
Trusted Community
A Trust-based Multi-Agent Organisation for Open Systems
Lukas Klejnowski
1
, Yvonne Bernard
1
, Gerrit Anders
2
, Christian M
¨
uller-Schloer
1
and Wolfgang Reif
2
1
Institute of Systems Engineering, Leibniz University Hannover, Hannover, Germany
2
Institute for Software & Systems Engineering, Augsburg University, Augsburg, Germany
Keywords:
Trust, Multi-Agent Systems, MAS Organisation, Organic Computing, Self-organisation, Desktop Grid.
Abstract:
In this paper, the multi-agent organisation Trusted Community is presented. Trusted Communities are formed
and joined by self-organised by agents with strong mutual trust relations and the purpose to increase their per-
sonal utility. Trusted Communities are maintained by management actions delegated by a designated member
called Trusted Community Manager, having the goal to preserve and optimise the composition and stability
of this organisation. This organisation provides performance benefits for their members by improving interac-
tion efficiency, information sharing and cooperation between the agents. In the work presented here, Trusted
Communities are conceptually defined and the application in an open Desktop Grid System is discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
When realising technical systems based on an
open multi-agent system model, we face challenges
through agents that join and leave the system arbi-
trarily and show various types of behaviours rang-
ing from cooperative to selfish or even adversary (in
terms of having the aim to disrupt the operation of
the system). In previous work, it has been shown that
in systems with these characteristics, trust can be ap-
plied to model the relationships between agents and
that these trust relations can be used to improve the
performance and robustness (towards misconducting
agents) of these systems. In this work, we take a step
further and present an approach where enduring and
mutual trust relations lead to a self-organising process
resulting in a higher form of organisation between
trustworthy agents. This organisation is referred to
as Trusted Community (TC) and is characterised by a
decentralised, yet hierarchically managed, operation
that provides performance benefits for their members
by improving interaction efficiency, information shar-
ing and cooperation. The management allows for op-
timisation of the composition and directed actions to
preserve the stability of the organisation. This is es-
sential, as composition and stability of an organisa-
tion consisting of self-interested members can easily
become issues in similar approaches, esp. when leav-
ing agents generate feedback effects.
This paper is organised as follows: Section 2 de-
fines the system model, Section 3 outlines the applica-
tion. Section 4 lays out the evaluation concept, while
related work is presented in Section 5. The paper is
concluded in Section 6.
2 SYSTEM MODEL
The Trusted Community is an organisation for agents
that have persistent mutual trust relations which allow
to establish a subsystem inside a hosting multi-agent
system as depicted in Figure 1. In this organisation,
Outbound
interactions
Trust
-
based
interactions
Inbound
(
member
)
interactions
Trusted Community
Open (hosting) system
Unassociated agents
Misconducting
agent
Figure 1: System view on Trusted Communities.
interaction partners are mainly chosen among mem-
bers (we refer to this as inbound or kinship-motivated
interactions). Agents in the examined systems are
self-interested, that is, they will only consider form-
ing and participating in such a subsystem when the
312
Klejnowski L., Bernard Y., Anders G., Müller-Schloer C. and Reif W..
Trusted Community - A Trust-based Multi-Agent Organisation for Open Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0004332003120317
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2013), pages 312-317
ISBN: 978-989-8565-38-9
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
benefit provided is measurably higher than in an unas-
sociated state (ignoring or being unable to join an ex-
istent Trusted Community). A TC thus does not pos-
tulate an explicit group goal, as for example a coali-
tion. To apply a TC in a hosting system, the follow-
ing requirements have to be met: The system needs
to be open, i.e. agents can join and leave at will. All
agents commit to using some standardised mechanics
(production engine) of the (technical) hosting system.
