
Identifying Learner’s Engagement in Learning Games
A Qualitative Approach based on Learner’s Traces of Interaction
Patrice Bouvier
1,2
,
´
Elise Lavou´e
1,3
, Karim Sehaba
1,4
and S´ebastien George
1,5
1
Universit´e de Lyon, CNRS, Lyon, France
2
Universit´e Lyon 1, LIRIS, UMR5205, F-69622 Villeurbanne, France
3
Universit´e Lyon 3, MAGELLAN, LIRIS, UMR5205, F-69355 Lyon, France
4
Universit´e Lyon 2, LIRIS, UMR5205, F-69676 Lyon, France
5
INSA-Lyon, LIRIS, UMR5205, F-69621 Villeurbanne, France
Keywords:
Game based Learning, Learner Behaviour, Engagement Measurement, Qualitative Approach, Digital Gaming,
Trace Theory.
Abstract:
This paper proposes a qualitative approach for identifying learners’ engagement from their traces of inter-
actions performed in the learning game. Learners’ engagement is an effective indicator of their motivation,
acceptance and attachment to the learning activity. Engagement also informs about the relevance of the content
and the effectiveness of the proposed interactive learning game. Designers, practitioners and teachers need in-
formation about engagement for analysing, designing and validating the learning game and also for modifying
and adapting learning games in order to maintain their effectiveness. Currently, most of the approaches pro-
vide quantitative information about learner’s engaged-behaviours. Thus, our objective is to extract qualitative
information from learners-generated data. In this paper, we propose an approach in three stages that combines
theoretical works on engagement and engaged-behaviours, Activity Theory and Trace Theory. By relying
on traces of interactions, this approach enables to identify engaged-behaviours in low-constraint interactive
games, directly, continuously, under ecological conditions and over a long time period. Then we present the
results of a user study that demonstrate the feasibility and the validity of our approach. This study has been
conducted on twelve traces composed of several thousands of learner-generated data.
1 INTRODUCTION
The features of digital games like multi-sensory im-
mersion, interactivity and immediate feedback stim-
ulate students’ motivation and facilitate the devel-
opment of skills like attention, problem-solving,
decision-making or collaborative work (de Aguilera
and Mendiz, 2003). Several studies (Gee, 2003;
Egenfeldt-Nielsen, 2006) argue in favour of the use
of digital games as efficient educational tools. This
explains why computer supported education practi-
tioners show a growing interest in digital game based
learning (Prensky, 2007).
Student’s engagement is considered as a useful in-
dicator in order to prevent school dropout (Reschly
and Christenson, 2006). Identifying engagement may
inform about learners’ motivation, acceptance and at-
tachment to the learning mediated activity. It can also
inform about the relevance of the content and the ef-
fectiveness of the proposed interactive technology or
service. These information may be used by design-
ers and teachers for testing, modifying or adapting
the content or features of the system. During class-
room lessons, teachers have the opportunities to as-
sess and influence students’ engagement (Skinner and
Belmont, 1993) by adapting the form or the content of
the lessons according to several students’ characteris-
tics such as personality, motivation, needs and affec-
tive states. With computer supported education, the
relationship between teachers and students is limited,
especially in the case of distance learning (Greenhow
et al., 2009). Two means are available for eliciting and
maintaining learners’ engagement in mediated learn-
ing activities: either the mediated activity is intrinsi-
cally engaging (this is what is expected with the learn-
ing games), or the teacher has some informationabout
learners’ engagement.
In this paper, we propose an approach for iden-
tifying learners’ engagement in learning games from
their traces of interaction (i.e. learner’s actions ac-
339
Bouvier P., Lavoué É., Sehaba K. and George S..
Identifying Learner’s Engagement in Learning Games - A Qualitative Approach based on Learner’s Traces of Interaction.
DOI: 10.5220/0004386903390350
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2013), pages 339-350
ISBN: 978-989-8565-53-2
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

tually performed within the mediated activity). This
approach, useful for both teachers and designers, en-
ables the direct and continuous analysis of students’
engaged-behaviours under ecological conditions. We
applied our approach through the analysis of 12 traces
of interaction in a digital game.
This paper is organised as follow. In section 2
we refine the concept of engagement and review the
methods for identifying it. In section 3 we describe
the three stages of our qualitative approach. In section
4 we present the results of a user study and discuss
them. Finally, in section 5, we conclude by show-
ing the implications for computer-supported educa-
tion and introduce some future works.
2 BACKGROUND AND RELATED
WORK
In this section we study the notions of engagement.
Our aim is to provide a definition that is applicable
in both entertainment and learning fields. Based on
this definition, we study the methods for identifying
engagement in digital gaming.
2.1 Defining Engagement in Digital
Gaming
(Boyle et al., 2012) observe in their systematic review
on engagement in digital games, that the nature of en-
gagement is still not well understood and that there is
still a lack of a widely accepted definition of engage-
ment. Defining an abstract concept like engagementis
useful in order to facilitate scientific exchanges, espe-
cially when the concept is used in several fields. Also,
it helps to be clear about what is aimed, or what is be-
ing measured. Thus, it improves the validity and ef-
fectiveness of the comparisons between several meth-
ods or approaches. (Brown and Cairns, 2004) define
engagement as ”the lowest level of immersion” be-
fore ”engrossment” and ”total immersion”. (Brock-
myer et al., 2009) consider engagement ”as a generic
indicator of game involvement” which can evolve on
a progressive scale whose levels are immersion (Jen-
nett et al., 2008), presence (Tamborini and Skalski,
2006), flow (Csikszentmihalyi, 1991) and psycholog-
ical absorption (total engagement).
In the field of education, engagement may be
considered as the ”behavioral intensity and emo-
tional quality of a person’s active involvement dur-
ing a task” (Reeve et al., 2004). After reviewing
the concept of school engagement, (Fredricks et al.,
2004) conclude that engagement is a ”meta con-
struct” which encompasses ”behavioral” (participa-
tion, positive conduct, effort), ”emotional” (interest,
positive emotions) and ”cognitive” (psychological in-
volvement in learning, self-regulation) dimensions.
