
A Coordination Protocol for User-customisable Cloud Policy Monitoring
Ming-Xue Wang, Lei Xu and Claus Pahl
School of Computing, Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Keywords:
Cloud Computing, Cloud Architecture, Customisation, Cloud Governance, Policy.
Abstract:
Cloud computing will see a increasing demand for end-user customisation and personalisation of multi-tenant
cloud service offerings. Combined with an identified need to address QoS and governance aspects in cloud
computing, a need to provide user-customised QoS and governance policy management and monitoring as
part of an SLA management infrastructure for clouds arises. We propose a user-customisable policy defini-
tion solution that can be enforced in multi-tenant cloud offerings through an automated instrumentation and
monitoring technique. We in particular allow service processes that are run by cloud and SaaS providers to be
made policy-aware in a transparent way.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing is service-based provisioning of
software, infrastructure and platform technology
(SaaS, IaaS, PaaS) (Buyya et al.,2011). SaaS
providers are the primary target of our policy defi-
nition, instrumentation and monitoring solution, but
also SaaS users such as end users and mashup
providers are important in the context of service pro-
cesses. Programmatic management interfaces and
multi-tenancy are often named as open cloud issues.
A customer needs to be allowed to better control and
customise cloud offerings through specific manage-
ment interfaces. For the provider, this is a multi-
tenancy environment where users have varying re-
quirements. Governance and QoS issues are concerns
for users. QoS responsibilities are usually split be-
tween provider and user. This requires a coordina-
tion solution to deal with monitoring and enforcement
where QoS-related and other policies can be config-
ured by the user and enforced and monitored by the
provider. Policies are specifications that formulate
user QoS and governance requirements.
Two key objectives of our coordination model and
protocol for policy definition, instrumentation and
monitoring can be singled out. Firstly, the benefit of
user-configured policy management for multi-tenancy
is to allow end-user customisable cloud computing,
i.e. creating a multitenant environment where user-
specific end-to-end SLAs can be formulated and spe-
cific needs specified and controlled by the user. Ma-
jor cloud providers often use a one-size-fits-all SLA
approach for their cloud platforms. Governance of
clouds needs to be more open for the actual user
to specify and enforce requirements better, which
of course also requires infrastructure support on the
provider side in multi-tenancy environments to man-
age the execution within SLAs. Secondly, our solu-
tion to process-level policy management will work
not only for service offerings, but also for process-
level architectures, where the provider implements an
offered service as a process. This is particularly im-
portant for a growing market of cloud prosumers that
provide mashups of existing services.
2 FRAMEWORK OVERVIEW
A framework for user-controlled management of pol-
icy (governance and QoS) aspects can facilitate intel-
ligent (self-)management of cloud resources. Our so-
lution allows to optimise usage (the provider perspec-
tive) based on monitoring compliancy SLA compli-
ance (the user perspective) based on monitoring poli-
cies (Leusse et al., 2009). Our assumption is that ser-
vices processes (rather than individual services) are
enacted by Cloud/SaaS providers or users. These are
• either provider processes which are customer
policy-enhanced using the proposed techniques.
An example is Amazon’s EC2 offering, which
provides an interface (API) described in WSDL
and accessible via SOAP, that is internally enacted
as a process (for instance WS-BPEL-based).
• or customer processes which are customer policy-
enhanced. This refers to the combination and in-
337
Wang M., Xu L. and Pahl C..
A Coordination Protocol for User-customisable Cloud Policy Monitoring.
DOI: 10.5220/0004367003370344
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER-2013), pages 337-344
ISBN: 978-989-8565-52-5
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

tegration of cloud services by intermediaries (i.e.
prosumers or brokers that provide mashups).
Technical challenges are multi-tenancy, user-
controlled end-to-end SLAs, and process-centricity.