The respective performance is measurable via a glob-
ally defined utility function for an agent i of the form
U
i
(r
i
, c
i
), contrasting a reward function r
i
with a func-
tion c
i
quantifying the cost to reach the reward. The
hosting system provides methods to discern trustwor-
thy from untrustworthy agents through interactions,
assigning trust values to each agent and providing rep-
utation information. The following design pattern de-
picted in Figure 2 formalises the requirements on the
underlying agent model:
TC
Agent
ReputationProvider
DirectTrustValue
ReputationValue
-repProv
1
1
-knownAgents 0..*0..*
-ratedAgent
1
0..*
-tcManager
1
0..*
«provides»
-members 2..*
0..*
-ratedAgent 1
0..*
-repProv 0..*
-agents 0..*
Figure 2: Trusted Community design pattern.
As shown here, a TC is composed of at least 2
member agents of which exactly one is the TC Man-
ager. The agents are able to assign direct trust val-
ues to each other based on the outcomes of their in-
teractions and by contacting a reputation provider,
they make these trust values available to other known
agents. The reputation provider is not further spec-
ified (central entity or realised as broadcast to other
agents to retrieve direct trust values), but the TC itself
is also a reputation provider meaning that members
can share a TC wide reputation.
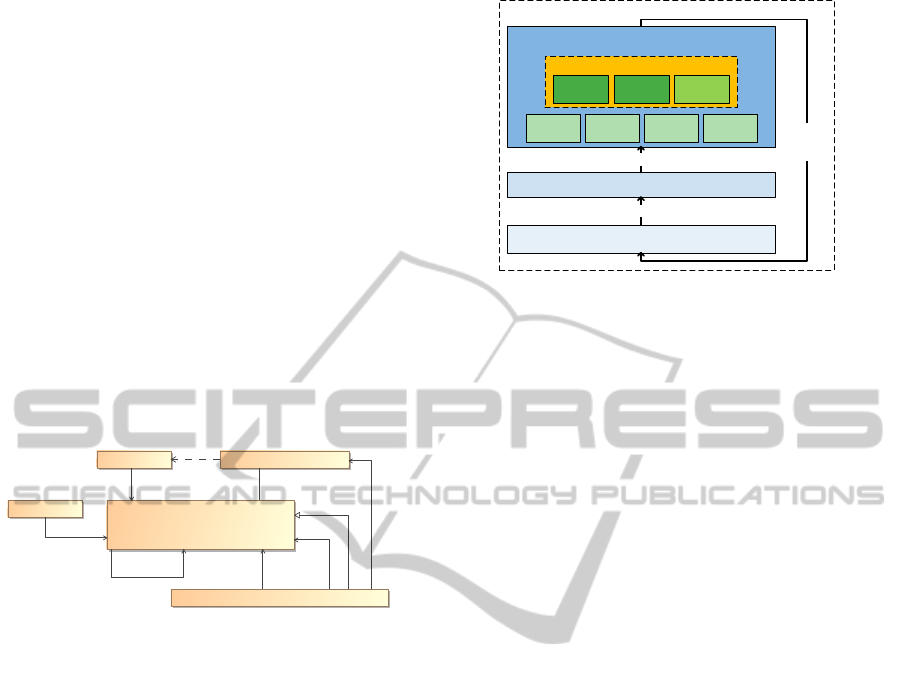
2.1 Trusted Community Lifecycle
Trusted Communities are formed self-organised by
unassociated agents in a hosting systems. Regarding
TCs, this system can be in one of the following three
phases depicted in Figure 3:
Pre-organisation Phase. The system is in a phase
where all agents are unassociated and no organisa-
tion exists. The agents have to apply safety measures
because of uncertainty about other agents’ behaviour
and constantly rate their interactions according to the
trust mechanics of the system. With time passing,
trustworthy agents develop mutual trust relations. At
Trust and reputation system
TC Maintenance Phase
Pre-Organisation Phase
TC Formation Phase
Agents initiate formation process
Initial management election
TC Manager
initiates
dissolution
Active TC-
Expansion
Strategies
Task
Delegation
Strategies
Member
Control
Strategies
Membership
Evaluation
Strategies
Organisation benefit strategies
Interaction
efficiency
Information
sharing
Cooperation
Figure 3: Trusted Community lifecycle and composition.
this time they consider forming a Trusted Commu-
nity in hope to improve their utility. This decision is
based on an analysis of their current utility U
i
and the
expected utility predictUtility(i, TC
j
) when being a
member of the TC j, formalised by formation criteria.
