
e-Inclusion and Knowledge Flows in e-Course Delivery
Ieva Vitolina
and Atis Kapenieks
Distance Education Study Centre, Riga Technical University, Āzenes iela 12, Riga, Latvia
Keywords: e-Inclusion, Digital Skills, Knowledge Flows.
Abstract: Our purpose of the study was to use the acceleration of knowledge flow to predict practical use of digital
skills. For this purpose, we identified certain variables to be correlated for practical uses probability as a
guide for their effectiveness for e-learning assessment. The study was based on evaluating a group of five
hundred learners. We designed four types of questionnaires and one telephone survey to assess different
aspects of the course topics that affect the practical uses of digital skills. We applied knowledge
management theory, basic principles of classical mechanics and statistical analysis. We developed a formula
for linear regression equations for practical uses of digital skills probability. As potential predictor for
effective delivery of different topics of an e-learning course we obtained knowledge flow acceleration. The
results indicated that one of the factors for determining practical uses probability in the e-inclusion model
for an e-learning course was related to knowledge flow acceleration.
1 INTRODUCTION
This study aims to address the issue of how to
facilitate the inclusion of everybody to enjoy the
benefits of information and communication
technology (ICT) (European Commission, 2010).
The progress report of the EU Digital Agenda states
that there still exists a sharp divide in digital use in
Europe between different population groups
(European Commission, 2011).
Nowadays the digital divide goes beyond the
issue of access to technology (Deursen and Dijk,
2009). The focus has shifted from access to ICT to
the meaningful use of ICT (Hargittai, 2000);
(McLean, 2006). Learning new skills and using them
are two separate steps (Lerchner et al., 2007).
This article is concerned with the second digital
divide, where individuals does have some digital
skills but lacks the ICT skills needed to fully engage
in their chosen professions. The second digital
divide is a significant issue for many professions and
population groups. This article will focus on
teachers who were the target group of our study. Our
study shows that vocational teachers are increasingly
expected to use ICT as a teaching and administrative
tool. This issue has been pointed out by the
European Commission and a number of scholars
who have studies this problem (Uzunboylu and
Tuncay, 2010). Digital literacy has today become a
"survival skill" for teachers. But teachers often
exhibit low self-confidence when applying digital
skills to teaching and other professional
requirements. Scholars have noted the critical nature
of this deficit and argue for the importance of
providing teachers with the training needed to allow
them to take full advantage of available ICT
opportunities (Abrantes et al., 2007); (Cort et al.,
2004).
A number of studies have been done regarding
the e-inclusion process (FreshMinds and UK Online
Centres, 2007). However, there is no unified point of
view on how to facilitate the practical use of learned
digital skills. This paper continues the authors'
investigation on how to promote practical use of
learned digital skills (Vitolina and Kapenieks, 2012).
The study contributes to research of the factors
influencing meaningful ICT use in e-learning
contexts by applying knowledge management
methods. In this paper it is argued that practical use
probability is related to knowledge flows
acceleration.
2 KNOWLEDGE FLOWS
PROCESSES
Knowledge flows processes are dynamics, they flow
in different directions and at different speeds. To
417
Vitolina I. and Kapenieks A..
e-Inclusion and Knowledge Flows in e-Course Delivery.
DOI: 10.5220/0004385204170422
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2013), pages 417-422
ISBN: 978-989-8565-53-2
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

determine what laws govern the knowledge flow
processes several authors based their research on
basic laws of physics (Hu and Wang, 2008); (Zhuge
et al., 2007). Moreover, Nissen used principles of
classical mechanics to describe, explain, and predict
knowledge flows processes (2006). For instance,
knowledge at rest tends to stay at rest. But some
kind of force is required for knowledge at rest to
move. Additionally, Nissen applied Newton’s
famous law: F = ma (that is, force equals mass times
acceleration) to analyze knowledge flow processes.
According to Nissen, the teacher may represent a
force but a simple chunk of knowledge may
represent the mass. This means that “the gifted
teacher and a simple concept may create rapid and
broad knowledge flows. A less-skilled teacher and
more complex knowledge may result in
comparatively slow and confined knowledge flows,
or even no flows at all” (Nissen, 2006, p. 32).
