
The Perceptive Puppet
Seamless Embodiment Exchange between Real and Virtual Humans
in Virtual Environments for Training
Andr
´
es Saraos Luna, Val
´
erie Gouranton, Thomas Lopez and Bruno Arnaldi
INSA de Rennes, Rennes, France
IRISA / INRIA, Rennes, France
Keywords:
Teamwork, Virtual Environment, Embodiment, Training.
Abstract:
We present a novel mechanism that allows real and virtual humans to dynamically exchange the control of
their embodiment in virtual environments. Such a mechanism raises two important issues: the possibility of
dynamic embodiment exchanges between real humans and virtual humans and the continuity of actions of the
team members after an exchange. To address these issues we introduce a new entity, the Perceptive Puppet
that abstracts real and virtual humans into one common entity containing its own knowledge.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Collaborative Virtual Environments for Training
(CVET), a group can learn and practice the comple-
tion of a task as a team using all the assets provided
by Virtual Reality: low cost and risk-free for the
trainees, no need for costly physical equipment, the
possibility to repeat the task as many times as neces-
sary and the trainees’ progress can be saved and used
later on for further analysis (Boulanger et al., 2006).
Another main asset is the introduction of virtual hu-
mans in the team training, as replacements for missing
team members and as collaborators working with the
trainees. They can act as collaborators that contribute
to the completion of the task, teachers that guide and
provide contextual help whenever they are needed or
even troublemakers that challenge the trainees. All
these different roles are classified in two main groups
(Sycara and Sukthankar, 2006): an equal team mem-
ber or an assistant to either the team as a whole or just
one particular individual.
In this paper we provide a mechanism that al-
lows real and virtual humans to exchange their em-
bodiments during the simulation. Such a mechanism
offers new usages for both designers and users of
CVETs. Industrial applications of VR training go
from maintenance procedure (Gerbaud et al., 2008)
to military applications (Fonseca et al., 2011). To
further illustrate this claim let us use an illustrative
scenario in industrial training. We consider various
groups of two workers trainees that are learning how
to operate a machine. In each group, one of the team
members is a real human, the other one is a virtual
one. The actions of all groups are being monitored
by an expert trainer who is not embodied in the vir-
tual world. The trainer can take over the control of
the virtual coworker’s embodiment and monitor the
on-going work directly in the field. From there, the
trainer has various options:
• if the trainee cannot operate correctly, the trainer
can take over the control of the trainee’s embodi-
ment in order to move forward with the procedure
before letting the trainee continues, now back on
his tracks.
• if the trainee has trouble achieving his tasks, the
trainer can help him by directly collaborating with
him in the virtual world as his coworker.
• if the trainee is doing well, perturbations can be
added to test his adaptive capabilities.
The trainee does not need to know that the control
of his coworker is being swapped, the whole process
is transparent for the trainee. This allows the trainer
to play a more active role in its teaching, while giv-
ing him more flexibility to test the trainees capacities.
Furthermore, the trainer can adapt its implication de-
pending on the level of each trainee. Similar scenarios
can be described for Medical Training (Gallagher and
Cates, 2004; Kunkler, 2006) and Emergency Training
(Dugdale et al., 2004) applications.
Our contribution proposes an exchange mecha-
nism by addressing: (1) an abstract representation of
373
Saraos Luna A., Gouranton V., Lopez T. and Arnaldi B..
The Perceptive Puppet - Seamless Embodiment Exchange between Real and Virtual Humans in Virtual Environments for Training.
DOI: 10.5220/0004300103730378
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications and International Conference on Information
Visualization Theory and Applications (GRAPP-2013), pages 373-378
ISBN: 978-989-8565-46-4
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

real and virtual humans, (2) knowledge management.
In section 2 we investigate previous work. In sections
3 and 4 we present our exchange mechanism along
with our current implementation before concluding in
section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
Our review of related work focuses on how the users
and their virtual teammates are modeled, and how the
knowledge is handled in existing work (CVET).
2.1 Users in CVETs
In the COVET (Oliveira et al., 2000) application and
in most medical collaborative training applications,
only one person can interact. Others are spectators
and learn the procedure. Each one is confined in its
initial role during the simulation.
