dimensional space (left image of Figure 10). The
depth information of these intersection points, com-
bined with the value of the sphere radius, contains
characteristic and unique information about the depth
value distribution in the surrounding area of the point
p
0
. However, taking the absolute depth values of this
intersection points is not reasonable (as already dis-
cussed for the line profiles in section 3.3) because they
are not independent with respect to translation and ro-
tation of the head. As a result, we create a reference
curve Q
0
that can be employed to calculate relative
depth information. To obtain this curve, we fit a plane
P through the set of intersection points. The plane
is determined with regression analysis by a singular
value decomposition that gives the surface normal of
the plane. The plane is now shifted along its normal
vector into the point p
0
. This results in a new plane
called P
0
(right image of Figure 10). In the next step
the curve Q is projected onto P
0
building a new curve
Q
0
. Now the curve Q
0
is sampled around the approxi-
mated surface normal at p
0
with a rotation angle of 15
degrees. For each sampled point in Q
0
the distance to
its corresponding point in Q is collected. The starting
position for the distance sampling needs to be equal
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
560

between the different images to obtain curves that are
comparable. Therefore, we define a starting position,
which is determined by a reference point p
re f
. The
reference point is located on the chin as marked in
Figure 9. The sphere radius length has to be deter-
mined such that the arising path does not protrude be-
yond the surface of the face and no background points
are sampled. The length of the radius is computed
from the eye distance d
eye
, multiplied by a factor f .
The eye distance is estimated from the distance be-
tween the mean positions of each eye. Mean posi-
tions are obtained by the landmark positions of each
eye (Figure 9). We use the following values for the
empirically determined factor f to extract five differ-
ent point signatures: 0.4, 0.5, 0.7, 0.8 and 1.0.
Sampling of the radial curve with a fixed interval
of 15 degrees generates 24 values per point signature.
The more point signatures are extracted, the more pre-
cisely the surface of the face can be described. How-
ever, a high amount of point signatures leads to a
high-dimensional feature space. We reduce the di-
mension of the feature vector by applying discrete co-
sine transform on each point signature as shown in
section 3.3. Again the first twelve coefficients are re-
tained.
Figure 10: Left image: Intersection curve Q of the sphere
with the 3D point cloud. Right image: The planes P (red)
and P
0
(magenta). The projected curve Q
0
is marked on P
0
.
3.5 Automation of the Feature
Extraction Process
The features presented above have in common that
certain facial areas need to be determined for extrac-
tion. These can be landmark positions or regions de-
rived from these landmark positions. Manual determi-
nation of the landmarks and regions is not feasible in a
real-world application. Thus, they have to be detected
automatically, which may lead to less accuracte local-
izations. We use two different approaches to test the
robustness of the presented features with respect to
these deviations. The first approach is the application
of Active Appearance Models (AAMs) for landmark
detection. The second approach is a threshold-based
localization of the nose tip position using curvature
analysis.
AAMs are mainly applied in the field of fa-
cial expression recognition on 2D gray-value im-
ages (Cootes et al., 2001). On the basis of several
training images a combined mean texture and shape
model is derived. The fitting of this mean model to
a new and unknown face is improved by determina-
tion of a coarse initialization position. We use the
Viola and Jones face detector to find an initial lo-
calization (Viola and Jones, 2004). In the next step
the AAM adapts itself to the new face by minimiz-
ing the error between the model intensities and the
image intensities. The parameters that describe the
fitted model are usually subjected to classification of
facial expressions. In constrast to this, the AAM can
be used for the mere detection of landmarks without
further consideration of the model parameters (Haase
and Denzler, 2011). In this paper we focus on the
application of AAMs for landmark detection. The
AAM is fitted on the 2D intensity images and we need
to transform these landmark positions to positions in
depth images. Therefore intrinsic and extrinsic cam-
era parameters were determined by camera calibra-
tion (Hartley and Zisserman, 2000). They can be
employed to align the 2.5D images with their corre-
sponding intensity images. As a result, correspond-
ing points have the same position in the images of
both channels and the labeled landmark positions can
be accordingly transferred. Additionally, these cam-
era parameters can be used to transform the points of
the 2.5D image to a discrete 3D point cloud (Hartley
and Zisserman, 2000).