The role of the instructor in sharing knowledge
decreases in the e-learning or blended e-learning
course. Knowledge sharing depends upon the quality
of the content, i.e. learning materials, and the
usability of the e-learning environment for
convenient use of content and communication with
the instructor. We proposed in the e-learning course
context to expand the meaning of force (1). We
assumed
that force (KFF) is related to the
instructor's willingness to share knowledge (IWS)
and to usability of e-learning environment (eLE) and
quality of e-learning materials (eLM). We included
student’s self-evaluations of his knowledge level
before learning of the e-course topic (KLBL) in the
force equation as well. We summed values of the
instructor willingness to share knowledge,
evaluation of the e-learning materials and e-learning
environment because they all together present the
“teaching force”. We determined that students’
knowledge level before learning is a critical value
for acquiring new knowledge. Therefore, we used
KLBL as a multiplier.
KFF=(IWS+eLE+eLM)*KLBL (1)
We proposed to determine the variable knowledge
flow mass (KFM) by the complexity of the e-course
topic (CT) (2).
KFM=CT (2)
According to Newton’s law Knowledge flow
acceleration (KFA) is knowledge flows force divided
by knowledge flows mass (3).
KFA=KFF/KFM (3)
3 PURPOSE OF STUDY
Our purpose was to use the acceleration of
knowledge flow to predict practical use of digital
skills for vocational teachers after completing the e-
course “Improvement of ICT skills”.
4 METHODS
4.1 Participants and Assigned Topics
Our participants were 500 vocational teachers. The
testing sample covered 80% of the participants in the
blended e-learning course “Improvement of ICT
skills”. The topics for the course related to the
improvement of instrumental knowledge and skills
for tool and media usage, advanced skills and
knowledge for communication, information
management, and meaningful participation in a
knowledge society. We analyzed eleven of these
topics. They included: setup of peripherals, Image
scanning, Web page design, PDF files, Computer
security, MS Access, Video processing, E-learning
materials, Social networks, Excel and e-mails. Each
topic included theoretical material in video and text
format and tests for knowledge assessment.
4.2 Measures
We designed four types of questionnaires to assess
different aspects that affect the practical use of
digital skills. The questionnaires collected
information about students' knowledge level before
and after each topic that included e-learning
environment usability, e-content quality, instructor's
willingness to share knowledge, and student's
predicted use of digital skills after completing e-
course. We used a Likert-type questionnaire on a
scale that ranged from 1 – strongly disagree to 5 –
strongly agree.
Additionally, we designed a telephone survey to
obtain data about the practical use of digital skills
after completing the e-learning course. For each
topic the students were classed in the three
categories depending on usage level of digital skills.
We also classified all topics in the three groups
according to their complexity in the range from 1 to
3.
Predictors. One predictor was knowledge flow
force (KFF). This was measured by four
independent variables: (I) students' evaluation of
instructor support in classroom seminars and in the
e-learning environment (IWS); (II) students'
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
418

evaluation of e-learning materials for the course
(eLM); (III) students' evaluation of e-learning
environment (eLE); (IV) students' self-evaluations of
their knowledge level before learning of the topics
(KLBL).
The second predictor was knowledge mass. This
predictor was measured by the independent variable:
the complexity of topic (CT).
Criterion Variables. Practical use probability
was the criterion variable. We determined it by three
variables: (I) students' prediction of digital skills
practical use (by means of the questionnaire), (II)
observed practical use of digital skills (by means of
the telephone survey) and (III) practical use (by
mean of the combination of predicted and observed
use).
4.3 Procedure
Data collection. We collected the data from the
students by means of questionnaires administered
from January 2012 until April 2012. The
questionnaires were a section part of the blended e-
learning course for digital skills improvement and
could be accessed through the Moodle learning
system. Moreover, we conducted telephone surveys
by phone from March 2012 to May 2012 to
determine the extent to which practical use of
learned digital skills were applied four to twelve
weeks after the course. The number of respondents
for each topic differs from 57 to 86 because the
completing of the questionnaires was voluntary.
