
Consensus-based Inter-camera Re-identification
Across Non-overlapping Views
Fouad Bousetouane
1
, Cina Motamed
2
and Lynda Dib
1
1
LASE-Embedded System Laboratory, Badji Mokhtar University, BP 12, Annaba, Algeria
2
LISIC Laboratory, University of Littoral Cote d’Opale, Dunkerque, France
Keywords:
Inter-camera Re-identification, Non-overlapping Views, Distributed Inferences, Low-level Contextual Cues,
Brightness Transfer Function, Consensus-based Algorithm.
Abstract:
Multi-object re-identification across cameras network with non-overlapping fields of view is a challenging
problem. Firstly, the visual signature of the same object might be very different from one camera to an-
other. Secondly, the blind zone between cameras creates the discontinuity in the observation of the same
object in terms of locations and travelling times. Centralized inferences proposed in literature for inter-camera
re-identification becomes insufficient in practice mostly with the requirement of real-time applications and
dynamic cameras network. In this paper we present a completely distributed approach for inter-camera re-
identification. The proposed approach based on the distributed inferences, where the set of smart-cameras
collaborate to reach a consensus about the identities of objects circulating in the network. Local and global
visual descriptors were combined into the proposed approach for inter-camera color mapping and invariant
objects description. Experimental results of applying this approach show improvement in inter-camera re-
identification and robustness in recovering from very complex conditions.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the technological advances in visual sensors de-
sign, in communication and in dynamic computer vi-
sion are stimulating the development of new applica-
tions that will transform traditional mono-camerasys-
tems into pervasive intelligent camera networks. The
multi-camera networks are the basis of several ap-
plications including video surveillance, visual robot
navigation, smart homes, military and scientific ap-
plications, etc. However, the aggregation and the
interpretation of distributed visual information from
multiple video streams in real-life scenarios is a very
complex problem. Which requires the development
of new algorithms and sophisticated techniques for
collaborative inferences able to analyse in real-time
the decentralized and distributed visual information.
In multi-camera network, three types of configuration
are possible relative to the overall views of the net-
work: (1) Overlapping multi-camera Networks. (2)
Non-overlapping multi-camera networks or networks
of disjoint cameras. (3) hybrid multi-camera net-
works. Material and economic constraints limiting
in general the number of cameras in the network and
prevent a full coverage of a large geographical area,
which creates discontinuities in the field of view of
the network. A major challenge in networks with dis-
joint cameras is inter-camera re-identification: when
an object appears in the field of view of a camera, it
comes to determine if this object has already been ob-
served and tracked by one of the network cameras.
Following the limits of centralized approaches pro-
posed in literature for inter-camera re-identification
in terms of difficulty in analysing a huge amount of
data centrally, dynamic camera network, overloaded
bandwidths, etc, it is also desirable that the inter-
camera re-identification mechanism be distributed.
In this paper we present a totally distributed ap-
proach for inter-camera multi-object re-identification
across non-overlapping views. The camera network
is modeled as a multi-agent system, where the smart-
cameras would have to act as autonomous agents and
decisions about the objects identities would have to
be taken in a distributed manner. However, to be able
to attribute a valid identities to all objects in the area
of interest, the smart-cameras should be working co-
operatively with each other. A consensus-based algo-
rithm for distributed inter-camera re-identification is
proposed in this work, where the smart-cameras col-
laborate to reach a consensus about objects identities.
341
bousetouane F., Motamed C. and Dib L..
Consensus-based Inter-camera Re-identification - Across Non-overlapping Views.
DOI: 10.5220/0004346803410346
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2013), pages 341-346
ISBN: 978-989-8565-48-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Unlike many approaches proposed in literature (Chen
et al., 2011)(Javed et al., 2008)(Motamed and Wal-
lart, 2007), where many restrictions are used about
the topologies of the network, cameras calibration,
travelling time, closed network, exit/entrance loca-
tions, off-line learning steps, etc. The proposed ap-
proach for distributed inter-camera re-identification
works in most cases without any restrictions, where
many realized experiments proved the robustness of
the proposed approach in many complex conditions.