Landmark detection by AAMs is complemented
by the detection of the nose tip using curvature anal-
ysis. Again, a coarse initalization is necessary to con-
strain the search space, e.g., by the Viola and Jones
face detector. Mean and Gaussian curvature is calcu-
lated for each 3D point that belongs to the delimited
search space. The largest region that fullfills certain
thresholds for both curvature measures is defined as
the nose region. Inside the nose region we search for
the point that has the lowest distance to the camera.
We evaluated this approach on 1485 images and 13
persons by comparing the manually labeled nose tip
to the nose tip detected by curvature analysis. For
94% of the images the distance in x-and y-direction
is smaller than 0.95cm. The nose tip detection algo-
rithm works, even if the head is slightly rotated. An
example can be seen in Figure 11. However large
rotations should be avoided in the whole application
scenario because therapeutic exercises can not be rec-
ognized and evaluated correctly if important regions
of the face are occluded.
AutomatedClassificationofTherapeuticFaceExercisesusingtheKinect
561

Figure 11: Left: Gray-value image. Center: Depth image
with nose tip position marked. Nose tip position was deter-
mined by curvature analysis. Right: Regions that fulfill the
necessary thresholds for Gaussian and mean curvature. The
largest region belongs to the region of the nose.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In the first section of the experimental part, we focus
on the dataset and the exercises that are used for our
experiments. The evaluation of the features discrimi-
native power with respect to the classification of ther-
apeutic exercises is presented in section 4.2. Results
from experiments that test the robustness of the fea-
tures related to variations of region borders are given
in the last section.
4.1 Exercises and Dataset
In cooperation with speech therapists, we selected a
set of nine therapeutic face exercises by certain crite-
rions. The exercises should train the lips, the cheeks
and the tongue and should be beneficial for various
types of facial muscle dysfunctions, e.g. paresis of
muscles or muscle imbalance. Furthermore, the se-
lected exercises should be easy to practice and should
build a set of sub-exercises that can be combined to
more complex dynamic exercise units, e.g. by alter-
nating between them. The exercises have to be per-
formed in an exaggerated manner, to enable a max-
imum training effect, and have to be retained for
around two or three seconds. The speed of the per-
formance is not important. Although some of these
are vocal exercises, it is not necessary to vocalize a
continuous sound while performing the shape. Im-
ages that visualize the exercise conduction are shown
in Figure 12.
Due to the lack of a public database that shows
the performance of therapeutic exercises, we recorded
a dataset, which contains eleven persons, who con-
duct the nine exercises. For each exercise, there are
around seven images, showing different states of ex-
ercise conduction. This amounts to a total size of 696
images in the dataset. Some parts of the scene that
is captured by the Kinect may be shadowed, if they
are seen by the depth camera but are not illuminated
by the infrared projector. This leads to invalid values
in the 2.5D image (Khoshelham, 2011). These values
Figure 12: Exercises that have been selected in cooperation
with speech therapists (from left to right and top to bottom):
pursed lips, taut lips, A-shape, I-shape, cheek poking (right/
left side), cheeks puffed (both/ right/ left side(s)). For better
visualization colour images are shown. Features, as previ-
ously mentioned, are extracted from depth images and point
clouds. For visualization of the nine exercises the shown
images were shot with a commercially obtainable camera
with higher resolution than the Kinect and are not part of
the dataset.
Figure 13: The 58 manually labeled landmark positions.
were removed by replacing them with the mean depth
values of adjacent valid neighbour pixels. For every
depth image, there exists a corresponding colour im-
age that has been recorded with maximum time differ-
ence of 16 milliseconds. The colour images have been
labeled manually with 58 landmark points that were
used for the training of the AAM (Figure 13) or for
the feature extraction from depth data. The transfer-
ability of landmark positions between the 2.5D image
and the colour image was further explained in sec-
tion 3.5.