The GVT
1
(Gerbaud et al., 2008) platform al-
lows collaborative training between real and virtual
humans. The trainees do not have direct control of
their embodiments. This system could allow the users
to pass on their commands to a different embodiment
during the simulation and thus perform an effective
exchange. However, it does not allow users to inter-
act directly with their environment thus simplifying
the process.
For the MASCARET (Buche et al., 2003) model,
implemented in the SecureVI application, the user
collaborates with virtual humans by collecting their
knowledge and giving them orders. A trainer over-
sees the training without being incarnated in the vir-
tual world. He has the possibility to play the role
of a working virtual human and act in its place. Al-
though this represents a first step to a full-fledged ex-
change mechanism, only the trainer has this ability,
virtual humans cannot initiate an exchange nor can
the trainee.
Our analysis shows that the possibility of an ex-
change between users has not been addressed thor-
oughly. Also we did not find an existing model that
gives both real humans and virtual humans a common
point of entry to the virtual environment that could be
exchanged at will.
2.2 Knowledge Base
Sycara et al. (Sycara and Sukthankar, 2006) describe
various theories that aim to depict team knowledge in
1
Generic Virtual Training - http://www.gvt-nexter.fr/
teams, mixed with real and virtual humans. This has
been the subject of relatively few research.
Among them, an interesting approach is the
shared mental model theory. According to the psy-
chology and cognitive science literature (Klimoski
and Mohammed, 1994), people use internal represen-
tations of the world to understand and act upon it.
They serve as reasoning mechanism that exists in a
person’s mind and allows to predict, reason and form
explanations of his surrounding environment.
One popular trend in teamwork related work is
the notion of a shared mental model used to improve
team performance (Jonker et al., 2010; Mathieu et al.,
2000). This theory is notably used in multi-agents
context (Yen et al., 2006).
None of the existing CVET has an implementa-
tion of team knowledge with mixed teams. The way
knowledge is handled is central to allow continuous
actions after an exchange is performed. One conve-
nient and often used way to include the knowledge
is to grant virtual humans with omniscience over the
whole environment, and assume the real users know
the procedure beforehand. This is how most CVETs,
including Dugdale’s fire simulation training (Dugdale
et al., 2004) and GVT (Gerbaud et al., 2008) handle
the knowledge of their virtual humans. Omniscience,
for real or virtual humans, is a very strong and not
realistic assumption because they are not supposed to
have the same access to a full knowledge base.
2.3 Synthesis
We review the key points of our analysis of existing
work. None of them successfully implements an ex-
change mechanism that would allow the scenarios de-
scribed in our introduction to be used. Real humans
and virtual humans are always considered as separate
entities and therefore interact with the virtual world
through different channels, making a generic control
exchange mechanism difficult. The continuity of ac-
tions may be achieved through omniscient agents al-
though the mechanism has not been tackled on di-
rectly. However there is a lack of a distributed ap-
proach that does not assume that the real humans also
have the privilege of omniscience.
3 THE PERCEPTIVE PUPPET
The objectives of our contributions are: (1) the defi-
nition of an abstraction of the team members encom-
passing both real and virtual humans, (2) the construc-
tion of a model, independent from the nature of the
GRAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerGraphicsTheoryandApplications
374

team member, that allows the continuity of actions af-
ter an exchange is performed, (3) the formalization of
the exchange process.
For this purpose we introduce the Perceptive Pup-
pet, an abstraction (section 3.1) encompassing both
real and virtual humans that combines an interaction
model (section 3.2) and a knowledge base (section
3.3) to address the issues an exchange mechanism
rises (section 3.4).
3.1 Concept
We introduce a specific element, the Perceptive Pup-
pet (Fig. 1). It serves as a mediator that connects
together the real or virtual humans and the virtual
world. The Perceptive Puppet serves as a gateway
unifying the actions sent by the team members and
relaying the knowledge acquired from within the vir-
tual world. However, it is deprived of any kind of de-
cision process and cannot interact in the virtual world
without some puppeteer pulling the strings. The team
members thus act as puppeteers taking control of their
respective Perceptive Puppets to act upon the virtual
world. As the acquired knowledge is independent
from the controlling team member, they benefit from
the perceptive capabilities, the knowledge base and
the interactive abilities of the Perceptive Puppet they
are controlling as a base to their decision process.