This paper is organized as follows: In section.2 we
present the problem formulation of inter-camera re-
identification. In section.3, we review some inter-
esting approaches in the state-of-the-art for inter-
camera re-identification. Section.4 describes the pro-
posed decentralized system architecture based on the
distributed artificial intelligence. In section.5, we
detail the proposed approach for distributed inter-
camera re-identification based on the consensus prin-
cipal and the collaboration between agents. Finally, in
section.6, a set of realized online experiments in ad-
hoc multi-camera network with disjoints views will
be presented and discussed.
2 PROBLEM FORMULATION
Suppose that we have a system of n cameras
CAM
1
,CAM
2
,,CAM
n
with non-overlapping views.
Assume that there are k objects in the environment
p
1
, p
2
,, p
k
. Let, O the set of objects observation
O
CAM j
=
O
CAM
1
j
,O
CAM
2
j
,,O
CAM
k
j
, where O
CAM
1
j
is
the observation generated by the object p
1
and ob-
served by the camera CAM
j
. Let, O
CAM
a
i
the ob-
servation of a given object p
a
exiting the field of
view of the camera CAM
i
and entering the filed of
view of another cameraCAM
j
with a new observation
O
CAM
b
j
. The problem of inter-camera re-identification
is essentially to find which of the observations in the
system of cameras belong to the same object (Javed
et al., 2008). Under this definition the inter-camera re-
identification problem lies in inter-camera matching
between the observation O
CAM
a
i
and the observation
O
C
AM
b
j
. If a high similarity is calculated between
the two observations O
CAM
a
i
and O
CAM
b
j
then the ob-
servations corresponding to the same object p
k
. The
process of inter-camera matching between two obser-
vations is named by many researchers inter-camera
tracking (Javed et al., 2008). In a probabilistic con-
text, the probability that the observation O
CAM
a
i
ob-
served by the camera CAM
i
corresponds to the ob-
servation O
CAM
b
j
observed by the camera CAM
j
can
be described by: P(a = b|O
CAM
a
i
,O
CAM
b
j
). The most
likely correspondence must maximize the similarity
between the two observations O
CAM
a
i
and O
CAM
b
j
:
S
k
= ArgMax(P(a = b|O
CAM
a
i
,O
CAM
b
j
)) (1)
S
k
∈ L
s
, L
s
is the set of objects in the transfer list
(i.e. candidates objects observation). In this work
we present a new approach for estimating the solution
space S
k
in a totally decentralized manner.
3 RELATED WORK
For estimating the solution space S
k
(equation.1) or
maximizing the similarity between the two observa-
tions a and b, many approaches have been proposed
in the literature. These approaches can be subdivided
into two main groups: (1) Approaches based on local
visual descriptors named by many researchers inter-
camera re-identification. (2) Approaches based on
global visual descriptors named by many researchers
inter-camera tracking or inter-camera matching.
3.1 Inter-camera Re-identification
Based on local descriptors extracted from the images
of the objects of interest, these approaches attempt to
attribute valid identities to objects circulating in the
covered zone. The main goal of these approaches
is to find the best invariant inter-camera visual local
descriptors for object representation. In this context
many notable research works have been published, in
this section we review the most recent and interesting
works. (Meden et al., 2011) proposed a mixed-State
Particle Filtering that estimates for simultaneously
the positions and identities of objects in closed non-
overlapping camera networks. In this work authors
used off-line training phase to learn the appearance of
the objects based on color histograms. Viewpoint in-
variance is instead the main issue addressed in (Gray
and Tao, 2008), where the spatial and color informa-
tion are combined for inter-camera re-identification
using an ensemble of discriminant localized features
and classiers. In (Farenzena et al., 2010) a set of local
features were accumulated invariant inter-camera ob-
ject representation. For generate a multi-shot visual
signature of objects for inter-camera re-identification
(Doretto et al., 2011) proposed a new strategy for ag-
gregates a set of local features based on Hog descrip-
tor, color and structural information. Inter-camera re-
identification remains in the heart of cameras network
research, but the challenges raised in the choice of the
local descriptors (i.e. invariant inter-camera and dis-
criminant inter-object). This work is part of this ori-
entation.