Data analysis. The authors employed correlation
and regression calculations with the SPSS for
Windows (version 17.0) for analysis.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Knowledge Flow Acceleration
The first step in this study was to calculate the
average of the Knowledge flow acceleration (KFA)
for all topics following the formula (3). Maximum
KFA (100% of possible KFA) was not observed.
Our obtained results showed that the percentages of
KFA could vary from 38% to 65% (Table 1).
Moreover, we observed that the KFA was lower for
the topics MS Access (38%), Web page design
(38%) and MS Excel (40%). But KFA was higher
for other topics such as improved skills for e-mail
usage (65%), how to scan image (53%), and how to
find e-learning materials on the Web (52%). Our
study indicated that knowledge flow acceleration
varies according to a topic.
Table 1: Maximum values of the knowledge flow
acceleration for various topics.
Topic KFA (%)
E-mail 65
Image scanning 53
E-learning materials 52
Setup of peripherals 49
PDF files 48
Video processing 47
Social networks 47
Computer security 46
Excel 40
Web page design 38
MS Access 38
5.2 Correlations of Knowledge Flow
Acceleration
Then we analyzed the correlations between the
percentage of maximum possible knowledge flow
acceleration and digital skills practical use
probability. Table 2 shows correlation coefficients
for all topics.
For all topics predicted use has a statistically
significant correlation with knowledge flow
acceleration. The topics themselves have medium
correlation in the range from .377(**) to .618(**).
The highest correlations are for the Video processing
topic.
Next, we analyzed observed use. Table 2 shows
that correlation between observed use and
knowledge flow acceleration is statistically
insignificant for most of the topics. In four topics
observed, use has a statistically significant
correlations in the range from .310* to .392**.
Furthermore, we examined a combination of
predicted and observed use. Table 1 illustrates that
for all topics the correlation is significant. Moreover,
most topics have medium strength correlations in the
range from .411(**) to .628(**). The highest
correlation is for the topic Social networks. Only one
topic MS Excel has correlations that are significant
at the 0.05 level: .273(*).
In this study it was found that knowledge flow
acceleration is a predictor of the learned skills
practical use possibility for vocational tteachers.
e-InclusionandKnowledgeFlowsine-CourseDelivery
419
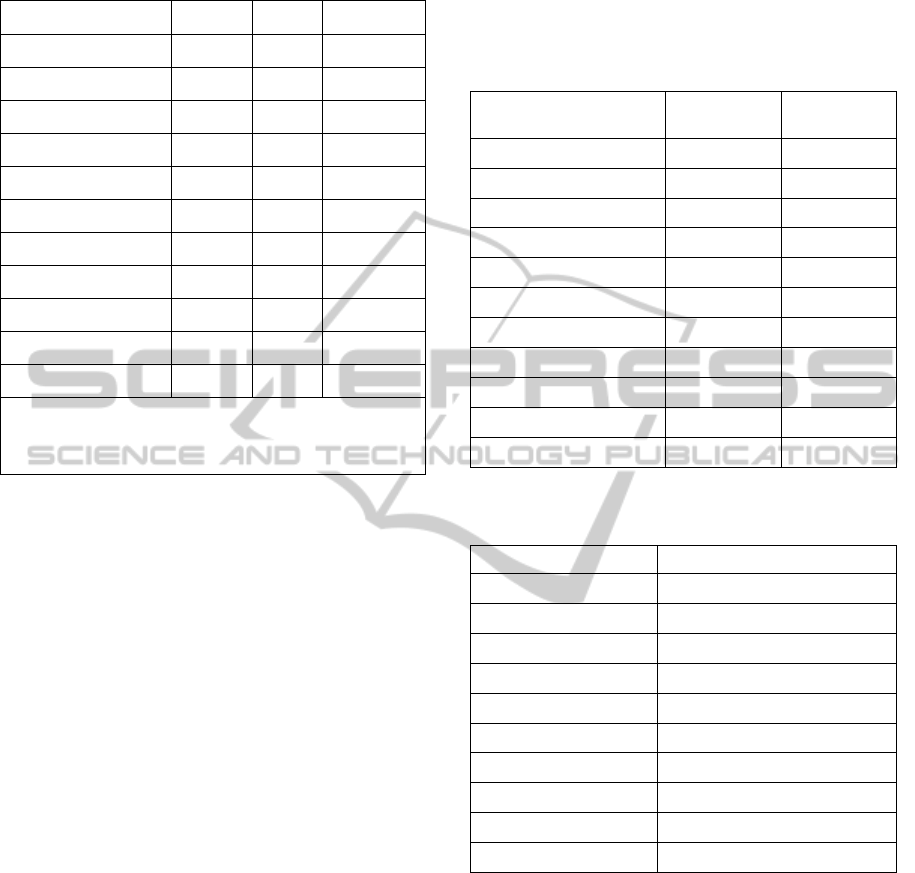
Table 2: Correlations between knowledge flow
acceleration and probability of practical use.