Mutual trust alone does not initiate TC formation, as
this would force the formation of TCs per design. In-
stead we want to apply TCs only when beneficial (in-
crease in U
i
) and adaptive towards the hosting system
state. When a critical number of agents decide to ini-
tiate the formation process, the next phase is reached.
TC Formation Phase. The formation phase is charac-
terised by negotiations of the potential members about
membership of additional agents. This is necessary as
not all agents have had the same interaction partners.
Finally, in this phase the manager of the TC is elected,
starting the maintenance phase.
TC Maintenance Phase. This is the main phase in
the TC lifecycle. Here, the TC is already assembled,
having a TC manager that can assign roles to mem-
bers and release norms, as well as agents that actively
work together in an organised fashion. As the agents
joined in order to improve their utility U
i
, they ex-
ecute periodic checks that are related to the initial
analysis predictUtility(i, TC
j
) in the pre-organisation
phase (but can be performed with more information at
hand). If members discover that their utility U
i
did not
improve (comparing to their utility when being unas-
sociated), they leave the TC. If a critical number of
members leave, the dissolution of the organisation is
initiated and the pre-organisation phase restored.
Apart from the members of the Trusted Commu-
nity, the unassociated agents continue to interact with
each other and with the TC members (constrained by
interaction rules of the TC). These agents may then
reach a state where they find joining the TC benefi-
cial, as well as acceptable from the point of view of
the TC. As we are considering a dynamic system, the
threshold to joining a TC can be reached at different
TrustedCommunity-ATrust-basedMulti-AgentOrganisationforOpenSystems
313

phases of the system: Consider for example an agent
joining late and thus having no trust relations to the
initial members of the TC, thus being unable to be an
initial member itself.
These mechanics are referred to as lifecycle of
the Trusted Community as we have transitions from
the maintenance phase where a TC exists, to the pre-
organisation phase. In this phase, another TC can
form if the trust requirements and formation criteria
are met again by agents. A TC thus emerges depen-
dent on significant criteria and the state of the hosting
system. In the following, we focus on the operation
of a TC in the maintenance phase.
2.2 Organisation Benefit Strategies
Forming/joining a Trusted Community is an act of
self-interest for agents because TCs provide benefits
that increase the utility U
i
of member agents. Obvi-
ously, the nature of these benefits depends on the un-
derlying application: Still, member agents have the
same utility definition U
i
as unassociated agents, ben-
efits must therefore be directed at improving the exact
interactions that unassociated agents have, increasing
the same reward function r
i
. Despite their application-
dependency, we can affirm that the organisation ben-
efit strategies are part of the following classes:
Interaction Efficiency. Interactions that are executable
within the hosting system but profit from being exe-
cuted between agents with high mutual trust, thus TC
members. This refers mainly to subadditive costs or
superadditive benefit interactions. Consider for ex-
ample the search for a suited interaction partner, or
the execution of interactions without the necessity to
apply additional safety measures.
Cooperation. This class represents strategies that can-
not be executed in an environment with uncertainty
about the trustworthiness of the involved interaction
partners, because of safety considerations. Hence,
strategies here are exclusive to member agents. Ex-
amples are the delegation of the execution of funda-
mental tasks to a central entity (e.g. the TC Manager)
or the cooperative detection of collusion (relying on
the absence of colluding agents in the composition).
Information Sharing. In general, sharing informa-
tion is necessary in order to perform other organisa-
tion benefit strategies. Additionally, agents will not
share certain information in the hosting system when
the trustworthiness of the recipient is in doubt. The
TC provides a structure where this information can
be shared and processed safely and in scale (among
TC members). An example of sensitive information,
with access restricted to members, are personal obser-
vations (local world model) which could be abused by
untrustworthy agents.
By providing adequate organisation benefit strate-
gies, the additional overhead of being a member
of a TC (contributing to c
i
) is marginalised and
the formation of a TC a worthwhile goal for self-
interested agents. In the following, the Trusted Com-
munity Manager is described and the mechanics of
the Trusted Community (which produce the over-
head) are detailed.