Multi-tenancy applications, i.e. cloud applications
provided to many users, are manageable as long as
a one-size-fits-all approach works, but a management
scalability problem arises if different users have dif-
ferent requirements (Mietzner et al., 2009). A con-
figurable policy monitoring technique is the proposed
solution (Wang et al., 2009). Customisation of policy
management requires a fine-granular multi-tenancy
model, where end users can configure and enact (re-
motely) their specific requirements. Two types of in-
terfaces in cloud applications exist that are internally
enacted through service proceses. Firstly, the upload
and management of resources, executed by a provider
BPEL process. Secondly, functionality that the appli-
cation uses as a process (the cloud acts as a middle-
ware). Here, policy monitoring is a customer service.
Both are, however, subject to SLAs/policy specifica-
tions. Our solution consist of:
• A policy model captures a range of cloud com-
puting context aspects in order to allow users to
specify their dynamic quality and governance re-
quirements. User-specific requirements and set-
tings will be validated and converted into an ex-
ecutable, commonly used (standardised) format
that can be enacted by providers.
• A policy coordination and instrumentation tool in-
struments services at process level with the user
policies. For the process view, mashups (compo-
sition) need to address composition of functional-
ity as well as composition of quality aspects and
their respective policy specifications.
We have implemented components for policies
[A], policy validation [B], policy instrumentation [C],
validation monitoring [D], and policy customisation
at the end user side [E] (Wang et al., 2009) to support
the policy definition and monitoring approach.
1. Police definitions are collections of XML rules.
Customised policies are stored at customer-end or
in a common repository.
2. A target process based on customer requirements.
3. Policy instrumentation for dynamic coordination
using pre/post conditions attached to constituent
Web services of the selected process.
4. A policy validation engine is needed.
5. Policy validation results are monitored. Monitor-
ing provides feedback for policy customisation -
implemented as a listener service for the process.
3 POLICY MODEL
The policy model needs to allow end-users to for-
mulate policies supported by policy validation tech-
niques and mechanisms for SLA-policy language in-
tegration and translation (Weigand et al., 2008). This
section introduces a policy model for process con-
sumers to formalize business policies as a customiza-
tion of business processes of process providers. A
range of sample policies, covering business aspects
(receipts, billing) and technical aspects (response
time), are the following:
• Buyer receipts need be issued for every checkout.
• Shipping is calculated for before payment.
• Retry the service for card processing if it fails, but
no more 5 times in the last minute, and no more
30 times in the last 5 minutes.
• Credit card processing should be completed in
less than 700 ms without faults. for each order
should less than 5 seconds.
The business policies are defined after the business
processes they are meant to be applied to are imple-
mented and provided for process consumers. This
makes policy-first process development for processes,
as in the conventional business rules approach, not
applicable. A new policy language for consumers
to formalize the business policies for pre-developed
processes is then a customization language of pre-
pared business processes. The defined policies are
enforced on business processes by providers for the
consumers. This is a process-level contract between
process consumers and providers (Pahl, 2005). The
mechanism for process providers to carry out the con-
tract is a process coordination and governability tech-
nique - see next section. Hence the development of
the policy model is based on a coordination protocol
for runtime governance between process consumers
and providers to achieve on-the-fly customization.
The core of the policy model is a language model
for process consumers to express business policies
for existing provided processes as process customiza-
tion metadata. The language model is inspired by the
XACML access control modelling language. The pol-
icy language model is based on standard syntax for
grouping rules into policies and policy sets. It is used
by business analysts and developers of process con-
sumers to express different rule categories of policies.
Flexibility rules are business-oriented rules (like the
first two above) that would not result in any suspen-
sion or termination of the process. Constraint rules,
like the last two above, must be satisfied; otherwise
the process will not proceed. Fault rules refer to tech-
nical/infrastructure problems. A range of standard re-
CLOSER2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
338

actions such as suspend, alert or log for the consumer
and validate, ignore or replace for the provider are
defined. The policy language model also provides
features such as matching and and combination al-
gorithms for policy developers to resolve conflicts of
multiple policies. This allows policy developers to
express and reason about complex business policies,
such as policy hierarchies. As we focus on the coor-
dination, a detailed description of the policy model is
omitted here, but can be found in (Wang, 2012).