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
342

3.2 Inter-camera Matching
There have been notable research works in this orien-
tation for inter-camera matching based on global vi-
sual descriptors. (Porikli and Divakaran, 2003) pro-
posed an inter-camera color calibration model adapt-
ing the appearance histograms of the objects in dif-
ferent views, and then combined spatio-temporal and
appearance cues to track objects inter-camera. In
the same context of inter-camera color adaptation,
(Prosser et al., 2008) proposed a cumulative BTF for
mapping colors between cameras. (Javed et al., 2008)
presented an extension of the color adaptation through
a combination of appearance and spatio-temporal
cues. This system learned the camera network topol-
ogy and path probabilities of objects using Parzen
windows with manual correspondence in an initial
training phase. (Gilbert and Bowden, 2006) proposed
an approach based on a spatio-temporal cues, where
the entry/exit zones inter-camera was learned incre-
mentally. (Chen et al., 2011) proposed an unsuper-
vised method based on batch-learning, which learns
adaptively the true valid links among the entry/exit
zones of cameras from the correspondence. Until
now, this orientation of inter-camera matching based
on global descriptors is over-active.
The majority of the proposed approaches in litera-
ture for inter-camera re-identification from the above
orientations based on centralized systems. The need
for materially economical solutions, scalable, able to
analyse the distributed visual information in dynamic
cameras networks makes the centralised architectures
that lead to centralized inter-camera re-identification
insufficient solutions.
4 COOPERATIVE MULTI-AGENT
ARCHITECTURE
The main goal of this paper is to develop a dis-
tributed inter-camera approach for multi-object re-
identification in a dynamic cameras network with dis-
joint fields of vision. The ad-hoc nature and in-
herently distributed of the dynamic cameras network
and the need of real-time application have increas-
ingly oriented many researchers to distributed infer-
ences techniques and game theory (Soto et al., 2009).
The most proposed distributed techniques until now
remains in position estimation in overlapping views
such as Kalman consensus (Olfati-Saber and Sandell,
2008). To the best of our knowledge distributed
inter-camera re-identification across non-overlapping
views based on distributed inferences through consen-
sus have not been done before in the state-of the art.
In this work the cameras network is modelled with a
multi-agent system, where each camera is modelled
as an intelligent agent. Each agent is considered as
autonomous relative to the local decision and process-
ing. Each agent has a processing unite independent of
the other agents. The set of agents collaborate to reach
a consensus about identities of the interest objects
inter-camera. We consider a multi-camera ad-hoc
network CAM
x
, contains n cameras. The interaction
topology of a network of multi-camera is represented
using a graph G = (C,E), where C is the set of nodes
C = 1, 2, 3,...,n and E = CxC is the edge between
nodes. Each node represents an intelligent agent that
coversa small specific area relative to the field of view
of the network. A modular modelling of each agent is
proposed, where each agent incorporates six essen-
tial module: (1) Moving object extraction, based on
background subtraction with statistical modelling of
the background followed by adaptive post process-
ing and common region labelling step (Bousetouane
et al., 2011). (2) Inter-camera color adaptation based
on Mean Brightness Transfer Function (MBTF)for
inter-camera color mapping. (3) Features extraction
and objects representation based on a combination of
statistic moments and low-level contextual informa-
tion computed through the co-occurrencefor invariant
inter-camera object description (Bousetouane et al.,
2012). (4) The proposed distributed inter-camera
re-identification algorithm based on the consensus
principal ensured through the collaboration between
agents (smart-cameras). (5) Intra-camera tracking
based on mixed state condensation for estimating the
trajectory of an object after the attribution of a valid
identity. (6) Communication module based on selec-
tive diffusion to avoid the overload of the transmis-
sion channels especially in wireless networks. Figure
(Fig.1) illustrates the proposed overall distributed ar-
chitecture based on the multi-agent paradigm for dis-
tributed inter-camera re-identification. In this paper
we are focused especially in the re-identification mod-
ule where a distributed approach is proposed based on
the cooperation between agents.