2.3 Trusted Community Manager
The Trusted Community Manager (TCM) is the
elected leader of the Trusted Community. As such
it acts as an the active representative of an institution
releasing norms and sanctioning infringement. Main
goals of this entity are to regulate access to the organ-
isation, improve the experience of the members, and
most importantly to preserve the existence of the TC.
The according function blocks (depicted in Figure 3
in the maintenance phase) are composed of mainly
recurring tasks that can be delegated to members or
executed by the TCM itself. Examples of tasks are
the gathering of data through observation or specific
interactions with non-member agents. In the follow-
ing, the function blocks are detailed:
Active TC Expansion Strategies. The initial compo-
sition of a Trusted Community is based on the form-
ing agents. Due to connectivity and dynamics aspects
of the hosting system, possibly not all suited agents
were involved in the formation process. The task of
the Trusted Community Manager is therefore to find,
observe and evaluate potential members with the goal
to optimise the composition of the Trusted Commu-
nity and in order to improve its effectiveness.
Membership Evaluation Strategies. Agents join the
Trusted Community with the expectancy to experi-
ence a higher utility U
i
. Therefore members periodi-
cally check whether their membership satisfies this by
evaluating c
i
, the overhead (through delegated tasks,
kinship commitment etc.), and r
i
, here the interaction
efficiency. Members leaving the TC as a result of
these examinations are degrading the efficiency of the
TC, as they reduce the number of available member
interaction partners and thus r
i
of remaining mem-
bers. Besides, management tasks delegated by the
TCM have to be distributed among less agents, in-
creasing c
i
of single members leading to the threat
of a positive feedback effect. The TC Manager is
therefore obliged to try and improve the utility U
i
of
a potentially leaving member i. This can e.g. be re-
alised by means of (short-term) reduction of the over-
head of this agent via re-delegation of its management
tasks, increasing its benefits by means of prioritisa-
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
314

tion. However, the TCM needs to balance the costs of
preserving the membership of this agent with the ad-
ditional overhead introduced for other members. The
key of this function block is therefore an opportunity
cost analysis for under-performing members.
Member Control Strategies. This function block re-
gards the necessity to observe and influence the be-
haviour of member agents. The requirement to ob-
serve member behaviour despite their (proven) trust-
worthiness stems from the fact that we are dealing
with self-interested agents and dynamic systems, a
combination that can lead to various forms of mis-
conduct. Consider for example agents with a strategy
that lets them behave trustworthy until membership in
a TC is accomplished, only to start to defect, reaping
benefits without committing themselves to any tasks.
The TC Manager is given the capability to observe
the behaviour of member agents, be it at random, pe-
riodically or in case of suspicion. This can be realised
by utilising a light-weight version of the reputation
mechanism of the hosting system. Again, the over-
head of introducing safety measures needs to be care-
fully balanced in order to preserve the effectiveness
of the TC. Finally, when detecting misconduct, the
TCM will sanction the agent, the exclusion from the
TC being the ultimate form of punishment.
Task Delegation Strategies. All function blocks are
composed of tasks and the Trusted Community Man-
ager cannot execute all these tasks itself - this would
reduce its utility U
i
and imply leaving the TC, intro-
ducing a high membership fluctuation and render the
TC unmanageable. Consequently, the TCM has to
apply a task delegation model with the requirement
of fairness, as an unbalanced delegation would lead
to under-performing agents and thus to leaving mem-
bers. Besides being fair, the task delegation needs
to be adaptive to short-term relief of single agents as
mentioned in the description of the membership eval-
uation function block. The supervision of task execu-
tion is subject to member control strategies.