4 COORDINATION AND
INSTRUMENTATION
A coordination framework with protocols as real con-
tracts makes process consumers and providers con-
tribute together to governance to ensure that defined
policies are enforced. For a business transaction re-
quested by a process consumer, there are a num-
ber of activities including those from subprocesses
within a process that will participate in the trans-
action. The WS-Coordination specifications are de-
signed for transactions of distributed Web services
(Barrett et al., 2006) rather than transactions of busi-
ness processes. Adaptive processes for handling pro-
cesses transactions lack coordination mechanisms for
our case to guarantee all participants working together
in a unified manner. The coordination framework we
designed is a response to these limitations. It includes
defined protocols as contracts for all participants for
any business transactions of business processes.
We develop a coordination model which focuses
on message exchange or coordination contexts be-
tween participants and coordinators. A coordination
protocol for policy enforcement in business transac-
tions is also defined. Then, we design an approach
which offers BPEL templates to implement the proto-
cols with BPEL processes for providers, but also with
the multi-tenancy capability.
4.1 The Coordination Model
The coordination model is inspired by the WS-
Coordination and XACML policy framework, re-
defined for the needs of our coordination protocol
and mechanism for policy enforcement. The co-
ordination model defines two types of subcoordina-
tors for process consumers and providers. Thus,
each participant only interacts with its own type of
coordinator. The coordination model is defined as
< COOR,COOR
context
>, where COOR = COOR
c
∪
COOR
p
and coor
c
∈ COOR
c
is a coordinator associ-
ated with the consumer and coor
p
∈ COOR
p
is a co-
ordinator associated with the provider. coor
context
∈
COOR
context
captures coordinaton context informa-
tion. coor
c
and coor
p
interact in a coordination con-
version. Protocol X and services X
c
and X
p
are in-
stances in this coordination protocol.
1. The process consumer sends a create coordina-
tion context request to the activation service of
coor
c
, getting back an initialized coor
context
(Cc)
that contains the identification, a service reference
of the coor
c
’s protocol service and other informa-
tion for starting a coordination conversation.
2. The process consumer then sends a process re-
quest to the provider or business process contain-
ing the coor
context
.
3. The coor
context
is extracted from the SOAP mes-
sage and passed to the protocol service X
p
at
coor
p
. At this point, the protocol service X
c
ser-
vice reference is known to the protocol service X
p
and the communication between the protocol ser-
vices can be established.
4. The coordination conversation ends with the com-
pletion of the process execution.
4.2 Process Activity Protocol
The process activity protocol defines a coordination
type for coordination conversations. It relies on the
coordination model. A coordination conversation of a
business process is established upon coordination of
all activities which are within the overall process and
subprocesses for the consumer. The conceptual mod-
elling of the coordination protocol is activity-centric,
so it can be applied to any process regardless of flow
logic, without losing the aspects related to business
processes. This coordination protocol applies to all
activities of business processes to be governed during
execution. A coordination protocol comprises three
definitions in its identification (ct ∈ coor
context
).
1. a protocol message schema defines the message
data structure needed for protocol services com-
munication between COOR
c
and COOR
p
for the
extension element of the COOR
context
.
2. a Finite State Machine (FSM) of COOR
c
and
COOR
p
, described in more detail below.
The process activity protocol defines runtime gov-
ernability available for business processes and the re-
sponsibilities of process providers and consumers as
a contract. This should satisfy the requirements of all
rule categories in the policy model. It is formalized
as an FSM of the coordination protocol. It defines
a completed FSM for every activity in the business
processes, and describes the system behaviours of
ACoordinationProtocolforUser-customisableCloudPolicyMonitoring
339

COOR
c
and COOR
p
on coordination conversations.
The idea behind the FSM design is to instrument the
governance states into the process flow as these gov-
ernance states are core to offer process governability.
The full FSM is divided into two parts for a pro-
tocol, which are responsible for COOR
c
and COOR
p
respectively. The FSM of COOR
c
is a submachine
state of FSM of COOR
p
. The process providers only
follow the part of the protocol which is defined for
COOR
p
. The consumers follow the FSM of COOR
c
.