Topic PU OU PU&OU
E-mail .423** .079 .411**
Image scanning .508** .184 .490**
E-learning materials .490** .215 .479**
Setup of peripherals .452** .154 .419**
PDF files .464** .387** .521**
Video processing .618** .216 .608**
Social networks .545** .392** .628**
Computer security .442** .310* .524**
Excel .377** .023 .273*
Web page design .524** .021 .442**
MS Access .475** .329** .518**
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
*. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed).
PU – Predicted use; OU – Observed use
5.3 Linear Regression
for the Knowledge Flow
Acceleration
and Practical use Probability
The results shown on Table 3 demonstrate R Square
of the linear regression models. There is a
significant relationship (p < 0.05) between
knowledge flow acceleration and predicted use of
digital skills for all the topics, the exception is Excel
topic. Moreover, there is a significant relationship
between knowledge flow acceleration and predicted
and observed use of digital skills.
The linear regression model explained 18% to
38% of the total number of variations for predicted
use. The highest percentages of variations were for
the Video processing topic. The lowest percentages
were for E-mail topic.
For the combination of the predicted and
observed use the regression model accounted for
17% to 39% of the variance. Video processing topic
had the highest percentage. Again, E-mail topic had
the lowest percentage of the identified variations.
Table 4 and 5 present equations for regression
models of predicted uses as well as the combination
of predicted and observed uses.
Regression coefficients are in the range from
0.027 (E-mail) to 0.125 (Video processing) for the
predicted use model. In the model combination of
predicted and observed use, regression coefficients
are in the range from 0.029 (E-mail) to 0.155 (Video
processing).
Table 3: R Square of linear regression model of predicted
use (PU) and combination of predicted and observed use
(PU&OU).
Topic R Square PU
R Square
PU&OU
E-mail 0.179 0.169
Image scanning 0.258 0.240
E-learning materials 0.240 0.229
Setup of peripherals 0.204 0.176
PDF files 0.215 0.271
Video processing 0.382 0.370
Social networks 0.297 0.394
Computer security 0.196 0.275
Excel 0.142 0.075
Web page design 0.275 0.195
MS Access 0.225 0.269
Table 4: Linear regression equations for predicted use of
digital skills.
Topic Equation
E-mail PU=0.027KFA+3.069+ε
Image scanning PU=0.060KFA+2.836+ε
E-learning materials PU=0.029KFA+2.779+ε
Setup of peripherals PU=0.057KFA+2.836+ε
PDF files PU=0.058KFA+2.937+ε
Video processing PU=0.125KFA+2.262+ε
Social networks PU=0.041KFA+2.433+ε
Computer security PU=0.053KFA+3.324+ε
Web page design PU=0.121KFA+2.129+ε
MS Access PU=0.097KFA+2.540+ε
The value of constants of the regression
equations is in the range from 2.129 (Web page
design) to 3.324 (Computer security) for the
predicted usage model. However, in the model for
combination of predicted and observed use, the
range of constants are from 2.492 (Web page design)
to 4.174 (E-mail).