5 PROPOSED
CONSENSUS-BASED
INTER-CAMERA
RE-IDENTIFICATION
The distributed nature of the proposed system based
on multi-autonomous agents leads to completely dis-
tributed approach for inter-camera re-identification.
In the multi-agent systems literature, the consensus
Consensus-basedInter-cameraRe-identification-AcrossNon-overlappingViews
343
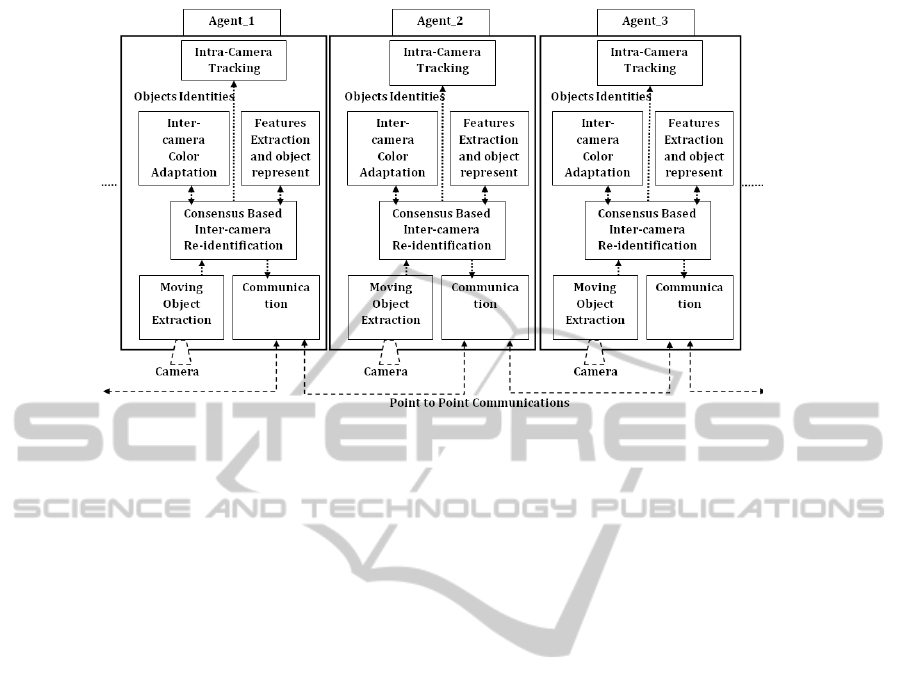
Figure 1: Proposed decentralized system based multi-agent with three neighbouring smart cameras for distributed inter-camera
re-identification.
defined in (Soto et al., 2009) as a way (protocol,
algorithm, etc) to reach an agreement regarding a
certain quantity of interest that depends on the state
of all sensors or other information may be captured
by the perceptual systems of autonomous agents in
camera networks. In our case we define the consensus
as a visual protocol that allows to define the interac-
tion rules for exchange information and knowledge
between an agent and its neighbours. Consequently,
the set of autonomous agents collaborate to reach a
consensus about the identities of objects circulating
in the covered area by the cameras network. As
mentioned earlier, the interaction topology between
smart-cameras in the proposed multi-agent system
is represented by the graph G = (C,E), the number
of nodes is equal to the number of cameras. Each
camera have an identity and each agent have a
data-set T that contains the history of communication
between agents. Let CAM
x
the set of cameras in the
network, CAM
x
= CAM
1
,CAM
2
,...,CAM
n
. We de-
fine the subset Sub
C
⊆ CAM
x
of all cameras where an
object has been already detected and tracked. Ned
C
is the subset of camera where no object has been
already detected Ned
C
∪ Sub
C
= CAM
x
. Each camera
CAM
i
will also have its set of neighbouring cameras
CAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
. O
CAM
a
i
is the observation produced by
the object Obj
a
and captured by the camera CAM
i
,
where CAM
i
⊂ Sub
C
. In the proposed distributed
system the camera CAM
i
where a new observation
is detected will be the initiator of the cooperation
between its neighbourhood CAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
for reach
a consensus about the identity of this observation.