The first issue with these definitions is the refer-
ence to ambiguous concepts like involvement and im-
mersion. The second issue is that these definitions are
context-dependent (for example the definitions in the
entertainment field seem to address more specifically
the immersive games). As we aim to provide a def-
inition that is valid in the both fields, we think more
relevantto answer through a conceptualdefinition that
focuses on the state of engagement rather than to its
outcomes.
So we consider engagement as ”the willingness
to have emotions, affect and thoughts directed to-
wards and determined by the mediated activity”. En-
gagement occurs if players or learners’ expectations
(perceptual, intellectual, interactional) are fulfilled.
Then, in a process similar to the suspension of dis-
belief
1
(Coleridge, 1969) players and learners may
willing to get engaged in order to live more intensely
the activity. Then they accept that, during a given
time (perhaps beyond the duration of the mediated
activity), their emotions, affect and thoughts will be
mainly elicited by the mediated activity (here the digi-
tal game-based learning). The consequenceof this en-
gaged state, is that players’ or learners’ attention will
remain on the game and their motivation will make
them keep playing and coming back (again and again)
in the game.
2.2 Identifying Engagement in Digital
Gaming
Our objective is to analyse learner’s engagement di-
rectly (i.e. from their actions and not a posteriori),
continuously and over a long time period (i.e. ses-
sion after session across weeks and months) and un-
der ecological conditions (i.e. at home and without
interfering with the learner’s activity nor impacting
the system). Our approach must allow to analyse
the whole population of users rather than a selected
sample and must be effective with interactive sys-
tems that offer a wide range of actions. Therefore,
we do not address in this section psychophysiological
or self-report, interview and observation methods (see
respectively (Kivikangas et al., 2011) and (Fredricks
and McColskey, 2012) for recent reviews).
Metrics approaches are used in industry and aca-
demics for meeting the previously mentioned con-
1
Suspension of disbelief is the willingness to accept,
despite the technical or narrative shortcomings, a fictional
work as being the reality.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
340

straints. It consists in automatically collecting and
storing any users’ actions performed through input
devices towards the system such as, users’ choices,
location changes, modifying character’s characteris-
tics, interaction with other character but also informa-
tion like time spent or the level reached. Thus, it is
possible to record all the users’ course and process
during the activity. Then, some data mining methods
can be applied on these user-generated data in order
to derive valuable (i.e. interesting, interpretable and
useful) information. See (Romero and Ventura, 2010)
for a review addressing specifically learner-generated
data. As metrics only inform on what users are do-
ing but not why, one may see a limit in aiming to
identify engagement (i.e. an abstract quantity) from
metrics (Canossa and Drachen, 2009).
As engagement influences the behaviour, some
measurable quantities can be considered for identify-
ing engaged-behaviours(Bauckhage et al., 2012). For
studying the impact of tutorials on players’ engage-
ment in digital entertainment games, (Andersen et al.,
2012) collect some raw data like the number of unique
levels completed, the total playing time and the num-
ber of times players have loaded the game. Expect-
ing to predict when players will stop playing, (Bauck-
hage et al., 2012) study how engagement evolves over
time. They apply techniques from lifetime analysis on
player’s playing times information (when they play
and for how long) collected from five AAA-games
like Tomb Raider or Crysis. (Weber et al., 2011)
study players’ engagement in terms of player reten-
tion within an American football game. For that pur-
pose they collect preference data such as the game
mode selected and behavioural data like averageyards
gained or ratio of possession. Dealing with learner’s
disengagementdetection in web-based e-learning sys-
tem, (Cocea and Weibelzahl, 2009) compare eight
machine learning techniques on several raw data. The
latter are mainly related to reading pages (number of
pages read, time spent reading pages) and quizzes
events. The previous methods conduct quantitative
measure on isolated (i.e. unlinked) data item. Thus,
rather than addressing engaged-behaviouras a whole,
they stay at a basic level by only considering some
parts of an engaged-behaviour.
Some approaches are considering user’s engaged-
behaviour through some sequences of actions. (Beal
et al., 2006) propose a classification approach of
learner’s engagement within a mathematics ITS.
For that purpose, they defined five student’s time-
dependent patterns of actions based on time traces
of actions within the ITS. More recently, (K¨ock and
Paramythis, 2011) adopt a clustering approach for de-
tecting sequences of learner’s actions in the Andes
ITS. These studies only occur in high-constraint envi-
ronment like ITS. In such environments, the variety of
actions is tight and fully determined by the interactive
system (attempts, request for hint, results etc.). In this
case the number of items is limited. Thus, sequence-
mining may constitute an efficient method for dis-
covering some statistically relevant sequences of ac-
tions. But, in low-constrained interactive systems like
learning game, a wide range of actions may be possi-
ble. Then, sequence-mining could return a too large
number of sequences. Also, as the temporal succes-
sion of actions does no imply that there is a coher-
ence between these actions, these actions may be not
useful in order to derive valuable information about
a high-level engaged-behaviour. Moreover, machine
learning for sequential data mining suffers from sev-
eral issues like long-distance interactions (Dietterich,
2002). This can be problematic if, within an engaged-
behaviour, a long period occurs between items.
3 AN APPROACH FOR
IDENTIFYING
ENGAGED-BEHAVIOURS
In this section we present our qualitative approach for
analysing directly, continuously and under ecologi-
cal conditions learner’s engaged-behaviours in low-
constraint interactive games and over a long time pe-
riod. For that purpose we consider learner’s behaviour
as a chain of actions actually performed in the dig-
ital game. A chain of actions is an aggregation of
learner’s actions selected from temporal constraints
and/or characteristics of the action. By aggregating
several actions, we expect a comprehensive contex-
tual information about learner’s engagement. Also we
adopt a theory-driven perspective by firstly determin-
ing some engaged-behaviours. Therefore, the chal-
lenge is to identify, among the wide variety of possi-
ble actions, those that are inherent to the engagement.