Figure 1: The relation between the team members, the Per-
ceptive Puppet and the Virtual World.
A Perceptive Puppet is composed of two main
parts: (1) an Interaction model that describes how the
Perceptive Puppet interacts with the virtual world and
how it can be controlled by a real or virtual human,
(2) a Knowledge base fueled by the perceptive capa-
bilities of the Perceptive Puppet. The knowledge is
independent of the real or virtual human that controls
it.
With the Perceptive Puppet, an exchange of em-
bodiment between real and virtual humans is defined
as an exchange of control over the real and virtual hu-
mans’ respective Perceptive Puppets. As the Percep-
tive Puppet contains its own knowledge base at the
real and virtual humans’ disposal, the controlling real
or virtual human can gather data about the actions
previously undertaken by the Perceptive Puppet and
carry them on.
3.2 Interaction Model
Our goal with the exchange mechanism is to allow
any team member to exchange their Perceptive Puppet
with another one. The interaction model has to take
into account that: (1) each team member takes control
of a Perceptive Puppet, (2) the Perceptive Puppet in-
teracts with other objects, (3) objects can interact with
each other.
We defined an interaction model, called
Collaborative-STORM (Saraos Luna et al., 2012) that
is an extension of the STORM model (Mollet et al.,
2007) and therefore shares the same core mechan-
ics. The STORM model links together behavioral
objects, composed of internal behaviors and a set of
communicating interfaces, that are interacting with
each other. The combination of an internal behavior
and a communication channel is called a capacity.
A relation is defined as a link between objects that
are in interaction through matching capacities. The
models are a complete solution to design complex
behavioral objects and complex interactions between
such objects in virtual environments.
Figure 2: Collaborative-STORM Example: a team member,
either real or virtual, is controlling a Perceptive Puppet in
the virtual world. Through the Perceptive Puppet, it controls
a screwdriver and a screw. He then can trigger the screwing
relation by using these objects with a female plug.
The Collaborative-STORM model introduces a
new relation, the Control Relation that allows one ob-
ject to take control of a set of parameters of another
ThePerceptivePuppet-SeamlessEmbodimentExchangebetweenRealandVirtualHumansinVirtualEnvironmentsfor
Training
375

object. In this way, one object could take control of
one or several properties of another object. Our ad-
dition to this model is the definition of the Perceptive
Puppet as an object controllable through the Control
Relation. This mechanism allows the team members,
modeled as a Collaborative-STORM object, to take
control of a Perceptive Puppet. The Perceptive Pup-
pet can in turn interact with other objects of the envi-
ronment (Fig. 2).
3.3 Knowledge Base
After an exchange, any team member, real or virtual,
need to be able to pursue the actions of the previ-
ous owner of the Perceptive Puppet he now controls.
It needs to have an understanding of what was the
previous team member’s actions and goals using the
Perceptive Puppet knowledge, self-contained and in-
dependent of its controlling entity. The knowledge
base of the Perceptive Puppet needs to be compati-
ble and usable by all team members, particularly the
real humans. This knowledge needs to be accessible
so that all team members, especially real humans, can
find relevant information in the Perceptive Puppet’s
knowledge base.
The perceptive abilities of a Perceptive Puppet are
its main source of information. It is composed of two
parts: the Sensory Channels and the Filter Pipeline.
The Sensory Channels acquire data from the virtual
environment through perceptive abilities such as vi-
sion or sound. The Filter Pipeline then filters the data
according to various criteria such as relevance, spatial
proximity or usefulness in the current task.
By giving the Perceptive Puppet its own knowl-
edge and perceptive abilities, we assure that the data
gathered is independent of the controlling team mem-
ber. This assures us that when an exchange is per-
formed, the knowledge of the Perceptive Puppet re-
mains consistent.
3.4 The Exchange Protocol
We formalize the usage of an exchange of embodi-
ments in a dedicated protocol that handles how the ex-
changes of Perceptive Puppets are performed. When
a team member wants to take control of another Per-
ceptive Puppet, the protocol ensures the transaction
can be done before performing the exchange.