Since the implementation of the FSM will be executed
at the consumer and provider separately, the COOR
c
must have sufficient information about the process ex-
ecution for its part of the state machine execution, as
the process executes on the provider side. In our de-
sign of the entire FSM, the FSM of COOR
c
defined
for the submachine state in FSM of COOR
p
is iso-
lated from the business process. As a result, the pro-
tocol message schema only covers the complete infor-
mation about the activity rather than the process state
information. The execution of the FSM of COOR
c
does not require information other than the weav-
ing request, which is defined in the protocol message
schema. The execution of the FSM of COOR
p
does
not require information other than the weaving re-
sponse. The rationale behind this is that, firstly, the
same protocol message schema can be used for dif-
ferent coordination protocols. A process consumer
can customize the FSM of COOR
c
for itself with-
out affecting the FSM of COOR
p
and other process
consumers. Secondly, it avoids possible complexity
in state machine implementation for both sides. One
side does not need to know the implementation details
of other side for its own implementation.
The two part design reduces the number of gov-
ernance states in the FSM of COOR
p
, hence reduc-
ing the message exchange times required between
COOR
c
and COOR
p
on coordination conversations.
The advantage is that it can reduce the performance
overhead caused by communication between the pro-
tocol services. Depending on the network situations
between a process consumer and providers, the mes-
sage exchange between them could be expensive in
some cases. Reducing required message exchange
times improves the overall coordination efficiency.
The FSM of COOR
p
specifies the protocol which
is responsible for COOR
p
- the FSM of COOR
c
is
specified in full detail in (Wang, 2012). FSM of
COOR
p
is defined as a 5-tuple (S, s
start
, F, TA, δ),
where
• S = S
g
∪ S
¬g
is a set of states. S
g
is a set of gov-
ernance states {s
man val
pre
, s
man val
post
, s
handling
pre
,
s
handling
pre
, s
cancelling
} directly involved with pro-
cess consumers or policies. The S
¬g
is a
set of non-governance states {s
start
, s
violated
pre
,
s
executing
, s
replacing
, s
waiting
, s
skipping
, s
violated
post
,
s
compensating
, s
com+rep
, s
com+ign
, s
completed
, s
end
}
not directly involved with consumers.
• s
start
∈ S
¬g
is an initial state. The activity coordi-
nation can only be started by the process provider,
and is not directly involved with consumers.
• F ⊆ S
¬g
is a set of final states {s
end
}.
• TA = TA
g
∪ TA
¬g
is a set of input symbols of
transaction actions. TA
g
is a set of transaction ac-
tions {ta
violate
, ta
validated
, ta
ignore
, ta
replace
, ta
skip
,
ta
cancel
, ta
compensate
, ta
retry
, ta
com+ign
, ta
com+rep
}
expected from process consumers. TA
¬g
is a set
of transaction actions which are not expected from
process consumers {0, 1}. The input stream of
the FSM regarding TA
¬g
is decided by the pro-
cess providers based on the process state informa-
tion which is not covered by the FSM (the FSM is
only activity-scoped).
• δ is a transition system δ : S ×TA → S, see transi-
tion graph in Figure 2.
4.3 Coordination Implementation and
BPEL Instrumentation
The coordination protocol needs to be implemented to
enable coordination. The difficulty is on the provider
side, since all activities within a business process need
to comply with the protocol during the process or
BPEL execution.
We designed a set of templates for BPEL to avoid
platform dependency. In this case, the protocol would
be implemented with a BPEL process as a coor
p
for
activities. The process contains the flow logic to be
executed and can be driven by protocol messages. A
process instance, not the BPEL process, is associated
with a coordination conversation belonging to a con-
sumer to enable multi-tenancy.
We divide the FSM of COOR
p
into two parts.
The first is process-independent, i.e., does not require
awareness of the process states. The implementation
of this part is wrapped up in the main BPEL process.
The second part continues the FSM to the end state
of activities of the main process. The first part can be
implemented in BPEL processes, but separated from
the main process. Through this hybrid design, we of-
fer a platform-independent approach that keeps the
main BPEL simple. However, the BPEL processes
are protocol-specific.