These actions can refer to a high number of dimen-
sions of the interactive systems and be collected at
different granularity of temporal and spatial resolu-
tion. So, three main issues have to be overcome:
1. Determining some high-level engaged-
behaviours.
2. Characterising these engaged-behavioursby iden-
tifying the underlying chains of actions.
3. Detecting these chains of actions among all the
actions recorded.
Our strategy for tackling these three issues is in
three stages. Each stage is described in the following
three sub-sections.
IdentifyingLearner'sEngagementinLearningGames-AQualitativeApproachbasedonLearner'sTracesofInteraction
341

3.1 Determining Engaged-behaviours
In this section we describe how we determine some
high-level engaged-behaviours. To decide whether a
behaviour reflects, or not, an engagement, we con-
sider the question of the learners’ motives and needs
that determine engagement. This is useful in order
to give meaning, in relation to their engagement, to
users’ actions.
(Przybylski et al., 2010) use the Self-
Determination Theory (SDT) (Ryan and Deci,
2000) for explaining digital game engagement. The
SDT identifies three basic psychological needs: com-
petence (sense of efficacy), autonomy (volition and
personal agency) and relatedness (social interaction).
This perspective is different from other works based
on empirical observations on players’ behaviours.
(Lazzaro, 2004) identifies four motivational factors
for playing game labelled hard fun (challenge), easy
fun (curiosity, fantasy), altered state (positive emo-
tions) and people factor (social experiences). (Yee,
2006) observes three main components: achievement,
social and immersion.
Even if these motivational factors are closed to the
basic psychological needs previously mentioned. The
basic psychological needs perspective has several ad-
vantages. As it is not based on empirical observation
of players’ behaviours on specific games, it does not
depend on the gameplay
2
of the game. Thus, basic
psychological needs perspective can be applied on all
current or future gameplay. By being more versatile,
this approach enables to determine a wide and non-
stereotyped range of behaviours. Our aim is neither to
determine a user model nor to provide a model of en-
gagement but to identify some behaviours that signif-
icantly reflect learner’s engagement (i.e. that are not
determined by the gameplay of the learning game).
Thus, for qualifying a behaviour of being engaged,
we link users’ behaviours to the universal needs iden-
tified by the SDT that they satisfied.
For structuring the analysis of engaged-
behaviours, we consider that digital gaming consists
in performing some actions (decision-making pro-
cess), directly or through a character, within an
environment (or at least on a frame) which may in-
volve social interaction with human or virtual agents.
Thus, the gaming activity has the following four
dimensions: environmental (in relation with the au-
tonomy need), social (in relation with the relatedness
need), self (in relation with the autonomy need) and
action (in relation with the competence and autonomy
2
In digital gaming, gameplay is a blanket term which
refers to the structure, the dynamics or the interactive as-
pects of a game.
needs). Of course, according to the type of learning
game (simulation game, computer supported collab-
orative learning), the components will not always be
present, nor with the same intensity. Each component
encompasses several engaged-behaviours including
those observed by (Lazzaro, 2004) and (Yee, 2006).
See Table 1 for an overall summary of the four
components of players engagement.
3.1.1 Environmental Engagement
Player’s engagement is directed towards the environ-
ment or the world depicted in the game. This engage-
ment encompasses two main behaviours: the contem-
plation and the curiosity. Contemplatives like to stroll
in the game area. Curious seek to know the physical
and geographical boundaries of the game world. They
may also be interested in configuring the features of
the game. The goal is not to win but to increase their
knowledge about the game.
3.1.2 Social Engagement
Social engagement refers to the social connections
within the game. In this case, the game is an opportu-
nity to create and expand social relations toward other
players. The purpose is to develop and/or to maintain
her/his social network. This player will massively
use the communication channels provided, will pro-
mote the game to increase the number of participants,
will enjoy teamwork (collaborative work in a serious
game, within a team or guild in a digital game).
3.1.3 Self Engagement
Self engagement concerns the connection between
players and their character through identification
and/or ownership aspects. These players like to cus-
tomize their avatar and choose accessories for some
other reasons than performance. Players experienc-
ing this type of engagement will be particularly in-
volved in shopping stage (for a new sword, costume,
skills etc.). Thus, they may spend a long time to study
the characteristics of accessories or skills. This player
will take care about the role play.
3.1.4 Action Engagement
Player’s engagement is directed towards the actions
to perform in the situation depicted by the game. The
core of the game is the main interest for these play-
ers. Players will try to quickly pass the levels, to win
experience points, to complete challenge etc.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
342

Table 1: Categorisation of (non-exhaustive) players’ behaviours through the four components of engagement and some asso-
ciated activities.
Environmental en-
gagement
Social engagement Self engagement Action engagement
Learner’s
behaviours
Contemplative
Curious
Collaboration
Competition
Social relatedness
Managing an avatar Surpassing oneself
Enhancing skills
Activities Virtual trip
Trying to reach the
limit of the game
Discovering extra-
content
Expanding social
network
Liven up the group
of real friends
Enjoyment with
others
Customizing the
character
Developing a
story around the
character
Be a top scorer
Completing chal-
lenges
3.2 Characterising Engaged-behaviours
The previous section on engagement enables to de-
termine some engaged-behaviours by establishing the
relationships between needs, motives and engaged-
behaviours. This section describes how we charac-
terise these engaged-behaviours. By characterising an
engaged-behaviour we mean identifying the underly-
ing actions and chains of actions performed by the
learner within the learning game. Our aim is to select,
among the various dimensions of the game, the rele-
vant user-generated data i.e. the ones underpinning an
engaged-behaviour. To reach this objective, we base
on the Activity Theory to establish the relationship
between the learners’ needs, the object and motive of
the activity and the actual realization of actions.