The Trusted Community Manager is a key ele-
ment in the Trusted Community concept. On the one
hand, it represents a higher-ranking level among the
otherwise equal members of the Trusted Community,
yet on the other hand, the TCM is just an agent partic-
ipating in the Trusted Community in order to increase
its own utility. This is fundamental to the concept in
order to avoid the introduction of an external element
with goals that are beyond justification. With regard
to the self-interest of the agent being TCM, compen-
sation is necessary for the aforementioned tasks exe-
cuted by the TCM to balance its r
i
and c
i
. The most
general form of compensation is to assign all sys-
tem interactions that do not aim at managing the TC
(but generate benefit) to other member agents - these
agents then act on behalf of their manager. Finally,
in consideration of the open nature of the system, a
Trusted Community Manager has to be elected anew
whenever the current TCM either leaves the Trusted
Community (utility considerations) or the system as
such. This election is performed analogously to the
initial election at formation phase.
3 APPLICATION SCENARIO
In this section we describe how Trusted Communities
can be deployed in an exemplary hosting system from
the Desktop Grid Computing domain: We assume an
open, distributed and volunteer-based Desktop Grid
System in the tradition of systems like XtremWeb
(Fedak et al., 2001), to which we refer as Trusted
Desktop Grid (TDG). The system is designed with-
out central control (p2p) and the applications regarded
produce bag-of-task jobs, i.e. they are composed of
tasks (work units) that are independent of each other.
A system like this is suited for scenarios where most
clients run applications that produce grid jobs and
thus are in high demand of computing resources. Ad-
ditionally, we are considering agents that are in charge
of the grid client on the machines and make decisions
on behalf of their users (especially about resource se-
lection). Due to the open nature of the system, we
have to deal with agents that show various types of be-
haviour (from altruistic to untrustworthy) in order to
achieve their self-interested goal of scheduling their
own jobs as efficiently as possible. According to the
taxonomy of (Choi et al., 2008) and taking the re-
source perspective, we therefore classify the poten-
tially participating agents of this Desktop Grid Sys-
tem as: egoistic, volatile, distributed over the internet,
dynamic, faulty and heterogeneous.
In previous work, for example (Bernard et al.,
2011), we have shown that by using a trust and repu-
tation mechanism combined with techniques from Or-
ganic Computing, cf. (M
¨
uller-Schloer and Schmeck,
2011), we are able to isolate uncooperative agents
and minimise their influence on the system perfor-
mance in systems like this. The result of the isolation
process was an implicit Trusted Community (iTC), a
loose coupling of interaction partners without global
membership function. ITCs, despite being successful,
leave room for improvement, as unassociated agents
miss essential opportunities to increase their utility,
because they have to account for the general uncer-
tainty. By applying the MAS organisation Trusted
Community (as detailed in section 2), we plan to ac-
count for these opportunities and further raise the util-
TrustedCommunity-ATrust-basedMulti-AgentOrganisationforOpenSystems
315

ity of the agents by providing them benefits through
interaction efficiency, information sharing and coop-
eration.
To allow for a self-organised formation of a TC in
a suited hosting system, we need to define agent util-
ity, formation criteria and organisation benefit strate-
gies. The remaining mechanics (lifecyle, mainte-
nance etc.) of the Trusted Community are generic.
In the Trusted Desktop Grid, agents use each others’
spare resources to process jobs generated by user ap-
plications. Their goal is to schedule single work units
on available worker agents (resource selection), such
that they minimise the time it takes to receive valid
results. This is formalised in Desktop Grid metrics
like flow time, makespan and turnaroundtime, cf. for
example (Zhou and Lo, 2006). On the other hand,
overhead is introduced through communication with
other agents and working for other agents, because al-
though a user volunteers its machine, we assume that
from the user perspective it is best to receive good
performance for own jobs without having to commit
resources. A utility function U
i
for the TDG thus in-
corporates these aspects in r
i
and c
i
.
Formation criteria for initiating TC formation are
drawn from suboptimal agent states. These are for ex-
ample indicated by a low submit/work-ratio, meaning
that an agent has a high overhead due to commitment,
or a high average number of communication acts nec-
essary to find a suited worker that accepts own work
units. Being a member of a Trusted Community is
likely to improve these states, as TCs provide scala-
bility and kinship commitment to members, therefore
TC formation is aspired.
