
A Study of Decision-making Model Considering Priorities based on Two
Kinds of Evaluation
Decision Making Methodology Applying Risk Evaluation based on Prospect Theory
Rumiko Azuma
1
and Shinya Nozaki
2
1
Department of Social Informatics, Aoyama Gakuin University, Sagamihara, Kanagawa, Japan
2
Transdisciplinary Research Organization for Subtropics and Island Studies, University of the Ryukyus, Okinawa, Japan
Keywords:
Decision-making Model, Analytic Hierarchy Process, Risk Evaluation, Prospect Theory.
Abstract:
The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a multi-criteria decision-making approach aimed at reflecting a
human’s subjective judgment or vagueness. The conventional evaluation in AHP is considered to be a kind of
utility. However, there are some cases where the traditional utility theory cannot explain risk aversion. This
paper presents a new decision-making methodology for considering risk evaluation. We propose the hierarchy
model that contains return and risk categories, and an AHP method that applies prospect theory, which is
able to explain people’s decisions when they face situations involving risks. Therefore, by proposing an AHP
method that utilizes it, we enable the evaluation of alternatives under return and risk.
1 INTRODUCTION
In decision-making problems, it is necessary to si-
multaneously estimate benefits and risks. For ex-
ample, in assessing supply chains, when companies
find new suppliers for offshore sourcing decisions,
they consider positive criteria, which may include low
wages, lower-transportation costs, and higher reliabil-
ity. These elements are generally expressed with a
positive value as return. On the other hand, there are
various types of risk such as poor quality, logistical
failures, and natural disasters.
There are studies that solve the offshoring de-
cision problem. Schoenherr’s research (Schoenherr
et al., 2008) proposed a method using Saaty’s AHP
(Analytic Hierarchy Process) (Saaty, 1980) to assess
supply chain risks. The AHP is widely used for tack-
ling multi-attribute decision-making problems in real
situations. It uses a hierarchical model for the de-
cision problem and is based on the use of pairwise
comparisons, which lead to the elaboration of a ratio
scale. In AHP, the degree of risks is also determined
by a paired comparison. However, it is difficult to
evaluate risk using a humans subjective judgments.
In our previous study, we extended AHP method
for handling a satisfaction and a risk on the same
structure, and proposed a decision-making model
having pair criterion (Azuma and Miyagi, 2009). Be-
cause the conventional evaluation in AHP is consid-
ered to be a kind of utility, risk is represented by the
utility of the probability of damage in the model. Fur-
thermore, the expected utility is integrated, consider-
ing that satisfaction is a positive utility and damage
by risk is a negative utility. Then, we applied the ex-
pected utility theory to the model by defining satisfac-
tion as a positive utility and risk as a negative utility.
However, studies have shown that an actual behavior
of person is uncertain when choosing between risky
alternatives (Barberis et al., 2003). In this kind of sit-
uation, it is considered inappropriate to use the utility
theory for decision-making methods under risks.
In this study, we propose the introduction of the
prospect theory (Kahneman and Tversky, 1979) con-
cept to AHP for problem solving. The aim of our
study is to develop a method that evaluates alterna-
tives on the basis of return and risk standpoints.
2 PROSPECT THEORY
Prospect theory was developed as a psychologically
more accurate description of preferences compared
to expected utility theory. It is a theory of decision-
making under conditions of risk. The theory says that
555
Azuma R. and Nozaki S..
A Study of Decision-making Model Considering Priorities based on Two Kinds of Evaluation - Decision Making Methodology Applying Risk Evaluation
based on Prospect Theory.
DOI: 10.5220/0004326605550558
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2013), pages 555-558
ISBN: 978-989-8565-39-6
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

preferences between positive and negative prospects
are different.
The formula of prospect theory is given by
U =
n
∑
i=1
π(p
i
)v(x
i
), (1)
where U is the overall or expected utility of the
outcomes to the individual making the decision,
x
1
,x
2
,... are the potential outcomes and p
1
, p
2
,...
their respective probabilities. The function π is a
probability weighting. v is called value function that
is defined on deviations from s-shaped the reference
point. It expresses losses (= risk) have a significant
influence more than gains feel good. A value function
is displayed in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Example of a value function.
3 THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE
AHP MODEL BASED ON
PROSPECT THEORY
We propose a decision making model which evaluates
considering a satisfaction and a risk. The feature of
proposed model is that priorities of risk are evaluated
based on prospect theory. Generally, risk is defined
as the product of probability and resulting degree of
damage. On the other hand, some scholars redefined
the risk by using expected utility theory. We apply
prospect theory as a non-linear expected utility theory
for the evaluation of risks.