Assume that the mean brightness transfer functions
(MBTFs) (Gilbert and Bowden, 2006) between the
K pair of cameras have been already computed in
training phase, where K = n ∗ (n − 1)/2 (i.e. This
process is assured by the module number 2 of each
agent (Fig.1)). Let, F
O
CAM
a
i
=
f
1
, f
2
,..., f
n
is the
features vector that characterise the observation
O
CAM
a
i
extracted from the area of object on interest
Obj
a
, this vector aggregates the set of visual cues
(i.e. the features extraction and object representation
is assured by the module number 3 of each agent).
The proposed algorithm for distributed inter-camera
re-identification based on the consensus principle
reached through the collaboration between agent
subdivided into four essential steps:
1. If a new observation O
CAM
a
i
is detected in
the field of view of the camera CAM
i
, then the collab-
oration between this camera and its neighbourhood
CAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
is started.
2. For-each CAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
do
a. Computing the MBTFs functions between
CAM
i
and its neighbourhoodCAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
for inter-
camera color mapping.
b After inter-camera color adaptation, computing
the features vector F
O
CAM
a
i
from the image of the
object of interest Obj
a
.
3. Send message to each neighbourCAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
M
O
CAM
a
i
= (F
O
CAM
a
i
,CAM
i
).
End for-each
4. Receiving the messages: a message is received
from each camera CAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
,
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
344

M
O
CAM
a
j
= (Id
j
Obj
a
,CAM
j
,Bol).
If the observation O
CAM
a
i
of the object Ob j
a
char-
acterised by the features vector F
O
CAM
a
i
was already
identified and tracked by one of the cameras CAM
j
⊂
Sub
C
then the variable Bol = 1 and the identity of the
object Id
Obj
a
= Id
j
Obj
a
. Else if the variable Bol = 0
then Ob j
a
is a new object in the camera network and
the cameraCAM
i
attribute to this object the maximum
received identities from all cameras CAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
plus 1.
Id
Obj
a
= Max(Id
j
Obj
a
) + 1
When the neighbouring cameras CAM
j
⊂ Sub
C
re-
ceive the messages M
O
CAM
a
i
from the initiator cam-
era CAM
i
, an intra-camera identification process is
started to verify the existence of similar objects in
the cameras CAM
j
history to the object Ob j
a
. This
process based on the euclidean distance between the
features vector F
O
CAM
a
i
of the object Obj
a
and the fea-
tures vector F
O
CAM
b
j
of objects already identified by
these cameras CAM
j
and saved in the dataset T
j
of
each camera. After the attribution of valid identities
to the objects of interest, these identities will be ad-
dressed to the last module (intra-camera tracking) for
estimating the trajectory of each object over time.
In the next section we present a set of experimen-
tal results in real-time scenarios that demonstrate the
validity of the proposed consensus based algorithm
for distributed inter-camera re-identification.
6 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
In order to evaluate the performance of the proposed
distributed inter-camera re-identification approach,
online experiments are realized using ad-hoc network
of seven cameras with non-overlapping views in-
stalled at our laboratory (LASE-Annaba University).