3.2.1 Basic Concepts of Activity Theory
Activity Theory (Vygotsky, 1978; Leontiev, 1978)
aims to understand Human development through an
analysis of the ”genesis, structure and processes of
their activities” (Kaptelinin and Nardi, 2006). Three
different levels of analysis of the activity are distin-
guished :
• Activity. An activity is performed by a subject,
through a tool, in response to a specific need
or motive in order to achieve an object (objec-
tive). The need generates the motive, the motive
elicits the activity, the object structures and di-
rects (Kaptelinin, 2005) the activity towards a de-
sired and anticipated (Bardram, 1997) outcome.
Object is what characterises an activity and differ-
entiates an activity from another (Leontiev, 1978).
The object has to be of high significance i.e. be
self-sufficient.
• Action. An action (or chains of actions) can be
seen as the actual transcription of the activity. An
action can be used by different activities in or-
der to reach a goal. Thus, the goal of the ac-
tion depends on the activity to which it is subor-
dinated. The difference between objects (activity
level) and goals (action level) is the significance.
Actions are performed consciously and with effort
through operations.
• Operation. An operation enables the actual reali-
sation of the actions. Operations are automatized,
that means performed without conscious thoughts
or efforts. Operations are determined by the envi-
ronmental and contextual conditions of the activ-
ity. Operations can be used by different actions.
3.2.2 Characterising Engaged-behaviours with
Activity Theory
We use Activity Theory as a hierarchical framework
for conducting a comprehensive and structured anal-
ysis of the engaged-behaviours within the learning
game. This structuring tool enables to deconstruct an
engaged-behaviour in activity, chains of actions and
chains of operations actually performed in the inter-
active learning game by the students. So, within each
components of engagement, activities share the same
motive but have a different object. For example, the
activities ”Expanding social network” and ”Liven up
the Group of Friends” share the same motive (Feel-
ing emotions related to social interactions) which
is generated by the relatedness basic need but have
different objects (respectively Increasing the number
of Friends and Maintaining a group activity within
the Group). In this, we comply with Kaptelinin’s
call (Kaptelinin, 2005) by distinguishing between ob-
ject and motive of the activity.
Let’s consider an example (illustrated on Figure 1)
extracted from the user study presented in section 4.
In the social engagement component we identify the
activity : Expanding social network whose motive is
Feeling emotions related to social interactions and
object is Increasing the number of Friends. In our
IdentifyingLearner'sEngagementinLearningGames-AQualitativeApproachbasedonLearner'sTracesofInteraction
343
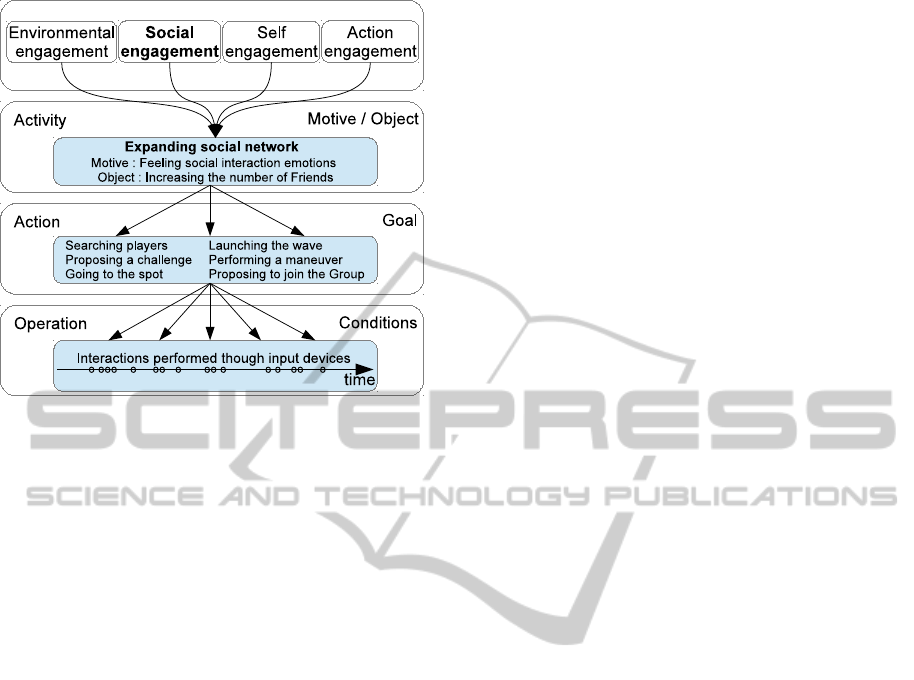
Figure 1: Social engagement in conjunction with Activity
Theory hierarchy within the user study presented in sec-
tion 4.
study this activity is deconstructed (i.e. supported) by
the following actions:
• Searching players living in a specific location
• Proposing a challenge to another player
• Going to the spot
• Launching the wave
• Performing a maneuver
• Proposing to join the Group of Friends
All these actions are realised in the game through
many operations actually performed with the input
devices provided. These operations can consist in
some mouse clicks or forms filling like for example
typing the name of a town in the form for searching
players or a button-pressed for launching a wave.
3.3 Detecting Engaged-behaviours
In section 3.1 we determine some engaged-
behaviours. In section 3.2 we characterise these
engaged-behaviours by deconstructing them in activ-
ities, actions and operations. This section describes
the last stage of our qualitative approach based on the
Trace Theory. The objective here is twofold. First we
detect within the recorded learner-generated data the
chains of operations identified in the previous stage.
Then, we reify the relationship between operations,
actions and activities. The objective is to extract the
identified activities from the raw learner-generated
data.
3.3.1 Concepts of Trace Theory
The trace analysis approach is a framework for col-
lecting, organizing and using user’s activity traces
(i.e. any player’s actions performed towards the learn-
ing game) (Clauzel et al., 2011). At the lowest level,
there is the observed elements (labelled obsels). Typ-
ically, an obsel corresponds to a player’s raw action
collected in the game (like a mouse click or a key
pressed on the keyboard). An obsel contains a type of
event, a timestamp and a set of contextual information
useful for characterising the event and to derive mean-
ing. A primary trace is a set of obsels temporally sit-
uated which may be connected. A primary trace may
contain a very large number of obsels whose informa-
tional level may be too low. So, it may be difficult to
derive knowledge from a primary trace.