The BPEL transaction scope concept is applied for
implementing the protocol with BPEL for supporting
long-running transactions (LRTs). LRTs in BPEL are
centred on scopes and scopes can be nested. Nested
CLOSER2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
340
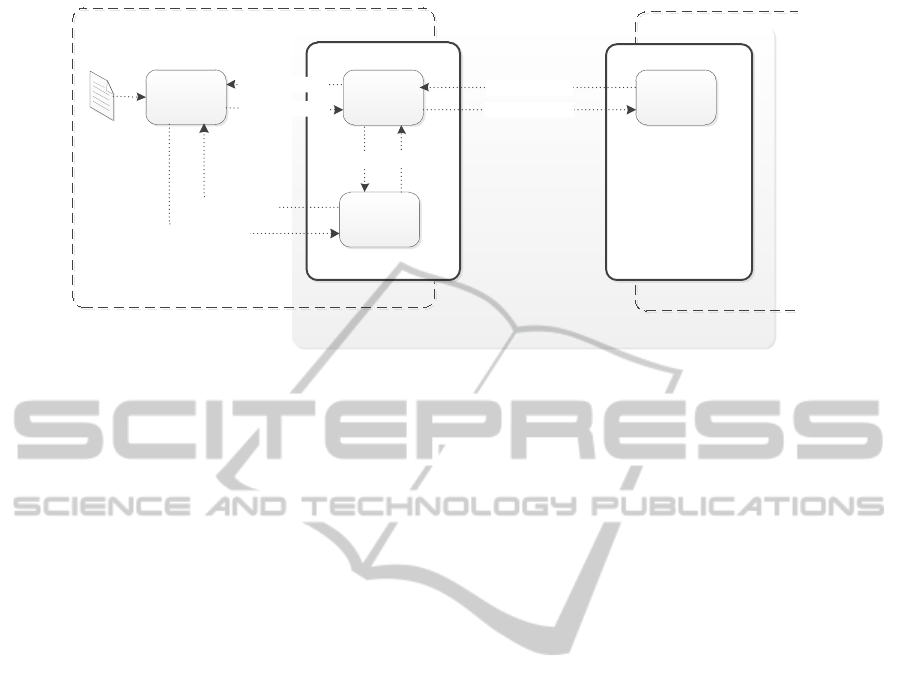
Coordination protocol
BP component
BP component
PG component
PG component
Coordinator P
FSM of
CoordinatorP
Coordinator C
Proxy
Policy weaver
WeavingRequest
WeavingReponse
WeavingReponse
WeavingRequest
Policies
Policies
FSM of
CoordinatorC
WeavingResponse
WeavingRequest
WeavingResponseWeavingRequest
Figure 1: Message flow diagram.
scopes can be standalone BPEL subprocesses which
are business activities of the parent process. When a
fault occurs, all previously committed activities can
either be compensated within the fault process, or
compensated as an activity in its parent process. This
is defined in the provided BPEL process and exposed
to process consumers.
Two templates for BPEL process development
minimise the development effort for protocol imple-
mentation. A template defines the program skeleton
of an algorithm from the template method pattern.
One or more of the algorithm steps can be overridden
by subclasses to allow differing behaviours while en-
suring that the overarching algorithm or the protocol
is still followed.
We extract the first part of FSM as the non-
transactional requirement FSM for business activities
of a process. The second part is an extension for busi-
ness activities to support process transaction require-
ment. The FSM is separated into two implementation
parts with two templates: the wrapper service tem-
plate and the main process template. We discuss the
latter in detail. The process template is an implemen-
tation of the second part of the FSM containing activ-
ity states from s
completed
to the s
end
state. When the
process is in cancelling status, previous successfully
executed activities should be compensated if neces-
sary. The template is designed with an activity scope
and a process scope.