Finally, the most fundamental aspects to define
when applying TCs are the organisation benefit strate-
gies. Figure 4 depicts these for the TDG Scenario:
Interaction
efficiency
Information
sharing
Cooperation
Omit safety
measures
(esp. replication)
Observed world
model (situation
description)
Utility
Coordinated
processing of
jobs
Shared trust and
reputation
management
Collusion
detection
Kinship-driven
interactions
realisation
Figure 4: Exemplary TDG organisation benefit strategies.
In the TDG, interactions between agents are
mainly restricted to the processing of each others’
work units, negotiations about the respective terms
and the exchange of information necessary for the
identification of suited partners (esp. reputation). For
TC members these interactions are more efficient be-
cause of scalability and kinship commitment. A par-
ticular interaction efficiency benefit is that no work
unit replication needs to be performed, as all work
units can be assigned to members and thus valid re-
sults can be expected.
Information to be shared inside a TC is sensi-
tive to trust reasoning. In the TDG, sharing the ob-
served world model or own utility of an agent with un-
trustworthy agents could be abused by misconducting
agents that adapt their strategies accordingly. Con-
sider for example an agent that gets to know the exact
resource selection criteria applied by an other agent.
A misconducting agent could actively adapt to ap-
pear as inappropriate worker in order to avoid being
requested to process a work unit and commit its re-
sources.
Unlike interaction efficiency strategies, coopera-
tion strategies provide interaction opportunities not
readily executable by unassociated agents in the host-
ing system. In the Trusted Desktop Grid, centralised
scheduling is a good motivation for TCs: Centralised
scheduling is generally more effective than decen-
tralised, because fairness and predictability can be
incorporated into scheduling strategies more easily.
However, centralised scheduling does not scale well
and is therefore hardly applicable in an open, un-
reliable, peer-to-peer environment - in contrast to
the size-constrained and trustworthy environment a
Trusted Community represents. Additional cooper-
ation opportunities for TC members in the TDG are
a shared trust and reputation management (less mes-
sage overhead, more information) and collusion de-
tection by cooperative observation of untrustworthy
agents.
4 EVALUATION
We will evaluate the Trusted Community concept
in the Trusted Desktop Grid applying the scenario-
dependent utility function, formation criteria and or-
ganisation benefit algorithms presented in the previ-
ous section. We will especially focus on showing that
in an open Desktop Grid, system states arise in which
agents profit from forming a TC. The reward r
i
of
utility U
i
of the agents will be composed of standard
Desktop Grid metrics like turnaroundtime. We will
continue to show that this organisation can be made
stable (low member fluctuation) and its composition
optimised, by introducing a TC Manager. Especially
its overhead balancing and short-time relief of man-
agement tasks capabilities are seen as promising can-
didates for keeping members associated. Our findings
will be compared with the application of related or-
ganisation paradigms in the same system, providing
additional evaluation data as contribution.
ICAART2013-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
316

5 RELATED WORK
In the survey on multi-agent organisation paradigms
by (Horling and Lesser, 2005), the MAS organisa-
tion clan proposed by (Griffiths, 2005) has been de-
scribed as closely paralleling the concept of congre-
gations by (Brooks and Durfee, 2003) but addition-
ally incorporating trust as a key aspect. Thus we
refer to clans as “congregations with trust” and in
the same line of argumentation we refer to Trusted
Communities as “congregations with trust and hierar-
chy” in regard of the role of the Trusted Community
Manager. Further theoretic work on MAS organisa-
tion mechanics has also been conducted by (Math-
ieu et al., 2002). As for our application scenario,
research on open, distributed, multi-agent-based and
trust-enhanced Desktop Grid systems can for instance
be found in (Domingues et al., 2007), (Shudo et al.,
2005) and (Dyson et al., 2004). Additional coverage
of MAS organisations in similar scenarios has also
been considered in (Thabet et al., 2011), (Abdallah
et al., 2004) and (Wang and Vassileva, 2004).