The formalization proposed by (Settouti et al.,
2009) aims to facilitate the transition from primary
traces to information that makes sense. This formal-
ization uses a model of trace in order to organise and
characterise the obsels within the trace. This model
defines the types of the obsels and the types of the
relation that compose the trace. It also considers a
model of transformation which is a set of rules whose
role is to transform a trace in a transformed trace of a
higher level. A rule consists in temporal constraints or
in operations on the contextual attributes performed
between obsels. The transformed traces help to de-
rive a more complex or abstract knowledge.
3.3.2 Detecting Engaged-behaviours with Trace
Theory
We use the Trace Theory for addressing the third
issue: detecting the engaged-behaviours among all
the actions recorded. We combine Activity Theory
and Trace Theory by establishing the following cor-
respondences between these two theories:
• operation ⇔ primary trace composed of obsels
• action ⇔ primary transformed trace
• activity ⇔ highest-level transformed trace
Trace Theory enables to detect the relevant oper-
ations among all the stored obsels and then to reify
(through the transformation process) the relationship
between operation, action and activity. The obsels
which compose the highest-level trace correspond
to the activities that belong to a specific engaged-
behaviour.
Lets consider an example illustrated by the Fig-
ure 2. During a session we collect many obsels
from several types (i.e. which correspond to specific
events such as asking another player to become friend,
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
344

Figure 2: Our approach combines a theoretical work on engagement and engaged-behaviour, Activity Theory and Trace
Theory for identifying engaged-behaviours from traces of interaction. An example extracts from the user study presented in
section 4.
launching a wave etc.). We define a model of pri-
mary trace in order to organise and characterise the
obsels within the primary trace. Then we also de-
fine a transformation model. In the latter we create
a rule labelled ”Searching players by town” (see sec-
tion 4.2.2 for an example of rule). This rule enables
to detect in the primary trace, according to some tem-
poral constraints, the presence of the pair of obsels
”open the social search form” and ”filling the play-
ers’ town form”. If they occurred within a certain
time interval then the transformation rule generates a
new obsel of higher-level (labelled ”Searching play-
ers living in a specific town”) in a new transformed
trace. The transformation model has also a rule la-
belled ”Proposing a challenge” and so on. A second
transformation model loads the previously generated
transformed trace in order to generate the highest-
level transformed trace. The latter may contain the
obsel of highest-level that corresponds to the activity
”Expanding social network”.
4 USER STUDY
The objective of our study is twofold. We want to
verify (1) the feasibility of the whole process (i.e. col-
lecting the user-generated data and determining, char-
acterising and detecting some engaged-behaviours)
and (2) the validity of our approach i.e. do the be-
haviours we detect reflect an engaged-behaviour?
We apply our approach on an online game. This
game enables to work on a base of 150 000 active
players per month and so on 150 000 traces. Also, this
game enables to analyse engaged-behaviours in low-
constraint interactive systems, directly, continuously
and under ecological conditions and over a long time
period. And finally the social and challenge dimen-
sions are strong enough for providing a wide variety
of engaged-behaviours. We first present the context
of our user study. Then we detail the whole process
for identifying some engaged-behaviours and present
some results.
4.1 Context
For this research, we rely on the games developed
by the company IntellySurf under the label YouRid-
ing
3
. We consider the YouRiding Bodyboarding
games which take advantage of the Unity
4
game en-
gine. The Bodyboarding game consists in travelling
3
YouRiding: http://www.youriding.com
4
Unity - Game Engine: http://unity3d.com
IdentifyingLearner'sEngagementinLearningGames-AQualitativeApproachbasedonLearner'sTracesofInteraction
345

Table 2: Deconstruction of the activity Completing challenges in actions and operations. The activity Completing chal-
lenges is supported by the chain of actions To obtain information about the challenge – To improve the equipment –
To improve the rider skills. The action To obtain information about the challenge is detecting through the operations
game open profile improvements and game open profile skills.
Activity Completing challenges
Actions Obtaining information
about the challenge
Improving the charac-
ter’s equipment
Improving the charac-
ter’s skills
Paying for new
credits
Operations open profile improvements
open
profile skills
open shop
shop
buy item
shop
buy with cash
open
profile quiver
item
equip
item
repair
open tricks
open
key config
open bank
process
bank
from spot to spot all over the world in order to select
the most effective waves for performing some maneu-
vers (like tube ride), completing a challenge or chal-
lenging other players. Players have to detect when
their character reaches the best zone of the wave to
perform a maneuver (lip or tube of the wave etc.) with
the right key combination. Players must also adopt
the right strategy for trying only maneuvers that their
character’s skills and equipment can perform. Play-
ers should also make the right choices concerning the
improvements of character’s skill and equipment.
4.2 Implementation of our Approach
In this section we describe the implementation of our
qualitative approach in the game used for the user
study. We first show how we determine and char-
acterise some engaged-behaviours. Then we explain
how we detect these engaged-behaviours among all
the interactions recorded.
4.2.1 Determination and Characterisation of
Engaged-behaviours
This is the theory-driven part of the process for iden-
tifying some engaged-behaviours. In this example
we consider the engaged-behaviour Completing chal-
lenges. The latter belongs to the Action Engagement
component presented in section 3.1.4.
Then we characterise this engaged-behaviour
through an Activity Theory perspective (see sec-
tion 3.2.2). The table 2 details all the elements of
this deconstruction. The analysis indicate that the
activity Completing challenges is supported by the
actions Obtaining information about the challenge
– Improving the character’s equipment – Improving
the character’s skills. A fourth action Paying for
new credits is an option. Indeed, some players may
buy some credits for improving their rider’s equip-
ment or skills. The action Obtaining information
about the challenge is realized through the operations
open profile improvements and open profile skills.
These two operations indicate that the player has open
the two pages that inform about the different chal-
lenges to complete.