In this network, each camera is connected to its own
processing unit (absence of a central unit), the topol-
ogy of the network is totally dynamic, the network is
scalable at any moment, cameras not calibrated ge-
ometrically, etc. In these conditions multi-object re-
identification remains a great challenge and the pro-
posed distributed inter-camera re-identification ap-
proach can be fully evaluated. In this paper we present
online experiment using three non-overlapping cam-
eras. This experiment consists of real life scenario
where three objects of interest move randomly inter-
camera in presence of complex conditions: occlu-
sion, non-rigid objects, scale change, unpredictable
transfer time inter-camera, jerky motion in the back-
ground, etc. The figure (Fig.2) illustrates the inter-
camera re-identification results and tracking using the
Figure 2: Inter-camera re-identification results using the
proposed distributed approach based on the consensus prin-
ciple and the collaboration between agents.
proposed completely distributed approach based on
the consensus principle. From the obtained results we
find that: (1) in camera (CAM1) three objects have
obtained coherent identities from 1 to 3. (2) when
these objects enter in the field of view of the cam-
era (CAM2) a collaboration between the cameras is
started based on the proposed consensus-based algo-
rithm to attribute a valid identity to these objects, each
object has obtained the same identity attributed by the
camera (CAM1). (3) Now, when these objects enter
in the field of view of the camera (CAM3) the same
procedure is started to reach a consensus about the
objects identities. The obtained results (Fig.2) from
this experiments prove the efficient and the ability of
the proposed distributed approach for inter-camera re-
identification in the absence of any restriction.
To evaluate quantitatively the obtained results, the
Receiver Operating Characteristic evaluation space
is used, where the rate of the true positive re-
identification (RTPr) against of the rate of the false
positive re-identification (RFPr) is plotted in figure
(Fig.3). The ratio of the ROC curve (RFPr, RTPr)
are calculated from inter-camera re-identification re-
sults at each frame using a set of video sequences.
The curve ROC illustrates the quality of the proposed
approach for distributed inter-camera re-identification
relative to the variation of the matching threshold be-
tween objects.
Consensus-basedInter-cameraRe-identification-AcrossNon-overlappingViews
345
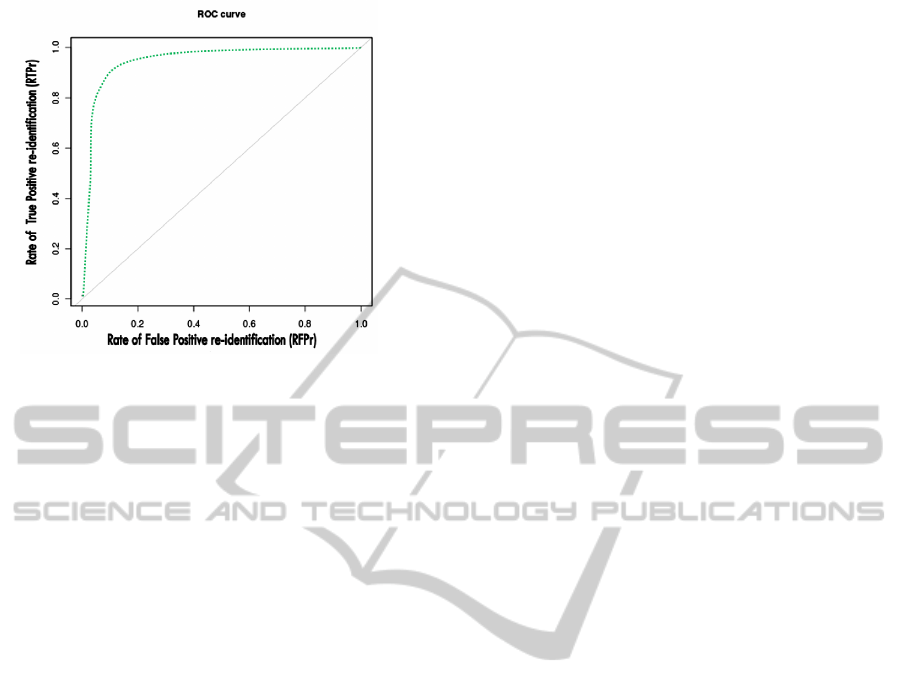
Figure 3: Roc Curve relativeto the variation of the matching
threshold between objects (RTPr in function of RFPr).