A BPEL template for the activity scope associ-
ated with activity states can be defined. The BPEL
template for each activity is a separate scope. There
are two services inside the template indicated by grey
boxes. The first service is the wrapper service for
the first part of the FSM implementation. The nec-
essary variables are passed into the BPEL process
by a BPEL <assign> activity. With the following
BPEL <if> control structure, a <throw> activity
throws a defined fault if the comp variable is set to
false. An attached BPEL <catchAll> handler catches
the fault and marks this scope as faulty. The BPEL
<compensationHandler> attachment would only be
triggered by a successful scope if the process in can-
celling status. In that case, e.g. if the s
executing
is
skipped in the first FSM part, the compensation han-
dler attached to the activity scope will not be triggered
as the scope is marked as faulty. The last <if> con-
trol structure will mark the process in cancelling sta-
tus, it throws a defined fault and will be caught in a
<catchAll> handler defined in the process scope tem-
plate. Hence, the <compensationHandler> handler
at activity scope would be triggered. The activities
of the process would be executed from the s
completed
to the s
cancelling
state if required. A utility service in-
side the <compensationHandler> transfers from the
s
cancelling
to the s
end
state of the activity.
Figure 3 illustrates the BPEL template for the pro-
cess scope. All activities of the process are inside a
process scope, which is associated with a <catchAll>
handler. If a defined fault for the process cancelling
is caught by the handler with the process scope, all
<compensationHandler>s of activity templates of
fault-free activity scopes are executed in reverse or-
der, which is specified in the process design. Activi-
ties in s
completed
will transition to the s
cancelling
state.
If this process is a subprocess and subprocess can-
celling is completed, the activity that represents this
subprocess would transition to s
violated
post
in its parent
process depending on constraint policies of the activ-
ity. The consequent violation handling depends on the
fault policy defined in the parent process.
ACoordinationProtocolforUser-customisableCloudPolicyMonitoring
341

1
1
0
1
Ignore
1
Cancel
Ignore
Cancel
1
Skip
1
Retry
1
0
Validated
Validated
1
Compensate
Ingore
Replace
Completed
Skipping
Waiting
Compensat
ing
Replacing
Handling Pre
Handling
Post
Violated
Pre
Violated
Post
Cancelling
Manipulating
Validating
Pre
Manipulating
Validating
Post
Executing
start
start
End
End
Compensate+Replace
Violate
Replace
Violate
Compensat
Ing+
Replacing
1
1
Compensate+Ignore
participant generated
coordinator_p generated
participant as activity
of process provider
Figure 2: Transition graph for FSM for Coor
p
.
5 EVALUATION
In this section we are going to discuss our coordina-
tion framework. We focus on evaluating the effec-
tiveness of the coordination framework and the per-
formance overhead in the coordination framework.
We defined 21 test cases (along the lines of the 4
examples given earlier) for a consumer that cover all
four types of rules to address effectiveness. A pur-
chase order checkout BPEL process was developed
for the experimental setup. All of the service context
information required for constraint validation and ser-
vice selection were manually and randomly assigned.
A test case in our case comprises of four parts: 1) a
target process of this test case (some test cases are
targeted on a sub process level), 2) as input a sec-
tion of SOAP message of the business process input
that contains the business object information, policies
defined for the business process, 3) an expected pro-
cess activity log in a process instance and 4) expected
output in the form of a SOAP message referring to
the expected output from the process instance. We
compared the real process execution and coordination
log with the expected process activity log to verify
whether the validations have correctly occurred.
With these test cases, we can demonstrate that our
approach provides an effective coordination solution
for governance in a distributed and multi-tenant en-
vironment. The activity centric process coordination
protocol design can be applied to any business pro-
cess. The process runtime governance is both process
instance and consumer based. In addition, there was
no interference between different consumers sharing
a single BPEL process at the same time, which high-
lights its multi-tenancy capability.
We need to implement coordination frameworks
on both the process provider and consumer side in
our approach. However, once developed, the policy
weavers and COOR
c
can be used for any business pro-
cess. The only question that needs to be raised re-
garding is the difficulty of BPEL development with
COOR
p
. As described, the process activity proto-
col is implemented with BPEL processes following
the templates. That means additional efforts are re-
quired in BPEL development compared to conven-
tional BPEL development. However, from our own
CLOSER2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
342

CatchALL
Compensate
Activity scope
template
Receive
Reply
Activity scope
template
Completed
Cancelling
Completed
Cancelling
Reply
End
End
Compensate 1
End
End
Compensate 2
Figure 3: Process scope BPEL template.
experience with development for this case study, the
effort required is small. The wrapper service develop-
ment only requires a few lines of code for a business
activity, once the first template is developed.