4.2.2 Detection of Engaged-behaviours from the
Traces of Interaction
We collect 89 types obsels (i.e. raw user-generated
data raw) such as fb link account (a player connect
her/his facebook account whith her/his account in the
game), challenge wait (a player propose a challenge)
or goto spot (a player go to a specific spot identified
with its id) etc. The collect uses a classic client-server
architecture with JavaScript and PHP scripts. The col-
lect is automatically triggered when the player per-
forms a targeted action (typically a click). The obsel
is then sent to a server for being stored, session after
session, in a MySQL database.
We use the tool D3KODE
5
(Champalle et al.,
2012) for analysing the traces and defining the trans-
formation rules (see section 3.3.1 on the Trace The-
ory). D3KODE provides the following features: load-
ing the data as a primary trace, creating the mod-
els of transformation and the rules associated and
a graphical visualization of the (primary and trans-
formed) traces (see Figure 3 for an illustration). So,
the data are exported from the MySQL database in
a CVS (Comma-Separated Values) file that is com-
patible with D3KODE. Each line of this file contains
two timestamps (the date and time of the beginning
and end of the event, most of the time it’s the same
value), the name of the obsel and at most three at-
tributes which may provide some contextual informa-
tion such as the name of the button pressed, the iden-
tification number of the spot or of the equipment etc.
Then we load the CVS file in D3KODE in order to
obtain a primary trace.
5
Define, Discover, and Disseminate Knowledge from
Observation to Develop Expertise
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
346

In order to visualise the action level we ap-
ply a transformation to the primary trace. This
transformation is a set of rules that enables to ag-
gregate several operations in order to generate a
high-level obsel. A rule can rely on temporal
constraints or on the contextual attributes. This
high-level obsel corresponds to an action. For
example the obsel open profile improvements and
open profile skills are aggregated in order to gener-
ate the action Obtaining information about the chal-
lenge. The following rule enables to select the in-
stances where the two pages Improvements and Skill
havebeen opened during an intervalof 2 minutes. The
analysis of several traces of interaction indicates that
players consult these two pages in this interval.
1 (
2 open p ro fi le s k i l l s . hasEnd < open
p r o f i l e improvements . hasBegin
3 ( open p r of il e improvements . hasBegin −
open p r o f i l e s k i l l s . hasEnd ) <=120
4 )
5 OR
6 (
7 open p r o fi l e improvements . hasEnd < open
p r o f i le s k i l l s . hasBegin
8 ( open p r of il e s k i l l s . hasBegin − open
p r o f i l e improvements . hasEnd ) <=
120)
9 )
We observe that the action Obtaining information
about the challenge occurs many time for some play-
ers in their whole traces and never for other play-
ers. In a similar manner we create all the rules that
enable to generate the four actions. And we iterate
the transformation process for aggregating the actions
and then generating the obsel of highest-level (i.e. the
one that indicates the activity Completing challenges).
In this case the temporal constraint may be larger as
for example the action Improving the rider’s equip-
ment occurs less often than the action Obtaining in-
formation about the challenge .
4.3 Results
We collected twelve player’s traces on the period from
January to April 2012. These traces from engaged-
players have been isolated by experts. A trace con-
tains 89 types of obsels and can be composed of sev-
eral thousands of obsels. We are able to detect 20 ac-
tions such as Promoting the game towards facebook,
Being interested in other players’ information, Im-
proving the equipment, Paying for new credits etc. We
identify six activities from the four components of en-
gagement such as Expanding social network, Animate
facebook group of friends, Completing challenges etc.
These results show the feasibility of the whole pro-
cess. This process is illustrated in Figure 3.
We also observe that the players who play the
most (the sessions of play are spread over the whole
period of four months) show several activities from
several components of engagement. On the contrary,
players who stop playing after only several sessions
of play (typically spread on only one month) show no
activities. This confirms that the behaviours we detect
reflect an engagement. Also it seems to indicate that
the variety of the performed activities is a relevant in-
formation regarding the engagement.
4.4 Discussion
Compared with a quantitative approach that would
have done some statistical measures on the number of
waves surfed by the player, our qualitative approach
go beyond this information by identifying in which
chains of actions a wave has been surfed. Indeed, we
know if a wave has been surfed in order to complete
a challenge or for challenging another player in order
to be introduced with her/him.
For this user study we worked on twelve traces for
implementing the transformation rules. The rules can
be used on other players’ traces of interaction from
the game studied in this paper. Also theses rules could
be applied to other digital games. From the designer
point of view, the adaptability to various game en-
gines would be fairly simple as few lines in JavaScript
are needed in order to trigger the sending of an event.
The activities and actions level, and the rules allow-
ing to infer activities from actions are broadly shared
by different types of games. For example, the action
Challenging another player has the same meaning as
soon as there is a confrontation between learners. But,
the operations are determined by the design and in-
terface of each game. Therefore, only the operations
level and the rules allowing to infer actions from op-
erations depend on the game. Also, the scalability
(number of players, volume of collected data) comes
to the Big Data issue. Thus, two points may be im-
proved: the asynchronous transmission (but features
of html5 such as WebSockets will facilitate it) and the
storage (NoSQL databases are a promising solution).
We already have done some preliminary compar-
isons with a sequence-mining algorithm. In the traces
we analysed, the four obsels goto map, goto zone,
goto spot and play start on spot represent more than
the half of the obsels that compose a player’s trace.
The results obtained with this algorithm mainly re-
fer to sequences combining these operations. These
are what we call trivial sequences are they are fully
determined by the gameplay of the game. These re-
IdentifyingLearner'sEngagementinLearningGames-AQualitativeApproachbasedonLearner'sTracesofInteraction
347

Figure 3: Graphical visualisation in D3KODE of the tranformation process from the obsels to a high-level engaged-behaviour.
sults seem to confirm the validity and effectiveness
of our approach compared to sequences mining meth-
ods. This may be particularly true when the variety of
actions within the interactive system is wide.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
5.1 Summary of the Contribution
We propose a theory-driven and qualitative approach
for identifying engagement from users’ traces of in-
teraction. This approach enables to identify engaged-
behaviours in low-constraint interactive systems, di-
rectly, continuously and under ecological conditions
and over a long time period.