The acceptance conditions are fully customizable
as they are platform and application dependent. The
protocol specifies who can initiate an exchange and if
virtual humans are allowed to be the instigators of an
exchange or not. From another point of view, a trainer
should always be able to initiate an exchange with a
trainee, even without warning him. It is the trainer’s
decision whether an exchange can benefit the trainee’s
training.
The protocol also specifies the situations in which
an exchange is acceptable. Indeed, team members
may not be authorized to engage in an exchange while
they are performing an action.
4 IMPLEMENTATION
In this section we provide an implementation of the
embodiment exchange in an existing CVET, the GVT
platform. We chose the GVT platform because its
latest version allows collaborative teamwork between
real humans and virtual humans. The GVT architec-
ture mainly contains three engines: (1) the Scenario
engine that describes the step by step procedure the
team has to realize, (2) the Interaction engine that
contains the environment composed of various be-
havioral objects, it follows the Collaborative-STORM
model and (3) the Humanoid engine that handles the
humanoid representation of the participants.
The Perceptive Puppet is added to the GVT plat-
form as an object of the environment. It is im-
plemented between the team members and their hu-
manoid representation. Each team member will con-
trol a Perceptive Puppet that will in turn control an hu-
manoid representation in the virtual environment. We
describe the implementation of the Perceptive Puppet
in section 4.1, the exchange protocol in section 4.2
and our test scenario used to validate our concept in
section 4.3.
4.1 Perceptive Puppets
The architecture proposed to implement the Percep-
tive Puppet (Fig. 3) is composed of three main parts:
• Each team member, virtual and real, is linked to
the Perceptive Puppets he controls.
• The Environment Interface (perception and inter-
action) is the link between the virtual environment
and the Perceptive Puppet.
• The Knowledge Base encompasses all the knowl-
edge base of the Perceptive Puppet.
We break down into three components: a per-
ceptive model, a knowledge base and an interaction
model. The first two ensure the continuity of actions
after an exchange is performed, the last one gives
real and virtual humans the ability to perform an ex-
change.
Perception: the Perceptive Puppet perceives its en-
vironment through a number of sensory channels. In
GRAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerGraphicsTheoryandApplications
376

Figure 3: Architecture Implementation.
our implementation, only a basic line of sight through
ray tracing is implemented. The acquired knowledge
is filtered by a pipeline of filters in order to only retain
the information deemed important by the Perceptive
Puppet. The filtered knowledge is then dispatched to
the knowledge base.
Knowledge: part of the knowledge is task-specific,
such as the actions and tasks that are possible or re-
quired by the simulation. Others, like the position of
objects and teammates and the team members’ skills,
are more generic and can be reused in different sim-
ulations. In our implementation, we take advantage
of the GVT platform scenario engine to fuel the ac-
tion related knowledge base of the Perceptive Pup-
pets. The Perceptive Puppet stores knowledge about
entities that are perceived through their sensory chan-
nels, for example storing the name of the object and
the last time they have seen it. If an already known
object is sighted, the time stamp is updated.
Interaction: an interaction relation is implemented
as a GVT relation. The relation links Interactors (ob-
ject that can take control of other objects) and Interac-
tive Objects (objects that can be controlled by others).
Once the relation is established, it passes on the com-
mands and parameters from the Interactor to the Inter-
active Object. The Perceptive Puppet is implemented
as a GVT object with the Interactive Object capacity.
Real and virtual humans both control the Perceptive
Puppet through this channel.
4.2 Exchange Protocol
The exchange protocol is encapsulated inside a ded-
icated GVT relation. This relation links two GVT
objects disclosing the Exchange Capacity, and han-
dles the exchange of control. The Perceptive Pup-
pet is thus constructed as a GVT object containing
amongst other capacities the exchange capacity. The
current parameters are: virtual humans always agree
to an exchange, virtual humans cannot initiate an ex-
change, real humans are asked if they want to perform
an exchange and an exchange can be performed at any
time.
During the simulation, a real human triggers the
exchange relation by selecting another Perceptive
Puppet. If the selected Perceptive Puppet is controlled
by another virtual human, the exchange is performed
right away. If a real human is controlling it, a pop-up
window informs him of the exchange demand and he
has the choice to either validate or refuse the demand.