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
562

4.2 Evaluation of the Discriminative
Power
The following section gives an overview of the clas-
sification results. Since we want to evaluate the ba-
sic suitability of the selected features for the task of
classifying therapeutic exercises, we extract the fea-
tures from regions obtained from manually labeled
landmarks, thus excluding other influences like devi-
ating region borders. We evaluate each feature group
individually and in combination. Training and clas-
sification is performed by applying Support Vector
Machines (SVMs) of the LIBSVM package (Chang
and Lin, 2011). We tested linear SVM and a Ra-
dial Basis Function kernel. Optimal values for the
penalty parameter C and the kernel parameter γ were
obtained by a grid search on the training set (Hsu
et al., 2009). To avoid overfitting to the training set,
we employed a 5-fold cross-validation during param-
eter optimization. In combination with the amount of
data (696 images, 232 feature dimensions), the lin-
ear SVM leads to the best results because it avoids
overfitting. The dataset was split up into training and
test set using the leave-one-out cross-validation. Ad-
ditionally, all images of the person present in the test
image are excluded from the training set. This ap-
proach is consistent with the mentioned application
scenario in which the images of the test person will
not be part of the training data. We obtained an av-
erage recognition accuracy over the nine classes of
82.4%. The use of linear discriminant analysis (LDA)
prior to the linear SVM classification improves the re-
sults to 91.2% average recognition accuracy. LDA is
a linear transformation of the feature space that max-
imizes the between-class separability and minimizes
the within-class variablity (Webb et al., 2011). As a
result of LDA the number of feature dimensions is re-
duced from 232 to 8. Detailed results that show the
classification accuracy for each of the nine classes are
given in Table 2.
4.3 Evaluation of Feature Extraction
from Automatically Determined
Regions
As mentioned before, in a real-world scenario regions
and landmark points for feature extraction have to
be detected automatically. Therefore, in this section
we evaluate the robustness of our features with re-
spect to varying region borders and landmark posi-
tions. Figure 14 shows the results for the three fea-
ture types for manually and automatically detected
landmarks. Automated detection was done by the
fitting of AAMs. Compared to the point signatures
and line profiles, curvature analysis is weaker with
respect to the discrimination of the nine therapeutic
exercises. However, it achieves better results for au-
tomatically detected landmarks. The deviations of the
landmarks that were determined by AAM-fitting are,
compared to the manually labeled landmarks: in x-
direction −1.88 pixels (mean value) with a standard
deviation of 4.7 and in y-direction at an average of
6.0 pixels with a standard deviation of 15.94. Consid-
ering the distances of our persons to the camera six
pixel correspond to about 0.95 centimetres. As shown
in section 3.4, the point signature needs exactly two
landmarks: the nose tip and a reference point. For
further examination of the point signatures, indepen-
dent from the AAM fitting, we detect the nose tip by
curvature analysis. The reference point is determined
under the assumption that only very small in-plane ro-
tations of the face occur in our dataset. Therefore,
we estimate the reference direction by a vector par-
allel to the y-axis of the image in positive direction
(with the origin of the coordinate system in the upper
left corner of the image). Compared to the average
recognition rate that was obtain for the point signa-
tures using AAMs for landmark detection (44.5%) we
gain a significant improvement to 72.6%. Combining
these features with the curvatures and the line pro-
files that were extracted based on the AAM an over-
all average recognition rate of 75.1% is obtained. By
only combining curvature analysis and point signa-
tures a rate of 75.6% is obtained. This shows that
the line profiles - in conjunction with the current au-
tomated landmark estimation method - do not con-
tribute to the classification success. However, the re-
sults of line profiles using manual landmarks suggest
that further effort for more precise landmark localiza-
tions may be beneficial. A certain robustness of the
line profiles can be assumed because even the manu-
ally labeled landmarks may be subject to deviations.
In colour images (in which the landmarks were la-
beled), especially on the chin silhouette distinctive
points are missing. Therefore, variations in position
and landmark-to-landmark distance occur on the chin
positions more likely than in the corners of the eyes
or the mouth. Figure 15 presents the comparison of
the results for the manual approach and the two auto-
mated localization methods.
5 DISCUSSION
In this paper we have discussed several aspects that
are necessary for the conception and implementation
of an automated training platform for persons with fa-
AutomatedClassificationofTherapeuticFaceExercisesusingtheKinect
563

Table 2: Confusion matrix of the classification results (in %). Features were extracted from regions and points that have been
determined on the basis of manually labeled landmarks. The rows contain the ground truth, columns the assignments resulting
from classification. The average recognition rate is 91.2%. LDA was applied to transform the feature space and to reduce
the feature space dimensionality. The term tongue refers to the exercise cheek boxing and cheek to cheek puffed. L and R are
abbreviations for left and right.