For using qualitatively, rather than quantitatively,
learners-generated data, we propose an approach in
three stages: (1) determination of high-levelengaged-
behaviours, (2) deconstruction, from an Activity The-
ory perspective, of these engaged-behaviours in ac-
tivities, actions and operations, (3) detection of
the chains of actions among all the stored learner-
generated data based on Trace Theory in order to ex-
tract the engaged-behaviours.
We present the results of our user study on twelve
traces of interactions in order to demonstrate the fea-
sibility of the whole process and to validate the ap-
proach.
5.2 Implications
Besides the psychological, physical, cognitive, social
and cultural learner’s factor, the effectiveness of the
learning game depends on two categories of factors:
the immersive and interactive features and the con-
tent (consistency and authenticity, narrative process,
aesthetics) (Dondlinger, 2007). Our approach pro-
vides a structured tool for analysing the actual use of
the game. The results may be different from design-
ers’ intuitions. It may also inform about what players
want, what is missing in the game (like a wrong bal-
ance between the components of engagement). Thus,
designers may modify the game in order to improve
the player’s experience.
Moreover, the process of engagement (Brien and
Toms, 2008) (point of engagement, engagement, dis-
engagement, reengagement) enables to deal with the
aspect of temporality, i.e. how engagement evolves
over time. Thus, the identification of learner’s en-
gagement during several sessions may be a useful in-
formation for teachers for maintaining engagement by
adapting the content or the form of the learning activ-
ity. Also this information could be directly used by
the interactive system for an automatic adaptation or
for giving a feedback to learners.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
348

We consider that engagement might be a concept
easier to grasp and to identify than the user experi-
ence
6
in learning game. Thus, engagement and our
approach for identifying it might provide a relevant
information for designers, practitioners and teachers
for analysing, designing and validating the learning
game but also for modifying and adapting it in order
to maintain the effectiveness of the learning games.
Also, our approach is not limited to immersive
games like the one used for our user study. Indeed,
our approach can be applied as soon as learners have
some choices to perform (and thus there is some
chains of action to analyse). Finally, this approach
is not limited to engaged-behaviours and can be ap-
plied for identifying any evolution of behaviour from
any type.
5.3 Future Works
Our approach is currently carrying out a posteriori
and manually. But by conducting a regression analy-
sis on players’ actions, it could be possible to detect
and then to select the most relevant (i.e. the most dis-
criminant) activities and actions. Thus, by reducing
the complexity of the calculations, it may be possible
to automatise the method in order to identify engage-
ment in real-time (i.e. during the mediated activity).
The next step would be the automatic adaptation of
the system to elicit and to maintain the engagement.
We plan to conduct a concurrent triangulation
mixed-method by comparing and contrasting our re-
sults with subjective method like questionnaire or in-
terview applied to ”real” players. We should also
compare our qualitative results with quantitative sta-
tistical ones such as number and duration time of the
playing session, payments done etc.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is conducted within the QuEJAnT
project which brings together the LIRIS Laboratory
and the video games companies Corexpert, Intelly-
surf and Kiniro. Funding for this project was provided
by a grant from la R´egion Rhˆone Alpes and le Grand
Lyon. The QuEJAnT project is labelled by the french
competitiveness cluster Imaginove.
6
According to ISO 9241-210, user experience refers to
”a person’s perceptions and responses that result from the
use or anticipated use of a product, system or service”
REFERENCES
Andersen, E., O’Rourke, E., Liu, Y.-E., Snider, R., Low-
dermilk, J., Truong, D., Cooper, S., and Popovic, Z.
(2012). The impact of tutorials on games of varying
complexity. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Confer-
ence on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI
’12, pages 59–68, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Bardram, J. E. (1997). Plans as situated action: an activity
theory approach to workflow systems. In Proceedings
of the fifth conference on European Conference on
Computer-Supported Cooperative Work, ECSCW’97,
pages 17–32. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Bauckhage, C., Kersting, K., Sifa, R., Thurau, C., Drachen,
A., and Canossa, A. (2012). How players lose in-
terest in playing a game: An empirical study based
on distributions of total playing times. In S. Lu-
cas, S.–B. Cho, M. S. E., editor, Proceedings of the
IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and
Games (CIG), Granada, Spain.
Beal, C. R., Qu, L., and Lee, H. (2006). Classify-
ing learner engagement through integration of mul-
tiple data sources. In Proceedings of the 21st na-
tional conference on Artificial intelligence - Volume
1, AAAI’06, pages 151–156. AAAI Press.
Boyle, E. A., Connolly, T. M., Hainey, T., and Boyle, J. M.
(2012). Engagement in digital entertainment games:
A systematic review. Computers in Human Behavior,
28(3):771–780.
Brien, H. L. O. and Toms, E. G. (2008). What is user en-
gagement ? a conceptual framework for defining user
engagement with technology. Journal of the American
Society for Information Science, 59(6):938–955.
Brockmyer, J. H., Fox, C. M., Curtiss, K. A., McBroom, E.,
Burkhart, K. M., and Pidruzny, J. N. (2009). The de-
velopment of the game engagement questionnaire: A
measure of engagement in video game-playing. Jour-
nal of Experimental Social Psychology, 45(4):624–
634.
Brown, E. and Cairns, P. (2004). A grounded investigation
of game immersion. In CHI ’04 extended abstracts
on Human factors in computing systems, CHI EA ’04,
pages 1297–1300, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Canossa, A. and Drachen, A. (2009). Patterns of play: Play-
personas in user-centred game development. In Barry,
A., Helen, K., and Tanya, K., editors, Breaking New
Ground: Innovation in Games, Play, Practice and
Theory: Proceedings of the 2009 Digital Games Re-
search Association Conference, London. Brunel Uni-
versity.