Regarding performance, we have generated 1000
test cases. Using a standard PC configuration, the co-
ordination overhead is less than 2 ms for a new related
policy. The overall overhead can increase when we
apply it in networks with consideration of the network
latency. However, we still consider the performance
overhead is quite small, as long running business ac-
tivities take a few hours or even a few days for execu-
tion in a process with LRT. In some cases with utility
services (e.g. email notification), the business activ-
ity is expected with instant activities response. For
example, the average execution time including a real-
world email notification service only takes 854 ms. In
this case, our coordination overhead would be greater
than 29.7% and 14.9% with an additional cache en-
abled (see (Wang, 2012) for details). Since business
processes usually are mixed with long running activi-
ties for LRTs, the performance overhead for the over-
all process again is very small and acceptable.
In a violation situation, the coordination overhead
mean value for adaptation is 598ms (cache disabled).
If we deduct the time cost in a violation-free situation
(245ms), the overhead on adaptation would be 598-
245=254 ms for each process. Yet, it is possible to set
a permanent adaptation to avoid remedy overhead on
each process instance. However, the instance adap-
tation would avoid to store activity service informa-
tion on the provider side anyway. Still, we consider
the overhead to be acceptable compared with inherent
time delays of long running activities.
6 RELATED WORK
Current open research concerns for cloud computing
include end-user definition of governance and quality
policies and the non-intrusive instrumentation of pro-
cesses with policies. Today, one-size-fits-all service
monitoring techniques are in place. However, their
inherent inflexibility makes multi-tenancy difficult to
manage and adapt to individual needs. We discuss
related work in the field of policy enforcement and
adaptive BPEL process. These solutions are generally
not tailored for the multi-tenancy problem.
The first category is located at the BPEL layer.
BPEL processes are usually designed or generated to
serve their purpose, but also to realize a platform-
independent approach. (Wu and Doshi, 2008) pro-
vides a similar approach, where the BPEL specifica-
tion itself is extended with a fault policy specification.
Exception handling policies are bound into process
schemas as a BPEL extension. The SRRF framework
(Kareliotis et al., 2007) generates SRRF-aware BPEL
processes according to the defined policies. However,
with these approaches, binding policies into business
processes or static policies are certainly not an option
for our objective, as it impossible to support multi-
tenancy adequately.
The second category is located at the BPEL engine
layer. The BPEL process is maintained to be simpli-
fied, but the solution is platform-dependent. The dis-
advantage of the Dynamo project (Baresi and Guinea,
2011) in this regards is that BPEL event handlers must
be statically embedded into the process prior to de-
ployment, meaning that the recovery logic is defined
once and for all, and that it can only be personalized
through the parametrization of the event handler it-
self (Baresi and Guinea, 2011). This approach does
not support dynamic policies and does not support a
multi-tenancy environment. The TWSO framework
(Hrastnik and Winiwarter, 2005) addresses process
transactions. The PAWS framework (Ardagna et al.,
2007) extends the ActiveBPEL engine to provide a
flexible process that can change its behaviour dynam-
ically, according to variable execution contexts. Sim-
ilar frameworks (Mosincat and Binder, 2008), (Erradi
et al., 2006) also extend the BPEL engine for pro-
cess adaptation, but without an awareness of multi-
tenancy.
ACoordinationProtocolforUser-customisableCloudPolicyMonitoring
343

Furthermore, process-centricity is a major aim.
Recently, business-processes-as-a-service is being
discussed. While not addressed here, this perspective
needs to be further complemented by an architectural
style for its implementation (Wang, 2012).
7 CONCLUSIONS
Governance technology is crucial for the current trend
towards Software as a Service (SaaS). According to
technology reports the 451 Group, ”nearly 90% of or-
ganisations expect to maintain or grow their SaaS us-
age, with more than one third transitioning from on-
premises to SaaS” indicating that IT consumers need
more trustworthy infrastructures.