Specifically, flowchart of proposed method in Fig-
ure 2 is described as follows.
Step 1). Decision-maker is asked to extract the deci-
sion criteria and alternatives and to make up a hierar-
chy structure. This hierarchy model involves criteria
of both satisfactions and risks, the structure of which
can be seen in Figure 3.
Step 2). In this step, decision-maker makes up pair-
wise comparison matrices in criteria of satisfaction
Figure 2: Flowchart in the proposed method based on AHP
for risk.
Figure 3: The hierarchy model for satisfaction and risk.
and risk. This procedure is same as AHP which is rel-
ative measurement approach. To calculate its eigen-
vector determines the weight of criteria.
The pairwise comparison matrix S in criteria of
satisfaction is constructed:
S = [s
ii
′
], i,i
′
= 1,2,...,m, (2)
and (i,i
′
) is the number of criteria. The value of s
ii
′
is given by linguistic scale of decision-maker as in
Table 1. The scale is ratio-scale measure. In Table
1, the value is chosen under each criterion by an-
swering question such as : How important is low-
cost than high-quality when you determine a offshore
company? Decision criteria are compared in pairs to
assign weights. The relation between matrix S, its
eigenvector w
s
and maximum eigenvalue λ
max
is rep-
resented as
Sw
s
= λ
max
w
s
, (3)
where
w
T
s
= (ω
s
1
,ω
s
2
,...,ω
s
m
),
and ω
s
i
represents a weight of ith criterion.
Similarly, we define the pairwise comparison ma-
trix R in criteria of risk as
R = [r
kk
′
], k,k
′
= 1,2,...,n. (4)
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
556
By the same approach, we derive the vector of priori-
ties for the matrix R
Rw
r
= λ
′
max
w
r
, (5)
where w
T
r
= (ω
r
1
,ω
r
2
,...,ω
r
n
).
and ω
r
j
represents a weight of jth criterion in risk.
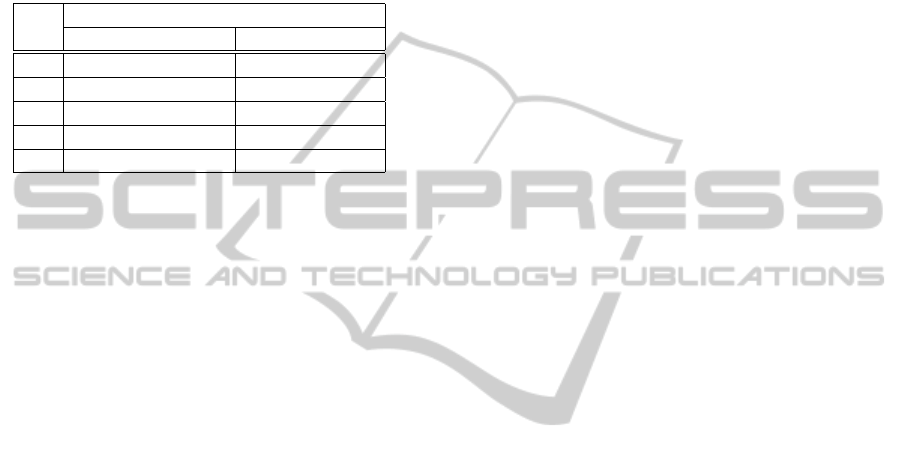
Table 1: Example of linguistic scale of paired comparison.
linguistic scale
value satisfaction risk
1 equally important equally damage
3 moderate important moderate damage
5 important strong damage
7 very important heavy damage
9 absolutely important extreme damage
Step 3). The next step derives the weights of al-
ternatives under each criterion. Then, we analyze
weight of alternatives for satisfaction. The weights
in satisfaction are derived by the same technique
as Saaty’s AHP. Decision-maker compares the al-
ternatives based on each criterion S
i
respectively,
then constructs pairwise comparison matrices A
s
i
(i =
1,... , m) of alternative. The weights are acquired
by calculating each eigenvector from matrices. The
eigenvector of A
s
i
regards as weight vector w
s
i
, then
it can be represented by Eq.(6).
w
T
s
i
= (ω
s
i
a
k
) = (ω
s
i
a
1
,ω
s
i
a
2
,...,ω
s
i
a
l
), (6)
k = 1, 2,...,l.