Pursed Taut A-Shape I-Shape Tongue L Tongue R Cheek Cheek L Cheek R
Pursed 83.75 0 1.25 0 2.5 12.5 0 0 0
Taut 2.53 81.01 0 16.46 0 0 0 0 0
A-Shape 0 0 96.43 0 0 3.57 0 0
I-Shape 0 8.33 0 91.67 0 0 0 0 0
Tongue L 0 0 0 0 100 0 0 0 0
Tongue R 4.11 0 4.11 0 0 90.41 0 0 1.37
Cheek 0 1.2 0 0 0 1.2 93.98 1.2 2.41
Cheek L 2.82 0 0 0 1.41 0 1.41 94.36 0
Cheek R 0 0 0 1.37 0 2.74 6.85 0 89.04
Table 3: Confusion matrix of the classification results (in %). Features were extracted from regions and points that have been
determined on the basis of automatically located landmarks. The average recognition rate is 75.1%.
Pursed Taut A-Shape I-Shape Tongue L Tongue R Cheek Cheek L Cheek R
Pursed 61.25 8.75 15.00 1.25 5.00 1.25 6.25 1.25 0
Taut 1.27 70.89 2.53 21.52 1.27 0 0 0 1.27
A-Shape 5.95 2.38 82.14 7.14 1.19 0 0 1.19
I-Shape 1.39 22.22 1.39 73.61 1.39 0 0 0 0
Tongue L 8.64 2.47 1.23 1.23 81.48 4.94 0 0 0
Tongue R 1.37 5.48 4.11 5.48 0 79.45 0 0 4.11
Cheek 1.20 3.61 0 0 1.2 1.2 74.70 9.64 8.43
Cheek L 5.63 7.04 1.41 1.41 0 0 8.45 74.65 1.41
Cheek R 0 1.37 0 1.37 0 12.33 6.85 0 78.08
curvature analysis point signature line profiles
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
average recognition rate
manually
manually+LDA
AAM
AAM+LDA
Figure 14: The bar plot shows the average recognition rates
(in %) for each of the three feature groups. As expected
feature extraction from manually determined regions and
landmarks leads to better results than the extraction from
automatically determined areas. The local features point
signatures and line profiles (with LDA) lead to better re-
sults than the curvature analysis. However, they are more
prone to landmark position deviations.
cial muscle dysfuctions. We presented nine therapeu-
tic exercises, which - in cooperation with speech lan-
guage therapists - were determined as beneficial for
the planned application scenario. Additionally, the
automated classification of these exercises was eval-
uated. The presented approach employs 2.5D depth
manually AAM AAM + nose tip localization
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
average recognition rate
no LDA
LDA
Figure 15: Comparison of the average recognition rates (%)
for the nine exercises and all features. Again, rates strongly
depend on the landmark localization method. With manu-
ally labeled landmarks a rate of 91.2% is obtained. A com-
bination of the AAMs with the nose tip detection gives the
best results for the automated approaches (75.1%). In con-
trast to this, the sole use of the AAMs results in 62.9% av-
erage recognition rate.
images and 3D point clouds and is based on three dif-
ferent feature types: curvature analysis, point signa-
tures and line profiles. The features were evaluated
with respect to their discriminative power for exer-
cise classification. Additionally, we examined their
robustness regarding varying locations of feature ex-
traction. This is relevant for all applications, planned
for practical use, were a manual detection of land-
marks is not feasible.