In this study it was found that the relationship
between knowledge flow acceleration and practical
use of digital skills can be modeled by a linear
regression equation.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
420

Table 5: Linear regression equations for combination of
predicted and observed use of digital skills.
Topic Equation
E-mail PU&OU=0.029KFA+4.174+ε
Image scanning PU&OU=0.074KFA+3.756+ε
E-learning materials PU&OU=0.037KFA+3.606+ε
Setup of peripherals PU&OU=0.068KFA+3.796+ε
PDF files PU&OU=0.093KFA+3.293+ε
Video processing PU&OU=0.155KFA+2.564+ε
Social networks PU&OU=0.056KFA+2.691+ε
Computer security PU&OU=0.079KFA+3.974+ε
Web page design PU&OU=0.123KFA+2.492+ε
MS Access PU&OU=0.137KFA+2.559+ε
6 DISCUSSION
The purpose of the study was to predict whether the
knowledge flow acceleration has an impact on the
practical use of newly learned digital skills for
vocational teachers.
First, we observed that for different e-course
topics the average of the knowledge flow
acceleration varies. Second, our study indicated that
knowledge flow acceleration is a predictor of the
practical use of newly learned digital skills for
vocational teachers in an e-course context. Third, we
proposed the linear regression model for predicting
practical use possibility for different e-course topics.
On the one hand, our findings about knowledge
flow acceleration for the topics means that the level
of their complexity may vary. The rate of
acceleration was lower for topics that were related to
specific software. For example, MS Access, Web
page design, and MS Excel. However, acceleration
was higher for topics that encompassed lighter
themes such as e-mail, image scanning and
searching the web for e-learning materials. On the
other hand, the variations in knowledge flow
acceleration for the assigned topics may also be
explained by other factors: the different knowledge
levels that the students possessed upon entering the
course, the quality of the e-learning environment and
materials, and the instructor’s willingness to share
knowledge.
Furthermore, knowledge flow acceleration was
predictor of the practical use of ICT skills
possibility. That means that a higher acceleration of
knowledge flow leads to a higher possibility of a
meaningful use of ICT. Our results showed that the
rate of acceleration is related to the instructor’s
willingness to share knowledge, the quality of the e-
learning environment and materials and the student's
knowledge upon entering the course.
Our results confirmed the research of our
previous study regarding the significance of e-
learning material and environment quality as
predictors of practical use of digital skills (Vitolina
and Kapenieks, 2012). Our findings are in
accordance with the results obtained by others
researchers studying these issues who argue that
when learners felt positively about the quality of the
training (learning materials, and environment), they
were able to acquire more knowledge and apply
acquired skill to their professional and practical lives
(Sulčič and Lesjak, 2009).
Our other results indicated to us how various
factors influenced future use of newly acquired ICT
skills. The models that we developed to profile the
linear regression calculations showed that the
variation range was 17% to 39% for the different e-
course topics for practical use possibility. That
means that not only knowledge flow acceleration but
also other factors could impact upon learning
behavior after e-course completion. We are going to
continue our research regarding the other factors that
reveal student attitudes, interests and capacity to
learn.
Our results for regression coefficients equations
indicated that depending on a topic’s average value,
practical use possibility generally increases by 0.027
to 0.155 for each additional unit that knowledge
flow was accelerated. We observed that for more
complex topics such as Web page design, Video
processing and MS Access practical use possibilities
increased at a slower rate than for other topics. We
concluded from these results that to reach a higher
practical use possibility level for complex topics it is
necessary to provide high quality e- learning
materials and e-learning environment. Additionally,
the instructor's willingness to share knowledge and
the learner's knowledge level upon entering the
course should be at a high level.