Here, ω
s
i
a
k
is a weight of alternative A
k
based on cri-
terion S
i
. After calculating weights for each level of a
class, the final weights of satisfaction are derived by
these results as
u
s
= (u
sa
k
) = [w
s
1
,w
s
2
,...,w
s
m
] · w
s
, (7)
where u
sa
k
is a priority weight of alternative A
k
in sat-
isfaction.
Step 4). In order to calculate the weights in risk, we
utilize the utility of damage and its probability. In
evaluation of risk, to calculate the weight of alterna-
tive A
k
for each criterion R
j
, we adopt prospect theory.
p
jk
represents a probability that risk R
j
will occur un-
der A
k
. According to prospect theory, when the dam-
age of R
j
under A
k
is represented as x
jk
, the weight
ω
r
j
a
k
of A
k
based on R
j
can be expressed as follows
using Eq.(1).
w
T
r
j
= (ω
r
j
a
k
) = (ω
r
j
a
1
,ω
r
j
a
2
,...,ω
r
i
a
l
), (8)
k = 1,2, . . . ,l
ω
r
j
a
k
= π(p
jk
)v(x
jk
) (9)
where w
r
j
is a weight vector of alternatives based on
risk R
j
. In a case that probability of a risk is not able
to be expressed as a objective value, it is given as sub-
jective value by linguistic scale, such as quite high,
very high, high and so on (Takemura, 1996). All the
weight vectors are generated after normalization.
From these results, weights of the whole hierarchy
about risks are estimated. Assume weights of each
alternative in risk are u
ra
1
,u
ra
2
,...,u
ra
l
, respectively.
Then, a weight vector u
r
can be formulated as
u
r
= (u
ra
k
) = [w
r
1
,w
r
2
,...,w
r
n
] · w
r
(10)
Step 5). Final evaluation is obtained in Step 5. The
ultimate priority vector U is finally acquired by satis-
faction evaluation and risk evaluation of alternatives.
It is calculated from the ratio of each degree of satis-
faction to a risk as
U = (u
a
k
) = (u
sa
k
/u
ra
k
) (11)
= (u
sa
1
/u
ra
1
,u
sa
2
/u
ra
2
,...,u
sa
l
/u
ra
l
)
T
.
We reach the final weights after normalization such
that
l
∑
k=1
u
a
k
= 1. (12)
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study suggested a new approach to construct a
decision-making model for risk management. The
proposed method is based on Saaty’s AHP method
and applied prospect theory for evaluating risk. By
applying prospect theory to AHP it makes possible
to quantify damage, which is derived by a human’s
judgments under risks. As a result, we think our ap-
proach enables people to make a decision about prob-
lems involving risk such as decision problems in sup-
ply chains.
In this study, the linear measurement of Saaty is
used as the measurement of return in a paired com-
parison. On the other hand, since the measurement of
a risk is calculated based on a value function which
is nonlinear. In our future works, it needs to exam-
ine consistency of each measurement. One plan is to
use the exponential measurement as relative value of
return. We have to reconsider the method of compre-
hensive evaluation which is expressed in Eq.(11) in
the case.
Moreover , in our previous model, we assumed
that one criterion consists of the pair of return and
risk. Then, we proposed a method for evaluating the
AStudyofDecision-makingModelConsideringPrioritiesbasedonTwoKindsofEvaluation-DecisionMaking
MethodologyApplyingRiskEvaluationbasedonProspectTheory
557

weights of alternativesfor criteria using expected util-
ity. Therefore, one of the future areas of study in-
volves applying a new method using prospect theory
to our previous model instead of the expected utility.
Furthermore, it is necessary to verify the effectiveness
of our proposed method by comparing it with other
methods.
REFERENCES
Azuma, R. and Miyagi, H. (2009). Ahp for risk manage-
ment based on expected utility theory. In IEEJC,EISS.
IEEJ.
Barberis, N., Huang, M., and Thaler, R. (2003). Indivi-
sual preferences, monetary gambles and the equity
premium. In Working paper, University of Chicago.
University of Chicago.
Kahneman, D. and Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory :
An analysis of decision under risk. In Econometrica.
Wiley-Blackwell.
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The Analytic Hierarchy Process. Mc-
GrawHill, NewYork.
Schoenherr, T., Tummala, V. M. R., and Harrison, T. P.
(2008). Assessing supply chain risks with the ana-
lytic hierarchy process. In Journal of Purchasing and
Supply Management. Elseview.
Takemura, K. (1996). Ishikettei No Shinri (in Japanese).
Fukumura Shuppan, Tokyo.
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
558