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have proposed a novel multi-agent
organisation called Trusted Community for the use in
open, distributed systems where trust considerations
are important. We have defined the system model, de-
scribing the lifecycle and management mechanics of
a TC. In particular, we have emphasized the necessity
to balance organisation benefit algorithms and over-
head introduced by membership, as agents form and
join TCs out of self-interest. We have further sketched
how TCs can be deployed in a Trusted Desktop Grid
scenario and how we will evaluate the applicability in
future work. Finally, we have stated how our research
is related to similar work in the area of multi-agent
organisations and agent-based Desktop Grid systems.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is funded by the research unit “OC-
Trust” (FOR 1085) of the German research founda-
tion (DFG).
REFERENCES
Abdallah, S., Zhang, H., and Lesser, V. (2004). The role
of an agent organization in a grid computing envi-
ronment. In Proc of the 14th Int Conf on Automated
Planning and Scheduling, Workshop on Planning and
Scheduling for Web and Grid Services.
Bernard, Y., Klejnowski, L., Cakar, E., H
¨
ahner, J., and
M
¨
uller-Schloer, C. (2011). Efficiency and Robust-
ness Using Trusted Communities in a Trusted Desk-
top Grid. In 5th IEEE Conference on Self-Adaptive
and Self-Organizing Systems Workshops. IEEE.
Brooks, C. and Durfee, E. (2003). Congregation formation
in multiagent systems. Autonomous Agents and Multi-
Agent Systems, 7(1).
Choi, S., Buyya, R., Kim, H., and Byun, E. (2008). A Tax-
onomy of Desktop Grids and its Mapping to State of
the Art Systems. Technical report, Grid Computing
and Distributed Systems Laboratory, The University
of Melbourne.
Domingues, P., Sousa, B., and Moura Silva, L. (2007).
Sabotage-tolerance and trustmanagement in desktop
grid computing. In Fut. Gener. Comput. Syst. 23, 7.
Dyson, J., Griffiths, N., Lim, H., Jarvis, S., and Nudd, G.
(2004). Trusting agents for grid computing. 2004
IEEE Int Conf on Systems, Man and Cybernetics
(IEEE Cat. No.04CH37583).
Fedak, G., Germain, C., Neri, V., and Cappello, F. (2001).
XtremWeb: a generic global computing system. In
Proc First IEEE/ACM Int Symp on Cluster Computing
and the Grid. IEEE Comput. Soc.
Griffiths, N. (2005). Cooperative clans. Kybernetes,
34(9/10).
Horling, B. and Lesser, V. (2005). A Survey of Multi-Agent
Organizational Paradigms. The Knowledge Engineer-
ing Review, 19(4).
Mathieu, P., Routier, J.-C., and Secq, Y. (2002). Princi-
ples for dynamic multi-agent organizations. In Intel-
ligent Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, volume 2413
of LNCS. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
M
¨
uller-Schloer, C. and Schmeck, H. (2011). Organic Com-
puting - Quo Vadis? In Organic Computing - A
Paradigm Shift for Complex Systems, chapter 6.2.
Birkh
¨
auser Verlag.
Shudo, K., Tanaka, Y., and Sekiguchi, S. (2005). P3: P2p-
based middleware enabling transfer and aggregation
of computational resources. In Proc. IEEE Int Symp
on Cluster Computing and the Grid CCGrid ’05, vol-
ume 1.
Thabet, I., Bouslimi, I., Hanachi, C., and Gh
´
edira, K.
(2011). A multi-agent organizational model for grid
scheduling. In Agent and Multi-Agent Systems: Tech-
nologies and Applications, LNCS. Springer Berlin /
Heidelberg.
Wang, Y. and Vassileva, J. (2004). Trust-based commu-
nity formation in peer-to-peer file sharing networks.
In Proc of the 2004 IEEE/WIC/ACM Int Conf on Web
Intelligence, WI ’04, Washington, DC, USA. IEEE
Computer Soc.
Zhou, D. and Lo, V. (2006). WaveGrid: a scalable fast-
turnaround heterogeneous peer-based desktop grid
system. In Proc 20th IEEE Int Parallel & Distributed
Processing Symp. IEEE.
TrustedCommunity-ATrust-basedMulti-AgentOrganisationforOpenSystems
317