4.3 Test Scenario
Our test application consists of a team of five soldiers
having to perform a specific procedure to open fire
with their armored vehicle. They need to perform a
serie of coordinated actions on various parts of the
vehicle. Each soldier has a well-defined role that has
to be handled by a real or virtual human.
At launch, the trainee is prompted to select a role
to begin the scenario. He is then given control of the
corresponding Perceptive Puppet and can perform his
part of the procedure regardless of the nature of the
other team members. The other roles, and the asso-
ciated Perceptive Puppets, are controlled by virtual
humans or by other trainees. The trainee is notified
of any new knowledge the Perceptive Puppet gains
through its perceptive ability. The Perceptive Pup-
pets could see their environment and keep all the per-
ceived knowledge in their knowledge base. All the
objects contained in the knowledge of the team mem-
ber’s Perceptive Puppet are listed in a GUI window
and the trainee can select a specific object to obtain
detailed information about it such as the last time it
has been seen or its last known location (Fig. 4).
At any time during its work, any team member
can perform an exchange with another team member
by selecting its Perceptive Puppet in the application.
Once the exchange has been accepted, the Percep-
tive Puppet controls are exchanged between the two
team members. He can thus continue the process in a
brand new role by using the knowledge contained in
the Perceptive Puppet. This test scenario successfully
demonstrates the exchange mechanism at work.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We defined a new object, the Perceptive Puppet, that
provides new issues: (1) an abstraction encompassing
both real human and virtual human and (2) a set of
tools to ensure the continuity of actions once an ex-
change is performed. The Perceptive Puppet mainly
ThePerceptivePuppet-SeamlessEmbodimentExchangebetweenRealandVirtualHumansinVirtualEnvironmentsfor
Training
377
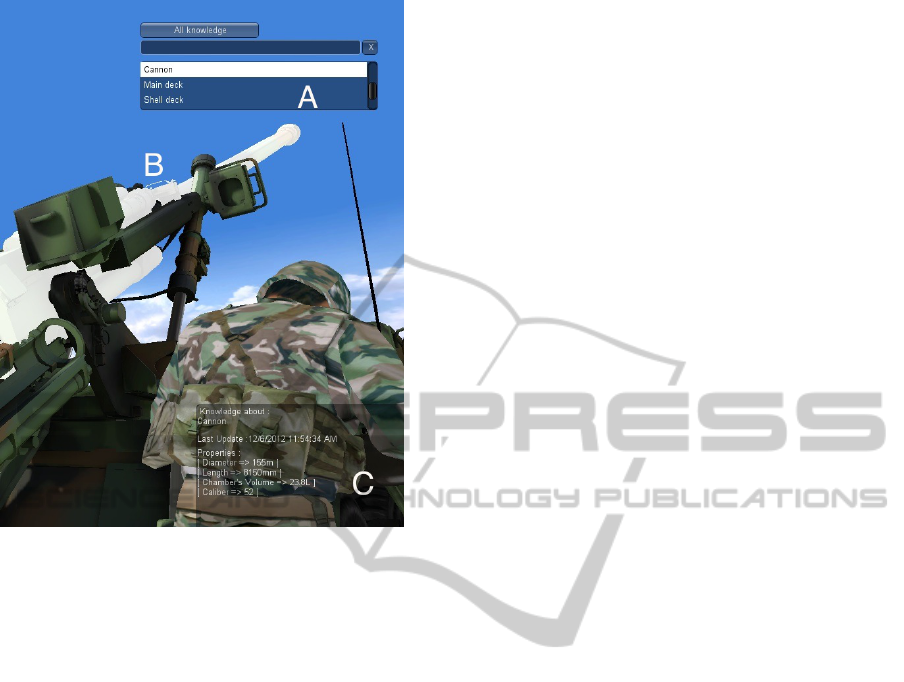
Figure 4: User interface allowing Real Humans to browse
the knowledge of the Perceptive Puppet it controls. The
knowledge about the cannon is selected (A). The cannon is
thus highlighted in the environment (B), and all the known
data about it is displayed (C).
achieves this by acting as a mediator between the team
members, real or virtual, and the virtual world. The
Perceptive Puppet and its controlling entity are con-
nected through an interaction link that works the same
way for real humans and virtual humans. Addition-
ally the Perceptive Puppet has its own knowledge and
perceptive channels, independently of any controlling
team member.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by the French Re-
search National Agency project named CORVETTE
(ANR-10-CONTINT-CORD-012) and by the OSEO
project named FUI11 SIFORAS.