Champalle, O., Sehaba, K., Cosmas, D., Mille, A., and Pri´e,
Y. (2012). Assistance to trainers for the observation
and analysis activities of operators trainees on nuclear
power plant full-scope simulator. In Xhafa, F., Barolli,
L., Pop, F., 0001, X. C., and Cristea, V., editors, In-
ternational Conference on Intelligent Networking and
Collaborative Systems (INCoS 2012), pages 33–40.
IEEE Computer Society.
Clauzel, D., Sehaba, K., and Pri´e, Y. (2011). Enhancing
synchronous collaboration by using interactive visu-
alisation of modelled traces. Simulation Modelling
Practice and Theory, 19(1):84–97.
IdentifyingLearner'sEngagementinLearningGames-AQualitativeApproachbasedonLearner'sTracesofInteraction
349

Cocea, M. and Weibelzahl, S. (2009). Log file analy-
sis for disengagement detection in e-learning environ-
ments. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction,
19(4):341–385.
Coleridge, S. T. (1969). The collected works of Samuel Tay-
lor Coleridge. Routledge and K. Paul ; Princeton Uni-
versity Press, [London] : [Princeton] :.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1991). Flow: The Psychology of Op-
timal Experience. Harper Perennial.
de Aguilera, M. and Mendiz, A. (2003). Video games
and education: (education in the face of a ”parallel
school”). Computers in Entertainment, 1(1):1–10.
Dietterich, T. G. (2002). Machine learning for sequential
data: A review. In Proceedings of the Joint IAPR
International Workshop on Structural, Syntactic, and
Statistical Pattern Recognition, pages 15–30, London,
UK. Springer-Verlag.
Dondlinger, M. J. (2007). Educational Video Game Design:
A Review of the Literature. Journal of Applied Edu-
cational Technology, 4(1):21–31.
Egenfeldt-Nielsen, S. (2006). Overview of research on the
educational use of video games. Digital Kompetanse,
1(3):184–213.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., and Paris, A. H. (2004).
School Engagement: Potential of the Concept, State
of the Evidence. Review of Educational Research,
74:59–109.
Fredricks, J. A. and McColskey, W. (2012). The measure-
ment of student engagement: A comparative analy-
sis of various methods and student self-report instru-
ments. In Christenson, S. L., Reschly, A. L., and
Wylie, C., editors, Handbook of Research on Student
Engagement, pages 763–782. Springer US.
Gee, J. P. (2003). What video games have to teach us about
learning and literacy. Computers in Entertainment,
1(1):20–20.
Greenhow, C., Robelia, B., and Hughes, J. E. (2009). Learn-
ing, Teaching, and Scholarship in a Digital Age: Web
2.0 and Classroom Research–What Path Should We
Take ”Now”? Educational Researcher, 38(4):246–
259.
Jennett, C., Cox, A. L., Cairns, P., Dhoparee, S., Epps,
A., Tijs, T., and Walton, A. (2008). Measuring
and defining the experience of immersion in games.
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,
66(9):641–661.
Kaptelinin, V. (2005). The object of activity: Making
sense of the sense-maker. Mind, Culture, and Activity,
12(1):4–18.
Kaptelinin, V. and Nardi, B. A. (2006). Acting with Tech-
nology: Activity Theory and Interaction Design. The
MIT Press.
Kivikangas, J. M., Chanel, G., Cowley, B., Ekman, I.,
Salminen, M., Jrvel, S., and Ravaja, N. (2011). A
review of the use of psychophysiological methods
in game research. Journal of Gaming and Virtual
Worlds, 3(3):181–199.
K¨ock, M. and Paramythis, A. (2011). Activity sequence
modelling and dynamic clustering for personalized e-
learning. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interac-
tion, 21(1-2):51–97.
Lazzaro, N. (2004). Why We Play Games: Four Keys to
More Emotion Without Story. In Game Developers
Conference.
Leontiev, A. N. (1978). Activity, consciousness and person-
ality. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Prensky, M. (2007). Digital Game-Based Learning.
Paragon House.
Przybylski, A. K., Rigby, C. S., and Ryan, R. M. (2010). A
motivational model of video game engagement. Re-
view of General Psychology, 14(2):154–166.
Reeve, J., Jang, H., Carrell, D., Jeon, S., and Barch, J.
(2004). Enhancing students’ engagement by increas-
ing teachers’ autonomy support. Motivation and Emo-
tion, 28:147–169.
Reschly, A. L. and Christenson, S. L. (2006). Research
leading to a predictive model of dropout and comple-
tion among students with mild disabilities and the role
of student engagement. Remedial and Special Educa-
tion, 27:276–292.
Romero, C. and Ventura, S. (2010). Educational data min-
ing: a review of the state of the art. Transactions on
Systems, Man, and Cybernetics–Part C: Applications
and Reviews, 40(6):601–618.
Ryan, R. M. and Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination the-
ory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social
development, and well-being. The American psychol-
ogist, 55:68–78.
Settouti, L. S., Pri´e, Y., Marty, J.-C., and Mille, A. (2009).
A trace-based system for technology-enhanced learn-
ing systems personalisation. In Proceedings of the
2009 Ninth IEEE International Conference on Ad-
vanced Learning Technologies, ICALT ’09, pages 93–
97, Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Skinner, E. A. and Belmont, M. J. (1993). Motivation in the
classroom: Reciprocal effects of teacher behavior and
student engagement across the school year. Journal of
Educational Psychology, 85(4):571–581.
Tamborini, R. and Skalski, P. (2006). The role of presence
in the experience of electronic games. In Vorderer,
P. and Bryant, J., editors, Playing video games - mo-
tives, responses, and consequences, pages 225–240.
Lawrence Erlbaum.
Vygotsky, L. (1978). Mind in Society: The Development of
Higher Psychological Processes. Harvard University
Press, Cambridge, MA.
Weber, B. G., Mateas, M., and Jhala, A. (2011). Using data
mining to model player experience. In FDG Work-
shop on Evaluating Player Experience in Games, Bor-
deaux, France. ACM, ACM.
Yee, N. (2006). Motivations for play in online games. Cy-
berpsychology and Behavior, 9(6):772–775.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
350