Curvature analysis, in the form we have imple-
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
564

mented it, is rather global compared to point signa-
tures and line profiles and showed a relatively robust
performance. However, with suitable landmark local-
izations point signatures and line profiles outperform
curvature analyis. We used two approaches for auto-
mated landmark detection: Active Appearance Mod-
els and nose tip estimation by curvatures. The com-
bination of both lead to the best results. Line pro-
files showed weak contribution to the classification
process, if landmark positions are detected automat-
ically. Nevertheless, the results based on manually
defined regions are promising. Besides considera-
tions of making the line profiles more robust, a more
sophisticated approach for automated landmark de-
tection might be the most beneficial solution. Con-
strained AAMs (Cootes and Taylor, 2001) including
prior estimates of some shape point positions will
be investigated in order to improve the fitting of the
AAM. Curvature analysis and a-priori knowledge re-
lated to the anatomy of the face may be valuable for
the estimation of these prior positions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the m&i Fachklinik Bad
Liebenstein (in particular Prof. Dr. med. Gustav
Pfeiffer, Eva Schillikowski) and Logop
¨
adische Praxis
Irina Stangenberger, who supported our work by giv-
ing valuable insights into rehabilitation and speech-
language therapy requirements and praxis. This work
is partially funded by the TMBWK ProExzellenz ini-
tiative, Graduate School on Image Processing and Im-
age Interpretation.
REFERENCES
Besl, P. and Jain, R. (1986). Invariant surface characteristics
for 3d object recognition in range images. Computer
Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 33(1):33–
80.
Chang, C.-C. and Lin, C.-J. (2011). LIBSVM:
A library for support vector machines. ACM
Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technol-
ogy, 2:27:1–27:27. Software available at url-
http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/ cjlin/libsvm.
Chua, C.-S., Han, F., and Ho, Y.-K. (2000). 3d human face
recognition using point signature. In Proceedings of
the 4th Int. Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition
Conf., pages 233–238.
Chua, C. S. and Jarvis, R. (1997). Point signature: a new
representation for 3d object recognition. In Int. Jour-
nal of Computer Vision, volume 25, pages 63–85.
Colombo, A., Cusano, C., and Schettini, R. (2006). 3d face
detection using curvature analysis. Pattern Recogni-
tion, 39(3):444–455.
Cootes, T., Edwards, G., and Taylor, C. (2001). Active ap-
pearance models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Anal-
ysis and Machine Intelligence, 23(6):681–685.
Cootes, T. and Taylor, C. (2001). Constrained active ap-
pearance models. In Proceedings of the 8th Int. Conf.
on Computer Vision, volume 1, pages 748–754.
Gebhard, A., Paulus, D., Suchy, B., and Wolf, S. (2000). A
system for diagnosis support of patients with facialis
paresis. Kl, 3/2000:40–42.
Grosse, M., Schaffer, M., Harendt, B., and Kowarschik, R.
(2011). Fast data acquisition for three-dimensional
shape measurement using fixed-pattern projection and
temporal coding. Optical Engineering, 50:100503.
Haase, D. and Denzler, J. (2011). Anatomical landmark
tracking for the analysis of animal locomotion in x-
ray videos using active appearance models. In Image
Analysis, volume 6688 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 604–615.
Hartley, R. and Zisserman, A. (2000). Multiple view geom-
etry in computer vision. Cambridge University Press.
Hsu, C., Chang, C., and Lin, C. (2009). A prac-
tical guide to support vector classification.
TR available at http://www. csie. ntu. edu.
tw/ cjlin/papers/guide/guide. pdf.
Khoshelham, K. (2011). Accuracy analysis of kinect depth
data. In ISPRS Workshop Laser Scanning, volume 38.
Nakamura, K., Toda, N., Sakamaki, K., Kashima,
K., and Takeda, N. (2003). Biofeedback reha-
bilitation for prevention of synkinesis after facial
palsy. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery,
128(4):539–543.
Salomon, D. (2004). Data compression: the complete ref-
erence. Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
Viola, P. and Jones, M. (2004). Robust real-time face detec-
tion. Int. Journal of Computer Vision, 57(2):137–154.
Wang, J., Yin, L., Wei, X., and Sun, Y. (2006). 3d facial
expression recognition based on primitive surface fea-
ture distribution. Int. Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, 2:1399–1406.
Wang, Y., Chua, C.-S., and Ho, Y.-K. (2002). Facial fea-
ture detection and face recognition from 2d and 3d
images. In Pattern Recognition Letters, volume 23,
pages 1191–1202.
Webb, A., Copsey, K., and Cawley, G. (2011). Statistical
pattern recognition. Wiley.
AutomatedClassificationofTherapeuticFaceExercisesusingtheKinect
565