We presented a coordinator framework with pro-
tocols that ensures that consumer-defined and con-
trolled policies are enforced during business transac-
tions for business processes between consumers and
providers. We defined a coordination model and a
protocol for the policy-based governance of business
processes on business transactions. The BPEL tem-
plates are offered in order to provide best-practice so-
lution templates for the implementation with BPEL
business processes. Our overall approach supports
transaction management, adaptation for flexible pro-
cesses, and multi-tenancy capability.
We have indicated some limitations in the evalu-
ation. BPEL process implementations are protocol-
specific. The BPEL activities of a business activity
must be placed in a BPEL scope. Better consumer
support for policy definition, e.g. through repositories
of common rules and adequate interfaces and meth-
ods for semantic policy specification and customisa-
tion, needs to be investigated (Pahl et al., 2009; Pahl
et al., 2007).
REFERENCES
Ardagna, D., Comuzzi, M., Mussi, E., Pernici, B. and
Plebani, P. (2007). Paws: A framework for execut-
ing adaptive web-service processes. IEEE Software,
24(6):39–46.
Baresi, L. and Guinea, S. (2011). Self-supervising bpel pro-
cesses. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering,
37(2):247 – 263,
R. Barrett, L. M. Patcas, J. Murphy, and C. Pahl. (2006).
Model Driven Distribution Pattern Design for Dy-
namic Web Service Compositions. International Con-
ference on Web Engineering ICWE06. Palo Alto, US.
ACM Press.
Buyya, R., Broberg, J., and Goscinski, A. (2011). Cloud
Computing - Principles and Paradigms. Wiley. 2011.
Erradi, A., Maheshwari, P. and Tosic, V. (2006). Policy-
driven middleware for self-adaptation of web services
compositions. ACM/IFIP/USENIX International Mid-
dleware Conference.
Hrastnik, P. and Winiwarter, W. (2005). Twso - transac-
tional web service orchestrations. International Con-
ference on Next Generation Web Services Practices.
Kareliotis, C., Vassilakis, C., and Panayiotis, G. (2007). En-
hancing bpel scenarios with dynamic relevance-based
exception handling. IEEE International Conference
on Web Services.
Leusse, P.D., Dimitrakos,T., and Brossard, D. (2009). A
governance model for SOA. IEEE International Con-
ference on Web Services.
Mietzner, R., Unger, T., Titze, R., and Leymann, F. ”Com-
bining different multi-tenancy patterns in service-
oriented applications,” in IEEE Intl Enterprise Dis-
tributed Object Computing Conf, 2009.
Mosincat, A. and Binder, W. (2008). Transparent runtime
adaptability for bpel processes. Intl Conf on Service-
Oriented Computing.
Pahl, C. (2005). Layered Ontological Modelling for Web
Service-oriented Model-Driven Architecture. Eu-
ropean Conference on Model-Driven Architecture -
Foundations and Applications ECMDA05. Springer.
Pahl, Giesecke, S. and Hasselbring, W. (2009). Ontology-
based Modelling of Architectural Styles. Information
and Software Technology. 1(12): 1739-1749
Pahl, Giesecke, S. and Hasselbring, W. (2007). An
Ontology-based Approach for Modelling Architec-
tural Styles. European Conference on Software Ar-
chitecture ECSA2007. Springer.
Subramanian, S., Thiran, P., Narendra, N.C., Mostefaoui,
C.K., and Maamar, Z. (2008). On the enhancement
of BPEL engines for self-healing composite web ser-
vices. Intl Symp on Applications and the Internet. pp.
33-39.
Wang, M.X., Bandara, K.Y. and Pahl, C. (2009). Inte-
grated constraint violation handling for dynamic ser-
vice composition. IEEE Intl Conf on Services Com-
puting. pp. 168-175.
Wang, M.X. (2012). A Policy-based Governance Frame-
work for Cloud Service Process Architectures. Ph.D.
Thesis. Dublin City University.
Weigand, H., Heuvel, W.-J. v. d. and Hiel, M. (2008). Rule-
based service composition and service-oriented busi-
ness rule management. Interdisciplinary Workshop
Regulations Modelling and Deployment.
Wu, Y. and Doshi, P. (2008). Making bpel flexible and
adapting in the context of coordination constraints us-
ing ws-bpel. Intl Conf on Services Computing.
CLOSER2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
344