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have presented a new distributed ap-
proach for inter-camera re-identification based on the
consensus principle reached through the collaboration
between smart-cameras. Firstly, we have presented
a completely decentralized system based on the dis-
tributed inferences where each camera is modelled
by an autonomous agents. Secondly, to reach a con-
sensus about objects identities a new distributed ap-
proach was presented based on the collaboration be-
tween agents. The obtained results proved the ro-
bustness of the proposed approach. From this work
we conclude that the decentralisation of the infer-
ences is an important issue to the design of real-time
and robust re-identificationand tracking frameworkin
multi-camera/Multi-sensor network. In the same con-
text we need to developed sophisticated algorithms
able to reach a consensus between smart-cameras. Fu-
ture works including the integration of auctions for
ambiguity management to reach a consensus and im-
proved the inter-camera color mapping through the
use of invariant visual cues inter-camera.
REFERENCES
Bousetouane, F., Dib, L., and Snoussi, H. (2011). Robust
detection and tracking pedestrian object for real time
surveillance applications. In SPIE, volume 8285, page
828508.
Bousetouane, F., Dib, L., and Snoussi, H. (2012). Improved
mean shift integrating texture and color features for
robust real time object tracking. The Visual Computer
J, Springer, pages 1–16.
Chen, K.-W., Lai, C.-C., Lee, P.-J., Chen, C.-S., and
Hung, Y.-P. (2011). Adaptive learning for target track-
ing and true linking discovering across multiple non-
overlapping cameras. Multimedia, IEEE Transactions
on, 13(4):625 –638.
Doretto, G., Sebastian, T., Tu, P., and Rittscher, J. (2011).
Appearance-based person reidentification in camera
networks: problem overview and current approaches.
Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Com-
puting, 2:127–151.
Farenzena, M., Bazzani, L., Perina, A., Murino, V., and
Cristani, M. (2010). Person re-identification by
symmetry-driven accumulation of local features. In
(CVPR),IEEE Conference on, pages 2360 –2367.
Gilbert, A. and Bowden, R. (2006). Tracking ob-
jects across cameras by incrementally learning inter-
camera colour calibration and patterns of activity. In
Computer Vision ECCV 2006, volume 3952 of LNCS,
pages 125–136. Springer.
Gray, D. and Tao, H. (2008). Viewpoint invariant pedes-
trian recognition with an ensemble of localized fea-
tures. In Proceedings of the 10th ECCV, pages 262–
275. Springer.
Javed, O., Shafique, K., Rasheed, Z., and Shah, M. (2008).
Modeling inter-camera space-time and appearance re-
lationships for tracking across non-overlapping views.
Comput. Vis. Image Underst., 109(2):146–162.
Meden, B., Sayd, P., and Lerasle, F. (2011). Mixed-state
particle filtering for simultaneous tracking and re-
identification in non-overlapping camera networks. In
Image Analysis, LNCS, pages 124–133. Springer.
Motamed, C. and Wallart, O. (2007). A temporal fusion
strategy for cross-camera data association. Pattern
Recognition Letters, 28(2):233–245.
Olfati-Saber, R. and Sandell, N. (2008). Distributed track-
ing in sensor networks with limited sensing range. In
American Control Conference, pages 3157 –3162.
Porikli, F. and Divakaran, A. (2003). Multi-camera calibra-
tion, object tracking and query generation. In ICME
’03. Proceedings., volume 1, pages I – 653–6 vol.1.
Prosser, B., Gong, S., and Xiang, T. (2008). Multi-camera
matching using bi-directional cumulative brightness
transfer functions. In Proceedings of the BMVC, pages
64.1–64.10. BMVA Press.
Soto, C., Song, B., and Roy-Chowdhury, A. (2009). Dis-
tributed multi-target tracking in a self-configuring
camera network. In CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference
on, pages 1486 –1493.
VISAPP2013-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
346