REFERENCES
Boulanger, P., Wu, G., Bischof, W., and Yang, X.
(2006). Hapto-audio-visual environments for collabo-
rative training of ophthalmic surgery over optical net-
work. In Haptic Audio Visual Environments and their
Applications, 2006. HAVE 2006. IEEE International
Workshop on, pages 21–26. IEEE.
Buche, C., Querrec, R., Loor, P. D., and Chevaillier, P.
(2003). MASCARET: pedagogical Multi-Agents sys-
tem for virtual environment for training. Cyberworlds,
International Conference on, page 423.
Dugdale, J., Pavard, B., Pallamin, N., el Jed, M., and Mau-
gan, C. L. (2004). Emergency fire incident training in
a virtual world. In Proceedings ISCRAM2004, volume
167.
Fonseca, B., Paredes, H., Rafael, L., Morgado, L., and Mar-
tins, P. (2011). A software architecture for collab-
orative training in virtual worlds: F-16 airplane en-
gine maintenance. In Vivacqua, A., Gutwin, C., and
Borges, M., editors, Collaboration and Technology,
volume 6969 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 102–109. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Gallagher, A. and Cates, C. (2004). Virtual reality train-
ing for the operating room and cardiac catheterisation
laboratory. The Lancet, 364(9444):1538–1540.
Gerbaud, S., Mollet, N., Ganier, F., Arnaldi, B., and Tis-
seau, J. (2008). GVT: a platform to create virtual en-
vironments for procedural training. In IEEE Virtual
Reality, pages 225–232, Reno Etats-Unis.
Jonker, C. M., van Riemsdijk, M. B., and Vermeulen, B.
(2010). Shared mental models: A conceptual analysis.
Coordination, Organization, Institutions and Norms
in Multi-Agent Systems@ AAMAS2010, page 41.
Klimoski, R. and Mohammed, S. (1994). Team mental
model: Construct or metaphor? Journal of manage-
ment, 20(2):403–437.
Kunkler, K. (2006). The role of medical simulation:
an overview. The International Journal of Medical
Robotics and Computer Assisted Surgery, 2(3):203–
210.
Mathieu, J., Heffner, T., Goodwin, G., Salas, E., and
Cannon-Bowers, J. (2000). The influence of shared
mental models on team process and performance.
Journal of Applied Psychology, 85(2):273.
Mollet, N., Gerbaud, S., and Arnaldi, B. (2007). STORM:
a generic interaction and behavioral model for 3D
objects and humanoids in a virtual environment. In
IPT-EGVE the 13th Eurographics Symposium on Vir-
tual Environments, volume Short Papers and Posters,
pages 95–100, Weimar Allemagne.
Oliveira, J., Hosseini, M., Shirmohammadi, S., Cordea, M.,
Petriu, E., Petriu, D., and Georganas, N. (2000). Vir-
tual theater for industrial training: A collaborative vir-
tual environment. Proc. 4th WORLD MULTICON-
FERENCE on Circuits, Systems, Communications &
Computers (CSCC 2000), Greece.
Saraos Luna, A., Gouranton, V., and Arnaldi, B. (2012).
Collaborative Virtual Environments For Training: A
Unified Interaction Model For Real Humans And Vir-
tual Humans. In International Conference on Serious
Games and Edutainment, pages 1–12, Germany.
Sycara, K. and Sukthankar, G. (2006). Literature review of
teamwork models. Technical Report CMU-RI-TR-06-
50, Robotics Institute, Pittsburgh, PA.
Yen, J., Fan, X., Sun, S., Hanratty, T., and Dumer, J.
(2006). Agents with shared mental models for en-
hancing team decision makings. Decision Support
Systems, 41(3):634–653.
GRAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerGraphicsTheoryandApplications
378