A few methodological limitations should be
noted. The sample used in the current study included
only vocational teachers and the sample size for
specific course topics was relatively small. Further
study with a larger sample is needed to analyse the
validity of the current findings to obtain more
comprehensive and realistic data about practical use
of learned digital skills it is necessary to prolong the
period of vocational teacher observation from three
to six month after completing course training.
e-InclusionandKnowledgeFlowsine-CourseDelivery
421

7 CONCLUSIONS
Our results identified factors that promote e-
inclusion. We concluded that a higher rate of
knowledge flow acceleration predicts a higher use
possibility of newly acquired digital skills by
vocational teachers after e-course completion. The
results confirmed the importance of designing
quality e-learning materials and e-environment to
attract e-excluded individuals. Other important
factors that promote e-inclusion are an instructor's
capacity to share knowledge and student's
knowledge level upon course entry. The
implications
of the research should encourage organizations and
enterprises that are responsible for e-course design
to take these factors into account in their future
development efforts.
This study addressed the issues concerned with
the second digital divide. It focused on identifying
relevant factors for narrowing the second digital
divide that inhibited vocational teachers from
applying digital skills in a meaningful way and
showed ways to remove these obstacles so that these
teachers could meaningfully participate in their
professions and enrich their personal lives. In our
study knowledge flow acceleration served as a
potential predictor for the effectiveness of e-course
delivery for the various topics we had assigned.
Moreover, we developed a linear regression model
for predicting practical use probability for designing
post-course surveys that can measure the long-range
impact of a delivery e-course.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The travel costs and participation fee to conference
was supported by the European Regional
Development Fund project «Development of
international cooperation projects and capacity in
science and technology Riga Technical University»,
Nr. 2DP/2.1.1.2.0/10/APIA/VIAA/003.
REFERENCES
Abrantes, J., Seabra, C. and Lages, L. (2007). Pedagogical
affect, student interest, and learning performance.
Journal of Business Research, 60(9), 960-964.
Cort, P., Härkönen, A. and Volmari, K. (2004). PROFF –
Professionalisation of VET Teachers for the Future.
Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the
European Communities.
Deursen, A. J. A. M. v. and Dijk, J. A. G. M. v. (2009).
Improving digital skills for the use of online public
information and services. Government
Information Quarterly, 26, 333-340.
European Commission. (2010). Digital agenda for
Europe: what would it do for me? Retrieved March
15, 2012, from http://europa.eu
European Commission. (2011). Digital agenda
scoreboard 2011. Retrieved March 15, 2012, from
http://ec.europa.eu
FreshMinds and UK Online Centres (2007). Digital
Inclusion. A Discussion of the Evidence Base,
Retrieved March 15, 2012, from
http://www.ukonlinecentres.com
Hargittai, E. (2000). Second-level Digital Divide:
Differences in People’s Online. Retrieved September
1, 2012, from Skillschnm.gmu.edu
Hu, L. and Wang, X. (2008). Studies on the Knowledge
Energy of Learning Organization and its Movement.
Paper presented at the 2008 International Conference
on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile
Computing, WiCOM 2008. Retrieved March 15, 2012,
from www.scopus.com
Lerchner, A., Camera, G., L. and Richmond, B. (2007).
Knowing Without Doing. Nature Neuroscience, 10(1).
Retrieved September 1, 2012, from
http://ebookbrowse.com
McLean, R. (2006). A tale of two e-citizens: a
consideration of engagement in the e-society in two
contexts. In Proceedings of the 14th European
Conference on Information Systems (ECIS) 12th-14th
of June. Retrieved September 1, 2012, from
http://csrc.lse.ac.uk/asp/aspecis/20060173.pdf
Nissen, M. E. (2006). Harnessing Knowledge Dynamics:
Principled Organizational Knowing & Learning.
London: IRM Press.
Sulčič, V. and Lesjak, D. (2009). E-learning and study
effectiveness. Journal Of Computer Information
Systems, 49(3), 40-47
Uzunboylu, H. and Tuncay, N. (2010). Divergence of
digital world of teachers. Journal of Educational
Technology & Society, 13(1), 186-194.
Vitolina, I. and Kapenieks, A. (2012). e-Inclusion
measurement by e-learning course delivery. In Annual
Proceedings of Vidzeme of Applied Sciences “ICTE in
Regional Development”, (to be published).
Zhuge, H., Guo, W. and Li, X. (2007). The Potential
Energy of Knowledge Flow. Concurrency &
Computation: Practice & Experience, 19(15), 2067-
2090.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
422
